Supplementary Information. Gauge size. midline. arcuate 10 < n < 15 5 < n < 10 1 < n < < n < 15 5 < n < 10 1 < n < 5. principal principal
|
|
|
- Damian Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information set set = Reward = Reward Gauge size Gauge size 3 Numer of correct trials 3 Numer of correct trials Supplementary Fig.. Principle of the Gauge increase. The gauge size (y axis) increases linearly following 7 steps depending on the numer of correct Cued trials (x axis) performed in the main task. The total numer of correct trials required to earn each onus varies randomly from one lock to another, defining different speed of gauge increase. It was or 3 trials in a first set of sessions (left, used for monkey D) or,, 9 or 3 trials in a second set (right, used during the recording period for monkeys A and H). Note that the gauge stays full until monkeys check for it (dashed lue lines on top). ArcGen (AP +7.mm) ArcGen (AP +.mm) Post Post Ant Ant midline midline < n < < n < < n < < n < < n < < n < n = 9 n = 9 ArcGen ArcGen mm mm midline midline < n < < n < < n < < n < < n < < n < n = 97 Post Ant n = Post Ant Supplementary Fig.. Recording locations in monkey H and A. Recording grid reconstructions from neuronavigation and from each monkey's anatomical MRI (T,.T). Top, reconstructions of a grid over the 3D surface of the cortex to show the location of recordings in the dorsal frontal and prefrontal cortex (). Major sulci are indicated, as well as the rostro-caudal level of the genu of the sulcus (Arc Gen). Bottom, line drawing of the cortex of the dorsal ank of the cingulate sulcus () taken from an MRI section perpendicular to the electrode tracks. Colored disk size indicates the numer of single units recorded at each location. 'n' indicates the total numer of single units for each structure in each monkey.
2 Firing Rate (spk/sec) Firing Rate (spk/sec) Feedack Feedack / / Cued Cued ADWBTDQHT3 Ch_U9 ADWBTDQHT Ch_U HGPLPMU_9_Ch3_U3 ACYCUDPJU_3_Ch_U7 AIWHTGRDXCVDS Ch_U HFOKMMR Ch_U Time (ms) Touch Touch Supplementary Fig 3. Examples of single unit activity. Average firing rates and rasters for different single unit activities in (top 3 rows) and (ottom 3 rows) during negative/positive feedack (), vs. decisions (Middle), and Cued decisions in the main task (). Black lines on time axis and gray ackground highlight the time periods where the difference in firing rate is significant (Kruskall-Wallis test, p<.).
3 a n = n = n = 37 n = 39 7 n = 9 n = FEEDBACK # CHECK vs. WORK CUED # n = 9 n = 9 n = 3 n = 3 n = 3 n = numer of cells 7 Feedack 7 / 7 Cued numer of cells s On s On c Estimates for Gauge variale p < Supplementary Fig.. Single-suject data. The figures present population data for each monkey ( and H) with conventions as in main Figs. and 7a. (a) Population data of neurons presenting discrimination for Feedack, vs. decisions, and Cued decisions in the main task. Symol # indicates a significant difference etween regions for oth monkeys (Chi-square tests, p<-). () Sliding glm on single unit activity for Feedack, vs., and Cued decisions in the main task. (c) Estimates for the covariate Gauge extracted from the population glm (see main text and Methods).
