Effects of radiofrequency radiation on root tip cells of Zea mays
|
|
|
- Meagan Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Roumanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 14, No. 3, 2009, pp Copyright 2008 Bucharest University Printed in Romania. All rights reserved Roumanian Society of Biological Sciences ORIGINAL PAPER Effects of radiofrequency radiation on root tip cells of Zea mays Received for publication, November 8, 2008 Accepted, March 3, 2009 Abstract 4366 MİHAELA RĂCUCİU Lucian Blaga University, Faculty of Science, 5-7 Dr. Ratiu Street, , Sibiu, Romania, In this study, the mutagenic effects of low power radiofrequency radiation on Zea mays root tip were studied. Cells in different division phases and chromosomal aberration assay were used to determine the mitotic index and chromosomal aberration frequency of Zea mays root tip cells induced by 900MHz radiofrequency radiation. Zea mays seeds, having a uniform genophond, have been exposed to RF field of low power density, for different time intervals, between 1.0 and 36.0 hours. Exposure to RF field was applied to seeds before germination process. Continuous wave on 900 MHz was used for irradiation. Incident field distribution in the irradiation area was characterized, so as an as possible as uniform field to be applied in the volume of the sample. The results showed that the mitotic index and chromosomal aberration frequency showed linear increasing for radiofrequency radiation treatment of increased exposure time. Keywords: magnetic nanoparticles, cell proliferation, chromosomal aberrations, mitotic index. Introduction Radiofrequency electromagnetic radiations are human survival environmental factors. Radiofrequency energy is a type of non-ionizing radiation, including electromagnetic radiation produced by cellular phones, and is not strong enough to cause ionization of atoms and molecules. Effects of radiofrequency (RF) irradiation on agricultural plants have scarcely been studied yet, especially their harmful effects on biology. Alongside with the network communication, broad-cast television and electric appliance became common people accept more and more electromagnetic radiation presence, which has already become an environmental pollution problem, affecting directly living conditions. Effects of electromagnetic radiations on biology had been reported of many researchers [1-5]. Tkalec et al. exposed Lemna minor L. plants to electromagnetic radiations at the frequencies 900MHz and observed that the growth of plants exposed for 2 hours significantly decreased in comparison with the control [6]. Tambiev et al. enumerates a series of effects on photosynthetic microorganisms and plants of EHF radiation of low intensity [7]. Recently, Tkalec et al. reported that the germination rate and root length did not change significantly after 900MHz electromagnetic field exposure, but modulated field significantly of 4 hours exposure time increased mitotic index compared to corresponding controls in the Allium cepa seeds case [8]. The percentage of mitotic abnormalities increased with all the given field conditions. Cell proliferation is known as rather sensitive to external and internal factors whatever their origin. The cell nucleus may experience the action of electromagnetic radiation as a source of chromosomal aberrations and, further, genetic mutations. In this study, we
2 Effects of radiofrequency radiation on root tip cells of Zea mays investigated the capacity of the 900MHz radiofrequency radiation to influence germination, as well as to influence both the mitotic index and the chromosomal aberration percentage, carried out by means of cytogenetically tests. Materials and methods Biological samples were composed by Zea mays seeds, harvested from an experimental population with ensured uniform genophond. The seeds have been exposed to RF field of low power density (20mW), for different time intervals, between 1 and 36.0 hours. Exposure to the RF field was applied to seeds before the germination process. The Petri dishes containing seeds were exposed inside a TEM cell (model IFI CC-104SEXX), which was supplied from an RF signal generator (model Hameg HM ) (Fig.1). Continuous wave on 900 MHz was used for seeds irradiation. Incident field distribution