Supporting Information
|
|
|
- Joan Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Information For Heterologous production of thiostrepton A and biosynthetic engineering of thiostrepton analogs Chaoxuan Li, Feifei Zhang, and Wendy L. Kelly* Table of Contents Figure S1. PCR analysis of S. actuosus FZ1 and S. lividans FZ1 S1 Figure S2. PCR analysis of S. actuosus FZ2 and S. lividans FZ2 S1 Figure S3. HPLC-MS analysis of S. actuosus culture extracts S2 Figure S4. HPLC-MS analysis of S. lividans culture extracts S3 Figure S5. Strategy used to construct S. laurentii NDS1 S4 Figure S6. Confirmation of tsra deletion mutant S. laurentii NDS1 by PCR S5 Figure S7. Strategy used to construct tsra site-directed mutants in int-3a1 S6 Figure S8. HPLC-MS analysis of culture extracts from S. laurentii mutant strains.s7 Figure S9. Structures of thiostrepton Ala2Gly and thiostrepton Ala4Gly S11 Figure S1. HPLC-MS analysis of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S12 Figure S11. 1 H NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S13 Figure S C NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S14 Figure S13. DEPT spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S15 Figure S14. ghsqc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S16 Figure S15. gcosy spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S17 Figure S16. ghmbc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S18 Figure S17. HPLC-MS analysis of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S19 Figure S18. 1 H NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S2 Figure S C NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S21 Figure S2. DEPT spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S22 Figure S21. ghsqc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S23 Figure S22. gcosy spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S24 Figure S23. ghmbc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S25 Table S1. 1 H and 13 C NMR assignments of thiostrepton Ala2Gly S26 Table S2. 1 H and 13 C NMR assignments of thiostrepton Ala4Gly S28 Table S3. Strains and plasmids used in this study S3 Table S4. PCR Primers used in this study....s32 References... S33
2 A B C M M M kb 1 kb 1.5 kb 1 kb 1 kb.5 kb Figure S1. PCR analysis of S. actuosus FZ1 and S. lividans FZ1. (A) Amplification of tsrk using primers TSRK-F and TSRK-R. (B) Amplification of tsrv using primers TSRV-F and TSRV-R. (C) Amplification of tsrn using primers TSRN-F and TSRN-R. Lanes: (M) 1 kb ladder; (1) JA3A1; (2) pcc1fos; (3) S. actuosus FZ1; (4) S. actuosus FZ2; (5) S. lividans FZ1; (6) S. lividans FZ2. 1 kb M kb.1 kb Figure S2. PCR analysis of S. actuosus FZ2 and S. lividans FZ2 using primers CTSR3-F and CTSR3-R. Lanes: (M) 1 kb ladder; (1) JA3A1; (2) pcc1fos; (3) S. actuosus FZ1; (4) S. actuosus FZ2; (5) S. lividans FZ1; (6) S. lividans FZ2. S1
3 Figure S3. HPLC-MS of culture extracts from S. actuosus FZ1 and S. actuosus FZ2. (A) HPLC-MS of the culture extract from S. actuosus FZ1. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833 [M+2H] 2+ from S. actuosus FZ1. (2) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton A from S. actuosus FZ1 eluting at t R = 27.8 min. (1) Zhang_984_ e Time S6. S (2) [M+2H] e5 6.6e [M+H] m/z (B) HPLC-MS chromatogram extracted for m/z 833 [M+2H] 2+ from the S. actuosus FZ2 culture extract. Zhang_984_ e Time S2
4 Figure S4. HPLC-MS of culture extracts from S. lividans FZ1 and S. lividans FZ2. (A) HPLC-MS of the culture extract from S. lividans FZ1. (1) HPLC-MS chromatogram extracted for m/z 833 [M+2H] 2+ from S. lividans FZ1. (2) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton A from S. lividans FZ1 eluting at t R = 27.8 min. (1) Zhang_9714_ e Time (2) e5 5.68e4 [M+2H] m/z (B) HPLC-MS chromatogram extracted for m/z 833 [M+2H] 2+ from the S. lividans FZ2 culture extract. Zhang_9714_ p y e Time S3
5 tsro tsra tsrb Fosmid JA3A1 A chl R HindIII NdeI SbfI NdeI HindIII SbfI pleft tsro tsrb pright B HindIII NdeI HindIII SbfI tsro tsrb plr C kan R aada orit HindIII NdeI HindIII SbfI pnds1 D tsro tsrb tsro tsra tsrb Chromosomal DNA of S. laurentii tsro NdeI tsrb Chromosomal DNA of S. laurentii NDS1 Figure S5. Strategy used to construct S. laurentii NDS1, an in-frame deletion mutant of tsra. (A) The regions flanking tsra were amplified by PCR from fosmid JA3A1, generating pleft and pright. The indicated restriction sites were engineered into the PCR primers. (B) The NdeI-SbfI fragment from pright was ligated into pleft, generating plr. (C) The HindIII fragment from plr was ligated into pgm16hkss, generating pnds1. (D) pnds1 was introduced into S. laurentii by intergeneric conjugation. Homologous recombination between pnds1 and the chromosome of S. laurentii gave rise to S. laurentii NDS1. S4
6 M DTSR3-F 182 bp DTSR3-R 1.5 kb tsro tsra tsrb 1 kb 182 bp 935 bp Wild-type S. laurentii DTSR3-F 935 bp DTSR3-R.5 kb tsro NdeI tsrb S. laurentii NDS1.1 kb Figure S6. Confirmation of the tsra deletion mutant S. laurentii NDS1 by PCR. (M) 1 bp DNA ladder; (1) genomic DNA of S. laurentii; (2) pnds1; (3)-(5), genomic DNA purified from three colonies of S. laurentii NDS1. S5
7 A B P1 chl R sacb P2 P1 chl R sacb P2 pdc3 disruption cassette tsro tsra tsrb apra R int-3a1 C D * tsro tsra* tsrb kan R apra R tsro P1 chl R sacb P2 tsrb * tsra* * tsro tsra* tsrb apra R int-3a1 int-3a11 to int-3a13 Figure S7. Strategy used to construct tsra site-directed mutants in an integrative E. coli- Streptomyces shuttle fosmid. (A) The pdc3 disruption cassette was amplified by PCR with primers containing a 39 nt tsra sequence at the 5 end of the primer and a 2 nt P1 or P2 sequence at the 3 end of the primer. (B) Homologous recombination between the PCR product and int-3a1 generated int-3a1. (C) tsra mutant sequences were amplified by PCR from three plasmids, pcl61 to pcl63, as appropriate. (D) Homologous recombination between the PCR product and int-3a1 gave rise to a chloramphenicol-sensitive and sucrose-resistant strain of E. coli possessing the tsra sitedirected mutant in the fosmid. S6
8 Figure S8. HPLC-MS analysis of culture extracts from S. laurentii tsra mutant strains. (A) HPLC-MS chromatogram of the S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a1 (thiostrepton A) culture extract. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 818. (2) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 811. (3) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826. (4) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833. (5) Total ion chromatogram. (6) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton A from S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a1 eluting at t R = 27.7 min (calculated m/z [M+2H] 2+, observed m/z 833. [M+2H] 2+ ; calculated m/z [M+H] +, observed m/z [M+H] + ). (1) Li_9122_ , y e (2) Li_9122_ e (3) Li_9122_ e (4) Li_9122_ e7 (5) Li_9122_ TIC 3.15e8 (6) Time [M+2H] e [M+H] m/z S7
9 (B) HPLC-MS chromatogram of the S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a11 (thiostrepton Ala2Gly) culture extract. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 818. (2) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 811. (3) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826. (4) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833. (5) Total ion chromatogram. (6) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly from S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a11 eluting at t R = 25. min (calculated m/z [M+2H] 2+, observed m/z 826. [M+2H] 2+ ). (1) (2) Li_9122_4 1 Li_9122_ e e (3) Li_9122_ e (4) (5) Li_9122_ Li_9122_ e6 TIC 3.23e Time (6) [M+2H] e6 1.17e m/z S8
