Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Derrick Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 181 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis P. A. DIEPPE From the Brompton Hospital, Fulham Road, London Dieppe, P. A. (1975). Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases, 34, 181. Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis. Case notes of the last 67 patients to present at the Brompton Hospital with nontuberculous empyemas, and without malignant disease, have been examined. Three cases of empyema in association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were found, and these cases are reported. Previous literature concerning this association is reviewed. It is concluded that two types of empyema may occur in patients with RA. Some develop in association with nodular pleuropulmonary disease and the formation of pyopneumothoraces; in other cases large, recurrent, primary empyemas build up in the presence of active rheumatoid disease alone. As with rheumatoid pleural effusions, middle-aged men seem to be particularly susceptible. Pleural effusions are now recognized as a not uncommon complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Walker and Wright, 1967; Scadding, 1969). They occur particularly in middle-aged men, may be bilateral, and often run a protracted course. Diagnosis is partly by exclusion of other causes, but may be aided by demonstration of a low sugar content (Carr and Mayne, 1962; Lillington, Carr, and Mayne, 1971), and socalled 'rheumatoid arthritis cells' in the pleural fluid (Carmichael and Golding, 1967; Lillington and others, 1971), or pleural histology consistent with RA (Carr and Mayne, 1962; Walker and Wright, 1967; Campbell and Ferrington, 1968; Lillington and others, 1971). An increased incidence of many infections has been described in RA (Cobb, Anderson, and Bauer, 1953; Kellgren, Ball, Fairbrother, and Barnes, 1958; Baum, 1971), and chest infections including chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, and bronchiectasis all occur more commonly than in control groups (Walker, 1967; Kay, 1967). However, in spite of this and the well-recognized incidence of pleural effusions, little has been written concerning the occurrence of empyema in RA. There are a small number of case reports (Kellgren and others, 1958; Cudkowicz, Madoff, and Abelmann, 1961; Hindle and Yates, 1965; Basten, Camens, and Schwartz, 1966; Davies, 1966; Rubin, Gordon, and Thelmo, 1967; Walker and Wright, 1967; Huskisson and Hart, 1972; Sahn, Lakshminarayan, and Char, 1973), and in 1971 Jones and Blodgett described 5 cases and suggested that empyema should be regarded as a complication of RA. In a recent survey of all patients with nontuberculous empyema, excluding those due to malignant disease, who have presented to the Brompton Hospital over the last 15 years, 67 case histories have been examined. Three cases of empyema in association with RA were found and are reported below. The common features of these and other cases which have been described are discussed. Case reports CASE 1 A 53-year-old man was well until the age of 41 when he developed classical seropositive, nodular RA. He was initially treated with salicylates and indomethacin and had one course of chrysotherapy in In 1969, because of increasing disease activity, corticosteroid therapy was initiated and he has been taking between 5 and 15 mg prednisolone daily ever since. In December 1970 he developed increasing dyspnoea and malaise without cough or sputum production. On examination he was febrile, and had a large right-sided pleural effusion (Fig. 1). Thick, purulent fluid, with a white cell count of >50-0 x (>50 000/mm3), predominantly neutrophils, was aspirated and was sterile on culture. Treatment was with antibiotics and continuous drainage, and the empyema resolved over the next 6 weeks. In March 1971 he developed a left-sided pleural effusion and again sterile pus was obtained on the first aspiration. Later in that year pus again accumulated on both sides of the chest and he also developed septic lesions on the feet. In December 1971 a left thoracotomy and partial decortication was performed. At operation nodules were noted on the pleura, and histology was consistent with rheumatoid pleuritis. In spite of the operation he continued to accumulate pus in both pleural spaces, and in 1972 developed a right pyopneumothorax. In August 1972 Escherichia coli was isolated from pus on the left side, and this was treated by pleural washouts with appropriate antibiotics. He was readmitted in August 1973 with pus Accepted for publication July 14, Present address of Dr. P. A. Dieppe: Rheumatology and Experimental Pathology Department, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College, West Smithfield, London, ECIA 7BE.
