Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
|
|
|
- Herbert Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD
2 Introduction Barkovich has classified posterior fossa developmental malformations into two subgroups, hypoplasia (incomplete formation) and dysplasia (abnormal formation) 1 Each subgroup in turn can be broken into focal and diffuse, suggesting local insult compared with generalized process (e.g. genetic or metabolic) 1 We also consider atrophy to represent a distinct subgroup
3 Introduction Our experience with developmental posterior fossa abnormalities has led us to realize that occasionally associated supratentorial anomalies are present Lack of attention to the cerebellum has delayed understanding of cerebellar developmental abnormalities in general, let alone their associations with supratentorial anomalies
4 Methods and Materials Review of our database of posterior fossa developmental abnormalities was performed to evaluate for associated supratentorial findings Attempt was then made to group the supratentorial abnormalities into various subtypes to better understand the potential associations
5 Results A total of 69 cases of developmental posterior fossa abnormalities were reviewed, revealing 17 cases with associated supratentorial findings Supratentorial anomalies included: dysplasia, heterotopia, corpus callosal and septal malformations, white matter de/dysmyelination, polymicrogyria, microcephaly and volume loss, hippocampal unfolding, basal ganglia malformations, and encephalocele
6 Table of Contents by Supratentorial Findings Dysplasia 3 Heterotopia Corpus callosal and septal malformations White matter de/dysmyelination Polymicrogyria 6 10 Microcephaly and volume loss Hippocampal unfolding Basal ganglia malformations Encephalocele 22 Bonus!
7 Conclusions Various supratentorial findings can be seen with developmental posterior fossa abnormalities A better appreciation of observed associations and their imaging characteristics can improve search patterns within the supratentorium when a developmental posterior fossa abnormality is identified
8 Conclusions While it may be premature to attempt understanding of supratentorial anomalies associated with posterior fossa developmental abnormalities given the poor overall comprehension of posterior fossa development, ultimately, understanding relations between supratentorial anomalies and developmental posterior fossa abnormalities may aid in attaining a robust fundamental genetic understanding of brain development BEGIN AGAIN
9 Bibliography 1. Barkovich AJ. Congenital malformations of the brain and skull. In: Barkovich AJ, eds. Pediatric Neuroimaging, 4 th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005: Bindal A, Storrs B, McLone D. Management of the Dandy-Walker syndrome. Pediatr Neurosci ;16: Goldowitz D, Hamre K. The cells and molecules that make a cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 1998;21: Goldowitz D, Hamre K, et al. Granule cells and cerebellar boundaries: analysis of Unc5h3 mutant chimeras. J Neurosci 2000;20: Millen K, Millonig J, Wingate R, et al. Neurogenetics of the cerebellar system. J Child Neurol 1999; 14: Murray J, Johnson J, Bird T. Dandy-Walker malformation: etiologic heterogeneity and empiric recurrence risks. Clin Genet 1985;28: Osenbach R, Menezes A. Diagnosis and management of the Dandy-Walker malformation: 30 years of experience. Pediatr Neurosurg 1992;18: Patel S, Barkovich AJ. Analysis and classification of cerebellar malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23: Rodriguez C, Dymecki S. Origin of the precerebellar system. Neuron 2000;27: Rubenstein J, Anderson S, et al. Genetic control of cortical regionalization and connectivity. Cereb Cortex 1999;9: Tamraz J, Retmore M, et al. Contributions of MRI to the knowledge of CNS malformations related to chromosomal aberrations. Hum Genet 1987;76: Utsunomiya H, Takano K, et al. Rhomboencephalosynapsis: cerebellar embryogenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19:547-9 BEGIN AGAIN
10 Case 1 Posterior Fossa Findings: Hypoplastic cerebellum Note that the pons appears normal Supratentorial Findings: Microcephaly High T2 SI within medial frontoparietal cortex & subcortical white matter Note that the corpus callosum is present
11 Case 1 Posterior fossa finding: High T2 SI within cerebellar white matter
12 Case 1 Mosaic trisomy 21 MRI obtained for severe developmental delay Posterior fossa findings could be considered generalized hypoplasia without cyst formation We believe that the posterior fossa findings and microcephaly are typical for trisomy 21 11, although the pons is not hypoplastic Aside from microcephaly, we believe that the supratentorial signal abnormalities may reflect a prior insult
13 Case 2 Posterior fossa findings: Hypoplastic vermis High fastigium Thin pontomesencephalic junction Supratentorial finding: Mild atrophy Note that the corpus callosum is formed