10 (C) HPLC-MS chromatogram of the S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a12 (thiostrepton Ala4Gly) culture extract. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 818. (2) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 811. (3) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826. (4) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833. (5) Total ion chromatogram. (6) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly from S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a12 eluting at t R = 2.5 min (calculated m/z [M+2H] 2+, observed m/z 826. [M+2H] 2+ ; calculated m/z [M+H] +, observed m/z [M+H] + ). (1) (2) Li_9122_6 1 Li_9122_ y e e (3) (4) (5) Li_9122_6 1 Li_9122_ Li_9122_ e e TIC 3.6e8 (6) Time [M+2H] e6 1.6e [M+H] m/z S9
11 (D) HPLC-MS chromatogram of the S. laurentii NDS1 int-3a13 (thiostrepton Thr7Gly) culture extract. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 818. (2) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 811. (3) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826. (4) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833. (5) Total ion chromatogram. (1) Li_9122_ y e (2) Li_9122_ e (3) Li_9122_ e (4) Li_9122_ e (5) Li_9122_ TIC 3.21e Time (E) HPLC-MS chromatogram of the S. laurentii NDS1 culture extract. (1) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 833. (2) Total ion chromatogram. (1) Zhang_1511_ e (2) Zhang_1511_ TIC 3.87e Time S1
12 Figure S9. Structures of and numbering systems used for (A) thiostrepton Ala2Gly and (B) thiostrepton Ala4Gly. (A) Thiostrepton Ala2Gly (B) Thiostrepton Ala4Gly S11
13 Figure S1. HPLC-MS of thiostrepton Ala2Gly isolated from S. laurentii NDS1 int- 3A11. (A) Total ion chromatogram of thiostrepton Ala2Gly. Zhang_133_ TIC 2.9e8 Relative Abundance Time Time (min) (B) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826 of thiostrepton Ala2Gly. Zhang_133_ e7 Relative Abundance Time (min) (C) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly eluting at t R = 25.2 min [M+2H] 2+ Scan 1.73e6 ES+ 1.73e Relative Abundance [M+H] m/z S12
14 Figure S11. 1H NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (5 MHz, CDCl3-CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S13
15 Figure S12. 13C NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (125 MHz, CDCl3-CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S14
16 Figure S13. DEPT-135 NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (125 MHz, CDCl3CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S15
17 Figure S14. ghsqc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S16
18 Figure S15. gcosy spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S17
19 Figure S16. ghmbc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala2Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S18
20 Figure S17. HPLC-MS of thiostrepton Ala4Gly isolated from S. laurentii NDS1 int- 3A12. (A) Total ion chromatogram of thiostrepton Ala4Gly. Zhang_133_ TIC 4.4e8 Relative Abundance Time Time (min) (B) Chromatogram extracted for m/z 826 for thiostrepton Ala4Gly. Zhang_133_ e7 Relative Abundance Time (min) (C) Mass spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly eluting at t R = 2.6 min. Zhang_133_7 281 (2.598) Sm (SG, 2x.2); Cm (279: :323) [M+2H] 2+ Scan 2.2e6 ES+ 2.2e Relative Abundance [M+H] m/z S19
21 Figure S18. 1H NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (5 MHz, CDCl3-CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S2
22 Figure S19. 13C NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (125 MHz, CDCl3-CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S21
23 Figure S2. DEPT-135 NMR spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (125 MHz, CDCl3CD3OD 4:1, 25 C). S22
24 Figure S21. ghsqc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S23
25 Figure S22. gcosy spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S24
26 Figure S23. ghmbc spectrum of thiostrepton Ala4Gly (5 MHz, CDCl 3 -CD 3 OD 4:1, 25 C). S25
27 Table S1. 1 H and 13 C NMR assignments of thiostrepton Ala2Gly Position δ C [ppm]; mult δ H [ppm] (mult, J in Hz) HMBC a COSY b Ile1 Ile ; C q Ile ; CH 2.89 (s) Ile ; CH 1.83 (m) Ile1-1 Ile1-6, Ile1-4-H B Ile ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B :.93 (m) Ile1-4-H A, Ile1-5 Ile1-3, Ile1-4-H B, Ile1-5 Ile ; CH 3.73 (t, 7.3) Ile1-3, Ile1-4 Ile1-4-H A, Ile1-4-H B Ile ; CH 3.88 (d, 6.9) Ile1-2, Ile1-3, Ile1-4 Ile1-3 Gly2 Gly ; C q Gly ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B : 3.33 (d, 17.2) Gly2-1 Dha3 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 5.65 (s) Dha3-1, Dha3-2 H B : 5.23 (bs) Dha3-1 Ala4 Ala ; C q Ala ; CH 4.61 (q, 6.2) Dha3-1, Ala4-1 Ala4-3 Ala ; CH (d, 6.4) Ala4-1, Ala4-2 Ala4-2 Gly2-2-H B Gly2-2-H A Dha3-3-H B Dha3-3-H A Pip Pip ; C q Pip ; CH (m) Pip-4-H B Pip ; CH 2 H A : 3.95 c, H B : 2.16 (d, 13.1) Pip-4-H B Pip-4-H A, Pip-3 Pip ; C q Pip ; CH 5.19 (s) Pip-2, Pip-5, Thz13-2, Thz13-3, Thz15-4 Thz6 Thz ; C q Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.4 (s) Thz6-2, Thz6-4 Thz ; C q Thr7 Thr ; C q Thr ; CH 4.29 (d, 3.) Thz6-1 Thr7-3, Thr7-NH Thr ; CH (m) Thr7-4 Thr ; CH 3.68 (d, 4.7) Thr7-2, Thr7-3 Thr7-3 Thr7-NH d 7. (d, 6.2) Thr7-2 Dhb8 Dhb ; C q Dhb ; CH 6.1 (q, 6.9) Dhb8-2, Tzn9-4 Dhb8-4 Dhb ; CH (d, 7.) Dhb8-2, Dhb8-3, Tzn9-4 Dhb8-3 Tzn9 Tzn ; C q Tzn ; CH 4.85 (dd, 12.3, 9.4) Tzn9-1, Tzn9-4 Tzn9-3-H A, Tzn9-3-H B Tzn ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B : 3.4 (t, 12.1) Tzn9-2, Tzn9-4 Tzn9-1, Tzn9-2 Tzn9-2, Tzn9-3-H B, Tzn9-2, Tzn9-3-H A Tzn ; C q Ile1 Ile ; CH 5.62 (d, 9.9) Tzn9-1, Ile1-3, Thz11-4 Ile1-NH Ile ; C q Ile ; CH 3.68 (q, 6.4) Ile1-2, Ile1-3, Ile1-5, Ile1-6 Ile1-5 Ile ; CH (d, 6.4) Ile1-3, Ile1-4, Ile1-6 Ile1-4 Ile ; CH (s) Ile1-2, Ile1-3, Ile1-4, Ile1-5 Ile1-NH d (m) Ile1-2 Thz11 Thz ; C q Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.16 (s) Thz11-1, Thz11-2, Thz11-4 Thz ; C q S26
28 Position δ C [ppm]; mult δ H [ppm] (mult, J in Hz) HMBC a COSY b Thr12 Thr ; CH 5.65 (s) Thz11-1, Thz13-4 Thr12-NH Thr ; CH 6.24 (m) Q-1 Thr12-4 Thr ; CH (d, 6.4) Thr12-2, Thr12-3 Thr12-3 Thr12-NH d 8.67 (d, 8.8) Thr12-2 Thz13 Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 7.44 (s) Pip-6, Thz13-2, Thz13-4 Thz ; C q Thz15 Thz ; C q Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.16 (s) Thz15-1, Thz15-2, Thz15-4 Thz ; C q Dha16 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 6.57 (d, 1.8) H B : 5.48 (d, 1.7) Dha16-1, Dha16-2 Dha16-1, Dha16-2 Dha17 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 6.4 (s) Dha17-1, Dha17-2 H B : 5.55 (s) Dha17-1, Dha17-2 Q Q ; C q Q ; C q Q ; CH 7.19 (s) Q-5 Q ; C q Q ; C q Q ; CH 6.78 (d, 9.9) Q-5, Q-8, Q-1 Q-7 Q ; CH 6.29 (dd, 9.5, 5.7) Q-5 Q-6, Q-8 Q ; CH (m) Q-7 Q ; CH 4.25 (s) Q ; C q Q ; CH (m) Q-12 Q ; CH (d, 6.6) Q-4, Q-11 Q-11 a HMBC correlations are from the proton to the indicated carbon. b COSY correlations are from the proton to the proton attached to the indicated position. c The δ of this resonance was determined by HSQC due to overlap with the methanol-d 4 peak. d Only those amide resonances demonstrating COSY correlations to neighboring protons were assigned. Dha16-3-H B Dha16-3-H A Dha17-3-H B Dha17-3-H A S27
