Prognostic value of mirna-181a in human colorectal cancer evaluated by in situ hybridization
|
|
|
- Evelyn Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Prognostic value of mirna-181a in human colorectal cancer evaluated by in situ hybridization Shu Lin 1,2, Lin Zhao 1,2, Xinyue Song 1,2, Jing Zhang 1,2, Yan Wang 1,2, Longyang Jiang 1,2, Lifeng Yu 1,2, Jia Bi 1,2, Minjie Wei 1,2 1 Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, 2 Liaoning Key Laboratory of Molecular Targeted Anti-Tumor Drug Development and Evaluation, China Medical University, Shenyang , China Contributions: (I) Conception and design: M Wei, L Zhao; (II) Administrative support: M Wei, L Zhao; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: J Zhang, Y Wang; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: X Song, S Lin; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: L Zhao, S Lin; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Minjie Wei, PhD. Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, China Medical University, No.77 Puhe Road, Shenyang North New Area, Shenyang , China. weiminjiecmu@163.com. Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers in the world and the 5th leading cause of cancer death in China. CRC affects the gastrointestinal tract and has a high mortality rate. Recent studies have demonstrated the abnormal expression of mirna-181a in a wide variety of tumors. However, the clinical significance of mirna-181a in CRC is still unclear. Methods: The detection of mirna-181a was performed by probe hybridization using 3' and 5' end LNAmodified DNA probes. And we evaluated the survival probabilities by the Kaplan-Meier method and the logrank test. Furthermore, the univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression model were used for assessing the association of the mirna-181a expression and prognosis. Results: MiRNA-181a was highly expressed in CRC (P<1) compared with tumor-adjacent control tissue and was further validated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Tumor size, clinical stage, peritoneal and liver metastasis were significantly associated with high expression of mirna-181a (P<01, P=03, P=18 and P=04). We also found that high expression of mirna-181a was associated with poor prognosis (P<01). Furthermore, CRC patients with low expression of mirna-181a were more benefit for adjuvant chemotherapy (P<1). In addition, Cox multiple regression analysis suggested that mirna-181a was an independent prognostic factor for CRC. Conclusions: These results indicated that expression levels of mirna-181a could be an important indicator for prognosis and survival for CRC patients. Keywords: Colorectal cancer (CRC); mirna-181a; prognosis; chemotherapy Submitted Oct 18, Accepted for publication Jan 16, doi: 11037/tcr View this article at: Introduction Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth most common factor for cancer-related deaths (1,2). Although new anticancer agents and molecular-targeted therapies for CRC have been developed, the prognosis for advanced stage CRC patients is very poor. This is because of the high incidence of tumor recurrence from distal metastasis (3,4). The 5-year survival rate for early stage cancer patients is approximately 80 90%, however, with tumor recurrence after distal metastasis, the survival rate drastically drops to 10 20% (5,6). The dysregulation of mirnas has been reported to influence carcinogenesis, aggressiveness and metastasis. Hence, research to identify biomarkers involved with the progression of cancer is urgently needed. MicroRNAs (mirnas) comprise of a class of small noncoding RNA molecules, usually 20 to 22 nucleotides in
2 122 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC length that regulate post-transcriptional processes of several genes. mirnas regulate protein-coding genes in biological processes, including tumorigenesis and chemoresistance (7). mirnas negatively regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level through the degradation of mrna and inhibition of translation (8). Abnormal expression of oncogenic mirnas can lead to tumor occurrence by facilitating tumor proliferation and apoptosis resistance (9). In CRC, it has been reported that dysregulation of mirnas affects tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis. MiRNA-143 and mirna-145 were first identified as dysregulated mirnas in CRC in 2003 (10). Since then, numerous mirnas have been studied for their relevance in CRC prognosis. Recently, the higher expression level of mirna- 181a has been demonstrated in a number of cancers. MiRNA-181a has been identified as a prognostic biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia and non-small cell lung cancer (11,12). In addition, mirna-181a levels have been correlated with cancer chemoresistance. Overexpression of mirna- 181a in prostate cancer cells contributes to tumor resistance to docetaxel and cabazitaxel (13). MiRNA-181a also promotes cancer resistance to radiation therapy by targeting the pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene (14) and modulates glioma tumor growth and chemotherapy resistance to temozolomide (TMZ) through the PTEN pathway (15). However, there have been limited studies regarding the association between mirna-181a expression levels and the prognosis of CRC. In our study, we investigated the expression of mirna- 181a using in situ hybridization (ISH) high-throughput platforms and the effect it had on the prognosis of CRC. In addition, we selected CRC patients undergoing chemotherapy to assess the ability of mirna-181a to affect the prognosis of CRC patients. Methods Ethics statement This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of China Medical University at the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University. All patients agreed to the study protocols and signed informed consent forms to participate in the study. All tumor samples were anonymized before analysis using ISH. Patients and tissue samples CRC patients were recruited between June 2005 and March 2010 by the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (I) incomplete patient medical records and/or no follow-up information; (II) lack of clinical samples for proper evaluation; (III) severe postoperative complications including intestinal fistulas and anastomotic obstructions; (IV) preoperative adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Tumor tissue and surrounding intestinal