Carboxylic acid derivatives
|
|
|
- Gerard Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Carboxylic acid derivatives Nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction Among the most important reactions of carboxylic acids are those that convert the carboxyl group into other acid derivatives by a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. Cl 1 N 2 ' ' Dr. Solomon Derese 57
2 Acyl chloride Preparation of acyl chlorides Acid chlorides can not be prepared by reaction between carboxylic acid and Cl. This is because the carbonyl carbon is not electrophilic enough to be attacked by chloride and also the fact that the hydroxyl group is a bad leaving group. X We use PCl 5 (an acid chloride of phosphoric acid), PCl 3 (an acid chloride of phosphorous acid), SCl 2 (Thionyl chloride), an acid chloride of sulfurous acid, or oxalyl chloride, an acid chloride of oxalic acid. Dr. Solomon Derese 58
3 PCl 3 PCl 5 Cl Cl Dr. Solomon Derese 59
4 Very reactive Good Leaving Group Good electrophile Dr. Solomon Derese 60
5 eaction of acyl chlorides Acyl chlorides are the most reactive of acyl compounds towards nucleophiles. Lower molecular weight saturated acyl chlorides react explosively with water, and even more rapidly with stronger nucleophiles. Because of their reactivity and the ease with which they can be prepared from carboxlylic acids, acyl chlorides are the most commonly used starting materials for the synthesis of carboxylic acid derivatives in general. Dr. Solomon Derese 61
6 ydrolysis ' 2 Cl Acid chloride N 1 2 [] SCl 2 Most nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions of acyl chlorides are irreversible. Dr. Solomon Derese 62
7 ydrolysis: Conversion into acids Acyl chlorides are hydrolyzed by water to give the corresponding carboxylic acid. 2 N Pyridine scavenges the Cl Dr. Solomon Derese 63
8 Alcoholysis: Ester formation In most cases this reaction is carried out in the presence of a base such as triethylamine, pyridine which will scavenge the acid (Cl). Dr. Solomon Derese 64
9 Ammonlysis: Conversion into amides The reaction is carried out using an excess of the amine, which serves to remove the acid (Cl) as a salt. Example DEET, the active ingredient in the most widely used insect repellents, is effective against mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks. Dr. Solomon Derese 65
10 Ammonolysis reactions carried with Na are sometimes referred to as Schotten Baumann reaction. Trimetozine (palene, Trimolide, Trioxazine) is a sedative that has been marketed in Europe since It also has mild tranquilizing effects and has been used in the treatment of anxiety. Dr. Solomon Derese 66
11 Application: Nylon 6,6 The search for a synthetic fiber with properties similar to silk led to the discovery of nylon a polyamide. There are several different kinds of nylon, but the most well known is called nylon 6,6. It can be synthesized from two six-carbon monomers (hence its name) adipoyl chloride (ClC-(C 2 ) 4 - CCl) and hexamethylenediamine ( 2 N(C 2 ) 6 N 2 ). Dr. Solomon Derese 67
12 eduction: Conversion into alcohols Example The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated if the less powerful reducing agent, LiAl (t-bu) 3. Example Dr. Solomon Derese 68
13 eaction with aromatic compounds The Friedel Crafts acylation ' Cl ' AlCl 3 eaction with rganometallic reagents Acyl benzene Grignard reagent rganolithiums react similarly to give tertiary alcohols. Dr. Solomon Derese 69
14 rganocopper ( 2 CuLi) (Gilman) reagents Less reactive than Grignard/organolithium reagent and yield ketones rather than tertiary alcohols. Example The ester functional group is not affected. Dr. Solomon Derese 70
15 Summary of the reactions of acid chlorides N 1 2 ' Pyridine 2 Pyridine ' N 1 2 (excess) 'MgBr or 'Li ' 2 CuLi Cl ' " ' 1. LiAl AlCl 3 LiAl(tBu) 3 Dr. Solomon Derese 71
16 Assignment 21 I. ow do you achieve the following transformation? II. Qiana, a polyamide fiber with a silky texture, has the following structure. What are the monomer units used in the synthesis of Qiana? Dr. Solomon Derese 72
17 Acid anhydrides The 2 nd most reactive carboxylic acid derivatives. Preparation of acetic anhydrides From acid chlorides Most commonly used bases are pyridine and triethylamine. Dr. Solomon Derese 73
18 Example Mechanism Cl Dr. Solomon Derese 74
19 eactions of acid anhydrides The chemistry of anhydrides is similar to that of acid chlorides except that anhydrides react more slowly, but the kind of reactions the two groups undergo are the same. Dr. Solomon Derese 75
20 Examples Dr. Solomon Derese 76
21 Esters Acid component ' Alcohol component Many simple low molecular weight esters are pleasant smelling liquids that are responsible for the fragrant odors of fruits and flowers. Dr. Solomon Derese 77
22 Commercial applications of esters The characteristics fruity smell of esters lead to their use in artificial fruit essences. Methyl 3-methylbutanoate Propyl propionate Butyl acetate 3-Methylbutyl acetate Methyl octanoate Benzyl butanoate Dr. Solomon Derese 78
23 Preparation of esters Fisher esterification General reaction Catalyzed by conc. 2 S 4 or Cl. Equilibrium reaction and yield can be increased by: a) Use of excess of acid or alcohol b) emoving water from the reaction mixtures as it is formed. Dr. Solomon Derese 79
24 Mechanism 1 Dr. Solomon Derese 80
25 Carboxylic acids whose molecules have a hydroxyl group on a g- or d- carbon undergo intramolecular esterification to give cyclic esters (Lactones) known as g- or d- lactones. Example ydroxy acid 3 -Lactone Dr. Solomon Derese 81
26 From acid chlorides/acid anhydride/carboxylic acid salts General reaction Williamson ester synthesis Dr. Solomon Derese 82
27 Diazomethane esterification Diazomethane, C 2 N 2, which is best drawn as a hybrid of two contributing structures, can be used to synthesize esters from carboxylic acid. N N 2 C N N Example Dr. Solomon Derese 83
