HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF MENINGIOMA IN CIVIL
|
|
|
- Wilfred Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
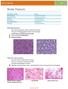
1 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 03 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 23/12/12 Revised on: 14/01/13 Accepted on: 03/02/13 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF MENINGIOMA IN CIVIL HOSPITAL, AHMEDABAD Smita Shah, R. N. Gonsai, Rinku Makwana Department of Pathology, B. J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, India of Corresponding Author: ABSTRACT Objective: This study was done to determine the clinical and histological pattern of intracranial meningioma, to determine the sociodemographic characteristic and clinical presentation and correlate this to the clinical patterns of intracranial meningioma, to find out the anatomical location of meningioma and to document the WHO histological grade of meningioma. Materials and Methods: We have studied 51 cases of meningioma. Meningioma was diagnosed primarily by contrast enhanced CT Scan and Magnetic Resonence Imaging (MRI) of brain. This was confirmed by histopathological examination. Histopatholgical results were examined according to age and sex distribution, anatomical location of tumor, histological type and WHO grading of tumor. Correlation of clinical features and radiological findings were made with histpathological results. Results and conclusion: Most of the sufferer was female 34 (67%). The commonest age group was years. The commonest site of tumor was convexity of brain 26 (60%). The commonest histopathological type was meningotheliomatous meningioma 20 (39%). The 92% of the meningioma was WHO GRADE I tumor. Keywords: meningioma, WHO grading of meningioma, prognosis of meningioma, INTRODUCTION The tumor originating from the meninges was termed as meningioma by Cushing in Meningiomas originate from the arachanoidal cap cell, a meningothelial cell in the arachnoidal membrane. They generally arise were arachnoidal villi are many 2. The arachnoid cap cells are most prevalent near collections of arachnoid villi at the dural venous sinuses and their large tributaries. Meningiomas may arise anywhere the cap cells are located 2. Meningiomas are account for 15% of all intracranial tumors. They commonly occur in the fourth to sixth decades of life, with a mean age of 45 years at diagnosis. Females have meningiomas more often than males; ratio is 2:1 for intracranial and 4:1 for spinal meningiomas 3. The etiology of meningioma is unknown. Cases exist in which the tumor has arisen under a fracture, from an area of scared dura, or around a retained foreign body. Low and high dose radiation has been implicated in meningioma formation especially during childhood. Neurofibromatosis 1 and 2 genetic diseases inherited in autosomal dominant fashion may be associated with meningioma 4. 90% of meningiomas are located intracranialy and of these 90% are supratentorial. According to site meningiomas are located at parasaggital, convexity, sphenoid ridge, suprasellar, posterior fossa, olfactory groove, middle fossa, tentorial, peritorcular, lateral ventricle, foramen magnum, spinal, orbit or optic nerve sheath, few located at ectopic site 5. At spinal level meningioma clearly favors the thoracic region. Cervical being uncommon and lumber is rare. Also recognized are epidural, calvarial and intrapetrous as well as Page 76
2 variant located entirely outside the craniospinal confines 6. Although most meningiomas are benign, they have a surprisingly broad spectrum of clinical characteristics, and histologically distinct subsets are associated with high risk of recurrence, even after seemingly complete resection. In rare instances, meningiomas are malignant. The WHO classification aims to better predict the divergent clinical characteristics of meningiomas with a histological grading system based on statistically significant clinicopathological correlations. Meningiomas are classified as benign, atypical, or malignant. Benign meningiomas are not encapsulated; they grow invaginating, but demarcated, from the brain. They grow with finger-like projections, and penetrate surrounding mesenchymal tissue, including bone. They may produce both an osteoblastic and a lytic reaction 2. Meningiomas show positive immunostain with vimentin, desmoplakin, and epithelial membrane antigen. They have a grade 1 biological behaviour. Meningiomas grow in 3 primary histologic patterns: (1) meningothelial, (2) fibroblastic, or (3) transitional, a combination of meningothelial and fibrous. Meningothelial meningiomas consist of lobules of cells with oval pale nuclei, with chromatin marginated around the nucleus. The cell has an ill-defined cellular membrane, and nuclear and cytoplasmic invaginations often produce pseudoinclusions 2. Fibroblastic meningiomas have parallel interlacing bundles of spindle-shaped cells with abundant collagen and reticulin between cells. Transitional meningiomas have a mixed pattern of both meningothelial and fibroblastic features. They more often contain whorls or psammoma bodies. Benign meningiomas of WHO grade I can invade the dura, dural sinuses, skull, and even extracranial compartments, such as orbit, soft tissue, and skin. Although these types of invasion make it more difficult to resect the tumour, they are not considered as atypical or malignant. By contrast, brain invasion is associated with recurrence and mortality rates similar to atypical meningiomas in general, even if the tumour seems completely benign otherwise 8. WHO grade II meningiomas include