Value of CD34 and CD10 Immunostaining in the Differentiation between Basal Cell Carcinoma and Trichoepithelioma
|
|
|
- Darrell Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, June: 71-76, Value of CD34 and CD10 Immunostaining in the Differentiation between Basal Cell Carcinoma and Trichoepithelioma MOHEBAT H. GOUDA, M.D.; GHADA A. ABD EL-FATTAH, M.D. and ADEL Z. EL-SAEDIY, M.D. The Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University Abstract Purpose: Trichoepithelioma (TE) is a benign skin tumor with follicular differentiation, which is sometimes difficult to distinguish clinically and histologically from basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Both are characterized morphologically by the proliferation of basaloid cells; however, BCCs are clinically associated with a more aggressive behavior. It is important to distinguish these neoplasms for effective and appropriate therapeutic planning. The present study aims at investigating the role of CD10 & CD34 in differentiation between TE and BCC. Patients and Methods: This study includes 30 cases of BCC and 10 cases of TE. Cases were collected from Pathology Department of Faculty of Medicine-Benha University and Egyptian National Cancer Institute (NCI) in the period CD34 and CD10 immunohistochemistry was performed in all cases and the patterns of expression were analyzed. Results: The pattern of CD34 expression in BCC copmared to that of TE was statistically significant (p<0.05). Trichoepithelioma exhibited stromal expression in the immediate stromal cells adjacent to the tumor islands while in BCC, the surrounding stroma was immunoreactive to CD34 with a clear zone of negatively stained cells separating epithelial islands from the positive mesenchymal stromal cells. The pattern of CD10 expression in BCC and TE was statistically highly significant (p<0.01). Seventy percent of TE cases exhibited pure stromal cells staining while 70% of BCC cases showed staining of basaloid cells. Conclusion: This study suggests CD10 and CD34 as useful markers for the differential diagnosis between TE and BCC with preference to CD10. Key Words: CD34 CD10 Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) Trichoepithelioma (TE) Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Introduction WORLDWIDE Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common malignant cutaneous tumor, Correspondence to: Dr. Mohebat H. Gouda, The Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University accounting for approximately 80% of nonmelanoma skin cancers. BCC is of low grade malignancy, locally aggressive, and metastasis is very unusual [1,2]. In Egypt, the NCI registry data of years 2000 to 2011 revealed that BCC constitutes 43% of nonmelanoma skin cancers [3]. Trichoepithelioma (TE) is a benign tumor derived from basal cells in the hair follicle. It may be sporadic or as a part of a common genetic disorder called multiple familial trichoepithelioma characterized by the presence of many small tumors predominantly on face, inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern [4,5]. Trichoepithelioma in some instances may resemble BCC, so the differentiaion of BCC from TE can be problematic based on clinical presentation and routine hematoxylin and eosin stained sections. Attempts have been made to identify immunohistochemical markers helpful in differentiating them [4,5]. The correct diagnosis of these tumors is important because the tumors are treated differently; basal cell carcinoma is a locally aggressive neoplasm and must be totally excised with safe margins. However, trichoepithelioma is a benign neoplasm, which may be partially excised by shaving [6,7]. CD34 is a 110-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein present on leukemic cells, endothelial cells, and stem cells [3]. In addition, it is localized on cells of the splenic marginal zone, dendritic interstitial cells around vessels, nerves, hair follicles, muscle bundles, and sweat glands in a variety of tissues and organs [7]. Its function is still unclear. It is used for leukemia diagnosis and subclassification and for diagnosis of vascular tumors. Antibodies 71
2 72 Value of CD34 & CD10 Immunostaining in the Differentiation to CD34 also strongly label gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and the antigen is invariably found in solitary fibrous tumor and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans [8]. CD10 is a cell-surface zinc metalloproteinase of 100 KD that is also known as common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA). It was originally found to be expressed on the cell surface of most cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and was soon found in many other types of neoplasms [9]. CD10 expression has been shown in tumors of follicular differentiation, including trichoepithelioma, pilomatricoma, basaloid follicular hamartoma and BCC [10]. A few studies have indicated its expression in BCC and TE but this marker has not been used routinely for differentiating BCC and TE because of the limited number of available studies [11]. The purpose of this study is to investigate the usefulness of CD 10 and CD34 in distinguishing BCC and TE. Material and Methods The retrospective studied group included random 30 cases of BCC and 10 cases of TE, collected from histopathologic archive of files of Pathology Department of Faculty of Medicine-Benha University and Egyptian National Cancer Institute (NCI) in the period Paraffin-embedded tissue sections were obtained from archival tissue blocks of the hospital. Hematoxylin and eosin sections were reviewed to confirm diagnosis. Immunohistochemical staining: Paraffinembedded tissue sections, 3-4 micron thick were mounted on positively-charged slides and heated at 60 C