4 a Post Ant 7 * * FEEDBACK CHECK vs. WORK CUED n = 9 < n < < n < < n < midline 9/ A B Percent of cells 3 DR / A B DR n=3 n= n= n=3 Supplementary Fig.. Homogeneous coding etween regions identified in the. (a) Recording grid reconstruction pooled for oth monkeys and highlighting the numer of recorded neurons in each suregions. The separation etween areas is ased on the description made in Morecraft et al. Cytoarchitecture and cortical connections of the anterior cingulate and adjacent somatomotor fields in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res Bull 7, 7-97 (). () Proportions of neurons (and the actual numer within ars) discriminating Feedack, vs. and Cued decisions in each area. Significant Chi-square comparisons are reported on the figure: * p<., p<.. The main difference was a smaller discrimination of Cued decisions in area B compared to the others. However the numer of recorded neurons in each area was not sufficient to go further in the differentiation etween areas. a Control Ch Control Wo Firing Rate (spk/sec) / s ADVBUCRIT_3_Ch_U9 Cued s time (sec) Touch Touch Supplementary Fig.. vs. compared with the Control task. The control task consists in touching a visual item presented at the position of one of the two levers. No reward is given (see Method). (a) One typical example neuron (recorded in the ) discriminating vs. decisions ut not control trials (left panel, green and pink dashed lines, and rasters on top) nor vs. choices in cued decisions (right panel) (green:, pink:, Blue:, Orange: choices). () Numer of cells in each structure for which a significant effect of vs. (green) or of Control vs. (grey) were oserved. The two histograms present the data for different thresholds, successive significant time ins (on the right, as in the main data analyses), and at a weaker threshold (3 ins, on the left). The figure shows that even at low threshold single units were very much involved in encoding vs. ut not the spatial position of the lever in the Control task. Percent Correct Decoding (%) 9 7 Feedack 9 7 numer of cells with significant effect (3 ins) / 3 39/ /93 / Control 7/9 / numer of cells with significant effect ( ins) Cued s / /93 / Control /9 / Linear Decoding Gaussian SVM Supplementary Fig. 7. Comparison of population coding using linear and non-linear decoding methods. The results otained from non-linear support vector machine (SVM) classifiers with a Gaussian kernel (right lack and lue, for and respectively) are superimposed on the results shown in Fig. a using linear decoding methods (light colors). Both methods used the same overall procedures (see Method). Only the random trial selections differ etween classifiers, which could in principle account for minor deviations. Nevertheless, non-linear SVM classifiers perform as well as linear classifiers, oth in terms of strength or latency of significant decoding (highlighted in old, p<.).
5 a Distance of Aggregation 7 3 Distance of Aggregation 3 N of neurons N of neurons Distance N of neurons Distance N of neurons c Clust Clust Clust Clust Clust Clust d Average Z-values Average firing rate (spk/s) Clust Time (s) Clust FEEDBACK CHECK vs. WORK CUED Cor Inc s Clust Time (s) Supplementary Fig.. Hierarchical clustering of SUAs. (a) Dendrograms for (left) and (right) representing the trees of classification constructed y the hierarchical clustering algorithm. () Similarity matrices otained from the dendrogram at a specific threshold (red line in a). Neurons are sorted ased on their appartenance to a given cluster. (c) Average z-values of each detected clusters for the 3 parameters considered (Feedack, vs. and Cued decisions) revealing classes of neurons with different encoding properties. The sign of z-values indicates the selectivity indicated within ars (e.g. positive z-values for feedack indicate more activity for Negative () than for positive feedack). (d) Average firing rate around feedack and (top and middle rows) and targets selection (ottom row) for the main clusters displayed in c (Clusters 3, & for, and & 3 for, from left to right). The clustering procedure highlights the preponderance of feedack in the as well as the co-expression of feedack and check-related activity. However, neurons were mostly grouped depending on their Cued decision preference in the main task.
