SCCEP 2013 LLSA Course Article 10 AHA/ASA Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous ICH
|
|
|
- Alexander Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCCEP 2013 LLSA Course Article 10 AHA/ASA Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous ICH Morgenstern LB, Hemphill JC. Stroke July 2010;41: Article: This article presents guidelines whose "aim is to present current and comprehensive recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of acute, spontaneous ICH." Policy adopted by AHA/ASA Due to updated 2013 Conflicts reported: Pages and pages detailed in article. Half of writers and 1/6 reviewers. Introduction Methods: Formal English language MEDLINE search. Data were synthesized with use of evidence tables. Writers teleconferenced to discuss data-derived recommendations, which were graded using the AHA Stoke Council's Levels of Evidence grading algorithm. Draft guidelines were reviewed by 6 expert peer reviewers, and by the members of the both the Stroke Council Scientific Statements Oversight and Leadership Committees. Evidence Classification: (Differs significantly from ACEP and others) Class I: Treatment/Procedure is useful, effective, SHOULD be performed Level A: Multiple RCTS or meta-analyses of RCTs. Level B: Single RCT or cohort and case controlled studies (non-random) Level C: Case studies and reports, standard of care, expert opinions. Class IIa: It is REASONABLE to perform Treatment/Procedure (need focused studies) Level A: Some conflicting evidence from multiple RCTS or meta-analyses of RCTs. Level B: Some conflicting evidence from single RCT or non-randomized studies Level C: Only diverging expert opinion, case studies or standard of care. Class IIb: Treatment/Procedure MAY BE CONSIDERED (need broad studies, registry data) Level A: Greater conflicting evidence from multiple RCTS or meta-analyses of RCTs.. Level B: Greater conflicting evidence from single RCT or non-randomized studies Level C: Only diverging expert opinion, case studies or standard of care. Class III: Treatment/Procedure SHOULD NOT be done: not helpful/harmful Level A: Multiple RCTS or meta-analyses of RCTs. Level B: Single RCT or cohort and case controlled studies (non-random) Level C: Case studies and reports, standard of care, expert opinions.
2 Scope of Guidelines: From diagnosis to rehab, guidelines are offered. Authors acknowledge that there are NO SPECIFIC TARGERTED THERAPIES but state that there are successes with aggressive surgical and medical care. Included: Adult ED Patients presenting with symptoms or signs of ICH. Excluded: Pediatrics, since a recent guideline has been published Emergency Diagnosis and Assessment of ICH and Its Causes 20% of Pts have a decrease in GCS >2 between EMS and initial ED assessment Average decrease in this 20% is 6 on GCS and mortality is 75% ( i.e. dying people do poorly right before they die) 15% of Pts in ED have decrease in GCS >2 Prehospital Management: o Provide ventilatory and CV support o Obtain focus history, med list, any drug use o Advanced notice to ED of incoming stroke ED Management: o "UTMOST" importance that every ED have a plan to treat or transfer ICH Neurosurgical evacuation or drainage, pressure monitoring BP management, Intubation Reversal of coagulopathy (ed note...increasingly not possible) A. Neuro-Imaging: Early CT or MRI imaging in mandatory, as symptoms of ICH and ischemic stroke are non-specific and overlapping with other clinical conditions as well. 1. Class I (Level A): Rapid Neuroimaging to distinguish ischemia and ICH 2. Class IIb (Level B): CT Angiography and Contrast CT may identify patients at risk for hematoma expansion 3. Class IIa (Level B): Advanced CT and MRI techniques may help identify underlying tumors and AVMs when there is clinical or radiologic suspicion Medical Treatment for ICH B. Hemostasis by reversal of OACs, correction of acquired or congenital factor deficiencies, transfusion of platelets, and DVT prophylaxis. There are many ongoing trials of newer factor replacement products such as rfviia and Prothrombin Complex Concentrates(PCC), compared with FFP and Vitamin K IV. Unfortunately, many newer agents(e.g. Pradaxa), unlike wafarin, lack reversal agents
3 1. Class I (Level C): Pts with severe coagulation factor deficiency or severe thrombocytopenia should respectively receive appropriate factor replacement therapy or platelets 2. Class I (Level C): Pts with elevated INR due to wafarin should have it withheld and receive therapy to replace Vit-K dependent factors and correct the INR and receive IV Vit K Class IIa (Level B): PCCs have not been shown improved outcomes compared with FFP, but may have fewer complications and are reasonable to consider as an alternative to FFP Class III (Level C): rfviia does not replace all clotting factors and although the INR may be lower, clotting in vivo may not be restored; therefore rfviia is NOT routinely recommended as a sole agent for OAC reversal in ICH 3. Class III (Level A): Although rfviia can limit the extent of hematoma expansion in NONCOAGULOPATHIC ICH, there is an increase in thromboembolic risk and no clear benefit in unselected patients. Therefore, rfviia is NOT recommended in unselected patients 4. Class IIb (Level B): The usefulness of platelet transfusions in ICH patients on antiplatelet therapy is unclear and is considered investigational 5. Class I (Level B): Patients should have intermittent pneumatic compression for prevention of DVT in addition to elastic stockings 6. Class IIb (Level B): After documentation of the cessation of bleeding, low dose SQ LMWH may be considered for the prevention of DVT in patient with lack of mobility 1-4 days after onset C. Blood Pressure: ICH patients who present with SBP > 150 do worse. Two recent studies, one Chinese, one smaller and done with nicardipine as the agent showed no worse outcomes when acutely lowering SBP in ICH from > 180 mm Hg towards 140 mm Hg. Note that there was no benefit shown beyond a "relatively" smaller hematoma size. 1. Class IIb (Level C): Physicians must manage BP on the basis of incomplete efficacy evidence. Recommendations are summarized in Table If SBP is > 200 mm Hg or MAP is > 150 mm Hg, then consider aggressive reduction of BP with continuous IV infusion, with BP monitoring every 5 min. 2. If SBP is > 180 mm Hg or MAP is > 130 mm Hg and there is the possibility of elevated ICP, then consider monitoring ICP and reducing BP using intermittent or continuous IV meds while maintaining a CPP > 60 mm Hg. 3. If SBP is > 180 mm Hg or MAP is > 130 mm Hg and there is not evidence of elevated ICP, then consider a modest reduction of BP (eg, MAP of 110 mm Hg or target BP of 160/90 mm Hg) using intermittent or continuous IV meds BP and clinically reexamine the patient every 15 min.