29 Table S2. 1 H and 13 C NMR assignments of thiostrepton Ala4Gly Position δ C [ppm]; mult δ H [ppm] (mult, J in Hz) HMBC a COSY b Ile1 Ile ; C q Ile ; CH 2.87 (s) Ile1-3 Ile ; CH 1.83 (m) Ile1-1 Ile1-4-H B, Ile1-6 Ile ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B :.97 (m) Ile1-4-H B, Ile1-5 Ile1-3, Ile1-4-H A, Ile1-5 Ile ; CH 3.77 (t, 7.3) Ile1-3, Ile1-4, Ile1-6 Ile1-4-H A, Ile1-4-H B Ile ; CH 3.9 (d, 6.9) Ile1-1, Ile1-2, Ile1-3, Ile1-4, Ile1-5 Ile1-3 Ala2 Ala ; C q Ala ; CH 3.69 (q, 6.3) Ala2-3 Ala ; CH (br) Ala2-2 Dha3 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 5.74 (s) H B : 5.26 (s) Dha3-3- H A Gly4 Gly ; C q Gly ; CH 2 H A : 4.47 (br) H B : (m) Gly4-2-H B Gly4-2-H A Gly4-NH d 6.95 (d, 8.2) Gly4-2-H A Pip Pip ; C q Pip ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B : 2.94 (m) Pip-4-H B Pip ; CH 2 H A : (m) c H B : (m) Pip-4-H B Pip-4-H A, Pip-3-H B Pip ; C q Pip ; CH 5.14 (s) Thz6 Thz ; C q Thz6-1 Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.4 (s) Thz6-2, Thz6-4 Thz ; C q Thr7 Thr ; C q Thr ; CH 4.32 (d, 2.6) Thr7-3 Thr ; CH 1.37 (br) Thr7-4 Thr ; CH 3.73 (br s) Thr7-3 Dhb8 Dhb ; C q Dhb ; CH 6.11 (s) Dhb8-4 Dhb ; CH (d, 6.4) Dhb8-2, Dhb8-3 Dhb8-3 Tzn9 Tzn ; C q Tzn ; CH 4.86 (t, 1.7) Tzn9-3-H A, Tzn9-3-H B Tzn ; CH 2 H A : (m) H B : 3.6 (t, 11.2) Tzn9-4 Tzn9-2, Tzn9-3-H B Tzn9-2, Tzn9-3-H A Tzn ; C q Ile1 Ile ; CH 5.61 (s) Ile ; C q Ile ; CH 3.69 (q, 6.3) Ile1-3, Ile1-6 Ile1-5 Ile ; CH (d, 6.4) Ile1-3, Ile1-4, Ile1-6 Ile1-4 Ile ; CH (s) Ile1-2, Ile1-C3, Ile1-4, Ile1-5 Thz11 Thz ; C q Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.18 (s) Thz11-2, Thz11-4 Thz ; C q S28
30 Position δ C [ppm]; mult δ H [ppm] (mult, J in Hz) HMBC a COSY b Thr12 Thr ; CH 5.66 (s) Thr ; CH 6.26 (s) Thr12-4 Thr ; CH (d, 5.6) Thr12-3 Thz13 Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 7.41 (s) Thz ; C q Thz15 Thz ; C q Thz ; C q Thz ; CH 8.17 (s) Thz15-1, Thz15-C2, Thz15-C4 Thz ; C q Dha16 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 6.58 (s) H B : 5.5 (s) Dha17 Dha ; C q Dha ; C q Dha ; CH 2 H A : 6.42 (s) H B : 5.56 (s) Dha17-1, Dha17-2 Dha17-1 Dha3-16- H B Dha3-16- H A Dha3-17- H B Dha3-17- H A Q Q ; C q Q ; C q Q ; CH 7.21 (s) Q ; C q Q ; C q Q ; CH 6.77 (d, 9.7) Q-7 Q ; CH 6.26 (s) Q-6, Q-8 Q ; CH (m) Q-7 Q ; CH 4.3 (m) Q-9-OH Q ; C q Q ; CH 5.19 (br) Q-12 Q ; CH (br) Q-11 Q-9-OH 6.95 (d, 8.2) Q-9 a HMBC correlations are from the proton to the indicated carbon. b COSY correlations are from the proton to the proton attached to the indicated position. c The δ of this resonance was determined by HSQC due to overlap with the methanol-d 4 peak. d Only this amide resonance demonstrating COSY correlation to neighboring proton was assigned. S29
31 Table S3. Strains and plasmids used in this study Strain/Plasmid Description Reference or source Streptomyces strains S. laurentii ATCC Wild-type, thiostrepton producer ATCC S. actuosus ATCC Wild-type, nosiheptide producer ATCC S. lividans TK24 A common host for Streptomyces gene expression and 1 manipulation S. coelicolor CH999 A common host for Streptomyces gene expression and 2 manipulation S. actuosus FZ1 S. actuosus containing int-3a1 This study S. actuosus FZ2 S. actuosus containing int-pcc1fos This study S. lividans FZ1 S. lividans containing int-3a1 This study S. lividans FZ2 S. lividans containing int-pcc1fos This study S. laurentii NDS1 S. laurentii containing an in-frame deletion of tsra This study S. laurentii NDS1/int-3A1 S. laurentii NDS1 containing int-3a1 This study S. laurentii NDS1/int-3A11 S. laurentii NDS1 containing int-3a11 This study S. laurentii NDS1/int-3A12 S. laurentii NDS1 containing int-3a12 This study S. laurentii NDS1/int-3A13 S. laurentii NDS1 containing int-3a13 This study E. coli strains BW25113/pKD46 ET12567/pUZ82 Host for PCR-targeted disruption of a gene from a fosmid or plasmid Host for conjugation with Streptomyces species 3 4 Strains used for antimicrobial assays Bacillus sp. ATCC Wild-type ATCC Escherichia coli ATCC Wild-type ATCC Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 1537 Methicillin-resistant ATCC Enterococcus faecium ATCC Vancomycin-resistant ATCC Plasmids pcc1fos Fosmid used for genomic library construction Epicentre Inc. psc-b-amp/kan A routine vector from StrataClone Blunt PCR Cloning Kit, Agilent Technologies for cloning blunt-end PCR product JA3A1 Fosmid containing the tsr biosynthetic gene cluster 5 int- pcc1fos A fosmid containing all essential genes for the conjugal This study transfer and integration into a streptomycete chromosome int-3a1 A fosmid containing the entire tsr gene cluster and all This study essential genes for the conjugal transfer and integration into a streptomycete chromosome pset152 An integrative plasmid containing the apramycin resistance 6 gene and all essential genes for the conjugal transfer and integration into a streptomycete chromosome pse34 Plasmid containing the thiostrepton resistance gene Pfizer pij778 A plasmid containing the spectinomycin/streptomycin 4 resistance cassette pleft psc-b-amp/kan vector harboring the 122 nt sequence This study upstream of tsra pright psc-b-amp/kan vector harboring the 13 nt sequence This study downstream of tsra plr pleft containing a 1 kb insert from the NdeI-SbfI digestion This study of pright pgm16hk A derivative of pgm16k 5 in which a 1.6 kb HindIIIdigested This study fragment was deleted pgm16hkss A derivative of pgm16hk, in which the ampicillin This study resistance gene was replaced by the spectinomycinstreptomycin resistance cassette. It is a conjugal and temperature-sensitive E. coli-streptomyces shuttle vector pnds1 pgm16hkss containing a 2 kb insert from HindIII This study digestion of plr pdc1 Vector psc-b-amp/kan containing a.9 kb chl R gene This study pdc2 Vector psc-b-amp/kan containing a 1.8 kb sacb gene This study amplified from pex1t with primers: SacB-F and SacB-R pdc3 Plasmid containing the dual-marker cassette (chl R and sacb) This study pjp11 pcr4-blunt vector harboring a 1.8 kb fragment PCR amplified from S. laurentii genomic DNA, which contains the.2 kb tsra gene and its two flanking.8 kb region 5 S3
32 pcl61 Plasmid containing the tsra variant encoding the Ala2Gly This study mutation pcl62 Plasmid containing the tsra variant encoding the Ala4Gly This study mutation pcl63 Plasmid containing the tsra variant encoding the Thr7Gly This study mutation int-3a1 Derived from int-3a1. tsra is replaced by chl R sacb This study cassette int-3a11 Derived from int-3a1. The chl R sacb cassette is replaced This study by the tsra variant encoding the Ala2Gly mutation int-3a12 Derived from int-3a1. The chl R sacb cassette is replaced This study by the tsra variant encoding the Ala4Gly mutation int-3a13 Derived from int-3a1. The chl R sacb cassette is replaced This study by the tsra variant encoding the Thr7Gly mutation pex1t Plasmid containing sacb gene ATCC S31
