A218 : Esophagus cancer tissues. (formalin fixed)
|
|
|
- Avis Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 40 Tissue type: Esophagus cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (80 spots) 4 non-neoplastic spots (4 spots) Total spots: 84 Corresponding normal tissues with cancers: Yes Diameter: 1. 0 mm Documents: Product specification: layout, summary of tissue spots H&E stained images Detailed pathological information Layout:
2 (formalin fixed) For research use only Summary of tissue spots No. Coordinate Sex Age Key Word Type TNM Stage Tumor Size ( cm ) 1 1,2 m 66 well T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 8.0* ,4 m 67 well T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 2.8*1.7 3 A 5,6 m 69 in situ well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.0*2.0 anthracosis 4 7,8 m 60 well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 4.5* ,10 m 50 well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.8* ,2 m 79 moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 3.0* ,4 m 59 carcinoma in situ moderate T3N1M1 ( Ⅳ ) 5.3*2.5 8 B 5,6 m 54 dysplasia moderate T1N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 1.7* ,8 m 69 moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 2.0* ,10 m 55 moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 1.8* ,2 m 73 moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 5.0* ,4 m 63 in situ moderate T4N0M0 ( Ⅲ ) 2.8* ,6 m 57 moderate T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 5.5* ,8 m 58 moderate T2N1M1 ( Ⅳ ) 4.0*3.0*1.0 C esophagus squamous cell 15 9,10 m 75 carcinoma stomach adenocarcinoma stomach signet ring cell moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 4.5*3.5 carcinoma stomach tubular adenoma 16 1,2 f 64 moderate T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) ,4 f 58 moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 4.5* D 5,6 m 67 moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.3* ,8 m 77 moderate T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.5* ,10 m 69 moderate T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 3.5*2.3* ,2 m 61 moderate T3N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 1.3* ,4 m 56 moderate T1N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 3.0* E 5,6 m 68 moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 5.5* ,8 m 61 moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0* ,10 m 60 moderate T4N0M0 ( Ⅲ ) 3.0*2.0* ,2 m 71 GIST moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 8.0* ,4 m 61 moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.0* F 5,6 m 62 moderate T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 4.0* ,8 m 60 eiomyoma moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0* ,10 m 62 poorly T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.0*1.3
3 (formalin fixed) For research use only Summary of tissue spots No. Coordinate Sex Age Key Word Type TNM Stage Tumor Size ( cm ) 31 1,2 m 66 poorly T3N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 3.1* ,4 m 73 poorly T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) ,6 m 56 poorly T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0* ,8 m 69 T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 3.5*2.3*1.4 G 35 9,10 m 73 sarcoma malignant fibrous histiocytoma 3.2*2.4*1.0 double cancer 36 1,2 m 70 moderately -well T1N0M1 ( Ⅳ ) 3.0*2.7 moderately 37 3,4 m 68 T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 4.0*3.0 -well H moderately 38 5,6 m 71 T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 4.0*1.5 to poorly 39 7,8 m 80 T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 5.0* ,10 m 68 T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) non-neoplastic, from A3, non-neoplastic, from E5, 6 I 43 9 non-neoplastic, from D9, non-neoplastic, from G1, 2
4 (formalin fixed) QC sheet_lot# Hematoxylin and Eosin staining For research use only A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9 B10 C1 C2 C3 C4
5 (formalin fixed) QC sheet_lot# Hematoxylin and Eosin staining For research use only C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 E7 E8
6 (formalin fixed) QC sheet_lot# Hematoxylin and Eosin staining For research use only E9 E10 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 G6 G7 G8 G9 G10 H1 H2
7 (formalin fixed) QC sheet_lot# Hematoxylin and Eosin staining For research use only H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9 H10 I7 I8 I9 I10
8 1. Esophagus: 1), well differentiated, ulceroinfiltrative, extension to subserosal fat tissue arising frome sophagus 2) resection margin, proximal: extension of tumor 2. Jejunal margin: free of tumor 3. Separately submitted segmemt of small bowel:free of tumor 4. Pancreas: free of tumor 1 A 1,2 m Spleen: free of tumor 6. Regional lymph nodes, N3 (1/13), N4 (0/1), N8 (0/2), N10 (0/1), (1/17): metastasis in 1 out of 17 nodes 7. Soft tissue labelled as N1,N2: absence of node 8. Pancreas and spleen labelled as N10 AND N11: 1) ecotpic pancreas 2) accessory spleen well T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 8.0*7.0 2 A 3,4 m 67 3 A 5,6 m 69 Esophagus, segmental resection: 1), well differentiated with extension to submucosa 2) beingn stromal tumor, gastroesophagel junction 3) resection margin: free of tumor 4) lymph node, regional: metastatic in one out of 12. (paraesophageal (0/1), inferior pulmonary (0/1), subscalular (0/3), perigastric (1/7)) 1. fungating, well differentiated with focal necrosis with 1) tumor extension to the submucosa 2) no lymphovascular permeation 3) no perineural invasion 4) adjacent in situ 5) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor in situ 2. Regional lymph nodes, paraaortic (0/2), inferior pulmonary ligament (0/3), hilar anthracosis (0/8), paraesophageal (0/2) : (0/15): 1) free of tumor in all 15 lymph nodes 2) anthracosilicosis 3. Soft tissue, labelled as "paraspinal mass": myelolipoma 4. Omentum: free of tumor well T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 2.8*1.7 well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.0*2.0 4 A 7,8 m 60 1) fungating, well differentiated, with extension to the outer 1/3 of lamina propria no lymphovascular permeation 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) regional lymph nodes: free of tumor (0/1) well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 4.5*2.5
