DIFFUSION MRI OF FOCAL LIVER LESIONS
|
|
|
- Duane Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIFFUSION MRI OF FOCAL LIVER LESIONS Iman Abbas Hosny Department of Radiodiagnosis, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt. : ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the diagnostic contribution of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for characterization of hepatic masses and differentiation of benign and malignant lesions. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty-eight patients with focal liver lesions that were detected by US or CT scan underwent diffusionweighted MRI (DWI) in addition to routine MRI. Two b values (b=0 s/mm 2, 1000 s/mm 2 ) were used and the quantitative analysis of the diffusion (ADC) was calculated. RESULTS: The liver masses were diagnosed on histology or had characteristic MRI findings and follow up of more than 6 months. The analyzed lesions were hemangioma (n = 9), cysts (n = 2), hepatocellular cancer (HCC) (n = 20), and metastases (n = 7). CONCLUSION: The diffusion-weighted MRI sequence is a useful diagnostic tool and it can contribute to accurate diagnosis and discrimination between benign and malignant hepatic masses. The single-shot EPI with ipat and fat suppression has produced very satisfactory body diffusion results. DWI can significantly reduce the need for intravenous administration of contrast medium in evaluation of malignancies. Key Words: DW MRI liver; focal liver lesions; ADC of focal liver lesions Introduction Diffusion is the term used for the randomized microscopic movement of water molecules known as Brownian motion. Diffusion is known to be a sensitive parameter in microscopic tissue characterization. Diffusionweighted imaging can be performed after strong bipolar pulses are added to spin echo or gradient echo sequences with various b-values. The b-value represents the diffusion factor (measured in s/mm 2 ) and the strength of the diffusion gradients. The ideal b-value for lesion characterization is a trade-off between signal attenuation and perfusion contamination. This is generally possible using b-values between 400 and 1000 s/mm 2 for liver imaging. Pure diffusion contrast is obtained when using b-values above 1000 s/mm 2. However, image quality can be limited by signal loss that occurs at such b-values and higher. 1 Diffusion-weighted MRI examinations have many technical restrictions such as respiratory, cardiac, or Correspondence : Dr. Iman Abbas Hosny A. Professor of Radiodiagnosis, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt. imanabbas95@yahoo.com peristaltic physiologic activity, all of which affect image quality and make evaluation, which is very sensitive to motion, more difficult. Consequently, prior to the development of fast MRI techniques, diffusion-weighted imaging was limited to cranial examinations.with the development of echo-planar imaging (EPI), a fast MRI technique, radiologists have overcome the long imaging times and related artifacts of conventional techniques, and diffusion-weighted MRI is now available for abdominal evaluations as well. 2 The amount of diffusion is defined using the diffusion coefficient. Diffusion coefficient measurement in vivo is affected by several factors in biological tissues. Capillary perfusion, temperature, magnetic sensitivity of the tissue, and motion affect the actual diffusion; therefore, the term apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) is used rather than diffusion coefficient. 3 Material and Methods Thirty-eight patients (27 men, 11 women; aged 75 to 35 years,mean age, 48 years) with focal liver lesions 01
2 that were detected by US or CT scan underwent diffusion-weighted MRI in addition to routine MRI using 1.5-T whole body Philips machine and a body phasedarray coil.the imaging parameters of DW MRI with SE-echo planar imaging (EPI) sequence were set as follows: repetition time ms/echo time ms: 1000/120; matrix: ; field of view: 36 cm 36 cm; section thickness: 8 mm; gap: 2 mm. Two b values (b=0 s/mm 2, 1000 s/mm 2 ) were used, and scan time of 3 to 4 minutes. The quantitative analysis of the diffusion (ADC) was calculated on a workstation by applying a ROI on the image. Following DWI, contrast enhanced dynamic imaging was performed with an axial 3D gradient-echo T1-weighted MR sequence during and after administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine in a dose of 0.1 mmol/kg of body weight as a bolus injection. All patients included in this study gave informed consent prior to MRI examination. The diagnosis of all cases of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic metastasis was confirmed by -fetal protein, clinical data, ultrasound or CT, MR imaging, and pathology. Whereas the diagnosis of all the cases of cavernous hemangioma and hepatic cyst was confirmed by clinical data, ultrasound or CT, MR imaging, and follow-up observation. The following criteria were used to categorize focal liver lesions on MRI. A lesion was considered benign (mostly cyst and hemangioma) if the lesion was hyperintense on T2- weighted images and on DW images at b-0 s/mm 2 with a strong signal intensity decrease at b-1000 s/mm 2 and an ADC that was subjectively higher than that of the liver. A lesion was considered malignant (mostly metastasis or HCC) if the lesion was mildly to moderately hyperintense on T2-weighted images and on DW images at b-0 s/mm 2 and remained hyperintense compared with liver parenchyma at b-1000 s/mm 2, with an ADC qualitatively lower than that of the surrounding liver. ADC map measurements of benign and malignant hepatic masses were significantly different. Cysts and hemangiomas had the highest ADC values while malignant masses had the lowest. (Tab. 1) Number of cases Focal hepatic lesions Hepatic cyst Hepatic hemangioma Hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatic metastasis ADC Table 1: ADC value in the 38 focal hepatic lesions (b-1000 s/mm 2, mean SD) Figure 1A: x10-3 s/mm x 10-3 s/mm x10-3 s/mm x 10-3s/mm 2 Results The liver masses were diagnosed on histology or had characteristic MRI findings and follow up of more than 6 months. The analyzed lesions were cysts (n = 2), hemangioma (n = 9 ), hepatocellular cancer (HCC) (n = 20), and metastases (n = 7). In the present study, Figure 2A: 02