4 . 2. Class IIb (Level B): In pts with SBP of mm Hg, acute lowering to 140 mm Hg is probably safe. (Single Chinese Study) D. Monitoring ICH Patients Acutely 1. Class I (Level B): initial monitoring and management of ICH Pts should take place in an ICU with physician and nursing neuroscience ICU expertise E. Management of Glucose: a single study from 2001 in surgical ICU patients demonstrated improved outcomes with very tight glucose control ( mg/dl) Multiple studies since then have shown possible increased in mortality, and hypoglycemic events. 1. Class I (Level C): Monitored glucose and normoglycemia is recommended. F. Management of Temperature: Incidence of fever in basal ganglion and lobar ICH is high, and fever, especially after 72 hours portends a worse outcome, but there is no data on therapeutic cooling in ICH. G. Management of Seizures and Antiepileptics: Seizures are common after ICH and EEG abnormalities even more common, even in patients on prophylactic antiepileptics. However, in prospective and population-based studies, seizures are not associated with a worse outcome or mortality. One population based study and a single are or a randomized study showed increased mortality at 90 days for phenytoin. 1. Class I (Level A): Treat clinical seizures with antiepileptic drugs 2. Class IIa (Level B): Continuous EEG monitoring is probably indicated in pts with depressed mental status out of proportion to brain 3. Class I (Level C): Patients with change in mental status who are found to have electrographic seizures on EEG should be treated with antiepileptics 4. Class III (Level B): Prophylactic anticonvulsants should NOT be used Procedures/Surgery H. ICP Monitoring and Treatment: Elevated ICP usually due to hydrocephalus from IVH, or mass effect or edema, so patients with small hematomas usually don't require ICP monitoring. Parenchymal or ventricular catheters can be inserted at bedside using fiberoptic techniques. A ventricular catheter can be used to drain CSF and lower ICP. Coagulation status of patient should be assessed before placing and coagulopathies corrected. There is a lack of published studies showing that ICP management improves outcomes. 1. Class IIb (Level C): Pt with GCS <8, clinical evidence or transtentorial herniation or those with significant IVH or hydrocephalus might be
5 considered for ICP monitoring and treatment. A CPP of is reasonable to maintain depending on cerebral autoregulation status. 2. Class IIa (Level B): Ventricular drainage for hydrocephalus is reasonable in patients with decreased LOC I. Intraventricular Hemorrhage: IVH occurs in 45% of spontaneous ICH. May be primary, but most IVH are secondary to basal ganglion ICH. They can be drained with an intraventricular catheter, but it often clogs off, so tpa is being tested as an adjunct. 1. Class IIb (Level A): Although intraventricular administration of tpa in IVH has a fairly low complication rate, safety and efficacy are uncertain and it is considered investigational J. Clot Removal: Decision to surgically remove the ICH is controversial and recommendations are uncertain as risks of surgery on a acutely bleeding ICH patient may outweigh benefits of removing the clot and limiting the mechanical compression of the brain and the toxic effects of the blood on the brain. Craniotomy by Location of ICH: Cerebellar ICH > 3cm or with signs of brainstem compression do better with surgery 1. Class IIb (Level C): For most ICH Pts, usefulness of surgery is uncertain 2. Class I (Level B): Cerebellar ICH Pts that are deteriorating clinically or have brainstem compression or hydrocephalus should undergo surgical removal of hematoma ASAP. Initial treatment of these PTs with ventricular drainage alone is not recommended.{ Class III (Level C)} 3. Class IIb (Level B): Pts with supratentorial clots >30 ml and within 1 cm of surface might be considered for surgical evacuation 4. Class IIb (Level B): Effectiveness of minimally invasive clot evacuation with or without tpa is uncertain and investigational. 5. Class III (Level B): No clear evidence that ultra-early removal of SUPRATENTORIAL ICH improves outcome or mortality and may be harmful due to increase bleeding risk K. Outcome Prediction and Withdrawal of Technological Support: DNR orders are probably a surrogate marker for overall less-aggressive care, and probably lead to a selffulfilling prophecy of poor outcomes. it si difficult to prognosticate early inthge course of ICH 1. Class IIa (Level B): Aggressive early care and postponement of new DNR orders until at least the 2nd day of hospitalization is probably recommended. Pts with pre-existing DNR are not included in this recommendation. DNR pts should receive all other appropriate medical and surgical interventions unless otherwise explicitly indicated by advanced directives
6 L. Prevention of Recurrent ICH: Recurrence rates of 2-3% per year, much higher than their risk of subsequent ischemic stroke. High risk factor for recurrence is lobar location, probably due to association of amyloid vasculopathy with lobar bleeds. Brainstem and basal ganglia stokes due to HTN occur less frequently. Age, HTN, anticoagulation, frequent ETOH use and certain genetic markers are also associated with higher risk of recurrence. 1. Class IIa (Level B): In stratifying a patient risk for recurrent ICH when making management decisions, it is reasonable to consider these risk factors: Lobar location, older age, ongoing anticoagulation, apolipoprotien E e2 or e4 alleles, and presence of a greater number of microbleeds on MRI. 2. Class I (Level A): After the acute ICH period, BP should be well controlled, particularly in pts whose ICH location is typical of HTN bleeds. 3. Class IIa (Level B): After the acute ICH period, BP should be < 140/90 or 130/80 if diabetic or chronic kidney disease 4. Class IIa (Level B): Avoidance of anticoagulation after spontaneous lobar ICH in non-valvular A Fib pts is probably recommended based on high recurrence rate. Class IIb (Level B) After NON-lobar ICH anticoagulation and anti-platelet therapy might be considered if there are definite indications 5. Class IIa (Level B): Avoidance of heavy ETOH can be beneficial. Class IIa (Level C): There is insufficient evidence to recommend restrictions on the use of statins, or restricting physical or sexual activity. M. Rehabilitations and Recovery 1. Class IIa (Level B): All pts should have access to multi-disciplinary rehab Class IIa (Level B): When possible, rehab should begin as early as possible and continue at home and in the community seamlessly, with accelerated hospital discharge N. Future Considerations 1. Community based programs to control HTN 2. Prompt treatment, early imaging and aggressive care, since prognosticating with ICH is difficult 3. Research Areas: i. Early BP control in ICH. ii. Agents to chelate iron, or prevent secondary injury from hypoxia etc. iii. Minimally invasive surgical techniques to remove clot
Treatment of Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke 5th QSVS Neurovascular Conference Dar Dowlatshahi MD PhD FRCPC Sept 14, 2012
 Treatment of Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke 5th QSVS Neurovascular Conference Dar Dowlatshahi MD PhD FRCPC Sept 14, 2012 Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest Quebec Society of Vascular Sciences presents
