ISPUB.COM. Drug induced pulmonary diseases. S Verma, V Mahajan INTRODUCTION ETIOPATHOGENESIS EPIDEMIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Claribel Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 Drug induced pulmonary diseases S Verma, V Mahajan Citation S Verma, V Mahajan. Drug induced pulmonary diseases. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 9 Number 2. Abstract Drug reactions present to the clinician as a syndrome that may be due to a number of different causes, the patient's treatment being one possibility. In most clinical instances, a correct clinical diagnosis can be made if the physician is knowledgeable of the drugs which have been implicated in the pathogenesis of drug-induced lung reactions and recognizes the characteristic clinical and roentgenographic features present in each case. Management of pulmonary drug reactions consists in stopping the offending drug and if necessary, substituting a less harmful one. Corticosteroid therapy may be used in some cases. INTRODUCTION The number of drugs that adversely affect the respiratory system continues to increase and their effects pose a great challenge to all physicians. A review in 1972 identified only 19 drugs with the potential to cause pulmonary diseases; now, more than 350 drugs have been identified and the search is still on 1. The introduction of cytotoxic drugs in particular has increased both the range of mechanisms and the frequency of pulmonary drug reactions. The range of reactions is wide, from familial simple pharmacological effects (e.g. opiates causing respiratory depression or betablocking drugs causing bronchoconstriction) through less well understood reactions (e.g. aspirin induced asthma, eosinophilic reactions due to sulphonamides or fibrosis due to busulphan) to the infective complications of immunosuppressants. Because of the diverse nature of the drug-induced pulmonary diseases, the correct diagnosis in any individual case will be made only if physicians are knowledgeable of the drugs which have been implicated in the pathogenesis of these reactions and recognize the characteristic clinical and roentgenographic features associated with these drugs. EPIDEMIOLOGY The exact frequency of drug induced lung diseases is difficult to determine because of lack of an effective screening tool. Drug induced lung diseases are prevalent in both adults and children. Children receiving chemotherapy for brain tumours or lymphoma may lead to progressive pulmonary fibrosis and this can occur even 17 years after receiving chemotherapy 2.Certain diseases have sex predilection like aspirin induced asthma 3 and ACE inhibitors induced cough 4 are more common in women than in men. Similarly some ethnic groups are more prone to these diseases. Incidence of interstitial lung disease following administration of Geftinib for non small cell lung cancer is higher in Japanese population than rest of the world 5. Angioedema and cough have been reported more frequently in Nigerian patients receiving ACE inhibitors 4. ETIOPATHOGENESIS The common classes of drugs which can cause lung injury are antineoplastic drugs (Busulfan, Methotrexate, Bleomycin, Cyclophosphamide), antibiotics (Nitrofurantoin, Penicillin, Paraaminosalicylicacid, Sulphonamides), antihypertensive drugs, anticoagulants, drugs of abuse (heroin) and many others like Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorpropamide, Phenytoin, Methysergide etc 6. In addition to drugs, other potential inducers of respiratory disease are biomolecules(eg Interferons, Immunoglobulins, antithymocyte globulin), stem cell modulators (eg All-trans retinoic acid, Granulocyte-colony stimulating factors), transfusion of blood or blood products, stem-cell transplantation, herbs and dietery supplements. It is very difficult to know the exact mechanism of drug associated injury of the lung as we do not have any specific marker to differentiate drug associated interstitial lung disease from other pharmacologic processes. In addition, usage of many drugs at the same time or in close sequence, a practice that makes the assignment of toxicity to a specific agent difficult. By aiding the identification of more than 1000 proteins or peptides in blood samples, the field of 1 of 5
2 Proteomics will hopefully allow scientists to identify candidate markers. Drugs cause lung injury as a result of direct pharmacologic action, persistence or metabolism in the tissue or production of a reactive metabolite. The result of this injury ranges from cellular dysfunction to apoptosis and alteration of repair mechanisms essential for replacing critical tissue elements and function. In many cases, drug induced lung disease is dose related, particularly with cytotoxic agents. Other factors such as increasing patient age, decreased renal function, radiation therapy and oxygen therapy may enhance the toxic effects. TYPES OF REACTIONS Bronchoconstriction Aspirin and b-blockers are the two most common drugs causing bronchoconstriction. Aspirin, through its inhibitory action on cyclo-oxygenase pathway and b-blockers, through their direct pharmacological effect on airway smooth muscle can induce an attack of asthma 7.There can be a paradoxical worsening