for 30 minutes then deparaffinized and rehydrated through a series of xylene and alcohol before staining. After antigen retrieval with microwave treatment in 10mM citrate buffer (Neo- Markers, Cat. # AP-9003), ph 6.0, endogenous peroxidase was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes. Sections were washed 3 times with cold 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS). After blocking with 10% normal rabbit serum, sections were incubated with mouse monoclonal antibody against CD34 (Lab Vision, Thermo scientific, USA, Cat. # MS-363-R7, ready to use), mouse monoclonal CD 10 (Lab Vision, Thermo scientific, USA, Cat. # MS-728-R7, ready to use). Slides were incubated for 90 minutes with each antibody at room temperature. The freshly prepared DABsubstrate-chromogen solution was applied and incubated for 5-15 minutes until color intensity has been reached. Lastly, sections were counterstained with Mayer s hematoxylin. For CD 10, normal intestinal biopsy was used as positive control. CD10 stained the cytoplasm of the surface epithelial cells of small intestine 7.Sections of the tonsil for CD34 were used as a positive control 15. Negative controls were performed by omitting the primary antibody step. Interpretation of immunohistochemical staining of CD34: All specimens were examined under a light microscope. Positive reactions for CD34 appeared as a brownish cytoplasmic sometimes nuclear, granular staining of the tumor cells [18]. The amount of immunupositive tumor cells and stromal cells were evaluated by using a scale of [0] to [2+] as follows: [0], negative (<10% positive cells); [1+], regionally positive (10-50% positive cells); [2+], diffusely positive (>50% positive cells) [2]. Interpretation of immunohistochemical staining of CD10: Positive CD 10 staining was identified as brown cytoplasmic staining with or without cell membrane staining. For each case, 10 fields were examined at high magnification (x400), and the percent of positive cells was calculated as follow: 0-10% was judged as negative, 10-50% was judged as low expression, and >50% was judged as high expression. Localization of anti-cd10 to the stroma and/or tumor cells was determined in cases with immunoreactivity [1,11]. Statistical analysis: Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS (version 16.0 for windows) software package according to Sperman s correlation coefficient. Correlation between several variables was computed using Fisher s exact test. p-value less than 0.05 (<0.05) was considered significant and <0.01 was highly significant. Results A- Immunohistochemical results of CD34 staining: Among the 30 cases of BCC, 20 cases (66.7%) were positive to CD34 expression in stromal cells. In 16 cases (53.3%) of them, the immediate tumor stroma did not stain for CD34. A clear demarcation was found between the mesenchymal component intermixed with the epithelial tumor islands being
3 Mohebat H. Gouda, et al. 73 negative for CD34 and those stromal cells peripheral to the tumor (surrounding stroma) being CD34- positive (Fig. 2). The other 4 cases (13.3%) stained both immediate and surrounding stroma. Among the 20 positive cases, 17 cases showed focally positive CD34 expression and the other 3 cases were diffusely positive to it. The remaining 10 cases (33.3%) were negative for CD34 immunostaining. This study included 10 cases of TE, 8 of them (80%) were diffusely positive for CD34 expression in the form of stromal expression in the immediate stromal cells adjacent to the tumor islands. There was no buffer zone of negatively stained cells separating epithelial islands from the positive mesenchymal stromal cells (Fig. 2). Two cases (20%) were non-immunoreactive for CD34. This pattern of CD34 expression in BCC and TE was statistically significant (p<0.05), the pattern of CD34 expression in stromal cells was useful for differntiating BCC from TE (Table 1). Table (1): Expression of CD34 in BCC and TE. CD34 Pattern of expression Type of lesion Total Negative Immediate Surrounding Both immediate and stroma stroma surrounding stroma p-value BCC TE (33.3%) 0 16 (53.3%) 4 (13.3%) 10 2 (10%) 8 (80%) 0 0 p<0.05 BCC : Basal cell carcinoma. TE : Trichoepithelioma. N.B : The pattern of CD34 expression in BCC and TE was statistically significant (p<0.05). B- Immunohistochemical results of CD10 staining: Among the 30 cases of BCC, 29 cases (96.7%) were positive to CD 10 expression. Of these positive cases, there were 21 cases (70%) showed staining of basaloid cells (Fig. 3), of them 15 cases with high CD 10 expression and 6 cases with low CD 10 expression. Four cases (13.3%) showed staining of stromal cells and 4 cases (13.3%) showed staining of both basaloid and stromal cells with high expression of CD10 (Fig. 4). Only one case (3.3%) was negative for CD10 immunostaining. The 10 cases of TE, 9 of them (90%) were highly positive for CD10 expression. Seven cases (70%) exhibited pure stromal cells staining (Fig. 3), 2 cases exhibited staining of both stromal and basaloid cells, while no case (0%) showed staining of basaloid cells alone. One case (10%) was nonimmunoreactive for CD10 (Table 2). This pattern of CD10 expression in BCC and TE was statistically highly significant ( p<0.01), CD10 expression in stromal cells around basaloid nests was useful for differntiating TE from BCC. In contrast, CD10-positive basaloid cells and negative stromal cells were diagnostic for BCC (Table 2). Table (2): Expression of CD 10 in BCC and TE. CD10 Pattern of expression Type of lesion Total Negative Basaloid Stromal Both basaloid and cells cells stromal cells p-value BCC 30 TE 10 1 (3.3%) 21 (70%) 4 (13.3%) 4 (13.3%) 1 (10%) 0 7 (70%) 2 (20%) p<0.01 N.B: The pattern of CD10 expression in BCC and TE was statistically highly significant ( p<0.01).
