BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS
|
|
|
- Letitia Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT BOTH YOUR NAME, UW AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET AND WRITTEN ON ALL SHORT-ANSWER PAGES NOW - BEFORE YOU BEGIN. PAGES WITHOUT STUDENT NAME AND NUMBERS MAY NOT BE RECORDED. THIS EXAMINATION IS TIME LIMITED ANSWER SHEETS TURNED IN LATE WILL NOT BE GRADED. THIS EXAMINATION (300 POINTS TOTAL) CONTAINS 113 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1-70 and X01 X43) AND 2 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ON 25 PAGES MAKE SURE ALL PAGES ARE PRESENT. PUT ANSWERS FOR ITEMS 1-70 ON THE FRONT, AND FOR ITEMS X01 X43 ON THE BACK OF THE BACK OF THE ANSWER SHEET USING #2 PENCIL BE SURE TO TURN IN ANSWER SHEET AND THE SHORT ANSWER PAGE YOU MAY KEEP YOUR COPY OF THE EXAMINATION Some useful formulae: natural logarithm of 2 = F = AUCoral/AUCIV CL = Kelim * Vd Kelim = 0.693/half life half life = * Vd/CL CL = * Vd/half life Css = dosing rate * F/CL Vd = dose/conc Some commonly encountered abbreviations BID (twice daily) BPM beats per minute CHF congestive heart failure COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ER estrogen receptor GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease HT hypertension IM intramuscular, intramuscularly PRN (as needed) QID (four times daily) SOB shortness of breath BP blood pressure camp cyclic adenosine monophosphate CYP cytochrome P450 enzyme FEV 1 forced expired volume in 1 sec HR heart rate HS (at bedtime) IV intravenous, intravenously QD (daily) SubQ subcutaneous, subcutaneously TID (three times daily) HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 1
2 I. SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). Each numbered item or incomplete statement in this section is followed by answers or completions of the statement. For items 1 through 43 select the ONE lettered answer or statement that is BEST. 1. Acts on the central nervous system after systemic administration: A) echothiophate B) ipratropium C) methacholine D) physostigmine E) succinylcholine 2. A beta-adrenergic antagonist is contraindicated in a patient with: A) anxiety B) asthma C) glaucoma D) hypertension E) pheochromocytoma 3. Indicated with 2-PAM (pralidoxime) in the treatment of organophosphate poisoning: A) atenolol B) atropine C) phentolamine D) succinylcholine E) none of the above 4. The change in heart rate due to IV administration of phenoxybenzamine could be blocked by pretreatment with: A) botulinum toxin B) mecamylamine C) propranolol D) reserpine E) all of the above 5. Would potentiate the vasopressor effect due to subsequent administration of norepinephrine: A) acetylcholine B) cocaine C) labetalol D) phentolamine E) prazosin HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 2
3 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 6. Indicated in the treatment of malignant hyperthermia: A) acetylcholine B) dantrolene C) neostigmine D) pilocarpine E) tiotropium 7. IV administration causes an increase in total peripheral resistance and a decrease in heart rate: A) acetylcholine B) dobutamine C) isoproterenol D) phenylephrine E) none of the above 8. The main pathway for the termination of the action of norepinephrine is mediated by: A) catechol-o-methyltransferase B) dopa decarboxylase C) monoamine oxidase D) tyrosine hydroxylase E) none of the above 9. A low IV dose of dopamine would: A) block beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart B) cause vasodilation of mesenteric vasculature C) cause vasodilation of skeletal muscle vasculature D) cause vasoconstriction of skeletal muscle vasculature E) none of the above 10. A five year old male is brought into the emergency room in an abnormal mental state. His skin is red and dry, and he has a fever and tachycardia. The pupils are widely dilated. It is suspected that he may have accidentally ingested one of a number of agents available in the home of his grandparents. Given the symptoms, it appears that he may be overdosed on any of the following EXCEPT: A) atropine B) chlorpheniramine C) imipramine D) pilocarpine E) scopolamine HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 3
4 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 11. Adverse reactions caused by thiazides include each of the following EXCEPT: A) hypercalcemia B) hypoglycemia C) hypokalemia D) hyperlipidemia E) hyperuricemia 12. The usefulness of nitroglycerin in the treatment of stable angina is limited by each of the following EXCEPT: A) headache B) negative inotropic effect C) short duration of action D) tachycardia E) tolerance 13. A 28 year old college student with a history of moderately persistent asthma presents to the emergency department with dyspnea. He is sweating, anxious and using all accessory muscles to breath. Vital signs are: pulse 120, BP 140/95, RR 30, T 37.2 C, O2 saturation on room air is 92%. The diagnosis is acute asthma. In addition to oxygen and magnesium each of the following agents may be appropriate in the initial management of this patient EXCEPT: A) albuterol B) epinephrine C) ipratropium bromide D) prednisone E) salmeterol 14. A 58 year old male with hyperlipidemia has been treated with a statin drug for the past year. Control of lipid levels has been less than anticipated. Thus, it was recommended that an agent that inhibits the absorption of bile acids be tried instead. Which of the following agents would be most appropriate? A) atorvastatin B) cholesterol C) colestipol D) gemfibrozil E) niacin HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 4