atypical, chordoid, and clear cell meningiomas 9. Both grade II and III WHO classifications of meningiomas require brain invasion as a criterion 10. WHO grade II meningiomas make up 5% to 7% of all meningiomas 11. Some pathologists feel that a meningioma should be called malignant only when there is frank brain invasion, although brain invasion has been documented in benign, atypical, and anaplastic meningiomas and felt to be an additional criteria for malignant classification 8. Atypical meningiomas are diagnosed based on increased mitotic index of equal to or greater than 4 mitoses per 10 highpower fields or 3 or more of the following features: increased cellularity, small cells with high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, prominent nucleoli, uninterrupted patternless or sheet-like growth, and foci of "spontaneous" or "geographic necrosis" 10. Clear-cell and chordoid variants of meningioma are associated with higher recurrence rates even without the above criteria 12,13. Thus, these meningiomas are graded as WHO grade II by definition. Clear-cell meningiomas make up only 0.2% of all meningiomas. This type usually behaves aggressively and can metastasize to the CSF. Clear-cell meningiomas often occur in patients of younger age and occur more often in the spinal and cerebellar pontine region. Recurrence rate of clear-cell meningiomas is 46% to 80% 14. Clear-cell meningioma is composed of sheets of polygonal cells with clear, glycogen-rich cytoplasm positive for periodic acid Schiff, and dense perivascular and interstitial collagenisation. Chordoid meningiomas are histologically similar to chordoma, with cords of small epithelioid tumour cells that contain eosinophilic or vacuolated (i.e., resembling physaliferous cells) cytoplasm embedded in a basophilic, mucin-rich Page 77
3 matrix. Clear-cell meningiomas are most common in the spinal cord and posterior fossa, whereas chordoid meningiomas are typically supratentorial. WHO grade III meningiomas make up 1.0% to 2.8% of all meningiomas. These include anaplastic, rhabdoid, and papillary types 9. Malignant meningiomas have further increase in mitoses and cellularity with conspicuous necrosis 15. Anaplastic or malignant meningiomas by definition must have equal to or greater than 20 mitoses per 10 high-power field 10. Atypical and malignant meningiomas have a much higher recurrence rate after resection than do benign meningiomas. Recurrence rates were 6.9% for benign meningiomas, 34.6% for atypical meningiomas, and 72.7% for malignant meningiomas 8. Papillary and rhabdoid meningiomas are rare variants and have an aggressive clinical course and higher rates of recurrence, metastases, and mortality 10. Papillary meningiomas generally occur in the pediatric population. 9 Their cell processes terminate in papilla on blood vessels, with tapering of their processes to form pseudorosettes. Rhabdoid meningioma is a new pathologic variant of malignant meningioma with peritumoral edema, bone involvement, and significant cystic components on Magnetic Resonence Imaging (MRI) study of brain 16. The prognosis for meningiomas following gross total resection depends on the histology. In a single series of 1799 meningioma specimens from 1582 patients followed for an estimated average of 13 years, 93.1% of benign meningiomas, 65.4% of atypical meningiomas, and 27.3% of malignant meningiomas were cured by surgery 8. Recent research has investigated possible prognostic factors in atypical and malignant meningiomas specifically. In an analysis of 76 atypical meningiomas and 10 malignant meningiomas, high mitotic count, brain invasion, and parasagittal-falcine location were significantly associated with decreased recurrence-free survival 17. Also, Ki-67 index greater than 4% was also associated with decreased time to recurrence. These appear to be important pathologic indicators of aggressiveness of these tumor types. A recent study found that anatomic location of tumor also to have prognostic significance 18. They reviewed 378 patients with meningioma, looking for causes for high-grade pathology. They found that nonskull-base meningiomas, prior surgery, and male sex all increased risk of grade II or III pathology, which extrapolates to poorer prognosis and increased likelihood of recurrence. MATERIAL AND METHOD This was descriptive study. This study was carried out at the histopathology laboratory, Department of Pathology, B. J. medical college Ahmedabad, from January 2010 to August We have studied 51 cases. Histological subtype and WHO grading for all meningiomas were carried out. The parameters like patient s age, gender, location of tumor, microscopic appearance of tumor were studied. RESULTS The present study was conducted at pathology department of B. J. Medical College and Civil Hospital Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. A total of 51 cases diagnosed as meningioma by histopathological examination were studied. Detailed clinical history and radiological findings were assessed in all 51 cases. In our study meningiomas were most common in the age group of years (59%), followed by in the age group of years (21%). Meningiomas were least common in the age group of <20 years (06%). Out of 51 cases 34 (67%) were female and 17 (33%) were male. In our study most common clinical feature was headache, seen in 38 (75%) Page 78
