Macrolides. All macrolides are based on a large, macrocyclic ring +2 sugars (except telithromycin) methoxy0group. Telithromycin.
|
|
|
- Piers Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Macrolides All macrolides are based on a large, macrocyclic ring +2 sugars (except telithromycin) H H H C H H CH H 3 CH 3 H N( ) 2 H H H C H CH H 3 CH 3 methoxy0group H N( ) 2 N Erythromycin N Clarithromycin H H H C H N 1 6 CH H 3 methoxy0group H N( ) 2 N N CH 3 H N Azithromycin Telithromycin (a0ketolide)
2 Macrolides features Frequently used for community-acquired respiratory infections; also for skin, otitis media (ear) Alternative drug for Strep., Staph., H. flu infections for pen-allergic Erythromycin isolated 1952 from a soil microbe Streptomyces erythreus Later drugs (azithro-, clarithro-, telithro-) have broader spectra, especially Gm-, better acid stability and oral bioavailability Excellent tissue penetration, especially azithromycin and clarithromycin, but not to CNS Target the 50s large ribosomal subunit in bacteria, inhibit protein synthesis Similar MA to clindamycin and chloramphenical (shared binding site) Bacteriostatic, except at very high concentration can be bactericidal
3 30s Macrolides MA 50s aminoglycosides tetracyclines figure by Stephen Douthwaite, University of Southern Denmark macrolides chloramphenicol lincosamides streptogramins linezolid MACRLIDES: Bind to 50s subunit: Induce premature dissociation of peptidyl-trna from ribosome, hence premature termination Prevent addition of residues onto nascent polypeptide by blocking A to P translocation
4 Gram+ S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes S. aureus: MSSA but not MRSA General spectrum of activity Gram- H. influenzae (not erythromycin), M. cattarhalis Clarithromycin and azithromycin more potent than erythromycin Atypicals (not easily categorized by Gram stain technique) Mycoplasma pneumoniae ( walking pneumonia ; a very persistent cough) Legionella pneumophilia (Legionare s disease) Chlamydia trachomatis (STD) and Chlamydia (aka Chlamydophila) pneumoniae Mycobacterium avian complex (MAC): Clarithro- and azithro-
5 Distribution in the body Excellent tissue penetration Tissue:blood ratio :1. Drug highly concentrated in tissue Penetration into host cells too, so good for intracellular parasites such as Chlamydia ral bioavailability Erythromycin not acid stable (~25% orally bioavailable); take on empty stomach Clarithromycin and azithromycin more stable (~50% orally bioavailable); K w/ food Telithromycin more stable (~57% orally bioavailable); K w/ food
6 Erythromycin Not acid stable, poor oral bioavailability ~25% Short T1/2~1.5-2h Good Gm+ and reasonable Gm- activity Staph. aureus, but not MRSA S. pyogenes M. cattarhalis N. menengitidis Mycoplasma ( walking pneumonia ) Chlamydia H H H Not Enterobacteriacae, cannot penetrate outer cell membrane Not Pseudomonas Uses: URI, LRI: mild to moderate Skin: mild to moderate due to S. pyogenes Diphtheria Amebiasis N. gonorrhea: for pen-allergic Leigonare s disease C H H CH H 3 H N( ) 2
7 Erythromycin GI discomfort, diarrhea (13-32%) Induces peristalsis (gastroprokinetic); sometimes prescribed for this purpose. E.g. prior to endoscopy. Possible risk of QT elongation (time btxn Q and T waves in heart polarization), arrhythmias Drug interactions: P-glycoprotein inhibitor: e.g. interacts with digoxin CPY3A4 inhibitor: e.g. interacts with carbamazepine, cyclosporin CYP1A2 inhibitor: e.g. interacts with theophyline and caffeine P, IV, topical, opthalmic
8 Acid stable; oral bioavailability ~50% (metallic taste); P only 2-4x more potent than erythromycin T1/2~3-7h Broader spectrum of coverage compared to erythromycin, more Gram- Macrolide of choice for treatment of: Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC); common opportunist in AIDS H. pylori Uses: Phyaryngitis/tonsilitis Acute bacterial sinusitis Bronchitis CAP (community-acquired pneumo) titis media Skin Clarithromycin (Biaxin ) H H H C H CH H 3 H N( ) 2
