Faculty of Dentistry, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania b
|
|
|
- Teresa Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2014; 9(1): EDITORIAL Oral Leukoplakia an Update Ioanina PARLATESCU a ; Carmen GHEORGHE a ; Elena COCULESCU b ; Serban TOVARU a a Faculty of Dentistry, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania b Committee of Public Health of the Senate, Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT The main purpose of this paper was to assess the current state of science on oral leukoplakia. Although it is considered a potentially malignant disorder the overall malignant progression of oral leukoplakia is of the order of 5% and even more. Nowadays there are no currently accepted markers to distinguish those that may progress to cancer from those that may not. The current golden standard is considered the presence of epithelial dysplasia on the tissue biopsy of the lesion. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia is a rare form of OL which has multiple recurrences, is refractory to treatment and has malignant transformation in a short period. It is considered a true premalignant lesion. The management of oral leukoplakia varies from a wait and see attitude and topical chemopreventive agents to complete surgical removal. Keywords: oral leukoplakia, potentially malignant disorder INTRODUCTION It has been reported that oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with the presence of potentially malignant disorders in 15-48% cases (1). Oral leukoplakia (OL) is the most frequent potentially malignant disorder of oral mucosa. Although OL is mentioned in clinical reviews since 1969 (2), it was first defined by World Health Organization in 1978 (3) as a white patch or plaque which cannot otherwise be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease. Since then until now, the meaning of oral leukoplakia is not very much changed. In 1994 (4), after an international symposium held in Uppsala, Sweden in the definition, was added that oral leukoplakia is not associated with any physical or chemical cause, excepting smoking and it can become cancer. In 2007 it was decided that the name of leukoplakia should be limited only to a clinical diagnosis defined by exclusion of other white lesions such as oral lichen planus, white sponge nevus, nicotine stomatitis, leukoedema etc (5). In 2012 van der Waal (6) proposed a new definition which seems more oportune as it includes the histological confirma tion A predominantly white lesion or plaque of questionable behavior having excluded, clinically and histopathologically, any other definable white disease or disorder. This one hasn t been assessed yet by WHO but it has good chances for acceptance. Incidence. Demographic distribution The pooled estimated prevalence rate of oral leukoplakia in 2003 varied between 1.7 to 2.7% in general population (7). For this estimated rate, the author- Stefano Petti, in a metaanalysis including 23 primary studies from all over the world published in the period Address for correspondence: Ioanina Parlatescu, 4-6 Eforiei Street, 3 rd floor, room 18, Bucharest, Romania. ioanina_parlatescu@yahoo.com. Article received on the 29 th of January Article accepted on the 18 th of December Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
2 2002 found no difference between geographical areas and between younger and older patients. It has been reported that between 16% and 62% of oral squamous carcinomas are associated with oral leukoplakia (6). OL is often found among men, and its prevalence increases with age advancement. It has been estimated that it mainly affects men over 40 years (8). Etiology The etiology of OL is considered multifactorial, but smoking is appreciated to be a frequently involved factor. It is much more common among smokers than among non-smokers (5). Alcohol is thought to be an independent risk factor (4) but definitive data are still lacking. There are conflicting results of studies related to the possible role of human papillomavirus infection. As OL can mimic a large variety of lesions, in case a possible causal factor is suspected such as dental restoration, mechanical irritation. In the later case a subsequent evaluation in 4 weeks is needed (6). Clinical appearance OL is classified in two main types: homogeneous type which appears as a flat white lesion and non-.homogeneous type which includes speckled, nodular and verrucous leukoplakia (5). The homogeneous leukoplakia is a uniform, thin white area altering or not with normal mucosa (Figure 1). The speckled type is a white and red lesion, with a predominantly white surface (Figures 2 a and 2 b). Verrucous leukoplakia has an elevated, proliferative or corrugated surface appearance (Figure 3). The nodular type has small polypoid outgrowths, rounded predominantly white excrescences (5) (Figure 5). Proliferative verrrucous leukoplakia is a subtype of verrucous leukoplakia characterized by an aggressive evolution, a multifocal appearance, resistance to treatment, higher degree of recurrence and a high rate of malignant transformation (9). Histopathological features Histological appearance of oral leukoplakia varies between no dysplasia and carcinoma. Dysplasia reflects histological changes which are followed by the loss of uniformity or of the architecture of the epithelial cells. It can be related to disturbed cell proliferation (mentioned as 1-9 in Table 1) or to a disordered maturation FIGURE 1. Homogenous leukoplakia of the lingual versant of the gingiva. FIGURE 2A. Speckeled leukoplakia on the right retrocomisural mucosa in a hard smoker. FIGURE 2B. Speckeled leukoplakia on the left retrocomisural mucosa in the same patient (Candidal leukoplakia). Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
3 (10-13 in the Table 1) (10). At the last world seminar of Oral Medicine about potentially malignant lesions, London 2010 (11), it has been recommended a binary classification of histological changes (without risk or low risk and moderate or severe risk). This aims to reduce subjectivity in grading dysplasia, thus increasing the possibility of conformity between histological interpretations of different pathologists (5). Lesions are classified as non-dysplastic and dysplastic (mild dysplasia, moderate or severe). Some authors have already tested this system for grading dysplasia and confirmed these views (11). FIGURE 3. Verrucous leukoplakia on the floor of the mouth. FIGURE 4. Nodular leukoplakia of the soft palate. Histological changes 1. Loss of polarity of basal cells 2. More than one layer of cell with basaloid appearance 3. Drop-shaped rete-ridges 4. Increased nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio 5. Nuclear hyperchromatism 6. Enlarged nucleoli 7. Increased number of mitotis 8. Abnormal form of mitosis 9. The presence of mitotic cells in the superficial epithelium 10. Cellular and nuclear pleomorphism 11. Irregular epithelial stratification 12. Loss of intercellular adherence 13. Keratinization of single cells or cell groups in the prickle cell layer TABLE 1. Histological types of parotid tumor. Malignant transformation and specific biomarkers Oral squamous cell carcinoma is a common malignancy worldwide and the most encountered oral malignant tumor (12,13). It has a multifactorial etiology but the most important factors are tobacco and alcohol, separately and synergically (13). The cohort studies about oral leukoplakia are very rare, so it is difficult to appreciate its real malignant transformation rate due to various regional habits (6,14). Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia in annual average is 1% in different populations and geographic areas with the higher risk reported by 43% (15), hence the follow up in these patients should be active and long termed. The risk factors for malignancy of OL such as vicious habits (smoking, alcohol intake), clinical form, location of lesions were studied. Among them, tobacco cigarette smoking was reported to be the most important etiological factor for the development of oral premalignant lesions and to their progression into oral carcinoma (16). Napier and Speight have recently revised predictive clinical factors -age, gender, location of lesions but results vary between different study populations (12). In an Italian population oral premalignant lesions located on the tongue were more frequently dysplastic compared with the buccal mucosa. Conversely in the Indian population oral leukoplakia of the buccal mucosa is more involved in malignisation. Despite enormous progress in molecular biology at present there is no certain marker to predict malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia in a particular patient. As it was 20 years ago, epithelial dysplasia is still currently considered the gold standard for determining the risk of malignant transformation (15). According to Silverman (17), 36% of dysplastic lesions progress to carcinoma, and 16% of non-dysplastic lesions. However it is known that epithelial dysplasia is correlated with clinically het- 90 Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
4 erogeneous lesions that are considered to have the greatest risk. As histological examination has a degree of subjectivity, there is the need to improve its capacity to assess the dysplasia. This can be done using other markers or by the cross examination of two pathologists. Identification of biomarkers for oral carcinogenesis is based on markers of proliferation ( Ki-67) and component of cell cycle control such as tumor suppressor proteins p53, the retinoblastoma protein (prb) and cycline D1. But none of these markers are used in routine diagnosis. Expression of p53 and loss of expression of p16 are shown to be the earliest events in the malignisation process. In non-dysplastic leukoplakia a combined alteration of p53/ki67/ p16ink4a was proven to be a risk of progression (18). Another valuable predictive method is a mor phometric computer-assisted analysis was used the measure the size of the cell perimeter and the nuclear perimeter of normal mucosa, oral leukoplakia and oral carcinoma. This technique used computer images of histological stain ed sections. It showed that these dimensions increased gradually with significant difference from normal mucosa, oral leukoplakia and the highest level in oral carcinoma (19). Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL) was first described by Hansen (1985) has a high risk of transformation in oral carcinoma. PVL begins as one or more homogeneous leukoplakic areas and, in time it extends to more oral sites. It slowly grows and has a high tendency to recur after treatment. It has been reported that most frequently it affects the gingivae (20). But other authors also mention the buccal mucosa, gingiva, and alveola ridges (21). Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia has an uncertain etiology. The association of PVL and presence of Human Papilloma Virus has been suggested previously but wasn t confirmed by further studies so far (21). Also the association of PVL and Epstain-Barr virus (EBV) has been studied. Epstain- Barr virus is the proven etiologic cause of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, oral hairy leukoplakia, lymphoproliferative disease, B-cell lymphomas and lymphoepithelial carcinoma. EBV was examined by nested PCR in 10 cases of PVL, five with oral squamous carcinoma, and five normal mucosa samples. Epstein Barr virus was detected in 60% of the PVL cases and in 40% of oral carcinoma, but in none of the normal mucosa samples (22). The diagnosis of PVL based on clinical data is usually late, as the progressive evolution of the lesions from homogeneous leukoplakia spreading too many different locations and with the appearance of erythroplastic and verrucous forms takes time. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia has a high rate of recurrences after treatment and a high rate malignant transformation. This is appreciated to 74% of cases, with a tendency of multicentric foci (23). Multiple location lesions are more prone to finally develop with single location leukoplakia they found that widespread lesions have a higher potential for the cancer development than unique lesions. Adjunctive noninvasive methods of investigation The usual clinical examination of oral mucosa is most frequently visual. It is the standard conventional method for oral cancer screening. It depends on the experience and skills of the clinician. But the risk level of the lesion is difficult to measure. There are many variants of adjunctive techniques for the detection of potentially malignant disorders, including oral leu koplakia. Brush biopsy was designed for clinical lesions which initially based on clinical features did not require a biopsy. This is a noninvasive technique which collects the basal layer cells using a brush. It can be used for mass screening campaigns. It eliminates the need for surgical procedure in doubtful lesions (24). Since it was introduced in 1999, until now it shows great promise (25). Toluidine blue is an intravital staining for nucleic acids and abnormal tissue. Initially was used for mucosal lesions of the cervix. In the oral cavity the method was used as guidance for biopsy site selection. Chemiluminescence (reflective tissue fluorescence) was first applied for the detection of cervix dysplasia. It is based upon the normal fluorescence of the tissue when exposed to blue-white illumination. The technique has been adapted for oral mucosal inspection in the ViziLite system. It detects a variety of oral mucosa lesions including linea alba, hairy Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
