Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Sandra Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations) of disease within specific nuclei I. DEFINITIONS The term basal ganglia applies to a functionally-related group of subcortical nuclei which belong to the extrapyramidal motor system and which influence movement without initiating it. This group of nuclei are involved in automated patterns of movement (e.g., walking, riding a bicycle, driving a car, choreography), "remembering" movements, and in that sense is related to "motor memory". Lesion of basal ganglia nuclei produces movement disorders (dyskinesias) collectively referred to as basal ganglia disease," and includes Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. The basal ganglia affect motor function via loops (cortico-striato-pallido-thalamo-cortical) with the ipsilateral premotor cortex, particularly the supplementary motor area (M-II cortex) where movements are planned/programmed. These include the: Striatum: Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus (Note: lenticular nucleus = globus pallidus + putamen) Subthalamic Nucleus Substantia Nigra From Burt, Textbook of Neuroanatomy
2 II. STRIATUM - Caudate and Putamen A. HISTOLOGY: histologically, the caudate and putamen are parts of the same structure, separated by the anterior limb of the internal capsule; they contain two populations of neurons: Spiny neurons - principal cell type; GABA-ergic; give rise to all striatal efferent projections (e.g., striatopallidals, striatonigrals) Aspiny neurons - intrinsic interneurons (short axons, do not leave striatum); cholinergic; involved in intrinsic striatal connections. B. PATCH-MATRIX ORGANIZATION: Striosomes or patches that have high density of muscarinic cholinergic (ACh) receptors, higher concentration of D1 receptors, and dense opiate binding; their striatal neurons project primarily to the globus pallidus, internal segment (GPi; direct pathway ) and substantia nigra, pars compacta (SNc). Matrix - striatal areas surrounding striosomes which have a higher concentration of D2 receptors, and dense calbindin and somatostatin binding; its neurons project primarily to the globus pallidus, external segment (GPe; indirect pathway ) and substantia nigra, pars reticulata (SNr); Note: Striatal efferents (striatopallidals and striatonigrals) originate from spiny neurons, which are GABA-ergic (inhibitory).
3 C. AFFERENT CONNECTIONS: 1. Corticostriates - from broad areas of cerebral cortex (glutamate, excitatory) Sensorimotor cortex to putamen; associational cortex to caudate 2. Thalamostriates - from intralaminar complex of thalamus (glutamate, excitatory); centromedian (CM) nucleus to putamen; parafascicular (Pf) nucleus to caudate nucleus 3. Nigrostriates - from substantia nigra, pars compacta (dopaminergic); not excitatory or inhibitory, probably neuromodulatory (via second messengers) From Haines, Fundamental Neuroscience
4 D. EFFERENT CONNECTIONS - (GABA-ergic) 1. Striatopallidals - to globus pallidus, external and internal segments; striosomes to GPi ( direct loop to thalamus) and matrix to GPe ( indirect loop, ie. side loop with subthalamic nucleus) Modified from: Kandel et al, Principles of Neural Science 2. Striatonigrals - striatum to substantia nigra, pars compacta (SNc) and reticulata (SNr) Striosomes to SNc and matrix to SNr E. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Huntington s Disease - an inherited disease with onset in middle age Atrophy of striatum results in a major loss of the principal spiny neurons of the striatum (GABA-ergic) and loss of intrinsic small (aspiny) cholinergic (ACh) neurons Lesion (or atrophy) results in Huntington s Disease with choreiform ( dance-like ) movement disorder (writhing movements, primarily involves distal limb muscles)
5 II. GLOBUS PALLIDUS The globus pallidus has two portions: external segment (GPe) and internal segment (GPi) The use of the term lentiform nucleus (putamen + globus pallidus) has been largely discontinued.
