MED PHARM 501/801 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM FALL SEMESTER December 6, 2005
|
|
|
- Hannah French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MED PHARM 501/801 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM FALL SEMESTER December 6, Promethazine is an antihistaminic drug. Knowing that it is a weak base with a pk a of 9.1, you can predict that: A. it s urinary excretion would be accelerated by administration of NH4Cl B. it s urinary excretion would be accelerated by giving NaHCO 3 C. more of the drug would be ionized at blood ph than at stomach ph D. the drug would be absorbed faster from the stomach than from the small intestine E. hemodialysis is the only effective therapy to reduce blood levels. For each numbered statement (2-5) select the ONE lettered heading that is MOST clearly associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once, or not at all. A. Affinity B. Efficacy C. Antagonist D. Receptor E. Agonist 2. A/An has no efficacy 3. This is the property of a chemical that indicates an ability to bind to a receptor. 4. This term refers to the ability of a receptor ligand to induce a maximum response. 5. A/An provides the recognition site for a drug 6. What is the basic relationship which defines and determines a steady-state plasma concentration? A. rate out/rate in B. rate in C. dose rate/clearance D. half-life 7. The apparent volume of distribution for most drugs is: A. a meaningful value which equals a real physiological space B. an indication of the extent of drug movement out of the blood stream C. equal to total body water D. based upon the measurement of tissue concentrations of the drug 1
2 8. A competitive antagonist A. decreases the maximum response that the agonist can produce B. shifts the agonist dose-response curve "to the left". C. interacts chemically with receptors to form permanent covalent bonds D. can be overcome by higher concentrations of agonist. 9. Biotransformation produces metabolites which: A. are chemically distinct from the parent B. have restricted distribution C. have increased renal tubular reabsorption D. have decreased biliary excretion E. A and B 10. In the aged there is: A. decreased GI absorption of drugs B. decreased distribution of drugs C. decreased renal excretion of drugs D. decreased biotransformation of drugs E. all of the above 11. Formation of a metabolite from a drug allows the body to do all of the following to the metabolite EXCEPT: A. Restrict its distribution. B. Increase its hepatic (biliary) excretion. C. Decrease its renal (tubular) reabsorption. D. Increase the metabolite's access to the brain. E. Usually make it more water soluble, so it is more easily excreted. 12. The dose of drug required to produce a desired therapeutic endpoint in one-half of the subjects tested is referred to as the: A. LD50 B. ED50 C. TD50 D. therapeutic index 13. Pharmacogenetics influences: A. are exhibited in polymorphic phase I biotransformation B. are inherited C. affect isoniazid acetylation D. affect pseudocholinesterase mediated reactions E. all of the above 2
3 Response (% of maximum) log dose ( g/kg) an agonist From data provided in the figure above determine the following: 14. The D-50 dose for drug A is? A..3 ug/kg B. 1 ug/kg C. 3 ug/kg D. 10 ug/kg E. 100 ug/kg 15. The D-50 dose for drug B is? A..3 ug/kg B. 1 ug/kg C. 3 ug/kg D. 10 ug/kg E. 100 ug/kg 16. The D-50 for drug C is? A..3 ug/kg B. 1 ug/kg C. 3 ug/kg D. 10 ug/kg E. 100 ug/kg 3
4 17. How much more potent is drug A than drug B? A. 2 times B. 10 times C. 100 times D. Equipotent E. Cannot determine based on inadequate data 18. How much more potent is drug B than drug C? A. 2 times B. 10 times C. 100 times D. Equipotent E. Cannot determine based on inadequate data 19. Drug C could best be described as: A. 2 times less potent than drug B B. 2 times less potent than drug A C. A competitive antagonist D. A partial agonist E. A full but weakly potent agonist 20. For a given drug a therapeutic index with a small value means: A. Only a small dose of the drug will be needed to produce a 100% response. B. The drug is so potent that only a small dose is needed to produce a therapeutic effect. C. The drug is so weakly potent that only a large dose will be needed to produce an adverse or lethal effect. D. The difference in doses to produce a therapeutic effect from an adverse effect is of no consequence. E. The difference in dose to produce an adverse effect from a therapeutic effect is small. 21. Creatinine clearance is an important consideration when administering drugs to: A. Children between the ages of 5 and 15 years B. Elderly male and female patients without known kidney disease C. College age athletes with very large muscle to fat ratios D. Patients on high protein low carbohydrate diets 22. The decrease in diastolic blood pressure induced by a low dose of epinephrine can be blocked by administration of: A. atropine B. propranolol C. prazosin D. phentolamine 4