14 Case 2 Posterior fossa findings: Classic molar tooth sign seen with Joubert syndrome reflecting parallel, enlarged, horizontally oriented superior cerebellar peduncles Severe vermian hypoplasia
15 Case 2 MRI obtained for behavior problems, developmental delay, decreased muscular tone Sibling also has Joubert syndrome Posterior fossa findings considered focal cerebellar dysplasia of the vermis Molar tooth appearance is not diagnostic for Joubert and may be seen with other syndromes, some of which are associated with polymicrogyria, ocular anomalies, and hypothalamic anomalies 1
16 Case 3 Posterior fossa finding: Cystic dysplasia of the right cerebellar hemisphere inferior aspect Note that the pons and peduncles appear normal Supratentorial findings: Absent corpus callosum Colpocephaly
17 Case 3 Posterior fossa finding: Cystic dysplasia of the right cerebellar hemisphere inferior aspect Supratentorial findings: Right frontal anterolateral aspect cortical dysplasia Colpocephaly
18 Case 3 Posterior fossa finding: Cystic dysplasia of the right cerebellar hemisphere inferior aspect Supratentorial findings: Right posterior frontal periventricular heterotopia Colpocephaly
19 Case 3 MRI obtained for infantile spasms/ seizures Seizures resolved after right frontal resection Posterior fossa findings could be considered focal dysplasia, a poorly understood subject 1
20 Case 4 Posterior fossa findings: Cerebellar atrophy Thin cerebellar peduncles Note that the pons appears normal Supratentorial finding: Low T2 SI within the globus palladi
21 Case 4 Posterior fossa findings: Cerebellar atrophy Thin cerebellar peduncles Note that the pons appears normal Supratentorial findings: Atrophy Periventricular white matter high T2 SI
22 Case 4 MRI obtained for developmental delay and abnormal gait Mother also has developmental problems and is wheelchair bound Posterior fossa finding is considered atrophy with a normal sized pons Findings thought to represent cerebellar atrophy with ataxia, likely of a hereditary nature, although preliminary genetic tests have proven normal
23 Case 5 Posterior fossa findings: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Enlarged 4 th ventricle & foramen of Magendi Note that the pons and cerebellar peduncles appear normal Supratentorial findings: Microcephaly Severe corpus callosal dysgenesis Enlarged 3 rd & prominent lateral ventricles Simplified gyration
24 Case 5 Child was born slightly premature Multiple congenital abnormalities are present Phenotypically, child resembles Cornelia de Lange syndrome, but genetic tests have proven normal Posterior fossa findings are felt to primarily represent focal hypoplasia of the vermis
25 Case 6 Posterior fossa finding: Left mid cerebellar polymicrogyria Note that the pons and peduncles were normal in appearance (not shown) Supratentorial findings: Right periventricular heterotopia Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
26 Case 6 MRI obtained for seizures, which started at age 2.5 years Child also demonstrated hypotonia, spastic paraparesis with right hemiparesis, cognitive difficulties, and sensorineural hearing loss Posterior fossa finding is felt to represent focal dysplasia, a poorly understood topic
27 Case 7 Posterior fossa finding: Rhomboencephalosynapsis, i.e. absent vermis with fused cerebellar hemispheres, dentate nuclei, and superior cerebellar peduncles Supratentorial finding: Severe dysgenesis of the corpus callosum splenium & body
28 Case 7 Child born slightly premature due to hydrocephalus Multiple congenital abnormalities and developmental delay noted Abnormal genetic test, with BNORMAL male microarray CGH result arr cgh Xp22.31 ( )x2 [hg17; NCBI(B35)] Posterior fossa finding is considered focal dysplasia Various additional supratentorial findings have been noted, including fused thalami, absent septum pellucidum, olivary hypoplasia, limbic system anomalies, cortical malformations, and craniosynostosis 1 Appreciation of supratentorial findings in the setting of rhomboencephalosynapsis is important given that they appear to dominate the clinical picture 12 Fundamentally, this anomaly may represent a genetic malexpression affecting midline structures, as suggested by FGF8 gene activity in the cerebral midline (rostrodorsal septum) and the isthmic organizer (important in cerebellar induction) 10
29 Case 8 Posterior fossa finding: Right inferior cerebellar dysplasia Note that the pons and peduncles were normal in appearance (not shown) Supratentorial finding: Nodular subependymal heterotopia in the bilateral ventricular atrium region
30 Case 8 Ocular motor apraxia noted Given findings in sibling, question of X- linked nature of anomalies was raised Posterior fossa finding is considered focal dysplasia, a poorly understood subject
31 Case 9 Posterior fossa finding: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Dysplastic and hypoplastic cerebellar hemispheres Supratentorial finding: Atrophy