33 Table S4. Primers used in this study Primer Sequence Description CTSR1-F CTSR1-R 5 -TTTGAGTTATCGAGATTTTCAGGAGCTAAGG AAGCTAAAGCGGTGGTTTTTTTGTTTGCAAGC-3 5 -ACCAGGCGTTTAAGGGCACCAATAACTGCCTT AAAAAAACCGATGCAAAGTGCCGATCA-3 Primers for the replacement of chl R in pcc1fos, or fosmids based on it, with genes aac(3)iv, int, attp and orit amplified from pset152. pset152 sequence is underlined. CTSR2-F 5 -GCGGTGGTTTTTTTGTTTGCAAGC-3 Primers for the confirmation of CTSR2-R 5 -CCGATGCAAAGTGCCGATCA-3 int-pcc1fos and int-3a1. CTSR3-F 5 - GCGGTGGTTTTTTTGTTTGCAAGC-3 Primers for the confirmation of CTSR3-R 5 - CTACGGAAGGAGCTGTGGAC-3 int-pcc1fos and int-3a1. TSRK-F 5 -CCGATGCAAAGTGCCGATCA-3 Primers for the amplification of tsrk. TSRK-R 5 -TCGCTCGAGGCGCAGCACCTTGCC-3 TSRV-F 5 -TGCTGCATATGACGGGAGTCACCGAACCG-3 Primers for the amplification of tsrv. TSRV-R 5 -TTCCTCGAGTCAGTCTCCCGGCGCCTC -3 TSRN-F 5 -AGTATTCATATGACCGCCCCCGCGCTCCCGCTC-3 Primers for the amplification of tsrn. TSRN-R 5 - ACCCTCGAGTCAGACGGCGAGCCGCCGTTC-3 DTSR1-F 5 -AAGCTTGTGAGGGTCACCACGGATCC-3 Primers for the amplification of the region DTSR1-R 5 -CCTGCAGGCATATGCTCCAGGGCGGCATTGCT CAT-3 upstream of tsra. Underlined regions are the restriction sites of HindIII, NdeI and SbfI. DTSR2-F 5 -CATATGTGAGGTAACACCCGGCGCGGA-3 Primers for the amplification of the region DTSR2-R 5 -CCTGCAGGAAGCTTGCTCCAGGTCCGCGACGC CG-3 downstream of tsra. Underlined regions are restriction sites of HindIII, NdeI and SbfI. DTSR3-F 5 -ATCGTGTTGGGCTTGACG-3 Primers used to confirm the construction of DTSR3-R 5 -CGCGGTGCAATAGGACAT-3. S. laurentii NDS1. Chl-F Chl-R 5 -ATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACCAGATCTGCCGCTC CATGAGCTTATCG-3 5 -CCTGCAGGCATATGAATTACGCCCCGCCCTGCC-3 Primers for the amplification of chl R from pcc1fos. Underlined regions are restriction sites of BglII, NdeI and SbfI. pcc1fos sequence is italicized. SacB-F 5 -CATATGAACTTTATGCCCATGCAACAG-3 Primers for the amplification of sacb gene SacB-R 5 -CCTGCAGGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCAGATCTG AGAGTGCACCATAATCGGC-3 from pex1t. Underlined regions are restriction sites of BglII, NdeI and SbfI. pex1t sequence is italicized. A2G-F 5 -GTCACGATGATCGGCTCCGCCTCCTGC-3 Primers to generate TsrA Ala2Gly. A2G-R 5 -GCAGGAGGCGGAGCCGATCATCGTGAC-3 A4G-F 5 -GATGATCGCGTCCGGCTCCTGCACCACC-3 Primers to generate TsrA Ala4Gly. A4G-R 5 -GGTGGTGCAGGAGC CGGACGCGATCATC-3 T7G-F 5 -GTCCGCC TCCTGCGGCACCTGCATCTGC-3 Primers to generate TsrA Thr7Gly. T7G-R AmpSS-F AmpSS-R DC1-F DC1-R 5 -GCAGATGCAGGTGCCGCAGGA GGCGGAC-3 5 -CCAATGCTTAATCAGTGAGGCACCTATCTCAGCGATC TGGGAATAGGAACTTCATGAGC-3 5 -ATGAGTATTCAACATTTCCGTGTCGCCCTTATTCCCTT TGAAGTTCCCGCCAGCCTCGC-3 5 -ATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACCAGATCTGCCG CTCCATGAGCTTATCG-3 5 -CCTGCAGGCATATGAATTACGCCCCGCCCTG CC-3 Primers for the amplification of the spectinomycin-streptomycin resistance cassette from pij778 to replace ampicillin resistance gene in pgm16hk. Underlined regions are sequence of pij778. pgm16hk sequence is in italics. Primers for the amplification of chl R from pcc1fos. The SbfI and NdeI restriction sites are underlined and in italics, respectively. DC2-F 5 -CATATGAACTTTATGCCCATGCAACAG-3 Primers for the amplification of sacb from DC2-R 5 -CCTGCAGGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCAGA TCTGAGAGTGCACCATAATCGGC-3 pex1t. The SbfI and NdeI restriction sites are underlined and in italics, respectively. SD1-F SD1-R 5 -GCGCGATCGACGCGACCGCAGACTTGCCGA AAGGTTGTGATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC-3 5 -GGCGGGGAGGAACAGTCCTCCGCGCCGGGT GTTACCTCATGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC-3 Primers for the disruption of tsra in int-3a1. The underlined regions are homologous to tsra. SD2-F 5 -GCGCGATCGACGCGACCGCAG-3 Primers used in the amplification of tsra SD2-R 5 -GGCGGGGAGGAACAGTCCTCC-3 variants from pcl SD3-F SD3-R 5 -ATCGTGTTGGGCTTGACG-3 5 -CGCGGTGCAATAGGACAT-3 Primers used in DNA sequencing to confirm int-3a11 to 13. S32
34 References 1. D. A.Hopwood, G. Hintermann, T. Kieser, and H. M. Wright, Plasmid, 1984, 11, R. Ziermann and M. C. Betlach, BioTechniques, 1999, 26, K. A. Datsenko and B. L. Wanner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2, 97, B. Gust, G. L. Challis, K. Fowler, T. Kieser, and K. F. Chater, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 23, 1, W. L. Kelly, L. Pan, and C. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 29, 131, M. Bierman, R. Logan, K. O'Brien, E. T. Seno, R. N. Rao, and B. E. Schoner, Gene, 1992, 116, S33
Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted. residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue. Supplementary Figure 2. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant
Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue. Supplementary Figure 2. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant
Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin. macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens
 Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens Hoang-Chuong NGUYEN, Emmanuelle DARBN, Robert THAI, Jean-Luc PERNDET, Sylvie LAUTRU SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Figure
Post-PKS tailoring steps of the spiramycin macrolactone ring in Streptomyces ambofaciens Hoang-Chuong NGUYEN, Emmanuelle DARBN, Robert THAI, Jean-Luc PERNDET, Sylvie LAUTRU SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Figure
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn
 Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Bioscience, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia School of Biological Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland 1010, New Zealand
 Supporting Information for Biosynthesis of the Thiopeptins and Identification of an F 420 H 2 -dependent Dehydropiperidine Reductase Hiro Ichikawa 1, Ghader Bashiri 2, and Wendy L. Kelly 1* 1 School of
Supporting Information for Biosynthesis of the Thiopeptins and Identification of an F 420 H 2 -dependent Dehydropiperidine Reductase Hiro Ichikawa 1, Ghader Bashiri 2, and Wendy L. Kelly 1* 1 School of
Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M0042F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M42F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance chemical diversity Zhuo Shang, Ritesh Raju,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M42F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance chemical diversity Zhuo Shang, Ritesh Raju,
Preparation and Characterization of Cysteine Adducts of Deoxynivalenol
 Preparation and Characterization of Cysteine Adducts of Deoxynivalenol Ana Stanic, Silvio Uhlig, Anita Solhaug, Frode Rise, Alistair L. Wilkins, Christopher O. Miles S1 Figure S1. 1 H spectrum of 1 (DON)
Preparation and Characterization of Cysteine Adducts of Deoxynivalenol Ana Stanic, Silvio Uhlig, Anita Solhaug, Frode Rise, Alistair L. Wilkins, Christopher O. Miles S1 Figure S1. 1 H spectrum of 1 (DON)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 24, No. 12, S1-S21, 2013. Printed in Brazil - 2013 Sociedade Brasileira de Química 0103-5053 $6.00+0.00 SI Rui He, a,b,c Bochu Wang,*,b Toshiyuki Wakimoto,
Supplementary Information J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 24, No. 12, S1-S21, 2013. Printed in Brazil - 2013 Sociedade Brasileira de Química 0103-5053 $6.00+0.00 SI Rui He, a,b,c Bochu Wang,*,b Toshiyuki Wakimoto,
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the
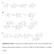 Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Lysoquinone-TH1, a new polyphenolic tridecaketide produced by expressing the lysolipin minimal PKS II in Streptomyces albus