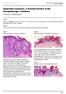
4 74 Value of CD34 & CD10 Immunostaining in the Differentiation Fig. (1): A- A case of TE revealed well circumscribed lesion composed of basaloid cells in small or large nodules within a variably cellular stroma; the basaloid cells are encircled by fibroblasts (H&E. x400). B- A case of BCC revealed multiple tumor islands occupying the upper dermis of different sizes & shapes composed of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading of the outer row of the basaloid cells in the tumor islands which are separated from the stroma by a cleft (H&E. x400). Fig. (2): A- CD34 expression in immediate stroma of TE ( ). B- CD34 expression in surrounding stroma of BCC ( ) (IHC, DAB x400) Fig. (3): A- CD10 expression in stroma of TE ( ), B- CD10 expression in basaloid cells of BCC ( ) (IHC, DAB x400). Fig. (4): CD10 expression in both basaloid cells ( ) and stromal cells ( ) in BCC ( IHC, DAB x400).
5 Mohebat H. Gouda, et al. 75 Discussion Trichoepithelioma is a benign skin tumor with follicular differentiation, whose distinction from basal cell carcinoma is sometimes difficult, clinically and histologically. Both tumors are composed of nests of basaloid cells with follicular differentiation. Sometimes it may be impossible to make a histopathologic differentiation on the basis of routine hematoxylin and eosin staining. Such distinction is clinically important because of the differences in prognosis and treatment of these tumors. Therefore, several laboratory techniques have been investigated as an aid in this differentiation. In these instances, immunohistochemical examinations may provide further information [4]. In the current study, 66.7% of BCC cases were positive to CD34 expression in stromal cells. In 53.3% of cases, there was CD34 expressions in the surrounding stroma of BCC nests with the adjacent zones (the immediate tumor stroma) which were not stained with CD34 and 13.3% of cases stained both immediate and surrounding stroma. As regard TE, 80% were diffusely positive for CD34 expression in the form of stromal expression in the immediate mesenchymal stromal cells adjacent to the tumor island (Fig. 2). This pattern of CD34 expression in BCC and TE was statistically significant (p<0.05). These results were in agreement with results reported by Zaky & Abdel-Rahman, [8] who found that in BCC cases, the immediate tumor stroma together with the spindle cells intermixing the tumor nests were CD34 negative, but in TE cases the immediate tumor stroma as well as the spindle cells surrounding the tumor islands were focally CD34 positive. Sengul et al., [2] reported a significant difference in CD34 expression between the two groups included in their study; stromal expression of CD34 for benign tumors of cutaneous appendages originating from hair follicles was observed just at the adjacent to the tumoral islands; it was not like that for BCC. There was CD34 expressions in the surrounding stromas of BCCs with the adjacent zones which were not stained with CD34. Another study by Basarab, et al., [12] found that CD34 staining of the immediate peritumoral spindle-shaped cells was observed in only 20% of TE compared with 7% of BCC. Kirchmann, et al., [13] reported that the spindle-shaped cells surrounding the islands of trichoepithelioma cells were focally strongly positive for CD34. In all basal cell carcinomas, the spindle-shaped cells surrounding the nests of tumor cells were negative. However, these studies concluded CD34 can be reliably used to differentiate between TE and BCC. CD 10 immune staining was performed on 10 cases of trichoepithelioma and 30 cases of basal cell carcinoma. Of these, 90% of trichoepithelioma and 96.7% of basal cell carcinoma biopsies were immunoreactive for CD10. The most frequently labeled were the tumor stroma, with positive readings in 70% of trichoepithelioma and 13.3% of basal cell carcinoma biopsies (Fig. 3). CD 10 staining was present in both the basaloid cells and the stroma in 20% of trichoepithelioma and 13.3% of basal cell carcinoma biopsies. CD 10 staining of only the basaloid cells was observed in 70% of basal cell carcinoma biopsies but not in any case of trichoepithelioma. The pattern of staining of basaloid cells and stromal cells in BCC and trichoepithelioma was highly statistically different (p<0.001). The current results were in agreement to results reported by Sengul et al., [14] and Naglaa & Naglaa, [15] who found that the pattern of staining with CD 10 in TE is stromal, whereas, in BCC lesions, it is cytoplasmic in epithelial cells, without expression in the surrounding stroma. This staining is more remarkable in the outermost basaloid cells. Also, Pham et al., [16] found that (92%) TE showed positive stromal immunoreactivity, and (8%) showed positivity of the basaloid cells. No TE demonstrated epithelial expression alone. On the other hand, expression of CD 10 by basaloid cells was identified in (87%) cases of BCC. Stromal positivity was also identified in three cases of BCC. Condensation of CD10-positive stromal cells around basaloid nests was statistically significant in differentiating TE from BCC (p< ). Conversely, CD 10-positive basaloid cells were seen predominantly in BCC (p<0.0001). Similarly, Heidarpour et al., [11] reported that in BCC cases, the expression of CD10 was noted in tumoral cells in (83.2%). Of these, 3 cases showed positivity of the stromal and basaloid cells, two cases demonstrated stromal expression alone and two BCCs were not immunoreactive. On the other hand, (83.3%) TEs showed positive stromal immunoreactivity. Of these, one case also showed positivity of the basaloid cells. One TE demonstrated epithelial expression alone and one TE was not immunoreactive. The pattern of staining of basaloid cells and stromal cells in BCC and trichoepithelioma was statistically different (p<0.001). Also, Aslani et al., [17] found that Comparison of CD10 expression between the BCC and TE groups dem-