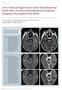
3 Figure 1C: Figure 2C: Figure 1A,B,C: MRI of 55-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer. The solitary metastatic lesion of segment 6 demonstrates restricted diffusion: It is hyperintense on T2 WI (a) and remains hyperintense on DW MRI at b s/mm 2 (b) with low ADC 0.85 s/mm 2 (c). Figure 2D: Figure 2E: Figure 2A: Figure 2B: Figure 2A,B,C,D,E: MR images in 68-year-old man with large HCC of the right lobe. The lesion presents low T1 (a), high T2 signal (b), remains hyperintense on DW MRI at b_1000 sec/mm 2 (c), low ADC 0.96 s/mm 2 (d), compatible with a malignant lesion. Postcontrast T1-weighted image (e), confirms arterial-phase vascular non homogenous enhancing lesion. 03
4 Discussion Figure 3A: Figure 3B: Figure 3C: Figure 3A,B,C: MR images in 38 year-old woman man with hemangioma of sgment 5. The hemangioma demonstrates free diffusion: It is hyperintense on T2 WI (a) and hypointense on DW MRI at b-1000 s/mm 2 (b), with high ADC 2.4 s/mm 2 (c). Although dynamic contrast enhanced examinations have become a routine component of abdominal imaging, the high cost/benefit ratio and risk of contrast media side effects remain an issue. Moreover, sometimes it is not possible to distinguish between highly vascular metastases and hemangiomas, even using dynamic examination. 4 Diffusion imaging is MRI technique that can be used to quantify diffusion of water molecules noninvasively in biological tissues. The random motion of water molecules outside of the body is uninhibited and called free diffusion. However, in vivo, the diffusion is restricted because of macromolecules and intact cell membranes. Diffusion restriction increases in highly cellular tissues. In contrast, it decreases in low cellular tissues with large extracellular space or with broken down cellular membranes. 5 DW images may be evaluated both qualitatively and quantitatively. The ADC, as a quantitative parameter calculated from DWI, combines the effects of capillary perfusion and water diffusion in the extracellular extravascular space. 6 The effect of perfusion on the ADC is most pronounced with low b values (e.g., b-0-50 s/mm ). By contrast, high b values mostly overcome this effect (e.g., b-1000 s/mm ). Areas of restricted diffusion show low ADC values and appear as a low signal area (opposite to DW images at high b values). 7 Our study was carried out with b values of 0 and 1000 s/mm 2. The primary application of DWI was neuroimaging, with its greatest use being for detection of acute cerebral stroke. 8 With the advent of the EPI technique, DWI of the abdomen has become possible with fast imaging times minimizing the effect of gross physiologic motion from respiration and cardiac movement. 9 In addition, the use of ipat (integrated Parallel Acquisition Techniques msense and GRAPPA) has improved the image quality in EPI DWI, by reducing susceptibility artifacts. 10 In our study,the used single-shot EPI with ipat and fat suppression has produced very satisfactory body diffusion results. Recent studies have used DWI to characterize liver lesions and have shown that benign lesions, such as liver cysts and hemangiomas, 04
5 show higher ADCs than malignant lesions. 11 This is likely related to free water motion in benign lesions, and restricted water motion in the presence of a tumor. However, ADC values often vary from one study to another, partially related to different equipment and different b-values. 12 Fat suppression is also an important issue in achieving best results. 13 In a study carried by Ichikawa etal, 14 b values were quite low (i.e.,1.6,16,and 55) and ADC values for abdominal organs were high. They reported that when the b value is kept low, factors like perfusion and T2 time have greater relative effect on ADC measurements. For that reason, they concluded that for abdominal diffusion studies, values >400 s/mm 2 might reflect ADC measurements more accurately. However, again, Ichikawa et al. reported that higher b values cause lower quality on diffusion weighted images and make evaluation harder. In our study, DW MRI was carried on using b values of 0 and 1000 s/mm 2. Adequate image quality was obtained by applying the parallel imaging technique, which uses the spatial information from a phased-array multicoil to reduce the number of signals needed for a given spatial resolution, thereby improving the quality of EPI and these results conform with those obtained with Zeich etal, 15 and K l kesmez etal. 16 On low b-value diffusion- weighted MR images, all masses were observed as hyperintense, whereas on high b-value images signals of cysts disappeared and signals of hemangiomas obviously decreased (Fig. 3). In contrast, since there is a limitation of diffusion in solid tumors, they were also observed as hyperintense on high b-value diffusion weighted image (Fig. 1,2) and these results conform with those obtained by several others. 