4 of cases followed by vomiting, seen in 9 (17%) of cases. In our study most common location of tumor was convexity of brain in 26 (51%) of cases. 46 (90.2%) cases were in intracranial location. In our study most common histological subtype was meningotheliomatous meningioma 19 case (37%). And most of the tumor was WHO GRADE I (47 case 92%). Whereas WHO GRADE II and WHO GRADE III tumor comprise respectively 8% and 0% of total cases. DISCUSSION: The present study was conducted in the department of Pathology, B. J. Medical College and Civil Hospital Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. In present study meningiomas were most common in the age group of years 59%. Haradhan et al studied 25 cases of meningiomas, with most tumor were in the age group of years 60%. Among the 51 patients, in our study 34 (67%) were female and 17 (33%) were male, with male to female ratio being 1:2. Akyildiz EU et al were studied 245 cases of meningioma, 74 (30.2%) were male and 171(69.8%) were female, with male to female ratio being 1:2.3. Joseph wanjeri et al a study of 78 cases of meningioma, females 69.2% were more affected than males 30.2% with male to female ratio being 1:2.3. In all of these studies meningiomas were most common in female, with male to female ratio nearly 1:2. Among the 51 patients, in our study most common location of tumor was intracranial 46(90.2%) cases, with tumor located most commonly at convexity of brain 26 (51%) of cases. Akyildiz EU et al 2010 study 20, intracranial location of tumor was found in 96% of cases. In our study most common clinical feature was headache (75%) followed by vomiting (17%). Haradhan deb nath et al study of 25 cases of meningioma, most common clinical feature was headache (72%) of cases followed by vomiting (60%) of cases. In our study most common histological type of tumor was meningothelial meningioma 37%, psammomatous meningioma 19% and fibroblastic meningioma 16%cases. Joseph wanjeri et al , The commonest cellular subtype were fibroblastic 25.4%, transitional (mixed) 25.4% and meningothelial (syncitial) 22.5%. Haradhan deb nath et al study, most common histological subtype was meningothelial meningioma 32% transitional meningioma 20% and fibroblastic meningioma 20% cases. In all three studies meningothelial meningioma and fibroblastic meningioma were common histological subtype. In our study, WHO GRADE I tumour were 92%, WHO GRADE II tumour were 08% and WHO GRADE III tumour were 0%. Joseph wanjeri et al study found that, According to WHO classification, the benign form (grade I) was the commonest at 94.7%. Grade II (atypical) and grade III (malignant) represented 4% and 1.3% respectively. Akyildiz EU et al 2010 study 20, WHO GRADE I tumour were 82%, WHO GRADE II tumour were 6%. Our result is consistent with above studies, in all these studies most common WHO GRADE were GRADE I. In our study we found two cases of clear cell meningioma. Both are in age group <20years and one is located in spinal region and other at CP angle, which are common locations for clear cell meningioma. In our study we found 4 cases of WHO GRADE II tumour. Two of them were clear cell meningioma, as clear cell meningioma entity itself put tumour into GRADE II. And out of other two, one was meningothelial meningioma and one was fibroblastic meningioma as both of them show increased mitotic activity, 4 mitoses per high power field. CONCLUSION Meningiomas occurred more frequently in females than in males with a female to male ratio Page 79
5 of 2:1. Adults were more affected than their elderly counterparts. The mean age was Majority of Patients presented with complain of headache of longer duration and vomiting. Most meningiomas were at intracranial location. Most intracranial meningiomas occur in the supratentorial compartment. Majority of meningioma are histologically benign with WHO GRADE I and hence curable by surgical resection. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. REFERENCES 1. Cushing H. The meningiomas (dural endotheliomas): their source, and favoured seats of origin. Brain 1922;45: Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW. Histological typing of tumours of the central nervous system. 2nd ed. World Health Organization. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1993: Das A. Tang WY. Smith Dr. meningiomas in Singapore, demographic and biological characteristics. J Neurooncol , Al-Mefty O, Kersh JE, Routh A, Smith RR. The long term side effects of radiation for benign brain tumors in adult. J Neurosurg 1990; 73; Christensen HC, Kosteljanetz M, Johanses C. Incidence of gliomas and meningiomas in Denmark to Neurosurgery 2003, 52: Lang FF, Macdonald OK, Fuller GN, DeMonte F. Primary extradural meningiomas. A report on nine cases and review of the literature from the era of computerized tomography scanning. J Neurosurg 2000,93: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK, International Agency for research on cancer, Pathology and genetics of tumors of nervous systems, Lyons: IARC Press Perry A, Scheithauer BW, Staff ord SL, Lohse CM, Wollan PC. Malignancy in meningiomas: a clinicopathologic study of 116 patients, with grading implications. Cancer 1999; 85: Bollag RJ, Vender JR, Sharma S. Anaplastic meningioma: Progression from atypical and chordoid morphotype with morphologic spectral variation at recurrence. Neuropathology 2010;30(3): Campbell BA, Jhamb A, Maguire JA, Toyota B, Ma R. Meningiomas in 2009: controversies and future challenges. Am J Clin Oncol 2009;32(1): McGovern SL, Aldape KD, Munsell MF, Mahajan A, Demonte F, Woo SY. A comparison of World Health Organization tumor grades at recurrence in patients with non-skull base and skull base meningiomas. J Neurosurg 2010;112(5): Zorludemir S, Scheithauer BW, Hirose T, Van Houten C, Miller G, Meyer FB. Clear cell meningioma. A clinicopathologic study of a potentially aggressive variant of meningioma. Am J Surg Pathol 1995; 19: Couce ME, Aker FV, Scheithauer BW. Chordoid meningioma: a clinicopathologic study of 42 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24: Tong-tong W, Li Juan B, Zhi L, Yang L, Bo- Ning L, Quan H. Clear cell meningioma with anaplastic features: case report and review of literature. Pathol Res Pract 2010;206(5): Maier H, Ofner D, Hittmair A, Kitz K, Budka H. Classic, atypical, and anaplastic Page 80