6 76 Value of CD34 & CD10 Immunostaining in the Differentiation onstrated a significant difference in both the tumor and stromal cells (p<0.001). Kirchmann et al., [18] speculated that benign TE had a stroma which components were closely resembled the mesenchymal component of stroma surrounding hair follicles in normal skin. On the contrary, BCC were surrounded by a stroma containing cells not normally found in the dermis. In the stroma surrounding BCC, there is a deposition of mucinous material and often cleft formation. Stromal differences, fibronectin, mucin production of glucoseaminoglycan, and mesenchymal bodies may cause that different staining pattern between BCC and TE [8,14]. Tebcherani et al., [7] reported that despite the use of panels of immune markers, histopathological criteria associated with clinical data certainly remain the best guideline for the differential diagnosis of trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma. However this study can suggest CD10 and CD34 as useful markers that aid in the differential diagnosis between TE and BCC with preference to CD 10. The limited number of the cases in this work was the handicap. So, larger series, and different research techniques, are necessary for more accurate diagnoses. References 1- HAYAM A.A. and HAYAM M.H.: Immunohistochemical Expression of CD10 in Cutaneous Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., 19 (3): , SENGUL D., SENGUL I., ASTARCI M.H., et al.: Differential diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma and benign tumors of cutaneous appendages originating from hair follicles by using CD34. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev., 11: , EL-BOLKAINY M., AKRAM M., GOUDA I., et al.: Pathology of Cancer, 4 th ed, Skin tumors, the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Cairo University, p , AHMED T.S., PRIORE J.D. and SEYKORA J.T.: Tumors of the epidermal appendages. In: Lever s histopathology of the skin. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp , FERNANDEZ A-FLORES: Advanced differentiation in trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma investigated by immunohistochemistry against neurofilaments. Folia Histochemica et Cytobiologica, 47 (1): 61-4, LEE Y.F, CHANG Y.T. and LIU H.N.: Differentiating Basal Cell Carcinoma from Trichoepithelioma by Using Androgen Receptor Expression. Dermatol. Sinica., 27: , TEBCHERANI A.J., De ANDRADE H.F. and SOTTO M.N.: Diagnostic utility of immunohistochemistry in distinguishing trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma: evaluation using tissue microarray samples. Modern Pathology, 25: , ZAKY A.M. and ABDEL-RAHMAN A.H.: CD34 Glycoprotein as a differentiating marker between basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 25: , CÓRDOBA A.1, GUERRERO D., LARRINAGA B., et al.: Bcl-2 and CD10 expression in the differential diagnosis of trichoblastoma, basal cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma with follicular differentiation. Int. J. Dermatol., 48 (7): 713-7, RAMOS-CEBALLOS F.I, PASHAEI S., KINCANNON J.M., et al.: Bcl-2, CD34 and CD10 expression in basaloid follicular hamartoma, vellus hair hamartoma and neurofollicular hamartoma demonstrate full follicular differentiation. J. Cutan. Pathol., 35 (5): , HEIDARPOUR M., RAJABI P. and SAJADI F.: CD10 expression helps to differentiate basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. J. Res. Med. Sci., 16 (7): , BASARAB T.1, ORCHARD G. and RUSSELL-JONES R.: The use of immunostaining for bcl-2 and CD34 and the lectin peanut agglutinin in differentiating between basal cell carcinomas and trichoepitheliomas. Am. J. Dermatopathol., 20 (5): , KIRCHMANN T.T., PRIETO V.G. and SMOLLER B.R: CD34 staining pattern distinguishes basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma. Arch. Dermatol., 130 (5): , SENGUL D., SENGUL I. and ASTARCI M.H.: CD 10 for the distinct differential diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma and benign tumours of cutaneous appendages originating from hair follicle. Pol. J. Pathol., 3: , NAGLAA A.A. and NAGLAA S.A.: Androgen receptor and CD10 expression in differential diagnosis of trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma. Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal, 9: , PHAM T.T., SELIM M.A., BURCHETTE J.L., et al.: CD10 expression in trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology, 33 (2): 123-8, ASLANI S.F.1, AKBARZADEH J.M. and JOWKAR F.: Value of CD10 Expression in Differentiating Cutaneous Basal from Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Basal Cell Carcinoma from Trichoepithelioma. Iran J. Med. Sci., 38 (2): 100-6, KIRCHMANN T., VICTOR G. and BRUCE S.: Use of CD34 in assessing the relationship between stroma and tumor in desmoplastic keratinocyte neoplasm. J. Cut. Pathol., 22: 422-6, 1995.