2 182 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases FIG. 1 Case 1. Massive right-sided empyema in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis again in both pleural spaces. The appearance of the chest x-ray after aspiration at that time is shown (Fig. 2). A similar readmission was necessary in January 1974, when he was found to have a pericardial effusion in addition to bilateral pleural pus. Investigations at that time included Hb 12-7 g/dl, WBC 13-8 x 109/l (13 800/mm3), ESR 95 mm/h, latex test positive, DAT 1:256. The patient has noticed a tendency for his arthritis to be worse when fluid accumulates in the chest. CASE 2 A 64-year-old man developed seropositive, nodular, RA in Three months after the onset of his arthritis he developed a small right-sided pleural effusion, and on aspiration a clear yellow fluid was obtained; his chest x-ray soon returned to normal. Between 1940 and 1960 his arthritis was treated with salicylates alone. In October 1960 he suddenly developed dyspnoea, fever, and malaise, but no cough or sputum production. Examination revealed a massive left-sided effusion (Fig. 3) as well as active nodular RA and arteritic lesions on the fingers. The first aspiration yielded thick pus from which a heavy growth of Staphylococcus aureus was isolated. Treatment was with repeated aspiration and systemic antibiotics, but the pus was slow to clear. After 2 months he was left with a posterior loculation of fluid, and was discharged from hospital. Investigations at the time of admission included: Hb 13 8 g/dl, WBC 6-2 x 109/l (6 200/mm3), ESR 92 mm/h, latex test positive, DAT 1:32. During regular follow-up he has had no further chest trouble, and his rheumatoid disease has required salicylate therapy alone. CASE 3 A 50-year-old man with a previous history of episodes of pneumonia in 1943 and 1946, and onset of chronic bronchitis in In 1958 he developed seropositive nodular RA and has been treated with salicylates, indomethacin, two courses of gold, and one of antimalarial therapy, but he has never been on steroids. In 1964 he was admitted to hospital with a short history of increasing cough, dyspnoea, and malaise; on examination he was febrile and had a large right-sided pleural effusion. Frank pus was aspirated at the first tap, but no organisms were isolated, perhaps because he had been receiving antibiotics from his general practitioner. The fluid slowly cleared over a 2-month period of antibiotic treatment and repeated drainage. In 1968 he was readmitted with a 3-week history of cough and dyspnoea. He was found to have active RA and a massive right-sided effusion from which sterile pus was again aspirated. Investigations at the time included Hb 12-5 g/dl, WBC 8 5 x 109/l (8 500/mm3), ESR 59 mm/h, latex test positive, DAT 1: 16. The pleural fluid was frankly purulent on macroscopical examination and had a white cell count of 54-0 x 109/l (54000/mm3), predominantly neutrophils. Repeated drainage and antibiotics again resulted in slow resolution. There has been no recurrence on follow-up, and he has
3 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis 183 FIG. 2 Case 1. Showing the development of bilateral pyopneumothoraces continued to take salicylates to control his RA. This patient had also noted worsening of his arthritis on admission for treatment of the empyema. Discussion A number of case reports of empyema in association with RA appears in the literature. In 1943 Baggenstoss and Rosenberg found pus in the pleural space in 2 of 30 autopsied cases of RA. In 1961 Cudkowicz and others described the case of a 63-year-old man with severe RA, treated with steroids, who developed repeated bilateral empyemas in the absence of prior evidence of intrapleural infection or pneumothorax. Similar cases have been described by Kellgren and others (1958), Walker and Wright (1967), Huskisson and Hart (1972), and Sahn and others (1973). In two of these papers the relevant cases were part of a series of patients showing severe, unusual infections in RA and more than one site of infection (Kellgren and others, 1958; Huskisson and Hart, 1972), as did Case 1 of the present series. Slightly different cases in which there was spontaneous development of a pyopneumothorax in patients with nodular rheumatoid pleuritis have been documented by Hindle and Yates (1965), Basten and others (1966), Davies (1966), and Rubin and others (1967). Davies (1966) has postulated that in these cases necrosis of the rheumatoid pleural nodules leads to communication between lung and pleural space, and the secondary development of a pyopneumothorax. In 1971, Jones and Blodgett reported a series of 10 cases of rheumatoid pleural effusion, 5 of which developed empyemas. Of these 5 cases, 4 were women and 3 were on steroids. 4 of them had previously developed serous pleural effusions which had been aspirated. The authors suggested that empyema might be regarded as a relatively common complication of rheumatoid pleuropulmonary disease; but Blau (1971) reported that of 75 cases of rheumatoid pleural effusions aspirated in his unit, none had developed an empyema and he suggested that introduction of infection may have occurred in some of Jones and Blodgett's cases. In this study the last 67 cases of empyema seen at a chest hospital were examined; one patient with mild RA developed an empyema after chest trauma, and another 3 cases with RA were found and these have been described above. From this it seems that empyema is a rare occurrence in association with RA.
