596 Index. quality of life, GPi DBS effects, 501 DYT1 gene, 73
|
|
|
- Spencer James Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index A Activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale, 335 Air embolism, after DBS, Alzheimer s disease, 292 Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), 44, 50 Anterior commissure (AC), 100 Aripiprazole, 327 Aspiny striatal neurons, 6 Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 322 Atypical parkinsonism (AP), DBS in diagnosis of MSA, diagnosis of the syndrome, features suggestive of an AP disorder, 292 future targets for, subthalamic nucleus (STN) DBS, 299 Axonal spikes, 113 B Bartholow, Roberts, 65 Basal ganglia (BG) integration across Cortico-BG circuits, 43 pallidal complex and SN, SNr, pathways of the GP/SNr, 46 role of, in parallel circuit and integrative network, SN, SNc and VTA, STN, striato-nigro-striatal network, striatum, functional organization of frontal cortical striatal projections, structures and connectivity, thalamo-cortico-thalamic interface, Basal ganglia thalamocortical network consequences of abnormalities dystonia, 17 effects of lesions, 15 hemiballism, 17 Parkinson s disease or parkinsonism, between cortical neurons, 5 dopamine receptors (D1-D5) in, 12 effect of DBS, general structure, 4 5 inputs to basal ganglia cortico-and thalamo-subthalamic projections, 10 sensorimotor corticostriatal projections, 7 8 thalamostriatal projections, 8 10 intrinsic connections direct and indirect pathways, dopaminergic projections, intrinsic neuronal organization of nuclei GABAergic projection neurons, 7 SNc neurons, 7 SNr neurons, 7 striatum, 5 7 output projections nigrofugal pathways, 13 pallidofugal pathways, role in motor control, segregation, anatomic concept of, 5 sensorimotor portion of, 5 Beck Depression Inventory, 87 Behr s syndrome, 224 Ben-Gun method, 117 Biochemical studies, of DBS mechanisms, 154 Bipolar stimulations, 479 Bipolar testing, 481 Blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD)-fMRI, 180 Botulinum toxin injection, 322 Burke Fahn Marsden (BFM) scale,
2 594 Index C Calbindin (CaBP), 41 Center of gravity (CoG) sway, 336 Centromedian-parafascicular complex (CM-Pf), 323, 325 Cholinergic interneurons, 12 Clinical applications, of DBS, Clonazepam, 322 Clonidine, 322, Clozapine, 327 Cognitive testing tools, 88 Complications and management, in DBS air embolism, damage to lead or lead extender due to patient manipulation of the IPG, electrolysis and gas production, 145 inadvertent thermal lesioning, 145 infections, long-term hardware-related, misplaced electrodes, 142 postoperative cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson s disease (PD), 146 reasons for failure of device, sterile clear fluid collections, stroke, Computer modeling, of DBS mechanisms, Cortex-basal ganglia-thalamic-cortical circuits, 4 Cortico-subthalamic projection, 10 D Deep brain stimulation (DBS), 3, 50. See also Microelectrode recordings affective effects of depth electrode stimulation, CAPSIT criteria, 84 case histories, circuit, combination with alternative technologies, commonly used tools for cognitive testing, 88 complications and management air embolism, damage to lead or lead extender due to patient manipulation of the IPG, electrolysis and gas production, 145 inadvertent thermal lesioning, 145 infections, long-term hardware-related, misplaced electrodes, 142 postoperative cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson s disease (PD), 146 reasons for failure of device, sterile clear fluid collections, stroke, components and materials used, cost effectiveness of, 503 in depression adverse effects, 516 background, mechanisms, simulation technique, 515 technical aspects, devices daily living, lead technology, simulation technology, dystonia clinical results, 306 complications of therapy, 312 dystonia-plus syndromes and other exceptional cases, 310 evaluation of the efficacy of treatment, 306 focal and segmental, generalized, management and practical issues, neuropsychological performance and mood, 312 patient selection, 313 safety, 312 secondary, stimulation arrest and safety, 313 emerging applications clinical applications, epilepsy, 576 for epilepsy, 73 approaches to, deep brain targets for, globus pallidus (GPi) adverse events, 285 clinical results of patients treated for PD, 280, 282 effect against cardinal features of PD and off disability, effect in the On medication state, functional imaging, treatment for PD, hardwares, 466 history of, 70, importance of multidisciplinary assessment prior to, 83 invasive testing, issues and recommendations, mechanisms of biochemical studies, 154 computer modeling, effect on neuronal activity, effect on the network, imaging, 154 methodologies, neural recordings, therapeutic,