Treatment of Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke 5th QSVS Neurovascular Conference Dar Dowlatshahi MD PhD FRCPC Sept 14, 2012 Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest Quebec Society of Vascular Sciences presents
Modern Management of ICH
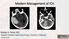 Modern Management of ICH Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh October 2018 ICH Background Assessment & Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management
Modern Management of ICH Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh October 2018 ICH Background Assessment & Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management
AHA/ASA Guideline. Downloaded from by on September 4, 2018
 AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association The American
AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association The American
Controversies in Hemorrhagic Stroke Management. Sarah L. Livesay, DNP, RN, ACNP-BC, ACNS-BC Associate Professor Rush University
 Controversies in Hemorrhagic Stroke Management Sarah L. Livesay, DNP, RN, ACNP-BC, ACNS-BC Associate Professor Rush University Disclosures AHA/ASA Outline Blood pressure VTE Coagulopathy Early mobilization
Controversies in Hemorrhagic Stroke Management Sarah L. Livesay, DNP, RN, ACNP-BC, ACNS-BC Associate Professor Rush University Disclosures AHA/ASA Outline Blood pressure VTE Coagulopathy Early mobilization
Benjamin Anyanwu,MD Medical Director In-patient Neurology and Neuroscience ICU Novant Health Forsyth Medical Center, Winston-Salem NC
 Benjamin Anyanwu,MD Medical Director In-patient Neurology and Neuroscience ICU Novant Health Forsyth Medical Center, Winston-Salem NC Emergency Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke Objectives Discuss the etiology
Benjamin Anyanwu,MD Medical Director In-patient Neurology and Neuroscience ICU Novant Health Forsyth Medical Center, Winston-Salem NC Emergency Treatment of Hemorrhagic Stroke Objectives Discuss the etiology
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
AHA/ASA Guideline. by guest on September 29, 2016
 AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association The American
AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association The American
SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE
 SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE Intracerebral hemorrhageis an acute and spontaneous extravasationof blood into the brain parenchyma that may extend into the ventricles and subarachnoid space. It is
SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE Intracerebral hemorrhageis an acute and spontaneous extravasationof blood into the brain parenchyma that may extend into the ventricles and subarachnoid space. It is
Stroke ESO.org. Csiba László.
 Stroke ESO.org Csiba László csiba@dote.hu Global mortality Cause of death Dept. of Neurology? 1938-1950 1990-2002 Tumor Stroke Tumor Infect. Stroke Normal lifestyle After MI 70-80% After stroke 10% Differential
Stroke ESO.org Csiba László csiba@dote.hu Global mortality Cause of death Dept. of Neurology? 1938-1950 1990-2002 Tumor Stroke Tumor Infect. Stroke Normal lifestyle After MI 70-80% After stroke 10% Differential
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine
 Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
11/27/2017. Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Conflict of interest. Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care
 Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Conflict of interest None Introduction Reperfusion therapy remains the mainstay in the treatment
Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Conflict of interest None Introduction Reperfusion therapy remains the mainstay in the treatment
Stroke Guidelines. November 19, 2011
 Stroke Guidelines November 19, 2011 Clinical Practice Guidelines American Stroke Association Guidelines are comprehensive statements that provide the highest level of scientific evidence for clinical practice.
Stroke Guidelines November 19, 2011 Clinical Practice Guidelines American Stroke Association Guidelines are comprehensive statements that provide the highest level of scientific evidence for clinical practice.
Traumatic Brain Injury:
 Traumatic Brain Injury: Changes in Management Across the Spectrum of Age and Time Omaha 2018 Trauma Symposium June 15, 2018 Gail T. Tominaga, M.D., F.A.C.S. Scripps Memorial Hospital La Jolla Outline Background
Traumatic Brain Injury: Changes in Management Across the Spectrum of Age and Time Omaha 2018 Trauma Symposium June 15, 2018 Gail T. Tominaga, M.D., F.A.C.S. Scripps Memorial Hospital La Jolla Outline Background
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage J. Claude Hemphill III, MD, MAS Kenneth Rainin Chair in Neurocritical Care Professor of Clinical Neurology and Neurological Surgery University of California, San Francisco Director,
Intracerebral Hemorrhage J. Claude Hemphill III, MD, MAS Kenneth Rainin Chair in Neurocritical Care Professor of Clinical Neurology and Neurological Surgery University of California, San Francisco Director,
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Review of Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Réza Behrouz, DO Assistant Professor of Neurology University of South Florida College of Medicine STROKE 85% ISCHEMIC 15% HEMORRHAGIC HEMORRHAGIC STROKE 1/3 Subarachnoid
Review of Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Réza Behrouz, DO Assistant Professor of Neurology University of South Florida College of Medicine STROKE 85% ISCHEMIC 15% HEMORRHAGIC HEMORRHAGIC STROKE 1/3 Subarachnoid
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Update on Intracerebral Hemorrhage November 8, 2013 Anne E. O Duffy, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Stroke Division Intracerebral Hemorrhage Traumatic Spontaneous Primary (80-88%): due to spontaneous
Update on Intracerebral Hemorrhage November 8, 2013 Anne E. O Duffy, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Stroke Division Intracerebral Hemorrhage Traumatic Spontaneous Primary (80-88%): due to spontaneous
Starting or Resuming Anticoagulation or Antiplatelet Therapy after ICH: A Neurology Perspective
 Starting or Resuming Anticoagulation or Antiplatelet Therapy after ICH: A Neurology Perspective Cathy Sila MD George M Humphrey II Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, Comprehensive Stroke Center
Starting or Resuming Anticoagulation or Antiplatelet Therapy after ICH: A Neurology Perspective Cathy Sila MD George M Humphrey II Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, Comprehensive Stroke Center
The Worst Headache of My Life Hemorrhagic Stroke
 The Worst Headache of My Life Hemorrhagic Stroke Lindsay Trantum ACNP-BC Neurocritical Care Nurse Practitioner Assistant in Anesthesiology, Division of Critical Care Objectives Identify the risk factors
The Worst Headache of My Life Hemorrhagic Stroke Lindsay Trantum ACNP-BC Neurocritical Care Nurse Practitioner Assistant in Anesthesiology, Division of Critical Care Objectives Identify the risk factors
Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Acute stroke management is progressing very rapidly. Our team offers several options for acute stroke therapy, including endovascular therapy and
Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Acute stroke management is progressing very rapidly. Our team offers several options for acute stroke therapy, including endovascular therapy and
