Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural. Neural Development
|
|
|
- Blaise Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp (sorta) 4 th ed, pp (sorta) References : Fainsod, A., Steinbeisser, H., & De Robertis, E. M. (1994). EMBO J, 13(21), Hemmati-Brivanlou, A., & Melton, D. (1997). Annu Rev Neurosci, 20, Melton, D. A. (1987). Nature, 328(6125), Sasai, Y., & De Robertis, E. M. (1997). Dev Biol, 182(1), Smith, W. C., & Harland, R. M. (1992). Cell, 70(5), Weeks, D. L., & Melton, D. A. (1987). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 84(9), Wilson, P. A., & Hemmati-Brivanlou, A. (1995). Nature, 376(6538), Xanthos, J. B., Kofron, M., Wylie, C., & Heasman, J. (2001)., 128(2), Zimmerman, L. B., de Jesus-Escobar, J. M., & Harland, R. M. (1996). Cell, 86(4), (pdfs on course websites: [[ 2 1
2 Embryogenesis 1. Maternal cytoplasmic determinants. 2. Fertilization creates dorsal-ventral axis. 3. Cell division. 4. Blastula created. 6. Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm created. by molecular signals along the Animal/Vegetal axis. 5. Gastrulation. 6. Spemann organizer creates anterior-posterior axis. 7. Notocord induces the Neural Plate. 8. Neurulation forms the Neural Tube. 9. Neural crest cells form the PNS. 10. Segmentation & Cephalization (anterior enlargement) 3 1) Cell Signaling 2) Discovery of the Organizer 3) How Could this Work? 4) The Answer 5) Blockers 6) Current View 7) Summary 4 2
3 Cell Signaling 5 Neuroinduction 6 3
4 Intracellular Signaling through a Kinase Cascade; Signal Amplification (Suppression) and Multiple Control Points 7 Endoderm and Mesoderm involute with gastrulation: Induction of the Neural Plate from Neuroectoderm, by the underlying, closely apposed Mesoderm. 8 4
5 Discovery of the Organizer 9 Hilde Mangold and Hans Spemann Key experiments performed in at the University of Freiburg, Germany. Hilde Mangold was a 24 year old graduate student when she performed these experiments. She died tragically in an accidental alcohol heater explosion. Hans Spemann was awarded the Nobel Prize in
6 Mangold Spemann Experiments (1924) 11 How Could this Work? 12 6
7 Explant Experiments with Animal Caps from Amphibian Blastula: Puzzling Results! 13 Isolating Inducing Factors that Promote Neuronal Differentiation; Sigma Catalog Experiments Result in Further Confusion (Many positives, including apparently non-biological factors!)? + Candidate Neuroinducing Factors (Intact) 14 7
8 Models for Neural Induction Model 1: Presumptive Neuroectoderm + Epidermal factor + Neuronal factor Epidermis Neurons Model 2: Presumptive Neuroectoderm + Neuronal factor Epidermis ( default ) Neurons Model 3: Presumptive Neuroectoderm + Epidermal factor Epidermis Neurons ( default ) 15 TGF-β Proteins Signal Through Heterodimeric Receptors and Smad Transcription Factors 16 8
9 The Answer 17 A Dominant-Negative Receptor Subunit Blocks Activation of the Signaling Pathway (Hemmati-Brivanlou and Melton, 1992) 18 9
10 Blocking TGF-β Signaling by a Dominant-Negative Receptor Causes Isolated Neuroectoderm to Become Neuronal (+Dominant-Negative Type II Receptor crna) Animal Cap (Intact) Animal Cap (Intact) TFG-β Signaling Blocked by expression of Dom-Neg Type II Receptor Subunit + TGF-β Signaling (Intact) + TGF-β Signaling 19 BMP-4 (TGF-β) Signaling Results in Neural Epidermal Induction TGF-β: Transforming Growth Factor - β BMP-4: Bone Morphogenic Protein
11 Models for Neural Induction Model 1: Presumptive Neuroectoderm + Epidermal factor + Neuronal factor Epidermis Neurons Model 2: Presumptive Neuroectoderm + Neuronal factor Epidermis ( default ) Neurons Model 3: Presumptive Neuroectoderm +BMP-4 Epidermis Neurons ( default ) 21 BMP-4 (Secreted by Neuroectodermal Cells) Inhibits Neuronal Fate and Promotes Epidermal Fate. Tissue Dissociation dilutes BMP-4 activity (Wilson and Hemmati-Brivanlou, 1995) Neural [BMP-4] (Endogenous BMP-4 Diluted) + BMP-4 Epidermal 22 11