5 tongue, leukoedema traumatic ulcers (25). Oral leukoplakia has a high degree of visibility and sharpness with proeminent and distinctive margins of the surrounding mucosa. ViziLite has a limitation in discriminating between benign, inflammatory and potentially malignant disorders and it has a low specifity (28%) in detection of dysplasia. As the test does not accurately distinguish between high risk and low risk leukoplakia it should be used with caution (26). The limit of all these methods or techniques is that they do not provide a definitive diagnosis. They are useful in evaluating a multicentric lesion as well as in noncompliant patient for motivating them to return for further controls. Treatment guidelines The main objective in oral leukoplakia s management of care is to detect and to prevent malignant transformation. At the first, the ceasing of the risk activities such as smoking is recommended. Further, the histopathological evaluation is needed. The degree of dysplasia will guide the choice of the treatment. Oral leukoplakia presenting low malignant risk (no dysplasia or simple displasia) may be either completely removed or not, and the decision should con sider other factors such as location, size and, in the case of smokers, the patient s engagement in smoking cessation (12). In the presence of moderate or severe epithelial dysplasia, surgical treatment is recommended (6). The surgical treatment can use conventional surgery or laser ablation, electrocauterization, or cryosurgery (27). Recurrence of OL after surgical treatment has been reported in more than 10% of cases (27). Surgical excision of OL does not lower the risk of subsequent malignant transformation but it brings the opportunity for a complete histolopathological examination of the lesion. Cryotherapy is not considered to be a first line therapy of oral leukoplakia. The risk of post-operative scarring, tissue contraction limit the use of the method (27). The medical treatment uses local and systemic chemopreventive agents such as vitamin A and retinoids, systemic beta carotene, lycopene (a carotenoid), ketorolac (as mouthwash), local bleomycin, and a mixture of tea used both topically and systemically with a reduced benefit (27). Another possible choice is an attitude of wait and see to keep oral leukoplakia under clinical and histological surveillance with frequent visits and biopsies without other treatment. This follow-up can observe an early malignant transformation and subsequent specific treatment (27). CONCLUSIONS The role of the dentist and general practitioner is important in the early diagnosis when leukoplakia is usually asymptomatic and it is simple to remove possible factors involved in its etiology -smoking, thus reducing the rate of malignant transformation. There is no satisfactory treatment for leukoplakia so far. It must be assumed that generally leukoplakia should be removed preferably totally, if possible and patients should be regularly monitored for any relevant mucosal change, and instructed to avoid the major risk factors of oral epithelial dysplasia, especially tobacco usage and alcohol consumption. Conflict of interests: none declared. Acknowledgement: This paper was supported by the Sectorial Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOP HRD) , financed from the European Social Fund and by the Romanian Government under the contract number POSDRU/107/1.5/S/ REFERENCES 1. Hsue SS, Wang WC, Chen CH, et al. Malignant transformation in 1458 patients with potentially malignant oral mucosal disorders: a follow-up study based in a Taiwanese hospital. J Oral Pathol Med 2007; 36: Sugar L, Banoczy J Follow-up Studies in Oral Leukoplakia. Bull. Org. mond. Sante 1969; 41: Kramer IR, Lucas RB, Pindborg JJ, et al. Definition of leukoplakia and related lesions: an aid to studies on oral precancer. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. 1978; 46: Axéll T, Pindborg JJ, Smith CJ, et al. Oral white lesions with special reference to precancerous and tobacco- related lesions: conclusions of an international symposium held in Uppsala, Sweden, May International Collaborative Group on Oral White Lesions. J Oral Pathol Med. 1996; 25: Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson NW, Van der Waal I Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa. J Oral 92 Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
6 Pathol Med. 2007; 36: Brouns E, Baart JA, Bloemena E, et al. The relevance of uniform reporting in oral leukoplakia: Definition, certainty factor and staging based on experience with 275 patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012; Doi: / medoral 7. Petti S Pooled estimate of world leukoplakia prevalence: a systematic review. Oral Oncol 2003; 39: Napier SS, Speight PM Natural history of potentially malignant oral lesions and conditions: an overview of the literature. J Oral Pathol Med 2008; 37: Van der Waal I, Reichart PA Oral proliferative verrucous leukoplakia revisited. Oral Oncol 2008; 44: Warnakulasuriya JS Histological grading of oral epithelial dysplasia: revisited. Pathol 2001; 194: The American Academy of Oral Medicine, Clinician s guide, Diagnosis of Oral Cancer and Potentially Malignant Lesions, First Edition, Napier SS, Speight PM Natural history of potentially malignant oral lesions and conditions: an overview of the literature. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008; 37: Scully C Oral cancer aetiopathogenesis; past, present and future aspects. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011; 16:e Liu W, Wang YF, Zhou HW, et al. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: a retrospective cohort study of 218 Chinese patients. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: van der Waal I Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa; terminology, classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncology 2009; 45: Pentenero M, Pentenero M, Giaretti W, et al. Evidence for a possible anatomical subsite mediated effect of tobacco in oral potentially malignant disorders and carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011; 40: Silverman S, Gorsky M, Lozada F Oral leukoplakia and malignant transformation. A follow up study of 257 patients. Cancer 1984; 53: Nasser W, Flechtenmacher C, Holzinger D, et al. Aberrant expression of p53, p16ink4a and Ki-67 as basic biomarker for malignant progression of oral leukoplakias. J Oral Pathol Med 2011; 40: Smitha T, Sharada P, Girish HC Morphometry of thew basal cell layer of oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma using computer- aided image analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2011; 15: Bagan J, Scully C, Jimenez Y, et al. Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: a concise update. Oral Dis 2010; 16: Bagan JV, Jimenez Y, Murillo J, et al. Lack of association between proliferative verrucous leukoplakia and human papillomavirus infection. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007; 65: Bagan JV, Jimenez Y, Murillo J, et al. Epstein Bar virus in oral proliferative verrucous leukoplakia and squamous cell carcinoma: a preliminary study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2008; 13:E110-E Cabay RJ, Morton TH, Epstein JB Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia and its progression to oral carcinoma: a review of the literature. J Oral Pathol Med 2007; 36: Reddy SG, Reddy SG, Kanala S, et al. The sensitivity and specificity of computerized brush biopsy and scalpel biopsy in diagnosing oral premalignant lesions: A comparative study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012; 16: Lingen MW, Kalmar JR, Karrison T, et al. Critical Evaluation of Diagnostic Aids for the Detection of Oral Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2008; 44: Awan KH, Morgan PR, Warnakulasuriya S Utility of chemiluminescence (ViziLiteTM) in the detectionof oral potentially malignant disorders and benign keratoses. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011; 40: Lodi G, Porter S Management of potentially malignant disorders: evidence and critique. J Oral Pathol Med 2008; 37: Maedica A Journal of Clinical Medicine, Volume 9 No
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Epidemiology Clinical presentation
 LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
R. Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: Evaluation.