Recombinant Factor VIIa for Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Recombinant Factor VIIa for Intracerebral Hemorrhage January 24, 2006 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline 1. Introduction to patient case 2. Overview of intracerebral hemorrhage
Recombinant Factor VIIa for Intracerebral Hemorrhage January 24, 2006 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline 1. Introduction to patient case 2. Overview of intracerebral hemorrhage
Management of Intracerebral Haemorrhage
 Management of Intracerebral Haemorrhage It s the worst type of stroke. Least treatable form of stroke Evidence-base limited most Overall mortality 35-50% Half of these would die within first 24 hours
Management of Intracerebral Haemorrhage It s the worst type of stroke. Least treatable form of stroke Evidence-base limited most Overall mortality 35-50% Half of these would die within first 24 hours
Hypertensive Haemorrhagic Stroke. Dr Philip Lam Thuon Mine
 Hypertensive Haemorrhagic Stroke Dr Philip Lam Thuon Mine Intracerebral Haemorrhage Primary ICH Spontaneous rupture of small vessels damaged by HBP Basal ganglia, thalamus, pons and cerebellum Amyloid
Hypertensive Haemorrhagic Stroke Dr Philip Lam Thuon Mine Intracerebral Haemorrhage Primary ICH Spontaneous rupture of small vessels damaged by HBP Basal ganglia, thalamus, pons and cerebellum Amyloid
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
Update in Management of Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Haemorrhage
 Update in Management of Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Haemorrhage Aldy S. Rambe Neurology Department, School of Medicine EPIDEMIOLOGY Although ICH represents only about 9% of all stroke, it accounts
Update in Management of Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Haemorrhage Aldy S. Rambe Neurology Department, School of Medicine EPIDEMIOLOGY Although ICH represents only about 9% of all stroke, it accounts
Standardize comprehensive care of the patient with severe traumatic brain injury
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Management of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (GCS < 9) ADULT Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Iowa Methodist Medical Center Des Moines Management of Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (GCS < 9) ADULT Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma
AHA/ASA Guideline. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults
 AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults 2007 Update A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council,
AHA/ASA Guideline Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults 2007 Update A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council,
2018 Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke Guidelines Update
 2018 Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke Guidelines Update Brandi Bowman, PhC, Pharm.D. April 17, 2018 Pharmacist Objectives Describe the recommendations for emergency medical services and hospital
2018 Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke Guidelines Update Brandi Bowman, PhC, Pharm.D. April 17, 2018 Pharmacist Objectives Describe the recommendations for emergency medical services and hospital
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial Hemorrhage. Objectives. What Do Need to Know?
 Intracranial Hemorrhage What Do Need to Know? Kerry Brega, MD Associate Professor of Neurosurgery University of Colorado Objectives Know the common types of ICH. Know how they can be differentiated. Know
Intracranial Hemorrhage What Do Need to Know? Kerry Brega, MD Associate Professor of Neurosurgery University of Colorado Objectives Know the common types of ICH. Know how they can be differentiated. Know
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
 The Articles Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Brunham RC, Gottlieb SL, Paavonen J. Pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 2015 May;372(21):2039-48. 2018 LLSA Article Review Shared Decision-making Hess EP,
The Articles Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Brunham RC, Gottlieb SL, Paavonen J. Pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 2015 May;372(21):2039-48. 2018 LLSA Article Review Shared Decision-making Hess EP,
Objectives. Definition 3/21/2017. Spontaneous, Nontraumatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Mindy Mason, MSN, RN, ACNP-BC University of New Mexico Academic Medical Center Level I Trauma Center 24 bed Neuroscience ICU Albuquerque, NM Objectives
Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Mindy Mason, MSN, RN, ACNP-BC University of New Mexico Academic Medical Center Level I Trauma Center 24 bed Neuroscience ICU Albuquerque, NM Objectives
11/23/2015. Disclosures. Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care.
 Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Disclosures I have no relevant commercial relationships to disclose, and my presentations will not
Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Disclosures I have no relevant commercial relationships to disclose, and my presentations will not
Updated Ischemic Stroke Guidelines นพ.ส ชาต หาญไชยพ บ ลย ก ล นายแพทย ทรงค ณว ฒ สาขาประสาทว ทยา สถาบ นประสาทว ทยา กรมการแพทย กระทรวงสาธารณส ข
 Updated Ischemic Stroke Guidelines นพ.ส ชาต หาญไชยพ บ ลย ก ล นายแพทย ทรงค ณว ฒ สาขาประสาทว ทยา สถาบ นประสาทว ทยา กรมการแพทย กระทรวงสาธารณส ข Emergency start at community level: Prehospital care Acute stroke
Updated Ischemic Stroke Guidelines นพ.ส ชาต หาญไชยพ บ ลย ก ล นายแพทย ทรงค ณว ฒ สาขาประสาทว ทยา สถาบ นประสาทว ทยา กรมการแพทย กระทรวงสาธารณส ข Emergency start at community level: Prehospital care Acute stroke
Jan 5, Coma 8 years. Jan 11, 2014
 Jan 5, 2006 Coma 8 years Jan 11, 2014 CT Scan of Head showing large right frontal ICH The Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Team Approach Rodney Leacock MD Introduction Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a very
Jan 5, 2006 Coma 8 years Jan 11, 2014 CT Scan of Head showing large right frontal ICH The Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Team Approach Rodney Leacock MD Introduction Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a very
Acute Management of Anticoagulation-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Acute Management of Anticoagulation-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage Authors Joji B. Kuramatsu, Stefan T. Gerner, Hagen B. Huttner, Stefan Schwab Affiliation University Hospital Erlangen Department
Acute Management of Anticoagulation-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage Authors Joji B. Kuramatsu, Stefan T. Gerner, Hagen B. Huttner, Stefan Schwab Affiliation University Hospital Erlangen Department
Neurosurgical Management of Stroke
 Overview Hemorrhagic Stroke Ischemic Stroke Aneurysmal Subarachnoid hemorrhage Neurosurgical Management of Stroke Jesse Liu, MD Instructor, Neurological Surgery Initial management In hospital management
Overview Hemorrhagic Stroke Ischemic Stroke Aneurysmal Subarachnoid hemorrhage Neurosurgical Management of Stroke Jesse Liu, MD Instructor, Neurological Surgery Initial management In hospital management
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD.
 Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD, Julio A. Díaz MD, Sandro Perez MD, Julio C Martin MD, Daiyan Martin MD. Introduction: Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (SICH) represents one of the most severe
William Barr, M.D. January 28, 2017
 William Barr, M.D. January 28, 2017 Types of Stroke Ischemic Stroke Small vessel (20%) Large vessel (31%) Embolic (32%) Hemorrhagic Intracerebral Hemorrhage (10%) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (7%) The Majority
William Barr, M.D. January 28, 2017 Types of Stroke Ischemic Stroke Small vessel (20%) Large vessel (31%) Embolic (32%) Hemorrhagic Intracerebral Hemorrhage (10%) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (7%) The Majority
A few Neurosurgical Emergencies. Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015
 A few Neurosurgical Emergencies Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015 Outline Neuroanatomy and physiology (85 slides ) Raised
A few Neurosurgical Emergencies Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015 Outline Neuroanatomy and physiology (85 slides ) Raised
Primary Stroke Center Quality & Performance Measures
 Primary Stroke Center Quality & Performance Measures This section of the manual contains information related to the quality performance of Primary Stroke Centers. Brain Attack Coalition Definitions Recognition
Primary Stroke Center Quality & Performance Measures This section of the manual contains information related to the quality performance of Primary Stroke Centers. Brain Attack Coalition Definitions Recognition
The management of ICH when to operate when not to?
 The management of ICH when to operate when not to? Intracranial Hemorrhage High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
The management of ICH when to operate when not to? Intracranial Hemorrhage High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
excellence in care Procedure Neuroprotection For Review Aug 2015
 Neuro Projection HELI.CLI.14 Purpose This procedure outlines the management principles of patients being retrieved with traumatic brain injury (TBI), spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage (including subarachnoid
Neuro Projection HELI.CLI.14 Purpose This procedure outlines the management principles of patients being retrieved with traumatic brain injury (TBI), spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage (including subarachnoid
SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE: MEDICAL MANAGEMENT. Neeraj Naval, MD Baptist Neurological Institute
 SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE: MEDICAL MANAGEMENT Neeraj Naval, MD Baptist Neurological Institute Disclosures/ COI Nothing to disclose (what happens in Vegas stays in Vegas) No Conflict of interest
SPONTANEOUS INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE: MEDICAL MANAGEMENT Neeraj Naval, MD Baptist Neurological Institute Disclosures/ COI Nothing to disclose (what happens in Vegas stays in Vegas) No Conflict of interest
 www.yassermetwally.com MANAGEMENT OF CEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE (ICH): A QUICK GUIDE Overview 10% of strokes is caused by ICH. Main Causes: Less than 40 years old: vascular malformations and illicit drug use.
www.yassermetwally.com MANAGEMENT OF CEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE (ICH): A QUICK GUIDE Overview 10% of strokes is caused by ICH. Main Causes: Less than 40 years old: vascular malformations and illicit drug use.
UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY. Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center
 UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center DISCLOSURE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL INTEREST I, Vera Wilson,
UPDATE OF NEUROCRITICAL CARE PHARMACOTHERAPY Vera Wilson, PharmD, BCPS Emergency Services Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Johnson City Medical Center DISCLOSURE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL INTEREST I, Vera Wilson,
Treatment and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Treatment and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
Treatment and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
Hemorrhage. Dr. Al Jin Nov. 17, 2015
 Hemorrhage Dr. Al Jin Nov. 17, 2015 None Disclosures ICH Management in ER ABCs Treat hypertension What BP target? Reverse warfarin Hemorrhage vs Ischemic Stroke Lowering BP may be harmful in ischemic stroke
Hemorrhage Dr. Al Jin Nov. 17, 2015 None Disclosures ICH Management in ER ABCs Treat hypertension What BP target? Reverse warfarin Hemorrhage vs Ischemic Stroke Lowering BP may be harmful in ischemic stroke
Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH)
 Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Mindy Mason, MSN, RN, ACNP BC University of New Mexico Academic Medical Center Level I Trauma Center 24 bed Neuroscience ICU Albuquerque, NM 1 Objectives
Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Mindy Mason, MSN, RN, ACNP BC University of New Mexico Academic Medical Center Level I Trauma Center 24 bed Neuroscience ICU Albuquerque, NM 1 Objectives
Content 1. Relevance 2. Principles 3. Manangement
 Intracranial haemorrhage and anticoagulation Department of Neurology,, Germany Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Germany Department of Clinical Medicine Copenhagen University, Denmark
Intracranial haemorrhage and anticoagulation Department of Neurology,, Germany Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Germany Department of Clinical Medicine Copenhagen University, Denmark
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury
 Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
Update on Guidelines for Traumatic Brain Injury Current TBI Guidelines Shirley I. Stiver MD, PhD Department of Neurosurgery Guidelines for the management of traumatic brain injury Journal of Neurotrauma
NURSING DEPARTMENT CRITICAL CARE POLICY MANUAL CRITICAL CARE PROTOCOLS. ACUTE CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT TPA (ACTIVASE /alteplase) FOR THROMBOLYSIS