17,18,19 Also, the ADC measurements of benign and malignant hepatic masses were significantly different, which supports similar previous findings. 20,21,22 Cysts and hemangiomas had the highest ADC values while malignant masses had the lowest. The mean ADC value for cystic lesions was x10-3 s/mm 2, whereas for hemangiomas it was x 10-3 s/mm 2. The lowest ADC values among the malignant masses belonged to metastases x 10-3s/mm 2. This data is similar to Taouli et al. findings. 23 Mean ADC value for HCC was x10-3 s/mm2. According to Chan et al, 24 necrotic tumors present high ADC values.in our study, there were no necrotic or cystic lesions among the malignant tumors. Other limitation of our study, was the low number of lesions and the absence of solid benign hepatocellular lesions (e.g., hepatic adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia), abscesses and parasitic cysts. Benign hepatocellular mass lesions were first evaluated by Taouli et al 23 and their ADC values were found to be lower than cysts and hemangiomas, and higher than malignant masses. In another study carried by Demir etal, 25 the mean ADC values of the 2 hydatid cysts were not significantly different from simple cysts. On the other hand, the mean ADC value was significantly lower for hepatic abscesses compared to simple cysts. Conclusion The diffusion-weighted MRI sequence is a useful diagnostic tool with no need to use contrast media, and it can contribute to accurate diagnosis and discrimination between benign and malignant hepatic masses. The single-shot EPI with ipat and fat suppression has produced very satisfactory body diffusion results. This adds only 3 to 4 minutes to the entire examination and has proven very useful for the detection of primary as well as metastatic malignant tumors, differentiation between benign and malignant tumors. DWI significantly can reduce the need for intravenous administration of contrast medium in evaluation of focal liver lesions. References Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Sumi S. Focal liver masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology September 1997; 24: Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Beek LT. Improved focal liver lesion detection: comparison of singleshot diffusion-weighted echoplanar and single-shot T2 weighted turbo spin echo techniques. The British Journal of Radiology 2007; 80:
6 3. Sandrasegaran K, Akisik FM, C. The Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Characterizing Focal Liver Masses. Academic Radiology October 2009; 16 (10): Zheng WW, Zhou KR, Chen ZW, Shen JZ, Chen CZ, Zhang SJ. Characterization of focal hepatic lesions with SPIO enhanced MRI. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8 (1): Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H. Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999; 173: Sun XJ, Quan XY, Fan-Heng Huang FH et al. Quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of focal hepatic lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11 (41): Taouli BB, Ichiba N.Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Medical Solutions October 2005: Lutsep HL, Albers GW, DeCrespigny A, Kamat GN, Marks MP, Moseley ME. Clinical utility of diffusionweighted magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 1997; 41: Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with singleshot echo-planar imaging in the upper abdomen: preliminary clinical experience in 61 patients. Abdom Imaging 1999; 24: Yoshikawa T, Kawamitsu H, Mitchell DG. ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. Am J Roentgenol 2006; 187: Drew SJ,LeeVS, Wong S. Focal Liver Lesion Detection and Characterization with Diffusion weighted MR Imaging: Comparison with Standard Breath-hold T2-weighted Imaging. Radiology March 2008 ; 246 (3). 12. Bruegel M, Holzapfel K, Gaa J, Woertler K, Waldt S, Kiefer B, Stemmer A, Ganter C, Rummeny EJ. Characterization of focal liver lesions by ADC measurements using a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging technique.eur Radiol. March 2008; 18 (3): Bruegel M, Jochen G J. Diagnosis of hepatic metastasis: comparison of respiration-triggered diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI and five t2- weighted turbo spin-echo sequences AJR. American journal of roentgenol. 2008; 191(5): Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. Am J Roentgenol. February 1998; 170(2): Zech CJ, Herrmann KA, Dietrich O, Horger W, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. Black-blood diffusionweighted EPI acquisition of the liver with parallel imaging: comparison with a standard T2-weighted sequence for detection of focal liver lesions. Invest Radiol. April 2008; 43(4): K l kesmez O, Yirik G, Bayramoglu S, Cimilli T, Aydin S.Non breath hold high b value D W MRI parallel imaging techniquiewith : ADC determination in normal abdominal organs. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2008; 14 (2): Moteki T, Horikoshi H, Oya N, Aoki J, Endo K. Evaluation of hepatic lesions and hepatic parenchyma using diffusion weighted reordered turbo FLASH magnetic resonance images. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 15: Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Nawano S. Hepatic metastases: diffusion-weighted sensitivity encoding versus SPIOenhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2006; 239: Quan XY, Sun XJ, Yu ZJ, Tang M. Evaluation of diffusion weighted imaging of magnetic resonance imaging in small focal hepatic lesions: a quantitative study in 56 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. August 2005; 4 (3):