12 Recombinant BMP-4 Promotes Epidermal Fate and Inhibits Neuronal Fate (Wilson and Hemmati-Brivanlou, 1995) 23 BMP-4 mrna is Expressed in Presumptive Ectoderm 24 12
13 Blockers 25 Are there native anatgonists of BMP-4? Secreted from underlying mesoderm? Yes chordin / noggin / follistatin. And they are enriched in the Spemann-Mangold Organizer! 26 13
14 27 Differential Substractive Screen yields Chordin, a BMP-4 antagonist (1994) 28 14
15 Functional Expression Cloning yields noggin, a BMP-4 anatagonist (1992) 29 Chordin/Noggin/Follistatin directly bind to and inactivate BMP
16 Structure of Noggin-BMP complex 31 Molecular Mechanism of Neuralization 32 16
17 Current View 33 TGF-β proteins signal through heterodimeric receptors and Smad transcription factors 34 17
18 Neural induction mechanisms are conserved: Ligand Receptor Antagonist Transcription Factor Vertebrates BMP-4 Type I Type II Type III noggin chordin follistatin Smad1 Smad2 Smad3 Smad4 Smad5 Drosophila decapentaplegic (dpp) punt thick veins (tkv), saxophone (sax) Short-gastrulation (sog) Mothers against decapentaplegic (MAD) Medea 35 BMP-4 is only one member of the large evolutionarily conserved TGF-β gene family, which mediates many different tissue inductive events. Relationships between members of the TGF-β super family. (After Hogan, 1996) 36 18
19 Summary 37 Neurogenesis: Inductive Mechanisms 1. Neuroectodermal cells choose either a neuronal or epidermal fate. 2. Interactions between mesoderm and neuroectoderm induce neuroectoderm to adopt the neural fate. 3. Induction is signaled by Bone Morphogenic Protein-4 (BMP-4), a protein made and secreted by neuroectodermal cells. 4. BMP-4 inhibits neuralization and promotes the epidermal fate in neighboring cells. 5. Mesodermal cells secrete proteins (Chordin, Noggin, Follistatin) which directly bind and antagonizes BMP-4 activity
20 Neurogenesis: Inductive Mechanisms 6. Neuroectodermal cells become neurons by suppression of BMP-4 activity by secreted antagonists from underlying mesodermal cells. 7. The default state of neuroectodermal cells is neuronal. 8. This mechanism is conserved between vertebrates and invertebrates. 9. BMP-4 is a member of the Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-β) family of signaling molecules. 10. Similar signaling events in the nervous system mediate changes in later development stages and in adult plasticity. 39 END 40 20
Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
Cell Type Nervous System I. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation. Human issues.
 7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
Current Model for how cells become neural. Double Inhibition Model for Neural fate. Neural Development. How do cells become neurons?
 Current Model for how cells becoe neural 1) Default state is neural 2) Local secretion of BMPs by epideris inhibits neural fate 3) Local secretion of noggin, chordin by dorsal lip or esoder inhibits BMP
Current Model for how cells becoe neural 1) Default state is neural 2) Local secretion of BMPs by epideris inhibits neural fate 3) Local secretion of noggin, chordin by dorsal lip or esoder inhibits BMP
Patterning the Embryo
 Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System. Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D.
 Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Inner ear development Nervous system development
 Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development.
 Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND
 Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior A1: NEURAL DEVELOPMENT USE THE INFO IN THE PRESENTATION TO COMPLETE A1 NOTES GUIDE INFORMATION TAKEN FROM: HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND WARD BIOLOGY
Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior A1: NEURAL DEVELOPMENT USE THE INFO IN THE PRESENTATION TO COMPLETE A1 NOTES GUIDE INFORMATION TAKEN FROM: HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND WARD BIOLOGY
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 5345 Development 138, 5345-5356 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.068908 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
RESEARCH ARTICLE 5345 Development 138, 5345-5356 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.068908 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Gilbert Ch. 12. The Emergence of the Ectoderm: Central Nervous System and Epidermis November 30, 2006
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Gilbert Ch. 12. The Emergence of the Ectoderm: Central Nervous System and Epidermis November 30, 2006 Establishing the Neural Cells - neural plate - portion of the dorsal
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Gilbert Ch. 12. The Emergence of the Ectoderm: Central Nervous System and Epidermis November 30, 2006 Establishing the Neural Cells - neural plate - portion of the dorsal
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
The Evolution and Development of the Gut. Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department
 The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors. Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation?
 Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation? Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line Condition
Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation? Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line Condition
Subject Index. Acetylcholine synthesis and storage in Pleurodeles embryo. Body pattern
 383 Subject Index Acetylcholine synthesis and storage in Pleurodeles embryo cultures: DUPRAT AND OTHERS 167 Actin genes in Xenopus and their developmental control: GORDON, MOHUN, BRENNAN & CASCIO 125 role
383 Subject Index Acetylcholine synthesis and storage in Pleurodeles embryo cultures: DUPRAT AND OTHERS 167 Actin genes in Xenopus and their developmental control: GORDON, MOHUN, BRENNAN & CASCIO 125 role
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION. Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling.
 EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
A. Incorrect! It s not correct. Synergism of cytokines refers to two or more cytokines acting together.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
Supporting Information
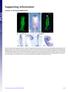 Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development
 Development 126, 2451-2460 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV2346 2451 Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development Massimiliano Andreazzoli 1,3, Gaia
Development 126, 2451-2460 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV2346 2451 Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development Massimiliano Andreazzoli 1,3, Gaia
Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β
 Manuscript EMBOR-2011-35178 Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β Anja Kietzmann, Yingqun Wang, Dominik Weber and Herbert Steinbeisser Corresponding author:
Manuscript EMBOR-2011-35178 Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β Anja Kietzmann, Yingqun Wang, Dominik Weber and Herbert Steinbeisser Corresponding author:
This is a published version of a paper published in PLoS genetics. Access to the published version may require subscription.
 Umeå University This is a published version of a paper published in PLoS genetics. Citation for the published paper: Holmqvist, P., Boija, A., Philip, P., Crona, F., Stenberg, P. et al. (2012) "Preferential
Umeå University This is a published version of a paper published in PLoS genetics. Citation for the published paper: Holmqvist, P., Boija, A., Philip, P., Crona, F., Stenberg, P. et al. (2012) "Preferential
Hepatogenesis I Liver development
 Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Fertilization. mitosis. N sperm pronucleus. fertilization. N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) 2N zygote nucleus
 Fertilization 2N pronucleus (suspended in meiotic metaphase) N polar body reduction division N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) mitosis 2N zygote nucleus N polar bodies (2): disintegrate membrane formation
Fertilization 2N pronucleus (suspended in meiotic metaphase) N polar body reduction division N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) mitosis 2N zygote nucleus N polar bodies (2): disintegrate membrane formation
Biology Developmental Biology Spring Quarter Midterm 1 Version A
 Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Spring Quarter 2013 Midterm 1 Version A 75 Total Points Open Book Choose 15 out the 20 questions to answer (5 pts each). Only the first 15 questions that are answered
Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Spring Quarter 2013 Midterm 1 Version A 75 Total Points Open Book Choose 15 out the 20 questions to answer (5 pts each). Only the first 15 questions that are answered
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS
 ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
ODONTOGENESIS- A HIGHLY COMPLEX CELL-CELL INTERACTION PROCESS AMBRISH KAUSHAL, MALA KAMBOJ Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital
4/18/2011. Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development
 Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla
 Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection of Activin into Xenopus Neurula Embryos
 Developmental Biology 221, 321 336 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9666, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection
Developmental Biology 221, 321 336 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9666, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection
Data Sheet. Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509
 Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Bio 3411 Midterm Review:
 Bio 3411 Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday October 26, 2011 1 2 THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed,
Bio 3411 Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday October 26, 2011 1 2 THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed,
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance
 Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Development, Stem Cells, and Cancer
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 16 Development, Stem Cells, and Cancer Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 16 Development, Stem Cells, and Cancer Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Role of oocyte-secreted factors in prevention of cumulus cell apoptosis and enhancement of oocyte developmental competence
 Role of oocyte-secreted factors in prevention of cumulus cell apoptosis and enhancement of oocyte developmental competence Tamer Hussein, MScMed Research Centre for Reproductive Health, Discipline of Obstetrics
Role of oocyte-secreted factors in prevention of cumulus cell apoptosis and enhancement of oocyte developmental competence Tamer Hussein, MScMed Research Centre for Reproductive Health, Discipline of Obstetrics
Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4493 4498, April 1997 Developmental Biology Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development (signal transduction
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4493 4498, April 1997 Developmental Biology Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development (signal transduction
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture. Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu
 Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
C. elegans Embryonic Development
 Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of November
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Week 14. Development of the Musculoskeletal System
 Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Differentiation of the Placode Ectoderm Neural Crest Derivatives
 Dr. Andrea D. Székely Differentiation of the Placode Ectoderm Neural Crest Derivatives Acknowledgements to Dr Károly Altdorfer Dr Nándor Nagy EARLY DEVELOPMENT The neural crest and craniofacial placodes
Dr. Andrea D. Székely Differentiation of the Placode Ectoderm Neural Crest Derivatives Acknowledgements to Dr Károly Altdorfer Dr Nándor Nagy EARLY DEVELOPMENT The neural crest and craniofacial placodes
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System
 Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Goals and Challenges of Communication. Communication and Signal Transduction. How Do Cells Communicate?
 Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem
 86 Review TRENDS in Cell Biology Vol.13 No.2 February 2003 Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem Pao-Tien Chuang 1 and Andrew P. McMahon 2 1 Cardiovascular Research
86 Review TRENDS in Cell Biology Vol.13 No.2 February 2003 Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem Pao-Tien Chuang 1 and Andrew P. McMahon 2 1 Cardiovascular Research
Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice. Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.
 Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.** Abstract Purpose: To investigate the effect of Bone morphogenetic
Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.** Abstract Purpose: To investigate the effect of Bone morphogenetic
Broca s Aphasia: Lesions in the left posterior frontal lobe. Can understand speech but have a disruption in expressing spontaneous speech and writing.
 9.09J/7.29J - Cellular Neurobiology, Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department of Biology Instructors: Professors William Quinn and Troy Littleton
9.09J/7.29J - Cellular Neurobiology, Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department of Biology Instructors: Professors William Quinn and Troy Littleton
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Solution Key EXAM 3 (4 / 29 / 13)