5 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 15. Drug synergism is also known as: A) denervation supersensitivity B) desensitization C) physiological antagonism D) potentiation E) tolerance 16. Some potential for abuse. Use may lead to low to moderate physical dependence or high psychological dependence. Prescriptions may be oral or written. Up to 5 renewals are permitted within 6 months. The controlled substance classification that best fits this description is: A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V 17. Each of the following agents that reduces arterial blood pressure does so by interfering with the activity of some part the sympathetic nervous system EXCEPT: A) amlodipine B) bretylium C) guanethidine D) propranolol E) reserpine 18. Which of the following is the best description of Phase III Clinical Drug Investigation? A) large number of normal human volunteers to determine toxicity in people B) large number of patients with a target illness C) patients in clinical practices monitored for toxicity D) small number of normal human volunteers to determine dose in people E) small number of patients with a target illness HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 5
6 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 19. A 29 year old female research lab technician has recently become pregnant. She describes to you that she is willing to take any drugs that you feel are needed during her pregnancy. She is even willing to take drugs for which there have been reports of risk in animals as long there is no evidence of risk in humans. In essence, she is telling you that she is willing to take drugs with the FDA Use-in-Pregnancy Rating of: A) A B) B C) C D) D E) X 20. One CYP isoenzyme is noteworthy in that it is highly expressed in the small intestine as well as the liver: A) 1A2 B) 2C9 C) 2C19 D) 2D6 E) 3A4 21. Each of the following drugs used in the treatment of asthma, is considered to be a controller EXCEPT A) beclomethasone dipropionate B) montelukast C) salmeterol D) terbutaline E) zileuton 22. A 40 year old female hospital administrator presents in the emergency department with diffuse pruritis, generalized urticaria and moderate wheezing and dyspnea. Her lips and face are swollen. The diagnosis is anaphylaxis. In addition to oxygen, each of the following medications is indicated EXCEPT: A) albuterol B) digoxin immune Fab C) diphenhydramine D) epinephrine E) prednisone HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 6
7 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 23. A 72-year old male, former smoker presents to the emergency department with a severe exacerbation of his underlying COPD and a possible pneumonia on top of long-standing hypertension. In addition to (titrated) oxygen each of the following drugs is indicated EXCEPT: A) albuterol to help relax airways B) an antibiotic selected to treat the pneumonia C) ipratropium to help relax airways and reduce bronchiolar secretions D) nadolol to reduce blood pressure E) prednisone to reduce inflammatory responses 24. The pd2 of drug Y in an isolated tissue chamber is the negative logarithm of the concentration of drug Y that: A) produces a 2-fold increase in contractions B) produces a 2-fold increase in the contraction produced by an agonist drug Z C) produces a two-fold shift to higher concentrations of the concentration effect relationship of the agonist drug Z D) causes a half-maximal effect E) increases by two-fold the maximal response produced by an agonist drug Z 25. A 50 year old female school bus driver with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is being treated with digoxin (0.5 mg daily, PO [a fairly high dose]) to control ventricular rate. She has been having some coughing and wheezing during an air pollution alert. Which of the following agents would be most useful to minimize ventricular rate in this patient without increasing digoxin toxicity or exacerbating her asthma? A) atenolol B) diltiazem C) furosemide D) propranolol E) spironolactone 26. Each of the following mechanisms is involved in the therapeutic effect of sublingual nitroglycerin in patients with stable angina EXCEPT: A) activation of guanylate cyclase B) decreased demand for oxygen by the heart C) efflux of Ca from vascular smooth muscle cells D) increased total coronary blood flow E) release of NO HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 7
8 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 27. Treatment of hyperlipidemia with atorvastatin plus niacin is associated with an increased risk of: A) constipation B) coronary heart disease C) glucose intolerance D) myopathy E) thrombocytopenia 28. Filgrastim (G-CSF) would be expected to be useful in limiting the toxicity associated with: A) tobramycin B) cyclophosphamide C) imatinib (Gleevec ) D) trastuzumab (Herceptin ) E.) glucocorticoids 29. Which of the following statements about the estrogen receptor (ER) is incorrect? A) when ERalpha binds estradiol it can interact with DNA elements to induce gene expression B) ERbeta can bind to tamoxifen and lead to gene induction C) estrogen receptors must bind directly to DNA to cause cellular effects D) tamoxifen acts as both an antagonist and agonist of ER depending on the tissue E) MAP kinase signaling pathways are induced by ER ligands 30. Irreversible aplastic anemia is a rare but frequently fatal side effect associated with: A) clindamycin B) bleomycin C) acyclovir D) chloramphenicol E) erythromycin 31. Induction of metallothionein in cancer cells could lead to resistance to: A) mechlorethamine B) methotrexate C) doxorubicin D) taxol E) irinotecan HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 8