28 eactions of Esters Dr. Solomon Derese 84
29 ydrolysis of Esters Examples eversible, Why? Dr. Solomon Derese Irreversible, Why? 85
30 Soaps Saponification Ester hydrolysis in base All soaps are salts of fatty acids. The main difference between soaps is the addition of other ingredients that do not alter their cleaning properties: dyes for color, scents for a pleasing odor, and oils for lubrication. Soaps that float are aerated so that they are less dense than water. Dr. Solomon Derese 86
31 Transesterification Transesterification is the conversion of an ester into another ester by heating it with an excess of either an alcohol or a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid or a base catalyst. In an equilibrium reaction, either the alcohol or the acid portion of the original ester is removed. Dr. Solomon Derese 87
32 Example The equilibrium is shifted to the right by allowing the low boiling alcohol to distil from the reaction mixture. Dr. Solomon Derese 88
33 Biodiesel Biodiesel is produced from renewable sources such as vegetable oils and animal fats and is a cleaner replacement for petroleum. It is nontoxic and biodegradable. It has physical properties similar to those of petroleum diesel. Dr. Solomon Derese 89
34 Assignment 22 Draw a stepwise mechanism for each reaction. Dr. Solomon Derese 90
35 Assignment 23 I. The following reactivity order has been found for the saponification of p-substituted methyl benzoates: Y = N 2 > Br > > C 3 > C 3 ow can you explain this reactivity order? Where would you expect Y = C and Y = N 2 to be in the reactivity list? II. When ethyl benzoate is heated in methanol containing a small amount of Cl, methyl benzoate is formed. Propose a mechanism for the reaction. Dr. Solomon Derese 91
36 eduction of Esters The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated if 1 equivalent of the less reactive reducing agent diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBA) is used instead of LiAl 4. The reaction is carried out at -78 C to avoid further reduction to the alcohol. Dr. Solomon Derese 92
37 Dr. Solomon Derese 93
38 Assignment 24 I. Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: II. Explain why ester A is more reactive than ester B in nucleophilic substitution. Dr. Solomon Derese 94
39 Amides No free rotation across the C-N bond Preparation of amides From acid chlorides Dr. Solomon Derese 95
40 From acid anhydrides From esters Dr. Solomon Derese 96
41 From carboxylic acids Carboxylic acids react with aqueous ammonia to form ammonium salts: Because of the low reactivity of the carboxylate ion toward nucleophilic substitution reaction, further reaction does not usually take place in aqueous solution. An ammonium carboxylate Dr. Solomon Derese 97
42 Amides are of great importance in life. The linkages that join individual amino acids together to form proteins are primarily amide linkages. Proteins/peptides are formed by reacting the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group another amino acid. amide linkages As a consequence, much research has been done to find convenient and mild ways for amide synthesis. Dialkylcarbodiimides (-N=C=N=), for example dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), are especially useful reagents for amide synthesis. Dr. Solomon Derese 98
43 N C N Diclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) The carbonyl carbon is now more electrophilic than the carboxyl and the bad leaving group is C N N replaced by a good leaving group. Dr. Solomon Derese 99
44 + N N 1 C 2 N N 2 + N C N 1 Dr. Solomon Derese 100
45 Assignment 25 The following reaction will not happen as shown. a. Show what would happen instead. b. ow could you obtain the desired product? Show the reagents to be used and the structures of any intermediates. Dr. Solomon Derese 101
46 eactions of amides ydrolysis Amides are hydrolyzed in either acidic or alkaline solution. In either case, the acid or base is a reactant, not a catalyst, and must be used in a 1.1 molar ratio or in excess. This property is at most important in biological systems for the stability of proteins. If the amide could hydrolyze easily we wont even be able to touch water. Dr. Solomon Derese 102
47 eduction Mechanism Dr. Solomon Derese 103
48 Assignment 26 I. Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: II. Propose a mechanism for each of the following transformations: Dr. Solomon Derese 104
49 Nitriles Preparation of nitriles I. From dehydration of amides Dr. Solomon Derese 105
50 Mechanism Cl S Cl 2 N N Cl S Example Dr. Solomon Derese 106
51 S N 2 reaction of cyanide ion with primary alkyl halides Example Dr. Solomon Derese 107
52 eactions of nitriles ydrolysis of nitrites eduction of nitriles C N 1. LiAl or 2 / Pd/C N 2 Dr. Solomon Derese 108
53 Mechanism C N Al N C Example Dr. Solomon Derese 109
54 eaction with organometalic reagents An alternative to Friedel-Crafts acylation Dr. Solomon Derese 110
55 N C 2 ' ' N 3 ' + N4 Dr. Solomon Derese 111
56 Assignment 27 I. Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: a) CN 1. LiAl b) Br 1. NaCN 2. MeMgBr 3. 3 c) CN 1. EtMgBr LiAl Dr. Solomon Derese 112
57 II. Propose a mechanism for the following transformation: III. Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: Dr. Solomon Derese 113
58 IV. Identify compounds A-M in the following reaction sequence. Dr. Solomon Derese 114
59 eduction of carboxylic acid General reaction Dr. Solomon Derese 115
60 Example B 3 / TF Selectively reduces carboxylic acids in the presence of aldhydes/ketones and esters Dr. Solomon Derese 116
61 Decarboxylation of β-keto acids and β- diacids Acids whose molecules have a carbonyl group one carbon removed from the carboxyl group, called β- keto acids, decarboxylate readily when they are heated to C. - Ketoacid Dr. Solomon Derese 117
62 There are two reasons for this ease of decarboxylation. 1) When the carboxylate ion decarboxylate, it forms a resonance stabilized enolate anion: - Ketoacid Dr. Solomon Derese esonance stabilized anion 118