5 23. Mrs. Smith is being treated for open-angle glaucoma with a drug that produces miosis and an increase in outflow of aqueous humor. Which of the following is the drug she is taking? A. atropine B. timolol C. pilocarpine D. phenylephrine 24. The vasodilation and decreased blood pressure produced by the intravenous administration of this drug is mediated by the release of nitric oxide: A. norepinephrine B. bethanechol C. atropine D. nicotine 25. Military personnel expecting exposure to "nerve gas" should be provided with: A. propranolol B. atropine C. neostigmine D. discharges E. bethanechol 26. Mr. Jones is taking neostigmine for his myasthenia gravis. He has problems of G.I. cramping, watery eyes and sweating. Which drug can best reduce these side effects? A. phenylephrine B. propranolol C. pilocarpine D. physostigmine E. atropine 27. Which one of the following would be contraindicated for patients with asthma? A. atropine B. prazosin C. propranolol D. phenylephrine E. ipratropium 28. The change in heart rate associated with intravenous administration of isoproterenol would be blocked by: A. atropine B. propranolol C. prazosin D. clonidine 5
6 For each numbered statement (29-33) select the ONE lettered heading that is MOST closely associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once, or not at all. A. Pilocarpine D. Atropine B. Clonidine E. Dobutamine C. Dopamine 29. This drug will produce contractions of the iris constrictor (sphincter) muscle and ciliary muscle. 30. Acts at presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors to reduce nerve impulse-induced release of norepinephrine. 31. A drug that effectively increases renal blood flow. 32. A patient presenting with fever, dilated pupils, urinary retention, dry skin and mouth, tachycardia and delirium is most likely suffering from intoxication with: 33. This drug increases cardiac contractile force without significant changes in peripheral vascular resistance. 34. All of the following are typical cholinergic effects EXCEPT: A. a decrease in heart rate B. a decrease in conduction velocity through the AV node C. an increase in sweat secretion D. contraction of bronchial muscle E. an increase in pupillary diameter 35. A patient arrives at your office after having taken a "few extra" decongestant pills. She is agitated and has a heart rate of 120. You determine that she took ephedrine. Which one of the following, if given, would you expect to reduce her heart rate? A. scopolamine B. metoprolol C. isoproterenol D. dobutamine E. epinephrine 36. A contraindication to the use of streptokinase or tissue type plasminogen activator (t-pa): A. recent pulmonary embolism B. acute myocardial infarction C. recent ophthalmic surgery D. treated hypertension E. heart failure 6
7 37. Your patient has hypertension and moderately severe congestive heart failure. The best choice for outpatient management using a single drug would be: A. metoprolol B. captopril C. furosemide D. sodium nitroprusside E. sublingual nitroglycerin 38. Digoxin causes all of the following EXCEPT: A. + + inhibits a cell membrane Na -Ka activated ATP-ase B. + causes the loss of K from myocardial cells C. causes an increase in intra-myocardial cell Na + D. 2+ causes a loss of Ca from myocardial cells 39. Which of the following is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with a small therapeutic index and produces a bronchodilator effect at a serum concentration of 5-15 mcg/ml? A. beclomethasone B. theophylline C. atropine D. prednisone E. ipratropium 40. All of the following are side effects of theophylline EXCEPT: A. nausea B. tremor C. insomnia D. osteoporosis E. agitation 41. Which of the following drugs used in treating obstructive airway disease inhibits the effect of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors on bronchial smooth muscle? A. albuterol B. theophylline C. prednisone D. ipratropium E. epinephrine 42. Propranolol administration will cause all of the following EXCEPT: A. increase in systemic vascular resistance B. renin suppression C. increase in myocardial contractility D. reduction in heart rate 7