in the irradiation area was characterized as an as possible as uniform field to be applied to the volume of the sample and the absorbed RF power was measured by using a Luxtron One probe (SAR<1W/kg). The seeds were let to germinate in controlled environmental conditions into a laboratory room. From root meristems tissue in early ontogenetic stages of germinated seeds, microscope slides for cell chromosome visualization were prepared by using the Squash method combined with Fuelgen techniques [9]. Carr modified dye was used to provide selective coloration in plant chromosomes. The cell mitotic index and chromosomal aberration percentage were examined and counted microscopically on squashes, and the aberrant cells were micro-photographed. The mitotic index is able to give the percentage of dividing cells in every sample while chromosomal aberration index represent the sum of aberrant cell divisions: total cells in division M. I. = 100 (1) total cells analized total chromosomal aberrations A. I. = 100 (2) total cells analized The counting of normal and aberrant dividing cells was carried out (using Nikon microscope) taking into account all cell division phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Results and discussion The experimental data about the influence of different exposure times of seeds on radiofrequency field upon the cells in different division phases, are given in Table 1. The results obtained in the frame of the cytogenetic investigation regarding the 900MHz radiofrequency field influence upon both proliferation capacity and abnormal division frequency are further discussed on the basis of the corresponding percentage data. The microscope analyses have revealed an increased influence of radiofrequency field for increased exposure time at chromosomal level. Furthermore, it is obvious that under the electromagnetic field influence increase of total prophase, metaphases, anaphases and telophases percentage occurred, especially for higher exposure times. The mitotic index is higher for all samples under the radiofrequency field influence in comparison to the control one and the aberration index have relatively low values for all analyzed samples (<3%) Roum. Biotechnol. Lett., Vol. 14, No. 3, (2009) 4367
3 MIHAELA RĂCUCIU (Fig.2). The highest value of the mitotic index data in the sample corresponding to the highest exposure time increased the control sample value 3 times. Table 1. Cytogenetically investigation results t RF (h) N M.I. A.I. I P M A T (t RF 900MHz radiofrequency field exposure time; N total number of analyzed cells; M.I. mitotic index; A.I.- aberration index; I - percentage of interphase cells; P percentage of prophase cells; M - percentage of metaphase cells; A - percentage of anaphase cells; T - percentage of telophase cells). One may observe that mitotic index has a linear increasing rate to the increased radiofrequency field exposure time. In Fig. 2, we supply the linear dependence with correlation coefficient (R 2 =0.98) for the mitotic index (M.I.). M.I. % Mitotic index y = x R 2 = exposure time (h) Fig.2. Mitotic index M.I. versus radiofrequency field exposure time (h) For the radiofrequency field exposed samples, we provide an ascendant dynamics (polynomial dependence) for the chromosomal aberrations index (low values for all samples < 3%) function of the radiofrequency field exposure time, with a correlation coefficient (R 2 =0.95), in Fig Aberration index A.I. % y = x x R 2 = exposure time (h) Fig.3. Dependence of chromosomal aberrations index (A.I.) for radiofrequency field exposed samples 4368 Roum. Biotechnol. Lett., Vol. 14, No. 3, (2009)
4 Effects of radiofrequency radiation on root tip cells of Zea mays Fig.4. Micronucleus in prophase (4h exposed sample left), chromosome fragment in telophase (24h exposed sample - right) Microscope examination found abnormal cell mitosis phenomenon in prophase (micronucleus Fig.4, left), metaphase, anaphase, telophase (chromosome fragment Fig.4, right) of Zea mays root tip meristem cells in the presence of the 900MHz electromagnetic field. The main types of simple chromosomal aberrations identified in the over 99,000 analyzed cells (microphotographed using a FUJI FinePix S5100 digital camera) are: micronucleus, interchromatin bridges, retard