 Supplemental Information Lysoquinone-TH1, a new polyphenolic tridecaketide produced by expressing the lysolipin minimal PKS II in Streptomyces albus Torben Hofeditz, 1 Claudia Eva-Maria Unsin 2, Jutta
Supplemental Information Lysoquinone-TH1, a new polyphenolic tridecaketide produced by expressing the lysolipin minimal PKS II in Streptomyces albus Torben Hofeditz, 1 Claudia Eva-Maria Unsin 2, Jutta
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information New Highly Oxygenated Germacranolides from Carpesium divaricatum and their Cytotoxic Activity Tao Zhang, 1 Jin-Guang Si, 1, 2 Qiu-Bo Zhang, 1 Gang Ding, 1 and Zhong-Mei Zou 1*
Supplementary Information New Highly Oxygenated Germacranolides from Carpesium divaricatum and their Cytotoxic Activity Tao Zhang, 1 Jin-Guang Si, 1, 2 Qiu-Bo Zhang, 1 Gang Ding, 1 and Zhong-Mei Zou 1*
Identification, characterization of a flavin-containing monooxygenase MoA and its function in a
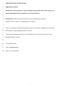 1 Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2 Supplementary Material 3 4 Identification, characterization of a flavin-containing monooxygenase MoA and its function in a specific sophorolipid molecule metabolism
1 Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2 Supplementary Material 3 4 Identification, characterization of a flavin-containing monooxygenase MoA and its function in a specific sophorolipid molecule metabolism
Enhanced pinocembrin production in Escherichia coli by regulating cinnamic acid metabolism
 1 Enhanced pinocembrin production in Escherichia coli by regulating cinnamic acid metabolism 2 Weijia Cao 1,2, Weichao Ma 1,2,3, Xin wang 1,2, Bowen Zhang 1,2, Xun Cao 1,2, Kequan Chen 1,2*, Yan Li 1,2
1 Enhanced pinocembrin production in Escherichia coli by regulating cinnamic acid metabolism 2 Weijia Cao 1,2, Weichao Ma 1,2,3, Xin wang 1,2, Bowen Zhang 1,2, Xun Cao 1,2, Kequan Chen 1,2*, Yan Li 1,2
Received 9 January 2005/Accepted 24 February 2005
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 3795 3799 Vol. 187, No. 11 0021-9193/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.187.11.3795 3799.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Alteration
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2005, p. 3795 3799 Vol. 187, No. 11 0021-9193/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.187.11.3795 3799.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Alteration
Identification of novel endophenaside antibiotics produced by Kitasatospora sp. MBT66
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION belonging to the manuscript: Identification of novel endophenaside antibiotics produced by Kitasatospora sp. MBT66 by Changsheng Wu 1, 2, Gilles P. van Wezel 1, *, and Young Hae
SUPPORTING INFORMATION belonging to the manuscript: Identification of novel endophenaside antibiotics produced by Kitasatospora sp. MBT66 by Changsheng Wu 1, 2, Gilles P. van Wezel 1, *, and Young Hae
Supplementary Figure 1. HGL-DTG levels in uninduced and herbivory induced leaves. Total HGL-
 Supplementary Figure 1. HGL-DTG levels in uninduced and herbivory induced leaves. Total HGL- DTG concentrations [F 1,4 = 36.88, P 0.0037; significant differences (threshold: P 0.05) between means (± SE)
Supplementary Figure 1. HGL-DTG levels in uninduced and herbivory induced leaves. Total HGL- DTG concentrations [F 1,4 = 36.88, P 0.0037; significant differences (threshold: P 0.05) between means (± SE)
Supporting information
 Supporting information for Pentaketide Ansamycin Microansamycins A I from Micromonospora sp. Reveal Diverse Post- PKS Modifications Jianxiong Wang,, Wen Li,, Haoxin Wang, and Chunhua Lu *, Key Laboratory
Supporting information for Pentaketide Ansamycin Microansamycins A I from Micromonospora sp. Reveal Diverse Post- PKS Modifications Jianxiong Wang,, Wen Li,, Haoxin Wang, and Chunhua Lu *, Key Laboratory
Prevalence of HPV-16 genomic variant carrying a 63-bp duplicated sequence within the E1 gene in Slovenian women
 Prevalence of HPV-16 genomic variant carrying a 63-bp duplicated sequence within the E1 gene in Slovenian women K E Y WORDS HPV-16, cervical cancer, E6-T350G variant A BSTRACT High-risk HPV, particularly
Prevalence of HPV-16 genomic variant carrying a 63-bp duplicated sequence within the E1 gene in Slovenian women K E Y WORDS HPV-16, cervical cancer, E6-T350G variant A BSTRACT High-risk HPV, particularly
Resistance to Tetracycline Antibiotics by Wangrong Yang, Ian F. Moore, Kalinka P. Koteva, Donald W. Hughes, David C. Bareich and Gerard D. Wright.
 Supplementary Data for TetX is a Flavin-Dependent Monooxygenase Conferring Resistance to Tetracycline Antibiotics by Wangrong Yang, Ian F. Moore, Kalinka P. Koteva, Donald W. Hughes, David C. Bareich and
Supplementary Data for TetX is a Flavin-Dependent Monooxygenase Conferring Resistance to Tetracycline Antibiotics by Wangrong Yang, Ian F. Moore, Kalinka P. Koteva, Donald W. Hughes, David C. Bareich and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A new series of cytotoxic pyrazoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis Hong Wang 1,, Jinhong Zheng 1,, Weijie Xu 1, Cheng Chen 1,
Supporting Information A new series of cytotoxic pyrazoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis Hong Wang 1,, Jinhong Zheng 1,, Weijie Xu 1, Cheng Chen 1,
Supporting information
 Supporting information Rhabdopeptide/Xenortide-like Peptides from Xenorhabdus innexi with Terminal Amines Showing Potent Anti-protozoal Activity Lei Zhao,, Marcel Kaiser,, Helge B. Bode *,, Molekulare
Supporting information Rhabdopeptide/Xenortide-like Peptides from Xenorhabdus innexi with Terminal Amines Showing Potent Anti-protozoal Activity Lei Zhao,, Marcel Kaiser,, Helge B. Bode *,, Molekulare
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008
 Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
Experimental Details Unless otherwise noted, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company and were used as received. 2-DOS and neamine were kindly provided by Dr. F. Huang. Paromamine
THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS. Polyketomycin, a New Antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. MK277-AF1. II. Structure Determination
 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS Polyketomycin, a New Antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. MK277-AF1 II. Structure Determination ISAO MOMOSE, WEI CHEN, HIKARU NAKAMURA, HIROSHI NAGANAWA, HIRONOBU IINUMA and TOMIO
THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS Polyketomycin, a New Antibiotic from Streptomyces sp. MK277-AF1 II. Structure Determination ISAO MOMOSE, WEI CHEN, HIKARU NAKAMURA, HIROSHI NAGANAWA, HIRONOBU IINUMA and TOMIO
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The conifer biomarkers dehydroabietic and abietic acids are widespread in Cyanobacteria Maria Sofia Costa, Adriana Rego, Vitor Ramos, Tiago Afonso, Sara Freitas, Marco Preto,
Supplementary Information The conifer biomarkers dehydroabietic and abietic acids are widespread in Cyanobacteria Maria Sofia Costa, Adriana Rego, Vitor Ramos, Tiago Afonso, Sara Freitas, Marco Preto,
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
What happens after activation of ascaridole? Reactive compounds and their implications for skin sensitization.