8 43. When considering digoxin therapy for Mr. Jones, which would be an unlikely risk factor for digoxin intoxication that you would consider: A. renal failure B. diuretic use C. hypokalemia D. liver failure E. old age 44. This can reverse the action of warfarin: A. heparin B. streptokinase C. vitamin K D. aspirin E. protamine sulfate 45. An antihypertensive drug that lowers blood pressure 10 mm Hg in one-half of patients tested at a dose of 8 mg and produces liver damage in one-half of patients tested at a dose of 80 mg. A. has a therapeutic index of 10 in terms of benefit to risk of hepatotoxicity B. will produce liver damage in most patients given any dose of the drug C. has a therapeutic index of 0.1 in terms of benefit to risk of hepatotoxicity D. will not produce liver damage in patients who receive less than 80 mg. 46. When given intravenously the effect of this drug on preload is secondary to vasodilation and a reduction in afterload due to resistance vessel dilation along with coronary artery dilation: A. captopril B. nitroglycerin C. prazosin D. propranolol 47. Degree of anticoaguability produced by this drug is monitored with the INR: A. aspirin B. streptokinase C. warfarin D. protamine sulfate 48. Drug interaction at the receptor level makes it impossible to use this antiarrhythmic drug in the patient receiving theophylline: A. propranolol B. lidocaine C. adenosine D. digoxin 8
9 49. Useful in the prevention of postoperative deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: A. aspirin B. streptokinase C. tissue plasminogen activator D. mini-dose subcutaneous heparin E. warfarin For each numbered statement (50-54) select the ONE lettered heading that is MOST closely associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once, or not at all. A. Acetazolamide D. Furosemide B. Mannitol E. Triamterene C. Spironolactone 50. An inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase that is NOT useful in long-term diuretic therapy. 51. Used by neurosurgeons to reduce cerebral swelling. 52. A competitive inhibitor of aldosterone. 53. Useful in the management of hypercalcemia, i.e., this drug promotes renal calcium excretion. 54. A drug acting on the late distal tubule and collecting duct which is not associated with a loss of potassium. For each numbered statement (55-59) select the ONE lettered heading that is MOST closely associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once, or not at all. A. Clonidine D. Prazosin B. Nifedipine E. Metoprolol C. Hydrochlorothiazide F. Captopril 55. Alpha -1 adrenergic receptor antagonist. 56. Alpha 2 adrenergic receptor agonist. 57. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. 58. Calcium channel antagonist. 59. Diuretic 9
10 For each numbered statement (60-62) select the ONE lettered heading that is MOST closely associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once, or not at all. A. Digoxin D. Verapamil B. Lidocaine E. Dobutamine C. Amiodarone 60. A drug with negative inotropic actions related to the impairment of calcium movement into cardiac muscle cells. 61. A drug used in sudden cardiac arrest that blocks sodium and potassium channels and is sympatholytic. 62. A drug with positive inotropic action that also impairs A-V nodal transmission 63. The mechanism of action of the anticoagulant effect of coumarin derivatives involves: A. interfering with actions of vitamin K in the synthesis of factors VII, IX and X B no effect on vitamin K C. an action that blocks the release of preformed prothrombin by the liver D. fibrinolysis 64. Which of the following has been associated with reflex tachycardia? A. nifedipine B. propranolol C. captopril D. metoprolol 65. Captopril has all of the following disadvantages EXCEPT: A. can only be used for mild to moderate hypertension B. may increase serum potassium C. may cause chronic cough D. is a teratogen 66. A drug whose actions can intensify the AV block caused by the digitalis glycosides is: A. nitroglycerin B. hydralazine C. epinephrine D. losartan E. verapamil 10
11 67. All of the following might be acceptable alternatives to the digitalis glycosides for the long-term management of CHF, EXCEPT: A. 1-adrenergic agonists B. antihypertensive drugs C. diuretic drugs D. dietary sodium restriction E. angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors 68. Identify drug X from the above graph: A. physostigmine B. propranolol C. prazosin D. scopolamine 69. Which of the following drugs used to lower cholesterol is not absorbed to any extent: A. simvastatin B. cholestyramine C. nicotinic Acid D. gemfibrozil 70. Glucocorticoids are used to treat all of the following diseases EXCEPT: A. asthma B. ulcerative colitis C. rheumatoid arthritis D. osteoporosis 71. Which of the following drugs is used to treat amenorrhea - galactorrhea syndrome? A. raloxifene B. metyrapone C. mifepristone D. bromocriptine E. clomiphene 11