9 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 32. The neurotoxicity of this drug can be prevented by co-administering pyridoxine (vitamin B6): A) gentamicin B) sulfamethoxazole C) chloramphenicol D) isoniazid E) erythromycin 33. Your patient has a tumor burden of 10 9 cells before treatment and after 1 dose with cisplatin you estimate the number of tumor cells at What would be the log kill? A) 3 B) 4 C) 5 D) 6 E) can not be determined 34. Most likely to cause anaphylactic immune reactions: A) doxycycline B) chloramphenicol C) ticarcillin D) trimethoprim E) acyclovir 35. Resistance to vancomycin: A) involves the synthesis of a novel peptidoglycan precursor B) involves production of a novel pump protein that increases efflux of the drug C) can be avoided by co-administering clavulanic acid D) has not yet been observed clinically E) usually occurs by covalent modification of the drug HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 9
10 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 36. Aminoglycosides are: A) well absorbed orally B) sensitive to inactivation by plasmid encoded enzymes C) associated with anemia and leukopenia D) highly toxic to the liver E) able to penetrate into the CNS 37. Paclitaxel (Taxol ) acts by: A) inhibiting topoisomerase II B) forming free radicals C) binding to DNA D) blocking the estrogen receptor E) stabilizing microtubules 38. Clavulanic acid is inactive as an antibacterial drug but is sometimes given together with amoxicillin because it: A) inhibits the anion pump in the kidney and prolongs the half life B) tends to reduce the potential for allergic reactions C) inhibits many beta-lactamases D) slows the absorption of drug and prolongs the duration of action of a single dose E) reduces gastric irritation 39. The major toxicities of aminoglycosides are thought to be caused by either binding of drug to phospholipids or: A) inhibition of ion channel function B) generation of free radicals C) inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis D) inhibition of axonal transport E) accumulation of high concentrations in the CSF HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 10
11 SELECT ONE BEST (4 points each). 40. In cells pretreated with interferon, an infecting virus: A) can not penetrate protected cells B) results in RNA degradation and inhibition of protein synthesis C) is degraded by secreted proteases D) becomes mutated during replication E) attaches to the cell surface and is attacked by a complement mediated immune response 41. Bilirubin displacement from serum binding proteins in newborns can lead to kernicterus. Which of the following is most likely to be associated with this toxicity? A) clindamycin B) doxycycline C) chloramphenicol D) vancomycin E) sulfisoxazole 42. Foscarnet is active against both CMV and HSV infections and can be useful when treating virus that have become resistant to other first line drugs. What is the basis for the selective toxicity of foscarnet? A) foscarnet concentrates specifically in virus infected cells B) foscarnet is selectively activated in virally infected cells by thymidine kinase C) the induction of interferon in virally infected cells makes them sensitive to activation of 2,5 A synthetase by foscarnet D) foscarnet inhibits the specific aspartate protease required for processing of the viral coat proteins E) foscarnet preferentially binds the pyrophosphate site on viral but not host DNA polymerase 43. You are treating a 23 year old female patient with bacterial meningitis and need to choose a drug without knowing the pathogen. Which one would be the best from the following: A. cefaclor B. ceftriaxone C. penicillin G D. isoniazid E. tobramycin HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 11
12 II. A, B, BOTH, NEITHER (2 points each). For items 44 through 59 select: A) if A is correct B) if B is correct C) if BOTH A AND B are correct D) if NEITHER A NOR B is correct 44. Preferentially acts as an agonist at alpha1 over alpha2 receptors: A) clonidine B) prazosin 45. Causes postural hypotension after systemic administration: A) bretylium B) mecamylamine 46. Decreases the production of the aqueous humor: A) physostigmine B) timolol 47. Causes fasciculations prior to paralysis: A) succinylcholine B) d-tubocurarine 48. Methacholine can be used for the diagnosis of : A) airway hyperreactivity B) atropine poisoning HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 12
13 A, B, BOTH, NEITHER (2 points each) 49. Acts on the adrenal medulla after systemic administration: A) guanethidine B) reserpine 50. Bethanechol acts as an agonist at acetylcholine receptors in: A) cardiac muscle B) skeletal muscle 51. Antiarrhythmic with prominent anticholinergic effects: A) lidocaine B) quinidine 52. Increased potassium conductance, as caused by activation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors, results in increased refractory period in: A) atrial muscle cells B) AV nodal cells 53. Is a potassium sparing diuretic because it acts as an inhibitor of Na-K-2Cl symport: A) spironolactone B) triamterene HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 13
14 A, B, BOTH, NEITHER (2 points each) 54. Antiarrhythmic drug in class Ia: A) amiodarone B) bretylium 55. A 58-year old male smoker presents to the emergency department with 2 hours of chest pressure. He has vomited and is diaphoretic. The diagnosis is acute coronary syndrome. In addition to oxygen, morphine, aspirin and heparin what other medication(s) is (are) indicated acutely? A) metoprolol B) nitroglycerin 56. The mechanism of bleomycin action involves: A) free radical generation B) crosslinking of G residues in the DNA 57. The selective toxicity of acyclovir is due to: A) preferential phosphorylation by the viral thymidine kinase B) specific inhibition of the viral DNA polymerase 58. Which of the following basic mechanisms /drug combinations are correct? A) inhibit formation of peptidoglycan precursor: cycloserine B) inhibit cross-linking of peptidoglycans: meropenem HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 14