6 meningioma: three histopathological subtypes of clinical relevance. J Neurosurg 1992;77: Kim EY, Weon YC, Kim ST, et al. Rhabdoid meningioma: clinical features and MR imaging findings in 15 patients. AJNR 2007;28(8): Vranic A, Popovic M, Cor A, Prestor B, Pizem J. Mitotic count, brain invasion, and location are independent predictors of recurrence-free survival in primary atypical and malignant meningiomas: a study of 86 patients. Neurosurgery 2010;67(4): Kane AJ, Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, et al. Anatomic location is a risk factor for atypical and malignant meningiomas. Cancer 2011;117(6): Haradhan Deb Nath, MD mainuddin, MD kmal Uddin, Ehsam mahmood et al, surgical outcome of supratentorial meningioma. A study of 25 cases. JCMCTA 2009; Alkyildiz EU, Oz B, Comunoglu N, Aki H et al. The relationship between histomorphological characteristics and ki67 proliferation index in meningioma Bratisl Lek listy 2010;111(9) Joseph. Wanjeri et al. Histology and clinical pattern of meningiomas at the Kenyatta National Hospital Nairobi, Kenya. A thesis submitted for the award of the degree of master of medicine in neurosurgery, University of Nairobi, Table 1: WHO criteria for meningioma grading 7 WHO grade Histological subtype histological features I II (atypical) any of three criteria III (anaplastic) either of one criteria Meningothelial, fibroblastic, 1) Lacks criteria of atypical and anaplastic meningioma transitional, angiomatous, microcystic, secretory, lymphoplasmacytic, metaplastic, psammomatous Choroid, clear cells 1) Mitotic index 4mitoses/ten HPF 2)Atleat three of five parameters: -Increased cellularity -High nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio (small cells) -Prominent nucleoli -uninterrupted pattern less or sheet like growth -foci of spontaneous necrosis 3)Brain invasion Papillary, rhabdoid 1) Mitotic index 20 mitoses/10 HPF 2) Anaplasia (sarcoma, carcinoma or melanoma like histology) Table 2: Distribution of the patient by age: Age Years Number Percentage < % % % > % Total % Page 81
7 Table 3: Distribution of patient by site of tumor Site Number Percentage Convexity of brain 26 51% CP angle 08 16% Sphenoidal sinus 04 07% Ventricles 03 06% Sellar region 01 02% Cerebellum 01 02% Spinal 04 08% Other 01 02% Table 4: Distribution of patient by Histological subtype and grade of tumor Histological subtype Number Percentage Meningothelial 19 37% Fibroblastic 08 16% Transitional 06 10% Microcystic 04 08% Psammomatous 10 19% Secretory 01 02% Clear cell 02 04% Total % Page 82
Histomorphological Spectrum of Meningioma with Variants and Grading
 Available online at www.jsciachv.com JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC ACHIEVEMENTS VOLUME 2, ISSUE 5, MAY 2017, PAGE: 18 22 RESEARCH ARTICLE Histomorphological Spectrum of Meningioma with Variants and Grading Abu
Available online at www.jsciachv.com JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC ACHIEVEMENTS VOLUME 2, ISSUE 5, MAY 2017, PAGE: 18 22 RESEARCH ARTICLE Histomorphological Spectrum of Meningioma with Variants and Grading Abu
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
WHO [2007] GRADING OF MENINGIOMA
![WHO [2007] GRADING OF MENINGIOMA WHO [2007] GRADING OF MENINGIOMA](/thumbs/89/100760056.jpg) SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-3; Issue-1 (Jan, 2017); p-25-29 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Original Research Article Histopathological analysis of meningiomas-
SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-3; Issue-1 (Jan, 2017); p-25-29 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Original Research Article Histopathological analysis of meningiomas-
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
Meningiomas account for approximately 4% of all
 Intraorbital Meningiomas A Pathologic Review Using Current World Health Organization Criteria Deepali Jain, MD; Katayoon B. Ebrahimi, MD; Neil R. Miller, MD; Charles G. Eberhart, MD, PhD N Context. Meningiomas
Intraorbital Meningiomas A Pathologic Review Using Current World Health Organization Criteria Deepali Jain, MD; Katayoon B. Ebrahimi, MD; Neil R. Miller, MD; Charles G. Eberhart, MD, PhD N Context. Meningiomas
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Case Report Xanthomatous meningioma: a case report with review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(10):2242-2246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1308033 Case Report Xanthomatous meningioma: a case report with review of the literature Mitsuaki Ishida 1, Tadateru Fukami
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(10):2242-2246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1308033 Case Report Xanthomatous meningioma: a case report with review of the literature Mitsuaki Ishida 1, Tadateru Fukami
Meningiomas represent between 13 and
 RESEARCH EXPERIMENTAL (LABORATORY) Mitotic Count, Brain Invasion, and Location Are Independent Predictors of Recurrence-Free Survival in Primary Atypical and Malignant Meningiomas: A Study of 86 Patients
RESEARCH EXPERIMENTAL (LABORATORY) Mitotic Count, Brain Invasion, and Location Are Independent Predictors of Recurrence-Free Survival in Primary Atypical and Malignant Meningiomas: A Study of 86 Patients