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center
 The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. BILATERAL RECURRENT SPECKLED LEUKOPLAKIA:
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. BILATERAL RECURRENT SPECKLED LEUKOPLAKIA:
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Oral leukoplakia, the ongoing discussion on definition and terminology
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.21007 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.21007, the ongoing discussion on definition and terminology Isaäc
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.21007 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.21007, the ongoing discussion on definition and terminology Isaäc
Gomes CC, Gomez RS. Oral leukoplakia: What is achieved by surgical treatment? Annals of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery 2013 Feb 01;1(1):9.
 Gomes CC, Gomez RS. Oral leukoplakia: What is achieved by surgical treatment? Annals of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery 2013 Feb 01;1(1):9. Licensee OA Publishing London 2013. Creative Commons Attribution
Gomes CC, Gomez RS. Oral leukoplakia: What is achieved by surgical treatment? Annals of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery 2013 Feb 01;1(1):9. Licensee OA Publishing London 2013. Creative Commons Attribution
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation
 Journal of Clinical and Anatomic Pathology Case Report Open Access Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation Nadereh Ghanee DMD, Selene Saraf
Journal of Clinical and Anatomic Pathology Case Report Open Access Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation Nadereh Ghanee DMD, Selene Saraf
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation
 CASE REPORT Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation M. Shaurya*, S. Ravindra, Sarvani Murthy *Post Graduate Student, Professor and Head, Department of Periodontics,
CASE REPORT Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva: A Rare Palatal Presentation M. Shaurya*, S. Ravindra, Sarvani Murthy *Post Graduate Student, Professor and Head, Department of Periodontics,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Treatment results of CO 2 laser vaporisation in a cohort of 35 patients with oral leukoplakia
 (2013) 19, 212 216 doi:10.1111/odi.12007 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S All rights reserved www.wiley.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment results of CO 2 laser vaporisation in a cohort of 35 patients with oral
(2013) 19, 212 216 doi:10.1111/odi.12007 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S All rights reserved www.wiley.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment results of CO 2 laser vaporisation in a cohort of 35 patients with oral
The relevance of uniform reporting in oral leukoplakia: Definition, certainty factor and staging based on experience with 275 patients
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18756 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18756 The relevance of uniform reporting in oral leukoplakia: Definition,
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18756 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18756 The relevance of uniform reporting in oral leukoplakia: Definition,
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies
 WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
Conclusion: It was concluded that laser provides good coagulation, healing, reduces surgical time and prevents high-grade infection.
 Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Chapter 5. Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer
 Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA IN A SOUTH AFRICAN SAMPLE: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY
 ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA IN A SOUTH AFRICAN SAMPLE: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY Rakesh Chandran A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA IN A SOUTH AFRICAN SAMPLE: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY Rakesh Chandran A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report
 Case Report: HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report Dr Gopal Sharma, Dr Deepa Das, Dr Prachi Naik, Dr Jaya Mukherjee Oral Medicine and Radiology Department, YMT Dental College and
Case Report: HPV induced Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia : Case Report Dr Gopal Sharma, Dr Deepa Das, Dr Prachi Naik, Dr Jaya Mukherjee Oral Medicine and Radiology Department, YMT Dental College and
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
Journal of American Science 2014;10(4)
 Detection of oral potentially malignant lesions among tobacco users; Identafi and Microlux versus histopathology Safia Al attas 1, Suzan Ibrahim 2, Zeinab Darwish 3, Hala Amer 4, Mona Hassan 5 1 Department
Detection of oral potentially malignant lesions among tobacco users; Identafi and Microlux versus histopathology Safia Al attas 1, Suzan Ibrahim 2, Zeinab Darwish 3, Hala Amer 4, Mona Hassan 5 1 Department
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson
 84 Peter Thomson DOI 10.1308/204268514X13939420839142 The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson Oral potentially malignant disorders are mucosal diseases
84 Peter Thomson DOI 10.1308/204268514X13939420839142 The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson Oral potentially malignant disorders are mucosal diseases
Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
 International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral leukoplakia
 Study Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral Minati Mishra, Janardan Mohanty*, Sujata Sengupta, Satyabrata Tripathy Department of Dermatology & Venereology, S.C.B. Medical College, *Department
Study Epidemiological and clinicopathological study of oral Minati Mishra, Janardan Mohanty*, Sujata Sengupta, Satyabrata Tripathy Department of Dermatology & Venereology, S.C.B. Medical College, *Department
Malignant Transformation in Leukoplakia and its Associated Factors in Southern Iran: A Hospital Based Experience