mucosa were collected during the surgery. The clinical staging was performed in line with the WHO and TNM staging guidelines (16). Based on tumor differentiation, patients were classified into grade 1 (poorly differentiated), grade 2 (medium differentiated) and grade 3 (well differentiated). All patients underwent enhanced CT examination of the pulmonary and abdominal regions prior to surgery. Patients received routine CT and colonoscopies during follow-up to detect efficacy, invasion and/or recurrence of the tumor. Tumor metastasis and vascular invasion were investigated by intraoperative and postoperative pathological examination respectively. The postoperative follow-up duration was 10 years. Tissue microarray (TMA) Fresh tissue from the central zone was paraformaldehydefixed, imbedded in paraffin and sliced into 4-μm sections. These sections were stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) and placed on coverslips with mounting medium for analysis. The stained and paraformaldehyde-fixed tissues were then placed in a TMA. A total of 7 TMAs (6 from tumors and 1 from adjacent mucosa) were used for ISH analysis. ISH ISH was conducted as previously described (17). Briefly, tissues with treated with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature for 10 min. Subsequently, the sections were boiled (95 to 100 ) in citric acid buffer for 15 min and incubated with protease at 37 for 8 min. The slides were then pre-hybridized in Exiqon hybridization buffer (Exiqon, Vedbæk, Denmark) at 65 for 2 h, hybridized with 50 nm mirna-181a probe overnight and washed stringently with 5 SSC, 1 SSC and SSC buffers at 65 for 30 min. DIG blocking reagent (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) was added for 15 min at 37 in maleic acid buffer with 2% sheep serum. After which, the alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-digoxigenin was added at 37 for 20 min (1:500 in
3 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February 2018 Roche blocking reagent). 4-nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) and 5-brom-4-chloro-3'-Indolylphosphate (BCIP) substrate (Roche) were used for enzymatic development to form darkblue NBT-formazan precipitates at 37 for 60 min. The sections were lightly counterstained with nuclear fast red (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) at 25 for 1 min and mounted. The probes for mirna-181a detection was as follows: 5' Dig-AACAUUCAACGCUGUCGGUGAGU- Dig 3' (Exiqon, Vedbæk, Denmark). Evaluation of ISH TMAs were scanned using Pannoramic MIDI (3D HISTECH, Budapest, Hungary) and anonymized samples were then analyzed. The number of cells in each slice that had positive staining was recorded. It was based on staining intensity and classified using semi-quantified values. The process of semi-quantification was conducted as follows: H-score = Σ(PI I) = (percentage of cells of negative intensity 0) + (percentage of cells of weak intensity 1) + (percentage of cells of moderate intensity 2) + (percentage of cells of strong intensity 3), where PI represents the percentage of positive cells to the total number of cells in the slice and I represents the intensity of the color. Five fields for each sample were selected randomly and the cutoff value for mirna-181a levels was determined through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 2 (Chicago, IL, USA). Pearson chi-square and Fisher s tests was used to compare the statistical data. Disease-free survival (DFS) referred to the date from the day of diagnosis to tumor local recurrence or metastasis. Overall survival () referred to the date from the day of diagnosis to tumor-related death. The Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test were used to evaluate survival probabilities. The association of multiple variables and prognosis was assessed using the multivariate Cox regression model. P values less than 5 was considered to have statistical significance. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database analysis The expression data for mirna-181a was obtained from the TCGA database for CRC, which contained 619 cases of colorectal tumors and 11 cases of adjacent normal tissues. The median age of these patients was 68 years, which 123 included 328 (53.0%) males and 291 (47.0%) females. The number of patients with tumor grade 1 + grade 2 and tumor grade 3 + grade 4 were 90 (19.6%) and 369 (8%) respectively. Of the 619 patients, 185 (47.5%) patients had lymph node metastasis and 152 (24.9%) patients had distant metastasis, 510 (85.1%) patients had clinical stage I III and 89 (14.9%) had clinical stage IV (Table S1). MiRNA-181a expression profiles were matched to the downloaded clinical data according to the TCGA code. Some patients had missing mirna-181a expression data, no follow-up data, or missing clinical information. The t-test was conducted to analyze the mirna-181a expression differences between cancer and normal tissues and the Kaplan-Meier method was performed to evaluate the association of mirna-181a levels with. Results Clinicopathological characteristics of CRC patients Table 1 summarizes the clinicopathological characteristics of the 329 CRC patients with mirna-181a expression levels. The median age of these patients was 63 years (range, years), which included 173 (52.6%) males and 156 (47.4%) females. The numbers of patients with histological grade G1 and G2 G3 tumors were 53 (16.1%) and 276 (83.9%) respectively. A total of 284 (86.3%) cases exhibited a tumor diameter of 30 mm and/or more, while 45 cases (13.7%) exhibited no more than 30 mm. Of the 329 patients, 43 (13.1%), 46 (14.0%), 22 (6.7%) and 29 (8.8%) patients had lymph node metastasis, liver, lung invasion and peritoneal dissemination respectively. A total of 238 (72.3%) patients had clinical stage I III and 91 (27.7%) had clinical stage IV. In total, 160 patients received chemotherapy treatment, which were 48.6% of the total number of CRC patients. MiRNA-181a is overexpressed in CRC tissues We evaluated the expression of mirna-181a levels in 329 samples from patients with CRC and 45 tumor-adjacent control samples utilizing ISH (Figure 1). Among the 329 samples, 302 (91.8%) were positive for mirna-181a expression in CRC tissues. In contrast, mirna-181a was detected in only 6 (13.3%) samples out of 45 tumor-adjacent control samples. MiRNA-181a expression in CRC tissue samples was significantly higher than in corresponding tumor-adjacent samples (P<1).