15 A, B, BOTH, NEITHER (2 points each) 59. Inhibitor of mycolic acid biosynthesis that is useful in the treatment of tuberculosis: A. pyrazinamide B. linezolid C. Both D. Neither III. GREATER THAN LESS THAN (1 point each). For items 60 through 70 select: A) if A is GREATER THAN B B) if B is GREATER THAN A C) if BOTH A and B are EQUAL or NEARLY EQUAL 60. Duration of action of: A) ephedrine B) epinephrine 61. Duration of action of: A) acetylcholine B) carbachol 62. Duration of action of: A) nadolol B) propranolol 63. Cardioselectivity of: A) nadolol B) propranolol 64. Reflex tachycardia due to administration of: A) phentolamine B) prazosin HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 15
16 GREATER THAN LESS THAN (1 point each). 65. Clinical efficacy for suppression of gastric acid secretion of: A) anticholinergic compounds B) proton pump inhibitors 66. Nitroglycerin, when given in low doses decreases: A) afterload B) preload 67. Dependence on intracellular stores of calcium ion for excitation-contraction coupling: A) cardiac muscle B) smooth muscle 68. Clinical efficacy of a diuretic drug that maximally decreases sodium reabsorption by A) 5% B) 10% 69. Refractory period of the AV node in a patient treated with: A) digoxin B) atropine plus digoxin 70. Apparent affinity of binding to its receptor of a(n): A) antagonist drug with pd2 of 5 B) partial agonist drug with pa2 of 5 HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 16
17 NOTE: IN ORDER FOR YOU TO PROPERLY ANSWER ITEMS X01 X43, YOU MUST PUT YOUR ANSWERS ON THE BACK OF THE ANSWER SHEET. IV. AUTONOMIC CHECKERBOARD (4 POINTS EACH) DIRECTIONS: (Items X01-X05) Please refer to the chart on page 18 (you may wish to remove page 18 for ease of comparison). Assume that each VERTICAL COLUMN represents a different animal which was pretreated with one or more drugs before the test drug sequence. Assume the pretreatment drugs are used in doses at least adequate to elicit their most characteristic pharmacological effects and that all pretreatment drugs act throughout the experiment. Assume further that test drugs are short-acting. The chart indicates the acute qualitative change (increase, decrease, no change, respectively) in TOTAL PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE after intravenous injection of each test drug. With careful attention to the key, you should choose the MINIMUM number of pretreatment drugs which would be required to account for and still be compatible with the observed results. SELECT: A Atropine B Cocaine C Nadolol D Famotidine E Phentolamine F Reserpine G Atropine and Prazosin H Nadolol and reserpine I Phenoxybenzamine and reserpine J Prazosin and propranolol K Atropine, propranolol, and phentolamine L Cocaine, phentolamine, and scopolamine M Atropine, mecamylamine, prazosin, and reserpine N Bretylium, mecamylamine, scopolamine, and timolol O Ipratropium, nadolol, prazosin, and reserpine P Chlorpheniramine, guanethidine, propranolol, ranitidine and scopolamine Q Cimetidine, diphenhydramine, propranolol, reserpine and scopolamine FOR EACH ITEM, FILL IN ONLY ONE CIRCLE ON YOUR ANSWER SHEETS. X01. Animal I was pretreated with: X02 Animal II was pretreated with: X03. Animal III was pretreated with: X04. Animal IV was pretreated with: X05. Animal V was pretreated with: HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 17
18 CONTROL NO PRETREATMENT ANIMAL I ANIMAL II ANIMAL III ANIMAL IV ANIMAL ACh AMP DMPP EPI HIST ISO MCN NE PHENYL V Where: ACh = acetylcholine AMP = amphetamine DMPP = dimethylphenylpiperazinium EPI = epinephrine HIST = histamine ISO = isoproterenol McN = McN-A343 NE = norepinephrine PHENYL = phenylephrine Suggestion: remove this page for easy comparison. HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 18
19 V. MATCHING (1 POINT EACH). For items X06-X26 choose the corresponding letter for the item on page 20 which BEST matches the description. Use each item once and only once. We suggest you remove page 20 for ease of matching. X06. Agent that blocks histamine receptors, useful in the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome X07. Agent that inhibits the release of histamine X08. Agent the inhibits the release of acetylcholine at synapses X09. Agent that promotes the release of histamine from mast cells X10. Agent with positive inotropic properties based on inhibition of PDE3 X11. Agonist with selectivity for beta-2 receptors X12. Antihistamine agent with significant anticholinergic properties X13. Antihypertensive agent that blocks smooth muscle Ca channels X14. Anticholinergic selective for M3 receptors X15. Ca channel blocker with significant negative inotropic effects X16. Extremely short acting vasodilator used to diagnose coronary artery disease X17. Glucocorticoid given orally in inflammatory disorders such as asthma X18. Hepatotoxic inhibitor of cyclooxygenase X19. Indirectly acting sympathomimetics amine X20. Inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase that reduces the incidence of acute mountain sickness X21. Inhibitor of the presynaptic amine re-uptake pump X22. Intravenously administered agent for the treatment of malignant hypertension X23. Leukotriene modifier (LTM) that acts as an antagonist of leukotriene receptors X24. Rapidly acting cardiac glycoside X25. Second generation H1 receptor antagonist X26. So-called high ceiling diuretic HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 19
