KYAMC Journal Vol. 8, No.-1, July Two Cases of Holoprosencephalies
|
|
|
- Brendan Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report Two Cases of Holoprosencephalies Sharif M M 1, Parvin K 2, Rahman M T 3, Ullah N 4, Islam S 5 Abstract Two pregnant women with around weeks of gestation were reported to Gynaecology and Obstetrics OPD of North Bengal Medical College Hospital, Bangladesh for last trimester antenatal checkup. They were primigravida with around years of ages without previous antenatal check up. Both of them had normal course of pregnancy. Ultrasounds of pregnancy profile were done. It was observed in first case that septum pellucidum was absent in brain with partially formed falx cerebri, interhemispheric fissure. Occipital horn was rudimentary and thalami and basal ganglia were partially separated. This case was diagnosed as a case of semi lobar holoprocencephaly. In another case, septum pellucidum, falx cerebri and interhemispheric fissure were absent. Ventricle was monoventricular in appearance and thalami were fused. This case was diagnosed as a case of alobar holoprosencephaly. The importances of these classical cases of alobar and semi lobar holoprosencephalies are to make aware the radiologists to the imaging manifestations of holoprosencephalies and come to early diagnosis. If these cases are being diagnosed at an early stage of pregnancy, medical termination of pregnancy can be performed and maternal psychological trauma of bearing a deformed fetus can be avoided. Key words: Alobar and semi lobar holoprosencephalies, Antenatal ultrasonography. Date of received: Date of acceptance: Introduction Holoprosencephaly (HP) is a congenital anomaly occurs due to lack of cleavage of the prosencephalon. Although relatively rare, it is the most common anomaly that involves both the brain and the face. Prenatal diagnosis of this anomaly using ultrasonography is difficult and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has recently become an important complement to ultrasound in prenatal diagnosis. HP is the most common anomaly affecting the ventral forebrain, occurring in 1/250 embryos and 1/ ,000 live births 1,2. Modern ultrasound imaging devices have increasingly allowed sophisticated prenatal diagnosis of fetal disorders. Embryopathologic and ultrasound findings are reported in five cases of alobar holoprosencephaly that were diagnosed prenatally, two cases as early as 23rd menstrual weeks 3. Classically three subtypes of Holoprosencephaly have been recognized, however additional entities are now included in the spectrum of the disease. The three main subtypes, in order of decreasing severity are alobar holoprosencephaly, semilobar holoprosencephaly and lobar holoprosencephaly. It is usually obvious at birth even if antenatal diagnosis has not been made, due to associated midline facial anomalies including 3 proboscis, cyclopia, cleft lip and/or palate, ocular hypotelorism and solitary median maxillary central incisor. Additionally these children also have systemic problems, with poor feeding, hypothalamic/pituitary dysfunction and developmental delay Dr. Md. Mofazzal Sharif, Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology & Imaging, KYAMCH, Enayetpur, Sirajgonj. 2. Dr. Khaleda Parvin, Consultant, United Hospitals, Dhaka. 3. Dr. Md. Towhidur Rahman, Assistant Professor, Birdem, Dhaka. 4. Dr. Nayeem Ullah, Junior Consultant, KYAMCH, Enayetpur, Sirajgonj. 5. Dr. Saiful Islam, Associate Professor, Rajshahi Medical College & Hospital, Rajshahi. Correspondence: Dr. Md. Mofazzal Sharif, Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology & Imaging, KYAMCH, Enayetpur, Sirajgonj. mofazzal.sharif@gamil.com 64
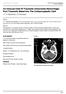
2 The fundamental problem is a failure of the developing brain to divide into left and right halves (which normally occurring at the end of the 5th week of gestation). This results in variable loss of midline structures of the brain and face as well as fusion of lateral ventricles and the 3rd ventricle. Environmental factors such as maternal diabetes mellitus, alcohol use, and retinoic acid have been implicated in the pathogenesis, as has mutation of a number of genes including Sonic hedgehog and ZIC2, on chromosome 13q32 5. Alobar holoprosencephaly is visible on all modalities, but in general is identified on antenatal ultrasound (if performed), and best characterized by MRI. On ultrasound there are monoventricle, fused thalami, absent corpus callosum, absent interhemispheric fissue, absent cavum septum pellucidum, absence of 3rd ventricle, middle and anterior cerebral arteries may be replaced by tangled branches of internal carotid and basilar vessels and severe facial malformations. On MRI, single midline monoventricle (or holosphere) with absence of lateral and third ventricles, absence of midline structures like absent septum pellucidum, agenesis or hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, interhemispheric fissure