6 A. AFFERENT CONNECTIONS: 1. Striatopallidals (GABA) - from striatum (caudate and putamen) Striosomes to internal segment (GPi)- direct loop Matrix to external segment (GPe)- indirect loop 2. Subthalamo-pallidals (glutamate) - from subthalamic nucleus to GPi (feedback part of indirect loop ) From Haines, Fundamental Neuroscience B. EFFERENT CONNECTIONS: 1. Pallidothalamics - GABA - internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi) produces a tonic inhibition of motor thalamic nuclei (VA); some pallidothalamics also terminate in the CM/Pf thalamic intralaminar nuclei (then feedback to straitum) Older names for pallidothalamic tracts: Fasciculus Lenticularis (H2) pallidothalamic fibers that cross thru internal capsule Ansa Lenticularis - pallidothalamics that loop around internal capsule Fasciculus lenticularis and ansa lenticularis join to form thalamic fasciculus (H1) to VA/VL nuclei of the thalamus 2. Pallidosubthalamic - (GABA)- GPe to subthalamic nucleus ( indirect loop )
7 C. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Since the principal outflow from the basal ganglia originates from the globus pallidus to the motor thalamus and cortex, it is often the target of neurosurgical interventions (pallidotomy or deep brain stimulation) to relieve tremors. III. SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS - Principal nucleus of subthalamus (ventral thalamus); its neurons are glutamatergic, excitatory (only excitatory neurons in the basal ganglia) The subthalamic nucleus is part of the subthalamus, ie. the part of the diencephalon ventral to the thalamus. Since it entertains connections with other parts of the basal ganglia and is associated with certain basal ganglia disease, it is included with this system. It is often the target of neurosurgical lesions to relieve basal ganglia-related tremors.
8 A. AFFERENT AND EFFERENT CONNECTIONS: Afferents - from globus pallidus, GPe (GABA)- indirect loop Efferents - to globus pallidus, GPi (glutamate)- indirect loop Indirect loop - increased subthalamic excitation of inhibitory pallidothalamics (in GPi) increases inhibition of the motor thalamus, reducing thalamocortical excitation of premotor cortex; decreased subthalamic excitation of GPi reduces inhibition of the motor thalamus and facilitates thalamocortical excitation of the premotor cortex (modified from Burt, Textbook of Neuroanatomy B. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Lesion: ballism (ballistic movements)- involves proximal limb and limb-girdle muscles, producing wild and flailing movements of the entire limb IV. SUBSTANTIA NIGRA A. SUBDIVISIONS: Pars compacta, SNc (DA) - heavily pigmented (neuromelanin, a by-product of catecholamine (DA) synthesis) Pars reticulata, SNr (GABA) - provides tonic inhibition to the motor thalamus (VA/VL) thalamic nuclei and superior colliculus (where a pause in activity allows eye movement to occur).
9 B. AFFERENT CONNECTIONS: 1. Striatonigrals - (GABA) -from striatum to pars reticulata (SNr) Striosomes - to SNc Matrix - to SNr C. EFFERENT CONNECTIONS: From Haines, Fundamental Neuroscience 1. Nigrostriates - (DA)- from pars compacta (SNc) to striatum 2. Nigrotectals - (GABA)- from pars reticulata (SNr) to superior colliculus 3. Nigrothalamics - (GABA)- from pars reticulata (SNr) to motor thalamus (VA/VL) and intralaminar thalamic nuclei
10 D. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: From Haines, Fundamental Neuroscience Parkinson s disease- loss of DA neurons (loss of neuromelanin pigmentation) Resting tremor Bradykinesia- slowness, stiffness of movement Festinating gait (baby steps) "Freezing" - inertia, difficulty initiating movements Rigidity (shuffling gait) Expressionless face- (akinesia of facial muscles)
11 V. MOTOR CIRCUIT OF THE BASAL GANGLIA WITH THE CORTEX The internal segment of the globus pallidus and substantia nigra, pars reticulata provide tonic inhibition of motor thalamus and superior colliculus. Movements initiated in response to sensory, memory, or motivationally contingent cues are correlated with pauses in the tonic activity of inhibitory GPi or SNr output neurons. Outflow from basal ganglia (from globus pallidus) via motor thalamus affects premotor area 6 cortex (especially supplementary motor area) - and automated movements.
12 From Niewenhuys, The Human Nervous System If there is pathology in the basal ganglia, it affects the ipsilateral motor cortex, and clinical deficits (via the pyramidal tract) are expressed on the opposite side of the body. Deficits from lesions of the basal ganglia are expressed contralaterally. A Self-Assessment is available for this lecture. * Netter Presenter Image Copyright 2004 Icon Learning Systems. All rights reserved.
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Connections of basal ganglia
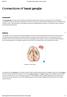 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
 STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Prof Yousry 10/15/17 Types of brain fibers THE WHITE MATTER OF THE BRAIN The white matter
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29:
 The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Basal ganglia macrocircuits
 Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Organization of the nervous system 2
 Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Organization of the nervous system 2 Raghav Rajan Bio 334 Neurobiology I August 22nd 2013 1 Orienting within the brain absolute axes and relative axes SUPERIOR (above) ANTERIOR (in front) Anterior/Posterior,
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion.
 BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion. Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. González Montaño, T. M. Zamorano Pozo, R.
BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement, cognition and emotion. Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. González Montaño, T. M. Zamorano Pozo, R.
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
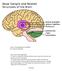 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing
 Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Neurocomputing 26}27 (1999) 687}692 Modeling the interplay of short-term memory and the basal ganglia in sequence processing Tomoki Fukai* Department of Electronics, Tokai University, Hiratsuka, Kanagawa
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges References... 3
 Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders
 Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders Chang, Won Seok Division of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University
Functional Neuroanatomy and Physiology for Movement Disorders Chang, Won Seok Division of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University
This is a repository copy of Basal Ganglia. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
 This is a repository copy of. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/114159/ Version: Accepted Version Book Section: Prescott, A.J. orcid.org/0000-0003-4927-5390,
This is a repository copy of. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/114159/ Version: Accepted Version Book Section: Prescott, A.J. orcid.org/0000-0003-4927-5390,
The basal ganglia (BG) are a group of nuclei located subcortically
 The Basal Ganglia and Disorders of Movement: Pathophysiological Mechanisms José A. Obeso, 1 María C. Rodríguez-Oroz, 1 Manuel Rodríguez, 4 Javier Arbizu, 2 and José M. Giménez-Amaya 3 Departments of 1
The Basal Ganglia and Disorders of Movement: Pathophysiological Mechanisms José A. Obeso, 1 María C. Rodríguez-Oroz, 1 Manuel Rodríguez, 4 Javier Arbizu, 2 and José M. Giménez-Amaya 3 Departments of 1
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational. Modeling Study. Karthik Kumaravelu
 Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
The basal ganglia work in concert with the
 Corticostriatal circuitry Suzanne N. Haber, PhD Introduction Corticostriatal connections play a central role in developing appropriate goal-directed behaviors, including the motivation and cognition to
Corticostriatal circuitry Suzanne N. Haber, PhD Introduction Corticostriatal connections play a central role in developing appropriate goal-directed behaviors, including the motivation and cognition to
BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW
 BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer Basal Ganglia An Integrative View http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/2976
BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer Basal Ganglia An Integrative View http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/2976
The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control
 NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control Henk J. Groenewegen Department ofanatomy, Research Institute Neurosciences Vrije Universiteit, Medical Center, Amsterdam,
NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control Henk J. Groenewegen Department ofanatomy, Research Institute Neurosciences Vrije Universiteit, Medical Center, Amsterdam,
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations
 The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
The Basal Ganglia in Parkinson s Disease: Current Concepts and Unexplained Observations Jose A. Obeso, PhD, MD, 1,2 Concepcio Marin, PhD, MD, 2,3 C. Rodriguez-Oroz, PhD, MD, 1,2 Javier Blesa, 1,2 B. Benitez-Temiño,
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N. GPi Superior colliculus. compacta reticulata
 . Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
. Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease
 Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Motor system. Guo-Fang Tseng
 Motor system Guo-Fang Tseng 1 Lower motoneuron: ~ final common path α-motoneuron γ-motoneuron Motor Unit Size principle Muscle spindle: nuclear bag ff. nuclear chain ff. Sensory: 1) from spindle type Ia:
Motor system Guo-Fang Tseng 1 Lower motoneuron: ~ final common path α-motoneuron γ-motoneuron Motor Unit Size principle Muscle spindle: nuclear bag ff. nuclear chain ff. Sensory: 1) from spindle type Ia:
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
PII: S (99) COMMENTARY
 Pergamon www.elsevier.com/locate/neuroscience Connections of the dopaminergic system with the striatum Neuroscience Vol. 96, No. 3, pp. 451 474, 2000 451 Copyright 2000 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science
Pergamon www.elsevier.com/locate/neuroscience Connections of the dopaminergic system with the striatum Neuroscience Vol. 96, No. 3, pp. 451 474, 2000 451 Copyright 2000 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia
 Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
Dynamic Behaviour of a Spiking Model of Action Selection in the Basal Ganglia Terrence C. Stewart (tcstewar@uwaterloo.ca) Xuan Choo (fchoo@uwaterloo.ca) Chris Eliasmith (celiasmith@uwaterloo.ca) Centre
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Degree of freedom problem
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