of asthma after inhalation of chromoglycate or of hypotonic nebulized solution of ipratropium bromide 8. The usual pattern of response to b-blockers is a gradual worsening of patients breathlessness and a failure to respond to treatment with b- agonist drugs. Sometimes the adverse effect of drugs persists for some months after it has been discontinued 9. A syndrome comprising asthma, nasal polyps and aspirin sensitivity has also been recognized. Other common drugs causing bronchoconstriction are antibiotics and contrast media used in radiology. Cough Though any drug causing bronchoconstriction can induce cough but dry cough caused by ACE inhibitors is of special mention as it is rarely if ever accompanied by bronchoconstriction. The cough usually starts after several months of treatment and is of a dry irritant nature. It ceases within a few days of stopping the drug. There is some evidence that administration of cromoglycate reduces the severity and frequency of cough in such patients 10. But it is better to change the treatment to angiotensin 2 antagonists. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia A syndrome of progressive breathlessness associated with increasing airflow obstruction has been described with the use of a number of drugs. The breathlessness is progressive, although the rate varies from a rapid progression over weeks to a slow course over years. Drug associated BOOP has been reported from use of several different types of medications, including anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents such as bleomycin sulphate, gold and methotrexate; antibiotics such as sulfasalazine, cephalosporins and amphotericin B; illicit use of cocaine and a massive dose of L-tryptophan. Minocycline associated BOOP has been reported in a woman who was taking this medication for acne 11. Phenytoin related BOOP with rapid improvement after corticosteroid therapy has been reported 12.There are case reports of patients having nitrofurantoin induced BOOP and their condition improved when nitrofurantoin was withdrawn and corticosteroid treatment commenced 13. Alveolitis Two patterns of drug induced alveolitis has been described. Mild eosinophilic pneumonitis is characterized by cough, breathlessness and fever of subacute to chronic onset with bilateral diffuse micronodular or patchy infilterates on radiography. There is often blood eosinophilia and lung biopsy may show inflammatory cells and eosinophils. Vasculitis may also be present. The condition usually recovers with withdrawl of drug and steroids. Common drugs associated with this condition are antibiotics(nitrofurantoin 14,sulphonamides,paraaminosalicyli cacid); anticonvulsants(phenytoin,carbamazepine);antiarrhythmics(a miodarone,procainamide) and cytotoxic agents (bleomycin, mitomycin, busulphan).in contrast to the non-cytotoxic drugs; the usual pulmonary injury with cytotoxic therapy is a progressive pulmonary fibrosis with relatively little of an inflammatory component and a tendency to cause irreversible lung damage. The second pattern described is of acute eosinophilic pneumonitis. This condition is typically caused by minocycline. Characteristic features are fever, skin-rash, an eosinophilic BAL fluid and has a favourable outcome on cessation of therapy. Acute noncardiogenic pulmonary edema A variety of drugs including opiates, aspirin, amiodarone, blood, blood products and tocolytic agents-can cause pulmonary vascular permeability alterations resulting in pulmonary edema. It occurs sometimes as an idiosyncratic reaction though usually in response to an excessive dose. In all cases, widespread bilateral alveolar or alveolar-interstitial infilterates are noted. The most frequent causes of drug induced pulmonary edema are overdoses of aspirin and opiates. Patients admitted to hospital with high salicylate levels after an overdose(>40 mg/dl) are at risk of developing acute pulmonary edema. The severity and outcome of these cases are quite variable. Most often the pulmonary edema is rapidly reversible. In some patients, however severe lung injury occurs and the clinical course progresses to the point where the case fulfills criteria for adult respiratory distress syndrome(ards). 2 of 5
3 Pulmonary vascular disease Acute alveolar haemorrhage and recurrent alveolar haemorrhage have been reported to occur in response to some drugs like oral anticoagulants, fibrinolytic agents and platelet glycoprotein inhibitors. Patients present with hemoptysis and chest radiographs show alveolar infilterates as well as diffuse ground glassing. In some cases, the alveolar haemorrhage occurs as part of a pulmonary-renal syndrome that is very similar to goodpasture's disease. On the other hand oestrogen containing oral contraceptives have been shown to increase the risk of pulmonary thromboembolism in women by about six to nine times as well as of thrombotic stroke and myocardial infarction. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis Common drugs causing hypersensitivity pneumonitis are methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, nitrofurantoin, antidepressants and chrysotherapy. Patient gets sensitized to the drug and develops cough and breathlessness with lymphocytic predominant bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. It has a favourable outcome and usually recovers with steroids or on dechallenge. Pleural and mediastinal fibrosis 15 Methysergide, used for migraine can cause fibrosis of the pleura and underlying lung and it is a dose-related complication. Patient develops shortness of breath after several years of treatment. Interestingly, all the other drugs that have been reported to cause pleural fibrosis are blockers of neurotransmission. Practolol, b-blocker may cause pleural, mediastinal and peritoneal fibrosis. Ergotamine and bromocriptine can also cause pleuro-pulmonary fibrosis. The course of pleural fibrosis is progressive, with a restrictive pattern of lung function. However, the condition remits when the drug is stopped and in most instances there is reduction in symptoms and some improvement in lung function, though residual fibrosis remains on the chest film. Other pulmonary reactions Drugs can also cause lung disease in an indirect manner like hypoventilation and respiratory failure may be provoked by overdose of narcotics or sedatives, particularly in the elderly or in those with previous airflow obstruction. Drugs acting on the immune system, used in the management of cancer, transplantation and vasculitic diseases can cause opportunistic pulmonary infections. DIAGNOSIS Recognition of drug-induced lung disease is difficult because the clinical,radiologic and histologic findings are nonspecific. The diagnosis is based on a history of drug exposure, histologic evidence of lung damage and exclusion of other causes of lung injury 16.The key to the diagnosis of drug-induced pulmonary disease is awareness of the possibility. Patient should be asked about all the drugs taken and any drug with unfamiliar names should be checked in reference books. First of all, appropriate base-line investigations should be carried out and the offending drug should be stopped. Base line investigations should include chest radiography, lung function testing, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, temperature records, total and differential cell counts and HRCT thorax. In case of doubt among a number of drugs, challenge test can be carried out but it should be performed only under hospital supervision. Lung biopsy, Gallium scanning and bronchoalveolar lavage can also play an important role in the differential diagnosis. Although conventional chest radiography is the first imaging option in evaluating patients for pulmonary manifestations of drug toxicity, the limitations of the pattern approach often predicate the use of other imaging techniques in addition to clinical and laboratory evaluation. In select cases, HRCT and radionuclide imaging have a role in detecting lung toxicity early when it is still reversible. Radiological manifestations Busulfan causes diffuse linear opacities, which may occasionally become reticulonodular. Bleomycin toxicity includes subpleural linear and/or nodular opacities at the lung bases. Methotrexate causes linear and/or reticulonodular opacities early in the process, followed by acinar filling. Bilateral basal interstitial opacities are commonly caused by nitrofurantoin. A common form of granulomatous reaction is caused by methotrexate, nitrofurantoin and chronic aspiration of mineral oils, which leads to the formation of chronic basilar, often conglomerate masses. Heroin or methadone overdose is often associated with pulmonary edema with widespread air-space consolidation. Amiodarone therapy is associated with alveolar and interstitial infilterates, peripheral consolidation, and pleural thickening adjacent to the consolidation. HRCT thorax The HRCT findings of chemotherapeutic drug-induced lung disease reflect the histologic findings 17. Interstitial pneumonitis and fibrosis result in ground-glass opacities, focal areas of consolidation and irregular linear opacities that tend to involve the lower zones of the lungs. Acute respiratory distress syndrome results in bilateral predominantly dependent air-space consolidation with onset occurring within days of chemotherapy administration. Approximately 6% of individuals receiving amiodarone 3 of 5
4 develop pulmonary toxicity 18. The most common HRCT finding of amiodarone toxicity is diffuse interstitial thickening or less commonly as nodular areas of subpleural consolidation. Amiodarone is an iodine containing compound; therefore, parenchymal lesions often show high attenuation with a range from 82 to 174 HU. Although this finding is helpful in suggesting amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity, it is not pathognomonic. Nitrofurantoin toxicity on HRCT shows air-space consolidation with a basilar predominance, a pattern consistent with cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Less commonly, chronic pneumonitis and fibrosis may ensue. On HRCT,this appearance mimics idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with bilateral predominantly basilar reticular opacities. Methotrexate toxicity reveals interstitial pneumonitis and ocassinally centrilobular nodules or a localized nodular air-space filling pattern. The use of illicit drugs like intravenous injection of talc may result in talcosis. HRCT shows diffuse micronodularity resulting from a foreign-body granulomatous response. The micronodules may become confluent and progress to conglomerate parahilar masses, which tend to have high attenuation caused by talc accumulation. 