9 Clarithromycin (Biaxin ) Metabolized in the liver. Some metabolites are even more active than parent compound. More potent, longer half-life than the parent compound. Precautions: Drug interactions. E.g. many anti-retroviral drugs interact (not used with HIV patients) QT prolongation. Careful with other drugs that can have QT prolongation Pregnancy category C (risk cannot be ruled out), safety in children < 6 mo. not established. Teratogenic effects observed in animal models Dizziness
10 Acid stable; oral bioavailability ~50% Azithromycin (Zithromax ) H H H C H N 1 More potent than erythromycin; higher tissue conc (e.g. lungs) than clarithro- T1/2~days Better Gm- coverage than clarithromycin, but less Gm+ than clarithromycin Alternative to clarithromycin for MAC Macrolide of choice for: Chlamydia trachomatis: 1gm single dose M. cat, H. flu N. gonorrhea (if patient is beta-lactam allergic); now used in combination w/ ceph. Legionella 6 CH H 3 H N( ) 2
11 Azithromycin (Zithromax ) Uses: even for some tougher infections Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CPD) CAP Bronchitis Sinusitis STD involving Chlamydia Skin titis media Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) Does not appear to affect liver function or other drug metabolism to the extent of other macrolides Precautions: Do not take with antacids, impairs absorption Rare hepatotoxicity Potential arrhythmias. Caution with patients with heart conditions. Pregnancy category B
12 Telithromycin (Ketek ) N Binds more tightly to bacterial ribosome, and in more than one site Bugs that are erythromycin resistant (and clarith-, azith- too) may be still susceptible to telithromycin Does not induce expression of erm (erythromycin ribosome methylase) that methylate parts of ribosomal RNA to reduce binding of other macrolides Similar spectrum to azithromycin, also covers PRSP, but not MRSA Potentially fatal liver toxicity found after it was on the market. Boxed warning Aggravates myesthenia gravis: autoimmune disorder in which antibodies block nerve/muscle signaling. Potentially fatal. Pregnancy category C N N N CH 3 H N
13 Telithromycin (Ketek ) Inhibits liver enzymes: drug-interactions prevalent Blurred vision Prolonged QT interval: can produce ventricular arrhythmias; avoid in patients with congenital elongated QT, on going arrhythmic conditions, and those taking antiarrhythmic agents Acid stable, oral bioavailability ~57%; P only Highest tissue penetration; even higher than azithromycin and clarithromycin E.g x above serum concentrations in some lung cells and macrophages Drug stays above MIC for most respiratory pathogens Due to potentially severe adverse effects, telithromycin not to be used for mild cases or to treat bronchitis, sinusitis. Removed indications for those. NW, only indicated use for CAP.
14 Resistance is on the rise E.g. between 1995 and 1999, S. pneumo resistance to macrolides rose from 10.6 to 20.4% Methylation of ribosome binding site via erm (erythromycin ribosomal methylation) enzymes Affects erythro-, clarithro-, azithro-, but NT telithromycin Erm expression is inducible Active macrolide efflux pumps Esterases cleave the lactone ring Macrolides Resistance Intrinsic Enterobacteriacea resistance due to outer membrane permeability
15 Macrolide summary Erythro-, Clarithro-, Azithro- commonly used for community-acquired respiratory infections Shut down protein synthesis by binding to bacterial 50s ribosomal subunit Newer macrolides (Az, Cl, Tel) are more acid stable and have a broader spectrum of coverage and greater potency than erythromycin. Variety of drug-interactions for Er, Cl, Tel but less so with Az Resistance due to change of target binding site (methylation of RNA) and efflux pumps in some bacteria Telithromycin to be used with caution, numerous adverse effects
16 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCCHCH2CH2NH2 H Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many H and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged and highly soluble at physiological ph. Not orally absorbed. All IV drugs. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall.