32 Case 9 Posterior fossa findings: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Enlarged 4 th ventricle & foramen of Magendie Note that the pons and peduncles are normal in appearance
33 Case 9 Child demonstrated craniosynostosis with absent sphenoid wing and severe developmental delay, as well as a few other congenital anomalies Balanced 1:7 translocation (p22q31.2) found Posterior fossa finding is most likely classified as a generalized dysplasia The extent of the posterior fossa abnormalities compared with the relative lack of supratentorial findings is striking and unusual
34 Case 10 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic cerebellar hemispheres Note the pons was normal in appearance Supratentorial findings: Corpus callosal dysgenesis Midline cyst in the quadrigeminal cistern
35 Case 10 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic cerebellar hemispheres Supratentorial findings: Severe colpocephaly Frontal polymicrogyria
36 Case 10 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic cerebellar hemispheres Supratentorial findings: Colpocephaly Mass-like subependymal heterotopia Note that poor hippocampal folding was also seen (not shown)
37 Case 10 Child had sensorineural hearing loss and mild motor developmental delay Case 11 is a sibling, with remarkably similar findings Possibility of Chudley-McCollough syndrome was raised Posterior fossa findings considered generalized dysplasia, in keeping with the severe supratentorial anomalies
38 Case 11 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic cerebellar hemispheres Supratentorial findings: Corpus callosal dysgenesis Midline cyst in the quadrigeminal cistern
39 Case 11 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic cerebellar hemispheres Supratentorial findings: Colpocephaly Mass-like subependymal heterotopia Note that polymicrogyria and poorly folded hippocampi were also noted (not shown)
40 Case 11 Child had sensorineural hearing loss Case 10 is sibling Possibility of Chudley-McCollough syndrome was raised Posterior fossa finding is considered generalized dysplasia, in keeping with the severe supratentorial anomalies
41 Case 12 Posterior fossa findings: Dysplastic vermis Small right middle cerebellar peduncle Supratentorial findings: Fused striatum Large lateral ventricles
42 Case 12 Posterior fossa finding: Dysplastic vermis
43 Case 12 Truncal hypotonia and developmental delay noted All genetic tests normal to date Posterior fossa finding likely represents focal dysplasia
44 Case 13 Posterior fossa findings: Cerebellar hypoplasia Flat pons High fastigium Dysplastic superior vermis Supratentorial findings: Dysgenetic corpus callosum Hydrocephalus Microcephaly Bilateral medial occipital gliosis
45 Case 13 Posterior fossa findings: Cerebellar hypoplasia Flat pons High fastigium Supratentorial findings: Fused striatum Hydrocephalus Note that partially absent septum pellucidum was also seen (not shown)
46 Case 13 Child had severe developmental delay, cortical blindness, and seizure disorder Child clinically thought to demonstrate septooptic dysplasia Posterior fossa findings likely classified as generalized hypoplasia, (with presence of focal dysplasia), with a normal fourth ventricle and no posterior fossa cyst and a hypoplastic pons, although likely not of the classically known pontocerebellar hypoplasia types I or II
47 Case 14 Posterior fossa findings: Cerebellar atrophy Small cerebellar peduncles Note that the pons appears normal Supratentorial findings: Severe corpus callosal thinning Severe atrophy Simplified gyration High T2 SI within white matter representing de/dysmyelination
48 Case 14 Global developmental delay and seizure disorder noted Two siblings demonstrated similar MR findings, one of whom died before 2 years of age Possibility of a muscle-eye-brain autosomal recessive disorder raised Posterior fossa finding is considered atrophy with a normal sized pons
49 Case 15 Posterior fossa findings: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Kissing cerebellar tonsils Note that the pons and cerebellar peduncles appear normal Supratentorial finding: Left temporoccipital subependymal heterotopia
50 Case 15 Posterior fossa findings: Inferior vermian hypoplasia Kissing cerebellar tonsils Note that the pons and cerebellar peduncles appear normal Supratentorial finding: Left temporoccipital subependymal heterotopia
51 Case 15 Posterior fossa finding is considered to be focal vermian hypoplasia
52 Case 16 Posterior fossa finding: Rhomboencephalosynapsis, i.e. absent vermis with fused cerebellar hemispheres, dentate nuclei, and superior cerebellar peduncles Note that there was normal appearing pons and cerebellar peduncles (not shown) Supratentorial finding: Thinned corpus callosum & absent septum pellucidum
