JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 9 Page September 2015
|
|
|
- Philip Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e) x DOI: Role of Mast cell in Oral lesions Authors Dr Isha Aggarwal 1, Dr Sunita Bhargava 2 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head 1,2 Department of Pathology, RNT Medical College, Udaipur, Rajasthan Corresponding Authors Dr. Isha Aggarwal- mittalishu88@yahoo.com Dr Sunita Bhargava- sunitabhargava57@gmail.com Abstract Background: The present study was carried out for quantitative analysis of the mean MCC/optical field and MCD/sq. mm in the benign, premalignant and malignant oral lesions. Objective: To analyse the role of mast cell in tumorogenesis. Study Design: This study was carried out in the Department of Pathology, RNT Medical College, Udaipur. Punch biopsy of various oral lesions were selected. The sections were obtained and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin and Toluidine blue. The number of mast cells/optical field and mast cell density/sq. mm were assessed. The following conclusions were drawn from our study. Result: An increase in both mean MCC/optical field and MCD/sq. mm was found as the disease progress from benign to premalignant and to malignant oral lesions. This increase in the values was statistically significant between benign v/s malignant and premalignant v/s malignant. However value was found to be non-significant between benign v/s premalignant. Keywords: Mast cells, Mast cell count, Mast cell density, Oral squamous cell carcinoma. INTRODUCTION Oral cancer is a global health problem. It is the sixth most common cancer in the world and accounts for 2 to 4% of malignancies in the West, but in the Indian subcontinent it accounts for 40% of all cancers [1]. Oral cancers include cancers of the lip and the oral mucosa (buccal mucosa, gums, soft and hard palate, tongue and the floor of the mouth). A significant proportion of oral squamous cell carcinoma develops from the premalignant lesions such as leukoplakia and oral submucous fibrosis. The primary aim in the management of premalignant is the early diagnosis and prevention of malignant transformation. The role of angiogenesis in neoplasia has been receiving increasing attention in recent times, since it can be used as independent prognostic indicator for tumour progression and metastasis. The induction of angiogenesis is mediated by several stimulatory and inhibitory molecules which are released by both the tumour and the host cells and it depends on a net balance between the stimulatory angiogenic and the inhibitory antiangiogenic factors [2]. Among the various host immune cells, the mast cells have been implicated in tumour progression because they promote angiogenesis. There is considerable controversy with regard to the number and distribution of the mast cells in Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7575
2 clinically normal oral tissues as compared to the inflamed and diseased tissue. Mast cells arise from a multipotent CD 34+ precursor in the bone marrow and circulate in the peripheral blood as agranular, monocytic appearing cells. They are small cells, round to ovoid in shape with a diameter of microns and are packed with numerous cytoplasmic granules of microns in size. As far as oral diseases are concerned, mast cells have been implicated in variety of diseases like periapical lesions, oral submucous fibrosis, odontogenic cysts, gingivitis, and pyogenic granulomas [3]. Mast cells exert their influence locally and systemically by releasing a variety of potent mediators through degranulation [4]. Hence a histochemical study using toluidine blue stain was conducted to quantify the number of mast cells in various oral lesions and to signify their role in tumour growth and progression. MATERIAL AND METHOD The present study was conducted on two hundred patients presenting with oral lesions in the ENT Outpatient Department and Histopathology section of Pathology Department, RNT Medical College, Udaipur, in the year Patients with suspicious oral inflammatory lesions, potentially malignant and malignant lesions, such as leukoplakia, erythroplakia, palatal erythema, actinic cheilosis, erosive lichen planus and oral carcinoma were selected irrespective of their age and gender. Punch biopsies of the oral lesions taken after thorough oral and general physical examination in the ENT department were sent in 10% formalin fixative solution to the histopathology section. The sections were standardized by maintaining the thickness at 3-4 microns. One set of sections were stained by Harris hematoxylin and eosin for histopathological diagnosis. The other section was stained with 1% toluidine blue for mast cells. The stained sections were examined under binocular research light microscope LABOMED. Mast cells were counted in 10 random high power fields (40X) having larger number of mast cells, and average per high field was determined [5]. Further the mast cell count was expressed per sq mm using the following formula: Radius of one high power field (40X) mm (measured with the occulo-micrometer). Area - 22/7r 2 Area of the field - 22/7x (0.235) 2 approximately 0.2 sq mm. Suppose number of mast cells counted per one high power field i.e. in 0.2 sq mm is A Mast