4 184 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases FIG. 3 Case 2. Left-sided empyema.-ix-4 :.! ii.9 U. Some features of these cases are worthy ofmention. All occurred in middle-aged men and in each case pus was aspirated at the first pleural tap. There wasno evidence of intrapulmonary infection, pneumothorax, or serous pleural effusion having been present immediately before the accumulation of pus, so these men have developed primary empyemas. All cases required prolonged treatment and Case 1 later developed a pyopneumothorax. In view of the size of the empyemas (Figs 1 and 3), systemic manifestations were perhaps not marked. Sahn and others (1973) have stressed the development of silent empyemas in patients on steroids, although this was only true in the first of these 3 cases. Two of the patients reported a marked 'flare' of their arthritis at times when fluid accumulated in the chest, and in these two bacteriological examination of the pus was repeatedly negative. This suggests that the active rheumatoid disease may have been contributing directly to the formation of pus in the pleural space. Only in Case 1 was rheumatoid pleuritis confirmed by a characteristic pleural biopsy, although in Case 2 the previous occurrence of a pleural effusion near the -time of onset of his arthritis seems to be good circumstantial evidence of the nature of the disease, and in Case 3 the diagnosis was made by exclusion of other causes for the empyema. In each case the pleural fluid was thick and macroscopically frankly purulent, and in the 2 cases in which the cell count was measured it was greater than 50-0 x 109/l (50 000/mm3) with neutrophils predominating. This clearly distinguishes the fluid in the above cases from that which accumulates in simple rheumatoid effusions, as the latter is usually thin and clear, with a cell count of less than 10.0 x 109/l (10000/mm3) and a pleomorphic cell picture. A number of infections are thought to occur more commonly in people with RA and the subject has recently been reviewed (Baum, 1971; British Medical Journal, 1972). Both Walker (1967) and Kay (1967) have reported an increased incidence of chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, and bronchiectasis in large groups of patients with RA compared with age- and sex-matched control groups with degenerative joint disease. In many cases the pulmonary disease seems to antedate the onset of the arthritis, although the cause for this susceptibility is unknown. It is of interest to note that Case 3 was a chronic bronchitic who had had 2 previous attacks of pneumonia before the onset of RA. There was, however, no evidence of any other pulmonary pathology, such as fibrosing alveolitis, in any of the 3 cases.