4 124 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of CRC patients (n=329) Features Number % Age at diagnosis (years) > Gender Male Female Histological grade G G2 G Tumor size (mm) 30 (small) >30 (large) Lymph node metastasis Absent Present Liver invasion Absent Present Lung invasion Absent Present Peritoneal dissemination Absent Present Clinical stage I III IV Receiving chemotherapy No Yes CRC, colorectal cancer. Selection of the cutoff value for mirna-181a expression levels ROC analysis was used to determine the appropriate cutoff score for mirna-181a expression level. ROC curves demonstrated mirna-181a expression levels were affected by liver invasion (P=02), peritoneal dissemination (P=29), histological grade (P=46), tumor size (P=01), (P<01) and clinical stage (P=35) (Figure 2). However, lung invasion, chemotherapy and lymph node metastasis were not associated (P=0.904, P=0.500, P=92). The largest area under the curve (AUC) of the ROC curve was corresponded to (Figure 2H). Based on these results, we defined the cut-off value of mirna-181a expression level at 147.8%. Tumors with H-scores >147.8% and 147.8% were considered as high and low expression of mirna-181a respectively. A total of 151 (45.9%) tumors had low expression of mirna-181a and 178 (54.1%) tumors had high expression of mirna-181a. Association of mirna-181a expression with clinicopathological characteristics of CRC The association between mirna-181a expression levels with clinical pathological parameters in CRC was investigated using Pearson χ 2 test (Table 2). The expression levels of mirna-181a were not correlated with the patients age, gender, histological grade, lymph node metastasis, lung invasion and receiving chemotherapy (Table 2, P>5). Tumors diameter >30 mm, liver invasion and peritoneal dissemination had significant association with mirna- 181a high expression (P<01, P=04, P=18, Table 2). The high expression of mirna-181a was also significantly correlated with tumor clinical stage (P=03, Table 2). Association of mirna-181a expression levels with survival The association of mirna-181a expression levels with and DFS were determined in CRC patients using Kaplan- Meier analysis. The high expression of mirna-181a was correlated with shorter and DFS in all CRC patients (n=329, P<01, P<01, Figure 3A,B). Given that adjuvant chemotherapy influenced patients survival, we analyzed the association between mirna-181a expression levels and its prognostic value in CRC patients receiving and not receiving chemotherapy. MiRNA-181a was highly associated with and DFS in patients who underwent chemotherapy than those who did not receive chemotherapy (Figure 3C,D,E,F). Moreover, the therapeutic efficacy of patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy with high mirna-181a expression was not beneficial compared to patients with low mirna- 181a expression levels (P<01, P<01, log-rank test, Figure 3C,D). These results suggested that mirna-181a
5 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February A Negative B Positive Cancer Cancer-adjacent C D 100 μm Figure 1 Representative micrographs showing negative (A,C) and positive (B,D) in situ hybridization staining of mir-181a in colorectal cancer-adjacent (A,B) and cancer tissue (C,D). The squares in the top right shows magnified regions and arrows indicate it in the insert (scale bar: 100 μm). expression levels could influence the prognosis of CRC patients by affecting the chemotherapy effect. In addition, we investigated the correlation of mirna-181a expression levels with and DFS in subgroups of CRC patients who were classified based on histological grade, liver invasion and peritoneal dissemination. High expression of mirna- 181a was significantly correlated with shorter, DFS in CRC patients with histological grade G2 G3 but not in G1 (P<01, P=15, log-rank test, Figure 4A,B). In liver metastatic-negative and peritoneal dissemination-negative patients, higher mirna-181a expression levels were significantly associated with shorter (P<01, P<01, Figure 4C,D). However, the expression of mirna-181a was not correlated with shorter in liver invasion-positive and peritoneal dissemination-positive patients (P=0.583, P=09, Figure 4E,F). This suggests that mirna-181a may be an important factor affecting and DFS of CRC patients with histological grade G2 G3, without liver invasion and peritoneal dissemination. Next, we used the univariate and multivariate Cox survival risk regression model to analyze the correlation between common clinical pathology parameters with mirna-181a expression levels for the prognosis of CRC patients. We found that the expression levels of mirna- 181a, together with lymph node metastasis, liver invasion, peritoneal dissemination, histological grade, tumor size, and clinical stage were significantly correlated with and DFS in CRC patients (P<01, P=15, P=04, P=08, P<01, P<01 and P=02 respectively for ; P<01, P=18, P=04, P=14, P=01, P<01 and P=05 respectively for DFS; Table 3). We selected P value <5 variables to conduct the multivariate Cox regression analysis. Multivariate analysis indicated that mirna- 181a expression levels, tumor size, histological grade and clinical stage were independent prognostic factors for and DFS in CRC patients (P<01, P=35, P=03 and P<01 respectively for ; P<01, P=46, P=05 and P<01 respectively for DFS; Table 4). This further demonstrated that mirna-181a expression level was an independent risk factor for and DFS [risk ratio (RR) =2.872,
6 126 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC A B Lung invasion Lymph node metastasis Liver invasion C AUC =96 P=0.904 cut-off value =106.1% AUC =0.580 P=92 cut-off value =122.9% AUC =40 P=02 cut-off value =124.3% D Peritoneal dissemination E Histological grade F Tumor size AUC =23 P=29 cut-off value =132.2% AUC =0.514 P=46 cut-off value =107.4% AUC =51 P=01 cut-off value =130.7% G Receiving chemotherapy H I Clinical stage AUC =78 P=0.500 cut-off value =107.6% AUC =0.706 P<01 cut-off value =147.8% AUC =37 P=35 cut-off value =131.4% Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves were used to determine the cut-off score for mirna-181a overexpression in CRC. The sensitivity and specificity for each outcome were plotted and the areas under the curve (AUCs), P value and cut-off value were indicated. (A) Lung invasion; (B) lymph node metastasis; (C) liver invasion; (D) peritoneal dissemination; (E) histological grade; (F) tumor size; (G) receiving chemotherapy; (H) ; (I) clinical stage. AUC, area under the curve;, overall survival; CRC, colorectal cancer.