53 Case 16 Child demonstrated ataxia and craniosynostosis Posterior fossa finding is considered to be focal dysplasia Various additional supratentorial findings have been noted, including fused thalami, olivary hypoplasia, limbic system anomalies, cortical malformations 1 Appreciation of supratentorial findings in the setting of rhomboencephalosynapsis is important given that they appear to dominate the clinical picture 12 Fundamentally, this anomaly may represent a genetic malexpression affecting midline structures, as suggested by FGF8 gene activity in the cerebral midline (rostrodorsal septum) and the isthmic organizer (important in cerebellar induction) 10
54 Case 17 Posterior fossa finding: Absent pons Supratentorial finding: Simplified gyration
55 Case 17 Child thought to demonstrate primary dysgenesis of the neural tube at the level of rhombomere-1 due to defective expression of homeobox gene EN2 for WNT1 Gene En2 appears to play a role in specifying cerebellar domains in embryos 5 Wnt family of signaling molecules appears to be involved in cerebellar development, restricting cerebellar granule cell migration, thus acting to guide axons within the developing brain 3,4,9 Additional congenital anomalies noted Both posterior fossa and supratentorial findings fail to fall within the classification schemes we have used, but we wanted to share this amazing case
56 Case 18 Posterior fossa findings: Severe cerebellar atrophy Small superior cerebellar peduncles Note that the pons appears normal Supratentorial findings: Severe atrophy Periventricular white matter high T2 SI representing de/dysmyelination
57 Case 18 Constellation of severe postnatal growth failure, developmental delay, light sensitivity, hearing loss, calcification of the basal ganglia, and retinal degeneration all suggest Cockayne syndrome Posterior fossa finding is considered atrophy with a normal appearing pons
58 Case 19 Posterior fossa findings: Classic Dandy-Walker syndrome, with enlarged posterior fossa with 4 th ventricle communicating with cystic space & absent vermis Flat pons High tentorium Supratentorial findings: Hydrocephalus Dysgenetic corpus callosum Absent septum pellucidum
59 Case 19 Posterior fossa findings: Dandy-Walker syndrome, with enlarged posterior fossa with 4 th ventricle communicating with cystic space & absent vermis Supratentorial finding: Hydrocephalus
60 Case 19 Dandy Walker malformation is an example of generalized hypoplasia with cyst formation in Barkovich s classification Presence of supratentorial anomalies in Dandy Walker malformation is associated with poorer prognosis 1 Hydrocephalus is present in 90% at time of diagnosis 7 Callosal anomalies are present in 32-55% 2,8 Polymicrogyria is present in 5-10% Occipital encephalocele is present in 16% 2 Dandy Walker malformation likely results from a genetic predisposition, with an observed sibling recurrence rate of 6% 6
61 Case 20 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Thinned corpus callosum Absence of myelin Hippocampal unfolding Simplified gyration
62 Case 20 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Small basal ganglia Enlarged ventricles Absence of myelin Simplified gyration Thinned corpus callosum
63 Case 20 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Absence of myelin Enlarged ventricles Simplified gyration Thinned corpus callosum
64 Case 20 Sibling of Case 21, with remarkably similar imaging findings Posterior fossa findings considered generalized hypoplasia with a small pons
65 Case 21 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Thinned corpus callosum Absence of myelin Simplified gyration
66 Case 21 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Small basal ganglia Ventriculomegaly Absence of myelin Simplified gyration Thinned corpus callosum
67 Case 21 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Absence of myelin Simplified gyration Thinned corpus callosum
68 Case 21 Posterior fossa findings: Pontocerebellar hypoplasia Supratentorial findings: Hippocampal unfolding Absence of myelin Simplified gyration Thinned corpus callosum
69 Case 21 Sibling of Case 20, with remarkably similar imaging findings Posterior fossa findings considered generalized hypoplasia with a small pons
70 Case 22 Posterior fossa findings: Right greater than left cerebellar hemisphere hypoplasia Dandy-Walker syndrome, with enlarged posterior fossa with 4 th ventricle communicating with cystic space & severely hypoplastic vermis Flat pons High tentorium Supratentorial finding: Occipital encephalocele
71 Case 22 Posterior fossa findings: Right greater than left cerebellar hemisphere hypoplasia Dandy-Walker syndrome, with enlarged posterior fossa with 4 th ventricle communicating with cystic space & severely hypoplastic vermis Supratentorial findings: Occipital encephalocele Simplified gyration