Original Article CD10 expression helps to differentiate basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma *
 Received: 20.12.2010 Accepted: 14.6.2011 Original Article CD10 expression helps to differentiate basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma * Mitra Heidarpour 1, Parvin Rajabi 2, Farzaneh Sajadi 3 Abstract
Received: 20.12.2010 Accepted: 14.6.2011 Original Article CD10 expression helps to differentiate basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma * Mitra Heidarpour 1, Parvin Rajabi 2, Farzaneh Sajadi 3 Abstract
The Role of Bcl-2, CD10 and CD34 Expression in Differentiation between Basal Cell Carcinoma and Trichoepithelioma
 Open Journal of Pathology, 2014, 4, 116-124 Published Online July 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpathology http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpathology.2014.43018 The Role of Bcl-2, CD10 and CD34
Open Journal of Pathology, 2014, 4, 116-124 Published Online July 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpathology http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpathology.2014.43018 The Role of Bcl-2, CD10 and CD34
Value of CD10 Expression in Differentiating Cutaneous Basal from Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Basal Cell Carcinoma from Trichoepithelioma
 IJMS Vol 38, No 2, June 2013 Original Article Value of CD10 Expression in Differentiating Cutaneous Basal from Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Basal Cell Carcinoma from Trichoepithelioma Fatemeh Sari Aslani,
IJMS Vol 38, No 2, June 2013 Original Article Value of CD10 Expression in Differentiating Cutaneous Basal from Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Basal Cell Carcinoma from Trichoepithelioma Fatemeh Sari Aslani,
CD10 immunoreactivity in cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinoma
 Original Article CD10 immunoreactivity in cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinoma Mitra Heidarpour 1, Parvin Rajabi 2, Mohammadreza Emami 3 ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to compare
Original Article CD10 immunoreactivity in cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinoma Mitra Heidarpour 1, Parvin Rajabi 2, Mohammadreza Emami 3 ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study was to compare
Value of P53, Ki-67 and CD10 in Differentiation between Keratoacanthoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 1, December: 795-801, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Value of P53, Ki-67 and CD10 in Differentiation between Keratoacanthoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 1, December: 795-801, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Value of P53, Ki-67 and CD10 in Differentiation between Keratoacanthoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma; a new case and review of the literature with emphasis on its differential diagnosis
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 135-139 Case Report Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma; a new case and review of the literature with emphasis on its differential diagnosis M Concha-Rogazy, S Alvarez-Veliz,
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 135-139 Case Report Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma; a new case and review of the literature with emphasis on its differential diagnosis M Concha-Rogazy, S Alvarez-Veliz,
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC) are the most
 Original Article Immunohistochemical expression of CD10 in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas Shahriar Shafaei (MD) 1 Mahnaz Sharifian (MD) *1 Karimollah Hajian-Tilaki (PhD) 2 1. Department of
Original Article Immunohistochemical expression of CD10 in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas Shahriar Shafaei (MD) 1 Mahnaz Sharifian (MD) *1 Karimollah Hajian-Tilaki (PhD) 2 1. Department of
Comparison of CD10 expression in stroma of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors of the breast
 Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery
 Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
- Selected Tumors of the Skin Appendages - Primary vs. Metastasis
 - Selected Tumors of the Skin Appendages - Primary vs. Metastasis Napa Valley 2018 Victor G. Prieto, MD, PhD Chair of Pathology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center vprieto@mdanderson.org Napa Valley in May Introduction
- Selected Tumors of the Skin Appendages - Primary vs. Metastasis Napa Valley 2018 Victor G. Prieto, MD, PhD Chair of Pathology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center vprieto@mdanderson.org Napa Valley in May Introduction
Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic skin*
 J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng
 ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Senior of Histopathology Department at Khartoum, Radiation and Isotopes Center
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP)
 Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris
 Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
Immunohistochemical Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Psoriasis Vulgaris Amina Gamal el Din 1 *, Hanan M Saleh 2, Nermeen Abdel Fattah 2 and Abdel Maksoud A 3 1.Pathology Department, Medical Research
Immunohistochemical Expression of CD10 in Cutaneous Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 19, No. 3, September: 195-201, 2007 Immunohistochemical Expression of CD10 in Cutaneous Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas HAYAM A. AIAD, M.D.* and HAYAM
