Imaging of acute cholecystitis and cholecystitisassociated complications in the emergency setting
|
|
|
- Harry Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(8): doi: /smedj CMEArticle Imaging of acute and associated complications in the emergency setting Ashish Chawla 1, DABR, Jerome Irai Bosco 1, MD, Tze Chwan Lim 1, FRCR, Sivasubramanian Srinivasan 1, FRCR, Hui Seong Teh 1, FRCR, Jagadish Narayana Shenoy 1, FRCR, FRANZCR ABSTRACT Acute is a common cause of right upper quadrant pain in patients presenting at the emergency department. Early diagnosis and recognition of associated complications, though challenging, are essential for timely management. Imaging studies, including ultrasonography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, are increasingly utilised for the evaluation of suspected cases of. These investigations help in diagnosis, identification of complications and surgical planning. Imaging features of acute have been described in the literature and are variable, depending on the stage of inflammation. This article discusses the spectrum of associated complications and their imaging manifestations. We also suggest a checklist for the prompt and accurate identification of complications in acute. Keywords:, CT, emphysematous, gallstone ileus, Mirizzi syndrome INTRODUCTION Acute is an acute inflammatory condition of the gallbladder; 95% of cases of acute are due to an obstructing calculus in the gallbladder neck or cystic duct. (1) Obstruction of the cystic duct results in an overdistension of the gallbladder and a rise in intraluminal pressure. This increased pressure, along with cholesterol-supersaturated bile, triggers an acute inflammatory response. Gallstones contribute to the inflammatory response by stimulating prostaglandins I 2 and E 2. (2) Secondary bacterial infection is present in 20% of cases of acute. Mural ischaemia resulting from the increased intraluminal pressure may also contribute to complications such as gangrenous and perforation. (3) Pathologically, there are three stages of inflammatory disease: (a) oedematous ; (b) necrotising ; and (c) suppurative. (1) Due to the wide availability of computed tomography (CT) scanners in emergency departments, increasing numbers of patients undergo CT examinations for suspected acute. Ultrasonography (US) remains the preferred initial imaging modality for the evaluation of suspected acute calculous due to its relatively low cost, easy accessibility, short examination duration and lack of ionising radiation (Fig. 1). (4) The distinct advantages of US over other imaging techniques are its high sensitivity and specificity in detecting gallstones, and its ability to elicit Murphy s sign using the ultrasound transducer. (4,5) However, US has limited value in the evaluation of underlying complications of acute. Evaluation of such complications may require cross-sectional imaging techniques, namely CT or magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, for accurate localisation and surgical planning. CT and MR imaging can also be used to evaluate or exclude other pathologies that can present with right upper quadrant pain. CT OF ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS AND ASSOCIATED COMPLICATIONS CT features of uncomplicated acute include a combination of overdistended gallbladder, mural thickening, mural enhancement, pericholecystic fat stranding and pericholecystic fluid. (6,7) Characteristically, there is an enhancement rim in the adjacent liver. (8) Classically, a calculus can be seen impacted in the gallbladder neck or cystic duct (Fig. 2). It is well known that CT has a relatively low sensitivity in detecting gallstones due to the variable composition of the stones. Even larger isodense gallstones may not be visible on CT. (9) US is more sensitive in detecting cholelithiasis and is useful in identifying the offending gallstone in some cases. Gallbladder mural thickening is the most common but the least specific finding and may be seen in a variety of other conditions, such as hepatitis, hypoproteinaemia, heart failure and acute pyelonephritis. (6,10,11) Gangrenous results from the downhill course of an episode of acute and occurs in up to 39% of patients with acute calculous. (12) It is associated with higher morbidity and mortality rates than uncomplicated acute. Elderly patients, and patients with a history of diabetes mellitus and white blood cell count > 15,000 cells/ml are at an increased risk of having gangrenous changes at presentation. (12) In addition to the typical imaging features of, CT findings of poorly enhancing walls, intraluminal membranes, striated and reduced mural enhancement, focal mural defects and pericholecystic abscesses have been described in cases of gangrenous, with specificity close to 90% (Figs. 3 & 4). (13) Based on our experience, it is important to evaluate the gallbladder wall for any presence of a focal bulge, which usually corresponds pathologically to a mural abscess (Fig. 5). If left untreated, these abscesses may increase in size and number, eventually resulting in a perforated gallbladder 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore Correspondence: Dr Ashish Chawla, Consultant, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, 90 Yishun Central, Singapore ashchawla@gmail.com 438