 Iran J Public Health, Vol. 46, No.8, Aug 2017, pp.1110-1117 Original Article Malignant Transformation in Leukoplakia and its Associated Factors in Southern Iran: A Hospital Based Experience Alireza BARFI
Iran J Public Health, Vol. 46, No.8, Aug 2017, pp.1110-1117 Original Article Malignant Transformation in Leukoplakia and its Associated Factors in Southern Iran: A Hospital Based Experience Alireza BARFI
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom
 Nankivell et al. Head & Neck Oncology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom Paul Nankivell 1,2, Janet Dunn 3, Michael Langman 4 and
Nankivell et al. Head & Neck Oncology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom Paul Nankivell 1,2, Janet Dunn 3, Michael Langman 4 and
Factors affecting Clinical Outcomes after Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia with CO 2 and Diode Laser
 JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Factors affecting Clinical Outcomes 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2125 after Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia Factors affecting Clinical Outcomes after Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia with
JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Factors affecting Clinical Outcomes 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2125 after Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia Factors affecting Clinical Outcomes after Treatment of Oral Leukoplakia with
Assessment of Clinical Risk Factors of Oral Leukoplakia in UP Population of India: An Institutional Study
 230 Int J Oral-Med Sci 12(4):230-234, 2014 Original Article Assessment of Clinical Risk Factors of Oral Leukoplakia in UP Population of India: An Institutional Study Preeti Sharma, Pooja Aggarwal, and
230 Int J Oral-Med Sci 12(4):230-234, 2014 Original Article Assessment of Clinical Risk Factors of Oral Leukoplakia in UP Population of India: An Institutional Study Preeti Sharma, Pooja Aggarwal, and
Early Detection of Oral Cancer Guidelines for Dental Practitioners K H Awan 1, Shankargouda Patil 2, S A Islam 3, Mohammed Jafer 4
 Received: 15 th October 2015 Accepted: 18 th January 2016 Conflict of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Review Article Doi: 10.2047/jioh-08-03-20 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Guidelines for Dental
Received: 15 th October 2015 Accepted: 18 th January 2016 Conflict of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Review Article Doi: 10.2047/jioh-08-03-20 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Guidelines for Dental
Oral Leukoplakia: An Insight
 Oral Leukoplakia: An Insight Gigi Roy 1, Anu Vijayan 2, Shamji Shajahan 3, Anuja S 4, Rashmi Elizabeth Mathen 5 1,3,4,5-Post Graduate, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Mar Baselios Dental College,
Oral Leukoplakia: An Insight Gigi Roy 1, Anu Vijayan 2, Shamji Shajahan 3, Anuja S 4, Rashmi Elizabeth Mathen 5 1,3,4,5-Post Graduate, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Mar Baselios Dental College,
Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other
 Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other disease. (Pindborg. 1978) Precancerous lesion
Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a white patch on the oral mucous membrane, which is undeliable and can not diagnose neither clinically nor pathologically as an other disease. (Pindborg. 1978) Precancerous lesion
Abstract Background: A wide variety of white lesions are encountered in general population and specially those people
 Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
Is there any benefit in surgery for potentially malignant disorders of the oral cavity?
 doi: 10.1111/jop.12088 (2014) 43: 239 244 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop REVIEW ARTICLE Is there any benefit in surgery for potentially
doi: 10.1111/jop.12088 (2014) 43: 239 244 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop REVIEW ARTICLE Is there any benefit in surgery for potentially
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem.
 Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus
 TOBACCO INDUCED DISEASES Vol. 2, No. 2: 103-108 (2004) PTID Society Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus Meir Gorsky, 1 Joel B. Epstein, 2 Haya Hasson-Kanfi, 1 Eliezer Kaufman
TOBACCO INDUCED DISEASES Vol. 2, No. 2: 103-108 (2004) PTID Society Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus Meir Gorsky, 1 Joel B. Epstein, 2 Haya Hasson-Kanfi, 1 Eliezer Kaufman
Oral Leukoplakia: a clinical, histopathological and molecular study
 Oral Leukoplakia: a clinical, histopathological and molecular study door Elisabeth Ruth Emma Adriana Brouns The studies presented in this thesis were conducted at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Oral Leukoplakia: a clinical, histopathological and molecular study door Elisabeth Ruth Emma Adriana Brouns The studies presented in this thesis were conducted at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Name of Policy: Oral Lesion Identification System (ViziLite, Velscope )
 Name of Policy: Oral Lesion Identification System (ViziLite, Velscope ) Policy #: 332 Latest Review Date: October 2010 Category: Medical/Dental Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular
Name of Policy: Oral Lesion Identification System (ViziLite, Velscope ) Policy #: 332 Latest Review Date: October 2010 Category: Medical/Dental Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular
That. Name QUIZ. 60 SEPTEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com
 QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
Review Article. Oral leukoplakia Tsvetanov TS1 ABSTRACT
 Oral leukoplakia Tsvetanov TS1 1 Dr Tsvetan Borisov Tsvetanov Chief Assistant Professor PhD, DDS, DMD Department of Oral Surgery Dental Faculty Medical University Plovdiv, Bulgaria Received: 19-06-2016
Oral leukoplakia Tsvetanov TS1 1 Dr Tsvetan Borisov Tsvetanov Chief Assistant Professor PhD, DDS, DMD Department of Oral Surgery Dental Faculty Medical University Plovdiv, Bulgaria Received: 19-06-2016
Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus
 EJSO 2002; 28: 838±843 doi:10.1053/ejso.2002.1302, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on 1 Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus M. D. Mignogna*, L. Lo Russo*, S.