3 Index 595 Deep brain stimulation (DBS) (Continued) medically intractable cluster headache clinical outcomes, complications, device programming, 554 documentation of electrode locations, 553 indications for, 549 mechanisms, pre-and postoperative evaluation, surgical technique, time course for stimulation-induced relief, 556 neuropsychological issues in areas of functioning assessed, depression, neurobehavioral outcomes in, dystonia, neurobehavioral outcomes in, epilepsy, neurobehavioral outcomes in, ET, neurobehavioral outcomes in, evaluation of patients, interpretative and practical challenges for the neuropsychologist, methods of neuropsychological evaluation for, MS, neurobehavioral outcomes in, 428 OCD, neurobehavioral outcomes in, 429 other conditions, neurobehavioral outcomes in, 430 overview, PD, neurobehavioral outcomes in, purposes of neuropsychological evaluation for, TS, neurobehavioral outcomes in, 430 noninvasive active testing, noninvasive testing, obsessive compulsive behavior (OCB) capsular, complications and adverse effects, description of acute effects, long-term follow-up, neurosurgical intervention, postoperative contact selection, randomized double blind crossover, for OCD, 73 74, for pain, 65 patient selection in dystonia, in essential tremor (ET), in neuropsychiatric disorders, 92 in PD, possible complications, 89 potential interactions, for primary depressive illness, programming for movement disorders amplitude, basic approach to, electrode configuration, frequency, future directions, 390 issues related to GPi, issues related to STN, issues related to targets, pulse width, stimulation parameters, published and reported adverse events, responsiveness of PD Symptoms with, 86 risk factors age, 89 imaging, medical co-morbidities, 90 patients with prior ablative surgery, 90 subthalamic nucleus (STN) adverse events, 285 aspects of gait, 261 balance, bladder functions, 264 clinical results of patients treated for PD, 279 cognitive effects, 262 dysarthria/hypophonia and weight gain effects, 267 dyskinesias, 259, 267 effect against cardinal features of PD and off disability, effect in the On medication state, effects on motor aspects, effects on nonmotor aspects, group of behaviors, indications and contraindications, motor fluctuations, postural instability, 268 psychiatric complications, quality of life, rationale, sexual functions, 264 side effects and complications, sleep, 264 subthalamotomy vs., system, technical alternatives in implantation procedure interventional MRI, localization using peri-operative and intra-operative imaging, Medtronic NexFrame, StarFix micro Targeting Platform, surgical navigation systems, testing methodology, of thalamus, general experience of VL DBS for MS, head tremor, Off-label vs. Experimental use of DBS and insurance coverage, selected studies of, ,
4 596 Index Deep brain stimulation (DBS) (Continued) surgical issues unique to non-et and non-pd tremor, 224 as symptomatic, 225 thalamotomy vs., for treatment of Parkinson s disease (PD) tremor, for tremors other than MS, 224 unilateral vs. bilateral stimulation, 209 voice tremor, Tourette s syndrome (TS) clinical and surgical evaluation, neuroanatomical basis for, other considerations, 329 reports on deep brain stimulation in patients, 330 treatment of postural stability and gait disorders in PD clinical assessments and quantitative measures, effect on PPN, effects, long-term effects of STN and GPi DBS on, 353 for tremor, 71 types of motor fluctuations, vs. psychosurgery, Dementia with Lewy bodies, 292 Depression background, deep brain stimulation (DBS) adverse effects, 516 background, mechanisms, simulation technique, 515 technical aspects, pathophysiology, 513 phenomenology, treatment resistance, 512 Depression, neurocircuitry of, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV TR), 322 Diagnostic Confidence Index (DCI), 327 Direct and indirect striatofugal projections, 10 Dopamine (DA) cells in striatum, functional correlates of the cells, 43 neurons, 37, 42 receptors, 37 transporter (DAT), 42 Dopaminergic projections, Dorsal pallidal segments, 39 Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), Dyskinesias, 259 Dystonia, 3, 17, 73, DBS in, neurobehavioral outcomes after DBS, quality of life, GPi DBS effects, 501 DYT1 gene, 73 E Electricity, therapeutic use on brain development modern era of DBS, stimulation between , stimulation between , stimulation up to 1700, use by ancient Greeks, 63 Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), 402 Electromyography (EMG) software, 482 Enkephalin (ENK), 37 Entopeduncular nucleus (EPN), 4 Epilepsy DBS anterior nucleus of the thalamus, effects of, 565 approaches to, caudate nucleus, effects of, 565 centromedian nucleus of thalamus, effects of, 565 cerebellar nuclei, effects of, 565 deep brain targets for, hippocampus and amygdala, effects of, locus coeruleus stimulation in humans, effects of, 566 neurobehavioral outcomes after DBS, stimulation of the STN, effects of, 566 overview, treatment approaches, Essential tremor (ET), thalamic DBS effects on quality of life, Extended Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scale, 216 External globus pallidus (GPe), 4, Extracellular recordings. See Microelectrode recordings F Faradic current, 65 Fibers, 39, 51 GPi, 40 FLASQ-PD, 85 [ 18 F] Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET technique, 180 Focal and segmental dystonia, FOG, DBS effects on, Functional imaging, of DBS globus pallidus (GPi) for generalized dystonia, for PD, subthalamic nucleus (STN ) acute, in a resting state visualized by, L-dopa effects, motor tasks, use and purpose of, 180 ventral intermediate nucleus (VIM) of essential tremor, of Parkinsonian tremor,