 What happens after activation of ascaridole? Reactive compounds and their implications for skin sensitization. Amar G. Chittiboyina,, * Cristina Avonto, and Ikhlas A. Khan., National Center for Natural
What happens after activation of ascaridole? Reactive compounds and their implications for skin sensitization. Amar G. Chittiboyina,, * Cristina Avonto, and Ikhlas A. Khan., National Center for Natural
Overexpression of the ABC transporter AvtAB increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis
 DOI 10.1007/s00253-011-3439-4 APPLIED GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOTECHNOLOGY Overexpression of the ABC transporter AvtAB increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis Jingfan Qiu & Ying Zhuo
DOI 10.1007/s00253-011-3439-4 APPLIED GENETICS AND MOLECULAR BIOTECHNOLOGY Overexpression of the ABC transporter AvtAB increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis Jingfan Qiu & Ying Zhuo
The Impact of a Transposon Insertion in phzf2 on the Specialized Metabolite. Production and Interkingdom Interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 1 2 3 Supplemental Material The Impact of a Transposon Insertion in phzf2 on the Specialized Metabolite Production and Interkingdom Interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4 5 6 7 Vanessa V. Phelan a, Wilna
1 2 3 Supplemental Material The Impact of a Transposon Insertion in phzf2 on the Specialized Metabolite Production and Interkingdom Interactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4 5 6 7 Vanessa V. Phelan a, Wilna
Characterizing fatty acids with advanced multinuclear NMR methods
 Characterizing fatty acids with advanced multinuclear NMR methods Fatty acids consist of long carbon chains ending with a carboxylic acid on one side and a methyl group on the other. Most naturally occurring
Characterizing fatty acids with advanced multinuclear NMR methods Fatty acids consist of long carbon chains ending with a carboxylic acid on one side and a methyl group on the other. Most naturally occurring
-Ketoacyl Acyl Carrier Protein Synthase III (FabH) Is Essential for Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2001, p. 3526 3530 Vol. 183, No. 11 0021-9193/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.11.3526 3530.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. -Ketoacyl
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2001, p. 3526 3530 Vol. 183, No. 11 0021-9193/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.11.3526 3530.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. -Ketoacyl
Culture Density (OD600) 0.1. Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600)
 A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
Unraveling and engineering the production of 23,24-bisnorcholenic steroids in sterol metabolism
 Unraveling and engineering the production of 23,24-bisnorcholenic steroids in sterol metabolism Li-Qin Xu, Yong-Jun Liu, Kang Yao, Hao-Hao Liu, Xin-Yi Tao, Feng-Qing Wang*, Dong-Zhi Wei* State Key Laboratory
Unraveling and engineering the production of 23,24-bisnorcholenic steroids in sterol metabolism Li-Qin Xu, Yong-Jun Liu, Kang Yao, Hao-Hao Liu, Xin-Yi Tao, Feng-Qing Wang*, Dong-Zhi Wei* State Key Laboratory
Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile
 Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile Roxanne E. Franckowski, M.S.* and Robert A. Thompson, Ph.D. U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration Special Testing and Research Laboratory
Eszopiclone (Lunesta ): An Analytical Profile Roxanne E. Franckowski, M.S.* and Robert A. Thompson, Ph.D. U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration Special Testing and Research Laboratory
Supplementary Figure 1. ESI/MS/MS analyses of native and de-acetylated S2A Supplementary Figure 2. Partial 1D 1H NMR spectrum of S2A
 Supplementary Figure 1. ESI/MS/MS analyses of native and de-acetylated S2A. Panel A, Positive ESI mass spectra of native (N) and de-acetylated (DA) non-active S2A were obtained, and demonstrated a shift
Supplementary Figure 1. ESI/MS/MS analyses of native and de-acetylated S2A. Panel A, Positive ESI mass spectra of native (N) and de-acetylated (DA) non-active S2A were obtained, and demonstrated a shift
End of the Note Book
 End of the Note Book 16 September 2016 Colonies PCR Mix (25 µl total volume reaction): + clones - 12.5 µl DreamTaq PCR Mastermix 2X (ThermoScientific) - 2.5 µl 10X DreamTaq Green Buffer (ThermoScientific)
End of the Note Book 16 September 2016 Colonies PCR Mix (25 µl total volume reaction): + clones - 12.5 µl DreamTaq PCR Mastermix 2X (ThermoScientific) - 2.5 µl 10X DreamTaq Green Buffer (ThermoScientific)
Naoya Takahashi, Keiya Hirota and Yoshitaka Saga* Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Facile transformation of the five-membered exocyclic E-ring in 13 2 -demethoxycarbonyl chlorophyll derivatives by molecular oxygen with titanium oxide in the dark Naoya Takahashi,
Supplementary material Facile transformation of the five-membered exocyclic E-ring in 13 2 -demethoxycarbonyl chlorophyll derivatives by molecular oxygen with titanium oxide in the dark Naoya Takahashi,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Discovery of linear low-cationic peptides to target methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vivo Yuan Liu, Meirong Song, Shuangyang Ding,, Kui Zhu*,,, Beijing Advanced Innovation
Supporting Information Discovery of linear low-cationic peptides to target methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vivo Yuan Liu, Meirong Song, Shuangyang Ding,, Kui Zhu*,,, Beijing Advanced Innovation
Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains
 Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains Name: Claire Ostertag-Hill Mentor: Dr. Ling Jin Bovine herpesvirus Bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) Pathogen
Investigation of the genetic differences between bovine herpesvirus type 1 variants and vaccine strains Name: Claire Ostertag-Hill Mentor: Dr. Ling Jin Bovine herpesvirus Bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) Pathogen
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany A Convergent Synthesis of N-Linked Glycopeptides Clyde M. Kaneshiro, Katja Michael* 1. LC-MS analysis of crude glycopeptide 16. 2. ESI-TOF
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany A Convergent Synthesis of N-Linked Glycopeptides Clyde M. Kaneshiro, Katja Michael* 1. LC-MS analysis of crude glycopeptide 16. 2. ESI-TOF
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 18; 09 September 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced to express
 Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Supplementary Figure 1. VapC-mt4 cleaves trna Ala2 in E. coli. Histograms representing the fold change in reads observed in trnas from the analysis of RNAs carrying a 5 -OH ends isolated from cells induced
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2008
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 9 Weinheim, 008 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 9 Weinheim, 008 Supporting Information for Streptomyces Phospholipase D Mutants
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 9 Weinheim, 008 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 9 Weinheim, 008 Supporting Information for Streptomyces Phospholipase D Mutants
USA. Supplemental Information
 Cloning and sequencing of the kedarcidin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus sp. ATCC 53650 revealing new insights into biosynthesis of the enediyne family of antitumor antibiotics Jeremy
Cloning and sequencing of the kedarcidin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus sp. ATCC 53650 revealing new insights into biosynthesis of the enediyne family of antitumor antibiotics Jeremy
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Your Name: Question 1. Spectrum Prediction I: Ethyl Acetoacetate. (15 points) ppm ppm ppm ppm. J(A,D) = 8 Hz = 0.
 Question 1. Spectrum Prediction I: Ethyl Acetoacetate. (15 points) A B C D 4.202 ppm 3.451 ppm 2.273 ppm 1.288 ppm J(A,D) = 8 Hz = 0.08 ppm (in CDCl 3 ) Draw the 100 MHz H-NMR spectrum to scale. Draw splitting
Question 1. Spectrum Prediction I: Ethyl Acetoacetate. (15 points) A B C D 4.202 ppm 3.451 ppm 2.273 ppm 1.288 ppm J(A,D) = 8 Hz = 0.08 ppm (in CDCl 3 ) Draw the 100 MHz H-NMR spectrum to scale. Draw splitting
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of prodigiosin analogues exploring the substrate specificity of PigC
 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of prodigiosin analogues exploring the substrate specificity of PigC Suresh R. Chawrai, eil R. Williamson, George P. C. Salmond and Finian J. Leeper Representative Experimental
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of prodigiosin analogues exploring the substrate specificity of PigC Suresh R. Chawrai, eil R. Williamson, George P. C. Salmond and Finian J. Leeper Representative Experimental
Cloning and Expression of a Subfamily 1.4 Lipase from Bacillus licheniformis IBRL-CHS2
 Tropical Life Sciences Research, 27(Supp. 1), 145 150, 2016 Cloning and Expression of a Subfamily 1.4 Lipase from Bacillus licheniformis IBRL-CHS2 1 Nidyaletchmy Subba Reddy, 1 Rashidah Abdul Rahim *,
Tropical Life Sciences Research, 27(Supp. 1), 145 150, 2016 Cloning and Expression of a Subfamily 1.4 Lipase from Bacillus licheniformis IBRL-CHS2 1 Nidyaletchmy Subba Reddy, 1 Rashidah Abdul Rahim *,
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Figure S1. Molecular confirmation of the precise insertion of the AsMCRkh2 cargo into the kh w locus.