7 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February 2018 Table 2 Association between mirna-181a expression and clinicopathological features of CRC patients Features Age at diagnosis (years) MiRNA-181a expression, n (%) High (n=178) Low (n=151) (55.8) 68 (44.2) >63 92 (52.6) 83 (47.4) P value a Gender 25 Male 88 (50.9) 85 (49.1) Female 90 (57.7) 66 (42.3) Histological grade G1 28 (52.8) 25 (47.2) G2 G3 150 (54.3) 126 (45.7) Tumor size (mm) <01 30 (small) 13 (28.9) 32 (71.1) >30 (large) 165 (58.1) 119 (41.9) Lymph node metastasis Absent 150 (52.4) 136 (47.6) Present 28 (65.1) 15 (34.9) Liver invasion 04 Absent 144 (50.9) 139 (49.1) Present 34 (73.9) 12 (26.1) Lung invasion Absent 166 (54.1) 141 (45.9) Present 12 (54.5) 10 (45.5) Peritoneal dissemination Absent 156 (52.0) 144 (48.0) Present 22 (75.9) 7 (24.1) 18 Clinical stage 03 I III 112 (47.1) 126 (52.9) IV 66 (72.5) 25 (27.5) Receiving chemotherapy No 93 (55.0) 76 (45.0) Yes 85 (53.1) 75 (46.9) a, P value obtained from Pearson Chi-squared or Fisher s exact test. CRC, colorectal cancer % CI: , P<01 for ; RR =3.024, 95% CI: , P<01 for DFS] (Table 4). MiRNA-181a expression levels are associated with CRC progression and prognosis based on the TCGA database In order to further confirm that mirna-181a expression levels had a high correlation with CRC, we analyzed mirna-181a expression in CRC tissues of 619 cases and 11 adjacent normal tissues using the TCGA database. The results demonstrated an obvious increase in mirna- 181a expression levels in CRC tissues (n=619) compared with normal tissues (n=11, P=36, Figure 5A). We then analyzed the mirna-181a expression in subgroups of CRC tissues classified based on T stage and lymph node metastases. The expression of mirna-181a in T3 + T4 (n=369) stage was remarkably higher than in T1 + T2 stage (n=90, P=33, Figure 5B) and mirna-181a expression was significantly lower in N0 (n=204) stage than those in N1 (n=104) and N2 (n=81) stage (P=15, P=01, Figure 5C). The results demonstrated that mirna-181a expression was increased significantly in advanced T stage and lymph node metastases, which was consistent with its effect on colorectal tumor progression. We next analyzed the correlation between mirna-181a expression and the prognosis of 619 cases of CRC patients based on the TCGA clinical database. The results showed that high expression of mirna-181a was significantly correlated with poor in CRC patients (P=14, Figure 5D). Furthermore, high expression of mirna-181a was associated with shorter in CRC patients with T3 + T4 stage tumors (P=06, Figure 5E). However, mirna-181a expression levels had no correlation in patients with T1 + T2 stage tumors (P=21, data not shown). The high expression of mirna-181a was also associated with a poor survival prognosis in CRC patients with lymph node metastases (P=14, Figure 5F) and had no association in CRC patients without lymph node metastases (P=0.302, data not shown). These results demonstrate that mirna-181a may play an important role in the development and progression of CRC and may be an indicator for CRC diagnosis and prognosis. Discussion Numerous studies have confirmed the significant role that mirna-181a plays in regulating tumorigenesis, proliferation and distant metastasis. However, the
8 128 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC A All patients B All patients mir-181a low (n=151) mir-181a low (n=151) mir-181a high (n=178) mir-181a high (n=178) P<01 P<01 C DFS With chemotherapy mir-181a low (n=75) D With chemotherapy mir-181a low (n=75) mir-181a high (n=85) mir-181a high (n=85) P<01 P<01 E Without chemotherapy mir-181a low (n=76) F DFS Without chemotherapy mir-181a low (n=76) mir-181a high (n=93) mir-181a high (n=93) P=60 P= DFS Figure 3 Associations between mirna-181a expression with survival and prognosis of CRC patients with and without adjuvant chemotherapy. (A,B) Kaplan-Meier plot of the cancer-specific mortality in CRC patients, which were classified into 2 groups: patients with mirna-181a-high expression and patients with 181a-low expression; (C,D) survival curves show the association between mirna-181a expression and overall survival () and disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with adjuvant chemotherapy; (E,F) survival curves show the association between mirna-181a expression and and DFS in patients without chemotherapy. CRC, colorectal cancer.