19, 20. So, in conclusion the HRCT manifestations of drug-induced lung disease imitate other entities such as infection, pulmonary fibrosis and disease recurrence. MANAGEMENT Management of drug induced pulmonary reactions consists in stopping the offending drug and, if necessary, substituting a less harmful one. Corticosteroid therapy may be used in some cases. In malignancy, pulmonary side-effects are relatively common and sometimes fatal as the cessation of drug can cause relapse of disease. Hyposensitisation or induction of tolerance can be tried if the drug is considered essential. The main interest of this subject currently centres on the induction of tolerance to aspirin and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs 21. However it should be done with great care as serious reactions can occur. Finally, we can say that the knowledge of adverse pulmonary drug reactions is very important for the pulmonary physicians for better management of patients. CORRESPONDENCE TO Dr. S.K.Verma Associate Professor Department of Pulmonary Medicine Chhatrpati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University,UP Lucknow (India) Phone drskverma@rediffmail.com References 1. Babu KS, Marshall BG. Drug induced airway diseases. Clin Chest Med 2004 Mar;25(1): O'Driscoll BR, Hasleton PS, Taylor PM. Active lung fibrosis up to 17 years after chemotherapy with carmustine(bcnu) in childhood. N Engl J Med 1990 Aug9;323(6): Kalyoncu AF, Karakaya G, Sahin AA, Bans YI. Occurence of allergic conditions in asthmatics with analgesic intolerance. Allergy 1999;54: Ajayi AA, Adigun AQ. Angioedema and cough in Nigerian patients receiving ACE inhibitors. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2000 Jul;50(1): Danson S, Blackhall F, Hulse P, Ranson M. Interstitial lung disease in lung cancer: separating disease progression from treatment effects. Drug Safety 2005;28(2): Michael E, Whitcomb. Drug induced lung disease. Chest 1973;63: Decalmer PBS, Chatterjee SS, Cruikshank JM. Betablockers and asthma. Br Heart J 1978;40: Price HV. Asthma attacks precipitated by cromoglycate in a boy with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Lancet 1982;2: Anderson EG, Calcraft B, Jariwalla AG, Al-Zaibak M. Persistent asthma after treatment with beta-blocking drugs. Br J Dis Chest 1979;73: Hargreaves MR, Benson MK. Inhaled sodium cromoglycate in angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor cough. Lancet 1995;345: Piperno D, Donne C, Loire R, Cordier JF. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with minocycline therapy:a possible cause. Eur Respir J 1995;8: Angle P, Thomas P, Chiu B, Freedman J. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia and cold agglutinin disease associated with phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome. Chest 1997;112: Cameron RJ, Kolbe J, Wilsher ML, Lambie N. Bronchiolitis obliterans associated with the use of nitrofurantoin. Thorax 2001 Feb;56(2): Holmberg L, Boman G. Pulmonary reactions to nitrofurantoin:447 cases reported to the Swedish adverse drug committee Eur J Respir Dis 1981;62: Huggins JT, Sahn SA. Drug- induced pleural disease. Clin Chest Med 2004 Mar;25(1): Fraser RS, Muller NL, Colman N, Pare PD. Diagnosis of diseases of the chest,4th ed.philadelphia:saunders,1999: Padley SPG, Adler B, Hansell DM, Muller NL. Highresolution computed tomography of drug-induced lung disease. Clin Radiol 1992;46: Aronchick JM, Gefter WB. Drug-induced pulmonary disorders. Semin Roentgenol 1995;30: Rosenow EC, Myers JL, Swensen SJ, Pisani RJ. Druginduced pulmonary disease:an update. Chest 1992;102: Wolff AJ, O'Donnell AE. Pulmonary effects of illicit drug use. Clin Chest Med 2004 Mar;25(1): Nasser SM, Patel M, Bell GS, Lee TH. The effect of aspirin desensitization on urinary leukotriene E4 concentrations in aspirin-sensitive subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995;151: of 5
5 Author Information S.K. Verma Associate Professor, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Chhatrpati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University Vineet Mahajan Resident, Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Chhatrpati Shahuji Maharaj Medical University 5 of 5
ISPUB.COM. How Drugs Affect The Lungs. S Kumar, S Mehra BACKGROUND AGE RACE LIMITED KNOWLEDGE SEX RISK FACTORS FREQUENCY
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 S Kumar, S Mehra Citation S Kumar, S Mehra.. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine. 2007 Volume 9 Number 2. Abstract Drug-induced
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 9 Number 2 S Kumar, S Mehra Citation S Kumar, S Mehra.. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine. 2007 Volume 9 Number 2. Abstract Drug-induced
DRUG INDUCED LUNG DISEASES
 DRUG INDUCED LUNG DISEASES CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS 1. CYTOTOXIC ANTIBIOTICS 2. ALKYLATING AGENTS 3. ANTIMETABOLITES 4. BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS CYTOTXIC ANTIBIOTICS BLEOMYCIN 1.CHRONIC PNEUMONITIS/