 NURSING DEPARTMENT CRITICAL CARE POLICY MANUAL CRITICAL CARE PROTOCOLS ACUTE CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT TPA (ACTIVASE /alteplase) FOR THROMBOLYSIS I. Purpose : A. To reduce morbidity and mortality associated
NURSING DEPARTMENT CRITICAL CARE POLICY MANUAL CRITICAL CARE PROTOCOLS ACUTE CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT TPA (ACTIVASE /alteplase) FOR THROMBOLYSIS I. Purpose : A. To reduce morbidity and mortality associated
Symptoms of small vessel strokes. Small Vessel stroke. What is this? Treatment. Large Vessel stroke 6/1/2018
 Stroke Stroke Megan Stevens MD Vascular Neurology SUDDEN Maximal at onset Lateralized weakness, lateralized numbness, vision loss (one eye or portion of field in both eyes), double vision, slurred speech,
Stroke Stroke Megan Stevens MD Vascular Neurology SUDDEN Maximal at onset Lateralized weakness, lateralized numbness, vision loss (one eye or portion of field in both eyes), double vision, slurred speech,
Traumatic Brain Injury
 Traumatic Brain Injury Mark J. Harris M.D. Associate Professor University of Utah Salt Lake City USA Overview In US HI responsible for 33% trauma deaths. Closed HI 80% Missile / Penetrating HI 20% Glasgow
Traumatic Brain Injury Mark J. Harris M.D. Associate Professor University of Utah Salt Lake City USA Overview In US HI responsible for 33% trauma deaths. Closed HI 80% Missile / Penetrating HI 20% Glasgow
Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery
 Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery 2 Stroke Stroke kills almost 130,000 Americans each year. - Third cause of all deaths in Arkansas. - Death Rate is highest in
Surgical Management of Stroke Brandon Evans, MD Department of Neurosurgery 2 Stroke Stroke kills almost 130,000 Americans each year. - Third cause of all deaths in Arkansas. - Death Rate is highest in
The Effect of Statin Therapy on Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage
 The Effect of Statin Therapy on Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage JENNIFER HANIFY, PHARM.D. PGY2 CRITICAL CARE RESIDENT UF HEALTH JACKSONVILLE JANUARY 23 RD 2016 Objectives Review benefits of statin therapy
The Effect of Statin Therapy on Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage JENNIFER HANIFY, PHARM.D. PGY2 CRITICAL CARE RESIDENT UF HEALTH JACKSONVILLE JANUARY 23 RD 2016 Objectives Review benefits of statin therapy
Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA
 Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA The traditional view: asah is a bad disease Pre-hospital mortality
Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA The traditional view: asah is a bad disease Pre-hospital mortality
Guidelines and Beyond: Traumatic Brain Injury
 Guidelines and Beyond: Traumatic Brain Injury Aimee Gowler, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Neuromedicine Critical Care Clinical Pharmacy Specialist UF Health Shands Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose.
Guidelines and Beyond: Traumatic Brain Injury Aimee Gowler, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Neuromedicine Critical Care Clinical Pharmacy Specialist UF Health Shands Disclosures I have no financial interests to disclose.
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Congenital Heart Disease and Critical Neurological Injury: Do Our Patients Belong in a Neurocritical Care Unit?
 Congenital Heart Disease and Critical Neurological Injury: Do Our Patients Belong in a Neurocritical Care Unit? Shriprasad R Deshpande, MBBS MS Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director, Mechanical
Congenital Heart Disease and Critical Neurological Injury: Do Our Patients Belong in a Neurocritical Care Unit? Shriprasad R Deshpande, MBBS MS Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director, Mechanical
Team Work in Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Diagnosis and Treatment in Acute Ischemic stroke July, 15 th 2016. Bach Mai Hospital Team Work in Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Prof. Pham Minh Thong 1 Time is brain Ischemic stroke: big global burden
Diagnosis and Treatment in Acute Ischemic stroke July, 15 th 2016. Bach Mai Hospital Team Work in Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Prof. Pham Minh Thong 1 Time is brain Ischemic stroke: big global burden
Hemorrhagic Stroke. Team Members: Nawaf Aldarwish, Rawan Alqahtani, Talal AlTukhaim, Fatima Altassan.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke Objectives: Introduction Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis and Imaging Treatment Team Members: Nawaf Aldarwish, Rawan Alqahtani, Talal AlTukhaim, Fatima Altassan.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Objectives: Introduction Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis and Imaging Treatment Team Members: Nawaf Aldarwish, Rawan Alqahtani, Talal AlTukhaim, Fatima Altassan.
Acute Medical Management. Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology
 Acute Medical Management Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology Outline Head-of-bed position Blood pressure management Antiplatelet therapy Anticoagulation Statin therapy Rehabilitation and
Acute Medical Management Bogachan Sahin, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology Outline Head-of-bed position Blood pressure management Antiplatelet therapy Anticoagulation Statin therapy Rehabilitation and
Updates from 2017 International Stroke Conferences
 Updates from 2017 International Stroke Conferences Ravi Menon, MD Swedish Neuroscience Institute May 11, 2017 Seattle, WA 1 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Clinical trial involvement: Former
Updates from 2017 International Stroke Conferences Ravi Menon, MD Swedish Neuroscience Institute May 11, 2017 Seattle, WA 1 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Clinical trial involvement: Former
4/10/2018. The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms. Aneurysm Locations. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Jerone Kennedy, M.D.