9 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February A Histological grade G2 G3 B Histological grade G1 n=98 n=20 mir-181a Low expression High expression P<01 n=178 mir-181a Low expression High expression P=15 n=33 C Without liver invasion Without peritoneal dissemination n=139 n=144 D mir-181a Low expression High expression P<01 n=144 mir-181a Low expression High expression P<01 n= E With liver invasion F With peritoneal dissemination n=12 mir-181a Low expression High expression n=34 mir-181a Low expression High expression n=22 n=7 P=0.583 P= Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of mirna-181a expression in CRC patients with different histological grade, liver invasion, and peritoneal dissemination status. The log-rank test was performed to test the statistical significance. Survival curves show the association between mirna-181a expression and overall survival () in histological grade G2 G3 patients (A), histological grade G1 patients (B), liver invasion-negative patients (C), peritoneal dissemination-negative patients (D), liver invasion-positive patients (E), peritoneal dissemination -positive patients (F).
10 130 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC Table 3 Univariate Cox regression analysis of and DFS in CRC patients Category Overall survival Disease-free survival RR (95% CI) P value RR (95% CI) P value Age (>63/ 63 years) ( ) ( ) Gender (male/female) 45 ( ) ( ) MiRNA-181a (positive/negative) ( ) < ( ) <01 Tumor size (>30/ 30 mm) ( ) < ( ) <01 Histological grade (G1/G2 G3) ( ) < ( ) 01 Liver invasion (positive/negative) ( ) ( ) 04 Lung invasion ( ) ( ) Peritoneal dissemination ( ) ( ) 14 Lymph node metastasis (yes/no) ( ) ( ) 18 Clinical stage (I III/IV) ( ) ( ) 05 RR, relative risk; CI, confidence interval;, overall survival; DFS, disease-free survival; CRC, colorectal cancer. Table 4 Multivariate Cox regression analysis of and DFS in CRC Category Overall survival Disease-free survival RR (95% CI) P value RR (95% CI) P value MiRNA-181a (positive/negative) ( ) < ( ) <01 Liver invasion (positive/negative) ( ) ( ) 71 Peritoneal dissemination 94 ( ) ( ) Tumor size (>30/ 30 mm) ( ) ( ) 46 Histological grade (G1/G2 G3) ( ) ( ) 05 Lymph node metastasis (yes/no) ( ) ( ) Clinical stage (I III/IV) ( ) < ( ) <01 RR, relative risk; CI, confidence interval;, overall survival; DFS, disease-free survival; CRC, colorectal cancer. association of mirna-181a with regards to CRC has yet to be determined. In the present study, we first conducted high-throughput TMA using ISH to determine the prognostic value of mirna-181a expression levels with CRC. We found that CRC had higher expression of mirna-181a than tumor-adjacent control samples. CRC patients with higher expression levels of mirna-181a had a higher clinical stage, increased liver metastasis, peritoneal dissemination and larger tumor size. Higher expression of mirna-181a was also correlated with shorter and DFS in CRC patients and was an independent prognostic factor for CRC progression. MicroRNAs are stably expressed in tumor tissues and are attributed to them being frequently used for detection (18,19). The majority of previous studies on mirna detection have been carried out using microarrays with RNA extracted from tumor tissues and tumor-adjacent stromal tissues, which may include a mixture of tumor cells and tumor related stromal cells, thus making the analysis difficult to interpret. However, ISH can detect positive signals precisely at the cellular level. For example, some mirnas are expressed abundantly in tumor related stromal cells but have no expression in tumor cells (20). Analysis using microarrays with RNA extracted from tumors will not be able to precisely delineate these differences. In addition, several mirnas act as tumor suppressors
11 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February A Relative expression of mir-181a (fold) 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 P=36 B Relative expression of mir-181a (fold) 15,000 10,000 5,000 P=33 C Relative expression of mir-181a (fold) 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 P=15 P=01 D 0 Normal n=11 Cancer n=619 0 T1+T2 n=90 T3+T4 n=369 0 N0 n=204 N1 n=104 All patients Patients with T3+T4 Patients with N1+N2 hsa-mir-181a high expression hsa-mir-181a low expression E hsa-mir-181a high expression hsa-mir-181a low expression F N2 n=81 hsa-mir-181a high expression hsa-mir-181a low expression Survival rate Survival rate Survival rate 0 n=619 P=14 n=369 P=06 n=185 P= Time (months) Time (months) Time (months) Figure 5 TCGA database analysis of mirna-181a expression difference between colorectal cancer and normal tissues and CRC prognosis. The t-test was conducted to analyze the expression differences of mirna-181a between cancer and normal tissues (A) and subgroups classified based on tumor stage (T1 T4) (B) and lymph node metastasis (N0 N2) (C). The Kaplan-Meier method was performed to evaluate the association of mirna-181a and overall survival in all patients (D) and T3 + T4 stage (E) and N1 + N2 stage (F). or oncogenes ( onco-mirna ), which would not have been detected if molecular and cellular composition is not utilized. Taking this into context, a pivotal but controversial role has been attributed to mirna-181a as an onco-mirna in different human cancers, including cervical, prostate, gastric, hepatocellular carcinoma and CRCs (13,21-24). Conversely, some studies have suggested that mirna- 181a plays an opposite role as a tumor suppressor in other types of cancers (11,25,26). For example, mirna-181a has been identified as frequently downregulated, contributes to apoptosis, and inhibition of growth and invasion in gliomas (27). However, in another study, low mirna-181a expression was significantly associated with poor cancerspecific survival in patients with CRC (28). Several studies have demonstrated that mirna-181a is overexpressed in CRC (23,29,30). As far as we know, only one publication has reported the prognostic value of mirna-181a expression levels in CRC using ISH (31). Consistent with our results, high mirna-181a expression was an independent and significant prognostic factor for CRC. Our study was also consistent with the report from Nishimura et al. (32). Nishimura et al. showed that high mirna-181a expression levels detected by RT-qPCR had a significantly poorer prognosis in CRC patients. However, in the report by Nishimura et al., the expression of mirna- 181a had no obvious differences between tumor-adjacent tissue and CRC tissue and had no association with any clinical pathological parameters. We hypothesized that these results were probably due to the different origin of tumor-adjacent tissues and the number and detection methods used between our two studies. The underlying mechanism how mirna-181a influences poor survival remains to be elucidated. MiRNA- 181a has been shown to inhibit the expression of several tumor suppressor genes, such as PTEN (23), MTMR3 (22), GPD1L (33) and WIF-1 (31,34). A recent study found that mirna-181a expression was transcriptionally regulated by signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) in CRC. STAT1/miRNA-181a/PTEN pathway in CRC adds new insights regarding the carcinogenesis and