cell density i.e. number of mast cells per sq mm = 5 x A The results were then subjected to statistical analysis for obtaining significance value using t and z test. RESULTS Out of 200 patients included in this study, 67 patients (33.5%) had benign lesion, 16 patients (8%) had premalignant lesion and 117 patients (58.5%) had malignant oral lesions. Amongst the malignant group, 55 patients (27.5%) had well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma while 62 patients (31%) had moderately keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Majority (76.5 per cent) of the patients were adults (31-70 years), however, the age ranged from Years. Males (77.0 per cent) were predominantly affected with male to female ratio of 3.3:1. The most commonly affected site was tongue (35.5 per cent) followed by buccal mucosa. Tobacco chewing and smoking were found to be equally responsible for both benign and malignant lesions. The patient with benign lesions were more commonly found in the age group of years. Those with premalignant lesions showed an equal predilection in the 5 th, 6 th and 7 th decade of life (25%) whereas most of the oral lesions (58.5 per cent) in our study were malignant and were common in the age group of years. Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7576
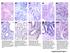
3 Staining of mast cells was carried out using Toluidine blue and enumeration of mast cells was done. Mast cells visible in each optical field (40X) were individually counted and the total number of mast cells per optical field was determined. Further the mast cell count was expressed per sq. mm. The mean mast cell count (MCC) per optical field and mast cell density (MCD) per sq. mm was calculated for benign, premalignant and malignant oral lesions. All the values were expressed in terms of mean ± Sd. The results obtained were tabulated and subjected to statistical analysis. Mean mast cell count/optical field was found to be in benign lesions, in pre malignant lesions and in malignant lesions. Mast cell density also showed a step wise increase as the lesion progressed form benign (20.194) to premalignant (20.250) to malignant lesion (36.077). The statistical analysis in the present study revealed p value to be non-significant between inflammatory and hyperplastic V/s dysplasia (p = 0.972). However p value was found to be highly significant between inflammatory and hyperplastic V/s malignant (p=0.000); dysplasia V/s malignant (p=0.000); and between well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma V/s moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (p=0.000). Figure1: (A) Microphotograph showing inflammatory oral lesion (H and E X 100). (B) Mast cells admixed with dense lymphocytic infiltrate (Toluidine blue X400). Figure 2 : (A) Dysplastic squamous epithelium (H and E X 100). (B) Toluidine blue stained section showing mast cells and dysplastic squamous epithelium (Toluidine blue X 400). Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7577
4 Figure 3: (A) Microphotograph showing squamous cell carcinoma (H and E X 100). (B) Hot spot showing numerous mast cells in squamous cell carcinoma (Toluidine blue X 400). DISCUSSION Mast cells were first described in 1878 by Paul Ehrlich as metachromatically-staining basophilic cells found in connective tissues [6] as fixed elements implicated in tissue tropism. Mast cells are being currently regarded as key effector cells in tissue vascularization, remodeling and homeostasis. Mast cells are ubiquitous cells that are dispersed throughout in almost all the major organs of the body. They are large spherical or elliptical mononuclear cells, mobile bone marrow-derived elements having a diameter of about of 12 microns. They have a life span of weeks to months [7]. These cells are found particularly in association with connective tissue structures such as blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves and in proximity to surfaces that interface the external environment such as those of the respiratory, genitourinary, gastrointestinal system and the skin. Mast cells typically contain granules that originate from hematopoietic stem cells [8]. Mast cells release low molecular weight substances, such as histamine, as well as cytokines and chemokines that exert profound effects on inflammation and cancer [9]. Mast cells also produce a variety of lipid & protein alpha mediators with pro-inflammatory activities including chemotactins, cell activating & cell growth factor. Histamine released from mast cells can induce tumour proliferation through H1 receptors and suppress the immune system through H2 receptors. Both may be involved in human carcinogenesis [10]. Angiogenesis is a critical process in tumour progression because the vascular network produced by the host is essential to allow neoplastic cell populations to form a clinically observable tumour [11]. Mast cells are an abundant source of angiogenic factors [12]. Under physiological conditions, mast cells are particularly prominent in the close vicinity of capillaries and lymphatic channels. In many inflammatory disorders characterized by a profound vascular remodeling, the infiltrate exhibits numerous mast cells that show the structural features of degranulating elements. In various tumour models, mast cells appear at the edges of invasive tumours, where they facilitate angiogenesis by releasing preformed mediators or by triggering proteolytic release of extracellular matrix-bound angiogenic compounds. The role of mast cells in bringing about neoangiogenesis has been studied in oral squamous cell carcinomas and a positive relation has been shown [13].There is also evidence that these cells, by regulating angiogenesis, can influence growth and progression in human cancer [4]. The present study showed mean mast cell count / optical field in benign oral lesions was found to be 4.039, in pre malignant lesions and in malignant lesions The findings was consistent with the study of Kinra et al [3] who Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7578