2 Pictorial Essay 1a 1b Fig. 1 Oblique coronal US images show (a) a normal gallbladder (GB); and (b) a thickened GB wall and thin layer of pericholecystic fluid (arrowhead), with an impacted calculus in the neck of the GB (arrow) in a patient with acute. LI: liver 2a 4a 2b Fig. 2 CT images of classical acute calculous show (a) a thickened enhancing gallbladder wall, pericholecystic fat stranding (white arrow) and reactive hyperaemia in the adjacent liver (black arrow) in the axial plane; and (b) a large calculus in the neck of the gallbladder (white arrow) and reactive hyperaemia (black arrow) in the adjacent liver in the coronal plane. 5a Fig. 3 Axial CT image of acute gangrenous shows thickened walls and focal defects (black arrow) in an enhancing mucosa with hyperdense sloughed mucosa floating in the dependent gallbladder (white arrow). Note the sunburst pattern of pericholecystic fat stranding. 5b 4b Fig. 4 Axial CT images of acute gangrenous show (a) a poorly enhancing gallbladder wall (black arrows) and a striated appearance of the medial wall (white arrow); and (b) poorly enhancing walls (black arrow) and a calculus (white arrow) impacted in the neck of the gallbladder. Note the presence of a few other gallstones. 5c Fig. 5 Evolving gangrenous in a 34-year-old man presenting with right hypochondrial pain. (a) Axial CT image on the day of presentation shows poor enhancement of the gallbladder wall (black arrow). No gallstone or definite cholecystic fat stranding was identified, and the patient was kept on conservative management. (b) Axial CT image on Day 3 shows a poorly enhancing wall (black arrow) and pericholecystic fat stranding (white arrow). (c) Axial CT image on Day 10 shows intramural abscesses (white arrows), a sign of gangrenous. The patient underwent urgent cholecystectomy, which confirmed gangrenous with mucosal ulcers and mural abscesses. (Fig. 6). The presence of a focal mural defect that is contiguous with pericholecystic fluid is an ominous sign and suggests perforation in the gallbladder, which can result in pericholecystic abscess, intrahepatic abscess (Fig. 7) or peritonitis, depending on the site of perforation.(14) A rapid increase in the amount of pericholecystic fluid, demonstrated in serial examinations (CT or US), is a reliable clue for diagnosing a perforated gallbladder (Fig. 8). 439 Emphysematous refers to the presence of gas in the gallbladder wall and is secondary to infections by gasforming organisms such as Clostridium welchi. Patients with diabetes mellitus are at a greater risk of developing this condition and may present initially with relatively milder symptoms. Plain radiography often shows the gallbladder wall being outlined by radiolucent gas (Fig. 9). CT is confirmatory, showing features of
3 Pictorial Essay 6a 6c 6b Fig. 6 Evolving gangrenous in a 55-year-old woman. (a) Axial CT image on the day of presentation shows pericholecystic inflammation and fluid with a focal bulge in the gallbladder wall (arrow). (b) CT image after one week of conservative treatment shows an increase in the size and number of bulges (arrows). (c) Axial T2-HASTE MR image one day after the second CT shows a further increase in the number of bulges (arrows). Laparotomy findings confirmed gangrenous with extensive inflammation around the gallbladder. Histopathological examination confirmed that these bulges corresponded to mucosal ulcers with mural abscesses. 8a Fig. 7 Intrahepatic perforation of the gallbladder. Axial CT image depicts a large hepatic abscess (white arrow) with air pockets. Outline of the neck of the gallbladder is identified (black arrow), but the rest of the gallbladder is not seen as separate from the abscess. 9a 8b Fig. 8 Perforated in a 70-year-old woman presenting with abdominal pain at the emergency department. (a) Axial CT image shows a poorly enhancing gallbladder wall (black arrow), with pericholecystic fat stranding and minimal fluid (white arrow). (b) CT image after two days, due to worsening symptoms, shows a wall defect in the fundus of the gallbladder (white arrow) with a significant increase in perihepatic fluid (black arrow). 9b 10a Fig. 9 Emphysematous. (a) Supine abdomen radiograph shows a pear-shaped curvilinear lucent line (white arrow) in the right upper quadrant with two radiopacities (black arrow) within it. (b) Axial CT image shows gas within the wall (white arrow) and in the lumen of the gallbladder. There is an impacted calculus in the gallbladder neck (black arrow). along with intramural gas. The progression to perforated is more frequently seen in emphysematous than in uncomplicated. Mirizzi syndrome results from an impacted gallstone in the gallbladder neck or cystic duct that causes extrinsic compression of the common hepatic duct. The result is biliary obstruction with dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts. A cholecystocholedochal fistula may form due to recurrent inflammation around the impacted gallstone in the cystic duct. Patients with this condition often present with abdominal pain, (15) 10b Fig. 10 Mirizzi syndrome in a 42-year-old woman presenting at the emergency department with fever and abdominal pain. (a) Coronal CT image shows a bulbous expansion of the neck of the gallbladder, due to a radiolucent calculus compressing the proximal hepatic duct (black arrow), with resultant dilatation of the central intrahepatic ducts (white arrow) but a normal distal duct. (b) Coronal MRCP image shows a large gallstone (arrow) compressing the proximal hepatic duct, with dilatation of the central intrahepatic ducts (arrowhead). fever and jaundice, without any pathognomonic pattern, which therefore makes clinical diagnosis difficult.(16) Preoperative diagnosis of Mirizzi syndrome is essential in planning surgeries, in view of the possibility of open cholecystectomy. CT can show 440