12 132 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC development of CRC (23). In addition, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is deregulated in CRC and mirna-181a could be directly up-regulated through the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (30). These results/findings could explain the reason for the high expression of mirna-181a in CRC. Regulating the expression of mirna-181a through modulating transcription factors may be a therapeutic option. Our research also analyzed the potential association between mirna-181a expression and a variety of clinical pathological parameters in CRC patients, as well as its prognostic value for survival. Our results demonstrated that high expression of mirna-181a was associated with tumor size, liver metastasis, peritoneal dissemination, clinical stage and shorter prognostic survival in CRC patients. We also showed that the expression of mirna-181a was significantly associated with poor prognosis, however, it did not have significant association with prognosis if patients had liver metastasis and peritoneal dissemination. This suggested that although the expression of mirna-181a had an obvious effect on proliferation of tumor cells and poor prognosis, it was not the dominant factor when liver metastasis or peritoneal dissemination was present. Furthermore, mirna-181a had a significant impact on regulating tumor drug-resistance in various cancers. Higher expression of mirna-181a increased tumor resistance to docetaxel and cabazitaxel in prostate cancer cells and inhibition of mirna-181a expression could restore treatment efficacy (13). TMZ-based chemotherapy is the standard treatment for glioma and mirna- 181a reduced the sensitivity to TMZ in glioma cancers through the inhibition of PTEN (15). In this study, we found that the prognostic value of mirna-181a-high patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy was poor, which suggested that high expression of mirna-181a may influence the progression and prognosis of CRC. Our previous published work demonstrated that mirna- 181a played a significant role in regulating macrophage polarization through directly targeting KLF6 and C/EBPα to induce macrophage polarization to the M2 phenotype, which leads to tumor development and drug resistance (35). These results further demonstrated that the expression of mirna-181a could be a potential therapeutic marker for CRC patients. Our results demonstrated for the first time that mirna-181a expression was significantly correlated with the survival and efficacy of chemotherapy treatment of CRC patients. Conclusions In summary, our results demonstrated that mirna-181a expression was significantly associated with tumor size, distant metastasis, clinical stage and prognostic survival of CRC patients, indicating that mirna-181a expression has a significant effect on the proliferation and progression of tumor cells of the disease. We also demonstrated that the expression of mirna-181a was significantly correlated with and DFS and may be an important indicator for prognosis of CRC patients. Acknowledgements Funding: This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No , ), Program for Liaoning Innovative Research Team in University (No. LT ), Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (No. LJQ ), Key Laboratory Foundation from Shenyang S&T Projects (F ). Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of China Medical University at the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University (ID: AF- SOP ). All patients agreed to the study protocols and signed informed consent forms to participate in the study. References 1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61: Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN Int J Cancer 2010;127: Heinemann V, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T, et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15: Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, et al. Initial therapy
13 Translational Cancer Research, Vol 7, No 1 February with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2014;371: Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6: Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the 'seed and soil' hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 2003;3: Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, et al. micrornas as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 2007;302: Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by micrornas: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 2008;9: Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - micrornas with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6: Michael MZ, SM OC, van Holst Pellekaan NG, et al. Reduced accumulation of specific micrornas in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res 2003;1: Schwind S, Maharry K, Radmacher MD, et al. Prognostic significance of expression of a single microrna, mir- 181a, in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. J Clin Oncol 2010;28: Gao W, Yu Y, Cao H, et al. Deregulated expression of mir- 21, mir-143 and mir-181a in non small cell lung cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Biomed Pharmacother 2010;64: Armstrong CM, Liu C, Lou W, et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2017;77: Ke G, Liang L, Yang JM, et al. MiR-181a confers resistance of cervical cancer to radiation therapy through targeting the pro-apoptotic PRKCD gene. Oncogene 2013;32: Liao Y, Shen L, Zhao H, et al. LncRNA CASC2 Interacts With mir-181a to Modulate Glioma Growth and Resistance to TMZ Through PTEN Pathway. J Cell Biochem 2017;118: Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 2004;240: Wang F, Flanagan J, Su N, et al. RNAscope: a novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded tissues. J Mol Diagn 2012;14: Xi Y, Nakajima G, Gavin E, et al. Systematic analysis of microrna expression of RNA extracted from fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. Rna 2007;13: Li J, Smyth P, Flavin R, et al. Comparison of mirna expression patterns using total RNA extracted from matched samples of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cells and snap frozen cells. BMC Biotechnol 2007;7: Hu Y, Correa AM, Hoque A, et al. Prognostic significance of differentially expressed mirnas in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer 2011;128: Yang M, Zhai X, Ge T, et al. MiR-181a-5p Promotes Proliferation and Invasion, and Inhibits Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells via Regulating Inositol Polyphosphate-5-Phosphatase A (INPP5A). Oncol Res [Epub ahead of print]. 22. Lin Y, Zhao J, Wang H, et al. mir-181a modulates proliferation, migration and autophagy in AGS gastric cancer cells and downregulates MTMR3. Mol Med Rep 2017;15: Zhang X, Li X, Tan F, et al. STAT1 Inhibits MiR- 181a Expression to Suppress Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation Through PTEN/Akt. J Cell Biochem 2017;118: Nishida N, Arizumi T, Hagiwara S, et al. MicroRNAs for the Prediction of Early Response to Sorafenib Treatment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2017;6: Cao Y, Zhao D, Li P, et al. MicroRNA-181a-5p Impedes IL-17-Induced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Migration through Targeting VCAM-1. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017;42: Lin F, Li Y, Yan S, et al. MicroRNA-181a inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness, and metastasis and is downregulated in gastric cancer. Oncol Res 2015;22: Shi L, Cheng Z, Zhang J, et al. hsa-mir-181a and hsa-mir- 181b function as tumor suppressors in human glioma cells. Brain Res 2008;1236: Pichler M, Winter E, Ress AL, et al. mir-181a is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer treated with EGFR inhibitor. J Clin Pathol 2014;67: Hai Ping P, Feng Bo T, Li L, et al. IL-1beta/NFkb signaling promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through mir-181a/pten axis. Arch Biochem Biophys 2016;604: Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, et al. The lncrna CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via mir-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer 2017;16:9.