5 Index 597 G GABAergic neurons, 4 5, 7, 38, 45 Gait disorder, DBS effects act of sit-to-stand, 345 initiation, long-term effects, 353 treatment of PPN, walking, Galen, 64 Galvani, Luigi, 64 Generalized dystonia, Gilbert, William, 63 Globus pallidus (GPi) altered sensory feedback, effect of DBS, 341 anatomy, DBS, functional imaging for generalized dystonia, for PD, DBS treatment for Parkinson s disease (PD) patients ADL scores off medication/on stimulation, 248 adverse events, 249 clinical results of patients treated, 280, 282 effect against cardinal features of PD and off disability, effect in the On medication state, impact on quality of life, status of, unilateral vs. bilateral stimulation, dystonia, external perturbations, effect of DBS, 341 medical adjustments, 389 optimal contact selection, 388 quality of life and DBS, 499 during quiet stance, effect of DBS, 341 rationale for targeting, 326 stimulantion-related adverse events, GP/SNr pathways, 46 H Haloperidol, 322, 327 Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, 87 Head tremor DBS, Heath, Robert, 68 Hemiballism, 17 Huntington s disease, 7 I Imaging, of DBS mechanisms, 154 Implantable pulse generator (IPG), 475 IMRI technique, 108 Infection, after DBS, Internal globus pallidus (GPi), 4, 72, 90 microelectrode recording, Intra-operative microelectrode recording anesthesia, 118 setup and procedure, single- vs. multitrajectory recording, 117 stimulation, Intrinsic neuronal organization, of nuclei GABAergic projection neurons, 7 SNc neurons, 7 SNr neurons, 7 striatum, 5 7 Invasive testing, L Largus, Scribbonius, 64 Lateral habenular nucleus, 4 Levodopa, 16, 68, 84, 324 Levodopa Equivalent Dose (LDED), Lormetazepam, 328 M Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (MDRS), 87 Medically intractable cluster headache DBS clinical outcomes, complications, device programming, 554 documentation of electrode locations, 553 indications for, 549 mechanisms, pre-and postoperative evaluation, surgical technique, time course for stimulation-induced relief, 556 evidence for hypothalamic involvement in, 548 overview, Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), 37 Medtronic Kinetra Model 7428 Neurostimulator, 578 Medtronic Soletra Model 7426 Neurostimulator, 578 Meige syndrome, 91 Methylphenidate, 322 MPTP-induced toxicity, 42 Microelectrode recordings benefits and risks, methods electronic equipment, intra-operative procedure, microelectrodes, physiology, target specific strategies internal globus pallidus (GPi), nucleus ventrointermedius thalami (VIM), subthalamic nucleus (STN), tetrodes, use of, Micro Targeting Platform (MTP), 104 Mini Mental State Exam (MMSE), 87
6 598 Index Monopolar impedances and currents, Monopolar stimulations, 479 Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale, 87 Montreal procedure, 65 Motor fluctuations, Movement disorders, 3 affective changes after DBS, MP35N, 475 MRI environment, potential interactions artifacts, gradient-induced currents, 462 RF field, static field interactions, MSN. See Medium spiny neurons (MSNs) Multiple sclerosis (MS), Multiple system atrophy (MSA), 255, 292 globus pallidus DBS, published case reports of, STN DBS in with features of PD, with typical MSA, 298 N Neural recordings, examining DBS mechanisms, Neuronal activity, effect of DBS computer models, neurochemical and gene expression studies, recordings in downstream nuclei, recordings in the stimulated nucleus, Neurostimulation, NexFrame, , Nigro-collicular fibers, 13 Nigrofugal pathways, 13 Nigro-tegmental projections, 13 Nitric oxide synthase (NOS), 38 Noninvasive active testing, Noninvasive testing, O Obsessive compulsive behavior (OCB), 322 capsulotomy for, 532 deep brain stimulation (DBS), capsular, complications and adverse effects, description of acute effects, long-term follow-up, neurosurgical intervention, postoperative contact selection, randomized double blind crossover, neurobehavioral outcomes after DBS, 429 treatment options, 532 Obsessive compulsive Disorder (OCD), neurocircuitry of, [ 15 O]H 2 O PET, 180 Olanzapine, 327 Orbital frontal cortex (OFC), 44 45, 50 P Pallidal complex, Pallidofugal pathways, PAN. See Phasically active neurons (PANs) Pantothenate kinase associated neurodegeneration (PANK2), Parkinsonism-plus syndromes. See Atypical parkinsonism (AP), DBS in Parkinson s disease, 3, 15 16, 40, 50, 68 DBS treatment of globus pallidus (GPi) ADL scores off medication/on stimulation, 248 adverse events, 249 impact on quality of life, status of, unilateral vs. bilateral stimulation, DBS treatment of subthalamic nucleus (STN) aspects of gait, 261 balance, bladder functions, 264 cognitive effects, 262 dysarthria/hypophonia and weight gain effects, 267 dyskinesias, 259, 267 effects on motor aspects, effects on nonmotor aspects, group of behaviors, indications and contraindications, motor fluctuations, postural instability, 268 psychiatric complications, quality of life, rationale, sexual functions, 264 side effects and complications, sleep, 264 subthalamotomy vs., idiopathic, 300 neurobehavioral outcomes after DBS, quality of life GPi DBS effects, 499 predictive indicators, STN DBS effects, thalamic DBS effects, 499 thalamic deep brain stimulation adverse effects, background, importance, patient selection, problem of progressive parkinsonism after, 232 results,