5 Empyema in rheumatoid arthritis 185 Empyemas are now rare, but RA is a common the pus may build up in the absence of very marked disease and it is difficult to conclude that any specific systemic symptoms and may be sterile. All cases complication is a direct result of the rheumatoid have proved difficult to treat, and the middle-aged, disease. However, from these cases and the previous or elderly male, appears to be particularly susceptible. literature, it seems that two distinct types ofempyema may occur in patients with RA. In the first group nodular pleuritis seems to lead to the development of couragement I am grateful with to Dr. this K. paper, M. Citron and for for his permission help and en- a pyopneumothorax. In the second group large publish Case 1. I would also to like to thank Dr. J. R. Bignall accumulations of pus are found in the presence of and Professor J. G. Scadding for permission to publish active RA, but in the absence of any other apparent Cases 2 and 3 respectively, and Drs. H. C. Burry and E. C. predisposing pleural or intrapulmonary condition, Huskisson for advice with the manuscript. References BAGGENSTOSS, A. H., AND ROSENBERG, E. F. (1943) Arch. Path., 35, 503 (Visceral lesions associated with chronic infectious (rheumatoid) arthritis) BASTEN, A., CAMENS, I., AND SCHWARTZ, C. J. (1966) Aust. Ann. Med., 15, 175 (Rheumatoid lung disease with report of a case) BAUM, J. (1971) Arthr. and Rheum., 14, 135 (Infection in rheumatoid arthritis) BLAU, S. P. (1971) Ann. intern. Med., 75, 476 (Empyema in rheumatoid lung disease) British Medical Journal (1972) 2, 549 (Infection in rheumatoid disease) CAMPBELL, G. D., AND FERRINGTON, E. (1968) Dis. Chest., 53, 521 (Rheumatoid pleuritis with effusion) CARMICHAEL, D. S., AND GOLDING, D. N. (1967) Brit. med. J., 2, 814 (Rheumatoid pleural effusion with 'R.A. cells' in the pleural fluid) CARR, D. T., AND MAYNE, J. G. (1962) Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis., 85, 345 (Pleurisy with effusion in rheumatoid arthritis with reference to the low concentration of glucose in the pleural fluid) COBB, S., ANDERSON, F., AND BAUER, W. (1953) Newl, Engl. J. Med., 249, 553 (Length of life and cause of death in rheumatoid arthritis) CUDKOWICZ, L., MADOFF, I. M., AND ABELMANN, W. H. (1961) Brit. J. Dis. Chest, 55, 35 (Rheumatoid lung disease: a case report which includes respiratory function studies and a lung biopsy) DAVIES, D. (1966) Thorax, 21, 230 (Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease) HINDLE, W., AND YATES, D. A. H. (1965) Ann. rheum. Dis., 24, 57 (Pyopneumothorax complicating rheumatoid lung disease) HUSKISSON, E. C., AND HART, F. D. (1972) Ibid., 31, 118 (Severe, unusual, and recurrent infections in rheumatoid arthritis) JONES, F. L., AND BLODGETT, R. C. (1971) Ann. intern. Med., 74, 665 (Empyema in rheumatoid pleuropulmonary disease) KAY, A. (1967) Lancet, 2, 152 (Infection in rheumatoid arthritis) KELLGREN, J. H., BALL, J., FAIRBROTHER, R. W., AND BARNES, K. L. (1958) Brit. med. J., 1, 1193 (Suppurative arthritis complicating rheumatoid arthritis) LILLINGTON, G. A., CARR, D. T., AND MAYNE, J. G. (1971) Arch. intern. Med., 128, 764 (Rheumatoid pleurisy with effusion) RUBIN, E. H., GORDON, M., AND THELMO, W. L. (1967) Amer. J. Med., 42, 567 (Nodular pleuropulmonary rheumatoid disease) SAHN, S. A., LAKSHMINARAYAN, S., AND CHAR, D. C. (1973) Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis., 107, 873 ('Silent' empyema in patients receiving corticosteroids) SCADDING, J. G. (1969) Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 62, 227 (The lungs in rheumatoid arthritis) WALKER, W. C. (1967) Quart. J. Med., 36,239 (Pulmonary infections and rheumatoid arthritis), AND WRIGHT, V. (1967) Ann. rheum. Dis., 26, 467 (Rheumatoid pleuritis)
Table 2: Outcomes measured. Table 1: Intrapleural alteplase instillation therapy protocol
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
Bacterial pneumonia with associated pleural empyema pleural effusion
 EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Modern Approaches to Empyema
 Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
Modern Approaches to Empyema Amit Bhargava, MD Attending Thoracic Surgeon Assistant Professor Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 1 Principles of Treatment Adequate drainage Sterilization
Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae
 Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
Thorax (1967), 22, 170. Empyema due to Klebsiella pneumoniae J. M. REID, R. S. BARCLAY, J. G. STEVENSON, T. M. WELSH, AND N. McSWAN From thle Cardio-thoracic Unit, Mearnskirk Hospital, Renifrewshire Three
PULMONARY INFECTIONS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 1
 239 PULMONARY INFECTIONS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 1 BY W. C. WALKER (From the Rheumatism Unit, General Infirmary at Leeds) IT is now widely held that a variety of pathological processes may involve the
239 PULMONARY INFECTIONS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS 1 BY W. C. WALKER (From the Rheumatism Unit, General Infirmary at Leeds) IT is now widely held that a variety of pathological processes may involve the
Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease
 Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Thorax (1966), 21, 230. Pyopneumothorax in rheumatoid lung disease DEWI DAVIES From Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Notts Rheumatoid nodules in the lung, in the absence of exposure to mineral dust, are uncommon.
Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong
 Working in partnership Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong chest physician pronounced ning qualified 1990 chief clinical information officer
Working in partnership Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong chest physician pronounced ning qualified 1990 chief clinical information officer
Fever in Lupus. 21 st April 2014
 Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
Fever in Lupus 21 st April 2014 Fever in lupus Cause of fever N= 487 % SLE fever 206 42 Infection in SLE 265 54.5 Active SLE and infection 8 1.6 Tumor fever 4 0.8 Miscellaneous 4 0.8 Crucial Question Infection
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
weeks after starting " prednisone," showed a titre of The blood urea was 25 mg. per 100 ml.
 Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
Thorax (1957), 12, 352. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY J. R. EDGE AND A. G. RICKARDS From High Carley Hospital, Ulverston, and the Royal Infirmary, Lancaster Since the original reports of Ellman (1947) and Ellman
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
received penicillin before admission, an organism was later grown from the bone at operation. The fifth patient (Case
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 40 Septic arthritis A. S. RUSSELL AND B. M. ANSELL M.R.C. Rheuimatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Maidenhead, Berks. Joint infection, particularly
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 40 Septic arthritis A. S. RUSSELL AND B. M. ANSELL M.R.C. Rheuimatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Maidenhead, Berks. Joint infection, particularly
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Patient History 1. Patient History 2. Social History. The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB. Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD
 Patient History 1 The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD September 16, 2010 42 y/o AA male was initially diagnosed with pansensitive pulmonary TB in 1986
Patient History 1 The Role of Surgery in the Management of TB Reynard McDonald, MD & Paul Bolanowski, MD September 16, 2010 42 y/o AA male was initially diagnosed with pansensitive pulmonary TB in 1986
Pleural Diseases. Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician
 Pleural Diseases Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician What do you need to know? What do you need to know? Pleura- normal anatomy and physiology Pleural effusions Causes and investigations
Pleural Diseases Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician What do you need to know? What do you need to know? Pleura- normal anatomy and physiology Pleural effusions Causes and investigations
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural
 Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 730604, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/730604 Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation Deepak Puri, Amit Kumar Mandal, Harinder Pal Kaur,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 730604, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/730604 Case Report Ruptured Hydatid Cyst with an Unusual Presentation Deepak Puri, Amit Kumar Mandal, Harinder Pal Kaur,
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Bronchiectasis Domiciliary treatment. Prof. Adam Hill Royal Infirmary and University of Edinburgh
 Bronchiectasis Domiciliary treatment Prof. Adam Hill Royal Infirmary and University of Edinburgh Plan of talk Background of bronchiectasis Who requires IV antibiotics Domiciliary treatment Results to date.
Bronchiectasis Domiciliary treatment Prof. Adam Hill Royal Infirmary and University of Edinburgh Plan of talk Background of bronchiectasis Who requires IV antibiotics Domiciliary treatment Results to date.
Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy
 Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Pleurisy: Findings of fluid between visceral
Pleural syndrome. Tubercular pleurisy Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology (OFCP) Pleurisy: Findings of fluid between visceral
Malignant Effusions. Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital
 Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
A COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 ORIGINAL PAPER A COMPARISON O THE EECTS O CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. P. INCH rom the Department of Physical Medicine and Regional Rheumatism Centre, The London Hospital THE
ORIGINAL PAPER A COMPARISON O THE EECTS O CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. P. INCH rom the Department of Physical Medicine and Regional Rheumatism Centre, The London Hospital THE
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012
 Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
 Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
Petru Emil Muntean muntean.petruemil@yahoo.com Pulmonology, Spitalul Clinic Judetean Mures, Targu Mures, Romania. A 50-year-old male with fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, weight loss and night sweats
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center
 CA-MRSA Pneumonia Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine Weill Cornell
CA-MRSA Pneumonia Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine Weill Cornell
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Acute Respiratory Infection. Dr Anthony Gibson
 Acute Respiratory Infection Dr Anthony Gibson Range of Conditions Upper tract Common Cold coryza Sore Throat- Pharyngitis Sinusitis Epiglottitis Range of Conditions Lower Acute Bronchitis Acute Exacerbation
Acute Respiratory Infection Dr Anthony Gibson Range of Conditions Upper tract Common Cold coryza Sore Throat- Pharyngitis Sinusitis Epiglottitis Range of Conditions Lower Acute Bronchitis Acute Exacerbation
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 229-234 Aortic regurgitation in seropositive juvenile arthritis A. M. LEAK,' M. W. MILLAR-CRAIG,2 AND BARBARA M. ANSELL1 From the 'Juvenile Rheumatism Unit,
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected
 Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
EMPYEMA. Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS. UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, Jeremy Hedges, M.D.
 EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
EMPYEMA Catheter Based Treatment vs. VATS UCHSC Department of Surgery Grand Rounds August 27 th, 2007 Jeremy Hedges, M.D. OVERVIEW Empyema Pathogenesis Treatment Catheter based treatment Fibrinolytics
BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 425. THE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA BY WALTER PAGEL AND SUSAN GOLDFARB From the Department of Pathology, Clare Hall Hospital, Herts (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 425. THE DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLEURAL BIOPSY IN BRONCHOPULMONARY CARCINOMA BY WALTER PAGEL AND SUSAN GOLDFARB From the Department of Pathology, Clare Hall Hospital, Herts (RECEIVED
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report
 303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
303) Persistent Spontaneous Pneumothorax for Four Years: A Case Report Mizuno Y., Iwata H., Shirahashi K., Matsui M., Takemura H. Department of General and Cardiothoracic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine,
Pneumonia. Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial
 Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax
 Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Case Report A Repeat Case of Idiopathic Spontaneous Hemothorax Felix R. Gaw, MD Jack H. Bloch, MD, PhD, FACS Nolan J. Anderson, MD, FACS Spontaneous hemothorax, a collection of blood in the pleural cavity
Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion
 Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
Immediate Drainage Is Not Required for All Patients with Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions*
 Immediate Drainage Is Not Required for All Patients with Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions* Herbert A. Berger; M.D.;t and Melvin L. Morganroth, M.D., F.C.C.P.t We retrospectively investigated if the
Immediate Drainage Is Not Required for All Patients with Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions* Herbert A. Berger; M.D.;t and Melvin L. Morganroth, M.D., F.C.C.P.t We retrospectively investigated if the
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
Surgical treatment of empyema in children
 Surgical treatment of empyema in children Jacques Janson Pierre Goussard Cardiothoracic Surgery, Paediatric Pulmonology Tygerberg Academic Hospital University of Stellenbosch Pleural space Netter, Frank
Surgical treatment of empyema in children Jacques Janson Pierre Goussard Cardiothoracic Surgery, Paediatric Pulmonology Tygerberg Academic Hospital University of Stellenbosch Pleural space Netter, Frank
Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 - Moscow, Russia Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of World Equine Veterinary Association Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 - Moscow, Russia Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Conference