9 1), well-differentiated, fungating type, extending into 5 A 9,10 m 50 submucosa without proper muscle involvement 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor well T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.8*1.5 3) regional lymph node (0/4): free of tumor 6 B 1,2 m 79 Esophagus, total gastrectomy: 1), moderately differentiated with Ⅰ) ulcerative gross type Ⅱ) extension to the adventitia Ⅲ) no lymphatic permeation 2) resection margin, proximal, distal and lateral: free of tumor 3) regional lymph nodes, LN1 (0/1), LN3(0/3), LN7(0/1), paraesophageal (0/1), regional LN (1/3) : (1/9): tumor metastasis in one lymph node out of 9 lymph nodes moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 3.0*3.0 7 B 3,4 m 59 carcinoma in situ Esophagus, resection: 1), moderately differentiated with I) fungating gross type II) extension to the adventitia with penetration ( involving lateral resection margin) Ⅲ) A few lymphatic invasion 2) carcinoma in situ in the adjacent mucosa 3) resection margin, proximal: Presence of carcinoma in the lymphatics 4) resection margin, distal: free of tumor 5) resection margin, lateral: extension of tumor 6) lymph nodes, subcarinal node (0/7), paraesophageal node (0/2), paratracheal node (1/1), perigastric node (0/8) : (1/18): metastasis in 1 out of 18 lymph nodes 7) fibroadipose tissue labelled as distal resection margin: free of tumor moderate T3N1M1 ( Ⅳ ) 5.3*2.5 8 B 5,6 m 54 dysplasia Esophagus, esophagogastrectomy: 1), moderately differentiated, multifocal with extension to the submucosa and occasional lymphatic permeation 2) multifocal epithelial dysplasia with in situ 3) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 4) regional lymph nodes (1/21): metastatic in 1 out of 21 nodes moderate T1N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 1.7*1.0
10 1), moderately differentiated with Ⅰ) fungating gross type Ⅱ) extension to lamina propria and submucosa 9 B 7,8 m 69 Ⅲ) occasional lymphatic permeation moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 2.0*1.5 2) Acanthosis glycogenosis, multiple 3) resection margin, proximal and distal: free of tumor 4) lymph node, subcarinal (0/10): free of tumor 10 B 9,10 m C 1,2 m 73 1) (superficial carcinoma), moderately differentiated with Ⅰ) extension to the lamina propria (mucosa) Ⅱ) infiltrative gross type 2) resection margin, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) lymph nodes, labelled as paraesophageal (0/3), No.7 (0/2), omentual (0/7) : (0/12): free of tumor 1. Esophagus with stomach, esophagogastrectomy: 1) moderately differentiated, with extension to the adventitia and multiple foci of carcinoma in situ. 2) resection margins, proximal: free of tumor 3) resection margins, distal: free of tumor 4) lymph nodes, regional (1/22): metastatic carcinoma 1 out of 22 lymph nodes 2. Adrenal gland, adrenalectomy: nodular hyperplasia. 3. Spleen, splenectomy: free of tumor moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 1.8*1.0 moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 5.0* C 3,4 m 63 1), moderately differentiated, fungating type with extension to adventitia (very close to the lateral surgical margin) 2) resection margin, proximal: in situ 3) focal in situ 4) resection margin, distal: free of tumor 5) regional lymph nodes, upper mediastinal (0/5), lower paratracheal (0/4), subcarcinal (0/4), omental (0/10) : (0/23): free of tumor in all 23 lymph nodes moderate T4N0M0 ( Ⅲ ) 2.8*1.7
11 7 1), moderately differentiated with Ⅰ) ulcerative gross type Ⅱ) extension to the adventitia Ⅲ) no lymphovascular invasion 13 C 5,6 m 57 Ⅳ) foreign body reaction to keratinous material and abscess formation moderate T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 5.5*5.0 around tumor 2) resection margin, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) lymph nodes, esophageal (0/3), hilar (0/1), subcrainal (0/6), No.7 (3/6) paratracheal (0/1) : (3/21): metastatic carcinoma in 3 out of 21 lymph nodes 14 C 7,8 m 58 Esophagus and stomach, total esophagectomy: Fungating, moderately differentiated, with 1) size: 4x3x1 cm 2) infiltrative growth pattern 3) penetration of proper muscle layer and extension to adventitia 4) frequent vascular and neural invasion 5) intact resection margins including proximal (esophagus), distal (stomach) and deep margin, see note 6) no lymph node metastasis (subcarinial (0/2), paraaortic ascending (0/2), hilar (0/15), perigastric (0/1) andomentum (0/0)) Note: The tumor is so close to deep resection margin (less than 1 mm) and shows significant vascular invasion. moderate T2N1M1 ( Ⅳ ) 4.0*3.0*1.0