 Solution Key- 7.013 EXAM 3 (4 / 29 / 13) Question 1 (20 points) Diabetes occurs either due to a reduced insulin hormone production by the pancreatic β cells or the resistance of target cells to insulin.
Solution Key- 7.013 EXAM 3 (4 / 29 / 13) Question 1 (20 points) Diabetes occurs either due to a reduced insulin hormone production by the pancreatic β cells or the resistance of target cells to insulin.
Chapter 17: Functional Organization of the Endocrine System
 Chapter 17: Functional Organization of the Endocrine System I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System A. Terminology 1. What does the term endocrine imply? 2. Endocrine glands secrete 3. A hormone
Chapter 17: Functional Organization of the Endocrine System I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System A. Terminology 1. What does the term endocrine imply? 2. Endocrine glands secrete 3. A hormone
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma. Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD
 Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
WNT and BMP regulate roadblocks toward cardiomyocyte differentiation: lessons learned from embryos inform human stem cell differentiation
 Editorial Page 1 of 5 and BMP regulate roadblocks toward cardiomyocyte differentiation: lessons learned from embryos inform human stem cell differentiation Andrea Münsterberg 1, Stefan Hoppler 2 1 School
Editorial Page 1 of 5 and BMP regulate roadblocks toward cardiomyocyte differentiation: lessons learned from embryos inform human stem cell differentiation Andrea Münsterberg 1, Stefan Hoppler 2 1 School
Organogenesis of Heart, Kidney, Nervous System & Sense Organs. [ GLOSSARY ]
![Organogenesis of Heart, Kidney, Nervous System & Sense Organs. [ GLOSSARY ] Organogenesis of Heart, Kidney, Nervous System & Sense Organs. [ GLOSSARY ]](/thumbs/86/94287046.jpg) Organogenesis of Heart, Kidney, Nervous System & Sense Organs. [ GLOSSARY ] Subject : Zoology Course : 3rd Year, B.Sc. Undergraduate UGC Syllabus, Model - 1 Paper No. : Z-305B & Title : Developmental Biology
Organogenesis of Heart, Kidney, Nervous System & Sense Organs. [ GLOSSARY ] Subject : Zoology Course : 3rd Year, B.Sc. Undergraduate UGC Syllabus, Model - 1 Paper No. : Z-305B & Title : Developmental Biology
Laith Abu Shekha. Omar Sami. Ebaa Alzayadneh
 24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
Name: Date: Per: Due Monday March18. Study Guide for Animal Systems Test
 Name: Date: Per: Study Guide for Animal Systems Test Due Monday March18 1. In a transfusion of blood or organ transplant what should the recipient cells have? Why? 2. Describe how a phagocytic cell of
Name: Date: Per: Study Guide for Animal Systems Test Due Monday March18 1. In a transfusion of blood or organ transplant what should the recipient cells have? Why? 2. Describe how a phagocytic cell of
Evidence for a Role of Smad6 in Chick Cardiac Development
 Developmental Biology 215, 48 61 (1999) Article ID dbio.1999.9419, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Evidence for a Role of Smad6 in Chick Cardiac Development Miho Yamada,*,1 Pablo I. Szendro,
Developmental Biology 215, 48 61 (1999) Article ID dbio.1999.9419, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Evidence for a Role of Smad6 in Chick Cardiac Development Miho Yamada,*,1 Pablo I. Szendro,
MODULATION OF CELL SIGNALING BY TOMOREGULINS IN EMBRYOGENESIS AND CANCER PAUL WILLIAM HARMS
 MODULATION OF CELL SIGNALING BY TOMOREGULINS IN EMBRYOGENESIS AND CANCER by PAUL WILLIAM HARMS CHENBEI CHANG, COMMITTEE CHAIR STUART J. FRANK LOUIS B. JUSTEMENT FANG-TSYR LIN ROSA A. SERRA A DISSERTATION
MODULATION OF CELL SIGNALING BY TOMOREGULINS IN EMBRYOGENESIS AND CANCER by PAUL WILLIAM HARMS CHENBEI CHANG, COMMITTEE CHAIR STUART J. FRANK LOUIS B. JUSTEMENT FANG-TSYR LIN ROSA A. SERRA A DISSERTATION
WORKSHOP REPORTS: WEAK ELECTRIC FIELD AND THERMAL EFFECTS
 WORKSHOP REPORTS: WEAK ELECTRIC FIELD AND THERMAL EFFECTS Richard Saunders Radiation and Environmental Health World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland Weak ELF Electric Field Effects in the Body.
WORKSHOP REPORTS: WEAK ELECTRIC FIELD AND THERMAL EFFECTS Richard Saunders Radiation and Environmental Health World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland Weak ELF Electric Field Effects in the Body.
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03.
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03 http://seemikedraw.files.wordpress.com/2007/07/biology-final.jpg Walsby's Square Bacteria Images of cells from 12 different colonies on blood agar
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03 http://seemikedraw.files.wordpress.com/2007/07/biology-final.jpg Walsby's Square Bacteria Images of cells from 12 different colonies on blood agar
HORMONES (Biomedical Importance)
 hormones HORMONES (Biomedical Importance) Hormones are the chemical messengers of the body. They are defined as organic substances secreted into blood stream to control the metabolic and biological activities.
hormones HORMONES (Biomedical Importance) Hormones are the chemical messengers of the body. They are defined as organic substances secreted into blood stream to control the metabolic and biological activities.