4 11a 11b 11c Fig. 11 Gallstone ileus in a 39-year-old man presenting at the emergency department with features of subacute bowel obstruction. (a) Supine abdominal radiograph shows dilatation of small bowel loops in the central abdomen. (b) Axial CT image shows a contracted gallbladder with a thickened wall (black arrow), with air in its lumen (white arrow). The gallbladder is inseparable from the first part of duodenum (arrowhead), and the duodenal wall is oedematous. (c) Coronal oblique CT image shows small bowel dilatation with a large peripherally calcified gallstone in the distal ileum (white arrow). The ileum distal to the gallstone is collapsed. Note the contracted, air-containing gallbladder (black arrow) abutting the proximal duodenum (arrowhead). Fig. 12 Acute with cholecystoenteric fistula. Coronal oblique CT image shows a contracted gallbladder (arrowhead) with pericholecystic fluid and inflammation with pneumobilia (white arrow), abutting an oedematous proximal duodenum (black arrow). Laparotomy confirmed a fistulous communication between the gallbladder and the first part of the duodenum. the dilated intrahepatic bile ducts with the common bile duct of normal calibre (Fig. 10). (17) MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) provides more information about the exact location and cause of the obstruction. (18) Gallstone ileus is a rare complication associated with a subclinical or milder episode of. Instead of right upper quadrant pain, the patient presents at the emergency department with signs and symptoms of bowel obstruction. (19) Intestinal obstruction is the outcome of an impacted ectopic gallstone, usually in the distal ileum. These gallstones are usually larger than 2.5 cm and enter the gastrointestinal tract via a fistulous communication between the gallbladder and duodenum or, in rare occasions, between the gallbladder and stomach. (20) Smaller gallstones may pass through the bowel loops asymptomatically without causing obstructions. CT, which can show Rigler s triad (small bowel obstruction, ectopic gallstone at point of transition and pneumobilia), is useful for accurate diagnosis of gallstone ileus. (21) Based on our experience, the absence of pneumobilia with equivocal features of gallbladder inflammation can be misleading for the radiologist. In such cases, the typical appearance of gallstones in the dilated small bowel proximal to the transition point provides a clue for diagnosing gallstone ileus (Fig. 11). The presence of an obstructing gallstone should prompt a search for more stones with similar morphology within the gallbladder lumen as well as in the upstream dilated small bowel. Bouveret s syndrome is a rare condition that results from impaction of a discharged gallstone in the gastroduodenal junction, leading to gastric outlet obstruction. (22) CT allows direct visualisation of the biliary-enteric fistula in 12.5% of patients with gallstone ileus. (20) Cholecystoenteric fistulas can develop in the setting of acute without a small bowel obstruction or ectopic gallstone. They can also develop due to trauma, peptic ulcer disease, inflammatory bowel disease and malignancy of the bowel and gallbladder. (23) It has been postulated that recurrent leads to adhesions between the gallbladder and bowel, with subsequent fistula formation. (24) Diagnosis of cholecystoenteric fistulas is important for surgeons but difficult for radiologists, particularly in the presence of a contracted gallbladder. We recommend that in the presence of unexplained pneumobilia, the relationship of the gallbladder with respect to the adjacent bowel should be evaluated. In demonstrating fistulas, multiplanar reconstructions are more helpful than conventional axial imaging (Fig. 12). We have summarised the CT findings in various complications associated with acute (Table I). We also recommend a quick checklist that can be helpful in quick and accurate identification of complications (Table II). CONCLUSION Patients with acute, as well as those with associated complications, present at the emergency department with nonspecific symptoms, such as pain in the right upper quadrant. 441
5 Table I. Summary of computed tomography findings in acute and associated complications. Diagnosis Acute calculus Gangrenous Emphysematous Perforated Gallstone ileus Cholecystoenteric fistula Mirizzi syndrome Computed tomography findings Gallstone in the gallbladder neck or cystic duct, thickened ( 0.3 cm) and enhancing wall, pericholecystic fat stranding with or without pericholecystic fluid, reactive enhancement in the adjacent liver Nonenhancing wall, sloughed membranes, mural striation, irregular enhancing wall with defect, with or without gallstone, pericholecystic fat stranding and fluid (more than that seen in uncomplicated ) Similar findings to acute, with presence of gas in the gallbladder wall (intraluminal gas can be due to fistula formation or other causes of pneumobilia) Similar findings to acute, with focal defect in the gallbladder wall, contiguous pericholecystic fluid or hepatic abscess Small bowel obstruction with gallstone(s) at the point of transition, cholelithiasis (with varying degrees of inflammatory changes around the gallbladder), possible presence of intraluminal gas in the gallbladder and pneumobilia Cholelithiasis (with varying degrees of inflammatory changes around the gallbladder), contracted gallbladder with luminal gas, a loop of bowel inseparable from the gallbladder wall Dilated intrahepatic bile ducts with the common bile duct of normal calibre, large