63 II. The decarboxylation takes place though a stable six - membered cyclic transition state. b-keto carboxylic acid Example Dr. Solomon Derese 119
64 Assignment 28 Write the organic product(s) and reaction mechanism of the following reaction: Dr. Solomon Derese 120
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON
 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles. Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 arboxylic Acid Derivatives The most important derivatives of carboxylic acids are l " ' ' acid halide acid anhydride an ester an amide Although not direct derivatives, nitriles, -, are related to carboxylic
arboxylic Acid Derivatives The most important derivatives of carboxylic acids are l " ' ' acid halide acid anhydride an ester an amide Although not direct derivatives, nitriles, -, are related to carboxylic
Chapter 18. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Carboxylic Acids: RCOOH (RCO 2 H)
 Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
1/3/2011. Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structures and reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading: Wade chapter 21, sections 21-1- 21-16 Study Problems: 21-45, 21-46, 21-48, 21-49, 21-50, 21-53, 21-56, 21-58, 21-63 Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the spectra of
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Reading: Wade chapter 21, sections 21-1- 21-16 Study Problems: 21-45, 21-46, 21-48, 21-49, 21-50, 21-53, 21-56, 21-58, 21-63 Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the spectra of
Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Deriva3ves. Nucleophilic Acyl Subs0tu0on (Addi0on- Elimina0on)
 Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Deriva3ves Nucleophilic Acyl Subs0tu0on (Addi0on- Elimina0on) 1 Carboxylic Compounds Acyl group bonded to X, an electronega3ve atom or leaving group Includes: X = halide
Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Deriva3ves Nucleophilic Acyl Subs0tu0on (Addi0on- Elimina0on) 1 Carboxylic Compounds Acyl group bonded to X, an electronega3ve atom or leaving group Includes: X = halide
R O R' Acid anhydride. Acid halide. Carboxylic acid. Ester O O O O. Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester. Amide
 Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic acid X Acid halide ' Acid anhydride Ester ' P N 2 C N S' Amide Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester The common structural feature of all these compounds
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic acid X Acid halide ' Acid anhydride Ester ' P N 2 C N S' Amide Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester The common structural feature of all these compounds
Esters of Carboxylic Acids These are derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group.
 Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are
Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are
Ch. 21: CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND NUCLEOPHILIC ACYL SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives:
 h. 21: ABXYLI AID DEIVATIVES AND NULEPILI AYL SUBSTITUTIN EATINS Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives: arboxylic acids "-oic acid" Examples: 3 2 Propanoic acid yclohexanecarboxylic acid 1 arboxylate
h. 21: ABXYLI AID DEIVATIVES AND NULEPILI AYL SUBSTITUTIN EATINS Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives: arboxylic acids "-oic acid" Examples: 3 2 Propanoic acid yclohexanecarboxylic acid 1 arboxylate
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 hapter 20: arboxylic Acid Derivatives: ucleophilic Acyl Substitution 20.1: omenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read) carboxylic acid -oic acid ' ester -oate ' lactone cyclic ester l acid
hapter 20: arboxylic Acid Derivatives: ucleophilic Acyl Substitution 20.1: omenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read) carboxylic acid -oic acid ' ester -oate ' lactone cyclic ester l acid
Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution 19.1: Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read)
 problem 18.33b - = 128.7 123.9 179.7 146.8 147.4 45.3 18.0 161 hapter 19: arboxylic Acid Derivatives: ucleophilic Acyl Substitution 19.1: omenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read) carboxylic
problem 18.33b - = 128.7 123.9 179.7 146.8 147.4 45.3 18.0 161 hapter 19: arboxylic Acid Derivatives: ucleophilic Acyl Substitution 19.1: omenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives (please read) carboxylic
Lecture'11:'February'21,'2013 Reac&ons*of*Deriva&ves*( )
 CM'224' 'rganic'chemistry'ii Spring'2013,'Des'Plaines' 'Prof.'Chad'Landrie Vegetable il (C 2 ) 7 (C 2 ) 7 (C 2 ) 7 LL (a triacylglyceride in soybean oil) (1) transesterification ac 3 Biodiesel 3 C 3 C
CM'224' 'rganic'chemistry'ii Spring'2013,'Des'Plaines' 'Prof.'Chad'Landrie Vegetable il (C 2 ) 7 (C 2 ) 7 (C 2 ) 7 LL (a triacylglyceride in soybean oil) (1) transesterification ac 3 Biodiesel 3 C 3 C
Lecture 20. Herman Emil Fischer Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines. April 4, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
Carboxylic Acids. The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H)
 Carboxylic Acids The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) Starting materials for acyl derivatives (esters, amides, and acid chlorides) Abundant in nature from oxidation of aldehydes and alcohols in
Carboxylic Acids The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) Starting materials for acyl derivatives (esters, amides, and acid chlorides) Abundant in nature from oxidation of aldehydes and alcohols in
10. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES 10.1 Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids 10.2 Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids 10.
 BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl Chlorides
 R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1)
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Dr. Ayad Kareem Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Collage of Pharmacy Al-Mustansiriyah University (2017-2018). Closely related
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Dr. Ayad Kareem Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Collage of Pharmacy Al-Mustansiriyah University (2017-2018). Closely related
Physical properties: C L = L. Cl, NH 2, OCH 3, OH, OCR O O O NH 2 CH 3 N(CH 3 ) 2. Sol. in H 2 O
 Lecture Notes hem 51 S. King hapter 22 arboxylic Acids and their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution I. Structure and Physical Properties: Type 2 carbonyl compounds (carboxylic acids and derivatives)
Lecture Notes hem 51 S. King hapter 22 arboxylic Acids and their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution I. Structure and Physical Properties: Type 2 carbonyl compounds (carboxylic acids and derivatives)
CH 3 C H 3 O. anhydride acid. ester amide. O acid O. amide. acid. amide. acid. nitriles
 C 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Topics: aming Interconversion of Acid Derivatives eactions of each functional group Connections: anhydride acid ester amide acid ester amide acid amide 2 acid nitriles
C 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Topics: aming Interconversion of Acid Derivatives eactions of each functional group Connections: anhydride acid ester amide acid ester amide acid amide 2 acid nitriles
Loudon Chapter 21 Review: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 3/20/2018
 Loudon Chapter 21 eview: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Jacquie ichardson, CU Boulder Last updated 3/20/2018 We learned how to make a lot of carboxylic acid derivatives from acids in Ch. 20, but now we ll
Loudon Chapter 21 eview: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Jacquie ichardson, CU Boulder Last updated 3/20/2018 We learned how to make a lot of carboxylic acid derivatives from acids in Ch. 20, but now we ll
Carbonyl Chemistry VI + C O C. 1pm In Geology Room 112. Exam is Monday 11am-1pm. Chemistry /06/02
 arbonyl hemistry VI Ō - + hemistry 391 11/06/02 Exam is Monday 11am-1pm 1pm In Geology Room 112 The Dibasic Acids h - My - Such - hemistry 391 11/06/02 Good- Apple- Pie- Fischer Esterification Esters can
arbonyl hemistry VI Ō - + hemistry 391 11/06/02 Exam is Monday 11am-1pm 1pm In Geology Room 112 The Dibasic Acids h - My - Such - hemistry 391 11/06/02 Good- Apple- Pie- Fischer Esterification Esters can
Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst n
 Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace ic acid with yl halide, such as propionyl chloride (a common
Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace ic acid with yl halide, such as propionyl chloride (a common
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Decarboxylation R H + CO 2. R OH Reaction type: Elimination. H H Malonic acid. Mechanism:
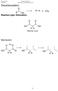 rganic hemistry arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Decarboxylation eaction type: Elimination 2 Malonic acid Mechanism: 235 rganic hemistry arboxylic Acids and Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution u Two
rganic hemistry arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Decarboxylation eaction type: Elimination 2 Malonic acid Mechanism: 235 rganic hemistry arboxylic Acids and Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution u Two
REACTIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES WITH NUCLEOPHILES A. Reactions of Acid Chlorides with Nucleophiles
 1016 CHAPTER 1 THE CHEMITRY F CARBXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE 1.8 REACTI F CARBXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE WITH UCLEPHILE ection 1.7 showed that all carboxylic acid derivatives hydrolyze to carboxylic acids. Water
1016 CHAPTER 1 THE CHEMITRY F CARBXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE 1.8 REACTI F CARBXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE WITH UCLEPHILE ection 1.7 showed that all carboxylic acid derivatives hydrolyze to carboxylic acids. Water
Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution. Reactions. - many carboxylic acid derivatives are known:
 hapter 21 arboxylic Acid Derivatives and ucleophilic Acyl Substitution eactions - many carboxylic acid derivatives are known: X ' carboxylic acid acid halide (X = F, l, Br, I) acid anhydride ' 2 ester
hapter 21 arboxylic Acid Derivatives and ucleophilic Acyl Substitution eactions - many carboxylic acid derivatives are known: X ' carboxylic acid acid halide (X = F, l, Br, I) acid anhydride ' 2 ester
Lecture 19. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y - + X - Y X R C X. April 2, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 19 Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution X Y - - Y X X - Y April 2, 2019 hemistry 328N Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) H H 3 H H H 2 H 3 Please study the mechanism hemistry
Lecture 19 Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution X Y - - Y X X - Y April 2, 2019 hemistry 328N Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) H H 3 H H H 2 H 3 Please study the mechanism hemistry
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids. Introduction
 hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives. Acyl chloride Acid anhydride Ester Amide Nucleophilic acyl substitution 19.1 Nomenclature
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives. Acyl chloride Acid anhydride Ester Amide Nucleophilic acyl substitution 19.1 Nomenclature
EXPERIMENT 8 (Organic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives
 EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
EXPERIMENT 8 (rganic Chemistry II) Carboxylic Acids Reactions and Derivatives Pahlavan/Cherif Materials Medium test tubes (6) Test tube rack Beakers (50, 150, 400 ml) Ice Hot plate Graduated cylinders
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Chapter 17. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chapter 17 suggested problems: 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 52, 54, 56, 62, 64, 66, 70 Class Notes I. Carboxylic acids (organic acids) and their derivatives A.
Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chapter 17 suggested problems: 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 52, 54, 56, 62, 64, 66, 70 Class Notes I. Carboxylic acids (organic acids) and their derivatives A.
DERIVATIVES OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
 13 Rl RH RNH 2 RR RR DERIVATIVES F ARBXYLI AIDS HAPTER SUMMARY 13.1 Structure and Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives A. Structure arboxylic acids and their derivatives can be expressed as variations
13 Rl RH RNH 2 RR RR DERIVATIVES F ARBXYLI AIDS HAPTER SUMMARY 13.1 Structure and Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives A. Structure arboxylic acids and their derivatives can be expressed as variations
Esterification. Preparation of β-d-glucose pentaacetate. Dr. Zerong Wang at UHCL. Table of contents
 Esterification Preparation of β-d-glucose pentaacetate Table of contents Ester eaction with carboxylic acids eaction with esters: transesterification eaction with acid anhydrides eaction with acid halides
Esterification Preparation of β-d-glucose pentaacetate Table of contents Ester eaction with carboxylic acids eaction with esters: transesterification eaction with acid anhydrides eaction with acid halides
TOPIC 4. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON (Chapter 17)
 L TPI 4. ABXYLI AIDS AND TEI DEIVATES: NULEPILI ADDITIN-ELIMINATIN AT TE AYL ABN (hapter 17) BJETIVES 1. Name carboxylic acids and acid derivatives: acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles
L TPI 4. ABXYLI AIDS AND TEI DEIVATES: NULEPILI ADDITIN-ELIMINATIN AT TE AYL ABN (hapter 17) BJETIVES 1. Name carboxylic acids and acid derivatives: acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
 Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Deriva7ves
 Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Deriva7ves Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 21 Overview 21.1 Nomenclature
Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Deriva7ves Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 21 Overview 21.1 Nomenclature
Oxidizing Alcohols. Questions. Prediction. Analysis. Safety Precautions. Materials. Conclusions. Procedure. 74 MHR Unit 1 Organic Chemistry
 xidizing Alcohols SKILL FUS Predicting Performing and recording Analyzing and interpreting Acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMn 4(aq), acts as an oxidizing agent when it comes in contact with
xidizing Alcohols SKILL FUS Predicting Performing and recording Analyzing and interpreting Acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMn 4(aq), acts as an oxidizing agent when it comes in contact with
13. Carboxylic Acids (text )
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 13.1 13. Carboxylic Acids (text 14.1 14.9) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carboxylic acid functional group results from the connection
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 13.1 13. Carboxylic Acids (text 14.1 14.9) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carboxylic acid functional group results from the connection
Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 31 Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon of Carbonyl Compounds
 Lecture Notes hemistry 342-2008 Mukund P. Sibi eactions at the Alpha-arbon of arbonyl ompounds Enolates are nucleophilic and undergo reaction with electrophiles. For example, one can do halogenation under
Lecture Notes hemistry 342-2008 Mukund P. Sibi eactions at the Alpha-arbon of arbonyl ompounds Enolates are nucleophilic and undergo reaction with electrophiles. For example, one can do halogenation under
H 3 C OCH 3 3 C N(CH 3 ) 2 H 3 C H H 3 C CH 3. ketone. pk a = 9 H H. 1,3-keto ester pk a = 11
 hapter 21: Ester Enolates 21.1: Ester α ydrogens and Their pk a s. The α-protons of s are less acidic that ketones and aldehydes. Typical pk a s of carbonyl compounds (α-protons): aldehydes 17 ketones
hapter 21: Ester Enolates 21.1: Ester α ydrogens and Their pk a s. The α-protons of s are less acidic that ketones and aldehydes. Typical pk a s of carbonyl compounds (α-protons): aldehydes 17 ketones
ORGANIC SYNTHESIS VIA ENOLATES
 1 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS VIA ENOLATES Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction at the carbonyl group. Further, α-hydrogen containing compounds are acidic in nature. In addition to carbonyl
1 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS VIA ENOLATES Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction at the carbonyl group. Further, α-hydrogen containing compounds are acidic in nature. In addition to carbonyl
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Amides Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Amides Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Amides Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Paper 9: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module17: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-II CHEMISTRY
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 9: ORGANIC -III (Reaction Mechanism-2) 17: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-1I CHE_P9_M17 Table of Contents 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 9: ORGANIC -III (Reaction Mechanism-2) 17: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-1I CHE_P9_M17 Table of Contents 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids
 The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry
Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
 Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids are compounds in which the OH of a carboxyl group has been replaced by CI, OOCR, NH2, or OR'to convert acid chlorides,anhydrides,
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids are compounds in which the OH of a carboxyl group has been replaced by CI, OOCR, NH2, or OR'to convert acid chlorides,anhydrides,
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH
 1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
Carboxylic Acids and Esters
 24 Carboxylic Acids and Esters The sour tang in fruit juice comes from carboxylic acids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and
24 Carboxylic Acids and Esters The sour tang in fruit juice comes from carboxylic acids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and
Nu: - Addition or Nu: - Acyl Substitution?