6 monkey A monkey H.. RT (s).. n-3 n- n- n Distance to check n n-3 n- n- n Distance to check n Supplementary Fig. 9. / response times. Violin representations of and response times depending on the distance to check, at trial n, for monkey A (left panel) and H (right panel). Distriutions of response times were compared using a two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, revealing a significant differences etween trial n compared to all others (n-, n- and n-3; p<-3). Other comparisons (etween n-,n- or n-3) were not significant (p>.3). Hence, the figure shows that monkeys' response times differed etween and decisions ut did not vary with the distance to check (n-3 to n-, i.e. etween decisions). Estimates. Estimates. Gauge Scan / p<..... p<. Supplementary Fig.. Fixed effects of Scan, Gauge and / decision on group activity in (left) and (right). The estimates correspond to the isolated fixed effects from the glmm (see Methods). We tested and found that the interaction in-per-in etween Scan and / was not significant. Nevertheless, oth have a positive influence on group activity in : activity is higher when the monkey checks, and when he scans oth levers. The horizontal lines indicate which ins (equal or more than successive) are at p<.. a Numer of cells discriminating Difficulty in the main task 7 Difficulty Time (s) s On vs. discrimination (z-value) / VS Difficulty r =. p =.9 r =. p =. Supplementary Fig.. Numer of neurons encoding difficulty in the main task and its relation with encoding vs.. (a) Time resolved numer of cells extracted from the sliding glm with a significant discrimination of difficulty in the main task. Dashed gray line represents the % level. () Scatter plot showing the relationship etween asolute maximal z-values for vs. discrimination for each neuron (extracted from the sliding glm, y-axis) and difficulty at the time of target onset in the main task (x-axis). Note that only weak, if any, encoding of difficulty was oserved, and note also the asence of correlation etween and Difficulty effects in oth areas (r and p indicated within the panels).. Difficulties discrimination (z-value) Difficulties discrimination (z-value)
7 deviance glmm-olre 9 AIC glmm OLRE / AIC glmm deviance glmm 3 time in Supplementary Fig.. Model comparisons etween poisson glmm with or without the Oservation-Level random effects (OLRE). The models named glmm and glmm-olre are compared for deviance (right) and AIC (left: ratio of the two AIC across time ins (for the two structures, and ). The models included Gauge,, and PreviousPerformance as fixed effects and SUA as random effect. Note that the glmm-olre has always smaller deviance and smaller AIC.
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Figure 1. Excerpt of stimulus presentation paradigm for Study I.
 Transition Visual Auditory Tactile Time 14 s Figure 1. Excerpt of stimulus presentation paradigm for Study I. Visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli were presented to sujects simultaneously during imaging.
Transition Visual Auditory Tactile Time 14 s Figure 1. Excerpt of stimulus presentation paradigm for Study I. Visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli were presented to sujects simultaneously during imaging.
Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons
 Supplementary Information for: Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons Steven W. Kennerley, Timothy E. J. Behrens & Jonathan D. Wallis Content list: Supplementary
Supplementary Information for: Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons Steven W. Kennerley, Timothy E. J. Behrens & Jonathan D. Wallis Content list: Supplementary
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Task timeline for Solo and Info trials.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Task timeline for Solo and Info trials. Each trial started with a New Round screen. Participants made a series of choices between two gambles, one of which was objectively riskier
Supplementary Figure 1 Task timeline for Solo and Info trials. Each trial started with a New Round screen. Participants made a series of choices between two gambles, one of which was objectively riskier
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro
 Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Perceptual learning in a non-human primate model of artificial vision
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Perceptual learning in a non-human primate model of artificial vision Nathaniel J. Killian 1,2, Milena Vurro 1,2, Sarah B. Keith 1, Margee J. Kyada 1, John S. Pezaris 1,2 1 Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Perceptual learning in a non-human primate model of artificial vision Nathaniel J. Killian 1,2, Milena Vurro 1,2, Sarah B. Keith 1, Margee J. Kyada 1, John S. Pezaris 1,2 1 Department
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex
 J Neurophysiol 90: 1790 1806, 2003. First published May 7, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00086.2003. From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex Jonathan D. Wallis and Earl K. Miller
J Neurophysiol 90: 1790 1806, 2003. First published May 7, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00086.2003. From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex Jonathan D. Wallis and Earl K. Miller
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Response time and signal detection time distributions SM Fig. 1. Correct response time (thick solid green curve) and error response time densities (dashed red curve), averaged across
1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Response time and signal detection time distributions SM Fig. 1. Correct response time (thick solid green curve) and error response time densities (dashed red curve), averaged across
U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material.
