Supplementary Materials for
|
|
|
- Phoebe McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan Zhang, Aditi Bhattacharya, Luis M. Pérez-Cuesta, Katrin Deinhardt, Charles A. Hoeffer, Thomas A. Neubert, Wen-biao Gan, Eric Klann,* Moses V. Chao* *Corresponding author. (E.K.); (M.V.C.) Published 14 January 2014, Sci. Signal. 7, ra4 (2014) DOI: /scisignal This PDF file includes: Fig. S1. Characterization of haloperidol-mediated pakt response. Fig. S2. Puromycin dosing and control experiments for genetic manipulations. Fig. S3. Proteomic analysis of measured proteins. Fig. S4. Haloperidol-induced proteins that react with a MAP2 antibody in mouse striatal neurons or rat striatal neurons in vitro. Fig. S5. DARPP32 can label spines in DIV14 cultured striatal neurons. Legends for tables S1 to S4 Table S5. Statistical significance for three biological replicates for selected proteins of interest. Other Supplementary Material for this manuscript includes the following: (available at Table S1 (Microsoft Excel format). Complete results of the 5-hour proteomic screen. Table S2 (Microsoft Excel format). Complete results of the 48-hour proteomic screens. Table S3 (Microsoft Excel format). Haloperidol-induced increases in proteins linked to mtorc1 signaling. Table S4 (Microsoft Excel format). Candidate proteins from cytoskeleton, translation, mrna, membrane, and release protein groups.
2 Fig. S1. Characterization of haloperidol-mediated pakt response. Mouse striatal neurons were cultured for 7 days then serum starved and treated with haloperidol or vehicle for 20 minutes. (A) The response of primary striatal neurons to the indicated concentrations of haloperidol. The most intense response and the highest proportion of responding neurons were achieved with 20 nm. Color scale and size scale same as in Figure 1D-E. Representative images are shown. (B) Verification of pakt signal in the presence and absence of an Akt inhibitor (Akti) and rapamycin (RAP) (data are shown as average +/- SEM, n=5, * indicates p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA). (C) Akt phosphorylation occurs in D 2 R-EGFP-positive neurons. Striatal neurons were prepared from D 2 R-EGFP transgenic mice and exposed to haloperidol. (Left)The pakt response is shown in red, D 2 R-positive cells are green, and nuclei are blue. (Right) the percent of total cells that respond, the % of total cells that are D 2 R positive, and the% overlap between pakt and D 2 R staining (data are shown as average +/- SEM, of 3 independent experiments). The * denotes non-responders (left panel, partially obscured by a D 2 R- and pakt-positive neuron) and the arrow denotes neurons positive for both pakt and D 2 R.
3 Fig. S2. Puromycin dosing and control experiments for genetic manipulations. (A) Determining the optimal concentration of puromycin. Primary striatal neurons were incubated with 1, 5, or 10 µg/ml puromycin for 6 hours and DMSO, haloperidol (HAL), serum (overstim), or cycloheximide for 6 hours and then samples were analyzed by Western blot using an antibody recognizing puromycin. Groups treated with the same dose of puromycin are outlined in red. GluR1 served as a loading control. 1 µg/ml was selected because it had the fewest truncated proteins (shorter proteins would indicate incomplete translation due to puromycin inhibiting the ribosome). (B) Striatal neurons expressing the empty vector, the doxycycline-inducible 4E-BP AA, or wild-type (WT) 4E-BP were incubated with puromycin and haloperidol or DMSO (Veh) for 30 minutes. Actin is a loading control. These blots demonstrate the effectiveness of the 4E-BP constructs used. (C) Striatal neurons were stimulated with an endogenous ligand, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and serum (B27) in the presence or absence of puromycin for 5 hours. The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an antibody recognizing puromycin. Newly synthesized proteins were detected by Western blot with the antibody to puromycin only in the puromycin-treated group, suggesting that the puromycin antibody works well for immunoprecipitation. (D) Striatal neurons were exposed to DMSO (Veh) or haloperidol in the presence of puromycin for 4 hours, lysed, and immunoprecipitated with an antibody recognizing puromycin. Samples were analyzed by Western blot with an antibody to puromycin. This demonstrates that immunoprecipitation with the puromycin antibody can enable detection of changes in nascent proteins in 4 hours. (E) Changes in the synthesis of specific proteins can be detected by Western blot following immunoprecipitation with the antibody recognizing puromycin. Striatal neurons were exposed to DMSO or haloperidol in the presence of puromycin for 4 hours and lysed. Nascent proteins were precipitated using an antibody recognizing puromycin, and probed for S6, a protein identified in the 5-hour screen as upregulated with haloperidol treatment. Actin is a loading control. Data in all panels are representative of multiple puromycin-treatment experiments. Black lines indicate that blots have been stripped after treatment with the antibody recognizing puromycin and re-probed for the loading control.