12 15 C 9,10 m 75 esophagus squamous cell carcinoma stomach adenocarcinoma stomach signet ring cell carcinoma stomach tubular adenoma 1.Esophagus, total esophagectomy:, moderately differentiated, with 1) ulceroinfiltrative gross type 2) extension to adventitia 3) occasional lymphatic permeation 4) presence of in situ in adjacent esophageal mucosa 2.Stomach, total gastrectomy: 1) adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated Ⅰ) ulceroinfiltrative gross type Ⅱ) mixed with signet ring cell carcinoma Ⅲ) with focal areas of extracellular mucin production Ⅳ) with extension to proper muscle layer Ⅴ) frequent lymphatic permeation 2) two tubular adenomas with low grade dysplasia 3) esophagus, proximal resection margin: focal dysplasia 4) duodenum, distal resection margin: free of tumor 5) regional lymph nodes, No.1 (1/5), No.2 (0/1), mediastinal (0/2) : (1/8): metastatic in one out of 8 lymph nodes 6) regional lymph node, No.3 (1/8), No.4 (0/0), No.5 (1/1), No.6 (5/6), No.7 (0/3), No.9 (0/8) : (7/26): metastatic adenocarcinoma in 7 out of 26 lymph nodes moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 4.5* D 1,2 f D 3,4 f 58 Infiltrative, moderately differentiated, with 1) size: 4cm in the greatest diameter 2) diffuse growth 3) penetration of muscle layer and extension into adventitia 4) perineural invasion 5) intact resetion margins (proximal and distal (stomach)) 1), moderately differentiated with extension to the proper muscle 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) lymph node, regional (0/1): free of tumor moderate T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 4 moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 4.5* D 5,6 m 67 1), moderately differentiated with extension to muscularis propria and occasional lymphatic permeation 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) regional lymph nodes, No.1 (0/2), No.2 (0/4) : (0/6): free of tumor moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.3*1.3
13 1), moderately differentiatd with extension through proper muscle to the adventitia (T3) 19 D 7,8 m 77 2) leiomyoma, small moderate T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.5*2.0 3) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 4) lymph nodes, paraesophageal (0/6) and regional (0/1) : (0/7): free of tumor 20 D 9,10 m E 1,2 m E 3,4 m 56 polypoid, moderately differentiated with 1) size: 3.5x2.3x1.4 cm 2) infiltrative growth 3) extension to inner muscle layer 4) frequent lymphovascular invasion 5) intramucosal metastasis 6) intact proximal (esophagus) and distal (stomach) resection margins 7) metastasis to regional lymph nodes (6/14: periesophageal (3/4), and celiac (3/10)) Esophagus, lower, esophagectomy: 1) ulcerative, moderately differentiated, with Ⅰ) extension to the periesophageal fat tissue Ⅱ) lateral margin: free of tumor Ⅲ) lymphovascular permeation: positive 2) resection margin, proximal, esophageal: free of tumor 3) resection margin, distal, gastric: free of tumor 4) regional lymph nodes: tumor metastasis to 3 out of 10 (3/10), in detail, gastric node (0/1), paraesophageal (0/6), celiac (3/3) 1. Esophagus, segmental resection: superficial, moderately differentiated with 1) size: 3.0x3.0cm approximately 2) superficial spreading growth with focal invasion to submucosal space 3) vascular invasion 4) intact proximal (esophagus) and distal (stomach) resection margins 5) metastasis to 1 out of 14 celiac lymph nodes 2. Stomach: consistent with Helicobacter pylori gastritis with multifocal atrophy with intestinal metaplasia moderate T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 3.5*2.3*1.4 moderate T3N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 1.3*0.6 moderate T1N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 3.0*3.0
14 Esophagus and stomach, Sweet's operation: 1), moderately differentiated, Ⅰ) arising from the gastroesophageal junction and extension to the esophagus and cardia of stomach. Ⅱ) fungating type Ⅲ) size: 5.5x4.5 cm Ⅳ) extension to the subadventitial and subserosal soft tissue (T2, no 23 E 5,6 m 68 adventitia involvement) Ⅴ) scant lymphovascular permeation moderate T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 5.5*4.5 2) separate mass of esophagus:, confined the mucosa and muscularis mucosa 3. Section margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 4. Regional lymph nodes: free of tumor in all nodes (0/30), in detail, celiac (0/2), left cardiac (0/11), greater curvature (0/0), #1 (0/14), #2 (0/3) 24 E 7,8 m 61 Ulcerofungating, moderately differentiated, 1) extension to the serosa (adventitia), not exposed to the mediastinum 2) size: 7x2.7 cm 3) lymphovascular permeation: positive 4) resection margin, proximal, esophageal: free of tumor 5) resection margin, distal, gastric: free of tumor 6) regional lymph nodes: tumor metastasis to 2 out of 32 (2/32), in detail, paraesophageal (0/3), celiac (0/1), hilar (0/2), regional (2/26) moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0* E 9,10 m 60, moderately differentiated, probably recurred, see note with 1) size: 2.5x2 cm 2) infiltrative growth 3) transmural involvement from mucosa to subserosal space 4) intact proximal and distal (stomach) resection margins but very close to deep margin 5) metastasis to 2 out of 33 regional lymph nodes (paraesophageal (0/6), right hilar (0/5), greater curvature (0/1), celiac (2/7), AP window (0/5), regional (0/9)) 6) chronic granulomatous infla mmation with necrosis, consistent with tuberculosis, in paraesophageal and AP window lymph nodes Note: The tumor was predominantly located in submucosal space without evidence of tumor occuring from the mucosatherefore, it could be recurred tumor of laryngeal carcinoma rather than primary esophageal carcinoma. moderate T4N0M0 ( Ⅲ ) 3.0*2.0*1.0