gallstone at the gallbladder neck or cystic duct with varying degrees of inflammatory changes around the gallbladder Table II. Checklist for identification of complications from. Gallbladder wall Thickness Enhancement Continuity Irregularity of wall Gas Gallbladder lumen Gallstone Gas High density fluid Sloughed mucosa Pericholecystic space Fat stranding Fluid Abscess Liver, peritoneal cavity and bowel Reactive hyperaemia in adjacent liver Liver abscess Peritoneal collection Dilated small bowel 0.3 cm is considered thickened Poor enhancement or irregular enhancement Focal wall defect suggests gangrenous ; focal defect with contiguous pericholecystic fluid suggests perforated Irregularity is a sign of acute Intramural gas is a sign of emphysematous Usually at the gallbladder neck Cholecystoenteric fistula with or without ileus Haemorrhagic fluid from gangrenous or gallbladder empyema Considered as a specific sign of gangrenous Hallmark of gallbladder inflammation Small amount is usually present in uncomplicated acute ; large amount is a red flag for gangrenous or perforated Pericholecystic abscess suggests gangrenous or perforated Sign of inflammation of the gallbladder (almost always seen) Small to huge, secondary to gallbladder perforation Large collection suggests perforated Presence suggests gallstone ileus The severity of clinical presentation may not be representative of the underlying complications. Cross-sectional imaging is critical in identifying the complications associated with acute. Familiarity with the spectrum of relevant imaging features, as presented here, is imperative for the emergency radiology team. REFERENCES 1. Kimura Y, Takada T, Kawarada Y, et al. Definitions, pathophysiology, and epidemiology of acute cholangitis and : Tokyo Guidelines. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2007; 14: Indar AA, Beckingham IJ. Acute. BMJ 2002; 325: Byrne JJ, Berger RL. The pathogenesis of acute. Arch Surg 1960; 81: Pinto A, Reginelli A, Cagini L, et al. Accuracy of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute calculous : review of the literature. Crit Ultrasound J 2013; 5:S Ralls PW, Colletti PM, Lapin SA, et al. Real-time sonography in suspected acute. Prospective evaluation of primary and secondary signs. Radiology 1985; 155: Fidler J, Paulson EK, Layfield L. CT evaluation of acute : findings and usefulness in diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 166: Paulson EK. Acute : CT findings. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2000; 21: Yamashita K, Jin MJ, Hirose Y, et al. CT finding of transient focal increased attenuation of the liver adjacent to the gallbladder in acute. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995; 164: Barakos JA, Ralls PW, Lapin SA, et al. Cholelithiasis: evaluation with CT. Radiology 1987; 162: Van Breda Vriesman AC, Engelbrecht MR, Smithuis RH, Puylaert JB. Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening: differential diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007; 188: Zissin R, Osadchy A, Gayer G, Kitay-Cohen Y. Extrarenal manifestations of severe acute pyelonephritis: CT findings in 21 cases. Emerg Radiol 2006; 13: Fagan SP, Awad SS, Rahwan K, et al. Prognostic factors for the development 442
6 of gangrenous. Am J Surg 2003; 186: Bennett GL, Rusinek H, Lisi V, et al. CT findings in acute gangrenous. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002; 178: Morris BS, Balpande PR, Morani AC, et al. The CT appearances of gallbladder perforation. Br J Radiol 2007; 80: Sunnapwar A, Raut AA, Nagar AM, Katre R. Emphysematous : Imaging findings in nine patients. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2011; 21: Safioleas M, Stamatakos M, Safioleas P, et al. Mirizzi Syndrome: an unexpected problem of cholelithiasis. Our experience with 27 cases. Int Semin Surg Oncol 2008; 5: Berland LL, Lawson TL, Stanley RJ. CT appearance of Mirizzi syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984; 8: Choi BW, Kim MJ, Chung JJ, et al. Radiologic findings of Mirizzi syndrome with emphasis on MRI. Yonsei Med J 2000; 41: Masannat Y, Massanat Y, Shatnawei A. Gallstone ileus: a review. Mt Sinai J Med 2006; 73: Lassandro F, Romano S, Ragozzino A, et al. Role of helical CT in diagnosis of gallstone ileus and related conditions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005; 185: Rigler LG, Borman CN, Noble JF. Gallstone obstruction. Pathogenesis and roentgen manifestations. JAMA 1941; 117: Pickhardt PJ, Friedland JA, Hruza DS, Fisher AJ. Case report. CT, MR cholangiopancreatography, and endoscopy findings in Bouveret s syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003; 180(4): LeBlanc KA, Barr LH, Rush BM. Spontaneous biliary enteric fistulas. South Med J 1983; 76: Stull JR, Thomford NR. Biliary intestinal fistula. Am J Surg 1970; 120:
7 SINGAPORE MEDICAL COUNCIL CATEGORY 3B CME PROGRAMME (Code SMJ B) Question 1. The following have gallbladder wall thickening as an imaging feature: (a) Acute. (b) Hypoproteinaemia. (c) Hepatitis. (d) Ascites. Question 2. The following indicate an increased risk of developing gangrenous : (a) Elderly patients. (b) Diabetes mellitus. (c) White blood cell count > 15,000 cells/ml. (d) Chronic anaemia. Question 3. The following computed tomography (CT) features suggest gangrenous : (a) Poorly enhancing gallbladder wall. (b) Curvilinear membranes in the gallbladder lumen. (c) Intramural abscesses. (d) Pericholecystic fat stranding. Question 4. The following CT features suggest Mirizzi syndrome: (a) Dilated intrahepatic ducts with nondilated common bile duct. (b) Dilated common bile duct and normal intrahepatic ducts. (c) Dilated pancreatic duct and common bile duct. (d) Dilated intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. Question 5. Regarding gallstone ileus: (a) Patients present with gastric outlet obstruction. (b) Offending gallstones are usually less than 2 cm. (c) Rigler s triad can be seen on CT. (d) Obstruction is usually at the level of the distal jejunum. True False Doctor s particulars: Name in full : MCR number : Specialty: address : SUBMISSION INSTRUCTIONS: (1) Log on at the SMJ website: and select the appropriate set of questions. (2) Provide your name, address and MCR number. (3) Select your answers and click Submit. RESULTS: (1) Answers will be published in the SMJ October 2015 issue. (2) The MCR numbers of successful candidates will be posted online at the SMJ website by 2 October (3) Passing mark is 60%. No mark will be deducted for incorrect answers. (4) The SMJ editorial office will submit the list of successful candidates to the Singapore Medical Council. (5) One CME point is awarded for successful candidates. Deadline for submission: (August 2015 SMJ 3B CME programme): 12 noon, 25 September
Case Cholecystoduodenal fistula with migrated gallstone leading to gastric outlet obstruction: Bouveret's syndrome
 Case 14613 Cholecystoduodenal fistula with migrated gallstone leading to gastric outlet obstruction: Bouveret's syndrome Eva De Backer 1, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4, Adelard De Backer5 1: Ghent University,
Case 14613 Cholecystoduodenal fistula with migrated gallstone leading to gastric outlet obstruction: Bouveret's syndrome Eva De Backer 1, Filip Vanhoenacker 2, 3, 4, Adelard De Backer5 1: Ghent University,
Evolving Gallstone Ileus. SUNY Downstate Case Conference January 12, 2012
 Evolving Gallstone Ileus SUNY Downstate Case Conference January 12, 2012 Initial Presentation HPI: 90 yo F c 1wk h/o abdominal pain and N/V. Denied F/C. Passing flatus/bm. PMH: DM, HTN, CAD. PSH: C-sections
Evolving Gallstone Ileus SUNY Downstate Case Conference January 12, 2012 Initial Presentation HPI: 90 yo F c 1wk h/o abdominal pain and N/V. Denied F/C. Passing flatus/bm. PMH: DM, HTN, CAD. PSH: C-sections
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center.
 Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma
 Saurabh et al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma Shireesh Saurabh, Andrew Camerota, Jeffrey Zavotsky ABSTRACT Introduction: Gallstone ileus is a rare complication
Saurabh et al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma Shireesh Saurabh, Andrew Camerota, Jeffrey Zavotsky ABSTRACT Introduction: Gallstone ileus is a rare complication
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Gallstone Ileus: Diagnostic and Surgical Dilemma
 Original Article Elmer Press Gallstone Ileus: Diagnostic and Surgical Dilemma Vincenzo Leone Abstract Background: The typical patient with Gallstone ileus is female, elderly, with concomitant medical diseases
Original Article Elmer Press Gallstone Ileus: Diagnostic and Surgical Dilemma Vincenzo Leone Abstract Background: The typical patient with Gallstone ileus is female, elderly, with concomitant medical diseases
CT Findings of Acute Cholecystitis and Its Complications
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Shakespear et al. CT of cute Cholecystitis Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.29 on 01/20/18 from IP address
Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Shakespear et al. CT of cute Cholecystitis Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.29 on 01/20/18 from IP address
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Sonography of Gall Bladder
 Sonography of Gall Bladder Vikram Dogra,MD Professor of Radiology, Urology and BME Director of Ultrasound Associate Chair of Education and Research University of Rochester, NY Objectives Describe the Congenital
Sonography of Gall Bladder Vikram Dogra,MD Professor of Radiology, Urology and BME Director of Ultrasound Associate Chair of Education and Research University of Rochester, NY Objectives Describe the Congenital
Imaging findings of acute and chronic cholecystitis
 Imaging findings of acute and chronic cholecystitis Award: I-MED Best Emergency Radiology Scientific Exhibit Prize Poster No.: R-0010 Congress: 2017 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lim, C. Hewavitharana;
Imaging findings of acute and chronic cholecystitis Award: I-MED Best Emergency Radiology Scientific Exhibit Prize Poster No.: R-0010 Congress: 2017 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lim, C. Hewavitharana;
X-ray Corner. Imaging of the Small Bowel. Pantongrag-Brown L. Case 1. A 63-year-old man presented with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
 THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Key points about gallstone ileus that all resident doctors should know
 Key points about gallstone ileus that all resident doctors should know Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. Martínez Fernández 1, L. Hernandez Munoz
Key points about gallstone ileus that all resident doctors should know Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. Martínez Fernández 1, L. Hernandez Munoz
Gallbladder perforation - radiological aspects, types and causes, ultrasound and CT findings
 Gallbladder perforation - radiological aspects, types and causes, ultrasound and CT findings Poster No.: C-1905 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Urban, M. Djosev, T. Nastasic, B.