4 Fig. S3. Proteomic analysis of measured proteins. (A) Immunoprecipitation of puromycin-labeled proteins increases the amount of SILAC-labeled proteins. Top: Following 5 hours of incubation with heavy arginine and lysine (SILAC) and puromycin, lysates of striatal neurons were collected and immunoprecipitated with a puromycin-specific antibody to enrich for SILAC-labeled proteins. The regions in the boxes represent the portion with significant SILAC labeling. Bottom: Measured proteins were normalized and the ratio of haloperidol to vehicle was plotted. Clustering around 0 represents basal translation in the neurons; the points (proteins) that are farther from 0 indicate more protein synthesis in the haloperidol-treated cells. (B) Overview of the 48-hour study method. DIV7 striatal primary cultures were exposed for 48 hours to haloperidol, SILAC labeled, and analyzed by mass spectrometry.
5 Fig. S4. Haloperidol-induced proteins that react with a MAP2 antibody in mouse striatal neurons or rat striatal neurons in vitro. (A) Rat striatal neurons were cultured for 7 days and then exposed to 20 nm haloperidol for 24 hours time. Lysates of vehicle and haloperidol-treated neurons were analyzed by Western blot with an antibody recognizing MAP2. (B) Mouse striatal neurons were cultured for 7 days and then exposed to 20 nm haloperidol for 24 hours. Samples on the right were from neurons expressing a MAP2-targeted shrna. Lysates of vehicle and haloperidol-treated neurons were analyzed by Western blot with an antibody recognizing MAP2. Note the increase in MAP2-dependent immunoreactive bands in the haloperidol-treated neurons that are not present in the MAP2 shrna lanes. Fig. S5. DARPP32 can label spines in DIV14 cultured striatal neurons. To ensure that the DARPP32 antibody labeled spines, we transfected striatal neurons with a GFP antibody and cocultured them with cortical neurons. Neurons were grown to DIV14, fixed, and stained. Arrows indicate examples of DARPP32 (red) and GFP (green) in spines.
6 Table S1. Complete results of the 5-hour proteomic screen. Primary striatal neurons were exposed for 5 hours to haloperidol or vehicle and puromycin and SILAC, lysed, and puromycin-tagged nascent proteins were immunoprecipitated and prepared for mass spectrometry. Protein ratios are presented as vehicle to haloperidol and thus proteins with lower ratios were increased with haloperidol treatment. (Excel file) Table S2. Complete results of the 48-hour proteomic screens. Primary striatal neurons were exposed for 48 hours to haloperidol or vehicle and SILAC, lysed, and prepared for mass spectrometry. (Excel file) Table S3. Haloperidol-induced increases in proteins linked to mtorc1 signaling. In Thoreen et al. (26) the ribosomal association of mrnas with known TOP sequence or established mtorc1-dependency, and suspected TOPlike sequences were measured in the presence and absence of a mtorc1 inhibitor. Those mrnas with decreased ribosomal association with inhibitor treatment (Column B), were considered mtorc1-sensitive. Here we compared these mtorc1-sensitive mrnas with our proteomic screen (5 hrs) and study (48 hrs), to see if any of those mrnas were altered at the protein level following mtorc1 induction by haloperidol. Several of these mtorc1-sensitive mrnas were increased at the protein level with haloperidol treatment at both time points. Increased or decreased denotes the direction of change in at least 2 detections by mass spectrometry unless otherwise noted. The term candidate refers to those proteins that met low stringency criteria. Their protein classification is provided if the class is not one that is highlighted in Table 2 or table S4. (Excel File) Table S4. Candidate proteins from cytoskeleton, translation, mrna, membrane, and release protein groups. Candidate proteins that met the low stringency, medium stringency, or high stringency criteria. Proteins that were detected and identified in common with previous antipsychotic treatment proteomic studies Chan et al. (28) and Ma et al. (27). (Excel File)
7 Table S5. Statistical significance for three biological replicates for selected proteins of interest. Significance was calculated using non-normalized peptide ratios subjected to t-test analysis for each mass spectrometry experiment. Direction indicates the proteins increased (up) with haloperidol treatment. ARMS was significantly increased in the first experiment and trend-level increased in the second. MAP2 was significantly increased in all experiments, and S6 was increased in 2/3 of the mass spectrometry experiments. Proteins are listed by their full name and UniProtKB ID number.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3218
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
Fig. S1. High K+ increases intracellular calcium level.
 Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A) Cells over-expressing hfgfr1-pcdna3 (+) or pcdna3 (-) were stimulated for 10 minutes with 50ng/ml FGF2 and lysates immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A) Cells over-expressing hfgfr1-pcdna3 (+) or pcdna3 (-) were stimulated for 10 minutes with 50ng/ml FGF2 and lysates immunoblotted
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
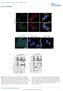 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome Yang Xu 1, Colin K.L. Phoon 2, Bob Berno 5, Kenneth D Souza 6, Esthelle Hoedt 4, Guoan Zhang 4, Thomas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome Yang Xu 1, Colin K.L. Phoon 2, Bob Berno 5, Kenneth D Souza 6, Esthelle Hoedt 4, Guoan Zhang 4, Thomas
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/471/eaah5085/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphorylation of the exocyst protein Exo84 by TBK1 promotes insulin-stimulated GLUT4 trafficking Maeran Uhm,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/471/eaah5085/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphorylation of the exocyst protein Exo84 by TBK1 promotes insulin-stimulated GLUT4 trafficking Maeran Uhm,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/389/ra79/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P 1 to limit vascular
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/389/ra79/dc1 Supplementary Materials for HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P 1 to limit vascular
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS. (A) Workflow for tumor cell line derivation and orthotopic implantation.
 SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/305/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Controlling Long-Term Signaling: Receptor Dynamics Determine Attenuation and Refractory Behavior of the TGF-β Pathway
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/305/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Controlling Long-Term Signaling: Receptor Dynamics Determine Attenuation and Refractory Behavior of the TGF-β Pathway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung
 Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Supporting Information. Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in. Mouse Rod Cells
 Supporting Information Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in Mouse Rod Cells David Salom,, Benlian Wang,, Zhiqian Dong, Wenyu Sun, Pius Padayatti, Steven
Supporting Information Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in Mouse Rod Cells David Salom,, Benlian Wang,, Zhiqian Dong, Wenyu Sun, Pius Padayatti, Steven
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2
 ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
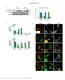
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
Supplemental Information. NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF. in p53-independent Tumor Suppression
 Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Molecular Cell, Volume 68 Supplemental Information NRF2 Is a Major Target of ARF in p53-independent Tumor Suppression Delin Chen, Omid Tavana, Bo Chu, Luke Erber, Yue Chen, Richard Baer, and Wei Gu Figure
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S2
 Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Figures S1-S5, Figure Legends, Table S1 List of primers used in the study
 Insulin receptor alternative splicing is regulated by insulin signaling and modulates beta cell survival Pushkar Malakar,4, Lital Chartarifsky,4, Ayat Hija, Gil Leibowitz 3, Benjamin Glaser 3, Yuval Dor,
Insulin receptor alternative splicing is regulated by insulin signaling and modulates beta cell survival Pushkar Malakar,4, Lital Chartarifsky,4, Ayat Hija, Gil Leibowitz 3, Benjamin Glaser 3, Yuval Dor,
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGF-induced Akt and Erk signaling. Effect of chloroquine on EGF-stimulated mtorc1, Akt and Erk
 EGF induced VATPase assembly and mtorc1 activation Supplemental Information Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGFinduced Akt and Erk signaling. A. Hepatocytes were treated
EGF induced VATPase assembly and mtorc1 activation Supplemental Information Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGFinduced Akt and Erk signaling. A. Hepatocytes were treated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
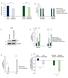 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1%
 FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig 1 (A) sumoylation pattern detected under denaturing condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1% SDS in the presence and absence
FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig 1 (A) sumoylation pattern detected under denaturing condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1% SDS in the presence and absence
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Expanded View Figures
 Sarah Kit Leng Lui et al USP26 stabilizes SM7 MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. USP26 enhances SM2 phosphorylation and T-b-mediated transcription. raph representing relative luciferase values obtained
Sarah Kit Leng Lui et al USP26 stabilizes SM7 MO reports xpanded View igures igure V1. USP26 enhances SM2 phosphorylation and T-b-mediated transcription. raph representing relative luciferase values obtained
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL-
 Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