7 Kandpal H, Sharma R, Madhusudhan KS, Kapoor KS. Respiratory-Triggered Versus Breath-Hold Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Liver Lesions: Comparison of Image Quality and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values. AJR 2009; 192 (4): Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Ter Beek L, Haspeslagh M, Bipat S, Stoker J, Steyaert L, Rigauts H.Evaluation of true diffusion, perfusion factor, and apparent diffusion coefficient in non-necrotic liver metastases and uncomplicated liver hemangiomas using black-blood echo planar imaging.eur J Radiol. January 2009; 69 (1): Coenegrachts K, Matos C, ter Beek L, Metens T, Haspeslagh M, Bipat S, Stoker J, Rigauts H. Focal liver lesion detection and characterization: comparison of non-contrast enhanced and SPIOenhanced diffusion-weighted single-shot spin echo echo planar and turbo spin echo T2-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. December 2009; 72 (3): Taouli B, Vilgrain V, Dumont E, Daire JL, Fan B, Menu Y. Evaluation of liver diffusion isotropy and characterization of focal hepatic lesions with two single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequences: prospective study in 66 patients. Radiology 2003; 226: Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH. Diffusion weighted MR imaging of the liver: distinguishing hepatic abscess from cystic or necrotic tumor. Abdom Imaging 2001; 26: Demir OI, Obuz F, Sa ol O. Contribution of diffusion-weighted MRI to the differential diagnosis of hepatic masses. Diagn Interv Radiol 2007; 13:
Diagnostic value of diffusion weighted MRI and ADC in differential diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma of the liver.
 Diagnostic value of diffusion weighted MRI and ADC in differential diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Ozlem Tokgoz 1, Ebru Unlu 2, Ilker Unal 3, Ismail Serifoglu 4, Ilker Oz 4, Elif Aktas
Diagnostic value of diffusion weighted MRI and ADC in differential diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Ozlem Tokgoz 1, Ebru Unlu 2, Ilker Unal 3, Ismail Serifoglu 4, Ilker Oz 4, Elif Aktas
Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) without ADC values in assessment of small focal nodules in cirrhotic liver
 Original Article Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) without ADC values in assessment of small focal nodules in cirrhotic liver Mai-Lin Chen, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Li-Ping Qi, Qing-Lei Shi, Bin Chen, Ying-Shi Sun
Original Article Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) without ADC values in assessment of small focal nodules in cirrhotic liver Mai-Lin Chen, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Li-Ping Qi, Qing-Lei Shi, Bin Chen, Ying-Shi Sun
Role of Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Focal Liver Lesions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2015), PP 10-22 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. I (July. 2015), PP 10-22 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance
Utility of Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Distinguishing Benign and Malignant Hepatic Lesions
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:138 147 (2010) Original Research Utility of Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Distinguishing Benign and Malignant Hepatic Lesions Frank H. Miller, MD,* Nancy Hammond, MD,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 32:138 147 (2010) Original Research Utility of Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Distinguishing Benign and Malignant Hepatic Lesions Frank H. Miller, MD,* Nancy Hammond, MD,
Role of DWI in Detection and Characterization of Focal Liver Lesions
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/20857:2187 Radiology Section Original Article Role of DWI in Detection and Characterization of Focal Liver Lesions Madhu SD, Jaipal R Beerappa, Pooja, RaghuRam P ABSTRACT Introduction:
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/20857:2187 Radiology Section Original Article Role of DWI in Detection and Characterization of Focal Liver Lesions Madhu SD, Jaipal R Beerappa, Pooja, RaghuRam P ABSTRACT Introduction:
European Journal of Radiology
 European Journal of Radiology 76 (2010) 89 95 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Characterization of small ( 10 mm)
European Journal of Radiology 76 (2010) 89 95 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Characterization of small ( 10 mm)
ADC Measurement of Abdominal Organs and Lesions Using Parallel Imaging Technique
 ADC Measurement of Abdomen Using Parallel Imaging Abdominal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Takeshi Yoshikawa 1 Hideaki Kawamitsu 2 Donald G. Mitchell 1 Yoshiharu
ADC Measurement of Abdomen Using Parallel Imaging Abdominal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Takeshi Yoshikawa 1 Hideaki Kawamitsu 2 Donald G. Mitchell 1 Yoshiharu
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page 1823-1827 Role of Diffusion Weighted MRI Imaging in Detection of Liver Metakstases Khalid E. Allam, Mennatallah H. Shalaby, Israa
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69 (2), Page 1823-1827 Role of Diffusion Weighted MRI Imaging in Detection of Liver Metakstases Khalid E. Allam, Mennatallah H. Shalaby, Israa