 Supporting Information Appendix Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. Table S3.
Supporting Information Appendix Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. Table S3.
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 30; 06 June 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site. Ying et al. Supporting Information. Contents. Supplementary note I p.
 Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site Ying et al Supporting Information Contents Supplementary note I p. 2 Supplementary note II p. 3-5 Supplementary note III p. 5-7 Supplementary
Gene expression scaled by distance to the genome replication site Ying et al Supporting Information Contents Supplementary note I p. 2 Supplementary note II p. 3-5 Supplementary note III p. 5-7 Supplementary
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
GtfA and GtfB are both required for protein O-glycosylation in Lactobacillus plantarum
 Supplemental information for: GtfA and GtfB are both required for protein O-glycosylation in Lactobacillus plantarum I-Chiao Lee, Iris I. van Swam, Satoru Tomita, Pierre Morsomme, Thomas Rolain, Pascal
Supplemental information for: GtfA and GtfB are both required for protein O-glycosylation in Lactobacillus plantarum I-Chiao Lee, Iris I. van Swam, Satoru Tomita, Pierre Morsomme, Thomas Rolain, Pascal
Steps Towards Deciphering the Post-Polyketide Synthase Tailoring Steps in the Phoslactomycin Biosynthesis Pathway
 Portland State University PDXScholar Dissertations and Theses Dissertations and Theses Spring 7-23-2015 Steps Towards Deciphering the Post-Polyketide Synthase Tailoring Steps in the Phoslactomycin Biosynthesis
Portland State University PDXScholar Dissertations and Theses Dissertations and Theses Spring 7-23-2015 Steps Towards Deciphering the Post-Polyketide Synthase Tailoring Steps in the Phoslactomycin Biosynthesis
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29; 31 July 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems. Expressway Mini Cell-Free Expression System
 Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Acaulins A and B, Trimeric Macrodiolides from Acaulium. Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Acaulins A and B, Trimeric Macrodiolides from Acaulium sp. H-JQSF Ting Ting Wang, Ying Jie Wei, Hui Ming Ge, Rui Hua Jiao, Ren Xiang Tan* * Corresponding author. E-mail: rxtan@nju.edu.cn
Supporting Information Acaulins A and B, Trimeric Macrodiolides from Acaulium sp. H-JQSF Ting Ting Wang, Ying Jie Wei, Hui Ming Ge, Rui Hua Jiao, Ren Xiang Tan* * Corresponding author. E-mail: rxtan@nju.edu.cn
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Screening of strong constitutive promoters in the S. albus transcriptome via RNA-seq The total RNA of S. albus J1074 was isolated after 24 hrs and 72 hrs of cultivation at 30 C
Supplemental Information Screening of strong constitutive promoters in the S. albus transcriptome via RNA-seq The total RNA of S. albus J1074 was isolated after 24 hrs and 72 hrs of cultivation at 30 C
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides and proteins under mild conditions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Facile Cu(II) mediated conjugation of thioesters and thioacids to peptides
TWO NEW ELLAGIC ACID GLYCOSIDES FROM LEAVES OF DIPLOPANAX STACHYANTHUS
 Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, December 2004, Vol. 6 (4), pp. 271 276 TWO NEW ELLAGIC ACID GLYCOSIDES FROM LEAVES OF DIPLOPANAX STACHYANTHUS XIAO-HONG YAN and YUE-WEI GUO* State Key Laboratory
Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, December 2004, Vol. 6 (4), pp. 271 276 TWO NEW ELLAGIC ACID GLYCOSIDES FROM LEAVES OF DIPLOPANAX STACHYANTHUS XIAO-HONG YAN and YUE-WEI GUO* State Key Laboratory
Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS
 Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS Alexander J. Pérez and Helge B. Bode -Supporting Information- Contents Experimental section Supplementary figures NMR spectra Page S2
Analysis of fatty acid metabolism using Click-Chemistry and HPLC-MS Alexander J. Pérez and Helge B. Bode -Supporting Information- Contents Experimental section Supplementary figures NMR spectra Page S2
Supporting information
 Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
Supporting information Figure legends Supplementary Table 1. Specific product ions obtained from fragmentation of lithium adducts in the positive ion mode comparing the different positional isomers of
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR
 SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
Supplemental Material for. Figure S1. Identification of TetR responsive promoters in F. novicida and E. coli.
 Supplemental Material for Synthetic promoters functional in Francisella novicida and Escherichia coli Ralph L. McWhinnie and Francis E. Nano Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria,
Supplemental Material for Synthetic promoters functional in Francisella novicida and Escherichia coli Ralph L. McWhinnie and Francis E. Nano Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria,
The Novel Enzymatic 3"-N-Acetylation of Arbekacin by an Aminoglycoside. KUNIMOTO HOTTA*, ATSUKO SUNADA, JUN ISHIKAWA and SATOSHI MIZUNO
 VOL. 51 NO. 8 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS The Novel Enzymatic 3"-N-Acetylation of Arbekacin by an Aminoglycoside KUNIMOTO HOTTA*, ATSUKO SUNADA, JUN ISHIKAWA and SATOSHI MIZUNO National Institute of Infectious
VOL. 51 NO. 8 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS The Novel Enzymatic 3"-N-Acetylation of Arbekacin by an Aminoglycoside KUNIMOTO HOTTA*, ATSUKO SUNADA, JUN ISHIKAWA and SATOSHI MIZUNO National Institute of Infectious
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
8 Suppression Analysis
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 8 Suppression Analysis OVERVIEW Suppression
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 8 Suppression Analysis OVERVIEW Suppression
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California Santa Cruz, 1156 High Street, Santa Cruz, CA 95064, USA
 Supplemental Information: Integration of high-content phenotypic screening and untargeted metabolomics analysis for the comprehensive functional annotation of complex natural products libraries. Kenji
Supplemental Information: Integration of high-content phenotypic screening and untargeted metabolomics analysis for the comprehensive functional annotation of complex natural products libraries. Kenji
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Fall 2013 Lecture 3 Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry June 19 2013 Chromatography Chromatography separation of a mixture into individual components Paper, Column,
TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
Lysianadioic acid, a carboxypeptidase B inhibitor from Lysiana subfalcata
 Lysianadioic acid, a carboxypeptidase B inhibitor from Lysiana subfalcata Author Buchanan, Malcolm, Carroll, Anthony, Edser, Annette, Sykes, Melissa, Fechner, Gregory, P. Guymer, Gordon, I. Forster, Paul,
Lysianadioic acid, a carboxypeptidase B inhibitor from Lysiana subfalcata Author Buchanan, Malcolm, Carroll, Anthony, Edser, Annette, Sykes, Melissa, Fechner, Gregory, P. Guymer, Gordon, I. Forster, Paul,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Isolation of mt-trnas and RNA-MS analysis of mt-trna Asn from M. nudus (a)m. nudus mt-trnas were isolated by RCC and resolved by 10% denaturing PAGE. The gel was stained with SYBR
Supplementary Figure 1 Isolation of mt-trnas and RNA-MS analysis of mt-trna Asn from M. nudus (a)m. nudus mt-trnas were isolated by RCC and resolved by 10% denaturing PAGE. The gel was stained with SYBR
In vitro conversion of chanoclavine-i aldehyde to the stereoisomers festuclavine and pyroclavine was controlled by the second reduction step
 1 Electronic Supporting Information to: In vitro conversion of chanoclavinei aldehyde to the stereoisomers festuclavine and pyroclavine was controlled by the second reduction step Marco Matuschek a, Christiane
1 Electronic Supporting Information to: In vitro conversion of chanoclavinei aldehyde to the stereoisomers festuclavine and pyroclavine was controlled by the second reduction step Marco Matuschek a, Christiane
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29;
 SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
Synthesis, evaluation of anti-hiv-1 and anti-hcv activity of novel 2,3 -dideoxy- 2,2 -difluoro-4 -azanucleosides
 Synthesis, evaluation of anti-hiv-1 and anti-hcv activity of novel 2,3 -dideoxy- 2,2 -difluoro-4 -azanucleosides Saúl Martínez-Montero, a,b Susana Fernández, a Yogesh S. Sanghvi, c Emmanuel A. Theodorakis,*
Synthesis, evaluation of anti-hiv-1 and anti-hcv activity of novel 2,3 -dideoxy- 2,2 -difluoro-4 -azanucleosides Saúl Martínez-Montero, a,b Susana Fernández, a Yogesh S. Sanghvi, c Emmanuel A. Theodorakis,*
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03
 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03 TEST 1 11 MARCH 2010 INSTRUCTOR: I. DIONNE PRINT YOUR NAME: Answers INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions in the space provided.