15 26 F 1,2 m 71 GIST ulcerofungating, moderately differentiated, with 1) size: 8x3cm 2) infiltrative growth 3) extension to 2/3 of submucosal space 4) no vascular and perineural invasion 5) intact proximal and distal resection margins 6) no metastasis to regional lymph nodes (celiac (0/2), periesophageal (0/7)) 7) gastrointestinal stromal tumor, benign, in upper body of stomach moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 8.0* F 3,4 m Esophagus, segmental resection:, moderately differentiated, ulceroinfiltrative type, with extension into submucosa, with clean surgical margin 2. Stomach, biopsy: free of tumor 3. Esophagus, separately submitted: free of tumor 4. Lymph nodes, dissection: Paraesophageal (0/1), celiac (0/2), lower paraesophageal (0/1), perigastric (0/3) : (0/7): free of tumor moderate T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 3.0* F 5,6 m 62 Esophagus, sweet operation: ulcerofungating, moderately differentiated, 1) size:4x3. 5cm 2) extension to the submucosa 3) lymphovascular permeation: unceratin 4) resection margin, proximal, esophageal: free of tumor 5) resection margin, distal, gastric: free of tumor 6) Regional lymph nodes: Tumor metastasis to 1 out of 3 (1/3), in detail, celiac node (0/2), lower paraesophageal node (1/1) moderate T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 4.0* F 7,8 m 60 eiomyoma Esophagus, resection: fungating, moderately differentiated, 1) size: 7x4.7cm 2) extension to the subserosa(no serosa involved) 3) lymphovascular permeation, present 4) separate mass: Leiomyoma, submucosal 5) resection margin, proximal, esophageal: free of tumor 6) resection margin, distal, gastric: free of tumor 7) regional lymph nodes: tumor metastasis to 2 out of 12 lymph nodes in detail, celiac (0/4),paraesophageal (1/3), regional (1/5) moderate T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0*4.7
16 Esophags, esophagectomy: 1), poorly differentiated, ulceroinfiltrative, extending 30 F 9,10 m 62 into muscularis propria without penetration 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor poorly T2N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 2.0*1.3 3) lymph node, regional (0/1), paraesophageal (0/4) : (0/5): free of tumor 31 G 1,2 m 66 Esophagus and lymph node, esophagectomy with lymph node dissection: ulcerofungating, poorly differentiated, with 1) extension to the adventitia(not exposed to the mediastinum) 2) size: 3.1x2 cm 3) lymphovascular permeation: scant 4) resection margin, proximal, esophageal: free of tumor 5) resection margin, distal, stomach: free of tumor 6) regional lymph nodes: tumor metastasis to 2 out of 3 (2/3), in detail, lower paraesophageal (0/1), celiac (2/2) poorly T3N0M1a ( ⅣA ) 3.1* G 3,4 m 73 Esophagus, segmental resection: ulcerofungating, poorly differentiated, with spindle cell and focal neuroendocrine differention with 1) size: about 9cm in the largest dimension along the longitudinal axis 2) infiltrative growth 3) invasion to submucosal space 4) vascular invasion 5) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 6) lymph nodes, paraesophageal (0/3) and No.1 (0/2): free of tumor metastasis in all 5 nodes poorly T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) G 5,6 m G 7,8 m 69 1), poorly differentiated with extension to the adventitia (T3) 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) lymph nodes, labelled as greater curvature (0/1), paraesophageal (0/3), IPL (1/9) and regional (0/15) : (1/28): metastatic carcinoma in 1 out of 28 lymph nodes Note: I mmunohistochemical staining results: NSE, Synaptophysin, poorly T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 7.0*6.0 Esophagus, resection margin, frozen biopsy: involving mucosa and submucosal lymphatic vessel T2N1M0 ( ⅡB ) 3.5*2.3*1.4
17 35 G 9,10 m 73 sarcoma malignant fibrous histiocytoma double cancer Esophagus : 1) mass, double tumors, sarcoma, most likely malignant fibrous histiocytoma, and 2) resection margin proximal,esophageal: free of tumor resection margin, distal, G-E junction: free of tumor 3) regional lymph node: free of tumor in all nodes (0/44), followings, mid paraesophageal (0/8), low paraesophageal (0/4), subcarinal (0/11), surrounding nodes (0/21) 3.2*2.4* H 1,2 m 70 Esophagus, total esophagectomy: moderately well-differentiated, predominantly confined to the lamina propria, with focal invasion into the muscularis mucosae, without involvement of the submucosa, muscularis propria, regional lymph nodes or surgical margins moderately -well T1N0M1 ( Ⅳ ) 3.0* H 3,4 m 68 Esophagus and stomach, esophagectomy and gastrectomy: 1) moderately/well differentiated with full thickness involvement of the esophageal wall, see note 2) regional lymph nodes, N1 (0/3), N2 (1/3) : (1/6): metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a lymph node, with extranodal extension, out of six lymph nodes 3) lymph nodes, labelled as "inferior pulmonary ligamental" (0/1) and labelled as "paratracheal" (0/5): pneumoconiotic nodules without involvement of tumor 4) resection margins, proximal (esophagus): free of tumor 5) resection margins, distal (jejunum): free of tumor 6) specimen, labelled as "mediastinal pleural nodule": metastatic squamous cell carcinoma a lymph node with extranodal extension Note: The stomach and the gastrojejunostomy site do not show any residual neoplasm. moderately -well T3N1M0 ( Ⅲ ) 4.0* H 5,6 m 71 1) Invasive, moderately to poorly differentiated, ulcerative, with penetration of entire wall and extension to the underlying resection margin and occasional lymphatic invasion 2) leiomyomatosis 3) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 4) lymph nodes(0/2): free of tumor metastasis in 2 nodes moderately to poorly T3N0M0 ( ⅡA ) 4.0*1.5
18 1. Esophagus, resection: 1) with focally glandular differentiation (adenosquamous carcinoma), confined to the submucosa but frequent lymphovascular permeation 39 H 7,8 m 80 T1N1M0 (ⅡB ) 5.0*4.8 2) resection margins, proximal and distal: free of tumor 3) regional lymph nodes, regional (1/1), No.2 (0/0), No.3 (0/0), No.7 (0/1), No.8 (0/0), No.11 (0/4): metastatic in 1 out of 6 nodes 2. Lung, wedge resection: bullae 1), multiple with Ⅰ) Infiltrative gross type Ⅱ) extension to the lamina propria and submucosa 40 H 9,10 m 68 Ⅲ) no lymphatic permeation T1N0M0 ( Ⅰ ) 1 Ⅳ) multifocal area of epithelial dysplasia, low to high grade 2) glycogenic acanthosis 3) resection margin: free of tumor 41 I 7 non-neoplastic non-neoplastic, from A3, 4 42 I 8 non-neoplastic non-neoplastic, from E5, 6 43 I 9 non-neoplastic non-neoplastic, from D9,10 44 I 10 non-neoplastic non-neoplastic, from G1, 2