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics
 Anatomic Pathology / CLAUDIN-1 IN MENINGIOMAS Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics Hejin P. Hahn, MD, PhD, Elizabeth A. Bundock, MD, PhD, and
Anatomic Pathology / CLAUDIN-1 IN MENINGIOMAS Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics Hejin P. Hahn, MD, PhD, Elizabeth A. Bundock, MD, PhD, and
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad
 Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
MENINGIOMA: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION. Nasrin Samadi & Seyed Ali Ahmadi
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 4, No., January 7 (46-5) ORIGINAL ARTICLE Department of Pathology, Sina Hospital, Hassan Abad Square, Tehran 64, Iran As yet no unifying grading system for meningiomas
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 4, No., January 7 (46-5) ORIGINAL ARTICLE Department of Pathology, Sina Hospital, Hassan Abad Square, Tehran 64, Iran As yet no unifying grading system for meningiomas
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
A Study of Meningiomas in Tertiary Care Center in South India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 07-12 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Meningiomas in Tertiary
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 07-12 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Meningiomas in Tertiary
Rhabdoid Meningioma In A Background Of Atypical Meningioma With Lipomatous Metaplasia: Case Report And Review Of Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Rhabdoid Meningioma In A Background Of Atypical Meningioma With Lipomatous Metaplasia: Case Report And Review Of Literature S Shuja, T Lucey,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 1 Rhabdoid Meningioma In A Background Of Atypical Meningioma With Lipomatous Metaplasia: Case Report And Review Of Literature S Shuja, T Lucey,
Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 131962, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/131962 Case Report Multiple Intracranial Meningiomas: A Review of the Literature and a Case Report F. Koech,
OMICS PUBLISHING GROUP/Clinical Meningioma with remarkable multiple rosette formation: A diagnostically difficult case
 OMICS PUBLISHING GROUP/Clinical Meningioma with remarkable multiple rosette formation: A diagnostically difficult case --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Short Title: Article Type: Section/Category:
OMICS PUBLISHING GROUP/Clinical Meningioma with remarkable multiple rosette formation: A diagnostically difficult case --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Short Title: Article Type: Section/Category:
Anna Maria Buccoliero Department of Biomedicine, Careggi Hospital Florence
 PEDIATRIC RHABDOID MENINGIOMA Anna Maria Buccoliero Department of Biomedicine, Careggi Hospital Florence CLINICAL HISTORY A 3-year-old boy, with a recent history of seizures, was admitted to the Neurosurgery
PEDIATRIC RHABDOID MENINGIOMA Anna Maria Buccoliero Department of Biomedicine, Careggi Hospital Florence CLINICAL HISTORY A 3-year-old boy, with a recent history of seizures, was admitted to the Neurosurgery
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report Oguz Baran, Sima Sayyahmeli, Taner Tanriverdi, Pamir Erdincler TURKEY DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0027
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rapid recurrence of a malignant meningioma: case report Oguz Baran, Sima Sayyahmeli, Taner Tanriverdi, Pamir Erdincler TURKEY DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0027
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology
 Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology If the brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn t Emerson Pugh What is your greatest difficulty in neuropathology?
Five Most Common Problems in Surgical Neuropathology If the brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn t Emerson Pugh What is your greatest difficulty in neuropathology?
A Clinicopathological Study of Meningioma with Special Reference on Variants and Grading in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Research Article A Clinicopathological Study of Meningioma with Special Reference on Variants and Grading in a Tertiary Care Centre Arpita Jindal 1, Shweta Choudhary 2* 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article A Clinicopathological Study of Meningioma with Special Reference on Variants and Grading in a Tertiary Care Centre Arpita Jindal 1, Shweta Choudhary 2* 1 Associate Professor,
MENINGIOMA: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION. Nasrin Samadi & Seyed Ali Ahmadi
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 14, No. 1, January 2007 (46-52) ORIGINAL ARTICLE MENINGIOMA: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Nasrin Samadi & Seyed Ali Ahmadi Department of Pathology, Sina
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 14, No. 1, January 2007 (46-52) ORIGINAL ARTICLE MENINGIOMA: A CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Nasrin Samadi & Seyed Ali Ahmadi Department of Pathology, Sina
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Meningioma tumor. Meningiomas are named according to their location (Fig. 1) and cause various symptoms: > 1
 Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT
 IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Meningiomas are the second most common primary intracranial
 Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas: is differential diagnosis possible?
 Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE
 THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE Mark R. Wick, M.D. University of Virginia Medical Center Charlottesville, VA CARCINOMA OF THE THYMUS General Clinical Features No apparent gender predilection Age range of 35-75
THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE Mark R. Wick, M.D. University of Virginia Medical Center Charlottesville, VA CARCINOMA OF THE THYMUS General Clinical Features No apparent gender predilection Age range of 35-75
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Advances In Orbital Neuropathology
 Advances In Orbital Neuropathology Charles G. Eberhart, MD PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, Ophthalmology and Oncology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Overview Non-neoplastic lesions Microphthalmos/pseudoglioma
Advances In Orbital Neuropathology Charles G. Eberhart, MD PhD Associate Professor of Pathology, Ophthalmology and Oncology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Overview Non-neoplastic lesions Microphthalmos/pseudoglioma
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Part 1. Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013
 Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
AGGRESSIVE VARIANTS OF PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS
 AGGRESSIVE VARIANTS OF PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA Clinical Any age Microscopic to large Female: Male= 2-4:1 Radiation history Lymph nodes Prognosis
AGGRESSIVE VARIANTS OF PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA Clinical Any age Microscopic to large Female: Male= 2-4:1 Radiation history Lymph nodes Prognosis
Spinal tumour: primary cervical extradural meningioma at an unusual location
 Case Report Spinal tumour: primary cervical extradural meningioma at an unusual location Ishita Pant 1, Vinod Kumar Singh Gautam 2, Rima Kumari 3, Sujata Chaturvedi 1 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department
Case Report Spinal tumour: primary cervical extradural meningioma at an unusual location Ishita Pant 1, Vinod Kumar Singh Gautam 2, Rima Kumari 3, Sujata Chaturvedi 1 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Department
Rapid Regrowth of Intracranial Clear Cell Meningioma After Craniotomy and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 44, 321 325, 2004 Rapid Regrowth of Intracranial Clear Cell Meningioma After Craniotomy and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Case Report Mitsunobu IDE, Masaaki YAMAMOTO, Shinji HAGIWARA,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 44, 321 325, 2004 Rapid Regrowth of Intracranial Clear Cell Meningioma After Craniotomy and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Case Report Mitsunobu IDE, Masaaki YAMAMOTO, Shinji HAGIWARA,
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a
 G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
Case Report A case report on intermediate-grade malignant meningeal melanocytoma with elevated cell proliferation index
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):11698-11703 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012900 Case Report A case report on intermediate-grade malignant meningeal melanocytoma with elevated cell proliferation
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):11698-11703 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012900 Case Report A case report on intermediate-grade malignant meningeal melanocytoma with elevated cell proliferation
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3
 SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
Rare case of multiple meningiomas in nonneurofibromatosis
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rare case of multiple meningiomas in nonneurofibromatosis patient at unusual locations Vikrant Setia, Deepashu Sachdeva, Shrinivas Odugoudar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 2 2017 April-June Article Rare case of multiple meningiomas in nonneurofibromatosis patient at unusual locations Vikrant Setia, Deepashu Sachdeva, Shrinivas Odugoudar,
STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms
 Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas: Report of five cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas: Report of five cases P Srilatha, V Manna, P Kanthilatha Citation P Srilatha, V Manna, P Kanthilatha..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas: Report of five cases P Srilatha, V Manna, P Kanthilatha Citation P Srilatha, V Manna, P Kanthilatha..
Clinical and radiological features related to the growth potential of meningioma
 Neurosurg Rev (2006) 29:293 297 DOI 10.1007/s10143-006-0039-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and radiological features related to the growth potential of meningioma Hidetoshi Kasuya & Osami Kubo & Masahiko
Neurosurg Rev (2006) 29:293 297 DOI 10.1007/s10143-006-0039-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and radiological features related to the growth potential of meningioma Hidetoshi Kasuya & Osami Kubo & Masahiko
Postoperative LINAC-Based Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Grade I Intracranial Meningioma in Subtype Classification
 Postoperative LINAC-Based Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Grade I Intracranial Meningioma in Subtype Classification Peerapong Lueangapapong MD*, Mantana Dhanachai MD**, Ake Hansasuta MD* * Division of Neurosurgery,
Postoperative LINAC-Based Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Grade I Intracranial Meningioma in Subtype Classification Peerapong Lueangapapong MD*, Mantana Dhanachai MD**, Ake Hansasuta MD* * Division of Neurosurgery,
Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors
 Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are
Multiple Primary and Histology Site Specific Coding Rules Benign and Borderline Intracranial and CNS Tumors 1 Prerequisites 2 Completion of Multiple Primary and Histology General Coding Rules 3 There are
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
CHONDROID CHORDOMA OF NASAL SEPTUM: A CASE REPORT Gayattre Kailas 1, Muniraju M 2, Archana Mathri 3
 CHONDROID CHORDOMA OF NASAL SEPTUM: A Gayattre Kailas 1, Muniraju M 2, Archana Mathri 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Gayattre Kailas, Muniraju M, Archana Mathri. Chondroid Chordoma of Nasal Septum: A Case