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03 TEST 1 11 MARCH 2010 INSTRUCTOR: I. DIONNE PRINT YOUR NAME: Answers INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions in the space provided.
igem2013 Microbiology BMB SDU
 igem2013 Microbiology BMB SDU Project type: Creation of Biobrick with Prenyltransferase Project title: Biobrick_Prenyltransferase Sub project: Creation date: 13.08.09 Written by: SIS Performed by: PRA,
igem2013 Microbiology BMB SDU Project type: Creation of Biobrick with Prenyltransferase Project title: Biobrick_Prenyltransferase Sub project: Creation date: 13.08.09 Written by: SIS Performed by: PRA,
Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids from Onosma kaheirei Teppner (Boraginaceae)
 Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 10:2 (2016) 221-227 Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids from nosma kaheirei Teppner (Boraginaceae) Ioanna-Maria rfanou 1, Harilaos Damianakos 1, Ioannis Bazos 2, Konstantia Graikou1
Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 10:2 (2016) 221-227 Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids from nosma kaheirei Teppner (Boraginaceae) Ioanna-Maria rfanou 1, Harilaos Damianakos 1, Ioannis Bazos 2, Konstantia Graikou1
Genomics-driven discovery of taiwachelin, a lipopeptide siderophore from Cupriavidus taiwanensis
 Supporting information Genomics-driven discovery of taiwachelin, a lipopeptide siderophore from Cupriavidus taiwanensis Martin F. Kreutzer and Markus Nett * Table of contents SI-2, SI-3 SI-4 SI-5 SI-6
Supporting information Genomics-driven discovery of taiwachelin, a lipopeptide siderophore from Cupriavidus taiwanensis Martin F. Kreutzer and Markus Nett * Table of contents SI-2, SI-3 SI-4 SI-5 SI-6
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
VOL. 56 NO. 2, FEB THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS pp YM and YM , Novel Thiopeptide Antibiotics Produced
 VOL. 56 NO. 2, FEB. 2003 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS pp. 129-134 YM-266183 and YM-266184, Novel Thiopeptide Antibiotics Produced by Bacillus cereus Isolated from a Marine Sponge II. Structure Elucidation
VOL. 56 NO. 2, FEB. 2003 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS pp. 129-134 YM-266183 and YM-266184, Novel Thiopeptide Antibiotics Produced by Bacillus cereus Isolated from a Marine Sponge II. Structure Elucidation
Topic 6 Structure Determination Revision Notes
 1) Introduction Topic 6 Structure Determination Revision Notes Mass spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy and NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine the structure of unknown compounds 2) Mass spectrometry
1) Introduction Topic 6 Structure Determination Revision Notes Mass spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy and NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine the structure of unknown compounds 2) Mass spectrometry
Evaluation of the Lytic Origins of Replication of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Virus/Human Herpesvirus 8 in the Context of the Viral Genome
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9905 9909 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01004-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of the Lytic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9905 9909 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01004-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of the Lytic
Synthesis and Blastocyst Implantation Inhibition Potential of Lupeol Derivatives in Female Mice
 Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 9:4 (2015) 561-566 Synthesis and Blastocyst Implantation Inhibition Potential of Lupeol Derivatives in Female Mice Anita Mahapatra 1*, Purvi Shah 1, Mehul Jivrajani
Supporting Information Rec. Nat. Prod. 9:4 (2015) 561-566 Synthesis and Blastocyst Implantation Inhibition Potential of Lupeol Derivatives in Female Mice Anita Mahapatra 1*, Purvi Shah 1, Mehul Jivrajani
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH
 SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory
 Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 14; 28 September 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA)
 Chapter 4 Results 4. RESULTS SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) Totally 92 wound samples were collected from the major sites of coastal area such as Cuddalore, Pondicherry,
Chapter 4 Results 4. RESULTS SCREENING OF METHICILLIN RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA) Totally 92 wound samples were collected from the major sites of coastal area such as Cuddalore, Pondicherry,
Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1
 Li et al. Cell & Bioscience 2014, 4:55 Cell & Bioscience SHORT REPORT Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 Open Access You Li 1,3, Dongwei Mao 2, Guoda
Li et al. Cell & Bioscience 2014, 4:55 Cell & Bioscience SHORT REPORT Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 Open Access You Li 1,3, Dongwei Mao 2, Guoda
MedKoo Biosciences Product Quality Control Data
 Compound ID:.7.6 8.64 8.55 8.37 7.57 8.35 7.33 7.3 6.87 GSK83875A-DMSO DMSO 4.3MHz 6.8 4. 4.8 4.6 3.78 3.33 3..8.8.5.5.6. Acquisition Parameters Date: 4-3-6T9:34: Pulse Sequence: zg3 Temperature: 96.7
Compound ID:.7.6 8.64 8.55 8.37 7.57 8.35 7.33 7.3 6.87 GSK83875A-DMSO DMSO 4.3MHz 6.8 4. 4.8 4.6 3.78 3.33 3..8.8.5.5.6. Acquisition Parameters Date: 4-3-6T9:34: Pulse Sequence: zg3 Temperature: 96.7
Gade Hyldgaard, Mette; Purup, Stig; Bond, Andrew David; Frete, Xavier; Qu, Haiyan; Teglgaard Jensen, Katrine; Christensen, Lars Porskjær
 Syddansk Universitet Guaianolides and a seco-eudesmane from the resinous exudates of cushion bush (Leucophyta brownii) and evaluation of their cytostatic and anti-inflammatory activity Gade Hyldgaard,
Syddansk Universitet Guaianolides and a seco-eudesmane from the resinous exudates of cushion bush (Leucophyta brownii) and evaluation of their cytostatic and anti-inflammatory activity Gade Hyldgaard,
Supporting Information. as the nitro source
 Supporting Information Efficient ipso-nitration of arylboronic acids with iron nitrate as the nitro source Min Jiang, a,b Haijun Yang,* a,b Yong Li, a,b Zhiying Jia b and Hua Fu b a Beijing Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Efficient ipso-nitration of arylboronic acids with iron nitrate as the nitro source Min Jiang, a,b Haijun Yang,* a,b Yong Li, a,b Zhiying Jia b and Hua Fu b a Beijing Key Laboratory
engineering analogs of compounds with demonstrated therapeutic activities [5,6].
![engineering analogs of compounds with demonstrated therapeutic activities [5,6]. engineering analogs of compounds with demonstrated therapeutic activities [5,6].](/thumbs/94/118481050.jpg) Research Paper 77 Formation of functional heterologous complexes using subunits from the picromycin, erythromycin and oleandomycin polyketide synthases Li Tang, Hong Fu and Robert McDaniel Background:
Research Paper 77 Formation of functional heterologous complexes using subunits from the picromycin, erythromycin and oleandomycin polyketide synthases Li Tang, Hong Fu and Robert McDaniel Background:
Application of LC-NMR for the quick identification of process. related impurities in the synthesis of Docetaxel intermediate
 124 Application of LC-NMR for the quick identification of process related impurities in the synthesis of Docetaxel intermediate 5.1 Introduction Taxol, a naturally occurring diterpene, has overwhelming
124 Application of LC-NMR for the quick identification of process related impurities in the synthesis of Docetaxel intermediate 5.1 Introduction Taxol, a naturally occurring diterpene, has overwhelming
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols. A-tailed DNA was ligated to T-tailed dutp adapters, circularized
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols. A-tailed DNA was ligated to T-tailed dutp adapters, circularized