 12. Apply nucleophilic addition and elimination concepts to nucleophilic acyl substution reactions of acids and derivatives (focus on esters and amides) In Class problems: 1. The reactive site of aldehydes,
12. Apply nucleophilic addition and elimination concepts to nucleophilic acyl substution reactions of acids and derivatives (focus on esters and amides) In Class problems: 1. The reactive site of aldehydes,
Topic 4.5 COMPOUNDS CONTAINING THE CARBONYL GROUP. Aldehydes and Ketones Carboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl Chlorides and Acid Anhydrides
 Topic 4.5 MPUNDS NTAINING TE ARBNYL GRUP Aldehydes and Ketones arboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides ALDEYDES AND KETNES 1. Introduction Aldehydes and ketones are collectively
Topic 4.5 MPUNDS NTAINING TE ARBNYL GRUP Aldehydes and Ketones arboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides ALDEYDES AND KETNES 1. Introduction Aldehydes and ketones are collectively
Esters. What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? δ + CH 3
 Esters What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? ow will these intermolecular forces affect their: Melting and boiling points compared to alkanes Solubility in water δ 3 δ + 3 Dipole dipole
Esters What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? ow will these intermolecular forces affect their: Melting and boiling points compared to alkanes Solubility in water δ 3 δ + 3 Dipole dipole
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 23. Hill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th. Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane CH 4 methyl CH 3
 hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
Carboxylic Acids and Esters
 arboxylic Acids and Esters N Goalby hemrevise.org - absorption IR Spectrum for arboxylic acids Butanoic acid 1 Solubility in Water The smaller carboxylic (up to 4) acids dissolve in water in all proportions
arboxylic Acids and Esters N Goalby hemrevise.org - absorption IR Spectrum for arboxylic acids Butanoic acid 1 Solubility in Water The smaller carboxylic (up to 4) acids dissolve in water in all proportions
Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react. methyl pentanoate. Name the type of reaction used to make an ester
 1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
Esters An Introduction To Organic Chemistry Reactions
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with esters an introduction
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with esters an introduction
Chapters 13/14: Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 CHM 201 (Elements of Organic Chemistry) Dr. Virgil Lee Cal Poly Pomona Chapters 13/14: Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives resonance stabilized OH group donates electron density to carbonyl
CHM 201 (Elements of Organic Chemistry) Dr. Virgil Lee Cal Poly Pomona Chapters 13/14: Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives resonance stabilized OH group donates electron density to carbonyl
H O. rapidly reduces. They dissolve. because they can hydrogen bond to the water molecules.
 3.9 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
3.9 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
Chem 263 Nov 26, 2013 O R' alkyl. acid. ethyl. acetic acid. ethyl acetate ethyl ethanoate
 hem 263 ov 26, 2013 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives omenclature Esters Systematic names for esters are derived by first giving the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen, and then identifying the
hem 263 ov 26, 2013 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives omenclature Esters Systematic names for esters are derived by first giving the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen, and then identifying the
A. Carboxylic acid functional groups contain the carboxyl structural feature. 1. Features of the carboxyl group
 Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chem 306 Roper I. Overview A. Carboxylic acid functional groups contain the carboxyl structural feature. 1. Features of the carboxyl group 2. The reactivity
Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chem 306 Roper I. Overview A. Carboxylic acid functional groups contain the carboxyl structural feature. 1. Features of the carboxyl group 2. The reactivity
REVIEW IN CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVES
 IASET: International Journal of Agricultural & Bio-Chemical Science (IASET: IJABS) ISSN(P): Applied; ISSN(E): Applied Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jan - Jun 2017, 49-66 IASET REVIEW IN CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVES
IASET: International Journal of Agricultural & Bio-Chemical Science (IASET: IJABS) ISSN(P): Applied; ISSN(E): Applied Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jan - Jun 2017, 49-66 IASET REVIEW IN CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVES
Chapter 15. Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols. B. Sources: there are two principal sources of simple aliphatic alcohols
 Chapter 15 Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols Chapter 15 suggested problems: 17, 19, 24, 28, 37, 39 I. Introduction A. The relevance of alcohols (from M&B: 497): "If an organic chemist were allowed to choose
Chapter 15 Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols Chapter 15 suggested problems: 17, 19, 24, 28, 37, 39 I. Introduction A. The relevance of alcohols (from M&B: 497): "If an organic chemist were allowed to choose
Chemistry Chapter 19
 hemistry 2100 hapter 19 arboxyl Derivatives In this chapter, we study three classes of compounds derived from carboxylic acids; anhydrides, esters, and amides. Each is related to a carboxyl group by loss
hemistry 2100 hapter 19 arboxyl Derivatives In this chapter, we study three classes of compounds derived from carboxylic acids; anhydrides, esters, and amides. Each is related to a carboxyl group by loss
Chapter 16 and GHW#6 Questions. Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives
 Chapter 16 and GHW#6 Questions Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives Bonding Characteristics of Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid has functional a carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a
Chapter 16 and GHW#6 Questions Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives Bonding Characteristics of Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid has functional a carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a
Identifying Functional Groups. (Chapter 2 in the Klein text)
 Identifying Functional Groups (Chapter 2 in the Klein text) Basic Ideas A functional group is a substructure within a molecule that will have the potential to undergo chemical change, i.e. the group has
Identifying Functional Groups (Chapter 2 in the Klein text) Basic Ideas A functional group is a substructure within a molecule that will have the potential to undergo chemical change, i.e. the group has
Experiment 15: Fischer Esterification and Combinatorial Chemistry Phill Rasnick Introduction
 28 November 2012 Experiment 15: Fischer Esterification and Combinatorial Chemistry Phill Rasnick Introduction Esterification reactions, which produce esters, have proven to have great importance in organic
28 November 2012 Experiment 15: Fischer Esterification and Combinatorial Chemistry Phill Rasnick Introduction Esterification reactions, which produce esters, have proven to have great importance in organic
22. The Fischer Esterification
 22. The Fischer Esterification A. Background Esters are an incredibly important functional group in organic chemistry. Esters are typically very pleasant smelling molecules and are therefore frequently
22. The Fischer Esterification A. Background Esters are an incredibly important functional group in organic chemistry. Esters are typically very pleasant smelling molecules and are therefore frequently
Organic & Biochemistry Pacing Guide. Day Date SCS Objectives Essential Questions Content Tasks/Strategies. How are covalent compounds formed?