12 72. Cardiovascular morbidity in women using progestin-estrogen oral contraceptive is increased by all of the following factors EXCEPT: A. hypertension B. smoking C. amount of estrogen in the combination estrogen-progesterone pill D. obesity E. use before the age of eighteen 73. Which of the following agents is used to treat patients with hypoparathyroidism? A. parathormone B. calcitonin C. Vitamin D D. alendronate 74. Which of the following compounds is used to treat diabetes insipidus? A. glipizide B. hydrochlorothiazide C. furosemide D. bromocriptine 75. The mineralocorticoid activity of some of the anti-inflammatory steroids would be most likely to induce: A. peptic ulcer B. hypokalemic alkalosis C. psychosis D. buffalo hump E. abdominal striae 76. Corticosteroids: A. may cause severe inflammatory responses B. stimulate protein synthesis C. cause fluid retention and edema D. may produce hypoglycemia 77. The following is characteristic of first-order elimination kinetics: A. half-life increases with dose B. clearance decreases with dose C. plasma concentration does not change with dose D. none of the above E. all of the above 12
13 78. Saturable or nonlinear elimination kinetics implies that: A. plasma concentration and dose are directly related at all doses B. response bears a predictable relationship to dose C. clearance decreases with dose D. all of the above E. none of the above 79. Drugs which undergo an extensive first-pass effect have the following factor in common: A. they are water-soluble B. they are primarily excreted by the kidney C. they have a low oral bioavailability D. none of the above 80. When designing a dosing regimen for an individual patient one should consider: A. average pharmacokinetic parameter values B. characteristics of the individual patient C the therapeutic concentration range D. all of the above 81. Recent evidence suggests that the first choice for treatment of peptic ulcer is: A. prostaglandins B. antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor C. antacids and H 2 histamine antagonist D. sucralfate and kaolin/pectin 82. The appropriate clinical strategy for patients suspected of peptic ulcer is: A. loperamide B. testing for H. pylori infection C. antacids D. sucralfate 83. Which of the following drugs has no demonstrated clinical efficacy in the management of diarrhea: A. cholestyramine (Questran) B. bismuth subsalicylate (PeptoBismol) C. diphenoxylate/atropine (Lomotil) D. loperamide (Immodium) E. kaolin and pectin (Kaopectate) 13
14 84. Mrs. Jones is a 68 year old woman with metastatic breast cancer who was admitted to the hospital for radiation therapy of painful bone metastases. She was given large amounts of meperidine to control her pain. Due to other problems she developed progressive renal failure and her serum creatinine increased from 1.4 mg/dl to 4.2 mg/dl. On her fifth hospital day she developed severe muscle jerking movements and then grand mal seizures. Other information: (1) Meperidine is cleared predominantly by Phase I biotransformation to normeperidine. (2) Normeperidine is excreted primarily by the kidneys. (3) Normeperidine is a CNS stimulant. Mrs. Jones side effects occurred because: A. Large amounts of meperidine will be formed in the liver but slowly cleared by the kidneys. B. Large amounts of normeperidine will be formed in the liver but slowly cleared by the kidneys. C. Meperidine was not adequately biotransformed by Phase II metabolism. D. Enterohepatic reabsorption of meperidine has resulted in toxic blood levels of meperidine. 85. Taking an oral tablet of acetaminophen lying down has been shown to delay esophageal transit which results in a delay in the rate of absorption but not the extent of absorption. Based on this finding, which of the following pharmacokinetic changes do you expect? A. Delay in the appearance of acetaminophen in the systemic blood when taking the drug lying down. B. Increased maximum plasma acetaminophen concentration when taking the drug lying down C. Decreased area under the plasma acetaminophen concentration-time profile when taking the drug lying down. D. All of the above 86. The following factor should be considered when calculating the loading dose of a drug for a clinical indication that needs quick onset of drug response A. Drug clearance B. Volume of distribution C. Maintenance dose D. All of the above 14
15 87. Physostigmine and bethanechol in small doses have significantly different effects on which one of the following: A. Gastric secretion B. Neuromuscular junction (skeletal muscle) C. Salivary glands D. Sweat glands E. Bladder muscle 88. Epinephrine can be used to treat: A Anaphylactic shock B. Glaucoma C. Prolong the duration of action of local anesthetics D. Cardiac arrest E. All of the above 89. Which of the following is a quaternary analogue of atropine and is poorly absorbed into the circulation when inhaled? A. Albuterol B. Ipratropium bromide C. Theophylline D. Montelukast E. Prednisone 15