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues
 A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
A916: rectum: adenocarcinoma
 General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
Gastric Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male Female Intersex/indeterminate
A220: Larynx cancer tissues. (formalin fixed)
 A220: Larynx cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Larynx cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90 spots) 4 non-neoplastic
A220: Larynx cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Larynx cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90 spots) 4 non-neoplastic
A301 VI- Various cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A301 VI- Various cancer tissues with (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 28 Tissue type: Various cancer tissues with No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (56 spots)
A301 VI- Various cancer tissues with (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 28 Tissue type: Various cancer tissues with No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (56 spots)
(formalin fixed) 6 non-neoplastic spots (6 spots) Corresponding normal tissues with cancers: Yes Diameter: 1. 0 mm
 CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
CBA729-Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 6 Tissue type: Test slide, Head and neck cancer tissues No. of spots: 6 spots from each
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Esophageal Cancer Staging Essentials: The New TNM Staging System (7th edition) and Clinicoradiologic Implications
 Esophageal Cancer Staging Essentials: The New TNM Staging System (7th edition) and Clinicoradiologic Implications Poster No.: E-0060 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Lee, T. J.
Esophageal Cancer Staging Essentials: The New TNM Staging System (7th edition) and Clinicoradiologic Implications Poster No.: E-0060 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Lee, T. J.
A103(9)- Normal tissues, more than single spots
 A103(9)- Normal tissues, more than single spots (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Normal tissues, more than single spots No. of spots: 2 spots from each
A103(9)- Normal tissues, more than single spots (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Normal tissues, more than single spots No. of spots: 2 spots from each
Case Scenario year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux.
 Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Small Intestine. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition
 Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Small Intestine Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the small intestine, including those with focal endocrine differentiation. Excludes carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, and stromal tumors (sarcomas).
Quiz Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been increasing in the last 20 years. a. True b. False
 Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS
 COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
COLLECTING CANCER DATA: STOMACH AND ESOPHAGUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
Tumours of the Oesophagus & Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given
Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition. Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW
 Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW Summary of changes New clinical stage prognostic groups, ctnm Postneoadjuvant therapy pathologic stage groupings, yptnm -
Gastric Cancer Staging AJCC eighth edition Duncan McLeod Westmead Hospital, NSW Summary of changes New clinical stage prognostic groups, ctnm Postneoadjuvant therapy pathologic stage groupings, yptnm -
Colon and Rectum. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6th edition
 Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Colon and Rectum Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Carcinoid tumors, lymphomas, sarcomas, and tumors of the vermiform appendix are excluded. Protocol revision date: January
Definition of Synoptic Reporting
 Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology
 Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology
 Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical & Partial Cystectomy, Cystoprostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical & Partial Cystectomy, Cystoprostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
A201(VI)- Various cancer tissues
 A201(VI)- Various cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 44 Tissue type: Various cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (88 spots) Total
A201(VI)- Various cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 44 Tissue type: Various cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (88 spots) Total
Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female. Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012
 Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012 Case HPI: 31 yo F, G5P3, 3 weeks s/p C-section, with gastric outlet obstruction. Pt
Gastric Cancer in a Young Postpartum Female Kings County Hospital Center SUNY Downstate Case Conference May 24, 2012 Case HPI: 31 yo F, G5P3, 3 weeks s/p C-section, with gastric outlet obstruction. Pt
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer
 Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours?
 Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours? Question #2: How are cardia tumours managed? Michael F. Humer December 3, 2005 Vancouver, BC Case
Surgical Problems in Proximal GI Cancer Management Cardia Tumours Question #1: What are cardia tumours? Question #2: How are cardia tumours managed? Michael F. Humer December 3, 2005 Vancouver, BC Case
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Stomach Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual For
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Stomach Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual For
위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행
 위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 문제의식 위궤양, 조기위암, 진행위암의내시경소견은배운다. 위암수술후소견은가끔배운다. 위암내시경시술후소견은배운적이없다. 관찰과조직검사에대한가이드라인이없다. ESD 후정상내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 처음의뢰되었을때의사진 ESD M/D, 18mm, LP, RM (-), L/V (-) 추적내시경소견 2
위 ESD 후내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 문제의식 위궤양, 조기위암, 진행위암의내시경소견은배운다. 위암수술후소견은가끔배운다. 위암내시경시술후소견은배운적이없다. 관찰과조직검사에대한가이드라인이없다. ESD 후정상내시경소견 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 처음의뢰되었을때의사진 ESD M/D, 18mm, LP, RM (-), L/V (-) 추적내시경소견 2
Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition
 22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C.
 Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Research Grants: Disclosures
Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Research Grants: Disclosures
Polyps in general: is a descriptive term of forming a mass that is exophytic & polypoid.
 ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
References. GI Biopsies. What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD
 What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
What Should Pathologists Assistants Know About Gastrointestinal Histopathology? James M Crawford, MD, PhD jcrawford1@nshs.edu Executive Director and Senior Vice President for Laboratory Services North
11/21/13 CEA: 1.7 WNL
 Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Patient. Male 76 year old C.C: abdominal pain
 Patient Male 76 year old C.C: abdominal pain Bowel stool retention Suspected pulmonary TB at right upper lung Infiltration in right lower lung Pleural thickening at the Right chest Localized dilated small
Patient Male 76 year old C.C: abdominal pain Bowel stool retention Suspected pulmonary TB at right upper lung Infiltration in right lower lung Pleural thickening at the Right chest Localized dilated small
Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. AJCC 8 th edition and CAP protocol updates
 Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco March 05, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco March 05, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
위암내시경진단 (2019) - 융기형위암을중심으로 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행
 위암내시경진단 (2019) - 융기형위암을중심으로 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 위암내시경진단 (2019) 위암검진에대한짧지않은 comment 융기형암은융기되어있는가? 함몰형암은함몰되어있는가? Semi-pedunculated polyp Sentinel polyp or EGJ cancer? IIa + IIc 위암검진에대한짧지않은 comment 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행
위암내시경진단 (2019) - 융기형위암을중심으로 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행 위암내시경진단 (2019) 위암검진에대한짧지않은 comment 융기형암은융기되어있는가? 함몰형암은함몰되어있는가? Semi-pedunculated polyp Sentinel polyp or EGJ cancer? IIa + IIc 위암검진에대한짧지않은 comment 성균관대학교의과대학내과이준행
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
 Re-audit of gastrointestinal tract specimens with respect to compliance with RCPath guidelines Dr Manisha Ram Dr Moina Kadri Background epidemiology and aetiology Over the past 20 years there has been
Re-audit of gastrointestinal tract specimens with respect to compliance with RCPath guidelines Dr Manisha Ram Dr Moina Kadri Background epidemiology and aetiology Over the past 20 years there has been
Lymph node metastasis in gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma in male patients
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6245 World J Gastroenterol 2013 October 7; 19(37): 6245-6257 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6245 World J Gastroenterol 2013 October 7; 19(37): 6245-6257 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CONSULTATION DURING SURGERY / NOT A FINAL DIAGNOSIS. FROZEN SECTION DIAGNOSIS: - A. High grade sarcoma. Wait for paraffin sections results.
 Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
TUMOR,NEOPLASM. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer
 Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
Oesophagus and Stomach update dysplasia and early cancer Dr Tim Bracey STR teaching 13/4/16 Please check pathkids.com for previous talks One of the biggest units in the country (100 major resections per
The surface mucous cells and the cardiac and pyloric glands secrete mucus which protects the stomach from self-digestion.
 PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
Is intestinal metaplasia a necessary precursor lesion for adenocarcinomas of the distal esophagus, gastroesophageal junction and gastric cardia?