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Characteristic. Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils
 ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
 WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
To Study The Cinico-Radiological Features And Associated Co-Morbid Conditions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
manifestations are uncommon. Initial descriptions of the disease (Rosai and Dorfman, 1969) specifically
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County
 Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Bernard Rubin, DO MPH Case 1: History A 45-year-old woman presents with severe dyspnea and cough. She was in excellent health until 4 weeks ago when
High Impact Rheumatology Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Bernard Rubin, DO MPH Case 1: History A 45-year-old woman presents with severe dyspnea and cough. She was in excellent health until 4 weeks ago when
REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS
 Séminaire de Pathologie Infectieuse Jeudi 25 juin 2008 Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont-Godinne, Yvoir NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS Dr Robert Wilson Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK Aetiology
Séminaire de Pathologie Infectieuse Jeudi 25 juin 2008 Cliniques Universitaires UCL de Mont-Godinne, Yvoir NON-CF BRONCHIECTASIS IN ADULTS Dr Robert Wilson Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK Aetiology
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
RETROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF EMPYEMA THORACIS IN HIV INFECTED AND NON-INFECTED PATIENTS WITH REGARDS TO AETIOLOGY AND OUTCOMES
 RETROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF EMPYEMA THORACIS IN HIV INFECTED AND NON-INFECTED PATIENTS WITH REGARDS TO AETIOLOGY AND OUTCOMES Dr Grace Helga Kaye-Eddie A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health
RETROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF EMPYEMA THORACIS IN HIV INFECTED AND NON-INFECTED PATIENTS WITH REGARDS TO AETIOLOGY AND OUTCOMES Dr Grace Helga Kaye-Eddie A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Case N 1. Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint. AFB in sputum not yet available. Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg
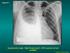 Case N 1 Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint. AFB in sputum not yet available Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg Case N 1 CXR: Right abundant pleural effusion. Notice the typical concave aspect of the superior
Case N 1 Dyspnea and cough. Right thoracic paint. AFB in sputum not yet available Courtesy Dr Van Den Homberg Case N 1 CXR: Right abundant pleural effusion. Notice the typical concave aspect of the superior
Pleural Effusions. Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) (602)
 Pleural Effusions Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) 275 8583 (602) 202 0351 None Disclosures Objectives Understand the presentation of a pleural effusion How to diagnose and treat Differentiate
Pleural Effusions Kyle J Henry, MD Pulmonary/ CCM Fellow PGY4 (210) 275 8583 (602) 202 0351 None Disclosures Objectives Understand the presentation of a pleural effusion How to diagnose and treat Differentiate
Acute pneumonia Simple complement
 Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Posttraumatic Empyema Thoracis
 Posttraumatic Empyema Thoracis Dr AG Jacobs STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL, UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA EMPYEMA THORACIS Derived from Greek word empyein Means pus-producing Refers to accumulation of pus within
Posttraumatic Empyema Thoracis Dr AG Jacobs STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL, UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA EMPYEMA THORACIS Derived from Greek word empyein Means pus-producing Refers to accumulation of pus within
PLEURAL EFFUSION. Prof. G. Zuliani
 PLEURAL EFFUSION Prof. G. Zuliani Anatomy of pleural membrane and pleural space Pleural membrane consists of parietal pleura and visceral pleura A space situated between parietal and visceral pleura is
PLEURAL EFFUSION Prof. G. Zuliani Anatomy of pleural membrane and pleural space Pleural membrane consists of parietal pleura and visceral pleura A space situated between parietal and visceral pleura is
A 24-Year-Old Woman With Bilateral Pulmonary Infiltrates, Pericardial Effusion, and Bilateral Pleural Effusions*
 A 24-Year-Old Woman With Bilateral Pulmonary Infiltrates, Pericardial Effusion, and Bilateral Pleural Effusions* Chandra K. Katikireddy, MD; Ganesh Krishna, MD; Gerald Berry, MD; John Faul, MD; and Ware
A 24-Year-Old Woman With Bilateral Pulmonary Infiltrates, Pericardial Effusion, and Bilateral Pleural Effusions* Chandra K. Katikireddy, MD; Ganesh Krishna, MD; Gerald Berry, MD; John Faul, MD; and Ware
Familial association of rheumatoid arthritis and fibrosing alveolitis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1974), 33, 191 Familial association of rheumatoid arthritis and fibrosing alveolitis R. C. HILTON AND D. A. PITKEATHLY Department of Rheumatology, Wrightington Hospital, Appley Bridge,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1974), 33, 191 Familial association of rheumatoid arthritis and fibrosing alveolitis R. C. HILTON AND D. A. PITKEATHLY Department of Rheumatology, Wrightington Hospital, Appley Bridge,