EJSO 2002; 28: 838±843 doi:10.1053/ejso.2002.1302, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on 1 Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus M. D. Mignogna*, L. Lo Russo*, S.
Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of dysplastic changes in the oral mucosa
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51121 Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51121 Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of
Oral Surgeons and the VELscope System: Partners in Early Detection & Diagnosis
 David Morgan, PhD Chief Science Officer LED Dental Inc. There is a growing trend within general dentistry stressing the importance of total oral health that is, not only health of the teeth and gums but
David Morgan, PhD Chief Science Officer LED Dental Inc. There is a growing trend within general dentistry stressing the importance of total oral health that is, not only health of the teeth and gums but
Diagnostic aids of oral cancer
 Diagnostic aids of oral cancer The World Health Organization has clearly indentified prevention and early detection as major objectives in the control of the oral cancer. At the present time, screening
Diagnostic aids of oral cancer The World Health Organization has clearly indentified prevention and early detection as major objectives in the control of the oral cancer. At the present time, screening
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Topical photodynamic therapy is very effective for oral verrucous hyperplasia and oral erythroleukoplakia
 J Oral Pathol Med (2010) 39: 624 630 ª 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Æ All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00935.x interscience.wiley.com/journal/jop Topical photodynamic therapy is very effective
J Oral Pathol Med (2010) 39: 624 630 ª 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S Æ All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00935.x interscience.wiley.com/journal/jop Topical photodynamic therapy is very effective
A clinical diagnosis of oral leukoplakia; A guide for dentists
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.22292 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22292 ; A guide for dentists Vinicius C. Carrard 1, Isaäc van der
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.22292 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22292 ; A guide for dentists Vinicius C. Carrard 1, Isaäc van der
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Finding Dangerous Mucosa
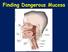 Finding Dangerous Mucosa 2 Oral Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma Salivary Gland Adenocarcinoma Malignant Lymphoma Metastatic Carcinoma Sarcoma 4 Incidence of Cancer in the United States For Oral and Oropharyngeal
Finding Dangerous Mucosa 2 Oral Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma Salivary Gland Adenocarcinoma Malignant Lymphoma Metastatic Carcinoma Sarcoma 4 Incidence of Cancer in the United States For Oral and Oropharyngeal
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology. Cancers of the Oral Cavity.
 Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
Gum Gardeners Study Club April 25, 2016 Early Detection of Oral Cancer Cindy Kleinegger, DDS, MS NW Oral Pathology Tigard, OR nworalpathology.com Role of the Dental Hygienist in Oral Pathology Work closely
J Interdiscipl Histopathol. Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia: A Case Report with Emphasis on Diagnosis and Treatment
 J Interdiscipl Histopathol Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia: A Case Report with Emphasis on Diagnosis and Treatment Journal Name : Journal of Interdisciplinary Histopathology Manuscript ID : JIHP-2016-05-032
J Interdiscipl Histopathol Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia: A Case Report with Emphasis on Diagnosis and Treatment Journal Name : Journal of Interdisciplinary Histopathology Manuscript ID : JIHP-2016-05-032
APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF PREMALIGNANT LESIONS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
 Review Article APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF PREMALIGNANT LESIONS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Authors: Mayura Paul*, Rohit Paul**, Kalyani Bhargava***, Deepak Bhargava****, Kanika Sethi***** ABSTRACT Dentists
Review Article APPROACH TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF PREMALIGNANT LESIONS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Authors: Mayura Paul*, Rohit Paul**, Kalyani Bhargava***, Deepak Bhargava****, Kanika Sethi***** ABSTRACT Dentists
North American Society for Head and Neck Pathology Companion Meeting USCAP Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia Valerie A.
 North American Society for Head and Neck Pathology Companion Meeting USCAP 2007 Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia Valerie A. Murrah DMD, MS Professor and Chair, Department of Diagnostic Sciences Director,
North American Society for Head and Neck Pathology Companion Meeting USCAP 2007 Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia Valerie A. Murrah DMD, MS Professor and Chair, Department of Diagnostic Sciences Director,
Pattern of oral lesions Cytohistopathological study in tertiary care centre.