5 also showed an increase in both mean MCC/optical field and MCD/sq. mm in oral submucous fibrosis, oral leukoplakia, oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma. The mast cell density in the present study also showed increasing trend from benign (20.194) to premalignant (20.250) to malignant lesions (36.077). Similar results were observed in the study carried out by Iamaroon et al [13]. The density of mast cells appeared to increase with disease progression. The mast cell counts were significantly higher in oral squamous cell carcinoma than in hyperkeratosis and normal oral mucosa. In our study the mean mast cell count of and was observed in well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. These findings were in consonance with the study carried out by Sharma et al [14] and Anuradha et al [15]. The latter study revealed that mast cells have significant role in the early stages of cancer progression and increase in mast cells is observed in the initial stages whereas, in second cancer phase, the mast cells decrease because the tumour cells are not dependent on them anymore for the neovascularization effect thereby resulting in the mast cells increase in moderately differentiated when compared to well-differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma. The findings were however, inconsistent with the study carried out by Kalra et al [16] on oral squamous cell carcinoma which showed decreased mast cell from well to moderately to poorly differentiated carcinoma and stated that this may be due to the massive degranulation of mast cell making their identification difficult. In the present study we observed a definitive increase in mast cells count with the disease progression which strengthens the possibility of role of mast cells in the pathogenesis of disease. The procedure of the assay of mast cell was cheap and easy to perform and hence can be targeted to enhance the prognosis of the disease. CONCLUSION As Oral Squamous cell carcinoma is associated with chronic inflammation in adjacent connective tissue, immune reaction and angiogenesis with the progression of dysplastic changes, there is a need to evaluate the role of mast cells in it. After analysing the results of the present study, it was concluded that there was definitive increase in mast cells count as the disease progresses thus substantiating their contributing role in tumour progression. Therapeutic intervention to influence the mast cell secretions should be considered at early precancerous stage. In our set up due to unavailability of sophisticated diagnostic techniques and the prevalence of tobacco and gutka chewing, mast cells may serve as a novel therapeutic target for cancer treatment and inhibiting mast cell functions may inhibit tumour growth. REFERENCES 1. Mehrotra R, Singh M, Kumar D, Pande AN, Gupta R K, Sinha U S: Age specific incidence rate and pathological spectrum or oral cancer in Allahabad. Ind J Med Sci 2003; 57: Michailidou EZ, Markopoulos AK, Antoniades DZ: Mast cells and angiogenesis in oral malignant and premalignant lesions. The Open Dentistry Journal 2008; 2: Kinra M, Ramalingam K, Sarkar A, Rehman F, Girish KL: Comparison of mast cell count and mast cell density in normal mucosa, oral leukoplakia, oral lichen planus, oral submucos fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation 2012; 1(2): Walsh LJ: Mast cells and oral inflammation. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol Med 2003; 14(3): Asboe-Hansen. The mast cells in health and disease. Acta Derm Venerol 1973; 53: 139. Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7579
6 6. Ehrlich P: Contributions to the Theory and Practice of Histological staining. Thesis, University of Leipzig, in Lawrence B: Haemolymphoid system. In: Lawrence B, Martin BM, Patricia C, Mary D, Juhan D, editors. Gray's Anatomy. 38 th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingston Harcourt Publishers Ltd 2000; Gurish MF, Austen KF: The diverse role of mast cells. J Exp Med 2001; 194: Galli SJ, Tsai M: Mast cells: Versatile regulators of inflammation, tissue remodeling, host defence and homeostasis. J Dermatol Sci 2008; 49: Conti P, Castellani ML, Kempuraj D: Role of mast cells in tumor growth. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2007; 37: Ribatti D, Vacca A, Dammacco F: The role of vascular phase in solid tumor growth: a historical review. Neoplasia 1999; 1: Norrby K: Mast cells and angiogenesis. APMIS 2002; 110: Iamaroon A, Pongsiriwet S, Jittidecharakas S, Pattanaporn K, Prapayasatok S, Wanachantararak S: Increase of mast cells and tumor angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 2003; 32: Sharma B, Sriram G, Saraswathi TR, Sivapathasundharam B: Immunohistochemical evaluation of mast cells and angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Indian J Dent Res 2010; 21: Anuradha A, Naik BK, Srinivas GV, Devi RS, Puneet HK. Incidence of Mast Cells in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Short Study. Journal of oncology 2014; Kalra M, Rao N, Nanda K, Rehman F, Girish KL, Tippu S, Arora A. The role of mast cells on angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2012; 17(2): Dr. Isha Aggarwal et al JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 09 September Page 7580
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
 MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
Pattern of oral lesions Cytohistopathological study in tertiary care centre.
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining
 Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining DR SHAN NAWAZ MALIK 1, DR ZANKANA VYAS 2, DR HEMANTH KOTARI 3, DR. VISHNUDAS DINESH PRABHU
Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining DR SHAN NAWAZ MALIK 1, DR ZANKANA VYAS 2, DR HEMANTH KOTARI 3, DR. VISHNUDAS DINESH PRABHU
Chapter 5. Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer
 Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
Chapter 5 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance Ratio for In Vivo Detection of oral Pre-cancer This work is published in: JB0 (SPIE) 13(4):041306 (1-10), 2008 Oxygenated Hemoglobin Diffuse Reflectance
Correlation between transforming growth factor-beta expression and mast cell count in different grades of oral submucous fibrosis
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 123 128 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between transforming growth factor-beta expression and mast cell count in different grades of oral submucous
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 123 128 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between transforming growth factor-beta expression and mast cell count in different grades of oral submucous
Table 1 Classification of oral biopsied lesions
 Original Article A Review of Biopsied Oral Lesions in Department of Oral Medicine, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay Mu Mu Win**, Thiri Su Myat Chel*, Su Mon Than*, Aye Mya Mya*, Aye Aye Thet*, Nandar
Original Article A Review of Biopsied Oral Lesions in Department of Oral Medicine, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay Mu Mu Win**, Thiri Su Myat Chel*, Su Mon Than*, Aye Mya Mya*, Aye Aye Thet*, Nandar
Histopathological study of neoplastic lesions of oral cavity and oropharynx
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
Mast cell profile in appendicitis
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0120 Mast cell profile in appendicitis G. Patil Anuradha 1, AM Anita 2, Saini Kr. Seemant 3,*, S. Pratima 4 1 HOD, 2 Associate Professor, 3 PG Student,
Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0120 Mast cell profile in appendicitis G. Patil Anuradha 1, AM Anita 2, Saini Kr. Seemant 3,*, S. Pratima 4 1 HOD, 2 Associate Professor, 3 PG Student,
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville, Jacksonville, FL 32209, USA
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
Department of Pathology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India 2
 original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 04 ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION Romita Dilip Gaikwad 1,Mukta Bhagwandas Motwani 2,Kalpana Anil
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 04 ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA: AN UNUSUAL PRESENTATION Romita Dilip Gaikwad 1,Mukta Bhagwandas Motwani 2,Kalpana Anil
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS
 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Abstract Background: A wide variety of white lesions are encountered in general population and specially those people
 Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
Original Article Assessment of white lesion in known population group: A Pilot Study Vandana Katoch 1, Sandeep Sidhu 2, Amit Kour 3, Saurav Saini 4, Priyanka Sharma 5 1 MDS, Department Of Oral and Maxillofacial
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA
 Page138 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA Archana Chirag Buch 1, Smit Sanjaybhai Patel 2, Shirish S. Chandanwale 3, Harsh Kumar
Page138 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF ORAL EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY IN TOBACCO CHEWERS OF WESTERN INDIA Archana Chirag Buch 1, Smit Sanjaybhai Patel 2, Shirish S. Chandanwale 3, Harsh Kumar
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek
 ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
 International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
International Journal Of Scientific Research And Education Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 1824-1830 September-2014 ISSN (e): 2321-7545 Website: http://ijsae.in Review Article- Leukoplakia: A mysterious white patch.