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment
 A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
TUBERCULOUS PERICARDIAL EFFUSION
 BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
BY S. SUZMAN From the Cardiographic Department, Guy's Hospital Received June 22, 1942 Tuberculous pericardial effusion is not common; and so the case described is of interest on account of the patient's
Prednisolone-2 I -stearoylglycolate in scleritis
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 394 Prednisolone- -stearoylglycolate in scleritis S. S. HAYREH* AND P. G. WATSON Scleritis Clinic, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London, E.C. i Scleritis is one of the
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1970) 54, 394 Prednisolone- -stearoylglycolate in scleritis S. S. HAYREH* AND P. G. WATSON Scleritis Clinic, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London, E.C. i Scleritis is one of the
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
PLEURAL EFFUSION: DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND DISPOSAL
 PLEURAL EFFUSION: DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND DISPOSAL 1. This replaces the DGAFMS Medical Memorandum No.63 on Primary (Idiopathic) Pleural Effusion, which dealt with tubercular pleural effusion. 2. Normally
PLEURAL EFFUSION: DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND DISPOSAL 1. This replaces the DGAFMS Medical Memorandum No.63 on Primary (Idiopathic) Pleural Effusion, which dealt with tubercular pleural effusion. 2. Normally
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids
 Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report
 Case Report A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report Jin-Young Ahn 1, Dohun Kim 2, Jong-Myeon Hong 2, Si-Wook
Case Report A recurrent empyema with peripheral bronchopleural fistulas treated by retrograde bronchial sealing with Gore Tex plugs: a case report Jin-Young Ahn 1, Dohun Kim 2, Jong-Myeon Hong 2, Si-Wook
Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 31, No. 4, December 2009 Thoracoscopic Management of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusions in Young Children Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Objective: To evaluate the role
Cholesterol pleural effusion in rheumatoid lung disease
 Cholesterol pleural effusion in rheumatoid lung disease G. C. FERGUSON Thorax (1966), 21, 577. From the Chest Clinic, Dundee, and the Department of Tuberculosis, University of St. Andrews Cholesterol pleural
Cholesterol pleural effusion in rheumatoid lung disease G. C. FERGUSON Thorax (1966), 21, 577. From the Chest Clinic, Dundee, and the Department of Tuberculosis, University of St. Andrews Cholesterol pleural
Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014
 Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014 TB Case Presentation Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH August 14, 2014 Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to
Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014 TB Case Presentation Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH August 14, 2014 Andrea Cruz, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy
 Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Pleural syndrome Tuberculous pleurisy Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Pleural effusion: Findings of fluid between
Malignant Pleurisy Associated with Primary Lung Cancer Well Controlled by Pleurodesis Using Distilled Water
 CASE REPORT Malignant Pleurisy Associated with Primary Lung Cancer Well Controlled by Pleurodesis Using Distilled Water Mitsuaki Sekiya, Toshiji Ishiwata, Kaku Yoshimi, Tetsutaro Nagaoka, Yoshiteru Morio,
CASE REPORT Malignant Pleurisy Associated with Primary Lung Cancer Well Controlled by Pleurodesis Using Distilled Water Mitsuaki Sekiya, Toshiji Ishiwata, Kaku Yoshimi, Tetsutaro Nagaoka, Yoshiteru Morio,
Preface. Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03
 Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03 Preface Tulip Group of companies believes in offering our valued customers the technical support and scientific information to keep updated with the latest international
Date: May 1, 2003 Vol.1/MX-2/05/03 Preface Tulip Group of companies believes in offering our valued customers the technical support and scientific information to keep updated with the latest international
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Session Guidelines. This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff
 Respiratory Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and coding
Respiratory Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and coding
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE:
 TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE: AN UNUSUAL CASE BY From the Medical and Surgical Units, University College Hospital Received May 15, 1941 Congestive cardiac failure associated with thyrotoxicosis
TOTAL THYROIDECTOMY FOR HEART FAILURE: AN UNUSUAL CASE BY From the Medical and Surgical Units, University College Hospital Received May 15, 1941 Congestive cardiac failure associated with thyrotoxicosis