17 Aminoglycoside properties Streptomycin Isolated in 1943 by Selman Waksman from Streptomyces griseus Breakthrough drug for treatment of tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) Gentamicin Isolated in 1963 from Micromonospora purpurea ( mycin only if from Strep.) Significant use in treatment of Gram- infections including Pseudomonas Amikacin Semi-synthetic, derived from Kanamycin Designed to overcome resistance due to modifying enzymes Streptomycin
18 Aminoglycoside properties Reserved for serious infections only Due to serious toxicity concerns: ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity Concentrations require monitoring IV only for systemic infections; majority passed unmodified in urine If the patient is predisposed to renal dysfunction, important to monitor closely P form for gut sterilization; none is absorbed into the blood, all goes through gut unmodified Does not cross blood-brain barrier into CNS Active against broad spectrum of Gram- aerobes and facultative anaerobes Weak coverage of Gram+ if used alone, but may be combined with another drug such as beta-lactams. E.g. possibly for enterococci such as E. faecium Poor coverage of obligate anaerobes AG can transit through porins, but... Anaerobes do not possess the transport machinery that would bring aminoglycosides into the cytosol
19 Reserved for serious infections only Aminoglycoside uses Empiric therapy of serious infections: Septicemia, complicated RTI, UTI, intra-abdominal, osteomyelitis Followed by switching to another less toxic antimicrobial once the pathogen is ID d Prophylaxis for gastrointestinal (oral) or urogenital tract surgery
20 Aminoglycosides target the 30s ribosomal subunit: MA 30s 50s aminoglycosides tetracyclines macrolides chloramphenicol lincosamides streptogramins linezolid Binds to 30s ribosomal subunit and interferes with protein synthesis in multiple ways Single binding site for streptomycin; other AG have more than one binding site on 30s subunit, hence harder for sufficient mutations to arise to knock out all their inhibitory effect uter membrane disruption (interacts w/ lipopolysaccharide) in Gram-negative bacteria leads to cell permeabilization and greater antibiotic uptake.
21 Aminoglycoside MA: 1) protein synthesis disruption A P E Binds to 30s ribosomal subunit and: with initiation, ribosome locked at AUG start codon of mrna (at higher Interferes concentrations) Premature termination of translation Incorporation of incorrect amino acid leading to nonsense proteins.
22 Aminoglycoside MA: 2) Membrane disruption fissures lipopolysaccharide Interacts with Gram- outer membrane and makes it leaky. This leads to increased penetration of the drug. Also plays a role in increasing penetration of other drugs. Bactericidal unlike most protein synthesis inhibitors. This is probably due to the activity against the membrane.
23 Aminoglycoside MA Bactericidal Concentration-dependent killing: increasing concentrations increases rate and extent of bacterial death How best to reach and maintain necessary therapeutic concentrations in balance with toxicities, which also are concentration dependent? Consolidated or single daily dose approach. Strong post-antibiotic effect (PAE): Persistent inhibition of bacterial growth even after systemic drug is cleared PAE gets stronger for higher concentrations, up to a point Seen with aminoglycosides in Gram- bacteria Staph. but not other Gram+ bacteria Also white blood cells show enhanced phagocytosis and bacterial killing after exposure to aminoglycosides.
24 Single vs multiple daily doses for aminoglycosides Concentration-dependent killing: Want to hit a certain optimal peak concentration, which can be hard to achieve with traditional, multi- dosing. More likely to hit those optimal concentrations w/ consolidated dose. Possible benefits: Lower cost Reduced toxicity (nephro only; does not reduce ototoxicity): Assume aminoglycoside renal and inner ear uptake can be saturated Do not want to have the trough concentrations stay elevated due to increased chance of nephrotoxicity Not necessarily effective for treatment of all bacteria (e.g. Gram+ don t show PAE)
25 Synergy ften combined with cell-wall inhibitor: Can help for Gram+ treatments (AG alone not effective) Beta-lactam + aminoglycoside: e.g. ampicillin + gentamicin Vancomycin + aminoglycoside Cell-wall disruptors may increase permeability of aminoglycoside into cell Examples: Infective endocarditis: Staph, Strep viridans, Enterococci Pseudomonas (Gram-): high intrinsic resistance to mono-therapies But beta-lactams and aminoglycosides in vitro at high concentrations can interact, undergo chemical reaction, and inactivate each other Do not mix in the same solution This effect varies based on pairing of beta-lactam and aminoglycoside
26 Spectrum and usage Gram- aerobes: Pseudomonas aeruginosa (tobramycin) Acinetobacter spp. Enterobacteriaceae: Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, Providencia... Haemophilus influenzae Etc. Gram+ aerobes: usually used in combination with a beta-lactam or vancomycin Streptococcus Staphylococcus Mycobacteria M. tuberculosis MAC Not much activity against anaerobes Believed that anaerobes lack the ability to actively take up AG into their cytosol