CHONDROID CHORDOMA OF NASAL SEPTUM: A Gayattre Kailas 1, Muniraju M 2, Archana Mathri 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Gayattre Kailas, Muniraju M, Archana Mathri. Chondroid Chordoma of Nasal Septum: A Case
Atypical and anaplastic meningiomas
 REVIEW DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF ATYPICAL AND ANAPLASTIC MENINGIOMAS: A REVIEW Ashok Modha, M.D. Neurosurgery Service, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and the Department of Neurological Surgery,
REVIEW DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF ATYPICAL AND ANAPLASTIC MENINGIOMAS: A REVIEW Ashok Modha, M.D. Neurosurgery Service, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and the Department of Neurological Surgery,
Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of M Sharma, V Velho, P Ghodgaonkar, D Palande
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Symtomatic Subependymoma Of The Lateral Ventricle: A Rare Entity A Case report and review of M Sharma, V Velho, P Ghodgaonkar, D Palande
NIFTP: Histopathology of a Cytological Monkey Wrench. B. Wehrli
 NIFTP: Histopathology of a Cytological Monkey Wrench B. Wehrli Non-Invasive Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Before 2016 Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like
NIFTP: Histopathology of a Cytological Monkey Wrench B. Wehrli Non-Invasive Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Before 2016 Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS
 0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a retrospective study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.7 March. (2018), PP 47-64 www.iosrjournals.org MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.7 March. (2018), PP 47-64 www.iosrjournals.org MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
04/09/2018. Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances
 Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory
Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Thyroid Nodules: Understanding FNA Cytology (The Bethesda System for Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology) Shamlal Mangray, MB, BS
 Thyroid Nodules: Understanding FNA Cytology (The Bethesda System for Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology) Shamlal Mangray, MB, BS Attending Pathologist Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI DISCLOSURE:
Thyroid Nodules: Understanding FNA Cytology (The Bethesda System for Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology) Shamlal Mangray, MB, BS Attending Pathologist Rhode Island Hospital, Providence, RI DISCLOSURE:
Chordoid Meningioma in a Pediatric Patient with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2014; 48: 302-306 BRIEF CASE REPORT Chordoid Meningioma in a Pediatric Patient with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Jiwon Lee Hee Joon Yu Jeehun Lee Ji Hye Kim 1 Hyung Jin Shin
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2014; 48: 302-306 BRIEF CASE REPORT Chordoid Meningioma in a Pediatric Patient with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Jiwon Lee Hee Joon Yu Jeehun Lee Ji Hye Kim 1 Hyung Jin Shin
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology. Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD
 Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
As with other brain tumors, patients with meningiomas
 124 It s Not Your Run of the Mill Meningioma: Characteristics Differentiating Low-Grade From High-Grade Meningeal Tumors Eileen Bohan, Deanna Glass-Macenka ABSTRACT Approximately 30% of primary brain tumors
124 It s Not Your Run of the Mill Meningioma: Characteristics Differentiating Low-Grade From High-Grade Meningeal Tumors Eileen Bohan, Deanna Glass-Macenka ABSTRACT Approximately 30% of primary brain tumors
CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall
 Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
Malaysian J Pathol 2015; 37(3) : 281 285 CASE REPORT Malignant transformation of breast ductal adenoma: a diagnostic pitfall Hiroko HAYASHI, Hiroshi OHTANI,* Junzo YAMAGUCHI,** and Isao SHIMOKAWA Department
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
Histopathology and MIB-1 Labeling Index Predicted Recurrence of Meningiomas. A Proposal of Diagnostic Criteria for Patients with Atypical Meningioma
 1538 Histopathology and MIB-1 Labeling Index Predicted Recurrence of Meningiomas A Proposal of Diagnostic Criteria for Patients with Atypical Meningioma Donald Ming-Tak Ho, M.D. 1,2 Chih-Yi Hsu, M.D. 1,2
1538 Histopathology and MIB-1 Labeling Index Predicted Recurrence of Meningiomas A Proposal of Diagnostic Criteria for Patients with Atypical Meningioma Donald Ming-Tak Ho, M.D. 1,2 Chih-Yi Hsu, M.D. 1,2
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors
 Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
 Chapter 2 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Introduction Included in this chapter are nasal cavities, frontal sinus, ethmoid complex, sphenoid sinus, and maxillary sinuses. These cavities and sinuses
Chapter 2 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Introduction Included in this chapter are nasal cavities, frontal sinus, ethmoid complex, sphenoid sinus, and maxillary sinuses. These cavities and sinuses
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Intracranial Solitary Fibrous Tumor with Pseudopapillary Architecture: An Uncommon Tumor with Unusual Histopathology
 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Oct 2016 Vol 9 No.4 181 Case Report Intracranial Solitary Fibrous Tumor with Pseudopapillary Architecture: An Uncommon Tumor with Unusual Histopathology Guang
North American Journal of Medicine and Science Oct 2016 Vol 9 No.4 181 Case Report Intracranial Solitary Fibrous Tumor with Pseudopapillary Architecture: An Uncommon Tumor with Unusual Histopathology Guang
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors
 Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Disclosures. The Thin Red Line Between Neuropathology and Head & Neck Pathology. Introduction CASE 1. Current Issues Tihan
 Disclosures I have nothing to disclose The Thin Red Line Between Neuropathology and Head & Neck Pathology Tarik Tihan, MD, PhD UCSF, Department of Pathology Neuropathology Division Introduction Three cases