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek
 ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA
 Page138 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA Archana Chirag Buch 1, Smit Sanjaybhai Patel 2, Shirish S. Chandanwale 3, Harsh Kumar
Page138 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA Archana Chirag Buch 1, Smit Sanjaybhai Patel 2, Shirish S. Chandanwale 3, Harsh Kumar
Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:140-146, 2009 Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia Sook-Bin Woo, DMD,* and Dorothy Lin Purpose: Morsicatio mucosae oris (MMO) presents
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:140-146, 2009 Morsicatio Mucosae Oris A Chronic Oral Frictional Keratosis, Not a Leukoplakia Sook-Bin Woo, DMD,* and Dorothy Lin Purpose: Morsicatio mucosae oris (MMO) presents
Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus
 Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus Girish HC* Sanjay Murgod**Savita JK*** *M.D.S, Professor & Head, **M.D.S, Professor,***M.D.S, Senior Lecturer,Dept of Oral Pathology, Raja Rajeswari Dental College
Epithelial dysplasia in lichenplanus Girish HC* Sanjay Murgod**Savita JK*** *M.D.S, Professor & Head, **M.D.S, Professor,***M.D.S, Senior Lecturer,Dept of Oral Pathology, Raja Rajeswari Dental College
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection
 Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
A clinical study on tongue lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients
 A clinical study on lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients Sura Ali Fuoad College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the frequency
A clinical study on lesions among Iraqi dental outpatients Sura Ali Fuoad College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the frequency
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients. Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology
 Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Oral Cancer. Online Course:
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Oral Cancer Course Author(s): Richard C. Jordan, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) FRCPath CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists, Dental Assistants, Dental
Continuing Education Brought to you by Oral Cancer Course Author(s): Richard C. Jordan, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) FRCPath CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists, Dental Assistants, Dental
Retinoids and proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL). A preliminary study
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e3 (PVL). A preliminary study Rafael Poveda-Roda 1, Jose V. Bagán 2, Yolanda Jiménez-Soriano 3, Jose-María
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e3 (PVL). A preliminary study Rafael Poveda-Roda 1, Jose V. Bagán 2, Yolanda Jiménez-Soriano 3, Jose-María
A Speckled Lesion. Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD
 A Speckled Lesion Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD The following Case Challenge is provided in conjunction with the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Case Summary This
A Speckled Lesion Angela C. Chi, DMD; Michele Carter Ravenel, DMD The following Case Challenge is provided in conjunction with the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Case Summary This
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Diajil A, Robinson CM, Sloan P, Thomson PJ. (23) Clinical Outcome Following Oral Potentially malignant Disorder Treatment: A patient Cohort Study. International Dentistry Volume
Newcastle University eprints Diajil A, Robinson CM, Sloan P, Thomson PJ. (23) Clinical Outcome Following Oral Potentially malignant Disorder Treatment: A patient Cohort Study. International Dentistry Volume
ASSOCIATION OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS B AND C VIRUS INFECTION: A CASE-CONTROL STUDY
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY MEDICINE Research article ASSOCIATION OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS B AND C VIRUS INFECTION: A CASE-CONTROL STUDY Carmen Larisa GHEORGHE¹, Bogdan-Ioan
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY MEDICINE Research article ASSOCIATION OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS B AND C VIRUS INFECTION: A CASE-CONTROL STUDY Carmen Larisa GHEORGHE¹, Bogdan-Ioan
Oral Cancer FAQs. What is oral cancer? How many people are diagnosed with oral cancer each year?
 Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
DIAGNOSIS OF ORAL PREMALIGNANT AND MALIGNANT LESIONS USING CYTOMORPHOMETRY
 DIAGNOSIS OF ORAL PREMALIGNANT AND MALIGNANT LESIONS USING CYTOMORPHOMETRY T. RAMAESH 1, B.R.R.N. MENDIS 2, N. RATNATUNGA 3, R.O. THATTIL 4 INTRODUCTION Oral cancer is a major health problem in South East
DIAGNOSIS OF ORAL PREMALIGNANT AND MALIGNANT LESIONS USING CYTOMORPHOMETRY T. RAMAESH 1, B.R.R.N. MENDIS 2, N. RATNATUNGA 3, R.O. THATTIL 4 INTRODUCTION Oral cancer is a major health problem in South East
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE
 CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution in Screening of Oral Premalignant and Malignant Lesions
 International Journal of Dental Medicine 2015; 1(1): 8-12 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijdm) doi: 10.11648/j.ijdm.20150101.12 Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution
International Journal of Dental Medicine 2015; 1(1): 8-12 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijdm) doi: 10.11648/j.ijdm.20150101.12 Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution
DENIS P. LYNCH, DDS, PHD
 140 TH ANNUAL MEETING MAY 6 MAY 7, 2010 JEWEL OF THE GREAT LAKES DENIS P. LYNCH, DDS, PHD FRIDAY, MAY 7, 2010 9:00 A.M. TO 12:00 NOON ORAL CANCER AND RELATED PREMALIGNANCY Oral Cancer and Premalignancy
140 TH ANNUAL MEETING MAY 6 MAY 7, 2010 JEWEL OF THE GREAT LAKES DENIS P. LYNCH, DDS, PHD FRIDAY, MAY 7, 2010 9:00 A.M. TO 12:00 NOON ORAL CANCER AND RELATED PREMALIGNANCY Oral Cancer and Premalignancy
Proliferative Verrucous Gingival Leukoplakia: A Sinister Condition
 CLINICAL REPORTS Proliferative Verrucous Gingival Leukoplakia: A Sinister Condition Mairéad Hayes, Phillip Tomson, Satyesh Parmar, Iain L.C. Chapple Proliferative verrucous leuoplakia (PVL) is widely accepted
CLINICAL REPORTS Proliferative Verrucous Gingival Leukoplakia: A Sinister Condition Mairéad Hayes, Phillip Tomson, Satyesh Parmar, Iain L.C. Chapple Proliferative verrucous leuoplakia (PVL) is widely accepted