7 Index 599 treatment of postural stability and gait disorders of clinical assessments and quantitative measures, effect DBS on the PPN, effect of DBS, long-term effects of STN and GPi DBS on, 353 Pars compacta (SNc), Pars reticulata (SNr), 38 40, 120, 156 Parvicellular reticular formation, 4 Patient selection, for DBS role of neurologist, role of neuropsychologist, role of neurosurgeon, 88 role of psychiatrist, PD. See Parkinson s disease Pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN), 4, 10, 16 Pergolide, 327 Peri-operative and intra-operative imaging, in DBS, Pharmacologic dopamine replacement therapy, 16 Phasically active neurons (PANs), T Philips Intera MRI, 107 Pimozide, 327 Pool, J. Lawrence, 66 Posterior commissure (PC), 100, 326, 550, 557 Postural stability clinical assessments, effect of DBS instability in PD, long-term effects, 353 long-term or adaptive changes, 343 treatment of PPN, underlying pathophysiology and theories, effect of medication, quantitative measures of kinematics-3-d motion analysis, 337 posturography, voluntary movement, Posturography, Primary depressive illness, Progressive supranuclear palsy, 292 Propofol Target Controlled Infusion, 328 Psychostimulants, 322 Psychosurgery, Q Quality of life DBS effect on multiple sclerosis (MS), dystonia, GPi DBS effects on, 501 GPi DBS effects in PD, 499 predictive indicators in PD, STN DBS effects in PD, subthalamic nucleus (STN), thalamic DBS effects in PD, 499 R RCBF SPECT, 180 Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms), Risperidone, 327 S Self-injurious behavior (SIB), 322 Sensorimotor corticostriatal projections, 7 8 SF-36 scale, 307, 309 SN. See Substantia nigra (SN) SNc. See Pars compacta (SNc) SNc neurons, 7 SNc-v neurons, 11 SNr. See Pars reticulata (SNr) SNr neurons, 7 Spiegel, Ernest, 67 Spiegel-Wycis device, 67 StarFix micro Targeting Platform, 101, Static electricity, 63 Status dystonicus, 310 StealthStation, 100 Sterile clear fluid collection, after DBS, STN. See Subthalamic nucleus (STN) Striato-nigro-striatal network, Striatum, 5 7 afferent connections, dorsolateral, 33 functional organization of frontal cortical striatal projections, intrinsic cells of, ventral, 38 Stroke, after DBS, avoidance, management of, 139 Stryker Navigation System, 100 Substance P (SP), 37 Substantia nigra (SN), Subthalamic nucleus (STN), 4, 40 41, 72 73, 107 altered sensory feedback, effect of DBS, 341 anatomy, 379 DBS with features of PD, in other forms of AP, 299 with typical MSA, 298 DBS, functional imaging acute, in a resting state visualized by, chronic state, L-dopa effects, local and distant effects of, 183 motion-related fmri activity, effects on, motion-related rcbf, effects on, motor tasks, motor tasks, in PET and SPECT, rcbf in cognitive tasks, effects on, 188
8 600 Index Subthalamic nucleus (STN), (Continued) DBS treatment for atypical parkinsonism, 299 DBS treatment for PD aspects of gait, 261 balance, bladder functions, 264 clinical results of patients, 279 cognitive effects, 262 dysarthria/hypophonia and weight gain effects, 267 dyskinesias, 259, 267 effect against cardinal features of PD and off disability, effect in the On medication state, effects on motor aspects, effects on nonmotor aspects, group of behaviors, indications and contraindications, motor fluctuations, postural instability, 268 psychiatric complications, quality of life, rationale, sexual functions, 264 side effects and complications, sleep, 264 subthalamotomy vs., electrophysiologic mapping, external perturbations, effect of DBS, 341 medication adjustments, optimal contact selection, quality of life and DBS, during quiet stance, effect of DBS, 341 stimulation-related adverse events, 383 target-related adverse events, therapeutic mechanisms, of DBS, Subthalamotomy, Sulpiride, 327 Superior colliculus, 4 T TANS. See Tonically active neurons (TANS) Tetrabenazine, 322 Thalamic deep brain stimulation general experience of VL DBS for MS, head tremor, Off-label vs. Experimental use of DBS and insurance coverage, and quality of life, rationale for targeting the medial portion, selected studies of, , surgical issues unique to non-et and non-pd tremor, 224 as symptomatic, 225 thalamotomy vs., for the treatment of Parkinson s disease (PD) tremor adverse effects, background, importance, patient selection, problem of progressive parkinsonism after, 232 results, for tremors other than MS, 224 unilateral vs. bilateral stimulation, 209 voice tremor, Thalamo-cortico-thalamic interface, Thalamostriatal projections, 8 10 Thalamotomy Pahwa and coworkers experiments, 212 Schuurman and colleagues experiments, 212 Tasker and colleagues experiments, 212 Theory of animal electricity, 64 Therapeutic mechanisms, of DBS, Tics, Tonically active neurons (TANS), 38 Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS), 90, 306, 310 Tourette s syndrome (TS) clinical characteristics and prevalence, DBS clinical and surgical evaluation, neuroanatomical basis for, other considerations, 329 reports on deep brain stimulation in patients, 330 neurobehavioral outcomes after DBS, 430 targets, treatment of, neurosurgical, Tremor Activities of Daily Living Scale (TADLS), 500 Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive interneurons, 7 U Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), 71 72, 84 85, 118, , 268, 335, 343 Unilateral vs. bilateral stimulation, 209 V Vascular pathology, 292 VectorVision, 100 Ventral intermediate nucleus (VIM) adverse effect of DBS, DBS for treatment of PD tremor, DBS, functional imaging of essential tremor, of Parkinsonian tremor, microelectrode recording of, stimulation, for PD, 70, 72