Gallbladder perforation - radiological aspects, types and causes, ultrasound and CT findings Poster No.: C-1905 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Urban, M. Djosev, T. Nastasic, B.
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno. Objectives. Why?
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Abdominal Imaging. Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings
 Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Emergencies of the Biliary Tract
 Emergencies of the Biliary Tract Caterina Missiroli, Mohammad Mansouri, and Ajay Singh 2 Introduction Gallstones are seen in 10 15% of the population, most commonly in middle-aged and elderly females.
Emergencies of the Biliary Tract Caterina Missiroli, Mohammad Mansouri, and Ajay Singh 2 Introduction Gallstones are seen in 10 15% of the population, most commonly in middle-aged and elderly females.
Diffuse Gallbladder Wall Thickening: Differential Diagnosis
 van reda Vriesman et al. Diffuse Gallbladder Wall Thickening Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay driaan C. van reda Vriesman 1 Marc R. Engelbrecht 2 Robin H. M. Smithuis 1 Julien. C. M. Puylaert 3 van
van reda Vriesman et al. Diffuse Gallbladder Wall Thickening Hepatobiliary Imaging Pictorial Essay driaan C. van reda Vriesman 1 Marc R. Engelbrecht 2 Robin H. M. Smithuis 1 Julien. C. M. Puylaert 3 van
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis
 INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
Gallstone Ileus A single center case series
 CASE SERIES Ferreira et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Gallstone Ileus A single center case series Manuel Alexandre Viana Ferreira, Diogo Pinto, Francisco Fazeres, Alberto Midões ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES Ferreira et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Gallstone Ileus A single center case series Manuel Alexandre Viana Ferreira, Diogo Pinto, Francisco Fazeres, Alberto Midões ABSTRACT Introduction:
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen
 CASE SERIES Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen Gupta MK 1, Ahmad K 1, Kumar A 1, Santhalia PK 1, Joshi BR 2, Rauniyar RK 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, 2 Department
CASE SERIES Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen Gupta MK 1, Ahmad K 1, Kumar A 1, Santhalia PK 1, Joshi BR 2, Rauniyar RK 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, 2 Department
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI)
 www.edoriumjournals.com clinical images PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Is it just another case of acute uncomplicated cholecystitis? A case of emphysematous cholecystitis an uncommon complication and associated
www.edoriumjournals.com clinical images PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Is it just another case of acute uncomplicated cholecystitis? A case of emphysematous cholecystitis an uncommon complication and associated
Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous.
 Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous. Anatomy of the gallbladder The gallbladder, a pear-shaped reservoir
Cholecystitis is defined as nonspecific inflammation of the gallbladder with or without cholelithiasis. Types: calculous and acalculous. Anatomy of the gallbladder The gallbladder, a pear-shaped reservoir
CT evaluation of gastrointestinal tract perforation by ingested fish bone.
 CT evaluation of gastrointestinal tract perforation by ingested fish bone. Poster No.: C-0875 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. B. Sanabria, R. Muñoz Carrasco, J. Escribano Fernández,
CT evaluation of gastrointestinal tract perforation by ingested fish bone. Poster No.: C-0875 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. B. Sanabria, R. Muñoz Carrasco, J. Escribano Fernández,
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento
 Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S
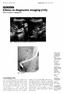 Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (4) : 361 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S fit. B CD - -0 o -5 r t -10 Fig. I US images of the upper right abdomen
Medical Education Singapore Med.1 2007, 48 (4) : 361 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (115) Wai C T, Seto K Y, Sutedja D S fit. B CD - -0 o -5 r t -10 Fig. I US images of the upper right abdomen
Imaging iconography of gallbladder cancer. Assessment by CT.