16 The illustration depicts the results of a trial designed to assess the effects of digoxin on morbidity and mortality of persons with moderate to severe left ventricular failure. Subjects were randomized to digoxin or placebo in addition to standard therapy including ACE inhibitors. 90. The data shown in Panel A suggests: A. B. C. D. E. 91. ACE inhibitors should not be used to treat left ventricular failure. Diuretics should be added to a regimen of therapy for heart failure in order to provide a survival benefit. There is no difference in mortality from any cause between treatment groups. Digoxin should not be used in the treatment of heart failure. Placebo therapy conferred survival benefit as compared to digoxin therapy. The data shown in Panel B suggests: A. B. C. D. E. Fewer persons in the digoxin group were hospitalized due to worsening heart failure. Digoxin is of no value in treating heart failure. Digoxin reduces any cause mortality. Digoxin exerts a positive inotropic action. Digoxin has a small therapeutic index. 16
17 92. Side effects associated with this drug include pulmonary fibrosis, skin discoloration and retinal pigmentation: A. Adenosine B. Lidocaine C. Amiodarone D. Digoxin E. Metoprolol 93. When administered to the hypertensive patient you can expect a 10 mm lowering of the blood pressure from all of the following EXCEPT: A. Hydrochlorothiazide B. Captopril C. Nifedipine D. Acetazolamide E. Metoprolol 94. Test of control for warfarin therapy A. Activated partial thromboplastin time B. Bleeding time C. Platelet count D. Prothrombin time/inr 95. Contraindicated for the patient taking isosorbide dinitrate A. Metoprolol B. Propranolol C. Sildenafil D. Digoxin E. Warfarin 96. Drugs with a relatively large volume of distribution (>200 L) probably have which characteristics: A. Highly water soluble B. Highly bound to proteins and tissues C. High clearance values D. None of the above 17
18 Plasma Concentration ug/ml Hrs. A 10.9 mg IV dose of drug X was administered to a patient producing the blood level pattern shown in the Figure above. Based on this pattern answer the following questions. 97. Drug X exhibits what type of elimination pattern A. First order, mono exponential elimination B. Zero order, mono exponential elimination C. Zero order, multi-exponential elimination D. First order, multi-exponential elimination 98. What is the apparent volume of distribution, if concentration is 10.9 g/ml? A. 10 L B. 1 L C. 900 L D. 90 L 99. This selective estrogen receptor modulator is used for the treatment of osteoporesis. A. Raloxifene B. Clomiphene C. Rosiglitazone D. Alendronate 18
19 1. A 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. D 6. C 7. B 8. D 9. E 10. E 11. D 12. B 13. E 14. B 15. D 16. D 17. B 18. D 19. D 20. E 21. B 22. B 23. C 24. B 25. B 26. E 27. C 28. B 29. A 30. B 31. C 32. D 33. E 34. E 35. B 36. C 37. B 38. D 39. B 40. D 41. D 42. C MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWER SHEET 43. D 44. C 45. A 46. B 47. C 48. C 49. D 50. A 51. B 52. C 53. D 54. E 55. D 56. A 57. F 58. B 59. C 60. D 61. C 62. A 63. A 64. A 65. A 66. E 67. A 68. C 69. B 70. D 71. D 72. E 73. C 74. B 75. B 76. C 77. D 78. C 79. C 80. D 81. B 82. B 83. E 84. B A 86. B 87. B 88. E 89. B 90. C 91. A 92. C 93. D 94. D 95. C 96. B 97. B 98. B 99. A
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
 PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROBLEMS 1. A 69 year old woman suffering from CHF has been treated with.25 mg Digoxin tablet daily for last 3 months. But the heart failure is not controlled adequately. What will be the
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Drugs Used in Heart Failure. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Drugs Used in Heart Failure Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Heart Failure Heart failure (HF), occurs when cardiac output is inadequate to
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
These drugs produce effects similar to the sympathetic nervous system
 Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
7/21/2017. Learning Objectives. Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Epinephrine. Cardiotonic Agents. Epinephrine. Epinephrine. Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT
 Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Pharmacology Second. - Contraction of detrusor muscle in the bladder.