DRUG INDUCED LUNG DISEASES CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS 1. CYTOTOXIC ANTIBIOTICS 2. ALKYLATING AGENTS 3. ANTIMETABOLITES 4. BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS CYTOTXIC ANTIBIOTICS BLEOMYCIN 1.CHRONIC PNEUMONITIS/
CHAPTER II DRUG INDUCED PULMONARY DISEASES. BY J. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy SRM UNIVERSITY
 CHAPTER II DRUG INDUCED PULMONARY DISEASES BY J. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy SRM UNIVERSITY Drug Induced Pulmonary Disorders Is almost always a diagnosis
CHAPTER II DRUG INDUCED PULMONARY DISEASES BY J. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy SRM UNIVERSITY Drug Induced Pulmonary Disorders Is almost always a diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions
 Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Review Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Journal of Clinical Radiology and Case Reports Radiological Imaging of Drug-Induced Pulmonary Lesions D souza M *, Rajiah P, Khan A and Irion K Department
Nitrofurantoin Pulmonary Toxicity: A Brief Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 B Vahid, B Wildemore Citation B Vahid, B Wildemore.. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine. 2005 Volume 6 Number 2. Abstract
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 B Vahid, B Wildemore Citation B Vahid, B Wildemore.. The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine. 2005 Volume 6 Number 2. Abstract
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Radiation Pneumonitis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Radiation Pneumonitis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History 16 year old with history of relapsed stage IV-A Hodgkin disease. Prior pulmonary involvement was irradiated. Diagnosis Radiation Pneumonitis
Radiation Pneumonitis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History 16 year old with history of relapsed stage IV-A Hodgkin disease. Prior pulmonary involvement was irradiated. Diagnosis Radiation Pneumonitis
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
HRCT in Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis. Where are the lymphatics? Anatomic distribution
 Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest
 Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest Michelle S. Ginsberg, MD Objectives Imaging Cancer Treatment Complications in the Chest To understand the mechanisms of action of different classes of
Radiologic findings of drug-induced lung disease
 Radiologic findings of drug-induced lung disease Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. I. C. Santos, A. F. Roque, R. Mamede, L. Oliveira, T. Saldanha; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
Radiologic findings of drug-induced lung disease Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. I. C. Santos, A. F. Roque, R. Mamede, L. Oliveira, T. Saldanha; Lisbon/PT Keywords:
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Management of drug-induced interstitial lung disease Amitava Ganguli BSc, MRCP and Munir Pirmohamed PhD, FRCP
 Management of drug-induced interstitial lung disease Amitava Ganguli BSc, MRCP and Munir Pirmohamed PhD, FRCP VM Our series on serious ADRs focusses on rare but potentially fatal drug reactions and how
Management of drug-induced interstitial lung disease Amitava Ganguli BSc, MRCP and Munir Pirmohamed PhD, FRCP VM Our series on serious ADRs focusses on rare but potentially fatal drug reactions and how
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Case 1: Question. 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule
 HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
DOWNLOAD PDF DRUG-INDUCED LUNG DISEASES AND RADIATION PNEUMONITIS
 Chapter 1 : Medicine-induced Lung Disease Keywords: Lung, adverse drug reaction, drug-induced lung disease, mechanism of pulmonary toxicity, diagnosis, treatment, review. INTRODUCTION The lungs are a target
Chapter 1 : Medicine-induced Lung Disease Keywords: Lung, adverse drug reaction, drug-induced lung disease, mechanism of pulmonary toxicity, diagnosis, treatment, review. INTRODUCTION The lungs are a target
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Spectrum of High-Resolution CT and Pathologic Findings
 CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Angel Coz MD, FCCP, DCE Assistant Professor of Medicine UCSF Fresno November 4, 2017 No disclosures OBJECTIVES Identify current trends and risk factors of ARDS Describe
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Severe fever and dyspnoea in a young girl with Hodgkin lymphoma
 Eleftheria Chaini 1, Dimitra Haini 2, Manos Antonakis 1, Miltos Vassiliou 3 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Corfu, Greece. 2 Radiology Lab, Nikea-Piraeus General Hospital, Athens,
Eleftheria Chaini 1, Dimitra Haini 2, Manos Antonakis 1, Miltos Vassiliou 3 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Corfu, Greece. 2 Radiology Lab, Nikea-Piraeus General Hospital, Athens,
International consensus statement on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014
 Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review.
 Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1
 Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1 Kee Hyuk Yang, M.D., Yo Won Choi, M.D., Seok Chol Jeon, M.D., Choong Ki Park, M.D., Kyung in Joo, M.D., Chang Kok Hahm, M.D., Seung Ro Lee, M.D.
Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus 1 Kee Hyuk Yang, M.D., Yo Won Choi, M.D., Seok Chol Jeon, M.D., Choong Ki Park, M.D., Kyung in Joo, M.D., Chang Kok Hahm, M.D., Seung Ro Lee, M.D.
Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease
 Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2006; 65: 2, 96-101 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease C. Robalo Cordeiro 1, S. Freitas 1, B. Rodrigues 1, A. Catarino 1,
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2006; 65: 2, 96-101 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease C. Robalo Cordeiro 1, S. Freitas 1, B. Rodrigues 1, A. Catarino 1,
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
Resident Case Review CHEST. Daria Manos CAR 2016
 Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia.
 Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease
 Disclosure Objectives Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease Tilman Humpl The Hospital for Sick Children University of Toronto, Canada Advisor/Research Grants Actelion Pfizer Historical aspects Epidemiology/Genetics
Disclosure Objectives Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease Tilman Humpl The Hospital for Sick Children University of Toronto, Canada Advisor/Research Grants Actelion Pfizer Historical aspects Epidemiology/Genetics
Disclosures. Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting. Relevant financial relationships: None. Off-label usage: None
 Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona
Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona
Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria. Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO
 Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO Asbestosis A declining disease in developed countries Most cases of asbestosis are due to occupational exposure
Asbestosis: diagnosis and attribution criteria Eduardo Algranti Serviço de Medicina FUNDACENTRO Asbestosis A declining disease in developed countries Most cases of asbestosis are due to occupational exposure
Radiologists toolbox to differentiate alveolar versus interstitial lung diseases
 Radiologists toolbox to differentiate alveolar versus interstitial lung diseases Dr Sumer Shikhare, Dr Trishna Shimpi, Dr Ashish Chawla Khoo Teck Puat Hospital Singapore. Relevant financial disclosures
Radiologists toolbox to differentiate alveolar versus interstitial lung diseases Dr Sumer Shikhare, Dr Trishna Shimpi, Dr Ashish Chawla Khoo Teck Puat Hospital Singapore. Relevant financial disclosures
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia: Serial High-Resolution CT Findings in 22 Patients
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Lee et al. High-Resolution CT of Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Ju Won Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 Ho Yun Lee 1 Man Pyo Chung
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Lee et al. High-Resolution CT of Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Ju Won Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 Ho Yun Lee 1 Man Pyo Chung
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases: Is There Really Anything New?
 : Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
: Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD)
 CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD) David Northrop MBA, RRT Assistant Director of Respiratory Therapy Services The University of Kansas Health System Clinical Assistant
CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD) David Northrop MBA, RRT Assistant Director of Respiratory Therapy Services The University of Kansas Health System Clinical Assistant
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker. Michael B. Gotway, MD
 August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka
 A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders
 Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders U. A. Saeed, MBBS FCPS, J. Nair, MBBS MD, R. Khosla, MD FRCR, K. Sayegh, MD FRCPC, J. Kosiuk, MD FRCPC, J. Taylor, MD FRCPC; Department of Radiology, McGill
Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders U. A. Saeed, MBBS FCPS, J. Nair, MBBS MD, R. Khosla, MD FRCR, K. Sayegh, MD FRCPC, J. Kosiuk, MD FRCPC, J. Taylor, MD FRCPC; Department of Radiology, McGill
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease
 Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
Pathologic Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease Dry and itchy? It could be eczema or fungal infection. We don t need to worry, the drugs aren t that dangerous. Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept. of Pathology
Bronkhorst colloquium Interstitiële longziekten. Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog
 Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Lung Injury after HCT
 Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know
 Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-0803 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, F. Japon Sola; Cádiz/ES
Eosinophilic lung diseases - what the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-0803 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, F. Japon Sola; Cádiz/ES
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
Pulmonary Complications of Antineoplastic Agents : Era of Targeted Therapy
 Pulmonary Complications of Antineoplastic Agents : Era of Targeted Therapy Poster No.: C-1230 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Y. Kim, J. H. Hwang, Y.-W. Chang, J. Y. Moon; Seoul/KR
Pulmonary Complications of Antineoplastic Agents : Era of Targeted Therapy Poster No.: C-1230 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Y. Kim, J. H. Hwang, Y.-W. Chang, J. Y. Moon; Seoul/KR
Pulmonary changes induced by radiotherapy. HRCT findings
 Pulmonary changes induced by radiotherapy. HRCT findings Poster No.: C-2299 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. Albert Antequera, K. Müller Campos, D. 1 2 4 3 1
Pulmonary changes induced by radiotherapy. HRCT findings Poster No.: C-2299 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. Albert Antequera, K. Müller Campos, D. 1 2 4 3 1
Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma
 Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma Moon Sung Kim 1, Ki-Nam Lee 1, Won Jin Choi 1, Bo Ra Kim 1, Eun-Ju Kang 1 1 Department of Radiology, Dong-A
Imaging Spectrum of Allergic Lung Disease: Hypersensitivity Reactions on the Lung Parenchyma Moon Sung Kim 1, Ki-Nam Lee 1, Won Jin Choi 1, Bo Ra Kim 1, Eun-Ju Kang 1 1 Department of Radiology, Dong-A
pulmonary and critical care pearls
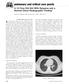 pulmonary and critical care pearls A 12-Year-Old Girl With Dyspnea and a Normal Chest Radiographic Finding* Kristin B. Highland, MD; and Patrick A. Flume, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2001; 120:1372 1376) A 12-year-old
pulmonary and critical care pearls A 12-Year-Old Girl With Dyspnea and a Normal Chest Radiographic Finding* Kristin B. Highland, MD; and Patrick A. Flume, MD, FCCP (CHEST 2001; 120:1372 1376) A 12-year-old
Immune-mediated lung disease. Ian Sabroe
 Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities
 Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression. Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale
 The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale The indications for iatrogenic immunosuppression Autoimmune/inflammatory disease Chemotherapy for malignant
The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale The indications for iatrogenic immunosuppression Autoimmune/inflammatory disease Chemotherapy for malignant
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines
 Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
Key words: CT scanners; interstitial lung diseases; polymyositis-dermatomyositis; x-ray
 Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Associated With Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis* Serial High-Resolution CT Findings and Functional Correlation Hiroaki Arakawa, MD; Hidehiro Yamada, MD; Yasuyuki Kurihara,
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte
 IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
IPF: Epidemiologia e stato dell arte Clinical Classification Diffuse parenchimal lung diseases Exposure-related: - occupational - environmental - medication Desquamative interstitial pneumonia Idiopathic
Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after smoking cessation
 Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 453 461 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015506 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Changes in HRCT findings in patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease after
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Anand Devaraj Affiliations: Dept of Radiology, St George s Hospital, London, UK. Correspondence: Anand Devaraj,
REVIEW IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS Imaging: how to recognise idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Anand Devaraj Affiliations: Dept of Radiology, St George s Hospital, London, UK. Correspondence: Anand Devaraj,
Monocast Description Indications
 Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 CASE REPORT JIACM 2008; 9(4): 321-5 CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature Shibani Mehra*, Shailendra Aggarwal Abstract The diagnosis of Wegener s granulomatosis
CASE REPORT JIACM 2008; 9(4): 321-5 CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature Shibani Mehra*, Shailendra Aggarwal Abstract The diagnosis of Wegener s granulomatosis
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9338-17 Intern Med 57: 1281-1285, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient Yuki Hosono, Nobuhiko Sawa,
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Anatomy. The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
 Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013
 Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013 Overview Radiography Computed Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nuclear Imaging Show All Multimedia Library References Overview For patients with
Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013 Overview Radiography Computed Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nuclear Imaging Show All Multimedia Library References Overview For patients with
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
