Appendix: Subcellular localization of MIG-14::GFP in C. elegans body wall muscle cells. Pei-Tzu Yang and Hendrik C. Korswagen
|
|
|
- Ira Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix: Subcellular localization of MIG-14::GFP in C. elegans body wall muscle cells Pei-Tzu Yang and Hendrik C. Korswagen 129
2
3 SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MIG-14 Abstract MIG-14/Wls is a Wnt binding protein that is required for the secretion of Wnt from Wnt producing cells. Based on our previous work (see Chapter 4), we propose a model in which MIG-14/Wls functions as a sorting receptor that transports Wnt from the Golgi to the plasma membrane for release. Next, MIG-14/Wls is internalized through AP-2 mediated endocytosis and is recycled back to the Golgi through a retromer complex dependent pathway. To further study the intracellular trafficking of MIG-14 in C. elegans, we have generated a panel of fluorescently tagged markers for different intracellular compartments. Here, we report a first analysis that shows localization of MIG-14 to different endosomal compartments and the Golgi. 131
4 CHAPTER 5 Introduction The Wnt binding protein MIG-14/Wls may function as a specific sorting receptor for Wnt. Based on our previous work (see Chapter 4), we propose a model in which MIG-14/Wls shuttles between the Golgi and the plasma membrane to mediate Wnt secretion. To further study the intracellular trafficking of MIG-14 in C. elegans, fluorescently labeled markers for different intracellular compartments are required. Work from several groups has led to the identification of proteins that can be used as markers for the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi, early and late endosomes, recycling endosomes and lysosomes (reviewed in Grant and Sato, 2005). Colocalization studies with such markers will enable us to determine in which intracellular compartments MIG-14 is present. Furthermore, it will allow us to study how the distribution of MIG-14 is affected in different mutant backgrounds. Here, we report the generation of a panel of marker transgenes that fluorescently label early and late endosomes, recycling endosomes and the Golgi. In agreement with our model, MIG-14 localizes to early and late endosomes and the Golgi. Interestingly, MIG-14 localizes to recycling endosomes as well, suggesting that MIG-14 may also shuttle between early endosomes and the plasma membrane. 132
5 SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MIG-14 Materials and methods Expression constructs and generation of transgenic lines The cdna of different rab genes, mannosidase and lmp-1 was fused in frame with mcherry encoding cdna (Shaner et al., 2004) in the myo-3 promoter vector ppd All constructs were injected at 20 ng/µl in dpy-20(e1282). As a coinjection marker, 50 ng/µl of the wild type dpy- 20 containing construct pmh86 was used to rescue the Dpy phenotype. Extrachromosomal transgenes were integrated by irradiation with 40 Gy of γ-radiation from a 137 Cs source. Confocal analysis Animals were anesthetized with 30 mm sodium azide in M9 buffer 5 minutes before confocal analysis. Images were recorded with a Bio-Rad Radiance 2100MP confocal and multiphoton system (Zeiss/Bio-Rad). 133
6 CHAPTER 5 Results and discussion Generation of fluorescently-tagged subcellular markers To study the subcellular localization of MIG-14, we generated a set of transgenes that express fusions of marker proteins with the monomeric red fluorescent protein mcherry. As markers for different subsets of endosomes, we used the Rab proteins RAB-5, RAB-7 and RAB-11 (Bonifacino and Rojas, 2006). RAB-5 was selected for labeling early endosomes (Bucci et al., 1992; Gorvel et al., 1991; Sonnichsen et al., 2000), RAB-7 for late endosomes (Lombardi et al., 1993) and RAB-11 for recycling endosomes (Casanova et al., 1999; Ren et al., 1998; Sonnichsen et al., 2000). Mannosidase (MANS) was used as a Golgi selective marker and LMP-1 was used as a marker for lysosomes (Rolls et al., 2002). The results with the LMP-1 marker are discussed in Chapter 4. mig-14 is strongly expressed in posterior body wall muscle cells (see Fig. 1 and S1, Chapter 4). These are relatively large cells that are ideally suited for detailed co-localization studies. The different markers were therefore specifically expressed in body wall muscle cells using the promoter of the muscle myosin gene myo-3 (Fire and Waterston, 1989). Body wall muscle cells