PARSING THE PROSENCEPHALON
 PARSING THE PROSENCEPHALON Murielle Rallu, Joshua G. Corbin and Gord Fishell The forebrain, or prosencephalon, consists of the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon is the conduit for ascending
PARSING THE PROSENCEPHALON Murielle Rallu, Joshua G. Corbin and Gord Fishell The forebrain, or prosencephalon, consists of the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon is the conduit for ascending
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
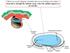 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Cell Communication and Cell Signaling
 Cell Communication and Cell Signaling Why is cell signaling important? Why is cell signaling important? Allows cells to communicate and coordinate functions/activities of the organism Usually involves
Cell Communication and Cell Signaling Why is cell signaling important? Why is cell signaling important? Allows cells to communicate and coordinate functions/activities of the organism Usually involves
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Genetic guidance, development and plasticity of the brain
 Genetic guidance, development and plasticity of the brain GDP1 Florent Meyniel CEA, Neurospin Learning objectives Know the main stages and mechanisms of the development of the nervous system and the human
Genetic guidance, development and plasticity of the brain GDP1 Florent Meyniel CEA, Neurospin Learning objectives Know the main stages and mechanisms of the development of the nervous system and the human
Chapter 11. Cell Communication. Signal Transduction Pathways
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication Signal Transduction Pathways Signal-Transduction Pathway Signal on a cell s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Local signaling (short distance) - Paracrine
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Signal Transduction Pathways Signal-Transduction Pathway Signal on a cell s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Local signaling (short distance) - Paracrine
Developmental Plasticity of CNS stem cells. Developmental Plasticity of CNS Stem Cells: Implications for Neurodevelopmental/Psychiatric Diseases
 Developmental Plasticity of CNS Stem Cells: Implications for Neurodevelopmental/Psychiatric Diseases 1 Abstract Interest in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diseases, including autism spectrum disorders,
Developmental Plasticity of CNS Stem Cells: Implications for Neurodevelopmental/Psychiatric Diseases 1 Abstract Interest in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diseases, including autism spectrum disorders,
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Gene Regulation. Bacteria. Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
 Development 130, 2225-2238 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00443 2225 Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
Development 130, 2225-2238 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00443 2225 Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November
 Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
TGFβ signaling positions the ciliary band and acts indirectly to pattern neurons in the sea urchin embryo
 TGFβ signaling positions the ciliary band and acts indirectly to pattern neurons in the sea urchin embryo Shunsuke Yaguchi 1,2,3, Junko Yaguchi 1,2,3, Robert C. Angerer 3, Lynne M. Angerer 3, Robert D.
TGFβ signaling positions the ciliary band and acts indirectly to pattern neurons in the sea urchin embryo Shunsuke Yaguchi 1,2,3, Junko Yaguchi 1,2,3, Robert C. Angerer 3, Lynne M. Angerer 3, Robert D.
Members of the transforming growth factor- (TGF- ) family
 Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase Ying Zhang*, Chenbei Chang, Daniel J. Gehling*, Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou, and Rik Derynck *Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular
Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase Ying Zhang*, Chenbei Chang, Daniel J. Gehling*, Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou, and Rik Derynck *Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular
قابليت القاي توليد بافت عصبي توسط عصاره مغز گوساله جنيني در عضالت موش صحرايي
 ارزيا يب قابليت القاي توليد بافت عصبي توسط عصاره مغز گوساله جنيني در عضالت موش صحرايي امين *1 بيغم صادق 4 3 2 احمد عريان رحمتاهلل فتاحيان دهكردي هاجر صادقينژاد چكيده دريافت: پذيرش: )GFAP(( و )Neuron Specific
ارزيا يب قابليت القاي توليد بافت عصبي توسط عصاره مغز گوساله جنيني در عضالت موش صحرايي امين *1 بيغم صادق 4 3 2 احمد عريان رحمتاهلل فتاحيان دهكردي هاجر صادقينژاد چكيده دريافت: پذيرش: )GFAP(( و )Neuron Specific
Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus mesoderm induction
 Development 128, 35-44 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2656 35 Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus
Development 128, 35-44 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2656 35 Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus
a) They are the most common cause of pediatric kidney failure. b) They are always symptomatic. c) They can be asymmetric.
 Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
LABORATÓRIUMI GYAKORLAT SILLABUSZ SYLLABUS OF A PRACTICAL DEMOSTRATION. financed by the program
 TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
Lecture VIII. The Spinal Cord, Reflexes and Brain Pathways!
 Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
Bio 3411 Midterm Review:
 Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday 1( 2( THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 9! Mid-line (sagittal)
Midterm Review: Structure/Development/Systems/ Plastics/Talents/Diseases/Genes Structure General Overview Wednesday 1( 2( THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 8! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed, p. 9! Mid-line (sagittal)