 Pharmacology Second 1) Which of the following is correct regarding the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? - Afferent neurons carry signals from the CNS to the effector organs. - The neurotransmitter at the
Pharmacology Second 1) Which of the following is correct regarding the autonomic nervous system (ANS)? - Afferent neurons carry signals from the CNS to the effector organs. - The neurotransmitter at the
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
number 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected by Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Doctor Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptors are targeted by drugs, the question now is how do these drugs
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
BIMM118. Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated;
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated;
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Low Efficacy Diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Osmotic diuretics. Miscellaneous
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Dr. Vishaal Bhat. anti-adrenergic drugs
 Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS. The Basics of cardiac pharmacology 2007
 WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
WRITER TRISTAN WALKER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. WHAT ARE THE MAJOR CLASSES OF CARDIAC DRUGS?...2 2. HOW DO THEY WORK?...3 3. CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT...7 4. SUMMARY TABLE...10 REFERENCES...14
Drug Classifications
 CLASSIFICATIONS: QUIZ 2 Drug Classifications 1. Which category of drugs is used to relieve minor to severe pain? a. Alkylates b. Analgesics c. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors d. Androgens e. Anesthetics
CLASSIFICATIONS: QUIZ 2 Drug Classifications 1. Which category of drugs is used to relieve minor to severe pain? a. Alkylates b. Analgesics c. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors d. Androgens e. Anesthetics
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Pharmacology Final. 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine?
 Pharmacology Final 1-Which of the following is inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter? a) Acetylcholine b) Dopamine c) Glutamate d) GABA* 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine? a) Dryness
Pharmacology Final 1-Which of the following is inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter? a) Acetylcholine b) Dopamine c) Glutamate d) GABA* 2-Which of the following side effect is not related to atropine? a) Dryness
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Malik
 number 21 Done by Corrected by Dania Alkouz Doctor Malik Dr. Malik is going to repeat what Dr. Omar said about the cholinergic agonists and antagonists. The Autonomic Nervous system (ANS) (Just a quick
number 21 Done by Corrected by Dania Alkouz Doctor Malik Dr. Malik is going to repeat what Dr. Omar said about the cholinergic agonists and antagonists. The Autonomic Nervous system (ANS) (Just a quick
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
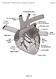 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Pharmacology med term exam
 1-drug discovery & development usually starts with : -preclinical studies on tissues and animals - an idea or a hypothesis -phase 0 clinical drug trials - acute toxicity studies -bioavailability bioequivalence
1-drug discovery & development usually starts with : -preclinical studies on tissues and animals - an idea or a hypothesis -phase 0 clinical drug trials - acute toxicity studies -bioavailability bioequivalence
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents
 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Cholinergic agents, Cholinomimetic drugs,
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-2 Cholinergic agents Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Cholinergic agents, Cholinomimetic drugs,
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Excretion of Drugs. Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College
 Excretion of Drugs Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College Excretion of Drugs By the end of this lecture, students should be able to! Identify main and minor routes of excretion including renal
Excretion of Drugs Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College Excretion of Drugs By the end of this lecture, students should be able to! Identify main and minor routes of excretion including renal
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Has little therapeutic value. Has multiple actions. Has short t ½ Activates muscarinic & nicotinic receptors. 10/17/2017 2
 Has little therapeutic value. Has multiple actions. Has short t ½ Activates muscarinic & nicotinic receptors. 10/17/2017 2 Muscarinic stimulation: On the CVS: -ve chronotropic & inotropic effects. Decrease