 Diseases of the Esophagus (2007) 20, 36 41 DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00638.x Blackwell Publishing Asia Original article Is intestinal metaplasia a necessary precursor lesion for adenocarcinomas of
Diseases of the Esophagus (2007) 20, 36 41 DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00638.x Blackwell Publishing Asia Original article Is intestinal metaplasia a necessary precursor lesion for adenocarcinomas of
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14
 Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Greater Manchester and Cheshire HPB Unit Guidelines for the Assessment & Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Chapter 14 Contents 14. Neuroendocrine Tumours 161 14.1. Diagnostic algorithm
Esophagus Stomach 4/2/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Esophagus & Stomach 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series April 2, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
Collecting Cancer Data: Esophagus & Stomach 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series April 2, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants
Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract
 Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract Tumors of The Salivary Glands Benign Malignant Pleomorphic adenoma (50%) Mucoepidermoid cc (15%) Warthin tumor (5%) Adenocarcinoma NOS (6%) Oncocytoma (2%)
Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract Tumors of The Salivary Glands Benign Malignant Pleomorphic adenoma (50%) Mucoepidermoid cc (15%) Warthin tumor (5%) Adenocarcinoma NOS (6%) Oncocytoma (2%)
LOINC. Clinical information. RCPA code. Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details. Absent.
 Complete as narrative or use the structured format below 55752-0 17.02.28593 Clinical information 22027-7 17.02.30001 Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details 52101004
Complete as narrative or use the structured format below 55752-0 17.02.28593 Clinical information 22027-7 17.02.30001 Record if different to report header Operating surgeon name and contact details 52101004
Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC. General overview of staging. When is staging required? 11/1/2017
 Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC Dale C. Snover, MD November 3, 2017 General overview of staging Reason for uniform staging Requirements to use AJCC manual and/or CAP protocols
Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC Dale C. Snover, MD November 3, 2017 General overview of staging Reason for uniform staging Requirements to use AJCC manual and/or CAP protocols
Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node
 2012 66 5 417 421 Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node a b* a a a a a a a b ʼ 418 Horio et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
2012 66 5 417 421 Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node a b* a a a a a a a b ʼ 418 Horio et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma DD MM YYYY
 Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY S1.02 Clinical details
Colorectal Cancer Structured Pathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.03). Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY S1.02 Clinical details
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
CAP Cancer Protocol and ecc Summary of Changes for August 2014 Thyroid Agile Release
 CAP Cancer Protocol and ecc Summary of Changes for August 2014 Thyroid Agile Release 2 REVISION HISTORY Date Author / Editor Comments 5/19/2014 Jaleh Mirza Created the document 8/12/2014 Samantha Spencer/Jaleh
CAP Cancer Protocol and ecc Summary of Changes for August 2014 Thyroid Agile Release 2 REVISION HISTORY Date Author / Editor Comments 5/19/2014 Jaleh Mirza Created the document 8/12/2014 Samantha Spencer/Jaleh
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology
 ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
Imaging Evaluation of Polyps. CT Colonography: Sessile Adenoma. Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon Objectives
 Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
Polyps, DALMs & Megacolon: Pathology and Imaging of the Colon and Rectum Angela D. Levy and Leslie H. Sobin Washington, DC Drs. Levy and Sobin have indicated that they have no relationships which, in the
1. Esophageal diverticulum located above the upper esophageal sphincter is called
 Test Bank for Robbins Basic Pathology 9th Edition by Kumar Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-basic-pathology-9thedition-by-kumar/ Chapter 14: Oral Cavity and Gastrointestinal
Test Bank for Robbins Basic Pathology 9th Edition by Kumar Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-basic-pathology-9thedition-by-kumar/ Chapter 14: Oral Cavity and Gastrointestinal
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares
 Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Earlyoesophagealcancer. dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty ofmedicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia
 Earlyoesophagealcancer dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty ofmedicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia Early carcinoma of oesophagus = tumor limited to mucosa or submucosa, not extending into
Earlyoesophagealcancer dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty ofmedicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia Early carcinoma of oesophagus = tumor limited to mucosa or submucosa, not extending into
COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING
 COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent Terms Terms that are NOT Equivalent
COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES ABSTRACTORS TRAINING COLON AND RECTUM SOLID TUMOR RULES Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent Terms Terms that are NOT Equivalent
Icd 10 code for esophageal cancer stage 4
 Icd 10 code for esophageal cancer stage 4 Search Risk factors for developing esophageal cancer include.. 150. 4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus convert 150. 4 to ICD - 10 -CM;. Free ICD
Icd 10 code for esophageal cancer stage 4 Search Risk factors for developing esophageal cancer include.. 150. 4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus convert 150. 4 to ICD - 10 -CM;. Free ICD