 1 REVISTA DE IMAGENOLOGIA- EII / Vol. XVI / Num. 2 Imaging iconography of gallbladder cancer. Assessment by CT. Doctors Crisci, Alejandro (1); Landó, Fernando.(2). CASMU CT Department Hospital of Tacuarembó
1 REVISTA DE IMAGENOLOGIA- EII / Vol. XVI / Num. 2 Imaging iconography of gallbladder cancer. Assessment by CT. Doctors Crisci, Alejandro (1); Landó, Fernando.(2). CASMU CT Department Hospital of Tacuarembó
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Radiological findings of gallstone ileus
 Radiological findings of gallstone ileus Poster No.: C-1623 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit C. BORREGO GONZALEZ, R. Muñoz Carrasco, M. E. Pérez Montilla, J. Escribano
Radiological findings of gallstone ileus Poster No.: C-1623 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit C. BORREGO GONZALEZ, R. Muñoz Carrasco, M. E. Pérez Montilla, J. Escribano
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Clearing the mind before the "caliber change": Diagnostic algorithm for small bowel obstruction.
 Clearing the mind before the "caliber change": Diagnostic algorithm for small bowel obstruction. Poster No.: C-0255 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, D. Oquillas Izquierdo,
Clearing the mind before the "caliber change": Diagnostic algorithm for small bowel obstruction. Poster No.: C-0255 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Santos Montón, D. Oquillas Izquierdo,
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction
 Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Abdominal extra-luminal gas - Is it always gastrointestinal perforation?
 Abdominal extra-luminal gas - Is it always gastrointestinal perforation? Poster No.: C-2526 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, I. Abreu, F. Caseiro Alves;
Abdominal extra-luminal gas - Is it always gastrointestinal perforation? Poster No.: C-2526 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barros, L. A. Ferreira, I. Abreu, F. Caseiro Alves;
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Imaging Features of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Ti et al. Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in CPD Patients Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Joanna P. Ti 1 li l-radi 2 Peter J. Conlon 2 Michael J. Lee 1 Martina
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
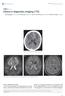 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
... Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment.
 Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Definition Inflammatory disorder of the colon that occurs as a complication of antibiotic treatment. " Epidemiology Humans represent the main reservoir of Clostridium difficile, which is not part of the
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction
 Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK, Leeds/UK
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK, Leeds/UK
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165)
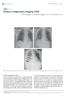 Singapore Med J 2016; 57(2): 92-96 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016033 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165) Wan Ying Chan 1, MBBS, Hsueh Wen Cheong 1, MBBS, FRCR, Tien Jin Tan 1, MBBS, FRCR 1a 1b 1c
Singapore Med J 2016; 57(2): 92-96 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016033 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (165) Wan Ying Chan 1, MBBS, Hsueh Wen Cheong 1, MBBS, FRCR, Tien Jin Tan 1, MBBS, FRCR 1a 1b 1c
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases
 Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
MDCT Features of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Induced Visceral Angioedema
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Vallurupalli and Coakley MDCT of Visceral ngioedema Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Kalyani Vallurupalli 1 Kevin J. Coakley 2 Vallurupalli K, Coakley KJ
Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Vallurupalli and Coakley MDCT of Visceral ngioedema Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay Kalyani Vallurupalli 1 Kevin J. Coakley 2 Vallurupalli K, Coakley KJ
The Radiologic Features of Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis: An Important Mimic of Gallbladder Carcinoma
 The Radiologic Features of Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis: An Important Mimic of Gallbladder Carcinoma Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit H. L. khosa
The Radiologic Features of Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis: An Important Mimic of Gallbladder Carcinoma Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit H. L. khosa
Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report
 Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Kawaguchi et al. Surgical Case Reports (2015) 1:51 DOI 10.1186/s40792-015-0052-2 CASE REPORT Mirizzi syndrome with an unusual type of biliobiliary fistula a case report Tsutomu Kawaguchi 1,2*, Tadao Itoh
Pocket-sized versus standard ultrasound machines in abdominal imaging
 Singapore Med J 2014; 55(6): 325-333 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2014078 CMEArticle Pocket-sized versus standard ultrasound machines in abdominal imaging Ka Hei Tse 1, MBChB, Wing Hang Luk 1, FRCR, FHKAM, Mau
Singapore Med J 2014; 55(6): 325-333 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2014078 CMEArticle Pocket-sized versus standard ultrasound machines in abdominal imaging Ka Hei Tse 1, MBChB, Wing Hang Luk 1, FRCR, FHKAM, Mau
Twice recurrent gallstone ileus: a case report
 Jones et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:362 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Twice recurrent gallstone ileus: a case report Rhys Jones 1*, Daniel Broman 1, Richard Hawkins
Jones et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:362 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Twice recurrent gallstone ileus: a case report Rhys Jones 1*, Daniel Broman 1, Richard Hawkins
Original Contributions
 PII S0736-4679(01)00329-8 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 7 13, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/01 $ see front matter
PII S0736-4679(01)00329-8 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 7 13, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/01 $ see front matter
Role of Helical CT in Diagnosis of Gallstone Ileus and Related Conditions
 CT of Gallstone Ileus Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Francesco Lassandro 1 Stefania Romano 1 Alfonso Ragozzino 1 Giovanni Rossi 2 Tullio Valente 2 Ilaria Ferrara 3 Lugia Romano 1 Roberto