 U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2003 23(12):5235 5246 5235 A Comparison of Primate
U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2003 23(12):5235 5246 5235 A Comparison of Primate
Orbitofrontal cortical activity during repeated free choice
 J Neurophysiol 107: 3246 3255, 2012. First published March 14, 2012; doi:10.1152/jn.00690.2010. Orbitofrontal cortical activity during repeated free choice Michael Campos, Kari Koppitch, Richard A. Andersen,
J Neurophysiol 107: 3246 3255, 2012. First published March 14, 2012; doi:10.1152/jn.00690.2010. Orbitofrontal cortical activity during repeated free choice Michael Campos, Kari Koppitch, Richard A. Andersen,
Supporting Information
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
NC bp. b 1481 bp
 Kcna3 NC 11 178 p 1481 p 346 p c *** *** d relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD4 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna Kcna6 Kcna7 Kcnn4 relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD8 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna
Kcna3 NC 11 178 p 1481 p 346 p c *** *** d relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD4 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna Kcna6 Kcna7 Kcnn4 relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD8 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings
 Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
 J Neurophysiol 12: 3352 3364, 29. First published September 23, 29; doi:1.1152/jn.273.29. Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
J Neurophysiol 12: 3352 3364, 29. First published September 23, 29; doi:1.1152/jn.273.29. Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation
 Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation GREGG H. RECANZONE 1 AND ROBERT H. WURTZ 2 1 Center for Neuroscience and Section of Neurobiology, Physiology and Behavior,
Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation GREGG H. RECANZONE 1 AND ROBERT H. WURTZ 2 1 Center for Neuroscience and Section of Neurobiology, Physiology and Behavior,
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation
 Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4.
 Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in primary visual cortex
 *Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
*Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
brain valuation & behavior
 brain valuation & behavior 9 Rangel, A, et al. (2008) Nature Neuroscience Reviews Vol 9 Stages in decision making process Problem is represented in the brain Brain evaluates the options Action is selected
brain valuation & behavior 9 Rangel, A, et al. (2008) Nature Neuroscience Reviews Vol 9 Stages in decision making process Problem is represented in the brain Brain evaluates the options Action is selected
Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2
 Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2 Hillyard(1973) Dichotic Listening Task N1 component enhanced for attended stimuli Supports early selection Effects of Voluntary
Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2 Hillyard(1973) Dichotic Listening Task N1 component enhanced for attended stimuli Supports early selection Effects of Voluntary
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load
 Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Hippocampal Time Cells : Time versus Path Integration
 Article Hippocampal Time Cells : Time versus Path Integration Benjamin J. Kraus, 1, * Robert J. Robinson II, 1 John A. White, 2 Howard Eichenbaum, 1 and Michael E. Hasselmo 1 1 Center for Memory and Brain,
Article Hippocampal Time Cells : Time versus Path Integration Benjamin J. Kraus, 1, * Robert J. Robinson II, 1 John A. White, 2 Howard Eichenbaum, 1 and Michael E. Hasselmo 1 1 Center for Memory and Brain,
Identification of Neuroimaging Biomarkers
 Identification of Neuroimaging Biomarkers Dan Goodwin, Tom Bleymaier, Shipra Bhal Advisor: Dr. Amit Etkin M.D./PhD, Stanford Psychiatry Department Abstract We present a supervised learning approach to
Identification of Neuroimaging Biomarkers Dan Goodwin, Tom Bleymaier, Shipra Bhal Advisor: Dr. Amit Etkin M.D./PhD, Stanford Psychiatry Department Abstract We present a supervised learning approach to
Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex
 Article Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex Adrián Hernández, 1 Verónica Nácher, 1 Rogelio Luna, 1 Antonio Zainos, 1 Luis Lemus, 1 Manuel Alvarez, 1 Yuriria Vázquez, 1 Liliana Camarillo,
Article Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex Adrián Hernández, 1 Verónica Nácher, 1 Rogelio Luna, 1 Antonio Zainos, 1 Luis Lemus, 1 Manuel Alvarez, 1 Yuriria Vázquez, 1 Liliana Camarillo,
Table 1. Summary of PET and fmri Methods. What is imaged PET fmri BOLD (T2*) Regional brain activation. Blood flow ( 15 O) Arterial spin tagging (AST)
 Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Neural Coding. Computing and the Brain. How Is Information Coded in Networks of Spiking Neurons?
 Neural Coding Computing and the Brain How Is Information Coded in Networks of Spiking Neurons? Coding in spike (AP) sequences from individual neurons Coding in activity of a population of neurons Spring
Neural Coding Computing and the Brain How Is Information Coded in Networks of Spiking Neurons? Coding in spike (AP) sequences from individual neurons Coding in activity of a population of neurons Spring
List of Figures. List of Tables. Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
List of Figures List of Tables Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xv xxv xxix xxxi 1 What Is R? 1 1.1 Introduction to R................................ 1 1.2 Downloading and Installing
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Statistics 202: Data Mining. c Jonathan Taylor. Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes.
 Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Paul-Chen Hsieh, Ming-Tsung Tseng, Chi-Chao Chao, Yea-Huey Lin Wen-Yih I. Tseng, Kuan-Hong Liu, Ming-Chang Chiang, Sung-Tsang Hsieh
 IMAGING SIGNATURES OF ALTERED BRAIN RESPONSES IN SMALL-FIBER NEUROPATHY: REDUCED FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY OF THE LIMBIC SYSTEM AFTER PERIPHERAL NERVE DEGENERATION Paul-Chen Hsieh, Ming-Tsung Tseng, Chi-Chao
IMAGING SIGNATURES OF ALTERED BRAIN RESPONSES IN SMALL-FIBER NEUROPATHY: REDUCED FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY OF THE LIMBIC SYSTEM AFTER PERIPHERAL NERVE DEGENERATION Paul-Chen Hsieh, Ming-Tsung Tseng, Chi-Chao
A toolbox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing
 A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
Supplemental Information. Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion
 Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
Single cell tuning curves vs population response. Encoding: Summary. Overview of the visual cortex. Overview of the visual cortex
 Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex
 Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex Luc Estebanez 1,2 *, Sami El Boustani 1 *, Alain Destexhe 1, Daniel E. Shulz 1 1 Unité de Neurosciences,
Supplementary Information for Correlated input reveals coexisting coding schemes in a sensory cortex Luc Estebanez 1,2 *, Sami El Boustani 1 *, Alain Destexhe 1, Daniel E. Shulz 1 1 Unité de Neurosciences,
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Representation of negative motivational value in the primate
 Representation of negative motivational value in the primate lateral habenula Masayuki Matsumoto & Okihide Hikosaka Supplementary Figure 1 Anticipatory licking and blinking. (a, b) The average normalized
Representation of negative motivational value in the primate lateral habenula Masayuki Matsumoto & Okihide Hikosaka Supplementary Figure 1 Anticipatory licking and blinking. (a, b) The average normalized
(Visual) Attention. October 3, PSY Visual Attention 1
 (Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
(Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Table 1 Patient characteristics Preoperative. language testing
 Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 11, 29 29(1):3259 327 3259 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Steven W. Kennerley and Jonathan D.
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 11, 29 29(1):3259 327 3259 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Steven W. Kennerley and Jonathan D.
Models of visual neuron function. Quantitative Biology Course Lecture Dan Butts
 Models of visual neuron function Quantitative Biology Course Lecture Dan Butts 1 What is the neural code"? 11 10 neurons 1,000-10,000 inputs Electrical activity: nerve impulses 2 ? How does neural activity
Models of visual neuron function Quantitative Biology Course Lecture Dan Butts 1 What is the neural code"? 11 10 neurons 1,000-10,000 inputs Electrical activity: nerve impulses 2 ? How does neural activity
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab
 TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type
 Article Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type Cory R. Hussar 1,2 and Tatiana Pasternak 1,2, * 1 Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy 2 Center for Visual Science
Article Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type Cory R. Hussar 1,2 and Tatiana Pasternak 1,2, * 1 Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy 2 Center for Visual Science
Neuronal Encoding of Subjective Value in Dorsal and Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 14, 2012 32(11):3791 3808 3791 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Neuronal Encoding of Subjective Value in Dorsal and Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Xinying Cai 1 and Camillo
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 14, 2012 32(11):3791 3808 3791 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Neuronal Encoding of Subjective Value in Dorsal and Ventral Anterior Cingulate Cortex Xinying Cai 1 and Camillo
Morton-Style Factorial Coding of Color in Primary Visual Cortex