14 134 Lin et al. Prognostic value of mir-181a in human CRC 31. Ji D, Chen Z, Li M, et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor suppressor WIF-1. Mol Cancer 2014;13: Nishimura J, Handa R, Yamamoto H, et al. microrna- 181a is associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 2012;28: Zhai X, Meng R, Li H, et al. mir-181a Modulates Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Targeting Glycerol-3- Phosphate Dehydrogenase 1-Like Protein (GPD1L) in Osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit 2017;23: Lyu X, Li J, Yun X, et al. mir-181a-5p, an inducer of Wnt-signaling, facilitates cell proliferation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol Rep 2017;37: Bi J, Zeng X, Zhao L, et al. mir-181a Induces Macrophage Polarized to M2 Phenotype and Promotes M2 Macrophage-mediated Tumor Cell Metastasis by Targeting KLF6 and C/EBPalpha. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2016;5:e368. Cite this article as: Lin S, Zhao L, Song X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Jiang L, Yu L, Bi J, Wei M. Prognostic value of mirna-181a in human colorectal cancer evaluated by in situ hybridization.. doi: 11037/ tcr
15 Supplementary Table S1 Clinicopathological characteristics of CRC patients in TCGA database Features Number % Age at diagnosis (n=619) 68 years >68 years Gender (n=619) Male Female Tumor stage (n=459) T1 + T T3 + T Lymph node (n=389) N N N Metastasis (n=610) M M Clinical stage (n=599) I III IV TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; CRC, colorectal cancer.
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis
 Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Cancer Cell Research 19 (2018)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 LncRNA RP11-597D13.9 expression and clinical significance in serous Ovarian Cancer based on TCGA database Xiaoyan Gu 1, Pengfei Xu 2, Sujuan
Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4087-4091 Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression C.-H. QU 1, Q.-Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4087-4091 Long non-coding RNA ROR is a novel prognosis factor associated with non-small-cell lung cancer progression C.-H. QU 1, Q.-Y.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Increasing expression of mir-5100 in non-small-cell lung cancer and correlation with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3592-3597 Increasing expression of mir-5100 in non-small-cell lung cancer and correlation with prognosis T. WANG 1, X. LIU 1, Q. TIAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3592-3597 Increasing expression of mir-5100 in non-small-cell lung cancer and correlation with prognosis T. WANG 1, X. LIU 1, Q. TIAN
Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection
 Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5696-5701 Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer G.-H. ZHOU 1, W.-H. YANG 2, B. SUN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5696-5701 Clinical impact of serum mir-661 in diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer G.-H. ZHOU 1, W.-H. YANG 2, B. SUN
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China
 1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
 Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Long noncoding RNA LINC01510 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and predicts favorable prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7710-7715 Long noncoding RNA LINC01510 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and predicts favorable prognosis J.-F. ZHOU, H.-G. WANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7710-7715 Long noncoding RNA LINC01510 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and predicts favorable prognosis J.-F. ZHOU, H.-G. WANG,
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis
 Original Article Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis Wenxian Wang 1, Zhengbo Song 1,2, Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department of Chemotherapy, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital,
Original Article Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis Wenxian Wang 1, Zhengbo Song 1,2, Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department of Chemotherapy, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital,
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8555-8559 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026997 Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis Qiong Pan,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8555-8559 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026997 Original Article microrna-217 was downregulated in ovarian cancer and was associated with poor prognosis Qiong Pan,
Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7704-7709 Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study Z.-Y. LIU, L. YANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7704-7709 Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study Z.-Y. LIU, L. YANG,
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Expression and significance of Bmi-1 and Ki67 in colorectal carcinoma tissues
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (9), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (9), Page 5298-5303 Prognostic Value of Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Mohammad Sabry Elkady, Ghada
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (9), Page 5298-5303 Prognostic Value of Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Mohammad Sabry Elkady, Ghada
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis
 Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
High levels of long non-coding RNA DICER1-AS1 are associated with poor clinical prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7640-7645 High levels of long non-coding RNA DICER1-AS1 are associated with poor clinical prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma X.-H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7640-7645 High levels of long non-coding RNA DICER1-AS1 are associated with poor clinical prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma X.-H.