9 Index 601 vs. thalamotomy, Ventral motor thalamic nuclei, 4 Ventral pallidum (VP), 39 Ventral tegmental area (VTA), 34, Ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus (VL) DBS conundrum, general experience, for MS, long-term efficacy, for MS, published literature on the efficacy of, unique pre-operative and postoperative issues related to non-et and non-pd tremor, Voice tremor DBS, Volta, Allesandro, 64 Volta s pile, 64 Von Musschebroek, Pieter, 64 W Weinhold, Karl, 65 Wilson s disease, 91 Wycis, Henry, 67 X X-linked progressive dystonia-parkinsonism, 6 Y Yale Global Tic Severity Scale (YGTSS), 328 Young Mania Scale, 87
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD
 PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD WHAT IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION? WHY SHOULD YOU CONSIDER DBS SURGERY FOR YOUR PATIENTS? HOW DOES DBS WORK? DBS electrical stimulation overrides abnormal
PACEMAKERS ARE NOT JUST FOR THE HEART! Ab Siadati MD WHAT IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION? WHY SHOULD YOU CONSIDER DBS SURGERY FOR YOUR PATIENTS? HOW DOES DBS WORK? DBS electrical stimulation overrides abnormal
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor
 Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor Albert Fenoy, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas at Houston, Health Science Center Current US Approvals Essential Tremor and Parkinsonian
Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease & Essential Tremor Albert Fenoy, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas at Houston, Health Science Center Current US Approvals Essential Tremor and Parkinsonian
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below for any prior authorization requirements
 Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: SUR Policy No: 395 1/1/19 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/17; 2/18; 12/18 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
Effective Date: 1/1/2019 Section: SUR Policy No: 395 1/1/19 Medical Policy Committee Approved Date: 8/17; 2/18; 12/18 Medical Officer Date APPLIES TO: Medicare Only See Policy CPT/HCPCS CODE section below
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Surgical Treatment of Movement Disorders. Surgical Treatment of Movement Disorders. New Techniques: Procedure is safer and better
 Surgical Treatment of Movement Stephen Grill, MD, PHD Johns Hopkins University and Parkinson s and Movement Center of Maryland Surgical Treatment of Movement Historical Aspects Preoperative Issues Surgical
Surgical Treatment of Movement Stephen Grill, MD, PHD Johns Hopkins University and Parkinson s and Movement Center of Maryland Surgical Treatment of Movement Historical Aspects Preoperative Issues Surgical
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
Deep Brain Stimulation: Surgical Process Kia Shahlaie, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Bronte Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research Director of Functional Neurosurgery Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Department
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Deep Brain Stimulation and Movement Disorders
 Deep Brain Stimulation and Movement Disorders Farrokh Farrokhi, MD Neurosurgery Maria Marsans, PA-C Neurosurgery Virginia Mason June 27, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understand the role of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation and Movement Disorders Farrokh Farrokhi, MD Neurosurgery Maria Marsans, PA-C Neurosurgery Virginia Mason June 27, 2017 OBJECTIVES Understand the role of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Connections of basal ganglia
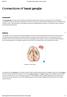 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology
 Deep Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology History of DBS 1 History of DBS 1987
Deep Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders Punit Agrawal, DO Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology Division of Movement Disorders OSU Department of Neurology History of DBS 1 History of DBS 1987
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications
 Deep Brain Stimulation Overview Kara D. Beasley, DO, MBe, FACOS Boulder Neurosurgical and Spine Associates (303) 562-1372 Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications Instrument of Change
Deep Brain Stimulation Overview Kara D. Beasley, DO, MBe, FACOS Boulder Neurosurgical and Spine Associates (303) 562-1372 Deep Brain Stimulation: Indications and Ethical Applications Instrument of Change
10/13/2017. Disclosures. Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders. Deep Brain Stimulation: Objectives.
 Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION
 DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA
 STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
STRUCTURE AND CIRCUITS OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Rastislav Druga Department of Anatomy, Second Faculty of Medicine 2017 Basal ganglia Nucleus caudatus, putamen, globus pallidus (medialis et lateralis), ncl.
NIH, American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA), Greater St. Louis Chapter of the APDA, McDonnell Center for Higher Brain Function, Barnes-Jewish
 Mechanism of Action of Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson Disease Samer D. Tabbal, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Washington University at St Louis Department of Neurology June 2011 Conflict of
Mechanism of Action of Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson Disease Samer D. Tabbal, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Washington University at St Louis Department of Neurology June 2011 Conflict of
Deep Brain Stimulation
 Deep Brain Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.63 Last Review: 8/2017 Origination: 8/2001 Next Review: 8/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for deep brain
Deep Brain Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.63 Last Review: 8/2017 Origination: 8/2001 Next Review: 8/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for deep brain
Basal ganglia motor circuit
 Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Name of Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation
 Name of Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation Policy #: 347 Latest Review Date: June 2013 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross and
Name of Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation Policy #: 347 Latest Review Date: June 2013 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross and
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Surgical Treatment for Movement Disorders
 Surgical Treatment for Movement Disorders Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence St Vincent
Surgical Treatment for Movement Disorders Seth F Oliveria, MD PhD The Oregon Clinic Neurosurgery Director of Functional Neurosurgery: Providence Brain and Spine Institute Portland, OR Providence St Vincent
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
Basal ganglia macrocircuits
 Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Tepper, Abercrombie & Bolam (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 160 ISSN 0079-6123 Copyright r 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 1 Basal ganglia macrocircuits J.M. Tepper 1,, E.D. Abercrombie
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.48 Deep Brain Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 7.01.48 Deep Brain Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
Deep Brain Stimulation. Description. Section: Surgery Effective Date: April 15, 2015
 Subject: Deep Brain Stimulation Page: 1 of 22 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Deep Brain Stimulation Description Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the stereotactic placement of an electrode into
Subject: Deep Brain Stimulation Page: 1 of 22 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Deep Brain Stimulation Description Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the stereotactic placement of an electrode into
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Modulation of the Neural Circuitry Underlying Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
 BRAIN STIMULATION LABORATORY Modulation of the Neural Circuitry Underlying Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD Awareness Day NOLAN WILLIAMS, M.D. Instructor Department of Psychiatry Stanford University October
BRAIN STIMULATION LABORATORY Modulation of the Neural Circuitry Underlying Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD Awareness Day NOLAN WILLIAMS, M.D. Instructor Department of Psychiatry Stanford University October
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale
 Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Gangli della Base: un network multifunzionale Prof. Giovanni Abbruzzese Centro per la Malattia di Parkinson e i Disordini del Movimento DiNOGMI, Università di Genova IRCCS AOU San Martino IST Basal Ganglia
Deep Brain Stimulation. Description
 Subject: Deep Brain Stimulation Page: 1 of 20 Last Review Status/Date: September 2013 Deep Brain Stimulation Description Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the stereotactic placement of an electrode
Subject: Deep Brain Stimulation Page: 1 of 20 Last Review Status/Date: September 2013 Deep Brain Stimulation Description Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the stereotactic placement of an electrode
Deep Brain Stimulation. Is It Right for You?