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 19, No. 3, September: 195-201, 2007 Immunohistochemical Expression of CD10 in Cutaneous Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas HAYAM A. AIAD, M.D.* and HAYAM
Diagnostic Value of CK19 and HMWCK 34BE12 in Differentiation between Selected Thyroid Neoplasms
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, December: 1035-1042, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diagnostic Value of CK19 and HMWCK 34BE12 in Differentiation between Selected Thyroid Neoplasms TAGHREED
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, December: 1035-1042, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diagnostic Value of CK19 and HMWCK 34BE12 in Differentiation between Selected Thyroid Neoplasms TAGHREED
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors
 Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Lesions with Predominant Follicular Differentiation Special Emphasis on Basal Cell Carcinoma 2014-04-01 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Hair
Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Lesions with Predominant Follicular Differentiation Special Emphasis on Basal Cell Carcinoma 2014-04-01 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Hair
BJD British Journal of Dermatology. Summary DERMATOPATHOLOGY
 DERMATOPATHOLOGY BJD British Journal of Dermatology CD10 and CD34 in fetal and adult human hair follicles: dynamic changes in their immunohistochemical expression during embryogenesis and hair cycling
DERMATOPATHOLOGY BJD British Journal of Dermatology CD10 and CD34 in fetal and adult human hair follicles: dynamic changes in their immunohistochemical expression during embryogenesis and hair cycling
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Immunohistochemical Expression of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Verruca Vulgaris
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, December: 923-927, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Immunohistochemical Expression of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Verruca Vulgaris AHMED A. SALEH, M.D.; FATMA
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, December: 923-927, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Immunohistochemical Expression of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Verruca Vulgaris AHMED A. SALEH, M.D.; FATMA
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A.
 BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (VI) No (I) January-June 2017 Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital Neeraja Barve*, Hansa Goswami**, Urvi Parikh *** Abstract
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (VI) No (I) January-June 2017 Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Histopathological Spectrum at a Tertiary Care Hospital Neeraja Barve*, Hansa Goswami**, Urvi Parikh *** Abstract
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization with Colorectal Carcinoma: A Pilot Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Clinicopathological Study of Adnexal Tumors of Skin in a Tertiary Care Research Hospital
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Clinicopathological Study of Adnexal Tumors of Skin in a Tertiary Care Research Hospital
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
CASE REPORT SOLITARY SEBACEOUS NEVUS OF JADASSOHN COMPLICATED BY SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AND BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
 CASE REPORT Dennis H. Kraus, MD, Section Editor SOLITARY SEBACEOUS NEVUS OF JADASSOHN COMPLICATED BY SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AND BASAL CELL CARCINOMA Ahmad Ridzwan Arshad, FRCS, 1 Wan S. Azman, MS, 1 Ayadurai
CASE REPORT Dennis H. Kraus, MD, Section Editor SOLITARY SEBACEOUS NEVUS OF JADASSOHN COMPLICATED BY SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AND BASAL CELL CARCINOMA Ahmad Ridzwan Arshad, FRCS, 1 Wan S. Azman, MS, 1 Ayadurai
BSD 2015 Case 19. Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is:
 BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy
 Volume 20, Article ID 450472, 4 pages doi:0.55/20/450472 Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy Akihiro Yoneta, Kohei Horimoto, Keiko
Volume 20, Article ID 450472, 4 pages doi:0.55/20/450472 Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy Akihiro Yoneta, Kohei Horimoto, Keiko
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VII (Apr. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VII (Apr. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org A 5 Year Histopathological Study of Skin
ER-P Expression in Different Thyroid Carcinomas: Immunohistochemical Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 6, September: 5-9, 17 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net ER-P Expression in Different Thyroid Carcinomas: Immunohistochemical Study MIRAN A. EL-KORDY, M.Sc.; FAHIMA
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 6, September: 5-9, 17 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net ER-P Expression in Different Thyroid Carcinomas: Immunohistochemical Study MIRAN A. EL-KORDY, M.Sc.; FAHIMA
3. Histopathology. 1. Introduction. 2. Case History. Volume 6 Issue 4, April Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
 Spiradenocylindroma with Trichoepithelioma A Collision Tumor with Multiple Differentiation R. Lavanya 1, S. K. Sridevi 2, P. Viswanathan 3, P. V. S.Prasad 4 1 II nd Year Post Graduate, Department of Pathology,
Spiradenocylindroma with Trichoepithelioma A Collision Tumor with Multiple Differentiation R. Lavanya 1, S. K. Sridevi 2, P. Viswanathan 3, P. V. S.Prasad 4 1 II nd Year Post Graduate, Department of Pathology,