consist of three parts: a contractile filament lattice, a non-contractile muscle body and muscle arms that provide connectivity with the nervous system (Fig. 1). The non-contractile body (also known as the muscle belly) contains the nucleus and other cellular organelles. We therefore focused our analysis to this part of the muscle cell. In this study, we describe the subcellular localization of MIG-14 in wild type animals. Future studies will address how the subcellular localization of MIG-14 changes in different mutant backgrounds. MIG-14 localizes to RAB-5 positive early endosomes As discussed in chapter 4, the AP-2 adaptin complex is required for MIG- 14 internalization. During the initiation of endocytosis, the AP-2 complex selects plasma membrane proteins for internalization. After the formation of a clathrin coated pit, an endocytic vesicle containing the selected plasma membrane proteins is formed. Next, the endocytic vesicle fuses 134
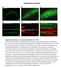
7 SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MIG-14 with an early endosome in a process that requires the Rab GTPase RAB- 5 (Olkkonen and Stenmark, 1997). As expected, we found that MIG-14 co-localizes with mcherry::rab-5 positive early endosomes (Fig. 2A). Indeed, most of the mcherry::rab-5 positive endosomes also contained MIG-14::GFP. These results are consistent with our model that MIG-14 is internalized from the plasma membrane. MIG-14 localizes to RAB-7 positive late endosomes To investigate whether MIG-14 is transported to late endosomes, we studied colocalization between MIG-14::GFP and the late endosomal marker mcherry::rab-7. As shown in Fig. 2B, a subset of the mcherry:: RAB-7 positive late endosomes also contain MIG-14::GFP. The retromer complex may transport MIG-14 from this late endosomal compartment to the Golgi. MIG-14 localizes to the Golgi Human Wls localizes to the Golgi in HeLa cells (see chapter 4). To investigate whether MIG-14 also localizes to the Golgi, we performed colocalization studies with the Golgi marker MANS::mCherry. As shown in Fig. 2C, we found extensive colocalization between MIG-14::GFP and MANS::mCherry, indicating that MIG-14 localizes to the Golgi as well. MIG-14 localizes to RAB-11 positive recycling endosomes We found that MIG-14::GFP also localizes to RAB-11 positive recycling endosomes (Fig. 2D). Recycling endosomes mediate the retrieval of specific plasma membrane proteins from early endosomes to the plasma membrane (reviewed in van IJzendoorn, 2006). These results suggest that in addition to retrieval of MIG-14 to the Golgi, as proposed in our model, MIG-14 may also be recycled to the plasma membrane. An interesting possibility is that Wnt is still bound to MIG-14 in recycling endosomes, as the Drosophila Wnt protein Wg can be found in this endosomal compartment in Wg producing cells (Pfeiffer et al., 2002). 135
8 CHAPTER 5 Fig. 1. Structure of a body wall muscle cell. The cell consists of a myofilament lattice on top of a non-contractile body called the muscle belly. This part contains the nucleus, mitochondria and organelles. All images in Fig. 2 derive from this region. Diagram is from Wormatlas (URL Fig. 2. Colocalization between MIG-14::GFP and different intracellular markers in adult body wall muscle cells. (A) Colocalization of MIG-14::GFP with the early endosomal marker mcherry::rab-5. (B) The late endosomal marker mcherry::rab-7. (C) The Golgi marker MANS::mCherry. (D) The recycling endosome marker mcherry::rab-11. Examples of colocalization are indicated by arrowheads. 136
9 SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF MIG-14 References Bonifacino, J. S., and Rojas, R. (2006). Retrograde transport from endosomes to the trans-golgi network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7, Bucci, C., Parton, R. G., Mather, I. H., Stunnenberg, H., Simons, K., Hoflack, B., and Zerial, M. (1992). The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell 70, Casanova, J. E., Wang, X., Kumar, R., Bhartur, S. G., Navarre, J., Woodrum, J. E., Altschuler, Y., Ray, G. S., and Goldenring, J. R. (1999). Association of Rab25 and Rab11a with the apical recycling system of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol Biol Cell 10, Fire, A., and Waterston, R. H. (1989). Proper expression of myosin genes in transgenic nematodes. EMBO J 8, Gorvel, J. P., Chavrier, P., Zerial, M., and Gruenberg, J. (1991). rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell 64, Grant, B., and Sato, M. (2005). Intracellular trafficking. Wormbook. ed. The C. elegans Research Community, doi/ /wormbook Lombardi, D., Soldati, T., Riederer, M. A., Goda, Y., Zerial, M., and Pfeffer, S. R. (1993). Rab9 functions in transport between late endosomes and the trans Golgi network. EMBO J 12, Olkkonen, V. M., and Stenmark, H. (1997). Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic. Int Rev Cytol 176, Pfeiffer, S., Ricardo, S., Manneville, J. B., Alexandre, C., and Vincent, J. P. (2002). Producing cells retain and recycle Wingless in Drosophila embryos. Curr Biol 12, Ren, M., Xu, G., Zeng, J., De Lemos-Chiarandini, C., Adesnik, M., and Sabatini, D. D. (1998). Hydrolysis of GTP on rab11 is required for the direct delivery of transferrin from the pericentriolar recycling compartment to the cell surface but not from sorting endosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95, Rolls, M. M., Hall, D. H., Victor, M., Stelzer, E. H., and Rapoport, T. A. (2002). Targeting of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins and ribosomes in invertebrate neurons. Mol Biol Cell 13, Shaner, N. C., Campbell, R. E., Steinbach, P. A., Giepmans, B. N., Palmer, A. E., and Tsien, R. Y. (2004). Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 22, Sonnichsen, B., De Renzis, S., Nielsen, E., Rietdorf, J., and Zerial, M. (2000). Distinct membrane domains on endosomes in the recycling pathway visualized by multicolor imaging of Rab4, Rab5, and Rab11. J Cell Biol 149, van IJzendoorn, S. C. (2006). Recycling endosomes. J Cell Sci 119,
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I
 01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Lipidne mikrodomene. funkcija
 Lipidne mikrodomene funkcija 1 Cellular processes involving lipid rafts - Signal transduction - Protein and lipid trafficking and sorting - Endosome(clathrin)-independent endocytosis: - potocytosis and
Lipidne mikrodomene funkcija 1 Cellular processes involving lipid rafts - Signal transduction - Protein and lipid trafficking and sorting - Endosome(clathrin)-independent endocytosis: - potocytosis and
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands
 CHA P T E R F IVE Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands Shinya Yamamoto, *,1 Wu-Lin Charng, *,1 and Hugo J. Bellen *,,, Contents 1. Notch Signaling and its Regulation by Endocytosis
CHA P T E R F IVE Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands Shinya Yamamoto, *,1 Wu-Lin Charng, *,1 and Hugo J. Bellen *,,, Contents 1. Notch Signaling and its Regulation by Endocytosis
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014
 Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18
 Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Review. Regulation of EGFR endocytic trafficking by rab proteins
 Histol Histopathol (2006) 21: 987-993 DOI: 10.14670/HH-21.987 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Review Regulation of EGFR endocytic trafficking by rab proteins
Histol Histopathol (2006) 21: 987-993 DOI: 10.14670/HH-21.987 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Review Regulation of EGFR endocytic trafficking by rab proteins
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport
 Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, Please print your name: Instructions:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Subcellular biochemistry
 Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Chapter 3. Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons. on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs bind protein factors to
 22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
7.06 Spring of PROBLEM SET #6
 7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport
 Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
TITLE: Effect of MUC1 Expression on EGFR Endocytosis and Degradation in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-06-1-0464 TITLE: Effect of MUC1 Expression on EGFR Endocytosis and Degradation in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rachid M El Bejjani CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-06-1-0464 TITLE: Effect of MUC1 Expression on EGFR Endocytosis and Degradation in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rachid M El Bejjani CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. PROTEIN SORTING. Lecture 10 BIOL 266/ Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S.
 PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role in Alzheimer s disease
 Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Active Lecture Questions for use with Classroom Response Systems Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Edited by William Wischusen, Louisiana State University
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
In the previous chapter we explored how proteins are targeted
 17 VESICULAR TRAFFIC, SECRETION, AND ENDOCYTOSIS Electron micrograph of clathrin cages, like those that surround clathrin-coated transport vesicles, formed by the in vitro polymerization of clathrin heavy
17 VESICULAR TRAFFIC, SECRETION, AND ENDOCYTOSIS Electron micrograph of clathrin cages, like those that surround clathrin-coated transport vesicles, formed by the in vitro polymerization of clathrin heavy
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
17/01/2017. Protein trafficking between cell compartments. Lecture 3: The cytosol. The mitochondrion - the power plant of the cell
 ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras
 Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Molecular Mechanisms and Drug Development in Aquaporin Water Channel Diseases: Water Channel Aquaporin-2 of Kidney Collecting Duct Cells
 J Pharmacol Sci 96, 255 259 (2004) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2004 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Forum Minireview Molecular Mechanisms and Drug Development in Aquaporin Water Channel Diseases:
J Pharmacol Sci 96, 255 259 (2004) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2004 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Forum Minireview Molecular Mechanisms and Drug Development in Aquaporin Water Channel Diseases:
Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued
 Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Wnt Signaling Requires Retromer-Dependent Recycling of MIG-14/Wntless in Wnt-Producing Cells
 Short Article Wnt Signaling Requires Retromer-Dependent Recycling of MIG-14/Wntless in Wnt-Producing Cells Pei-Tzu Yang, 1,2 Magdalena J. Lorenowicz, 1,2 Marie Silhankova, 1 Damien Y.M. Coudreuse, 1,3
Short Article Wnt Signaling Requires Retromer-Dependent Recycling of MIG-14/Wntless in Wnt-Producing Cells Pei-Tzu Yang, 1,2 Magdalena J. Lorenowicz, 1,2 Marie Silhankova, 1 Damien Y.M. Coudreuse, 1,3
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Dynamic Interaction of HIV-1 Nef with the Clathrin-Mediated Endocytic Pathway at the Plasma Membrane
 Traffic 2007; 8: 61 76 Blackwell Munksgaard Dynamic Interaction of HIV-1 Nef with the Clathrin-Mediated Endocytic Pathway at the Plasma Membrane # 2006 The Authors Journal compilation # 2006 Blackwell
Traffic 2007; 8: 61 76 Blackwell Munksgaard Dynamic Interaction of HIV-1 Nef with the Clathrin-Mediated Endocytic Pathway at the Plasma Membrane # 2006 The Authors Journal compilation # 2006 Blackwell
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH INTRACELLULAR PROTEIN TRANSPORT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS
 Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Rab14 is part of the early endosomal clathrin-coated TGN microdomain
 is part of the early endosomal clathrin-coated TGN microdomain Tassula Proikas-Cezanne a, *, Anja Gaugel a, Tancred Frickey b,1, Alfred Nordheim c,d a Autophagy Laboratory, Department of Molecular Biology,
is part of the early endosomal clathrin-coated TGN microdomain Tassula Proikas-Cezanne a, *, Anja Gaugel a, Tancred Frickey b,1, Alfred Nordheim c,d a Autophagy Laboratory, Department of Molecular Biology,
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking
 Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking Chi-Kuang Yao (IBC, Academia Sinica) 11-6-2017 ckyao@gate.sinica.edu.tw 1 Compartmentalization makes difference between bacteria and yeast 1. More compartments with specific
Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking Chi-Kuang Yao (IBC, Academia Sinica) 11-6-2017 ckyao@gate.sinica.edu.tw 1 Compartmentalization makes difference between bacteria and yeast 1. More compartments with specific
Diverse Autophagosome Membrane Sources Coalesce in Recycling Endosomes
 Diverse Autophagosome Membrane Sources Coalesce in Recycling Endosomes Claudia Puri, 1 Maurizio Renna, 1 Carla F. Bento, 1 Kevin Moreau, 1 and David C. Rubinsztein 1, * 1 Department of Medical Genetics,
Diverse Autophagosome Membrane Sources Coalesce in Recycling Endosomes Claudia Puri, 1 Maurizio Renna, 1 Carla F. Bento, 1 Kevin Moreau, 1 and David C. Rubinsztein 1, * 1 Department of Medical Genetics,
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Name: Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea)
 Exam 1 202 Oct. 5, 1999 Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea) 1. The lipids of a red blood cell membrane are all a. phospholipids b. amphipathic c. glycolipids d. unsaturated 2. The