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target?
 Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma
 Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5143-5147 Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5143-5147 Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists
 Original Article Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists Lixin Jiang, Zengwu Yao, Yifei Zhang, Jinchen
Original Article Comparison of lymph node number and prognosis in gastric cancer patients with perigastric lymph nodes retrieved by surgeons and pathologists Lixin Jiang, Zengwu Yao, Yifei Zhang, Jinchen
Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 expression is independently predictive of outcome in glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3605-3610 Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 expression is independently predictive of outcome in glioma X.-L. MA 1, W.-D. ZHU 2, L.-X. TIAN 2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3605-3610 Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 expression is independently predictive of outcome in glioma X.-L. MA 1, W.-D. ZHU 2, L.-X. TIAN 2,
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy
 Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
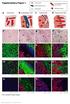 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer Zhanguo Chen MD PhD 1, Lili Wu BA 2, Qi Lin BA 3, Jing Shi MD 4, Xiangyang Lin MD, Liang Shi
Original Article Evaluation of mir-182/mir-100 Ratio for Diagnosis and Survival Prediction in Bladder Cancer Zhanguo Chen MD PhD 1, Lili Wu BA 2, Qi Lin BA 3, Jing Shi MD 4, Xiangyang Lin MD, Liang Shi
Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 1361-1366, 2016 Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma WEI DONG 1, WANG GANG 1, MIAOMIAO LIU 2 and HONGZHEN ZHANG 2 1 Department of Urology; 2 Department of
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 1361-1366, 2016 Analysis of the prognosis of patients with testicular seminoma WEI DONG 1, WANG GANG 1, MIAOMIAO LIU 2 and HONGZHEN ZHANG 2 1 Department of Urology; 2 Department of
Positive expression of mir-361-5p indicates better prognosis for breast cancer patients
 Original Article Positive expression of mir-361-5p indicates better prognosis for breast cancer patients Zhi-Gang Cao 1,2 *, Yan-Ni Huang 1,2 *, Ling Yao 1,2 *, Yi-Rong Liu 1,2, Xin Hu 1,2, Yi-Feng Hou
Original Article Positive expression of mir-361-5p indicates better prognosis for breast cancer patients Zhi-Gang Cao 1,2 *, Yan-Ni Huang 1,2 *, Ling Yao 1,2 *, Yi-Rong Liu 1,2, Xin Hu 1,2, Yi-Feng Hou
Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
Clinical significance of up-regulated lncrna NEAT1 in prognosis of ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 3373-3377 Clinical significance of up-regulated lncrna NEAT1 in prognosis of ovarian cancer Z.-J. CHEN, Z. ZHANG, B.-B. XIE, H.-Y. ZHANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 3373-3377 Clinical significance of up-regulated lncrna NEAT1 in prognosis of ovarian cancer Z.-J. CHEN, Z. ZHANG, B.-B. XIE, H.-Y. ZHANG
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 2328-2333 LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer Q.-M. SHEN 1,2, H.-Y. WANG 1,2, S. XU
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 2328-2333 LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer Q.-M. SHEN 1,2, H.-Y. WANG 1,2, S. XU
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Circulating PD-L1 in NSCLC patients and the correlation between the level of PD-L1 expression and the clinical characteristics
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Circulating PD-L1 in NSCLC patients and the correlation between the level of PD-L1 expression and the clinical characteristics Jie Zhang, Jing Gao, Yanyan
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Circulating PD-L1 in NSCLC patients and the correlation between the level of PD-L1 expression and the clinical characteristics Jie Zhang, Jing Gao, Yanyan
HOXC6 and HOXC8 are potentially novel prognosis predictors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 HOXC6 and HOXC8 are potentially novel prognosis predictors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Keneng Chen, M.D., PhD, RCSF Luyan Shen, M.D., PhD 2015/4/28 Department of Thoracic Surgery I, Key Laboratory
HOXC6 and HOXC8 are potentially novel prognosis predictors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Keneng Chen, M.D., PhD, RCSF Luyan Shen, M.D., PhD 2015/4/28 Department of Thoracic Surgery I, Key Laboratory
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer
 Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma
 Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
290 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: DOI /s
 290 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 290-295 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0290-9 Analysis of Prognostic Factors of Esophageal and Gastric Cardiac Carcinoma Patients after Radical Surgery Using Cox Proportional
290 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 290-295 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0290-9 Analysis of Prognostic Factors of Esophageal and Gastric Cardiac Carcinoma Patients after Radical Surgery Using Cox Proportional
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 is up-regulated and associated with poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3357-3362 Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 is up-regulated and associated with poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer H.-H. ZHANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3357-3362 Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 is up-regulated and associated with poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer H.-H. ZHANG