Introduction. Results. Discussion. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Results. conclusions,
 1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
ACCURACY OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY IN EVALUATION
 POL J PATHOL 2011; 2: 95-100 ACCURACY OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY IN EVALUATION OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL AND PERITONEAL EFFUSIONS FERESHTEH ENSANI, FARNAZ NEMATIZADEH, GITI IRVANLOU Department of Cytology, Cancer
POL J PATHOL 2011; 2: 95-100 ACCURACY OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY IN EVALUATION OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL AND PERITONEAL EFFUSIONS FERESHTEH ENSANI, FARNAZ NEMATIZADEH, GITI IRVANLOU Department of Cytology, Cancer
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland
 Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Stromal Fat Content of the Parathyroid Gland TAKAO OBARA,* YOSHIHIDE FUJIMOTO* AND MOTOHIKO AIBA** *Department of Endocrine Surgery and **Department of Surgical Pathology, Tokyo Women's Medical College,
Four Different Tumors Arising in a Nevus Sebaceous
 Published online: April 20, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1662 6567/16/0081 0075$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Published online: April 20, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1662 6567/16/0081 0075$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS. Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology
 SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study
 Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study V. Srinivas Kumar 1, V. Geeta 1*, Nikhil Kumar Voruganti 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3, Tamilarasi 4 1 Associate Professor
Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study V. Srinivas Kumar 1, V. Geeta 1*, Nikhil Kumar Voruganti 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3, Tamilarasi 4 1 Associate Professor
Analysis of immunohistochemical expression of CD10 in the malignant lesions of prostate
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2017), PP 78-82 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of immunohistochemical expression
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2017), PP 78-82 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of immunohistochemical expression
Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective. Naseema Vorajee August 2016
 Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective Naseema Vorajee August 2016 Naseema.vorajee@nhls.ac.za Pleural diseases (whether neoplastic, reactive or infective) may have similar
Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective Naseema Vorajee August 2016 Naseema.vorajee@nhls.ac.za Pleural diseases (whether neoplastic, reactive or infective) may have similar
Appendageal skin tumors
 Appendageal skin tumors Ibrahim Khalifeh, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Pathology American University of Beirut Medical Center Beirut, Lebanon Appendageal tumors Neoplasms whose differentiation
Appendageal skin tumors Ibrahim Khalifeh, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Pathology American University of Beirut Medical Center Beirut, Lebanon Appendageal tumors Neoplasms whose differentiation
In the third part of the present study tumours which previous were described as basal cell tumours but now have been reclassified as trichoblastomas
 170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
170 6. SUMMARY Immunhistochemical investigations for identifying the histogenesis of basaloid neoplasias and hyperplasias in the mamma parenchyma of the bitch, for the use of the human nuclear protein
Glycogen-rich adenocarcinoma in the lower lip: report of a case with particular emphasis on differential diagnosis
 Open Journal of Stomatology, 2011, 1, 109-113 doi:10.4236/ojst.2011.13017 Published Online September 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal//). Glycogen-rich adenocarcinoma in the lower lip: report of a case
Open Journal of Stomatology, 2011, 1, 109-113 doi:10.4236/ojst.2011.13017 Published Online September 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal//). Glycogen-rich adenocarcinoma in the lower lip: report of a case
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 543756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/543756 Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India Ankit Sharma, 1 Deepak
Skin Cancer, Article ID 543756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/543756 Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumours Institutional Study in South India Ankit Sharma, 1 Deepak
Prostate Immunohistochemistry. Literature Interpretation: Caveats. Must be aware of staining pattern of antibody in the relevant tissue
 IHC Interpretation: General Principles (1) Prostate Immunohistochemistry Murali Varma Cardiff, UK wptmv@cf.ac.uk Sarajevo Nov 2013 Must be aware of staining pattern of antibody in the relevant tissue Nuclear/cytoplasmic/membranous
IHC Interpretation: General Principles (1) Prostate Immunohistochemistry Murali Varma Cardiff, UK wptmv@cf.ac.uk Sarajevo Nov 2013 Must be aware of staining pattern of antibody in the relevant tissue Nuclear/cytoplasmic/membranous
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
Cellular Neurothekeoma
 Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
B. Environmental Factors. a. The major risk factor to papillary thyroid cancer is exposure to ionizing radiation, during the first 2 decades of life.