chromosomes and chromosome fragments (Fig.5). Fig.5. Chromosome fragments in anaphase (8h exposed sample left, 24h exposed sample middle, 36h exposed sample right) Complex aberrations were observed, such as combinations of retard chromosomes or chromosome fragments with inter-chromatin bridges (Fig.6), the formation of chromosomal bridges was accompanied by the occurrence of the chromosome fragments (Fig.6, right). Fig.6. Inter-chromatin bridge and retard chromosome in inaphase (12h exposed sample left), inter-chromatin bridge and chromosome fragments in inaphase (24h exposed sample right). Conclusions We may conclude that the low intensity 900MHz electromagnetic radiation can provide a low percentage of chromosomal aberrations in Zea mays root tip and an increased Roum. Biotechnol. Lett., Vol. 14, No. 3, (2009) 4369
5 MIHAELA RĂCUCIU mitotic index for increasing the seeds exposure time in the electromagnetic field presence, stimulating the plant proliferation in comparison to the control sample. It may presume that some chromosomal aberrations induced by suitable electromagnetic field exposure time of plant seeds may persist in the next generations so that some phenotypic characters may be modified. These modifications could be observed following the plant development, some of them being benefic for the cultivation of this agricultural species (Zea mays) with major role in people life. This way, the low power density of the 900MHz electromagnetic field could represent the molecular basis of a putative tool in the biotechnology of Zea mays growth with the advantages of being less toxic and easier to manipulate in comparison to ionizing radiation for instance [10]. References 1. LACY-HULBERT, J.C. METCALFE, R. HESKETH, Biological responses to electromagnetic field, Faseb. J., 12(6), , B.C. ZOOK, S.J. SIMMENS, The effects of 860 MHz radiofrequency radiation on the induction or promotion of brain tumors and other neoplasms in rats, Radiation Research, 155, , C. GOICEANU, A. ARTENIE, O.G. AVADANEI, V. ARTENIE, D. CREANGA, Some evidence of biological effects of ultra high frequency fields in Triticum, Proc.IXth Medit. Conf. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., Croatia, , D. SRIPAKDEE, K.L. SUKONTASON, S. PIANGJAI, R. NGERN-KLUN, K. SUKONTASON, Effect of microwave irradiation on the blow fly Chrysomya megacephala (F.) (Diptera: Calliphoridae), Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health., 36(4), , D.D. SANDU, C. GOICEANU, A. ISPAS, I. CREANGA, S. MICLAUS, D.E. CREANGA, Preliminary study on ultra high frequency fields effect in black locust chlorophyll, Acta Biologica Hungarica, 56 (1-2), , M. TKALEC, K. MALARIC, B. PEVALEK-KOZLINA, Influence of 400, 900, and 1900 MHz electromagnetic fields on Lemna minor growth and peroxidase activity, Bioelectromagnetics, 26(3), , A.H.TAMBIEV, N.N. KIRIKOVA, The prospects of use of EHF radiation in photobiotechnology, in: N.D. Deviatkov, O.V. Betskii (eds), Biological aspects of low intensity millimeter waves, Moscow Univ. Prospect, , M. TKALEC, Z. VIDAKOVIC-CIFREK, B. PEVALEK-KOZLINA, Evaluation of the Genotoxic Potential of Microwave Electromagnetic Fields in Onion (Allium Cepa), 2007 IEEE International Symposium on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC2007), Supplement to EMC Newsletter, 8-13 Hawaii, 44, J. JAHIER., A.M. CHEVRE, F. EBER, R. DELOURME, A.M. TANGUY, Techniques de cytogénétique végétale, INRA Ed., Paris, M. OKAMURA, N. YASUNO, M. OHTSUKA, A. TANAKA, N. SHIKAZONO, Y. HASE, Wide variety of flower-color and -shape mutants regenerated from leaf cultures irradiated with ion beams, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, , Roum. Biotechnol. Lett., Vol. 14, No. 3, (2009)
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC EXPOSURE TO ELF FIELDS INVESTIGATED AT THE LEVEL OF MERISTEMATIC TISSUES *
 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC EXPOSURE TO ELF FIELDS INVESTIGATED AT THE LEVEL OF MERISTEMATIC TISSUES * C. IONITA-MIRONESCU 1, D. VRINCIANU 1, I. BARA 2, D. CREANGA 1, M. RACUCIU 3 1 Univ. Al.
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC EXPOSURE TO ELF FIELDS INVESTIGATED AT THE LEVEL OF MERISTEMATIC TISSUES * C. IONITA-MIRONESCU 1, D. VRINCIANU 1, I. BARA 2, D. CREANGA 1, M. RACUCIU 3 1 Univ. Al.
Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division
 Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER PART 1. NORMAL MITOSIS IN PLANTS FIGURE 1. DIAGRAMATIC GUIDE TO THE STAGES OF MITOSIS
 Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion
 Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVIII, Issue 1/2013
 Annals of RSCB Vol. XVIII, Issue /3 CYTOGENETIC EFFECTS INDUCED BY DEPOSIT MYCOFLORA IN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS L. BEANS FROM THE COLLECTION OF SUCEAVA GENEBANK Diana Batîr-Rusu, C. Tudose * SUCEAVA GENEBANK,
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVIII, Issue /3 CYTOGENETIC EFFECTS INDUCED BY DEPOSIT MYCOFLORA IN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS L. BEANS FROM THE COLLECTION OF SUCEAVA GENEBANK Diana Batîr-Rusu, C. Tudose * SUCEAVA GENEBANK,
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test
 Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy Author copy
 Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 21, No. 1 (2012), 23-29 Original Research Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Emitted by Mobile Phones on Germination, Root Growth, and Root Tip Cell Mitotic Division of Lens culinaris
Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 21, No. 1 (2012), 23-29 Original Research Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Emitted by Mobile Phones on Germination, Root Growth, and Root Tip Cell Mitotic Division of Lens culinaris
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn)
 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical.
 Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab
 Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
COURTESY OF HENRY MILNE/ NSRC
 COURTESY OF HENRY MILNE/ NSRC 2Continuing PART the Cycle LESSON 8 Cell Division: Multiplying by Dividing 96 Inquiry 8.1 Inquiry 8.2 Simulating Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis 97 Creating a Model of
COURTESY OF HENRY MILNE/ NSRC 2Continuing PART the Cycle LESSON 8 Cell Division: Multiplying by Dividing 96 Inquiry 8.1 Inquiry 8.2 Simulating Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis 97 Creating a Model of
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie Tom. XX, Issue 2, 13, pp. 71-79 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS Maria-Mihaela ANTOFIE *, Elena DOROFTEI ** * Faculty of Agricultural
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie Tom. XX, Issue 2, 13, pp. 71-79 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS Maria-Mihaela ANTOFIE *, Elena DOROFTEI ** * Faculty of Agricultural
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle
 Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
UNIDENTIFIED MULTIABERRANT CELLS AS EVIDENCE OF γ-irradiation IN Allium cepa L.
 1 UNIDENTIFIED MULTIABERRANT CELLS AS EVIDENCE OF γ-irradiation IN Allium cepa L. Kutsokon N.K, Rashydov N.M., Grodzinsky D.M. Institute of Cell Biology and Genetic Engineering of the National Academy
1 UNIDENTIFIED MULTIABERRANT CELLS AS EVIDENCE OF γ-irradiation IN Allium cepa L. Kutsokon N.K, Rashydov N.M., Grodzinsky D.M. Institute of Cell Biology and Genetic Engineering of the National Academy
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1
 Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Unit 4: Reproduction. Traits. Heredity. Nucleus: The Control Center. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid 09/06/2016
 Unit 4: Reproduction Traits Traits: are physical features of an organism. They can vary in size or form from one individual to another. Examples include eye color, height and colour vision. Heredity Heredity:
Unit 4: Reproduction Traits Traits: are physical features of an organism. They can vary in size or form from one individual to another. Examples include eye color, height and colour vision. Heredity Heredity:
Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell)
 Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis
 Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
A. Incorrect! All the cells have the same set of genes. (D)Because different types of cells have different types of transcriptional factors.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
BIL Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data
 BIL 151 - Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data You and your teammates have chosen to examine the outcome of treating a rapidly dividing tissue (onion root tip) with a substance that either promotes
BIL 151 - Mechanisms of Mitosis PART III. Collecting Data You and your teammates have chosen to examine the outcome of treating a rapidly dividing tissue (onion root tip) with a substance that either promotes
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L.
 South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa
 Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials. What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think.
 Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Available online:
 VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE
 ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 9 Cellular Reproduction Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1. What can limit
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 9 Cellular Reproduction Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1. What can limit
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
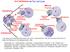 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Onion Root Tip Lab Report
 Onion Root Tip Lab Report Hannah Scott Biology Ms. Carpenter February 25, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis and Prediction In this lab experiment, Hannah was to analyze an onion root tip under a microscope to observe
Onion Root Tip Lab Report Hannah Scott Biology Ms. Carpenter February 25, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis and Prediction In this lab experiment, Hannah was to analyze an onion root tip under a microscope to observe
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Comparative effects of colchicine, 8-hydroxyquinoline and paradichlorobenzene on arm ratio of mitotic chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
Biology Diagrams. Biology Review
 Biology Diagrams Biology Review Matching A) Light source B) Respiratory System C) Mitochondria D) Nucleus E) Vacuole F) Cytokinesis G) Daughter cells H) Interphase I) Telophase J) Ocular lens K) Fine
Biology Diagrams Biology Review Matching A) Light source B) Respiratory System C) Mitochondria D) Nucleus E) Vacuole F) Cytokinesis G) Daughter cells H) Interphase I) Telophase J) Ocular lens K) Fine
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project
 LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 6101/01 Edexcel GCE Biology Biology (Human) Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 1
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6101/01 Edexcel GCE Biology Biology (Human) Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 1 Monday 4 June 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6101/01 Edexcel GCE Biology Biology (Human) Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 1 Monday 4 June 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Exploring Mitosis Lab IMPORTANT LEARNING OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report
 Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report Date Published: 05/19/2008 Page One 1. Lesson Plan Title: Cell Division and Mitosis 2. Subject Area: Living Environment 3. Topic(s): Mitosis 4. Suggested Grade
Science Lesson Plan Submission Profile Report Date Published: 05/19/2008 Page One 1. Lesson Plan Title: Cell Division and Mitosis 2. Subject Area: Living Environment 3. Topic(s): Mitosis 4. Suggested Grade
Cell division occurs in a series of stages, or phases.
 Mitosis Notes Cell division occurs in a series of stages, or phases. 1st: INTERPHASE Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome
Mitosis Notes Cell division occurs in a series of stages, or phases. 1st: INTERPHASE Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Exploring Mitosis Lab IMPORTANT LEARNING OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION cell cycle interphase division (mitosis)
 Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
Exploring Mitosis Lab Today s lab will give you a chance to get an up-close view of mitosis, the process by which eukaryotic cells divide to generate identical daughter cells. We re using garlic (A. sativium)
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
NOTES. Cell Cycle & Mitosis
 NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
Introduction: Alprazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorders and other anxiety
 DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
 Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA MUNGO (L.) HEPPER
 EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa
 Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI*
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 43(1): 107-111, 2014 (June) - Short communication GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI* College of Science, Department of Biology,
Bangladesh J. Bot. 43(1): 107-111, 2014 (June) - Short communication GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI* College of Science, Department of Biology,
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
Cell Size Limitations
 Cell Size Limitations Cells come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes. Considering this wide range of cells sizes, why then can t most organisms be just one giant cell? Diffusion limits cell size Although
Cell Size Limitations Cells come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes. Considering this wide range of cells sizes, why then can t most organisms be just one giant cell? Diffusion limits cell size Although
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES
 INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. Section 1. Meiosis
 Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body cells have 46 chromosomes! Each parent contributes 23 chromosomes! Homologous chromosomes one of two paired chromosomes, one from each parent Chromosomes and
Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body cells have 46 chromosomes! Each parent contributes 23 chromosomes! Homologous chromosomes one of two paired chromosomes, one from each parent Chromosomes and
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
LABORATORY. o Name, identify, and describe the events occurring during the four phases of the cell cycle.
 LABORATORY OVERVIEW According to the cell theory, all cells come from preexisting cells. New cells are formed by the process of c~1i division, which involves both division of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis)
LABORATORY OVERVIEW According to the cell theory, all cells come from preexisting cells. New cells are formed by the process of c~1i division, which involves both division of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis)
Effect of Two Brands of Cell Phone on Germination Rate and Seedling of Wheat (Triticum aestivum)
 Journal of Environment Pollution and Human Health, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 85-90 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/jephh/2/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/jephh-2-4-3 Effect of
Journal of Environment Pollution and Human Health, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 85-90 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/jephh/2/4/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/jephh-2-4-3 Effect of
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