 Morton-Style Factorial Coding of Color in Primary Visual Cortex Javier R. Movellan Institute for Neural Computation University of California San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0515 movellan@inc.ucsd.edu Thomas
Morton-Style Factorial Coding of Color in Primary Visual Cortex Javier R. Movellan Institute for Neural Computation University of California San Diego La Jolla, CA 92093-0515 movellan@inc.ucsd.edu Thomas
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson
 Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Chapter 1: Introduction... 1
 From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings. Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014
 Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Reward and choice encoding in terminals of midbrain dopamine neurons depends on striatal target
 Reward and encoding in terminals of midrain dopamine neurons depends on striatal target Nathan F Parker, Courtney M Cameron, Joshua P Taliaferro, Junuk Lee, Jung Yoon Choi, Thomas J Davidson, Nathaniel
Reward and encoding in terminals of midrain dopamine neurons depends on striatal target Nathan F Parker, Courtney M Cameron, Joshua P Taliaferro, Junuk Lee, Jung Yoon Choi, Thomas J Davidson, Nathaniel
A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum
 A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum Rahmat Muhammad 1, Jonathan D. Wallis 1,2, and Earl K. Miller 1 Abstract & The ability to
A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum Rahmat Muhammad 1, Jonathan D. Wallis 1,2, and Earl K. Miller 1 Abstract & The ability to
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Effects of Amygdala Lesions on Reward-Value Coding in Orbital and Medial Prefrontal Cortex
 Article Effects of Amygdala Lesions on Reward-Value Coding in Orbital and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Peter H. Rudebeck, 1, * Andrew R. Mitz, 1 Ravi V. Chacko, 1 and Elisabeth A. Murray 1 1 Section on the
Article Effects of Amygdala Lesions on Reward-Value Coding in Orbital and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Peter H. Rudebeck, 1, * Andrew R. Mitz, 1 Ravi V. Chacko, 1 and Elisabeth A. Murray 1 1 Section on the
A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $
 Neurocomputing 69 (26) 1327 1331 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $ Shinya Ishii a,1, Munetaka
Neurocomputing 69 (26) 1327 1331 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $ Shinya Ishii a,1, Munetaka
There are, in total, four free parameters. The learning rate a controls how sharply the model
 Supplemental esults The full model equations are: Initialization: V i (0) = 1 (for all actions i) c i (0) = 0 (for all actions i) earning: V i (t) = V i (t - 1) + a * (r(t) - V i (t 1)) ((for chosen action
Supplemental esults The full model equations are: Initialization: V i (0) = 1 (for all actions i) c i (0) = 0 (for all actions i) earning: V i (t) = V i (t - 1) + a * (r(t) - V i (t 1)) ((for chosen action
Consistency of Encoding in Monkey Visual Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 2001, 21(20):8210 8221 Consistency of Encoding in Monkey Visual Cortex Matthew C. Wiener, Mike W. Oram, Zheng Liu, and Barry J. Richmond Laboratory of Neuropsychology,
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 15, 2001, 21(20):8210 8221 Consistency of Encoding in Monkey Visual Cortex Matthew C. Wiener, Mike W. Oram, Zheng Liu, and Barry J. Richmond Laboratory of Neuropsychology,
Nov versus Fam. Fam 1 versus. Fam 2. Supplementary figure 1
 a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation. Tom Hartley
 Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition
 Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks
 Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Meaning-based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Early Learning vs Early Variability 1.5 r = p = Early Learning r = p = e 005. Early Learning 0.
 The temporal structure of motor variability is dynamically regulated and predicts individual differences in motor learning ability Howard Wu *, Yohsuke Miyamoto *, Luis Nicolas Gonzales-Castro, Bence P.
The temporal structure of motor variability is dynamically regulated and predicts individual differences in motor learning ability Howard Wu *, Yohsuke Miyamoto *, Luis Nicolas Gonzales-Castro, Bence P.