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin
 The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
The pathology of bladder cancer
 1 The pathology of bladder cancer Charles Jameson Introduction Carcinoma of the bladder is the seventh most common cancer worldwide [1]. It comprises 3.2% of all cancers, with an estimated 260 000 new
1 The pathology of bladder cancer Charles Jameson Introduction Carcinoma of the bladder is the seventh most common cancer worldwide [1]. It comprises 3.2% of all cancers, with an estimated 260 000 new
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours. Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath
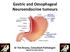 Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath Intestinal (and BO) endocrine cells in crypt bases NE cell (granules towards vessels) Paneth
Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath Intestinal (and BO) endocrine cells in crypt bases NE cell (granules towards vessels) Paneth
Gastrointestinal Malignancies. Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Gastrointestinal Malignancies Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline Esophagus normal anatomy Hollow tube 23-25cm long in adults Extends from pharynx to level of
Gastrointestinal Malignancies Dr Rodney ITAKI Pathology Division, SMHS, UPNG Anatomical Pathology Discipline Esophagus normal anatomy Hollow tube 23-25cm long in adults Extends from pharynx to level of
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Diagnosis and Preoperative Staging of Esophageal Cancer
 2 Diagnosis and Preoperative Staging of Esophageal Cancer ARNOLD J. MARKOWITZ, MD HANS GERDES, MD The clinical presentation of esophageal cancer in the United States and Europe has been changing, but unfortunately,
2 Diagnosis and Preoperative Staging of Esophageal Cancer ARNOLD J. MARKOWITZ, MD HANS GERDES, MD The clinical presentation of esophageal cancer in the United States and Europe has been changing, but unfortunately,
Radiology-Pathology Conference
 July 31, 2009 Radiology-Pathology Conference Daniel T Ginat, M.D., M.S. Sharlin Johnykutty,, M.D. Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2009 URMC Radiology Page 1 of
July 31, 2009 Radiology-Pathology Conference Daniel T Ginat, M.D., M.S. Sharlin Johnykutty,, M.D. Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2009 URMC Radiology Page 1 of
Neoplasms of the Colon and of the Rectum
 Neoplasms of the Colon and of the Rectum 2 0 1 5-2 0 1 6 F C D S E D U C A T I O N A L W E B C A S T S E R I E S S T E V E N P E A C E, B S, C T R F E B R U A R Y 1 8, 2 0 1 6 2016 Focus o Anatomy o SS
Neoplasms of the Colon and of the Rectum 2 0 1 5-2 0 1 6 F C D S E D U C A T I O N A L W E B C A S T S E R I E S S T E V E N P E A C E, B S, C T R F E B R U A R Y 1 8, 2 0 1 6 2016 Focus o Anatomy o SS
Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules
 2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
2018 SEER Solid Tumor Manual 2018 KCR SPRING TRAINING Colon and Rectum: 2018 Solid Tumor Rules 1 Colon and Rectum Solid Tumor Rules Separate sections for: Introduction Changes from 2007 MP/H rules Equivalent
Upper GIT IV Gastric cancer
 Upper GIT IV Gastric cancer Luigi Tornillo PathoBasic 23.10.2014 Pathology Introduction Classification Morphogenesis Problems Intraepithelial neoplasia Surveillance EGJ Predictive factors Gastric cancer
Upper GIT IV Gastric cancer Luigi Tornillo PathoBasic 23.10.2014 Pathology Introduction Classification Morphogenesis Problems Intraepithelial neoplasia Surveillance EGJ Predictive factors Gastric cancer
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting of Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting of Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Stephen Hayes, Dr David Bisset, Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting of Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Stephen Hayes, Dr David Bisset, Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
RTC Dec Felicitas Koller and Eric Grogan
 RTC Dec 11 2009 Felicitas Koller and Eric Grogan Cancer Statistics, United States Number of patients 200000 150000 100000 50000 0 Lung Breast New Cases Deaths Esophageal Colorectal Prostate http://www.cancer.org/statistics
RTC Dec 11 2009 Felicitas Koller and Eric Grogan Cancer Statistics, United States Number of patients 200000 150000 100000 50000 0 Lung Breast New Cases Deaths Esophageal Colorectal Prostate http://www.cancer.org/statistics
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples. VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė
 Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Adenocarcinoma of the distal esophagus is a recognized
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Adenocarcinomas of the Distal Esophagus and Gastric Cardia Are Predominantly Esophageal Carcinomas Parakrama Chandrasoma, MD, Kumari Wickramasinghe, MD, PhD, Yanling Ma, MD, and Tom DeMeester,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Adenocarcinomas of the Distal Esophagus and Gastric Cardia Are Predominantly Esophageal Carcinomas Parakrama Chandrasoma, MD, Kumari Wickramasinghe, MD, PhD, Yanling Ma, MD, and Tom DeMeester,
Boot Camp Case Scenarios
 Boot Camp Case Scenarios Case Scenario 1 Patient is a 69-year-old white female. She presents with dyspnea on exertion, cough, and right rib pain. Patient is a smoker. 9/21/12 CT Chest FINDINGS: There is
Boot Camp Case Scenarios Case Scenario 1 Patient is a 69-year-old white female. She presents with dyspnea on exertion, cough, and right rib pain. Patient is a smoker. 9/21/12 CT Chest FINDINGS: There is
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
GASTRIC CANCER DR AMIR ASHRAFI
 GASTRIC CANCER DR AMIR ASHRAFI Epidemiology Aetiologic factors Classification Clinical features Investigations Staging Treatment EPIDEMIOLOGY AND FACTS ü Worldwide, gastric cancer is the fourth most common
GASTRIC CANCER DR AMIR ASHRAFI Epidemiology Aetiologic factors Classification Clinical features Investigations Staging Treatment EPIDEMIOLOGY AND FACTS ü Worldwide, gastric cancer is the fourth most common
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