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging before and after Contrast Enhancement with Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide for Assessment of Hepatic Metastasis
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.825 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(4):825-833, 2012 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging before and after Contrast Enhancement with
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.825 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(4):825-833, 2012 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging before and after Contrast Enhancement with
Diffusion-weighted MRI of metastatic liver lesions: is there a difference between hypervascular and hypovascular metastases?
 Original Article Diffusion-weighted MRI of metastatic liver lesions: is there a difference between hypervascular and hypovascular metastases? Acta Radiologica 2014, Vol. 55(5) 515 523! The Foundation Acta
Original Article Diffusion-weighted MRI of metastatic liver lesions: is there a difference between hypervascular and hypovascular metastases? Acta Radiologica 2014, Vol. 55(5) 515 523! The Foundation Acta
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen
 Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen Poster No.: C-0234 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa 1, N. Aoyama 1, Y. Ohno 1, K. Kyotani 1, Y. Kassai 2, K. Sofue 1, M.
Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen Poster No.: C-0234 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa 1, N. Aoyama 1, Y. Ohno 1, K. Kyotani 1, Y. Kassai 2, K. Sofue 1, M.
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Diffusion- Weighted Imaging for Differential Diagnosis of Primary Solid and Cystic Renal Masses
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 209-215 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899984 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.06.08 Accepted: 2016.08.16 Published: 2017.04.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 209-215 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899984 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.06.08 Accepted: 2016.08.16 Published: 2017.04.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Liver: The Effect on T2 Relaxation Times and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC)
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 103-109 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.895701 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2015.08.19 Accepted: 2015.09.11 Published: 2016.03.12 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 103-109 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.895701 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2015.08.19 Accepted: 2015.09.11 Published: 2016.03.12 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Utility of ADC Measurements in the Discrimination between Benign and Lymphomatous Abdomino-Pelvic Lymph Nodes
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, September: 1-7, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Utility of ADC Measurements in the Discrimination between Benign and Lymphomatous Abdomino-Pelvic Lymph
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, September: 1-7, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Utility of ADC Measurements in the Discrimination between Benign and Lymphomatous Abdomino-Pelvic Lymph
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Altought liver (75%) and lung (15%) are the most commonly involved
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Factors associated with T2 Shine-Through Effect in Hepatic Hemangiomas on Diffusion-weighted MR Sequences
 Factors associated with T Shine-Through Effect in Hepatic Hemangiomas on Diffusion-weighted MR Sequences Poster No.: C-09 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Duran, M. Ronot, A. kerbaol,
Factors associated with T Shine-Through Effect in Hepatic Hemangiomas on Diffusion-weighted MR Sequences Poster No.: C-09 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Duran, M. Ronot, A. kerbaol,
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI
 Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Influence of cardiac motion on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the liver
 Magn Reson Mater Phy (2009) 22:319 325 DOI 10.1007/s10334-009-0183-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Influence of cardiac motion on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the liver Thomas C. Kwee Taro Takahara
Magn Reson Mater Phy (2009) 22:319 325 DOI 10.1007/s10334-009-0183-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Influence of cardiac motion on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the liver Thomas C. Kwee Taro Takahara
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES. M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly
 LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology
 Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Purpose. Background. Purpose
 Does diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) add diagnostic confidence in discriminating between malignant and benign solid focal lesions if included in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the
Does diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) add diagnostic confidence in discriminating between malignant and benign solid focal lesions if included in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the