Exam 1 202 Oct. 5, 1999 Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea) 1. The lipids of a red blood cell membrane are all a. phospholipids b. amphipathic c. glycolipids d. unsaturated 2. The
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs;
 regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Chapter 17: Vesicular traffic, secretion, and endocytosis
 Chapter 17: Vesicular traffic, secretion, and endocytosis SEM of the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles on the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane Outline: 1. Techniques for studying the secretory
Chapter 17: Vesicular traffic, secretion, and endocytosis SEM of the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles on the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane Outline: 1. Techniques for studying the secretory
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
RAB GTPASE REGULATION OF APICAL CYSTIC FIBROSIS TRANSMEMBRANE CONDUCTANCE REGULATOR RECYCLING IN POLARIZED INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS
 RAB GTPASE REGULATION OF APICAL CYSTIC FIBROSIS TRANSMEMBRANE CONDUCTANCE REGULATOR RECYCLING IN POLARIZED INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS by Mark Robert Silvis B.S. Biology, Geneva College, 1999 Submitted
RAB GTPASE REGULATION OF APICAL CYSTIC FIBROSIS TRANSMEMBRANE CONDUCTANCE REGULATOR RECYCLING IN POLARIZED INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS by Mark Robert Silvis B.S. Biology, Geneva College, 1999 Submitted
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Antigen presenting cells
 Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
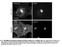 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion. Richard H. Scheller
 The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis
 Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Equipe «Trafic, Signalisation et Ciblage Intracellulaires»
 Equipe «Trafic, Signalisation et Ciblage Intracellulaires» L. Johannes & C.Lamaze D. Koester, thèse : cavéoles et mécanique membranaire R. Ruez, thèse: cavéoles/signal IFN E. Girard, thèse: trafic cholestérol
Equipe «Trafic, Signalisation et Ciblage Intracellulaires» L. Johannes & C.Lamaze D. Koester, thèse : cavéoles et mécanique membranaire R. Ruez, thèse: cavéoles/signal IFN E. Girard, thèse: trafic cholestérol
Reconstitution of recycling from the phagosomal compartment in streptolysin O-permeabilized macrophages: Role of Rab11
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/yexcr Research Article Reconstitution of recycling from the phagosomal compartment in streptolysin O-permeabilized macrophages: Role of Rab11
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/yexcr Research Article Reconstitution of recycling from the phagosomal compartment in streptolysin O-permeabilized macrophages: Role of Rab11
Legionella pneumophila: an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Prof. Craig Roy
 an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine 1 Legionella pneumophila Gram-negative bacterium Facultative intracellular pathogen Protozoa
an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine 1 Legionella pneumophila Gram-negative bacterium Facultative intracellular pathogen Protozoa
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma membrane?
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes. Chapter 5 Part 2
 A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Chapter 5 Part 2 5.5 Membrane Trafficking By processes of endocytosis and exocytosis, vesicles help cells take in and expel particles that are too big for transport proteins,
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Chapter 5 Part 2 5.5 Membrane Trafficking By processes of endocytosis and exocytosis, vesicles help cells take in and expel particles that are too big for transport proteins,
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Types of ER. Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles.
 WH Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles Types of ER Overview Play key role in synthesis (& hydrolysis) of macromolecules
WH Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles Types of ER Overview Play key role in synthesis (& hydrolysis) of macromolecules
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3.
 Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling: (LocLight TM Living cell imaging lentivirus for sub-cellular localization)
 Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling: (LocLight TM Living cell imaging lentivirus for sub-cellular localization) LocLight TM cell organelle labeling lentivirus is provided as 200ul/per
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling: (LocLight TM Living cell imaging lentivirus for sub-cellular localization) LocLight TM cell organelle labeling lentivirus is provided as 200ul/per
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Answer Key. Chapter Test A
 Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
Organization of ATPases
 The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