and falx cerebri, absent olfactory tract, dorsal cyst of holoprosencephaly, absent, fused or normal optic nerves and middle and anterior cerebral arteries may be replaced by tangled branches of internal carotid and basilar vessels. Associated craniofacial features may also be present which include proboscis, mono-orbit/ cyclopia, mono-nostril, hypotelorism and cebocephaly 6,7. As will most cerebral structural congenital abnormalities, semilobar Holoprosencephaly is visible on all modalities, but in general is identified on antenatal ultrasound, and best characterised by MRI. The basic structure of the cerebral lobes are present, but are fused most commonly anteriorly and at the thalami and there is partial diverticulation of brain (dorsal cyst). Features include 8-9 absence of septum pellucidum, monoventricle with partially developed occipital and temporal horns, rudimentary falx cerebri: absent anteriorly, incompletely formed interhemispheric fissure, partial or complete fusion of the thalami, absent olfactory tracts and bulbs, agenesis or hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and incomplete hippocampal formation. An easier approach might be to assess fusion of more than 50% of the frontal lobes which might be suggestive of semilobar HPE. In addition, this condition is associated with mild degree of facial abnormality such as hypotelorism and cleft lip. Case Report Two pregnant women with around weeks of gestation were reported to Gynaecology and Obstetrics OPD of North Bengal Medical College Hospital, Bangladesh for last trimester antenatal checkup. They were from shoal area from the bank of river Jamuna. Both parents were healthy and the marriage was nonconsanguineous. There was no family history of birth defects in both cases. They were primigravida with around years of ages. None of them had previous antenatal check up. Both of them had normal course of pregnancy. On examination, they were normotensive, mildly anaemic, non-icteric. On per abdominal examination, fundal height corresponded to 30 weeks of pregnancy. With this findings they were advised for CBC, RBS, Blood Grouping and Screening for HbsAg and ultrasonography of pregnancy profile. Blood chemistries were unremarkable. Ultrasounds of pregnancy profile were done at Department of Radiology and Imaging. It was observed in first case that septum pellucidum was absent in brain with partially formed falx cerebri, interhemispheric fissure with presence of large dorsal interhemispheric cyst (Figure 1). Figure No. 1: Ultrasonographic Scan of foetal head showing large dorsal interhemispheric cyst in semi lobar holoprocencephaly. 65
3 Occipital horn was rudimentary and thalami and basal ganglia were partially separated (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The spine, thoracic cage, heart, and limbs were sonologically normal. The posterior fossa structures were normal (Figure 3). This case was diagnosed as a case of semi lobar holoprocencephaly. In another case, septum pellucidum, falx cerebri and interhemispheric fissure were absent. Ventricle was monoventricular in appearance and thalami were fused (Figure 3 and figure 4). Figure No. 4: Coronal scan of foetal head of Alobar holoprocencephaly showing mono ventricle with fused thalami and absence of septum pellucidum, falx cerebri and interhemispheric fissure. Figure No. 2: Coronal ultrasonography of foetal head of semi lobar holoprocencephaly showing absence septum pellucidum in brain with partially formed falx cerebri, interhemispheric fissure. Figure No. 5: Coronal scan of foetal head of showing mono ventricle and absence of falx cerebri in Alobar holoprocencephaly. Figure No. 3: Ulrtasound scan showing rudimentary occipital horn and partially separated thalami and basal ganglia in semi lobar holoprocencephaly. This case was diagnosed as a case of alobar holoprocencephaly. Amniotic fluid was adequate in both of the cases at ultrasonography. Further evaluation by other imaging modalities were not possible in these two cases as parents did not give consent to perform any test and also refused to take treatment for this unfortunate pregnancies. 66
4 Figure No. 6: Coronal ultrasound image showing the fused thalami in the centre and large monoventricle (thick white arrow). The amniotic fluid around the fetus is normal in quantity. Discussion Holoprosencephaly is a spectrum of cerebrofacial anomalies resulting from the complete or partial failure of the diverticulation and cleavage of the primitive forebrain. During the 4th gestational week, the neural tube forms the three primary brain vesicles, namely, prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon. By the 5th week of intrauterine life, the prosencephalon further divides into the telencephalon and diencephalon. The telencephalon forms the two cerebral hemispheres whereas the diencephalon forms the thalami, the hypothalamus, and the basal ganglia. The prechordal mesoderm takes part in the formation of the midline facial