20 Below is a list of drugs arranged alphabetically by their generic names. For items X06-X26 on page 19 choose the corresponding letter which BEST matches the description. Use each item once and only once. A) acetaminophen B) acetazolamide C) adenosine D) amlodipine E) botulinum toxin F) bumetanide G) chlorpheniramine H) cocaine I) famotidine J) milrinone K) montelukast L) nedocromil M) ouabain N) prednisone O) ranitidine P) sodium nitroprusside Q) terbutaline R) tiotropium S) tyramine T) vancomycin U) verapamil Suggestion: remove this page for easy comparison. HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 20
21 VI. DATA MATCHING (2 POINTS EACH). Many types of data in pharmacology are plotted in graphical form with the horizontal axis designated as the X axis and the vertical axis as the Y axis. For items X27-X36, match the ONE lettered graph on page 22 that BEST describes the usual relationship between the X and Y variables. You may use each graph, once, more than once or not at all. Match the graph of the relationship when: X27. The X axis is plasma level of a drug in a population of human volunteers (some of whom are slow metabolizers) given a fixed dose of the drug and the Y axis is number of people in the population with a given plasma level of the drug X28. The X axis is time following IV injection of a drug that exhibits two-compartment behavior and is cleared by first order kinetics and the Y axis is logarithm of the plasma concentration of the drug X29. The X axis is concentration of an agonist drug in a chamber containing isolated strip of heart muscle and the Y axis is magnitude of the heart muscle contractions X30. The X axis is dose of a drug and the Y axis is cumulative percentage of patients responding to the drug with a given quantal response X31. The X axis is logarithm of the concentration of an agonist drug in a chamber containing an isolated strip of smooth muscle and the Y axis is magnitude of contractions produced by the drug X32. The X axis is time and the Y axis is fraction of the total amount of drug eliminated per hour for a drug eliminated by first order kinetics X33. The X axis is the dose of atropine in humans and the Y axis is the resting heart rate X34. The X axis is time during chemotherapeutic treatments that result in a reproducible log kill and the Y axis is the logarithm of the theoretical number of cancer cells in an experimental animal during multiple treatments X35. The X axis is time following the administration of a (perfectly calculated) loading dose and continued IV infusion at a constant rate of a drug and the Y axis is plasma concentration of the drug. X36. The X axis is time during steady state oral maintenance dosage of a drug and the Y axis is the plasma level of the drug HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 21
22 A B C D E F G H I J K L Suggestion: remove this page for easy comparison. HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 22
23 VII. For items X37 through X43 AND SA1 AND SA2 use the Table of Pharmacokinetic Values on page 24 (we suggest you remove that page for ease of consulting the data). For items X37 through X43 (2 points each) choose the ONE BEST drug (letter A through U) from the first column of the Table of Pharmacokinetic Values. Each drug may be chosen once, more than once, or not at all. X37. Which drug (all of which are bases) would be most ionized (i.e., have the greatest percentage of its molecules in an ionized state) in the stomach at a ph of 1.4? X38. Of drugs in this table for which appropriate information is available, which would be most likely to cause a pharmacokinetic augmentation of the effects of metoprolol? X39. Based on effective total plasma concentration, and ignoring other pharmacokinetic parameters, which drug appears to be the least potent on a weight basis? X40. Following time for distribution, which drug is present in the smallest total amount in the body of a patient when present at, the effective (i.e., therapeutic) concentration? X41. Of drugs in this table for which appropriate information is available, which drug appears to have the largest first pass effect? X42. Of the drugs in this table for which appropriate information is available, which appears to have the smallest 'therapeutic window', relatively speaking? X43. If dosing were begun at a constant rate, for which drug would it require the shortest time to achieve a steady state plasma concentration? HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 23
24 Suggestion: remove this page for easy comparison. HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 24
25 Name: Student Number: VIII. SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (5 points each) Based on the information available from the Table of Pharmacokinetic Values (page 24) answer items SA1 and SA2 in the spaces provided. Show your calculations. Please clearly write your answers in the spaces below. (Note : answers that are not sufficiently legible to be deciphered will be assumed to be incorrect!) SA1. A 60 kg female patient with acute anaphylaxis is being seen in the Emergency Department. After administration of epinephrine, it is desired to give a loading dose of diphenhydramine to bring her total plasma concentration up to the effective level. Theoretically, how much diphenhydramine would need to be injected IV to accomplish this goal? SA2. A 90 kg patient is to be given diltiazem by mouth. What is the daily dosage to theoretically achieve an effective average steady state plasma concentration of diltiazem in this patient? Be sure to turn in this page with your answer sheet and make sure your name is clearly written. This is the end of the EXAM. Good Luck on this and others. Have a great holiday! HuBio 543 Final Examination December 9, 2005 Page 25
BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS
 BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT BOTH YOUR NAME, UW AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET AND WRITTEN ON
BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT BOTH YOUR NAME, UW AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET AND WRITTEN ON
BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS
 BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT BOTH YOUR NAME, UW AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET AND WRITTEN ON
BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT BOTH YOUR NAME, UW AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET AND WRITTEN ON
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Pharmacology Second. - Contraction of detrusor muscle in the bladder.
 Pharmacology Second 1) Which of the following is correct regarding the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? - Afferent neurons carry signals from the CNS to the effector organs. - The neurotransmitter at the
Pharmacology Second 1) Which of the following is correct regarding the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? - Afferent neurons carry signals from the CNS to the effector organs. - The neurotransmitter at the
HuBio 543 Final Examination December 7, 2007 page 1
 BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT YOUR NAME, ASUW NUMBER AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID NUMBER (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET -
BEFORE YOU START: PLEASE NOTE THESE IMPORTANT ITEMS USING #2 PENCIL, MAKE SURE THAT YOUR NAME, ASUW NUMBER AND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE TEST ID NUMBER (SPECIAL CODES) NUMBERS ARE CODED ON THE ANSWER SHEET -
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS. Lecture 4
 AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II
 Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
 PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
Drugs Used in Heart Failure. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
PITTMed Cardiology. Pharmacology Modules. Learning Objectives. Site Contents. Fall 2018
 PITTMed Cardiology Fall 2018 Site Contents Pharmacology Modules Please complete the following modules during the first week of class: Adrenergics Cholinergics Adrenergic Drugs in Cardiology Hypercalcemia
PITTMed Cardiology Fall 2018 Site Contents Pharmacology Modules Please complete the following modules during the first week of class: Adrenergics Cholinergics Adrenergic Drugs in Cardiology Hypercalcemia
Neuro Basics SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5
 Neuro Basics SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5 1) Biogenic amines include ACh, NE, EPI and? a) Melatonin b) Dopamine c) Serotonin d) Histamine e) All of the neurotransmitters listed are biogenic amines.
Neuro Basics SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 5 1) Biogenic amines include ACh, NE, EPI and? a) Melatonin b) Dopamine c) Serotonin d) Histamine e) All of the neurotransmitters listed are biogenic amines.
Pharmacology Final. 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine?
 Pharmacology Final 1-Which of the following is inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter? a) Acetylcholine b) Dopamine c) Glutamate d) GABA* 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine? a) Dryness
Pharmacology Final 1-Which of the following is inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter? a) Acetylcholine b) Dopamine c) Glutamate d) GABA* 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine? a) Dryness
Intravenous Infusions
 Intravenous Infusions 1) An IV insulin infusion can be used for patients: a) with out of control diabetes b) with DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) c) after a heart attack 2) Hyperglycemia is an adaptive response
Intravenous Infusions 1) An IV insulin infusion can be used for patients: a) with out of control diabetes b) with DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis) c) after a heart attack 2) Hyperglycemia is an adaptive response
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology
 Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
These drugs produce effects similar to the sympathetic nervous system
 Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Pharmacology med term exam
 1-drug discovery & development usually starts with : -preclinical studies on tissues and animals - an idea or a hypothesis -phase 0 clinical drug trials - acute toxicity studies -bioavailability bioequivalence
1-drug discovery & development usually starts with : -preclinical studies on tissues and animals - an idea or a hypothesis -phase 0 clinical drug trials - acute toxicity studies -bioavailability bioequivalence
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
BIMM118. Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated; postganglionic axons are
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated; postganglionic axons are
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Guideline of Pharmacology for International Student
 Guideline of Pharmacology for International Student I Character and Objective of the Course 1. Character of the Course: Basic Medical Course. 2. Preparatory Course: Physiology, biochemistry, and pathophysiology.