 Organic & Biochemistry Pacing Guide Course Description: Course Description: This course is designed to provide students with an opportunity to continue their study of the principles of chemistry. The topics
Organic & Biochemistry Pacing Guide Course Description: Course Description: This course is designed to provide students with an opportunity to continue their study of the principles of chemistry. The topics
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH
 1 The alcohols form a homologous series. The first member is methanol and the fourth is butanol. 3 O methanol 3 2 2 2 O butanol (a) Give two general characteristics of a homologous series. (ii) alculate
1 The alcohols form a homologous series. The first member is methanol and the fourth is butanol. 3 O methanol 3 2 2 2 O butanol (a) Give two general characteristics of a homologous series. (ii) alculate
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
School of Chemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Westville Campus Chemical Reactivity 120R. Organic Reactions
 Boiling point (o) School of hemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-atal, Westville ampus hemical eactivity 120 rganic ALKAES Saturated hydrocarbons - contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, where
Boiling point (o) School of hemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-atal, Westville ampus hemical eactivity 120 rganic ALKAES Saturated hydrocarbons - contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, where
Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry. Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils. Page 1 of 11
 Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils Page 1 of 11 No. Learning Outcome Understanding? 1 An ester can be identified from the name containing the -yl-oate
Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils Page 1 of 11 No. Learning Outcome Understanding? 1 An ester can be identified from the name containing the -yl-oate
Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 3 3.1 a) Know that alcohols contain a hydroxy (-OH) group. Determine the IUPAC name for a given structure by determining the longest chain. b) Determine the number
Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 3 3.1 a) Know that alcohols contain a hydroxy (-OH) group. Determine the IUPAC name for a given structure by determining the longest chain. b) Determine the number
(iii). Decarboxylation (iv)kolbe Electrolysis
 ALKANOIC ACID/CARBOXYLIC ACID Contains carboxyl functional group COOH Two functional groups are contained in carboxyl- carbonyl (C=O)and hydroxyl (-OH) Saturated aliphatic alkanoic acids have general formula
ALKANOIC ACID/CARBOXYLIC ACID Contains carboxyl functional group COOH Two functional groups are contained in carboxyl- carbonyl (C=O)and hydroxyl (-OH) Saturated aliphatic alkanoic acids have general formula
Chapter 15 Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols
 Chapter 15 Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1 Sources of Alcohols Methanol Methanol is an industrial chemical end uses: solvent, antifreeze, fuel principal use: preparation of formaldehyde Methanol Methanol
Chapter 15 Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols 15.1 Sources of Alcohols Methanol Methanol is an industrial chemical end uses: solvent, antifreeze, fuel principal use: preparation of formaldehyde Methanol Methanol
Alkane C-C single bond (propane) Alkene C=C double bond (propene) Alcohol - OH group (1-propanol) major. minor
 Functional group* and name? Alkane - single bond (propane) *alkanes not really regarded as a functional group Alkene = double bond (propene) Addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to unsymmetrical alkene
Functional group* and name? Alkane - single bond (propane) *alkanes not really regarded as a functional group Alkene = double bond (propene) Addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to unsymmetrical alkene
Chem 263 B6 Notes March 30, 2006 Demo-In-Class: O
 hem 263 B6 otes March 30, 2006 Demo-In-lass: + 2 carbon dioxide carbonic acid arbon dioxide ( 2 ) is a solid at -78. It is dry ice. When it is added to water, we made carbonated water (as in soda pop).
hem 263 B6 otes March 30, 2006 Demo-In-lass: + 2 carbon dioxide carbonic acid arbon dioxide ( 2 ) is a solid at -78. It is dry ice. When it is added to water, we made carbonated water (as in soda pop).
Carboxylic Acids. Carboxylic acid groups are always terminal groups with a carbonyl carbon also bound to a hydroxyl For example:
 Carboxylic Acids The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. Structure of Carboxyl Carbon is sp 2 hybridized. Bond angles are close to 120. O-H eclipsed
Carboxylic Acids The functional group of carboxylic acids consists of a C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. Structure of Carboxyl Carbon is sp 2 hybridized. Bond angles are close to 120. O-H eclipsed
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS
 C24 09/17/2013 11:59:46 Page 350 CHAPTER 24 CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. (a) CH (d) (e) (f) (g) CH 2 CHCH (h) (i) CN (j) CNa (k) (l) (m) (CH 2 ) 16 CNa (n) H P H (o) H P H H
C24 09/17/2013 11:59:46 Page 350 CHAPTER 24 CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. (a) CH (d) (e) (f) (g) CH 2 CHCH (h) (i) CN (j) CNa (k) (l) (m) (CH 2 ) 16 CNa (n) H P H (o) H P H H
ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 P. GERGELY Department os Medical Chemistry Medical and Health Science Center University of Debrecen ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY FÓR MEDICAL STUDENTS THIRD EDITION University of Debrecen Medical and
P. GERGELY Department os Medical Chemistry Medical and Health Science Center University of Debrecen ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY FÓR MEDICAL STUDENTS THIRD EDITION University of Debrecen Medical and
6/9/2015. Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
 1-chloropropane 2-methylpropane 1-iodobutane Ethanoic Acid Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups 43 It Ain t Just Hydrocarbons There are all sorts of organic
1-chloropropane 2-methylpropane 1-iodobutane Ethanoic Acid Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups 43 It Ain t Just Hydrocarbons There are all sorts of organic
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank.