 The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Jerone Kennedy, M.D. Medical Director, Vascular Neurosurgery CentraCare Health-Neurosciences St. Cloud Hospital Aneurysm
The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Jerone Kennedy, M.D. Medical Director, Vascular Neurosurgery CentraCare Health-Neurosciences St. Cloud Hospital Aneurysm
Patients presenting with acute stroke while on DOACs
 Patients presenting with acute stroke while on DOACs Vemmos Kostas, MD, PhD Stroke Medicine Hellenic Cardiovascular Research Society Conflicts of interest Honoraria and speaker fees from: BAYER, SANOFI,
Patients presenting with acute stroke while on DOACs Vemmos Kostas, MD, PhD Stroke Medicine Hellenic Cardiovascular Research Society Conflicts of interest Honoraria and speaker fees from: BAYER, SANOFI,
8/29/2011. Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000. Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000
 Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
9/18/16. Management of Ischemic Stroke in the Intensive Care Unit. Outline. Introduction. Kyle B Walsh MD. Phases of Stroke Diagnosis and Treatment
 Management of Ischemic Stroke in the Intensive Care Unit Kyle B Walsh MD Assistant Professor - UC Dept of Emergency Medicine Fellow Physician - Neurocritical Care, Stroke, Research Outline Why ICU care
Management of Ischemic Stroke in the Intensive Care Unit Kyle B Walsh MD Assistant Professor - UC Dept of Emergency Medicine Fellow Physician - Neurocritical Care, Stroke, Research Outline Why ICU care
Introduction. Blood Pressure
 Introduction Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide [1]. Of a number of factors that have been linked to ICH (e.g., higher rates in Asians and
Introduction Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide [1]. Of a number of factors that have been linked to ICH (e.g., higher rates in Asians and
Required Annual Nursing Education Primary Stroke Center For ICU, Step-Down and Floor
 Required Annual Nursing Education Primary Stroke Center For ICU, Step-Down and Floor Lori Massaro, RN, MSN, CRNP Bethanne McCabe, RN, MSN, CNRN Sue Underwood, RN, MSN, CNRN Requirement RN s caring for
Required Annual Nursing Education Primary Stroke Center For ICU, Step-Down and Floor Lori Massaro, RN, MSN, CRNP Bethanne McCabe, RN, MSN, CNRN Sue Underwood, RN, MSN, CNRN Requirement RN s caring for
Shawke A. Soueidan, MD. Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists
 Shawke A. Soueidan, MD Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists 757-221-0110 Epidemiology of stroke 2018 Affects nearly 800,000 people in the US annually Approximately 600000 first-ever strokes and 185000
Shawke A. Soueidan, MD Riverside Neurology & Sleep Specialists 757-221-0110 Epidemiology of stroke 2018 Affects nearly 800,000 people in the US annually Approximately 600000 first-ever strokes and 185000
Traumatic Brain Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth. Objectives 11/7/2017
 Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
9/16/2018. Recognizing & Managing Seizures in Pediatric TBI. Objectives. Definitions and Epidemiology
 Recognizing & Managing Seizures in Pediatric TBI UW Medicine EMS & Trauma 2018 Conference September 17 and 18, 2018 Mark Wainwright MD PhD Herman and Faye Sarkowsky Professor of Neurology Division Head,
Recognizing & Managing Seizures in Pediatric TBI UW Medicine EMS & Trauma 2018 Conference September 17 and 18, 2018 Mark Wainwright MD PhD Herman and Faye Sarkowsky Professor of Neurology Division Head,
Review of the TICH-2 Trial
 Review of the TICH-2 Trial Mikaela Hofer, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds September 18, 2018 2018 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Review the pharmacologic options to limit hematoma expansion
Review of the TICH-2 Trial Mikaela Hofer, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds September 18, 2018 2018 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Review the pharmacologic options to limit hematoma expansion
Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs
 Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs Final Original Report May 2016 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs Final Original Report May 2016 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Giuseppe Micieli Dipartimento di Neurologia d Urgenza IRCCS Fondazione Istituto Neurologico Nazionale C Mondino, Pavia
 Giuseppe Micieli Dipartimento di Neurologia d Urgenza IRCCS Fondazione Istituto Neurologico Nazionale C Mondino, Pavia Charidimou et al, 2012 Pathogenesis of spontaneous and anticoagulationassociated
Giuseppe Micieli Dipartimento di Neurologia d Urgenza IRCCS Fondazione Istituto Neurologico Nazionale C Mondino, Pavia Charidimou et al, 2012 Pathogenesis of spontaneous and anticoagulationassociated
Stroke: What did we learn in the last year?
 Stroke: What did we learn in the last year? J. Claude Hemphill III, MD, MAS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology and Neurological Surgery University of California, San Francisco Director, Neurocritical
Stroke: What did we learn in the last year? J. Claude Hemphill III, MD, MAS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology and Neurological Surgery University of California, San Francisco Director, Neurocritical
Welcome to our Quarterly MISTIE III Safety Forum April 6, 2016
 Welcome to our Quarterly MISTIE III Safety Forum April 6, 2016 Agenda: Update from our Surgical Centers: Where we stand surgically Issam Awad, MD, University of Chicago Vascular Defect Screening in MISTIE
Welcome to our Quarterly MISTIE III Safety Forum April 6, 2016 Agenda: Update from our Surgical Centers: Where we stand surgically Issam Awad, MD, University of Chicago Vascular Defect Screening in MISTIE
Case 1 5/26/2017 ENDOVASCULAR MECHANICAL THROMBECTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 ENDOVASCULAR MECHANICAL THROMBECTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rhonda Whiteman Racing Against the Clock Workshop June 1, 2017 Objectives To discuss the hyperacute ischemic stroke management
ENDOVASCULAR MECHANICAL THROMBECTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rhonda Whiteman Racing Against the Clock Workshop June 1, 2017 Objectives To discuss the hyperacute ischemic stroke management
Outlook for intracerebral haemorrhage after a MISTIE spell
 Outlook for intracerebral haemorrhage after a MISTIE spell David J Werring PhD FRCP Stroke Research Centre, Department of Brain Repair and Rehabilitation, UCL Institute of Neurology, National Hospital
Outlook for intracerebral haemorrhage after a MISTIE spell David J Werring PhD FRCP Stroke Research Centre, Department of Brain Repair and Rehabilitation, UCL Institute of Neurology, National Hospital
Cerebral Autoregulation What s the Big Deal? Kathy Morrison MSN, RN, CNRN Gayle Watson MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN
 Cerebral Autoregulation What s the Big Deal? Kathy Morrison MSN, RN, CNRN Gayle Watson MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN Background 30% of patients have history of hypertension prior to stroke 80% will present with
Cerebral Autoregulation What s the Big Deal? Kathy Morrison MSN, RN, CNRN Gayle Watson MSN, RN, CCNS, CCRN Background 30% of patients have history of hypertension prior to stroke 80% will present with
The management of ICH when to operate when not to?