Guideline of Pharmacology for International Student I Character and Objective of the Course 1. Character of the Course: Basic Medical Course. 2. Preparatory Course: Physiology, biochemistry, and pathophysiology.
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 11 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Autonomic Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 533 through 552 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Vishaal Bhat. anti-adrenergic drugs
 Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Autonomic Nervous System
 ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
MED PHARM 501/801 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM FALL SEMESTER December 6, 2005
 MED PHARM 501/801 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM FALL SEMESTER December 6, 2005 1. Promethazine is an antihistaminic drug. Knowing that it is a weak base with a pk a of 9.1, you can predict that: A. it s urinary
MED PHARM 501/801 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM FALL SEMESTER December 6, 2005 1. Promethazine is an antihistaminic drug. Knowing that it is a weak base with a pk a of 9.1, you can predict that: A. it s urinary
Angina Pectoris. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room
 Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic
 Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Therefore, there is a strong interaction between pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
 PHRM20001: How Drugs Work TOPIC 1 Mechanism of Drug Action Lecture 1: Introduction Key principles learned from the history of pharmacology: - Risk vs Reward when treating people with a drug, many drugs
PHRM20001: How Drugs Work TOPIC 1 Mechanism of Drug Action Lecture 1: Introduction Key principles learned from the history of pharmacology: - Risk vs Reward when treating people with a drug, many drugs
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets
 METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
Treatment of T Angina reatment of By Ali Alalawi
 Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
Treatment of Angina By Ali Alalawi Determinants of Oxygen Demand Need to improve ratio of: Coronary blood flow / cardiac work Or Cardiac O2 Supply / Cardiac Requirement Coronary Circulation vs Other Circulation
7/21/2017. Learning Objectives. Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Epinephrine. Cardiotonic Agents. Epinephrine. Epinephrine. Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT
 Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Benztropine and trihexyphenidyl: Centrally acting antimuscarinic agents used for treatment of Parkinson disease & extrapyramidal symptoms.
 Scopolamine: Tertiary amine plant alkaloid. Produces peripheral effects similar to those of atropine. Unlike atropine, scopolamine has greater action on the CNS (observed at therapeutic doses). It has
Scopolamine: Tertiary amine plant alkaloid. Produces peripheral effects similar to those of atropine. Unlike atropine, scopolamine has greater action on the CNS (observed at therapeutic doses). It has
Pharmacodynamics. Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology
 Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS. The Basics of cardiac pharmacology 2007
 WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 5. Emergency Pharmacology
 Chapter 5 Emergency Pharmacology Chapter Goal Understand basic principles of pharmacology, & develop drug profiles for common emergency medications Learning Objectives Differentiate among chemical, generic
Chapter 5 Emergency Pharmacology Chapter Goal Understand basic principles of pharmacology, & develop drug profiles for common emergency medications Learning Objectives Differentiate among chemical, generic
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline, dopamine, dobutamine
 1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Pharmacodynamics. Drugs usually elicit more than one effect. What the drug does to the body. How do drugs work? What do they do?
 Pharmacology 203 Windward Community College Pharmacodynamics What the drug does to the body How do drugs work? What do they do? In this fact sheet, we will look at the fundamental mechanisms of drug action.
Pharmacology 203 Windward Community College Pharmacodynamics What the drug does to the body How do drugs work? What do they do? In this fact sheet, we will look at the fundamental mechanisms of drug action.
From the Text. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
I. OVERVIEW DIRECT. Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of
 THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
THE CHOLINERGIC NEURON 1 I. OVERVIEW DIRECT Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system (ANS) are divided into two groups according to the type of ACTING neuron involved in their mechanism of action.