structures. The degree of facial dysmorphism is proportional to the severity of the intracranial abnormalities and should direct the radiologist to search for the CNS anomalies 1,2,10. There are three main forms of holoprosencephaly, namely, alobar, semilobar and lobar varieties. The alobar holoprosencephaly is the most severe form and shows undifferentiated holosphere of the cerebral parenchyma with a central monoventricle and fused thalami 1,3. The falx, interhemispheric fissure, corpus callosum, optic tracts, olfactory bulbs, and the septum pellucidum are absent. Absence of septum pellucidum may be associated with septooptic dysplasia, holoprosencephaly, corpus callosal agenesis, schizencephaly, Chiari-II malformation, hydranencephaly, porencephaly, and cephaloceles (Figure 6) 5,6,10. In present case of alobar holoprocencephaly septum pellucidum, falx cerebri and interhemispheric fissure were absent. Ventricle was monoventricular in appearance and thalami were fused. A dorsal cyst may be observed in the posterior cranial fossa in very severe forms of holoprosencephaly (alobar) and some of these cases may also be associated with Dandy Walker malformation, agyria, polymicrogyria, and heterotopias 8,9. In present case reports dorsal cyst was seen in semi lobar holoprosencephaly. Alobar holoprosencephaly can be differentiated from hydrocephalus by the presence of midline echogenic falx, absent septum pellucidum, separated thalami, and distinct lateral ventricles in the latter. Hydranencephaly may also demonstrate absence or deviated falx but the thalami are not fused in this condition. In both hydranencephaly and Dandy Walker malformation, the falx cerebri, interhemispheric fissure, corpus callosum, and 3rd ventricle are present 1. However, the role of maternal MRI is in the confirmation of the sonographic findings and detection of any other additional anomaly. Postnatal MRI with diffusion fiber tractography may detect rare association of brain stem and long tract abnormalities in holoprosencephaly 10. The lobar and middle hemispheric variants are not associated with significant abnormalities of the white matter tracts whereas the alobar and semilobar forms are associated with abnormalities of the medial lemniscus and the corticospinal tracts 10. Ultrasonography features of semilobar holoprosencephaly include 8,9 absence of septum pellucidum, monoventricle with partially developed occipital and temporal horns, rudimentary falx cerebri: absent anteriorly, incompletely formed interhemispheric fissure, partial or complete fusion of the thalami, absent olfactory tracts and bulbs, agenesis or hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and incomplete hippocampal formation. In present case of semilobar holoprosencephaly, the septum pellucidum was absent in brain with partially formed falx cerebri, interhemispheric fissure with presence of large dorsal interhemispheric cyst. Occipital horn was rudimentary and thalami and basal ganglia were partially separated. Fetal karyotyping is advisable in all the cases of holoprosencephaly as most of them are associated with chromosomal anomalies 9,10. 67
5 However, karyotyping can not perform in all cases. Advanced investigations like fetal karyotyping is also not be available in all the places. So, antenatal diagnosis of holoprosencephaly by ultrasonography is essential in order to early diagnosis and to avoid the psychological pain of giving birth of a deformed baby at the end of pregnancy or delivering a still born baby. References 1. Sawhney S, Machado L, Jain R. Prenatal MRI Image of a Fetus with Semilobar Holoprosencephaly. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2008; 8(1): Wong Alex MC, Bilaniuk LT, Ng KK, Chang YL, Chao AS, Wai YY. Lobar holoprosencephaly: Prenatal diagnosis with post natal MR correlation. Prenat Diagn. 2005; 25: Filly RA, Chinn DH, Callen PW. Alobar holoprosencephaly: ultrasonographic prenatal diagnosis. RSNA 1984; 151 (2): Dubourg C, Bendavid C, Pasquier L et-al. Holoprosencephaly. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 2007; 2 (1): Simon EM, Hevner RF, Pinter JD et-al. The middle interhemispheric variant of holoprosencephaly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23 (1): Mcgahan JP, Nyberg DA, Mack LA. Sonography of facial features of alobar and semilobar holoprosencephaly. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154 (1): Paladini D, Volpe P. Ultrasound of Congenital Fetal Anomalies. Informa HealthCare. 8. Agarwal R. Prenatal diagnosis of holoprosencephaly: Pictorial essay. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2000; 10: Babcock DS. Sonography of congenital malformations of the brain. Neuroradiology 1986; 28: Raman R, Jagadesh GM. Antenatal Diagnosis of Alobar Holoprosencephaly. Case Reports in Radiology, Also available at: /2014/
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Alobar Holoprosencephaly Mauricio Castillo, 1 Thomas W. Bouldin, James H. Scat/iff, and Kinuko Suzuki Case Report After 37 weeks of gestation, a girl was born at another