Acknowledgements. Update of Focal Liver Lesions Goals. Focal Liver Lesions. Imaging Choices For Liver Lesions. Focal Liver Lesions
 Acknowledgements Update of Focal Liver Lesions 2012 Giles Boland Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures Dushyant Sahani Mukesh Harisinghani Goals Focal liver lesions Imaging
Acknowledgements Update of Focal Liver Lesions 2012 Giles Boland Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures Dushyant Sahani Mukesh Harisinghani Goals Focal liver lesions Imaging
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings
 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Schmidt, A. Pomoni, F. Becce, A. Denys,
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Schmidt, A. Pomoni, F. Becce, A. Denys,
Correlation of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging with Cellularity of Renal Tumours
 Correlation of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging with Cellularity of Renal Tumours ETTORE SQUILLACI 1, GUGLIELMO MANENTI 1, MARIA COVA 2, MAURO DI ROMA 1, ROBERTO MIANO 3, GIAMPIERO PALMIERI 4 and GIOVANNI
Correlation of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging with Cellularity of Renal Tumours ETTORE SQUILLACI 1, GUGLIELMO MANENTI 1, MARIA COVA 2, MAURO DI ROMA 1, ROBERTO MIANO 3, GIAMPIERO PALMIERI 4 and GIOVANNI
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad
 CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (11), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (11), Page 5547-5551 The Role of Dynamic MRI with Diffusion Weighted Images in Evaluation of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Hepatic Patients 1 Suzan
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (11), Page 5547-5551 The Role of Dynamic MRI with Diffusion Weighted Images in Evaluation of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Hepatic Patients 1 Suzan
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
Liver MRI in 30 minutes
 X Liver MRI in 30 minutes SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 18, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
X Liver MRI in 30 minutes SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 18, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma
 Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI
 The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI Poster No.: C-1137 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit V. Zampa, V. Vallini,
The follow-up of uterine fibroids treated with HIFU: role of DWI and Dynamic contrast-study MRI Poster No.: C-1137 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit V. Zampa, V. Vallini,
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Abdomen at 3.0 Tesla: Image Quality and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reproducibility Compared With 1.
 CME JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 33:128 135 (2011) Original Research Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Abdomen at 3.0 Tesla: Image Quality and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reproducibility Compared
CME JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 33:128 135 (2011) Original Research Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Abdomen at 3.0 Tesla: Image Quality and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reproducibility Compared
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy
 Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy Jing Cai, PhD, DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology Duke University Medical Center, Durham NC Advances in MRI Structural Imaging Fast Imaging
Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy Jing Cai, PhD, DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology Duke University Medical Center, Durham NC Advances in MRI Structural Imaging Fast Imaging
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
 Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
The Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Values for Breast Tumors
 The Role of iffusion-weighted Imaging and the Apparent iffusion Coefficient (AC) Values for Breast Tumors Mi Jung Park, M Eun Suk Cha, M Bong Joo Kang, M Yon Kwon Ihn, M Jun Hyun Baik, M Index terms: iffusion-weighted
The Role of iffusion-weighted Imaging and the Apparent iffusion Coefficient (AC) Values for Breast Tumors Mi Jung Park, M Eun Suk Cha, M Bong Joo Kang, M Yon Kwon Ihn, M Jun Hyun Baik, M Index terms: iffusion-weighted
Value of the Diffusion-Weighted MRI in the Differential Diagnostics of Malignant and Benign Kidney Neoplasms Our Clinical Experience
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2014; 79: 290-295 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.890604 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2014.02.27 Accepted: 2014.03.24 Published: 2014.09.01 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2014; 79: 290-295 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.890604 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2014.02.27 Accepted: 2014.03.24 Published: 2014.09.01 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
Can diffusion weighted imaging distinguish between benign and malignant solid or predominantly solid gynecological adnexal masses?
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 113 119 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 113 119 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Staging of liver metastases with MRI in oncological treatment planning.