CT of Gallstone Ileus Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Francesco Lassandro 1 Stefania Romano 1 Alfonso Ragozzino 1 Giovanni Rossi 2 Tullio Valente 2 Ilaria Ferrara 3 Lugia Romano 1 Roberto
Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction
 Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction Kyung Hoon Lee 1, Hyun Young Han 1, Hee Jin Kim 1, Hee Kyung Kim 1, Moon Soo Lee 2 Departments of 1 Radiology and 2 Surgery,
Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction Kyung Hoon Lee 1, Hyun Young Han 1, Hee Jin Kim 1, Hee Kyung Kim 1, Moon Soo Lee 2 Departments of 1 Radiology and 2 Surgery,
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
The nontraumatic acute abdomen
 CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management
 Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Case Report Spontaneous Intramural Duodenal Hematoma: Pancreatitis, Obstructive Jaundice, and Upper Intestinal Obstruction
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 5321081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5321081 Case Report Spontaneous Intramural Duodenal Hematoma: Pancreatitis, Obstructive Jaundice, and Upper
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 5321081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5321081 Case Report Spontaneous Intramural Duodenal Hematoma: Pancreatitis, Obstructive Jaundice, and Upper
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy for Gallstones in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy for Gallstones in Adults Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 22 December 2017 Version: 1718.3.01 Individual Funding Request
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Management of Gallbladder Disease
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Role of Ultrasound in Acute Non Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies
 ORIGINALARTICLE Role of Ultrasound in Acute Non Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies Kamlesh Gupta, Ramesh Chander, Arvinder Singh, Sohan Singh, Sandeep Singh Abstract The current study was undertaken to access
ORIGINALARTICLE Role of Ultrasound in Acute Non Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies Kamlesh Gupta, Ramesh Chander, Arvinder Singh, Sohan Singh, Sandeep Singh Abstract The current study was undertaken to access
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis
 Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135)
 Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions
 Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Role of multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) in diagnosis and staging of gall bladder carcinoma
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 1 7 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 1 7 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Società Medico Chirurgica di Ferrara 12 maggio Malattia diverticolare del colon. La TC in faseacuta
 Società Medico Chirurgica di Ferrara 12 maggio 2012 La TC in faseacuta Pier Marco Cervi U.O. Radiodiagnostica Ospedaliera Direttore Dott. Stefano Bighi Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria S. Anna di Ferrara
Società Medico Chirurgica di Ferrara 12 maggio 2012 La TC in faseacuta Pier Marco Cervi U.O. Radiodiagnostica Ospedaliera Direttore Dott. Stefano Bighi Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria S. Anna di Ferrara
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht
 Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma Frank Wessels, Maarten van Leeuwen, UMCU utrecht Content Anatomy Biliary strictures (Hilar) Cholangiocarcinoom Staging Biliary tract 1 st order Ductus hepatica dextra Ductus hepaticus
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice
 Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
Case 7729 Child with choledochal cyst presenting with episodes of vomitting and jaundice dos Santos R 1, Almeida J 1, Mendes PP 2, Pereira S 3, Borges C 3, Soares E 4. 1) Radiology resident, 2) Radiology
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Appendix B: Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE Post publication note: The title of this guideline changed during development. This scope was published before the guideline
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Case Rep Gastroenterol 2010;4:71 78 DOI: /
 71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
71 Gallstone Ileus, Bouveret s Syndrome and Choledocholithiasis in a Patient with Billroth II Gastrectomy A Case Report of Combined Endoscopic and Surgical Therapy R. Fejes G. Kurucsai A. Székely F. Luka
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency
 Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Biliary Tract Disease. Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010
 Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
Biliary Tract Disease Emmet Andrews Cork University Hospital 6 th September 2010 Overview Gallstones Biliary tract tumours Other conditions Acute acalculous cholecystitis Mirizzi s syndrome Primary Biliary
USMLE and COMLEX II. CE / CK Review. General Surgery. 1. Northwestern Medical Review
 USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Study between Laparoscopic and Open Cholecystectomy for Dr. B. Hemasankararao 1,
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings
 Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Radiological Investigations of Abdominal Trauma
 76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 62 (2018) 504 511 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Imaging in pancreas transplantation complications: Temporal classification Paula Gallego Ferrero and
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 62 (2018) 504 511 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Imaging in pancreas transplantation complications: Temporal classification Paula Gallego Ferrero and
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology
 Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology Faculty representative: David L. Burns, MD, CNSP Resident representative: Tom Castiglione, MD Revision date: March 6, 2006
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology Faculty representative: David L. Burns, MD, CNSP Resident representative: Tom Castiglione, MD Revision date: March 6, 2006
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog
 What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of 2018 Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog Presenting Complaint: The patient presented on 5/30/17 with signs of lethargy and
What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of 2018 Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog Presenting Complaint: The patient presented on 5/30/17 with signs of lethargy and