27 Specific Aminoglycoside properties Gentamycin (IV/IM, opthalmic, topical) The go-to aminoglycoside for Gram- aerobic infections Associated with ototoxicity, especially affecting vestibular system Tobramycin (IV/IM, opthalmic, topical) Greater potency compared to Gentamycin against Pseudomonas Less ototoxicity than Gentamycin, but auditory loss possible Kanamycin (IV/IM, P) Can be used for intestinal infections or as sterilizing prophylaxis of the gut, often combined with cell-wall disruptor (beta-lactam, vanco) Can be profoundly ototoxic, less impact on vestibular system H2N Amikacin (IV/IM) Less susceptible to enzymatic inactivation by resistance factors Powerful agent, reserved for cases that are resistant to Gentamycin/Tobramycin, so as not to foster resistance Somewhat less toxic to vestibular system than gentamycin If a bacteria is resistant to Amikacin, it is likely to be resistant to all the other aminoglycosides as well NHCCHCH2CH2NH2 H
28 Resistance Compared to other antibiotics, resistance to aminoglycosides is rare Primarily mediated by enzymatic modification of the H and NH 2 groups Phosphorylation Acetylation Adenylation Encoded on plasmids, transposons Pseudomonas Efflux pump removal of drug from cytosol Modified ribosomal binding site Methylation of 16s ribosomal RNA Single mod can knock out streptomycin binding since it has a single binding site; other AG have more than one, harder to evolve resistance
29 Resistance Gentamicin: multiple sites available for enzymatic modification Amikacin: side chain modification made Amikacin more resistant to enzyme modification Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 1999, 43:727
30 Toxicity: Nephrotoxicity Usually reversible More common than ototoxicity, 5-20% of patients Aminoglycoside accumulates in proximal tubules of renal cortex, kills the cells Tubular cell degeneration can lead to sloughing of cells and fine sediment in urine
31 Toxicity: totoxicity Irreversible Less common than nephrotoxicity; toxicities do not appear to be correlated Aminoglycoside accumulates in inner ear and leads to destruction of cochlear hair cells Produces reactive radicals that kill the hair cells Vestibular toxicity: imbalance, vertigo, tinnitus, nystagmus (involuntary eye movement) More frequently seen with gentamicin Auditory toxicity: high frequency hearing loss More common with amikacin, kanamycin (particularly damaging) Emergence unpredictable, could be after a single dose; can appear weeks after therapy is completed (continue monitoring) AG accumulate in inner ear fluids and are cleared slowly, hence latency Possibly a genetic factor: mutation on ribosomal RNA in mitochondria that enables AG to bind to human ribosomes; leading to disruption of mitochondrial protein synthesis
32 Toxicity: Neuromuscular blockage Rare Myasthenia gravis Drug induces auto-immune response that leads to blockage of neuromuscular communication Antibodies block acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions Fatigue, weakness
33 Aminoglycoside summary Reserved for serious infections in a nosocomial setting only Possibility of oto- and nephro-toxicity If the patient is predisposed to renal dysfunction, important to monitor closely Gram- aerobes and facultative anaerobes are the primary targets; broad spectral coverage Weak coverage of Gram+ if used alone, but often combined with another drug such as beta-lactams Multiple mechanisms of action: Protein synthesis disruption at more than one stage Membrane disruption in Gram- bacteria leading to increased drug penetration and cell trauma
Aminoglycosides. Not orally absorbed. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall. Aminoglycoside properties
 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Sulfonamides. Georg Domagk and colleagues at Bayer spent 5 years screening dye compounds for antibacterial activity
 Sulfonamides Prontosil Sulfanilamide Georg Domagk and colleagues at Bayer spent 5 years screening dye compounds for antibacterial activity Thought Prontosil was the active drug, in fact it is metabolized
Sulfonamides Prontosil Sulfanilamide Georg Domagk and colleagues at Bayer spent 5 years screening dye compounds for antibacterial activity Thought Prontosil was the active drug, in fact it is metabolized
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins
 Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Anti-Microbial Drugs
 Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
 Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Macrolides & Ketolides. Objectives. Protein Synthesis
 Macrolides & Ketolides Elizabeth D. Hermsen, Pharm.D. Infectious Diseases Research Fellow University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy bjectives Participant should be able to explain macrolide/ketolide
Macrolides & Ketolides Elizabeth D. Hermsen, Pharm.D. Infectious Diseases Research Fellow University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy bjectives Participant should be able to explain macrolide/ketolide
Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Aminoglycosides Macrolides
 Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Vancomycin. A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci.
 Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Overview of Translation (2) Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Overview of Translation (3) Lecture Outline. Overview of Translation (1)
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Oxazolidinones Streptogramins Lecture Outline Description of protein synthesis - translation Antibiotics
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Oxazolidinones Streptogramins Lecture Outline Description of protein synthesis - translation Antibiotics
Antibiotics.. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol
 Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
B. Incorrect! Peginterferon α-2a is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and may be preferable to interferon- α.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION :
 AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
Development of C sporins. Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins. Second generation C sporins. Targets - PBP s
 Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Beta-lactam antibiotics - Cephalosporins Development of C sporins Targets - PBP s Activity - Cidal - growing organisms (like the penicillins) Principles of action - Affinity for PBP s Permeability properties
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
gram neg.(semisynthetic) Bacteria Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis Drug Action Organisms Comments Spectrum of Action Mycobacterium
 Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Aminoglycosides John A. Bosso, Pharm.D.
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Therapeutics/PHRMP-73 Aminoglycoside Mechanism of Action Aminoglycosides bind to 30s ribosomal subunit resulting in mistranslation of mrna thus disrupting protein synthesis. They are rapidly
Other β-lactam. A. Carbapenems:
 A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
Initiating Aminoglycosides Safely. Last updated: July 2016, Version 5 Questions/Comments?
 Initiating Aminoglycosides Safely Last updated: July 2016, Version 5 Questions/Comments? Email Mark.McIntyre@uhn.ca Click orange buttons to navigate protocol. Index: Aminoglycoside Dosing Algorithms Objective
Initiating Aminoglycosides Safely Last updated: July 2016, Version 5 Questions/Comments? Email Mark.McIntyre@uhn.ca Click orange buttons to navigate protocol. Index: Aminoglycoside Dosing Algorithms Objective
Antituberculous Agents
 Antituberculous Agents Primary or First Line Drugs: Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin Rifadin or Rimactane Ethambutal Streptomycin Pyrazinamide Isoniazid(INH) Most active. Small molecule, water soluble, Structurally
Antituberculous Agents Primary or First Line Drugs: Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin Rifadin or Rimactane Ethambutal Streptomycin Pyrazinamide Isoniazid(INH) Most active. Small molecule, water soluble, Structurally
NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS. 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003
 NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003 The slides presented at this meeting are available on this site as "Web slide shows" and
NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003 The slides presented at this meeting are available on this site as "Web slide shows" and
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD)
 Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Clarithromycin. Brand Name: Biaxin Drug Class: Opportunistic Infection and Other Drugs
 Brand Name: Biaxin Drug Class: Opportunistic Infection and Other Drugs Drug Description is a semisynthetic macrolide antibiotic. It differs structurally from erythromycin by methylation of a hydroxyl group
Brand Name: Biaxin Drug Class: Opportunistic Infection and Other Drugs Drug Description is a semisynthetic macrolide antibiotic. It differs structurally from erythromycin by methylation of a hydroxyl group
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory. Neomycin Sulphate, Polymyxin B Sulfate and Bacitracin Zinc Powder
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory NEOSPORIN ANTIBIOTIC POWDER Neomycin Sulphate, Polymyxin B Sulfate and Bacitracin Zinc Powder QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory NEOSPORIN ANTIBIOTIC POWDER Neomycin Sulphate, Polymyxin B Sulfate and Bacitracin Zinc Powder QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE
AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM D O N E B Y
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM DONE BY: SARA ALARFAJ 2014 OUTLINE Introduction about Aminoglycosides. Spectrum/uses. TDM Aminoglycosides TDM Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics. Dosing in AG. Sampeling time and Monitoring.
AMINOGLYCOSIDES TDM DONE BY: SARA ALARFAJ 2014 OUTLINE Introduction about Aminoglycosides. Spectrum/uses. TDM Aminoglycosides TDM Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics. Dosing in AG. Sampeling time and Monitoring.
Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof
 Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof 1. Considérations générales et introductives 1 Facts about Antibiotics Alexander Fleming (1928) discovered penicillin Ignored until early 1940s with extensive
Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof 1. Considérations générales et introductives 1 Facts about Antibiotics Alexander Fleming (1928) discovered penicillin Ignored until early 1940s with extensive
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation)
 NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi
 number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
Beta-lactamase production should have no effect on Azithromycin activity.
 AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Action Azithromycin
AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Action Azithromycin
PHARMACOLOGY II. Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP
 PHARMACOLOGY II Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! THEY COME IN DIFFERENT SHAPES ANTIMICROBIAL SITES OF ACTION SULPHONAMIDES 1930, Physician/researcher
PHARMACOLOGY II Dr Shariq Syed Associate Professor AIKTC, SoP INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIA! THEY COME IN DIFFERENT SHAPES ANTIMICROBIAL SITES OF ACTION SULPHONAMIDES 1930, Physician/researcher
Amino glycosides. Initially passively diffuses via porin channels and then actively transported
 Pharmacology Week 7 Amino glycosides Streptomycin, Gentamicin, Amikacin Physical and chemical properties Water soluble, stable in solution, more active in alkaline ph MOA: Irreversible inhibitors of protein
Pharmacology Week 7 Amino glycosides Streptomycin, Gentamicin, Amikacin Physical and chemical properties Water soluble, stable in solution, more active in alkaline ph MOA: Irreversible inhibitors of protein
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets
 Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP)
 NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
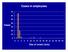 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
EASY AZITHROMYCIN 250 MG
 EASY AZITHROMYCIN 250 MG Easy Azithromycin 250 Mg Tacrolimus and levels azithromycin Taking azithromycin for bronchitis Buy treatment azithromycin chlamydia Uti for azithromycin can use u Digoxin azithromycin
EASY AZITHROMYCIN 250 MG Easy Azithromycin 250 Mg Tacrolimus and levels azithromycin Taking azithromycin for bronchitis Buy treatment azithromycin chlamydia Uti for azithromycin can use u Digoxin azithromycin
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Antimycobacterial drugs. Dr.Naza M.Ali lec Dec 2018
 Antimycobacterial drugs Dr.Naza M.Ali lec 14-15 6 Dec 2018 About one-third of the world s population is infected with M. tuberculosis With 30 million people having active disease. Worldwide, 9 million
Antimycobacterial drugs Dr.Naza M.Ali lec 14-15 6 Dec 2018 About one-third of the world s population is infected with M. tuberculosis With 30 million people having active disease. Worldwide, 9 million
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium
 Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Mesporin TM. Ceftriaxone sodium. Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections
 Ceftriaxone sodium Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections 1, 2, 3 Antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity Broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive* and gram-negative
Ceftriaxone sodium Rapid onset, sustained action, for a broad spectrum of infections 1, 2, 3 Antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity Broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive* and gram-negative
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin.
 Doctor leaflet 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONUROL 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin. Excipients: One sachet
Doctor leaflet 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONUROL 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin. Excipients: One sachet
Resistance to new anti-grampositive. Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France
 Resistance to new anti-grampositive agents Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France Recently available antimicrobials against MDR Gram-positive infections Cyclic lipopeptide: daptomycin
Resistance to new anti-grampositive agents Roland Leclercq, Microbiology, CHU Cote de Nacre, Caen, France Recently available antimicrobials against MDR Gram-positive infections Cyclic lipopeptide: daptomycin
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated
 Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Antibiotics for Research
 Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD)
 Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Sep Oct Nov Dec Total
 LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin the last one!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin the last one!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly
number Done by Corrected by Doctor مالك الزحلف
 number 30 Done by حسام أبو عوض Corrected by Shahd Alqudah Doctor مالك الزحلف Vancomycin As mentioned in the previous lecture, vancomycin is a pure gram-positive drug (has no effect on gram-negative bacteria),
number 30 Done by حسام أبو عوض Corrected by Shahd Alqudah Doctor مالك الزحلف Vancomycin As mentioned in the previous lecture, vancomycin is a pure gram-positive drug (has no effect on gram-negative bacteria),
Beta-lactamase production should have no effect on Azithromycin activity.
 AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules & Powder Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Azimex
AZIMEX Composition Azimex 250 Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 250 mg Capsules & Powder Azimex 500 mg Capsules Each capsule contains Azithromycin (as dihydrate) 500 mg Azimex
CAN AZITHROMYCIN CAUSE VAGINAL BLEEDING
 CAN AZITHROMYCIN CAUSE VAGINAL BLEEDING Can Azithromycin Cause Vaginal Bleeding Azithromycin capsules or tablets Can azithromycin be taken with alcohol Azithromycin best time to take Azithromycin for pneumonia
CAN AZITHROMYCIN CAUSE VAGINAL BLEEDING Can Azithromycin Cause Vaginal Bleeding Azithromycin capsules or tablets Can azithromycin be taken with alcohol Azithromycin best time to take Azithromycin for pneumonia
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP (Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules MANUFACTURER STANDARD) 250 mg Capsules ANTIBIOTIC DATE OF PREPARATION January 08, 2001 8250 Décarie Blvd, suite 110 Montréal,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP (Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules MANUFACTURER STANDARD) 250 mg Capsules ANTIBIOTIC DATE OF PREPARATION January 08, 2001 8250 Décarie Blvd, suite 110 Montréal,
ZINEX. Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg
 ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
TOBRAMYCIN Injection, USP. Rx only
 TOBRAMYCIN Injection, USP Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of tobramycin and other antibacterial drugs, tobramycin should be used only to treat
TOBRAMYCIN Injection, USP Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of tobramycin and other antibacterial drugs, tobramycin should be used only to treat
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 1 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly Gram (+)
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 1 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly Gram (+)
Antibiotics: Definition CHAPTER 37. Antibiotics. NDEG 26 A Pharmacology I Eliza Rivera-Mitu, RN, MSN. Antibiotics: Classes
 CHAPTER 37 Antibiotics NDEG 26 A Pharmacology I Eliza Rivera-Mitu, RN, MSN Antibiotics: Definition Medications used to treat bacterial infections Ideally, before beginning antibiotic therapy, the suspected
CHAPTER 37 Antibiotics NDEG 26 A Pharmacology I Eliza Rivera-Mitu, RN, MSN Antibiotics: Definition Medications used to treat bacterial infections Ideally, before beginning antibiotic therapy, the suspected
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
-Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection
 Urinary tract infections: -Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection -Urinary tract infection and respiratory infection together encompass about fifty
Urinary tract infections: -Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection -Urinary tract infection and respiratory infection together encompass about fifty
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
 DISCLAIMER All labeling reflected on this website is for informational and promotional purposes only. It is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing
DISCLAIMER All labeling reflected on this website is for informational and promotional purposes only. It is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin Coming soon!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: mode of action 3 Erythromycin:
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin Coming soon!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: mode of action 3 Erythromycin:
Tobramycin Injection, USP
 DISCLAIMER All labeling reflected on this website is for informational and promotional purposes only. It is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing
DISCLAIMER All labeling reflected on this website is for informational and promotional purposes only. It is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing
CAN AZITHROMYCIN TABLETS BE CUT IN HALF
 CAN AZITHROMYCIN TABLETS BE CUT IN HALF Can Azithromycin Tablets Be Cut In Half Azithromycin 500 mg liquid flavors list pdf Azithromycin for dog ear infection Azithromycin 250 mg safe during pregnancy
CAN AZITHROMYCIN TABLETS BE CUT IN HALF Can Azithromycin Tablets Be Cut In Half Azithromycin 500 mg liquid flavors list pdf Azithromycin for dog ear infection Azithromycin 250 mg safe during pregnancy
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Laboratory CLSI M100-S18 update. Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator
 Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology
 University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE?
 1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
Drug Class Review on Macrolides
 Drug Class Review on Macrolides Preliminary Scan Report 5 July 2014 Last Report: Original August 2006 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
Drug Class Review on Macrolides Preliminary Scan Report 5 July 2014 Last Report: Original August 2006 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn Series
 ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman, Department of Medicine SUNY at Stony Brook
 Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Chairman, Department of Medicine Winthrop-University Hospital Mineola, NY Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman,
Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Chairman, Department of Medicine Winthrop-University Hospital Mineola, NY Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman,
Severe β-lactam allergy. Alternative (use for mild-moderate β-lactam allergy) therapy
 Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Recommended Empirical Antibiotic Regimens for MICU Patients Notes: The antibiotic regimens shown are general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Always assess for antibiotic allergies.