72 Case 22 Dandy Walker malformation is an example of generalized hypoplasia with cyst formation in Barkovich s classification Presence of supratentorial anomalies in Dandy Walker malformation is associated with poorer prognosis 1 Occipital encephalocele is present in 16% 2 Hydrocephalus is present in 90% at time of diagnosis 7 Callosal anomalies are present in 32-55% 2,8 Polymicrogyria is present in 5-10% Dandy Walker malformation likely results from a genetic predisposition, with an observed sibling recurrence rate of 6% 6
Posterior fossa malformations
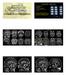 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (118)
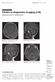 Medical Education Singapore Med 1 2007, 48 (9) : 869 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (118) Subramanian S, Hari S, Santosh Kumar S Fig. I Axial TI -W image of the brain taken at the level of the
Medical Education Singapore Med 1 2007, 48 (9) : 869 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (118) Subramanian S, Hari S, Santosh Kumar S Fig. I Axial TI -W image of the brain taken at the level of the
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42 cases
 Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus. Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto
 Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain
 The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of congenital brain malformations at a referral hospital in Saudi Arabia: An MRI study Ibrahim A. Alorainy BACKGROUND: More than 2000 different congenital cerebral malformations
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of congenital brain malformations at a referral hospital in Saudi Arabia: An MRI study Ibrahim A. Alorainy BACKGROUND: More than 2000 different congenital cerebral malformations
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 02 Page February 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects
 Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
January 2004 Use of MRI in Evaluating Fetal Ventriculomegaly Lisa McLeod, Harvard Medical School Year III http://bidmc.harvard.edu/content/departments/radiology/files/fetalatlas/default.htm Objectives:
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov Dandy-Walker Malformation
 REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations.
 MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations. Poster No.: C-0814 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cabaj, M. Bekiesinska-Figatowska, A. Duczkowska, M. Duczkowski;
MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations. Poster No.: C-0814 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cabaj, M. Bekiesinska-Figatowska, A. Duczkowska, M. Duczkowski;
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management?
 Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa Bosemani, Thangamadhan;
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa Bosemani, Thangamadhan;
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4
 A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Ningappa, Vaishali D. M, Vijayaraghavachari
A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Ningappa, Vaishali D. M, Vijayaraghavachari
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Science & Technologies. A CASE OF HYDROCEPHALUS AND DANDY-WALKER SYNDROME IN A CALF Murat ÇALIŞKAN 1, Soner ÇAĞATAY 1, Ömer BEŞALTI 1
 A CASE OF HYDROCEPHALUS AND DANDY-WALKER SYNDROME IN A CALF Murat ÇALIŞKAN 1, Soner ÇAĞATAY 1, Ömer BEŞALTI 1 1 Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Surgery, Ankara-Turkey Abstract
A CASE OF HYDROCEPHALUS AND DANDY-WALKER SYNDROME IN A CALF Murat ÇALIŞKAN 1, Soner ÇAĞATAY 1, Ömer BEŞALTI 1 1 Ankara University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Surgery, Ankara-Turkey Abstract
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
NYEIS Version 4.3 (ICD) ICD - 10 Codes Available in NYEIS at time of version launch (9/23/2015)
 D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Heterotopia represent malformations of cortical development
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Location of Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia Is Related to the Malformation Phenotype on MRI G. González, L. Vedolin, B. Barry, A. Poduri, C. Walsh, and A.J. Barkovich ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Location of Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia Is Related to the Malformation Phenotype on MRI G. González, L. Vedolin, B. Barry, A. Poduri, C. Walsh, and A.J. Barkovich ABSTRACT
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
Congenital microcephaly (a very small head at birth) can be
 Published March 31, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2440 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Adachi A. Poduri A. Kawaguch G. Yoon M.A. Salih F. Yamashita C.A. Walsh A.J. Barkovich Congenital Microcephaly with a Simplified Gyral
Published March 31, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2440 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Adachi A. Poduri A. Kawaguch G. Yoon M.A. Salih F. Yamashita C.A. Walsh A.J. Barkovich Congenital Microcephaly with a Simplified Gyral