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Alobar Holoprosencephaly Mauricio Castillo, 1 Thomas W. Bouldin, James H. Scat/iff, and Kinuko Suzuki Case Report After 37 weeks of gestation, a girl was born at another
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Case Report Interhypothalamic Adhesion in a 9-Month-Old Male with Cleft Palate
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 197415, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/197415 Case Report Interhypothalamic Adhesion in a 9-Month-Old Male with Cleft Palate Matthew T. Whitehead
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 197415, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/197415 Case Report Interhypothalamic Adhesion in a 9-Month-Old Male with Cleft Palate Matthew T. Whitehead
Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Fiber Tractography in Syntelencephaly
 BRAIN Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Fiber Tractography in Syntelencephaly S. Verschuuren, A. Poretti, A. Meoded, I. Izbudak, and T.A.G.M. Huisman ABSTRACT Syntelencephaly or the middle interhemispheric
BRAIN Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Fiber Tractography in Syntelencephaly S. Verschuuren, A. Poretti, A. Meoded, I. Izbudak, and T.A.G.M. Huisman ABSTRACT Syntelencephaly or the middle interhemispheric
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
The middle interhemispheric variant of holoprosencephaly
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:151 155, January 2002 The Middle Interhemispheric Variant of Holoprosencephaly Erin M. Simon, Robert F. Hevner, Joseph D. Pinter, Nancy J. Clegg, Mauricio Delgado, Stephen L. Kinsman,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:151 155, January 2002 The Middle Interhemispheric Variant of Holoprosencephaly Erin M. Simon, Robert F. Hevner, Joseph D. Pinter, Nancy J. Clegg, Mauricio Delgado, Stephen L. Kinsman,
Torch Infections and Prenatal Ultrasound Findings
 Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Ligneous conjunctivitis and holoprosencephaly a rare association
 Case Report Ligneous conjunctivitis and holoprosencephaly a rare association Divya Karuppannasamy*, Vikrant Kanagaraju**, Alo Sen* Department of Ophthalmology* and Radiology **, PSG Institute of Medical
Case Report Ligneous conjunctivitis and holoprosencephaly a rare association Divya Karuppannasamy*, Vikrant Kanagaraju**, Alo Sen* Department of Ophthalmology* and Radiology **, PSG Institute of Medical
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Fetal MRI. Page 1 of 69
 Fetal MRI Poster No.: C-0878 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Kocaba# Köksel, M. A. Oztek, C. Y. Sanhal, S. Toru, #. Mendilcio#lu, M. #im#ek, K. Karaali; Antalya/TR Keywords: Obstetrics,
Fetal MRI Poster No.: C-0878 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Kocaba# Köksel, M. A. Oztek, C. Y. Sanhal, S. Toru, #. Mendilcio#lu, M. #im#ek, K. Karaali; Antalya/TR Keywords: Obstetrics,
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management?
 Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
Spine and spinal cord
 NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
Apparent Atypical Callosal Dysgenesis: Analysis of MR Findings in
 333 pparent typical Callosal Dysgenesis: nalysis of MR Findings in Six Cases and Their Relationship to Holoprosencephaly. James arkovich 1 The MR scans of six pediatric patients with apparent atypical
333 pparent typical Callosal Dysgenesis: nalysis of MR Findings in Six Cases and Their Relationship to Holoprosencephaly. James arkovich 1 The MR scans of six pediatric patients with apparent atypical
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease. Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc.
 The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
Central Nervous System Malformations
 Review rticle Central 10.5005/jp-journals-10009-1472 Nervous System Malformations 1 D ddario Vincenzo, 2 Capuano Pasquale STRCT Ultrasound (US) is a useful tool to evaluate the normal morphology, the developmental
Review rticle Central 10.5005/jp-journals-10009-1472 Nervous System Malformations 1 D ddario Vincenzo, 2 Capuano Pasquale STRCT Ultrasound (US) is a useful tool to evaluate the normal morphology, the developmental
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 02 Page February 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
holoprosencephalic fetuses
 846 86 Med Genet 1991; 28: 846-855 The midline craniofacial skeleton in holoprosencephalic fetuses Inger Kjxr, Jean W Keeling, Niels Gram Abstract Craniofacial skeletal development in eight human holoprosencephalic
846 86 Med Genet 1991; 28: 846-855 The midline craniofacial skeleton in holoprosencephalic fetuses Inger Kjxr, Jean W Keeling, Niels Gram Abstract Craniofacial skeletal development in eight human holoprosencephalic
BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM..
 Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF ARACHNOID CYSTS
 REVIEW ARTICLE PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF ARACHNOID CYSTS Chih-Ping Chen* Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Mackay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, and Department of Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung,
REVIEW ARTICLE PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF ARACHNOID CYSTS Chih-Ping Chen* Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Mackay Memorial Hospital, Taipei, and Department of Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung,
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy. Basic Training
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects
 Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
 Agenesis of the corpus callosum What is a callosal disorder? Disorders of the corpus callosum are conditions in which the corpus callosum does not develop in a typical manner. Since these are disorders
Agenesis of the corpus callosum What is a callosal disorder? Disorders of the corpus callosum are conditions in which the corpus callosum does not develop in a typical manner. Since these are disorders
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO
 PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS, VOL. 16: 729-733 (1996) SHORT COMMUNICATION GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO JAMIYAH HASSAN*, WALDO SEPULVEDA*, JERONIMA TEIXEIRA*
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS, VOL. 16: 729-733 (1996) SHORT COMMUNICATION GLIOEPENDYMAL AND ARACHNOID CYSTS: UNUSUAL CAUSES OF EARLY VENTRICULOMEGALY IN UTERO JAMIYAH HASSAN*, WALDO SEPULVEDA*, JERONIMA TEIXEIRA*
International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI)
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Porencephalic cyst Mugtaba Alghazali, Ikhlas Abdelaziz, Hatim Zain Alabdeen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Porencephalic cyst Mugtaba Alghazali, Ikhlas Abdelaziz, Hatim Zain Alabdeen ABSTRACT Abstract is not required for Clinical Images International
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of:
 The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review
 Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele
 A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele Divyanshu Dubey, Sonjjay Pande, Pradeep Dubey, Anshudha Sawhney Vol. 3 No. 8 (August 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine
A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele Divyanshu Dubey, Sonjjay Pande, Pradeep Dubey, Anshudha Sawhney Vol. 3 No. 8 (August 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
I T IS well known that aneurysms occur at
 The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir. HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi
 Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus. Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto
 Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
The dorsal cyst in holoprosencephaly and the role of the thalamus in its formation
 Neuroradiology 2001) 43: 787±791 Ó Springer-Verlag 2001 PAEDIATRIC NEURORADIOLOGY E.M. Simon R. F. Hevner J. D. Pinter N. J. Clegg M. Delgado S. L. Kinsman J. S. Hahn A. J. Barkovich The dorsal cyst in
Neuroradiology 2001) 43: 787±791 Ó Springer-Verlag 2001 PAEDIATRIC NEURORADIOLOGY E.M. Simon R. F. Hevner J. D. Pinter N. J. Clegg M. Delgado S. L. Kinsman J. S. Hahn A. J. Barkovich The dorsal cyst in
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound
 From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound Without doubt, the B- Schwerdtfeger, R. tant diagnostic instrument. Furthermore, we use colour in feto- mode imaging is the most important
From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound Without doubt, the B- Schwerdtfeger, R. tant diagnostic instrument. Furthermore, we use colour in feto- mode imaging is the most important
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
MRI OF FETAL DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES
 MRI OF FETAL DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES Nadine J Girard, MD, PhD Department of Neuroradiology Timone Hospital 264 rue Saint Pierre, 13385 Marseille cedex 5, France nadine.girard@ap-hm.fr fax number : 33 4
MRI OF FETAL DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES Nadine J Girard, MD, PhD Department of Neuroradiology Timone Hospital 264 rue Saint Pierre, 13385 Marseille cedex 5, France nadine.girard@ap-hm.fr fax number : 33 4
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 8 years old male patient presented clinically with right sided hemiplegia since birth, Lennox Gastaut syndrome (with a history suggestive of infantile spasm during the
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: 8 years old male patient presented clinically with right sided hemiplegia since birth, Lennox Gastaut syndrome (with a history suggestive of infantile spasm during the
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