 Deep Brain Stimulation Is It Right for You? Northwestern Medicine Deep Brain Stimulation What is DBS? Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital is a regional destination for the treatment of movement
Deep Brain Stimulation Is It Right for You? Northwestern Medicine Deep Brain Stimulation What is DBS? Northwestern Medicine Central DuPage Hospital is a regional destination for the treatment of movement
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
CT, see computerized tomography 8-cyclopentyl-1,3- dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) 345
 Index ACC, see anterior cingulate cortex AD, see Alzheimer s disease adenosine 171, 340, 343 346, 348, 357, 359, 364 365, 368, 395 adenosine A1 receptors 346 adenosine oxidation 344, 367 adenosine triphosphate
Index ACC, see anterior cingulate cortex AD, see Alzheimer s disease adenosine 171, 340, 343 346, 348, 357, 359, 364 365, 368, 395 adenosine A1 receptors 346 adenosine oxidation 344, 367 adenosine triphosphate
Deep Brain Stimulation
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
Functional neurosurgery for the treatment of movement. Deep Brain Stimulation REVIEW ARTICLE. Drew S. Kern, MS,* and Rajeev Kumar, MD, FRCPC
 REVIEW ARTICLE Deep Brain Stimulation Drew S. Kern, MS,* and Rajeev Kumar, MD, FRCPC Background: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) for the treatment of neurologic diseases has markedly increased in popularity
REVIEW ARTICLE Deep Brain Stimulation Drew S. Kern, MS,* and Rajeev Kumar, MD, FRCPC Background: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) for the treatment of neurologic diseases has markedly increased in popularity
Huntington s Disease COGS 172
 Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Huntington s Disease COGS 172 Overview Part I: What is HD? - Clinical description and features - Genetic basis and neuropathology - Cell biology, mouse models and therapeutics Part II: HD as a model in
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Deep Brain Stimulation
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Surgical Treatment: Patient Edition
 Parkinson s Disease Clinic and Research Center University of California, San Francisco 505 Parnassus Ave., Rm. 795-M, Box 0114 San Francisco, CA 94143-0114 (415) 476-9276 http://pdcenter.neurology.ucsf.edu
Parkinson s Disease Clinic and Research Center University of California, San Francisco 505 Parnassus Ave., Rm. 795-M, Box 0114 San Francisco, CA 94143-0114 (415) 476-9276 http://pdcenter.neurology.ucsf.edu
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Medical Policy Deep Brain Stimulation. Description. Related Policies. Policy. Subsection. Effective Date February 27,
 7.01.63 Deep Brain Stimulation Section 7.0 Surgery Subsection Effective Date February 27, 2015 Original Policy Date December 18, 2009 Next Review Date February 2016 Medical Policy Description Deep brain
7.01.63 Deep Brain Stimulation Section 7.0 Surgery Subsection Effective Date February 27, 2015 Original Policy Date December 18, 2009 Next Review Date February 2016 Medical Policy Description Deep brain
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview
 Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
The basal ganglia work in concert with the
 Corticostriatal circuitry Suzanne N. Haber, PhD Introduction Corticostriatal connections play a central role in developing appropriate goal-directed behaviors, including the motivation and cognition to
Corticostriatal circuitry Suzanne N. Haber, PhD Introduction Corticostriatal connections play a central role in developing appropriate goal-directed behaviors, including the motivation and cognition to
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION
 UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Policy DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION Policy Number: CS030.F Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Policy DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION Policy Number: CS030.F Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease
 Surgical Surgical treatment treatment for for Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease the Present and the Future the Present and the Future Olga Klepitskaya, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Co-Director,
Surgical Surgical treatment treatment for for Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease the Present and the Future the Present and the Future Olga Klepitskaya, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Co-Director,
Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association.
 Deep Brain Stimulation Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. Title: Deep Brain Stimulation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Deep Brain Stimulation Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. Title: Deep Brain Stimulation Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
The possibility of deep brain stimulation to treat eating disorders.
 The possibility of deep brain stimulation to treat eating disorders. Andres M Lozano MD PhD Professor and Dan Family Chair of Neurosurgery Canada Research Chair in Neuroscience Toronto Western Hospital
The possibility of deep brain stimulation to treat eating disorders. Andres M Lozano MD PhD Professor and Dan Family Chair of Neurosurgery Canada Research Chair in Neuroscience Toronto Western Hospital
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
BME 701 Examples of Biomedical Instrumentation. Hubert de Bruin Ph D, P Eng
 BME 701 Examples of Biomedical Instrumentation Hubert de Bruin Ph D, P Eng 1 Instrumentation in Cardiology The major cellular components of the heart are: working muscle of the atria & ventricles specialized
BME 701 Examples of Biomedical Instrumentation Hubert de Bruin Ph D, P Eng 1 Instrumentation in Cardiology The major cellular components of the heart are: working muscle of the atria & ventricles specialized
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N. GPi Superior colliculus. compacta reticulata
 . Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
. Putamen & Caudate Putamen & Caudate GPe Neocortex Thalamus: VA VM, MD S N GPi Superior colliculus compacta reticulata Substantia Nigra Pedunculopontine nuc. of midbrain ret.form. Satellites of the corpus
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION Policy Number: 2018T0321T Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION Policy Number: 2018T0321T Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
Troubleshooting algorithms for common DBS related problems in tremor and dystonia
 Troubleshooting algorithms for common DBS related problems in tremor and dystonia Elena Moro, MD, PhD, FEAN, FAAN Movement Disorder Center, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble Alpes University, INSERM U1216, Grenoble,