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN
 PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT GRAM- NEGATIVE BACILLI INFECTION JOURNAL CLUB PRESENTATION Amal M. Al-Anizi, PharmD Candidate KSU, Infectious disease rotation
PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT GRAM- NEGATIVE BACILLI INFECTION JOURNAL CLUB PRESENTATION Amal M. Al-Anizi, PharmD Candidate KSU, Infectious disease rotation
JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
PRODUCT INFORMATION. Colistin Link. Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Colistin Link Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial For Intramuscular and Intravenous use. NAME OF THE MEDICINE Colistimethate sodium for injection,
PRODUCT INFORMATION Colistin Link Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial For Intramuscular and Intravenous use. NAME OF THE MEDICINE Colistimethate sodium for injection,
Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France
 Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
Marie Curie Actions Research Training Networks (RTN) Translocation Studies Mid-Term Review (MTR) Meeting Marseille, France F. Vidal-Aroca, M.G.P. Page and J. Dreier Background Deteriorating situation regarding
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
TELITHROMYCIN (KETEK ) A NEW ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT
 Volume 19, Issue 12 September 2004 TELITHROMYCIN (KETEK ) A NEW ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT Christopher Cha, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Infections that invade the lower respiratory tract, such as community-acquired
Volume 19, Issue 12 September 2004 TELITHROMYCIN (KETEK ) A NEW ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT Christopher Cha, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Infections that invade the lower respiratory tract, such as community-acquired
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory
 Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
To order products call or fax
 ANTIBIOTIC Tobramycin Injection, USP WARNINGS Patients treated with tobramycin injection and other aminoglycosides should be under close clinical observation, because these drugs have an inherent potential
ANTIBIOTIC Tobramycin Injection, USP WARNINGS Patients treated with tobramycin injection and other aminoglycosides should be under close clinical observation, because these drugs have an inherent potential
Gentamicin - Ototoxicity in children
 Second Meeting of the Subcommittee of the Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Geneva, 29 September to 3 October 2008 Gentamicin - Ototoxicity in children Summary Aminoglycosides
Second Meeting of the Subcommittee of the Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Geneva, 29 September to 3 October 2008 Gentamicin - Ototoxicity in children Summary Aminoglycosides
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Doxylin 50% WSP, powder for oral solution in pre-ruminant calves, pigs and chickens (BE, BG, NL, RO) Doxylin 50%, powder for
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT Doxylin 50% WSP, powder for oral solution in pre-ruminant calves, pigs and chickens (BE, BG, NL, RO) Doxylin 50%, powder for
Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center
 Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center Kathy Peters is a 63 y.o. patient that presents to your urgent care office today with a history
Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center Kathy Peters is a 63 y.o. patient that presents to your urgent care office today with a history
Ameba has two stages of development: cyst and trophozoite
 Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Issues Abx request. Sneezing w/ post- nasal d/c & redness mucous membranes Throat. Chest px w/ coughing, difficulty breathing
 Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
Week 5 Magic Bullets URTI + Pneumonia Presenting Sx Cough, sore throat & runny nose Aches & pains all over Shivers & fevers Respiratory Viruses Viruses causing flu Influenza A/B/C (orthomyxovirus) Respiratory
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT
 ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Where are we heading?
 Unit 4: Where are we heading? Unit 4: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 4: Where are we heading? Unit 4: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and the package leaflets
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and the package leaflets 22 Changes agreed by the CHMP to the product information of CMS-containing products for injection
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the summary of product characteristics and the package leaflets 22 Changes agreed by the CHMP to the product information of CMS-containing products for injection
List of teams: Practice question: Which of the following individuals was among the first to recognize the importance of handwashing?
 List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
List of teams: 1. Group 1 - Room 304 - Dr. Dobkin 2. Group 2 - Room 306 - Dr. Yin 3. Group 3 - Room 308 - Dr. Lowy 4. Group 4 - Room 310 - Dr. Neu 5. Group 5 - Room 316 - Dr. Prince 6. Group 6 - Room 320
Fraser Health pandemic preparedness
 Fraser Health pandemic preparedness DRAFT Last revised: April 2006 General Management of Patients in Acute Care Facilities During an Influenza Pandemic 1. OVERVIEW GENERAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS IN ACUTE
Fraser Health pandemic preparedness DRAFT Last revised: April 2006 General Management of Patients in Acute Care Facilities During an Influenza Pandemic 1. OVERVIEW GENERAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS IN ACUTE
The following languages are included in this packet:
 OSTEOSET T BONE GRAFT PRODUCTS 150826-2 The following languages are included in this packet: English (en) Deutsch (de) Nederlands (nl) Français (fr) Español (es) Italiano (it) Português (pt) Türkçe (tk)
OSTEOSET T BONE GRAFT PRODUCTS 150826-2 The following languages are included in this packet: English (en) Deutsch (de) Nederlands (nl) Français (fr) Español (es) Italiano (it) Português (pt) Türkçe (tk)
Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism
 Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism 1- Antibiotics with fused ring system: -Griseofulvin -Tetracyclines -[Fusidic acid] 2-Macrolide antibiotics 3-Polyene antibiotics Griseofulvin: Produced
Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism 1- Antibiotics with fused ring system: -Griseofulvin -Tetracyclines -[Fusidic acid] 2-Macrolide antibiotics 3-Polyene antibiotics Griseofulvin: Produced