 Investigations and research Staging of liver metastases with MRI in oncological treatment planning. K. Coenegrachts L. ter Beek H. Rigauts Department of Radiology, AZ St.-Jan AV (St. John s Academic Hospital),
Investigations and research Staging of liver metastases with MRI in oncological treatment planning. K. Coenegrachts L. ter Beek H. Rigauts Department of Radiology, AZ St.-Jan AV (St. John s Academic Hospital),
Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): features and potential applications in oncology
 Eur Radiol (2008) 18: 1937 1952 DOI 10.1007/s00330-008-0968-z MAGNETIC RESONANCE Thomas C. Kwee Taro Takahara Reiji Ochiai Rutger A. J. Nievelstein Peter R. Luijten Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging
Eur Radiol (2008) 18: 1937 1952 DOI 10.1007/s00330-008-0968-z MAGNETIC RESONANCE Thomas C. Kwee Taro Takahara Reiji Ochiai Rutger A. J. Nievelstein Peter R. Luijten Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 27: (2008)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 27:834 839 (2008) Original Research Evaluating Local Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Post-Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization: Is Diffusion-Weighted MRI Reliable
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 27:834 839 (2008) Original Research Evaluating Local Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Post-Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization: Is Diffusion-Weighted MRI Reliable
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Upper Abdomen: Technical Issues and Clinical Applications
 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Upper Abdomen: Technical Issues and Clinical Applications Leonardo K. Bittencourt, MD a, *, Celso Matos, MD b, Antonio C. Coutinho Jr, MD c KEYWORDS
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Upper Abdomen: Technical Issues and Clinical Applications Leonardo K. Bittencourt, MD a, *, Celso Matos, MD b, Antonio C. Coutinho Jr, MD c KEYWORDS
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, cont
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Francesco Agnello,
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Francesco Agnello,
 Malignant hepatic focal lesions: Improved detection and characterization by diffusion weighted MRI in comparison to TW with the use of parallel imaging SENSE and different b values 1 Reem H Basiouny, 1
Malignant hepatic focal lesions: Improved detection and characterization by diffusion weighted MRI in comparison to TW with the use of parallel imaging SENSE and different b values 1 Reem H Basiouny, 1
ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR
 ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR Frank Miller, M.D. FACR Professor of Radiology Chief, Body Imaging Section Medical Director, MR Imaging Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine fmiller@northwestern.edu
ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR Frank Miller, M.D. FACR Professor of Radiology Chief, Body Imaging Section Medical Director, MR Imaging Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine fmiller@northwestern.edu
Hepatic sclerosed hemangioma with special attention to diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
 Miyata et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0414-z CASE REPORT Open Access Hepatic sclerosed hemangioma with special attention to diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
Miyata et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s40792-017-0414-z CASE REPORT Open Access Hepatic sclerosed hemangioma with special attention to diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver Metastases
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71(1), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71(1), Page 2315-2321 Role of MRI in Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) after TACE (Trans-arterial Chemoembolization) with Persistent
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71(1), Page 2315-2321 Role of MRI in Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) after TACE (Trans-arterial Chemoembolization) with Persistent
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Mediastinal and Pulmonary Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE LIVER IN HEPATITIS B PATIENTS
 DIFFUSIO-WEIGHTED MAGETIC RESOACE IMAGIG OF THE LIVER I HEATITIS B ATIETS WITH CHILD-UGH A CIRRHOSIS Feng-O Hsu, 1 Yen-Yu Chiou, 1 Chiao-Yun Chen, 1,2 Gin-Chung Liu, 1,2 Hui-Chen Chu, 3 Hui-Cheng Liu,
DIFFUSIO-WEIGHTED MAGETIC RESOACE IMAGIG OF THE LIVER I HEATITIS B ATIETS WITH CHILD-UGH A CIRRHOSIS Feng-O Hsu, 1 Yen-Yu Chiou, 1 Chiao-Yun Chen, 1,2 Gin-Chung Liu, 1,2 Hui-Chen Chu, 3 Hui-Cheng Liu,
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses
 The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
Timothy L. Miao 1, Ania Z. Kielar 2,3, Rebecca M. Hibbert 2, Nicola Schieda 2,3
 DOES LESION T1 SIGNAL INTENSITY RELATIVE TO LIVER PARENCHYMA PREDICT VISIBILITY ON ULTRASOUND? A clinical tool to determine feasibility of ultrasound-guided percutaneous interventions Timothy L. Miao 1,
DOES LESION T1 SIGNAL INTENSITY RELATIVE TO LIVER PARENCHYMA PREDICT VISIBILITY ON ULTRASOUND? A clinical tool to determine feasibility of ultrasound-guided percutaneous interventions Timothy L. Miao 1,
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Lewis et al. DWI of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Sara Lewis 1 Amita Kamath 1 Manjil Chatterji 1 Amish Patel
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Lewis et al. DWI of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Sara Lewis 1 Amita Kamath 1 Manjil Chatterji 1 Amish Patel
The effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
 The effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of acute cholecystitis Poster No.: C-1805 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Beyazal,
The effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of acute cholecystitis Poster No.: C-1805 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Beyazal,
Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hepatic Tumors