Disclosures I have nothing to disclose The Thin Red Line Between Neuropathology and Head & Neck Pathology Tarik Tihan, MD, PhD UCSF, Department of Pathology Neuropathology Division Introduction Three cases
The Common Radiological Features of Meningiomas on CT scan and MRI among Patients at Major Hospitals in Eldoret, Kenya
 VOLUME 2 ISSUE 2 ISSN: 2320-4818 JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & INNOVATIVE RESEARCH ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE The Common Radiological Features of Meningiomas on CT scan and MRI among Patients at Major Hospitals
VOLUME 2 ISSUE 2 ISSN: 2320-4818 JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & INNOVATIVE RESEARCH ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE The Common Radiological Features of Meningiomas on CT scan and MRI among Patients at Major Hospitals
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity
 Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma
 AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
Prognostic Factors of Atypical Meningioma : Overall Survival Rate and Progression Free Survival Rate
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (6) : 661-666, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0303.008 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Prognostic Factors of Atypical Meningioma : Overall Survival Rate
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (6) : 661-666, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0303.008 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Prognostic Factors of Atypical Meningioma : Overall Survival Rate
Meningiomas account for between 16% and 20% of primary
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
CASE year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland
 CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
Anaplastic Meningioma Presenting as a Left Parietal Mass: A Case Report
 ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.905067 Received: 2017.04.27 Accepted: 2017.07.24 Published: 2017.11.04 Anaplastic Meningioma Presenting as a Left Parietal Mass: A Case Report Authors Contribution: Study
ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.905067 Received: 2017.04.27 Accepted: 2017.07.24 Published: 2017.11.04 Anaplastic Meningioma Presenting as a Left Parietal Mass: A Case Report Authors Contribution: Study
No financial or other disclosures
 Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Characterization of morphologically benign biologically aggressive meningiomas
 Characterization of morphologically benign biologically aggressive meningiomas Original Article Shalinee Rao, N. Sadiya, Saraswathi Doraiswami, D. Prathiba Department of Pathology, Sri Ramachandra Medical
Characterization of morphologically benign biologically aggressive meningiomas Original Article Shalinee Rao, N. Sadiya, Saraswathi Doraiswami, D. Prathiba Department of Pathology, Sri Ramachandra Medical
Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 815923, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/815923 Case Report Atypical Presentation of Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor in a Child Y. T.
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4
 USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4 B.K. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters MD University of Colorado Denver Denver, Colorado Sheep Mountain, Telluride, Colorado Clinical History The patient is a 46 year old male
USCAP Neuropathology night panel CASE 4 B.K. Kleinschmidt-DeMasters MD University of Colorado Denver Denver, Colorado Sheep Mountain, Telluride, Colorado Clinical History The patient is a 46 year old male
CASE REPORT What Is It? A Rare Presentation of a Meningioma
 CASE REPORT What Is It? A Rare Presentation of a Meningioma Matthew A. Applebaum, MS, a Connor Barnes, MD, b and Michael Harrington, MD MPH b a University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine,
CASE REPORT What Is It? A Rare Presentation of a Meningioma Matthew A. Applebaum, MS, a Connor Barnes, MD, b and Michael Harrington, MD MPH b a University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine,
Pathology of the Thyroid
 Pathology of the Thyroid Thyroid Carcinoma Arising from Follicular Cells 2015-01-19 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Carcinomas Arising from Follicular Cells Differentiated Carcinoma Papillary
Pathology of the Thyroid Thyroid Carcinoma Arising from Follicular Cells 2015-01-19 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Carcinomas Arising from Follicular Cells Differentiated Carcinoma Papillary
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDULLOBLASTOMA AND PNET CNS Site Group Medulloblastoma and PNET Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDULLOBLASTOMA AND PNET CNS Site Group Medulloblastoma and PNET Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
USCAP Neuropathology. Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC
 USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
USCAP Neuropathology Case No. 3 Elisabeth J. Rushing, MD Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, DC Clinical history The patient is a 9 year-old boy who has had seizures since age 2, at which time
Papillary meningioma of the jugular foramen: A case report
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 3655-3659, 2015 Papillary meningioma of the jugular foramen: A case report YING YU, HAIYANG XU, YUBO WANG and GANG ZHAO Department of Neurosurgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 3655-3659, 2015 Papillary meningioma of the jugular foramen: A case report YING YU, HAIYANG XU, YUBO WANG and GANG ZHAO Department of Neurosurgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University,
Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP)
 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular Variant Encapsulated Type Replaced by: Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP) Lester D. R. Thompson www.lester-thompson.com
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular Variant Encapsulated Type Replaced by: Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP) Lester D. R. Thompson www.lester-thompson.com