(PP XI) Dr. Samir Matloob
 DRUGS ACTING ON THE CHOLINERGIC SYSTEM AND THE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING DRUGS IV (NICOTINIC ANTAGONISTS) (PP XI) Dr. Samir Matloob Dept. of Pharmacology Baghdad College of Medicine Drugs acting on the cholinergic
DRUGS ACTING ON THE CHOLINERGIC SYSTEM AND THE NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING DRUGS IV (NICOTINIC ANTAGONISTS) (PP XI) Dr. Samir Matloob Dept. of Pharmacology Baghdad College of Medicine Drugs acting on the cholinergic
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
 Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists α-adrenergic Receptor Antagonists Unlike the β-adrenergic receptor antagonists, which bear clear structural similarities to the adrenergic agonists E, epinephrine, and isoproterenol,
Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists α-adrenergic Receptor Antagonists Unlike the β-adrenergic receptor antagonists, which bear clear structural similarities to the adrenergic agonists E, epinephrine, and isoproterenol,
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Autonomic Pharmacology
 Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System I
 Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System I Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System I Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS
 Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
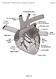 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
B-blockers. Effects not related to Beta-Blockade
 B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Creates a loss of Provide Used in EMS for sedation for cardioversion, RSI, and chemical restraint, Versed
 1 Chapter 6, Part 2 General Principles of Pharmacology 2 Drug Classifications There are numerous drug classifications in the medical field Most EMS medications are: medications medications Respiratory
1 Chapter 6, Part 2 General Principles of Pharmacology 2 Drug Classifications There are numerous drug classifications in the medical field Most EMS medications are: medications medications Respiratory
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Pharmacodynamics. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Introduction Pharmacology is the study of the biochemical and physiological aspects of the drug effects including absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination,
Pharmacodynamics Dr. Alia Shatanawi Introduction Pharmacology is the study of the biochemical and physiological aspects of the drug effects including absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination,
Cholinergic antagonists
 Cholinergic antagonists Cholinergic antagonists: They are also called anticholinergic drugs or cholinergic blockers, this group include: 1.Antimuscarinic agents ( atropine, ipratropium, scopolamine) 2.
Cholinergic antagonists Cholinergic antagonists: They are also called anticholinergic drugs or cholinergic blockers, this group include: 1.Antimuscarinic agents ( atropine, ipratropium, scopolamine) 2.
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Critical Care Medication Administration
 Critical Care Medication Administration 1. HEPARIN (units/hour): Given in LII, LI, HG, ER, HCHA, PACU, Cath Lab, MSONT Purpose: Anticoagulation. Used to treat Acute MI, CVA, DVT, etc. Identify concentration
Critical Care Medication Administration 1. HEPARIN (units/hour): Given in LII, LI, HG, ER, HCHA, PACU, Cath Lab, MSONT Purpose: Anticoagulation. Used to treat Acute MI, CVA, DVT, etc. Identify concentration
BIMM118. Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated;
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated;
Hypertension Update. Objectives 4/28/2015. Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015
 Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS. Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1. Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev. Date: September 16, Materials on: Exam #2
 ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview
 Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview Adapted from Gary Spanik, RPh Edited by Kate Reeves, Pharm D, RPh Jon Manocchio, Pharm D, RPh Pharmacist Responsibilities Be aware of basic ACLS tenets
Blanchard Valley Hospital Pharmacy Code Blue Overview Adapted from Gary Spanik, RPh Edited by Kate Reeves, Pharm D, RPh Jon Manocchio, Pharm D, RPh Pharmacist Responsibilities Be aware of basic ACLS tenets
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
SNS: Pharmacotherapeutics, Medication, and Neuropharmacology
 SNS: Pharmacotherapeutics, Medication, and Neuropharmacology Jeffrey Fudin, Pharm.D., DAAPM, FCCP Adjunct Associate Professor, Pharmacy Practice Albany College of Pharmacy CEO, NovaPain Associates Clinical
SNS: Pharmacotherapeutics, Medication, and Neuropharmacology Jeffrey Fudin, Pharm.D., DAAPM, FCCP Adjunct Associate Professor, Pharmacy Practice Albany College of Pharmacy CEO, NovaPain Associates Clinical
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
TELEMETRY EXAM. 1. Match the numeral in the right column with the correct drug in the left column. a. Pronestyl 1. Hypotension
 TELEMETRY EXAM 1. Match the numeral in the right column with the correct drug in the left column. a. Pronestyl 1. Hypotension b. Digitalis 2. Tachycardias c. Potassium 3. Assists in repolarization d. Inderal
TELEMETRY EXAM 1. Match the numeral in the right column with the correct drug in the left column. a. Pronestyl 1. Hypotension b. Digitalis 2. Tachycardias c. Potassium 3. Assists in repolarization d. Inderal
Basic Pharmacology. Understanding Drug Actions and Reactions
 Basic Pharmacology Understanding Drug Actions and Reactions MARIA A. HERNANDEZ Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Administrative College of Pharmacy Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale, Florida, U.S.A. APPU
Basic Pharmacology Understanding Drug Actions and Reactions MARIA A. HERNANDEZ Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Administrative College of Pharmacy Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale, Florida, U.S.A. APPU
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