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 12, No. 3, September: 191-198, 2000 Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hepatic Tumors MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ, M.D.*; IMAN ZAKY, M.D. and MOHAMAD
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 12, No. 3, September: 191-198, 2000 Magnetization Transfer Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Hepatic Tumors MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ, M.D.*; IMAN ZAKY, M.D. and MOHAMAD
Comparison of whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI and PET/ CT for detection of metastases
 Comparison of whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI and PET/ CT for detection of metastases Poster No.: R-0021 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. D. Nguyen Keywords: Oncology,
Comparison of whole-body diffusion-weighted MRI and PET/ CT for detection of metastases Poster No.: R-0021 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. D. Nguyen Keywords: Oncology,
Nodular thyroid is commonly detected on palpation in
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.A.K. Abdel Razek A.G. Sadek O.R. Kombar T.E. Elmahdy N. Nada Role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in Differentiation Between Malignant and Benign Solitary Thyroid BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.A.K. Abdel Razek A.G. Sadek O.R. Kombar T.E. Elmahdy N. Nada Role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in Differentiation Between Malignant and Benign Solitary Thyroid BACKGROUND
Value of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Assessing Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Sandrasegaran et al. DWI to Assess Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Kumaresan Sandrasegaran 1 Fatih M. Akisik 1 Chen Lin
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Sandrasegaran et al. DWI to Assess Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Kumaresan Sandrasegaran 1 Fatih M. Akisik 1 Chen Lin
Preoperative prediction of the malignancy or benignancy of
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Diffusion-Weighted MRI in the Body: Applications and Challenges in Oncology
 Koh and Collins DWI Applications and Challenges in Oncology MR Imaging Review Dow-Mu Koh 1,2 David J. Collins 1,2 Koh DM, Collins DJ Keywords: abdominal imaging, cancer, diffusion-weighted imaging, MRI,
Koh and Collins DWI Applications and Challenges in Oncology MR Imaging Review Dow-Mu Koh 1,2 David J. Collins 1,2 Koh DM, Collins DJ Keywords: abdominal imaging, cancer, diffusion-weighted imaging, MRI,
MRI of the Hepatobiliary System
 BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
High b Value Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Detecting Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Preliminary Results
 Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Detect Pancreatic denocarcinoma bdominal Imaging Original Research Tomoaki Ichikawa 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 2 Utarou Motosugi 1 Hironobu Sou 1 Hiroshi Iino 3 Tsutomu raki 1 Hideki
CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]
![CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE] CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]](/thumbs/86/94270487.jpg) ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo
 Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
The Frequency and Significance of Small (15 mm) Hepatic Lesions Detected by CT
 535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
ADRENAL MR: PEARLS AND PITFALLS
 ADRENAL MR: PEARLS AND PITFALLS Frank Miller, M.D. Lee F. Rogers MD Professor of Medical Education Chief, Body Imaging Section and Fellowship Medical Director, MR Imaging Professor of Radiology Northwestern
ADRENAL MR: PEARLS AND PITFALLS Frank Miller, M.D. Lee F. Rogers MD Professor of Medical Education Chief, Body Imaging Section and Fellowship Medical Director, MR Imaging Professor of Radiology Northwestern
AHMED M.W. AL-GEBALLY, M.D.*; AHMED M.S. NASR, M.D.* and WESAM AMR, M.D.**
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 281-286, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and ADC Value Measurement in Identification and Differentiation
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 281-286, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and ADC Value Measurement in Identification and Differentiation
European Journal of Radiology
 European Journal of Radiology 83 (2014) 1728 1733 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Usefulness of free-breathing readout-segmented
European Journal of Radiology 83 (2014) 1728 1733 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Usefulness of free-breathing readout-segmented
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Focal fatty sparing and focal fatty infiltration can be observed in the
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2011; 17:323 327 Turkish Society of Radiology 2011 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Focal sparing of iron and fat in liver tissue in patients with hemosiderosis: diagnosis with combination
Diagn Interv Radiol 2011; 17:323 327 Turkish Society of Radiology 2011 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Focal sparing of iron and fat in liver tissue in patients with hemosiderosis: diagnosis with combination
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, conta
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. M. Fatih Akisik,
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. M. Fatih Akisik,
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the
 Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Role of Conventional and Diffusion Weighted MRI in the Evaluation of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Tumors
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 1029-1037, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Conventional and Diffusion Weighted MRI in the Evaluation of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Tumors
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 1029-1037, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Conventional and Diffusion Weighted MRI in the Evaluation of Pediatric Musculoskeletal Tumors