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. 1. (3 points each) First set functional groups A. ether D. amine B.
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. 1. (3 points each) First set functional groups A. ether D. amine B.
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Carbonyl Compounds Cl H H N 2 1810 cm -1 (band 1) 1800 cm -1 1760 cm -1 both present (band 2) 1735 cm -1 1725 cm -1 1715 cm -1 1710 cm -1 1690 cm -1 Inductive Effects esonance Effects stronger bond W W
Carbonyl Compounds Cl H H N 2 1810 cm -1 (band 1) 1800 cm -1 1760 cm -1 both present (band 2) 1735 cm -1 1725 cm -1 1715 cm -1 1710 cm -1 1690 cm -1 Inductive Effects esonance Effects stronger bond W W
CCMR Educational Programs
 CCMR Educational Programs Title: Date Created: July 21, 2006 Author(s): Appropriate Level: Abstract: Time Requirement: Frank La Gatta Esterfication Regents and Honors Chemistry An ester is produced when
CCMR Educational Programs Title: Date Created: July 21, 2006 Author(s): Appropriate Level: Abstract: Time Requirement: Frank La Gatta Esterfication Regents and Honors Chemistry An ester is produced when
This is an addition reaction. (Other types of reaction have been substitution and elimination). Addition reactions are typically exothermic.
 Reactions of Alkenes Since bonds are stronger than bonds, double bonds tend to react to convert the double bond into bonds + X-Y X Y This is an addition reaction. (Other types of reaction have been substitution
Reactions of Alkenes Since bonds are stronger than bonds, double bonds tend to react to convert the double bond into bonds + X-Y X Y This is an addition reaction. (Other types of reaction have been substitution
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2
 Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids
 Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids 1 Classes of organic compounds 2 Alcohols Alcohols are organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to C atom. In an alcohol, -OH group replaces
Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids 1 Classes of organic compounds 2 Alcohols Alcohols are organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to C atom. In an alcohol, -OH group replaces
Carboxylic Acids. Seminar_7
 Seminar_7 1. Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids 2. Preparation of Carboxylic Acids 3. Reactivity 4. Soaps and Detergents 5. Fats and Oils TEST Carboxylic acides, esters and fats. Give the names Carboxylic
Seminar_7 1. Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids 2. Preparation of Carboxylic Acids 3. Reactivity 4. Soaps and Detergents 5. Fats and Oils TEST Carboxylic acides, esters and fats. Give the names Carboxylic
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016
 Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016 eactivity of Carboxylic acid Derivatives More eactive S 2 ' ' + a ' 2 - M + Less eactive Example: Acid chloride to anhydride Since an acid chloride is more reactive than an anhydride,
Chem 263 Dec 1, 2016 eactivity of Carboxylic acid Derivatives More eactive S 2 ' ' + a ' 2 - M + Less eactive Example: Acid chloride to anhydride Since an acid chloride is more reactive than an anhydride,
Dow Haltermann Custom Processing The World of Hydrogen Cyanide Chemistry
 Dow altermann Custom Processing The World of ydrogen Cyanide Chemistry Sharing Your Vision esourcing Your Success Specialists in ydrogen Cyanide Chemistry With Dow s acquisition of the ampshire Chemical
Dow altermann Custom Processing The World of ydrogen Cyanide Chemistry Sharing Your Vision esourcing Your Success Specialists in ydrogen Cyanide Chemistry With Dow s acquisition of the ampshire Chemical
Chem 263 Nov 21, 2013
 hem 263 Nov 21, 2013 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
hem 263 Nov 21, 2013 arbohydrates- emiacetal Formation You know from previous lectures that carbonyl compounds react with all kinds of nucleophiles. ydration and hemiacetal formation are typical examples.
ANSWERS BIOCHEMISTRY CARBOHYDRATES
 1. Fructose ANSWERS BIOCEMISTRY CARBOYDRATES 2. Sucrose or maltose 3. (C 6 10 O 5 ) n 4. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be further hydrolysed. 5. D(-) fructofuranose structure:
1. Fructose ANSWERS BIOCEMISTRY CARBOYDRATES 2. Sucrose or maltose 3. (C 6 10 O 5 ) n 4. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be further hydrolysed. 5. D(-) fructofuranose structure:
The Preparation of Fragrant Esters
 The Objective Esters are the product of reaction of an organic (carboxylic acid) with an alcohol. Many esters are components of the essential oils of flowers and fruits. Several esters with pleasant fragrances
The Objective Esters are the product of reaction of an organic (carboxylic acid) with an alcohol. Many esters are components of the essential oils of flowers and fruits. Several esters with pleasant fragrances
ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE
 ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE Organic compounds are carbon containing compounds. Carbon has the following unique bonding properties: 1) it has a covalence of four 2) carbon atoms
ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE Organic compounds are carbon containing compounds. Carbon has the following unique bonding properties: 1) it has a covalence of four 2) carbon atoms