Troubleshooting algorithms for common DBS related problems in tremor and dystonia Elena Moro, MD, PhD, FEAN, FAAN Movement Disorder Center, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble Alpes University, INSERM U1216, Grenoble,
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION
 DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: SURGERY 090.17 T2 Effective Date: March 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 CONDITIONS OF
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: SURGERY 090.17 T2 Effective Date: March 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 CONDITIONS OF
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE
 EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease and Other Movement Disorders
 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 005; Vol. 5, No. Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease and Other Movement Disorders An Evidence-Based Analysis March 005 Medical Advisory Secretariat
Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 005; Vol. 5, No. Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease and Other Movement Disorders An Evidence-Based Analysis March 005 Medical Advisory Secretariat
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical Policy:
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical Policy:
Circuits & Behavior. Daniel Huber
 Circuits & Behavior Daniel Huber How to study circuits? Anatomy (boundaries, tracers, viral tools) Inactivations (lesions, optogenetic, pharma, accidents) Activations (electrodes, magnets, optogenetic)
Circuits & Behavior Daniel Huber How to study circuits? Anatomy (boundaries, tracers, viral tools) Inactivations (lesions, optogenetic, pharma, accidents) Activations (electrodes, magnets, optogenetic)
DBS Programming. Paul S Fishman MD, PhD University of Maryland School of Medicine PFNCA 3/24/18
 DBS Programming Paul S Fishman MD, PhD University of Maryland School of Medicine PFNCA 3/24/18 Disclosure The University of Maryland has received research funding form InSightec and the Focused Ultrasound
DBS Programming Paul S Fishman MD, PhD University of Maryland School of Medicine PFNCA 3/24/18 Disclosure The University of Maryland has received research funding form InSightec and the Focused Ultrasound
DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici
 DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici TECNICHE DI NEUROMODULAZIONE Invasiva: odeep Brain Stimulation Non Invasiva: o Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) o Transcranial
DBS efficacia, complicanze in cronico e nuovi orizzonti terapeutici TECNICHE DI NEUROMODULAZIONE Invasiva: odeep Brain Stimulation Non Invasiva: o Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) o Transcranial
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION
 UnitedHealthcare of California (HMO) UnitedHealthcare Benefits Plan of California (EPO/POS) UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc.
UnitedHealthcare of California (HMO) UnitedHealthcare Benefits Plan of California (EPO/POS) UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc.
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease
 Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
Levodopa vs. deep brain stimulation: computational models of treatments for Parkinson's disease Abstract Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the dopaminergic neurons of the
History of Deep Brain Stimulation in la Pitié-Salpêtrière hospital
 History of Deep Brain Stimulation in la Pitié-Salpêtrière hospital Since the beginning of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) in the 80 s, DBS changed very much following evolution of technologies, but also following
History of Deep Brain Stimulation in la Pitié-Salpêtrière hospital Since the beginning of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) in the 80 s, DBS changed very much following evolution of technologies, but also following
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational. Modeling Study. Karthik Kumaravelu
 Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
Network Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson s Disease A Computational Modeling Study by Karthik Kumaravelu Department of Biomedical Engineering Duke University Date: Approved: Warren M. Grill,
DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION
 Oxford DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: SURGERY 090.19 T2 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Instructions for Use Table of Contents Page CONDITIONS
Oxford DEEP BRAIN AND CORTICAL STIMULATION UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: SURGERY 090.19 T2 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Instructions for Use Table of Contents Page CONDITIONS
Deep Brain Stimulation
 Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 84 Deep Brain Stimulation Next Review: March 2019 Last Review: April 2018 Effective: June 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are developed to provide
Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 84 Deep Brain Stimulation Next Review: March 2019 Last Review: April 2018 Effective: June 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are developed to provide
The Surgical Management of Essential Tremor
 The Surgical Management of Essential Tremor International Essential Tremor Foundation Learning About Essential Tremor: Diagnosis and Treatment Options Albuquerque, NM September 24, 2005 Neurosurgeon Overview:
The Surgical Management of Essential Tremor International Essential Tremor Foundation Learning About Essential Tremor: Diagnosis and Treatment Options Albuquerque, NM September 24, 2005 Neurosurgeon Overview:
symptoms of Parkinson s disease EXCEPT.
 M. Angele Theard, M.D Asst. Professor, Washington University, St. Louis, MO Quiz team; Shobana Rajan, M.D; Suneeta Gollapudy, MD; Verghese Cherian, M.D, M. Angele Theard, MD This quiz is being published
M. Angele Theard, M.D Asst. Professor, Washington University, St. Louis, MO Quiz team; Shobana Rajan, M.D; Suneeta Gollapudy, MD; Verghese Cherian, M.D, M. Angele Theard, MD This quiz is being published
BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW
 BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer Basal Ganglia An Integrative View http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/2976
BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer BASAL GANGLIA AN INTEGRATIVE VIEW Edited by Fernando A. Barrios and Clemens Bauer Basal Ganglia An Integrative View http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/2976
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL) Spring, 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 11 th edition 2006 Eman Al-Khateeb,
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