Error Detection based on neural signals
 Error Detection based on neural signals Nir Even- Chen and Igor Berman, Electrical Engineering, Stanford Introduction Brain computer interface (BCI) is a direct communication pathway between the brain
Error Detection based on neural signals Nir Even- Chen and Igor Berman, Electrical Engineering, Stanford Introduction Brain computer interface (BCI) is a direct communication pathway between the brain
Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates
 Cerebral Cortex 2007;17:i27-i40 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm086 Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates Genevie` ve Cadoret and Michael Petrides
Cerebral Cortex 2007;17:i27-i40 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm086 Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates Genevie` ve Cadoret and Michael Petrides
Feedback-Controlled Parallel Point Process Filter for Estimation of Goal-Directed Movements From Neural Signals
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL SYSTEMS AND REHABILITATION ENGINEERING, VOL. 21, NO. 1, JANUARY 2013 129 Feedback-Controlled Parallel Point Process Filter for Estimation of Goal-Directed Movements From Neural
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL SYSTEMS AND REHABILITATION ENGINEERING, VOL. 21, NO. 1, JANUARY 2013 129 Feedback-Controlled Parallel Point Process Filter for Estimation of Goal-Directed Movements From Neural
Supplementary Figure 2. Inter discharge intervals are consistent across electrophysiological scales and are related to seizure stage.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Progression of seizure activity recorded from a microelectrode array that was not recruited into the ictal core. (a) Raw LFP traces recorded from a single microelectrode during
Supplementary Figure 1. Progression of seizure activity recorded from a microelectrode array that was not recruited into the ictal core. (a) Raw LFP traces recorded from a single microelectrode during
Representation of Immediate and Final Behavioral Goals in the Monkey Prefrontal Cortex during an Instructed Delay Period
 Cerebral Cortex October 2005;15:1535--1546 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhi032 Advance Access publication February 9, 2005 Representation of Immediate and Final Behavioral Goals in the Monkey Prefrontal Cortex during
Cerebral Cortex October 2005;15:1535--1546 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhi032 Advance Access publication February 9, 2005 Representation of Immediate and Final Behavioral Goals in the Monkey Prefrontal Cortex during
A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas
 A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas Douglas A. Ruff a,1 and Marlene R. Cohen a a Department of Neuroscience and Center for the Neural Basis
A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas Douglas A. Ruff a,1 and Marlene R. Cohen a a Department of Neuroscience and Center for the Neural Basis
Supplementary Figures
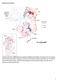 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1: Map of the ten countries included in the analysis. Showing the first sub-national administrative boundaries in light grey, and DHS survey locations representing
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1: Map of the ten countries included in the analysis. Showing the first sub-national administrative boundaries in light grey, and DHS survey locations representing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control Authors: Iñaki Iturrate 1,2, Ricardo Chavarriaga 2, Luis Montesano 1, Javier Minguez 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Teaching brain-machine interfaces as an alternative paradigm to neuroprosthetics control Authors: Iñaki Iturrate 1,2, Ricardo Chavarriaga 2, Luis Montesano 1, Javier Minguez 1,
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Parietal Reach Region Encodes Reach Depth Using Retinal Disparity and Vergence Angle Signals
 J Neurophysiol 12: 85 816, 29. First published May 13, 29; doi:1.12/jn.9359.28. Parietal Reach Region Encodes Reach Depth Using Retinal Disparity and Vergence Angle Signals Rajan Bhattacharyya, 1 Sam Musallam,
J Neurophysiol 12: 85 816, 29. First published May 13, 29; doi:1.12/jn.9359.28. Parietal Reach Region Encodes Reach Depth Using Retinal Disparity and Vergence Angle Signals Rajan Bhattacharyya, 1 Sam Musallam,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Population Comparisons
 Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Population Comparisons Polina Golland 1,BruceFischl 2, Mona Spiridon 3, Nancy Kanwisher 3, Randy L. Buckner 4, Martha E. Shenton 5, Ron Kikinis 6, and W. Eric L.
Discriminative Analysis for Image-Based Population Comparisons Polina Golland 1,BruceFischl 2, Mona Spiridon 3, Nancy Kanwisher 3, Randy L. Buckner 4, Martha E. Shenton 5, Ron Kikinis 6, and W. Eric L.
The primate amygdala combines information about space and value
 The primate amygdala combines information about space and Christopher J Peck 1,8, Brian Lau 1,7,8 & C Daniel Salzman 1 6 npg 213 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. A stimulus predicting reinforcement
The primate amygdala combines information about space and Christopher J Peck 1,8, Brian Lau 1,7,8 & C Daniel Salzman 1 6 npg 213 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. A stimulus predicting reinforcement
Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation. I. Scales of Measurement A Review
 Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation The description and presentation of results involves a number of topics. These include scales of measurement, descriptive statistics used to summarize
Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation The description and presentation of results involves a number of topics. These include scales of measurement, descriptive statistics used to summarize