 The management of ICH when to operate when not to? ICH is a Bad Disease High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
The management of ICH when to operate when not to? ICH is a Bad Disease High Incidence o Accounts for 10-15% of all strokes 1,2,5 o 80,000 cases in US; 2 million WW 2,5 o Incidence doubles for African-
Operation Stroke. How to Reduce the Risk of Stroke Complications
 Operation Stroke How to Reduce the Risk of Stroke Complications Objectives Focus on Acute Stroke as an active disease Discuss the most common stroke complications Describe how first 72 hours sets the stage
Operation Stroke How to Reduce the Risk of Stroke Complications Objectives Focus on Acute Stroke as an active disease Discuss the most common stroke complications Describe how first 72 hours sets the stage
Developing, implementing and scaling up an acute care bundle for intracerebral haemorrhage in Greater Manchester
 Developing, implementing and scaling up an acute care bundle for intracerebral haemorrhage in Greater Manchester Adrian Parry-Jones NIHR Clinician Scientist & Honorary Consultant Neurologist Manchester
Developing, implementing and scaling up an acute care bundle for intracerebral haemorrhage in Greater Manchester Adrian Parry-Jones NIHR Clinician Scientist & Honorary Consultant Neurologist Manchester
Stroke in the Rural Setting: How You Can Make A Difference. Susie Fisher, RN, BSN Program Manager Providence Stroke Center Portland, OR
 Stroke in the Rural Setting: How You Can Make A Difference. Susie Fisher, RN, BSN Program Manager Providence Stroke Center Portland, OR Outline State Statistics The Oregon Problem Time & Treatments Steps
Stroke in the Rural Setting: How You Can Make A Difference. Susie Fisher, RN, BSN Program Manager Providence Stroke Center Portland, OR Outline State Statistics The Oregon Problem Time & Treatments Steps
5/15/2018. Reduced Platelet Activity
 ASSOCIATION OF DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE ON OUTCOMES IN ACUTE INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE IN PATIENTS ON ANTIPLATELET THERAPY Jessica McManus, Pharm. D. PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident UF Health Jacksonville
ASSOCIATION OF DESMOPRESSIN ACETATE ON OUTCOMES IN ACUTE INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE IN PATIENTS ON ANTIPLATELET THERAPY Jessica McManus, Pharm. D. PGY2 Critical Care Pharmacy Resident UF Health Jacksonville
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
Review Clinical review: Critical care management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage Fred Rincon 1 and Stephan A Mayer 2
 Review Clinical review: Critical care management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage Fred Rincon 1 and Stephan A Mayer 2 1 Department of Medicine, Cooper University Hospital, The Robert Wood Johnson
Review Clinical review: Critical care management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage Fred Rincon 1 and Stephan A Mayer 2 1 Department of Medicine, Cooper University Hospital, The Robert Wood Johnson
Tyler Carson D.O., Vladamir Cortez D.O., Dan E. Miulli D.O.
 Bedside Intracranial Hematoma Evacuation and Intraparenchymal Drain Placement for Spontaneous Intracranial Hematoma Larger than 30 cc in Volume: Institutional Experience and Patient Outcomes Tyler Carson
Bedside Intracranial Hematoma Evacuation and Intraparenchymal Drain Placement for Spontaneous Intracranial Hematoma Larger than 30 cc in Volume: Institutional Experience and Patient Outcomes Tyler Carson
Incidence and Impact of Antithrombotic-related Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Incidence and Impact of Antithrombotic-related Intracerebral Hemorrhage John J. Lewin III, PharmD, MBA, BCCCP, FASHP, FCCM, FNCS Division Director, Critical Care & Surgery Pharmacy Services, The Johns
Incidence and Impact of Antithrombotic-related Intracerebral Hemorrhage John J. Lewin III, PharmD, MBA, BCCCP, FASHP, FCCM, FNCS Division Director, Critical Care & Surgery Pharmacy Services, The Johns
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 ANTICOAGULATION & INTRACRANIAL BLEEDS - MANAGEMENT OF THE ANTICOAGULATED PATIENT PRESENTING WITH INTRACRANIAL HAEMORRHAGE ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 82 12 th January 2008 Rebecca Appelboam, Exeter,
ANTICOAGULATION & INTRACRANIAL BLEEDS - MANAGEMENT OF THE ANTICOAGULATED PATIENT PRESENTING WITH INTRACRANIAL HAEMORRHAGE ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 82 12 th January 2008 Rebecca Appelboam, Exeter,
Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand
 Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand Evidence Pathophysiology Why? Management Non-degenerative, Non-congenital insult
Any closer to evidence based practice? Asma Salloo Chris Hani Baragwantah Academic Hospital University of Witwatersrand Evidence Pathophysiology Why? Management Non-degenerative, Non-congenital insult
Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK
 Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK Overview Haemostatic resuscitation Massive Transfusion Protocol Overview of NBA research guidelines Haemostatic resuscitation Permissive hypotension
Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK Overview Haemostatic resuscitation Massive Transfusion Protocol Overview of NBA research guidelines Haemostatic resuscitation Permissive hypotension
NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE BOARD REVIEW
 NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE BOARD REVIEW Deborah M. Stein, MD, MPH, FACS, FCCM Associate Professor of Surgery University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland 2013 Clinical
NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE BOARD REVIEW Deborah M. Stein, MD, MPH, FACS, FCCM Associate Professor of Surgery University of Maryland School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland 2013 Clinical
Head injuries. Severity of head injuries
 Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS
 Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
Michael Avant, M.D. The Children s Hospital of GHS OVERVIEW ER to ICU Transition Early Management Priorities the First 48 hours Organ System Support Complications THE FIRST 48 HOURS Communication Damage
Stroke: The First Critical Hour. Alina Candal, RN, PCC, MICN Kevin Andruss, MD, FACEP
 Stroke: The First Critical Hour Alina Candal, RN, PCC, MICN Kevin Andruss, MD, FACEP Disclosures We have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this presentation. Objectives Discuss
Stroke: The First Critical Hour Alina Candal, RN, PCC, MICN Kevin Andruss, MD, FACEP Disclosures We have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this presentation. Objectives Discuss
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