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
Original Research. Introduction Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains a serious problem of oral health worldwide. Cancer of the oral
 Received: 16 th July 2015 Accepted: 15 th October 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Correlation of Mast Cell and Angiogenesis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An
Received: 16 th July 2015 Accepted: 15 th October 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Correlation of Mast Cell and Angiogenesis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An
Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus
 TOBACCO INDUCED DISEASES Vol. 2, No. 2: 103-108 (2004) PTID Society Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus Meir Gorsky, 1 Joel B. Epstein, 2 Haya Hasson-Kanfi, 1 Eliezer Kaufman
TOBACCO INDUCED DISEASES Vol. 2, No. 2: 103-108 (2004) PTID Society Smoking Habits Among Patients Diagnosed with Oral Lichen Planus Meir Gorsky, 1 Joel B. Epstein, 2 Haya Hasson-Kanfi, 1 Eliezer Kaufman
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a public
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Mast Cell Density in the Tumor Microenvironment in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Rebeca C.M. Dantas, MSc,* Renata O. de Souza, MSc, Ludmila de
RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Mast Cell Density in the Tumor Microenvironment in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Rebeca C.M. Dantas, MSc,* Renata O. de Souza, MSc, Ludmila de
DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant
 DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant Maxillofacial Surgeon & Surgical Head, SUT Royal Hospitals,
DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant Maxillofacial Surgeon & Surgical Head, SUT Royal Hospitals,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Association of Histopathological Grading of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancers and Its Correlation
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Association of Histopathological Grading of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancers and Its Correlation
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Canadian Scientific Journal. Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
 Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Supplemental Figure 1
 A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution in Screening of Oral Premalignant and Malignant Lesions
 International Journal of Dental Medicine 2015; 1(1): 8-12 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijdm) doi: 10.11648/j.ijdm.20150101.12 Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution
International Journal of Dental Medicine 2015; 1(1): 8-12 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijdm) doi: 10.11648/j.ijdm.20150101.12 Use of Lugol s Iodine Solution
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.92 Clinicopathological Profile & Correlation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.92 Clinicopathological Profile & Correlation
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: ABSTRACT
 Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY The histopathological and immunohistochemical study of oral squamous carcinomas PhD Student: DRAGOMIR LUCIAN PAUL Scientific Coordinator:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY The histopathological and immunohistochemical study of oral squamous carcinomas PhD Student: DRAGOMIR LUCIAN PAUL Scientific Coordinator:
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Epidemiology Clinical presentation
 LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies
 WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
WHITE LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY - diagnostic appraisal & management strategies * Joshy V.R ** Hari.S * Reader, Dept of Oral Pathology, Yenepoya Dental College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore 575 018.
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
Conclusion: It was concluded that laser provides good coagulation, healing, reduces surgical time and prevents high-grade infection.
 Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Research AHB Article Adv Hum Biol 2014; 4(2):45-49. Clinical and Histopathological Evaluation of Healing After Excision of Leukoplakia with Diode Laser Kruti A Shah 1* Hemal R Brahmkshatriya 2 Rushit J
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines. Copyright Fehrenbach and rdhedu.com. All rights reserved.
 General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines Are you ready? Are you Ready? ARE YOU READY? TO LEARN AND EXPERIENCE real ORAL BIOLOGY??? BOOTCAMP STYLE Oral Biology BOOTCAMP through rdhedu.com For Oral Biology
General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines Are you ready? Are you Ready? ARE YOU READY? TO LEARN AND EXPERIENCE real ORAL BIOLOGY??? BOOTCAMP STYLE Oral Biology BOOTCAMP through rdhedu.com For Oral Biology
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School
 Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
ROLE OF MAST CELL IN ORAL PATHOLOGY
 ROLE OF MAST CELL IN ORAL PATHOLOGY Supriya Kheur Deepali Patekar Neeta Bagul Samapika Routray 1 Varsha Dhas Meena Kulkarni Department of Oral Pathology,Dr. D.Y.Patil Dental College and Hospital, Pimpri,
ROLE OF MAST CELL IN ORAL PATHOLOGY Supriya Kheur Deepali Patekar Neeta Bagul Samapika Routray 1 Varsha Dhas Meena Kulkarni Department of Oral Pathology,Dr. D.Y.Patil Dental College and Hospital, Pimpri,
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus
 EJSO 2002; 28: 838±843 doi:10.1053/ejso.2002.1302, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on 1 Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus M. D. Mignogna*, L. Lo Russo*, S.
EJSO 2002; 28: 838±843 doi:10.1053/ejso.2002.1302, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on 1 Clinical behaviour of malignant transforming oral lichen planus M. D. Mignogna*, L. Lo Russo*, S.
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions
 Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Oral Surgeons and the VELscope System: Partners in Early Detection & Diagnosis
 David Morgan, PhD Chief Science Officer LED Dental Inc. There is a growing trend within general dentistry stressing the importance of total oral health that is, not only health of the teeth and gums but
David Morgan, PhD Chief Science Officer LED Dental Inc. There is a growing trend within general dentistry stressing the importance of total oral health that is, not only health of the teeth and gums but
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.102 Original Research Gutka Facies in Oral
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.102 Original Research Gutka Facies in Oral
Oral Cancer FAQs. What is oral cancer? How many people are diagnosed with oral cancer each year?
 Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
Oral Cancer FAQs What is oral cancer? Oral cancer or oral cavity cancer, is cancer that starts in the mouth. Areas affected by this type of cancer are the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks
Secondary neck nodes from squamous cell carcinoma: a study of 67 patients from Tamil Nadu
 International Surgery Journal Sundresh J et al. Int Surg J. 2015 Nov;2(4):544-548 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151077
International Surgery Journal Sundresh J et al. Int Surg J. 2015 Nov;2(4):544-548 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151077
-1- Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks).
 -1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
-1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
Comparative Study of Mast Cell Count in Oral Reactive Lesions and Its Association with Inflammation
 Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01338 Comparative Study of Mast Cell Count in Oral Reactive Lesions and Its Association with Inflammation Hamideh Kadeh, Ghazal Derakhshanfar, Shirin saravani
Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01338 Comparative Study of Mast Cell Count in Oral Reactive Lesions and Its Association with Inflammation Hamideh Kadeh, Ghazal Derakhshanfar, Shirin saravani
JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 9 Page September 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i9.09 A Study of Histopathological Pattern of Ovarian Neoplasms and their Age Distribution in
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i9.09 A Study of Histopathological Pattern of Ovarian Neoplasms and their Age Distribution in
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Oral Cavity. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology. 1.2 Diagnosis and Treatment
 Oral Cavity 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The oral cavity extends from the lips to the palatoglossal folds and consists of the anterior two thirds of the tongue, floor of the mouth,
Oral Cavity 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The oral cavity extends from the lips to the palatoglossal folds and consists of the anterior two thirds of the tongue, floor of the mouth,
Tumor Associated Tissue Eosinophilia in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Histo- Chemical Analysis
 Original Article Tumor Associated Tissue Eosinophilia in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Histo- Chemical Analysis Priya Sahni, Anil Patel, Shylaja Md, Jayadeva Hallur, Pavan Kumar Gujjar Submitted: 28