 B. Environmental Factors. a. The major risk factor to papillary thyroid cancer is exposure to ionizing radiation, during the first 2 decades of life. b. Deficiency of dietary iodine: - Is linked with a
B. Environmental Factors. a. The major risk factor to papillary thyroid cancer is exposure to ionizing radiation, during the first 2 decades of life. b. Deficiency of dietary iodine: - Is linked with a
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches
 Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Sayed A. S. Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Cairo
 Role of expression of P53, Cyclin D1 and Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in some benign, intermediate and malignant spindle cell soft tissue tumors Sayed A. S. Pathology Department, Faculty of
Role of expression of P53, Cyclin D1 and Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in some benign, intermediate and malignant spindle cell soft tissue tumors Sayed A. S. Pathology Department, Faculty of
What is new on adnexal neoplasms. Omar P. Sangueza, MD. Professor and Director of Dermatopathology. Wake Forest University School of Medicine
 What is new on adnexal neoplasms Omar P. Sangueza, MD Professor and Director of Dermatopathology Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Carney complex is an autosomal dominant
What is new on adnexal neoplasms Omar P. Sangueza, MD Professor and Director of Dermatopathology Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Carney complex is an autosomal dominant
American College of Mohs Surgery. Diagnostic Quality Control Program (Review of Answers)
 American College of Mohs Surgery Diagnostic Quality Control Program 2010 (Review of Answers) Question 1 A flesh-colored plaque on the right ala of an otherwise healthy 57 year-old male is referred for
American College of Mohs Surgery Diagnostic Quality Control Program 2010 (Review of Answers) Question 1 A flesh-colored plaque on the right ala of an otherwise healthy 57 year-old male is referred for
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2
 Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
carcinoembryonic antigen
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 219-224 Granular cell myoblastoma: positive staining for carcinoembryonic antigen SAMI SHOUSHA AND THEO LYSSIOTIS From the Departments of Histopathology, The Charing
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 219-224 Granular cell myoblastoma: positive staining for carcinoembryonic antigen SAMI SHOUSHA AND THEO LYSSIOTIS From the Departments of Histopathology, The Charing
Stromal CD10 immunohistochemical expression in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder and correlation with clinicopathological parameters
 Marwa et al. SECI Oncology 2017 Stromal CD10 immunohistochemical expression in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder and correlation with clinicopathological parameters Marwa T. Hussien 1, Etemad Helmy
Marwa et al. SECI Oncology 2017 Stromal CD10 immunohistochemical expression in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder and correlation with clinicopathological parameters Marwa T. Hussien 1, Etemad Helmy
Case 18. M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case
 Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma. PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use
 Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use For countries outside of the United States, see the local
Interpretation Manual - Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmdx is FDA-approved for in vitro diagnostic use For countries outside of the United States, see the local
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 151-6 Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast Joo Yeon Song Hye-Kyoung Yoon Department of Pathology, Pusan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine,
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 151-6 Immunohistochemical Phenotypes of Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast Joo Yeon Song Hye-Kyoung Yoon Department of Pathology, Pusan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine,
The Role of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Differential Diagnosis of Prostate Tumors
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 10/ January 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) The Role of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Differential Diagnosis of Prostate
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 10/ January 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) The Role of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Differential Diagnosis of Prostate
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
CLEAR CELL BASAL CELL CARCINOMA- AN UNUSUAL ENTITY IN AN INDIAN MALE
 Indian Journal of Medical s ISSN: 2319 3832(Online) CLEAR CELL BASAL CELL CARCINOMA- AN UNUSUAL ENTITY IN AN INDIAN MALE * Cheena Garg 1, Arjun Agarwal 2, Bushra Siddiqui 3, Shahbaz Faridi 4, 1 Department
Indian Journal of Medical s ISSN: 2319 3832(Online) CLEAR CELL BASAL CELL CARCINOMA- AN UNUSUAL ENTITY IN AN INDIAN MALE * Cheena Garg 1, Arjun Agarwal 2, Bushra Siddiqui 3, Shahbaz Faridi 4, 1 Department
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
VENTANA MMR IHC Panel Interpretation Guide for Staining of Colorectal Tissue
 VENTANA MMR IHC Panel Interpretation Guide for Staining of Colorectal Tissue VENTANA anti-mlh1 (M1) Mouse Monoclonal Primary Antibody VENTANA anti-pms2 (A16-4) Mouse Monoclonal Primary Antibody VENTANA
VENTANA MMR IHC Panel Interpretation Guide for Staining of Colorectal Tissue VENTANA anti-mlh1 (M1) Mouse Monoclonal Primary Antibody VENTANA anti-pms2 (A16-4) Mouse Monoclonal Primary Antibody VENTANA
CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Pepsin Solution ready-to-use
 SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Središnja medicinska knjižnica
 Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Julia Winter, Hermann Kneitz, and Eva-B. Bröcker. 1. Introduction. 2. Material and Methods
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Skin Cancer Volume 2011, Article ID 241382, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/241382 Research Article Blood Vessel Density in Basal Cell Carcinomas and Benign Trichogenic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Skin Cancer Volume 2011, Article ID 241382, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/241382 Research Article Blood Vessel Density in Basal Cell Carcinomas and Benign Trichogenic
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