Has little therapeutic value. Has multiple actions. Has short t ½ Activates muscarinic & nicotinic receptors. 10/17/2017 2 Muscarinic stimulation: On the CVS: -ve chronotropic & inotropic effects. Decrease
Autonomic Pharmacology: Cholinergic agonists
 Autonomic Pharmacology: Cholinergic agonists Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 23.01.2013 1 Acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh), the naturally occurring neurotransmitter for
Autonomic Pharmacology: Cholinergic agonists Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 23.01.2013 1 Acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh), the naturally occurring neurotransmitter for
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals
 Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Table 1. Diuretics. Drugs Mechanisms of Action Indications Adverse Drug Effects. Table 2. Electrolyte Modifiers.
 Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS. Lecture 4
 AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Pharmacology for CHEMISTS
 Pharmacology for CHEMISTS JOSEPH G. CANNON ACS Professional Reference Book AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Washington D.C. New York Oxford 1999 CONTENTS I Chemical and Biological Bases
Pharmacology for CHEMISTS JOSEPH G. CANNON ACS Professional Reference Book AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Washington D.C. New York Oxford 1999 CONTENTS I Chemical and Biological Bases
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline, dopamine, dobutamine
 1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive Heart Failure - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@vcu.edu Heart failure:
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive Heart Failure - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@vcu.edu Heart failure:
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets
 METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
 Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy
 Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy Overview Mechanism of cardiovascular drugs Indications and clinical use in cardiology Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors, Angiotensin
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic agent.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 9 Cholinergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 9-1 through 9-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 9 Cholinergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 9-1 through 9-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Diuretics (Saluretics)
 Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Diuretics (Saluretics) Diuretics increase urine excretion mainly by reabsorption of salts and water from kidney tubules These agents are ion transport inhibitors that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at
Agonists: morphine, fentanyl Agonists-Antagonists: nalbuphine Antagonists: naloxone
 Opioid Definition All drugs, natural or synthetic, that bind to opiate receptors Agonists: morphine, fentanyl Agonists-Antagonists: nalbuphine Antagonists: naloxone Opioid agonists increase pain threshold
Opioid Definition All drugs, natural or synthetic, that bind to opiate receptors Agonists: morphine, fentanyl Agonists-Antagonists: nalbuphine Antagonists: naloxone Opioid agonists increase pain threshold
COMMON DRUG RELATED PROBLEMS SEEN IN PACE AND MECHANISMS TO MITIGATE RISK
 COMMON DRUG RELATED PROBLEMS SEEN IN PACE AND MECHANISMS TO MITIGATE RISK Robert L Alesiani, PharmD, CGP Chief Pharmacotherapy Officer CareKinesis, Inc. (a Tabula Rasa Healthcare Company) 2 3 4 5 Pharmacogenomics
COMMON DRUG RELATED PROBLEMS SEEN IN PACE AND MECHANISMS TO MITIGATE RISK Robert L Alesiani, PharmD, CGP Chief Pharmacotherapy Officer CareKinesis, Inc. (a Tabula Rasa Healthcare Company) 2 3 4 5 Pharmacogenomics
Ganglionic Blockers. Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of
 Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Cholinergic receptors( cholinoceptors ) are two families muscarinic and nicotinic depending on their affinities to cholinomimetic agents(agents that
 Cholinergic drugs Cholinergic drugs Are drugs act on receptors that are activated by acetylcholine(ach) which is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system. ACH is synthesized in the cholinergic
Cholinergic drugs Cholinergic drugs Are drugs act on receptors that are activated by acetylcholine(ach) which is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system. ACH is synthesized in the cholinergic
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS. Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1. Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev. Date: September 16, Materials on: Exam #2
 ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 5. Emergency Pharmacology
 Chapter 5 Emergency Pharmacology Chapter Goal Understand basic principles of pharmacology, & develop drug profiles for common emergency medications Learning Objectives Differentiate among chemical, generic
Chapter 5 Emergency Pharmacology Chapter Goal Understand basic principles of pharmacology, & develop drug profiles for common emergency medications Learning Objectives Differentiate among chemical, generic
DIURETICS. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Heart Failure. Dr. William Vosik. January, 2012
 Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Pharmacology of Corticosteroids
 Pharmacology of Corticosteroids Dr. Aliah Alshanwani Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine, KSU Feb 2018 1 The Corticosteroids are steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. They consist of two
Pharmacology of Corticosteroids Dr. Aliah Alshanwani Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine, KSU Feb 2018 1 The Corticosteroids are steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. They consist of two
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology
 Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
numbe r Done by Corrected Docto Alia Shatnawi
 numbe r 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Docto Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptor targets by the drugs, the question now how these drugs work on
numbe r 9 Done by Nazek Hyasat Corrected Bahaa Najjar & mohammed AL-shrouf Docto Alia Shatnawi HOW DO DRUGS WORK??? You know that receptor targets by the drugs, the question now how these drugs work on
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L
 Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Spironolactone has not been demonstrated to elevate serum uric acid, to precipitate gout or to alter carbohydrate metabolism.
 SPIRONE Composition Each tablet contains Spironolactone 100 mg. Tablets Action Spironolactone is a specific pharmacologic antagonist of aldosterone, acting primarily through competitive binding of receptors
SPIRONE Composition Each tablet contains Spironolactone 100 mg. Tablets Action Spironolactone is a specific pharmacologic antagonist of aldosterone, acting primarily through competitive binding of receptors
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Angina Pectoris. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room
 Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Angina Pectoris Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS
 PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN. Dr Nithish Jayakumar
 ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN Dr Nithish Jayakumar Contents 1. Anti-arrhythmics Pacemaker and myocardial potentials Drug classes mechanisms; s/e; contra-indications Management of common arrhythmias 2.
ANTI-ARRHYTHMICS AND WARFARIN Dr Nithish Jayakumar Contents 1. Anti-arrhythmics Pacemaker and myocardial potentials Drug classes mechanisms; s/e; contra-indications Management of common arrhythmias 2.
B-blockers. Effects not related to Beta-Blockade
 B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System ( PNS ) Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Somatic. Autonomic ( ANS ) Enteric.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System ( PNS ) Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Efferent (Motor) Afferent (Sensor) Autonomic ( ANS ) Somatic Parasympathetic Sympathetic Enteric Autonomic
NERVOUS SYSTEM Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System ( PNS ) Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Efferent (Motor) Afferent (Sensor) Autonomic ( ANS ) Somatic Parasympathetic Sympathetic Enteric Autonomic
Cardiac Output MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
Cholinoceptor Blocking Drugs. Drugs that block muscarinic cholinoceptors.
 Cholinoceptor Blocking Drugs Drugs that block muscarinic cholinoceptors. Absorption Natural alkaloids and most tertiary antimuscarinic drugs are well absorbed scopolamine is absorbed across the skin (transdermal
Cholinoceptor Blocking Drugs Drugs that block muscarinic cholinoceptors. Absorption Natural alkaloids and most tertiary antimuscarinic drugs are well absorbed scopolamine is absorbed across the skin (transdermal
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE HEART FAILURE
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE HEART FAILURE Mefri Yanni, MD Bagian Kardiologi dan Kedokteran Vaskular RS.DR.M.Djamil Padang The 3rd Symcard Padang, Mei 2013 Outline Diagnosis Diagnosis Treatment options
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE HEART FAILURE Mefri Yanni, MD Bagian Kardiologi dan Kedokteran Vaskular RS.DR.M.Djamil Padang The 3rd Symcard Padang, Mei 2013 Outline Diagnosis Diagnosis Treatment options