Original Article Tumor Associated Tissue Eosinophilia in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Histo- Chemical Analysis Priya Sahni, Anil Patel, Shylaja Md, Jayadeva Hallur, Pavan Kumar Gujjar Submitted: 28
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA
 442 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA T. LEHNER From the Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London, S.E.1 Received for publication April 17, 197 SUMMARY.-The lymphocyte
442 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA T. LEHNER From the Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London, S.E.1 Received for publication April 17, 197 SUMMARY.-The lymphocyte
Journal of American Science 2014;10(4)
 Detection of oral potentially malignant lesions among tobacco users; Identafi and Microlux versus histopathology Safia Al attas 1, Suzan Ibrahim 2, Zeinab Darwish 3, Hala Amer 4, Mona Hassan 5 1 Department
Detection of oral potentially malignant lesions among tobacco users; Identafi and Microlux versus histopathology Safia Al attas 1, Suzan Ibrahim 2, Zeinab Darwish 3, Hala Amer 4, Mona Hassan 5 1 Department
Contents. 1 Normal Anatomy Introduction... 17
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(7):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
Mouth Cancer in India A New Epidemic? Prakash C. Gupta. Epidemiology Research Unit, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai
 For the Journal of the Indian Medical Association Mouth Cancer in India A New Epidemic? Prakash C. Gupta Epidemiology Research Unit, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai Correspondence to Dr.
For the Journal of the Indian Medical Association Mouth Cancer in India A New Epidemic? Prakash C. Gupta Epidemiology Research Unit, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai Correspondence to Dr.
Original Research. Serum lipid profile in oral precancer and cancer...garg D et al
 Journal of International Oral Health 14; 6(2):33-39 Received: 1th August 13 Accepted: 15th December 13 Conflict of Interest: one Source of Support: il Original Research Serum lipid profile in oral precancer
Journal of International Oral Health 14; 6(2):33-39 Received: 1th August 13 Accepted: 15th December 13 Conflict of Interest: one Source of Support: il Original Research Serum lipid profile in oral precancer
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain
 Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System
 Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Melanoma Update: 8th Edition of AJCC Staging System Rosalie Elenitsas, M.D. Professor of Dermatology Director, Dermatopathology University of Pennsylvania DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY None
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection
 Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
Oral Cancer- Improving Early Detection GDC Recommended Subject Aims: To give an overview of the dental team's role in detecting the early signs of oral cancer; to give an overview of the risk factors associated
SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS Dimple H Darad 1, Aditi D Dholakia 2, Savitri Chauhan 1 1 Associate professor;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS Dimple H Darad 1, Aditi D Dholakia 2, Savitri Chauhan 1 1 Associate professor;
STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS
 Page222 IJPBS Volume 4 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2014 222-226 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 1 and Sujatha.P*
Page222 IJPBS Volume 4 Issue 2 APR-JUN 2014 222-226 Research Article Biological Sciences STUDY OF PROSTATIC LESION FOR A PERIOD OF FIVE YEARS B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 1 and Sujatha.P*
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients. Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology
 Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Catholic University of Louvain, St - Luc University Hospital Head and Neck Oncology Programme. Anatomopathology. Pathology 1 Sept.
 Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Anatomopathology Pathology 1 Anatomopathology Biopsies Frozen section Surgical specimen Peculiarities for various tumor site References Pathology 2 Biopsies Minimum data, which should be given by the pathologist
Effect of Topical Application of Sesame Oil on Oral Wound Healing in Rabbits
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 7, July 2017 885 Effect of Topical Application of Sesame Oil on Oral Wound Healing in Rabbits Bayan Jaber Hussein Assistant
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 7, July 2017 885 Effect of Topical Application of Sesame Oil on Oral Wound Healing in Rabbits Bayan Jaber Hussein Assistant
R. Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia: Evaluation.
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19424 Diagnostic criteria in proliferative verrucous leukoplakia:
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center
 The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem.
 Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