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients
 Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele
 A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele Divyanshu Dubey, Sonjjay Pande, Pradeep Dubey, Anshudha Sawhney Vol. 3 No. 8 (August 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine
A Case of Naso-Ethmoidal Meningoencephalocele Divyanshu Dubey, Sonjjay Pande, Pradeep Dubey, Anshudha Sawhney Vol. 3 No. 8 (August 2011) International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine
Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2012; 54: 605-611 Original Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases Faruk İncecik 1, M. Özlem Hergüner 1, Şakir Altunbaşak 1, Joseph G. Gleeson 2 1 Department of Pediatric
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2012; 54: 605-611 Original Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases Faruk İncecik 1, M. Özlem Hergüner 1, Şakir Altunbaşak 1, Joseph G. Gleeson 2 1 Department of Pediatric
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1037 1043, June/July 1999 Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations Woo Ho Cho, David Seidenwurm, and A. James Barkovich BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1037 1043, June/July 1999 Adult-Onset Neurologic Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Malformations Woo Ho Cho, David Seidenwurm, and A. James Barkovich BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Elliott Sherr, MD University of California, San Francisco
 University of California, San Francisco ACC AND A SSOCIATED F EATURES MRI features associated with ACC Clinical diagnoses found in individuals with ACC Clinical Syndromes in which ACC is a component or
University of California, San Francisco ACC AND A SSOCIATED F EATURES MRI features associated with ACC Clinical diagnoses found in individuals with ACC Clinical Syndromes in which ACC is a component or
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Partial rhombencephalosynapsis and Chiari II malformation; 局部後腦窩先天性畸形和 II 型小腦篇桃體延隨聯合畸形
 Title Partial rhombencephalosynapsis and Chiari II malformation; 局部後腦窩先天性畸形和 II 型小腦篇桃體延隨聯合畸形 Author(s) Wan, SMY; Khong, PL; Ip, P; Ooi, GC Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2005, v. 11 n. 4, p. 299-302;
Title Partial rhombencephalosynapsis and Chiari II malformation; 局部後腦窩先天性畸形和 II 型小腦篇桃體延隨聯合畸形 Author(s) Wan, SMY; Khong, PL; Ip, P; Ooi, GC Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2005, v. 11 n. 4, p. 299-302;
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES)
 AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
syndromes associated with brain malformation - dysmorphology Renske Oegema, MD, PhD clinical geneticist UMC Utrecht, NL Milano, 2018
 syndromes associated with brain malformation - dysmorphology Renske Oegema, MD, PhD clinical geneticist UMC Utrecht, NL Milano, 2018 Miller Dieker syndrome, del 17p13.3 incl LIS1 en YWHAE Postnatal mild
syndromes associated with brain malformation - dysmorphology Renske Oegema, MD, PhD clinical geneticist UMC Utrecht, NL Milano, 2018 Miller Dieker syndrome, del 17p13.3 incl LIS1 en YWHAE Postnatal mild
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Epilepsy in children: Review of the main causes detectable by MRI
 Epilepsy in children: Review of the main causes detectable by MRI Poster No.: C-2182 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. A. S. M. D. Santos, T. C. R. S. SANTOS, A. Monteiro ; 1 1 1
Epilepsy in children: Review of the main causes detectable by MRI Poster No.: C-2182 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. A. S. M. D. Santos, T. C. R. S. SANTOS, A. Monteiro ; 1 1 1
Anomalies of the Corpus Callosum: An MR Analysis of the Phenotypic Spectrum of Associated Malformations
 MRI of Anomalies of the Corpus Callosum Neuroradiology Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Steven W. Hetts 1 Elliott H. Sherr 2 Stephanie Chao 3 Sarah Gobuty 2 A. James Barkovich
MRI of Anomalies of the Corpus Callosum Neuroradiology Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Steven W. Hetts 1 Elliott H. Sherr 2 Stephanie Chao 3 Sarah Gobuty 2 A. James Barkovich
The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy MRI. Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation
 Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES)
 HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
Cerebellar Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Autism shares features with cerebellar syndromes
 NEWS Autism shares features with cerebellar syndromes BY KELLY RAE CHI 3 DECEMBER 2009 1 / 7 2 / 7 Misshapen structures: MRI scans show that, compared with controls (A), the cerebellum of a child with
NEWS Autism shares features with cerebellar syndromes BY KELLY RAE CHI 3 DECEMBER 2009 1 / 7 2 / 7 Misshapen structures: MRI scans show that, compared with controls (A), the cerebellum of a child with