International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Modern Education (IJMRME) Impact Factor: 6.725, ISSN (Online):
 AN UPDATED REVIEW ON ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Dr. Kavitaa Nedunchezhian Consultant Oral and Maxillofacial Radiologist, Chennai, Tamilnadu Cite This Article: Dr. Kavitaa Nedunchezhian, An Updated Review on Oral
AN UPDATED REVIEW ON ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Dr. Kavitaa Nedunchezhian Consultant Oral and Maxillofacial Radiologist, Chennai, Tamilnadu Cite This Article: Dr. Kavitaa Nedunchezhian, An Updated Review on Oral
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00582.x J Oral Pathol Med (2007) 36: 575 80 ª
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00582.x J Oral Pathol Med (2007) 36: 575 80 ª
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Original Article- A CYTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LEUKOPLASTIC LESIONS IN ORAL CAVITY
 Original Article- A CYTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LEUKOPLASTIC LESIONS IN ORAL CAVITY I. GUJRAL*, P. SINGH**, S. SHARMA***, N. GANGANE*** ABSTRACT Oral white lesions that cannot be clinically or pathologically
Original Article- A CYTOLOGICAL STUDY OF LEUKOPLASTIC LESIONS IN ORAL CAVITY I. GUJRAL*, P. SINGH**, S. SHARMA***, N. GANGANE*** ABSTRACT Oral white lesions that cannot be clinically or pathologically
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ORAL MUCOSA LEUKOPLAKIA
 Oral biology IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ORAL MUCOSA LEUKOPLAKIA Yu. G. KOLENKO 1 1 Associate Prof., PhD, Dept. Operative Dentistry, Faculty of Medical Dentistry, A.A. Bogomolets National Medical University,
Oral biology IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF ORAL MUCOSA LEUKOPLAKIA Yu. G. KOLENKO 1 1 Associate Prof., PhD, Dept. Operative Dentistry, Faculty of Medical Dentistry, A.A. Bogomolets National Medical University,
ORAL CANCER & EARLY DETECTION: A REVIEW
 Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 03 ORAL CANCER & EARLY DETECTION: A REVIEW Anshul Shah 1,Rushil Shah 2,Sonali Patel 3,Kuljit Singh 4,Sonali Chhabra 5
Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 03 ORAL CANCER & EARLY DETECTION: A REVIEW Anshul Shah 1,Rushil Shah 2,Sonali Patel 3,Kuljit Singh 4,Sonali Chhabra 5
PATTERN AND PRESENTATION OF ORAL WHITE LESIONS
 PATTERN AND PRESENTATION OF ORAL WHITE LESIONS 1 NASIR JAMAL BAIG MUHAMMAD WASIM IBRAHIM SYED GULZAR ALI BUKHARI UZAIR LUQMAN MUHAMMAD JUNAID 4 IRFAN SHAH ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Oral white lesions are
PATTERN AND PRESENTATION OF ORAL WHITE LESIONS 1 NASIR JAMAL BAIG MUHAMMAD WASIM IBRAHIM SYED GULZAR ALI BUKHARI UZAIR LUQMAN MUHAMMAD JUNAID 4 IRFAN SHAH ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Oral white lesions are
E rythroplakia and speckled leukoplakia are oral
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;75(2):295-9. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oral Erythroplakia and Speckled Leukoplakia: retrospective analysis of 13 cases Elaini Sickert Hosni 1, Fernanda Gonçalves Salum 2, Karen Cherubini
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;75(2):295-9. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oral Erythroplakia and Speckled Leukoplakia: retrospective analysis of 13 cases Elaini Sickert Hosni 1, Fernanda Gonçalves Salum 2, Karen Cherubini
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Oral Screening and Lesion Identification Systems
 Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Oral Screening and Lesion Identification Systems Number: 0760 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Additional Information Aetna considers
Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Oral Screening and Lesion Identification Systems Number: 0760 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Additional Information Aetna considers
RESULT OF SURVEY OF 1705 LAWSUITS* ORAL CANER: A significant Public Health Concern. ORAL CANCER: Other Epidemiologic Facts
 FAILURE TO DIAGNOSE ORAL CANCER AND OTHER PATHOLOGIC CONDITIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY Kalu U.E. Ogbureke, BDS, MSc, DMSc, JD, FDSRCS, FDSRCPS, FDSRCSEd, FRCPath Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial
FAILURE TO DIAGNOSE ORAL CANCER AND OTHER PATHOLOGIC CONDITIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY Kalu U.E. Ogbureke, BDS, MSc, DMSc, JD, FDSRCS, FDSRCPS, FDSRCSEd, FRCPath Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Reproducibility of grading systems in oral epithelial dysplasia
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Nov 1;17 (6):e935-42. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17749 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17749
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Nov 1;17 (6):e935-42. Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17749 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17749
Premalignant Conditions of the Oral Cavity
 Medscape Reference Reference News Reference Education MEDLINE Premalignant Conditions of the Oral Cavity Author: Toby Steele; Chief Editor: Arlen D Meyers, MD, MBA more... Updated: Aug 19, 2011 Overview
Medscape Reference Reference News Reference Education MEDLINE Premalignant Conditions of the Oral Cavity Author: Toby Steele; Chief Editor: Arlen D Meyers, MD, MBA more... Updated: Aug 19, 2011 Overview
Oral Health & HIV. Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape
 Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
Andre W. van Zyl, Marlene B van Heerden, Emil Langenegger, Willie F.P. van Heerden
 Correlation between Dysplasia and Ploidy Status in Oral Leukoplakia Andre W. van Zyl, Marlene B van Heerden, Emil Langenegger, Willie F.P. van Heerden AW van Zyl, E Langenegger Department of Periodontics
Correlation between Dysplasia and Ploidy Status in Oral Leukoplakia Andre W. van Zyl, Marlene B van Heerden, Emil Langenegger, Willie F.P. van Heerden AW van Zyl, E Langenegger Department of Periodontics
Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I)
 Introduction: Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I) Oral Epithelial Tumors may be: Benign tumors Sequamous cell Papilloma Malignant tumors Sequamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma
Introduction: Oral Epithelial Tumors, Melanocytic Nevi, and Melanoma (I) Oral Epithelial Tumors may be: Benign tumors Sequamous cell Papilloma Malignant tumors Sequamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma
