Q Fever LRN Meeting Bandera, TX 2/26/2015
|
|
|
- Leslie Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q Fever 2015 LRN Meeting Bandera, TX 2/26/2015 James L. Alexander, MPVM, DVM, DACVPM Zoonosis Control Program Texas Department of State Health Services Canyon, TX 3/12/2015 1
2 EVALUATION OF COXIELLA BURNETII IN RURAL AND URBAN ENVIRONMENTS N. E. Patterson, R. F. Massung, A. J. Candee, R. A. Priestley, A. M. Denison, J. L. Beebe, J. L. Alexander 3/12/2015 2
3 Q Fever 1937 Febrile illness in abattoir workers in Queensland, Australia (query fever) Coxiella burnetti (Cox and Burnet) 3/12/2015 3
4 Coxiella burnetii Obligate intracellular bacteria Infects humans and many animal species Worldwide distribution Human disease = Q fever Monocyte/macrophage infected Acute - flu-like febrile illness Pneumonia Hepatitis Chronic - endocarditis France 348 cases of culture negative endocarditis 167 (48%) Q fever 3/12/2015 4
5 Coxiella burnetii Both DHHS and USDA select agent Potential bioterrorism weapon: Spore-like form (small cell variant) Resistant to environmental conditions and many disinfectants Aerosol route of infection Single particle infectious C. burnetti weaponized in 1960 s Category B bioterrorism agent Treatable doxycycline Few fatalities from acute infection 3/12/2015 5
6 US 1946 Outbreaks in: Packing house workers in Chicago Livestock sale yard employees and packing house workers in Amarillo 3/12/2015 6
7 Coxiella burnetii Nucleus SCV LCV
8 Affected Species Cattle Goats Sheep Cats Dogs Avian Rodents Ticks Horses Camels Rabbits Swine Water Buffalo 3/12/2015 8
9 Some Key Q Fever Symptoms Almost all patients suffering from acute Q fever pneumonia present with a fever, usually associated with fatigue, chills, headaches, myalgia, and sweats. Headaches are often severe and retroorbital Radiographic findings may include single or multiple opacities of rounded configuration, increased reticular markings, atelectasis, and pleural effusion Cough was recorded in 24 to 90% of infected patients in different series of Q fever patients From: Maurin M, Raoult D. Q Fever. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, Oct. 1999, ;12:4
10 Human Exposure Method Aerosol inhalation, m.m. Ingestion Transplacental Autopsies Intradermal inoculation Blood transfusion Abortion/Parturition Arthropod??? 3/12/
11 Sources of Exposure/Environmental Contamination Animal parturition: >10 9 bacteria/gram of placenta (4.5 x bacteria/avg. bovine placenta) Feces Urine 3/12/
12 Q-fever Infection Dose, strain and host factor dependent (1 cell is all that is needed to infect) Agricultural association 1-3 week incubation flu-like illness Multiple syndromes 3/12/
13 Q-fever Infection Fever - Acute Prolonged/Undulating Pneumonia Hepatitis Myocarditis Pericarditis Skin Rash Chronic Endocarditis Vascular Inf. Osteoarticular Inf. Hepatitis Pulmonary Inf. Chronic fatigue syndrome Meningoencephalitis 13 others 3/12/
14 Q Fever in the USA? Prevalence in cattle (McQuiston et al, 2005) Milk from veterinary school dairy herds tested 92% of herds seropositive North Dakota sheep ranchers 3.4% positive Montana dairy farmers % Manitoba, Canada 15.9% general population Colorado % general population Active surveillance needed 3/12/
15 Community Acquired Pneumonia Generally affects patients > 65 years ~5 X 10 6 cases annually (CDC estimate) Major bacterial spp. seen in: Outpatients Non-ICU: Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus influenzae Chlamydophila pneumoniae Chlamydophila pneumoniae Legionella spp. UK estimation of 1% of CAP due to C. burnetii 3/12/
16 Q Fever Cases in USA? UK ~ 1% of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) estimated due to Q fever = 700 cases > 100 q fever cases/year USA ~ 5 million cases CAP/year 1% estimate = 50,000 cases of Q fever 3/12/
17 3/12/
18 Issues for the Attending Physician The list of primary drugs of choice for the most common causes of CAP generally does not include the drug of choice for acute q fever doxycycline Some C. burnetii strains are resistant to the drugs commonly used for CAP Improper treatment may lead to chronic infection Sero-conversion may take 3-4 weeks: 2nd week: 10% 3rd week: 50% 4th week: 70% 3/12/
19 Effects of Stress Guinea Pig Model Infected animals became culture and sero-negative Treatment with cyclophosphamide, high steroid doses or radiation resulted in recrudescence of infection 3/12/
20 Patient history Q Fever Diagnosis Age Environment Paired sera 3/12/
21 2006 Study 1999: Q fever became a nationally notifiable disease. Natural prevalence of C. burnetii unknown. Preliminary study undertaken to determine background levels as a baseline for testing in the event of a bioterrorism attack. 3/12/
22 Study Design 3 locations selected in cooperation with the state and local public health departments. 9 sample sites - urban and rural sites. ~10 environmental samples were taken from each site. 3/12/
23 3/12/
24 Sites Sampled Governmental Commercial Agricultural Social 3/12/
25 Sites Dairies 3 Cattle, 1 Goat Feedlot 1 Cattle, 1 Sheep Ranch - 1 Sale Yard 1 Research Farms 2 Veterinary Clinic 1 Post Office 1 Schools 3 Social Clubs 2 Livestock Exhibition venues 2 Businesses 5 Animal Control -1 FFA club site 1 Local Health Dept /12/
26 Samples Surface swabs taken with pre-moistened sponges Bulk soil samples Vacuum filter samples Type of samples determined by what was most appropriate for each site 3/12/
27 Floor Mats 3/12/
28 Bulk Samples 3/12/
29 Results Non-Ag Positive 69% (9/13) Sites 17% (29/173) Samples Ag Positive 50% (7/14) Sites 8% (14/165) Samples Combined Positive 59% (16/27) Sites 12% (43/338) Samples 3/12/
30 Q Fever M. Maurin and D. Raoult Clinical Microbiology Reviews, Oct. 1999, p /12/
31 Investigation of a Q Fever Outbreak in the Texas Panhandle Investigating A Suspected Q Fever Outbreak James L. Alexander, DVM, MPVM Zoonosis Control Division Texas Department of Health Canyon, Texas
32 Coxiella burnetii Source of Organism Birthing fluids, urine and feces of livestock and cats and dogs
33 Coxiella burnetii The Panhandle has an abundance of livestock
34 Coxiella burnetii The Panhandle has an abundance of wind
35 Coxiella burnetii Spreads by aerosolization of contaminated dust/soil West Texas has plenty of aerosolized dust and soil
36 A Light Breeze in the Panhandle
37 June 12, 2008 Late in the day began receiving calls about an illness at an ethanol plant construction site at Hereford, Texas Symptoms reported were more consistent with food-poisoning Workers were going to the hospital to be tested for q fever
38 Hereford, Texas ~ 40 miles SW of Amarillo You are here
39 June 13, 2008 Met with personnel from the company that owned the ethanol plant Met with Hereford City Officials Participated in media interviews Visited Infection Control hospital
40 Hereford is known for feedlots The Beef Capital of the World
41
42
43 Manure-fueled Ethanol Plant
44
45
46
47
48
49
50 N
51 Companies 14 were on site during the 60 days prior to the discovery of q fever titers in the work force The majority left that Friday or in the next week Interviews and follow-up testing delayed Many returned in late July but some were lost to follow-up
52
53 Investigation 198 people received at least 1 test 36 people received at least 2 tests 5 people were tested 3 times 238 samples collected No one that did not already have a titer of >128 developed a higher titer
54 Surveyed Population Of 198 Workers Tested 17 had titers > 128 (8.6%) 1:4096 was the highest titer based on a retest of the index case
55 Surveyed Population 122 (62%) of the Tested people were interviewed 15 of the 17 with titers 5 asymptomatic (33.3%) 10 symptomatic (67.7%) 42 interviewees with compatible symptoms (32 w/o titers) 80 interviewees without compatible symptoms (5 with titers)
56 Tested Population 15 Females (7.6%) Age: with > 128 (13.3%) Ages 22 and 48 (mean = 35) 13 without titers Ages (mean = 37.8)
57 Tested Population 183 Males (92%) Age: with > 128 (8.2%) Age: (mean = 40.6) 168 without titers Ages (mean = 39.8)
58 Information Obtained Demographics and health history Work location on site Job title/occupation Past livestock exposure Animal exposure in past 60 days Exposure to aborting animal Illness and symptoms Use of PPE Proximity to manure
59 Predominant Symptoms of Cases and Non-titered People Reporting Illness 10 Cases 32 Non-cases Weakness 10 (100%) 24 (75%) Malaise 8 (80%) 22 (69%) Chills 7 (70%) 22 (69%) Sweating 7 (70%) 21 (66%) Headache 6 (60%) 27 (75%) Myalgia 4 (40%) 17 (53%) Lymphadenitis 3 (30%) 4 (12.5%)
60 Evaluated Proximity to manure not significant Employer not significant Prior contact with livestock not significant
61 Plant Owner Modifications Tarp to block wind at unloading site Water misting during manure unloading Removal of grinder from manure processing system Halting manure delivery when wind direction was from the manure site toward areas occupied by personnel
62 Actions Taken by Contractor Invited OSHA to visit - declined Invited NIOSH to visit accepted Required Tyvek suits and respirators Established PPE zones
63
64 NIOSH Recommendations No Tyvek suits Shower and laundry facilities on-site No work clothes or footwear to leave the site Move the contractor office trailers and install running water to improve hand sanitation Medical screening for symptomatic personnel Cleaning shoes at office doorways and proper cleaning techniques for offices Appropriate respiratory-protection equipment based on the job function
65 Q FEVER IN THE PANHANDLE THE SAGA CONTINUES James L. Alexander, DSHS Kelly Fitzpatrick, CDC Lindsay Oliver, CDC Gilbert Kersh, CDC Robert Massung, CDC Kevin McClaran, DSHS
66 What is the prevalence of antibodies to q fever in the Panhandle population?
67 Netherlands 2009: 2,357 new human q fever cases US 43,855 (109) Slaughtered about 62,500 pregnant goats and sheep 455,000 doses of vaccine distributed Vaccinated about 90% of sheep/goat herds
68 2009 Sero-survey for Q-fever DSHS collaborated with the local blood bank IRB approval obtained Donors were apprised of the project, given a fact sheet and asked if they would participate DSHS provided a vacuum tube which the phlebotomists used when collecting the routine samples for screening tests. A questionnaire was administered by a DSHS representative.
69 2009 Sero-survey for Q-fever 589 donors in the study 19 blood drive events in 17 counties
70 2009 Sero-survey for Q-fever Residents from 23 counties participated Tubes were centrifuged, serum was pipetted and samples were stored on dry ice until they could be placed in a -80 o C -80 o C until shipped to CDC for testing.
71 2009 Sero-survey for Q-fever CDC Test Protocol u All samples screened by ELISA u All ELISA positive/equivocal samples tested by 1:16 u Samples 1:16 were titrated to their endpoint
72 Prevalence 589 samples utilized in the study Antibody prevalence: 10.7% in 589 people from 23 Counties
73
74 Prevalence Counties Donation Sites 6 Counties with 0% 2 Sites with 0% 1-6 donors (14) 8 and 35 donors (43) 9 Counties with 3-8% 10 Sites with 3-8% donors (385) donors (350) 8 Counties with 16-50% 8 Sites with 19-43% 5-68 donors (190) 4-72 donors (196)
75 Symptoms Do you recall having an illness, possibly lasting 7 days or more, that began suddenly with fever, chills, profuse sweating, muscle and joint pains, severe headache and fatigue for which a definitive diagnosis was not made?
76 Symptoms 11.1% of people with seropositive results said Yes Male (6): 14% Female (1): 5% All White Non-Hispanic
77 Symptoms 10.3% of people with negative results also said Yes Male (23): 8.7% Female (31): 12%
78 Age Data Positives: All Pos Neg Range Mean Median Mode 53, 55 38, 49, 51 55
79 Demographics Racial Percentages Survey Pop n White Non-Hispanic Hispanic Black Non-Hispanic Amer. Indian/Alaskan Native Asian-Pacific Islander Black Hispanic 0.2 NA None Provided 0.3 NA
80 US Sero-prevalence Study Seroprevalence of Q Fever in the United States, , Anderson, et al Stratified for age Part of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey program
81 Comparison of Studies Anderson, et al 1 Panhandle (> 20 y.o.) (> 18 y.o.) Sample Size Sero-prevalence 3.1%* 10.7% (>1:16) (>1:128) * Weighted pop n estimate 1 Seroprevalence of Q Fever in the United States,
82 Comparison of Studies Anderson, et al Panhandle Male + 3.8% 14% Female + 2.4% 7% Male:Female 1.5:1 2:1 Age Age Risk No Effect Seroprevalence of Q Fever in the United States, 20
83 Comparison of Studies Anderson, et al Panhandle Male vs Female 1.5 OR ( ) 2.1 OR ( ) White Non-Hispanic 2.8% 10.4% Hispanics 7.4% 10.7% Geometric mean 95 ( ) 597 ( ) (Phase II IgG)
84 Panhandle Study Limitations Of 19 counties with more than 1 participant, 5 were under-represented and 14 were overrepresented. Residents of 4 counties provided 50% of the samples 2 of those counties (large pop n) were over represented and 2 (moderate pop n) were under represented
85 Study Limitations Used healthy blood donors Racial/ethnic representation did not match the area s diversity Convenience sample Not stratified for age
86 Conclusions Exposure to Coxiella burnetii appears to be significant in some parts of the Texas Panhandle If the healthy, blood donor population has a 10.7% prevalence, it is logical to suspect that a random sample across our population might detect a higher prevalence Analysis continues to examine risk factors, including occupation, association with livestock and location of residence
87 Important Points About Q-fever C. burnetii prevalence is high in both urban and rural settings that were sampled Q-fever is under diagnosed Q-fever seroconversion may be delayed 2 nd week: 10% 3 rd week: 50% 4 th week: 70% CAP cases in US should be evaluated Cats should be surveyed 3/12/
88 Important Points About Q-fever Dahlgren, et al, estimate that at least 13 cases of q fever are undiagnosed for everyone detected. They also estimated that in two reporting systems, deaths are underreported by factors of 5 (MCD) and 14 (CRF). Healy, et al, found only a 35% concordance between three reference labs on the same samples. 3/12/
89 Unidentified Agent in the Panhandle 3 Patients with pneumonia treated with standard antibiotic protocols All with symptoms compatible with Q Fever All lived in Hereford, TX All were on vents and considered terminal Doxycycline was added to regimen All recovered All negative for Q Fever on serology vv 89
90 James L. Alexander, DVM, MPVM, DACVPM Texas Department of State Health Services Zoonosis Control Program WTAMU Box Canyon, TX /12/
Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know
 Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know Dr. Stephen Graves Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory Director, Division of Microbiology, Pathology North (Hunter) NSW Health Pathology,
Q Fever What men and women on the land need to know Dr. Stephen Graves Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory Director, Division of Microbiology, Pathology North (Hunter) NSW Health Pathology,
Q FEVER Australian and global perspectives including the recent Netherlands outbreak
 Q FEVER Australian and global perspectives including the recent Netherlands outbreak Coxiella burnetii, the causative bacterium for Q Fever is ubiquitous. Thought to be present in every land mass with
Q FEVER Australian and global perspectives including the recent Netherlands outbreak Coxiella burnetii, the causative bacterium for Q Fever is ubiquitous. Thought to be present in every land mass with
Q FEVER: what the meat industry needs to know. Prof Stephen R. Graves Medical Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory
 Q FEVER: what the meat industry needs to know Prof Stephen R. Graves Medical Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory 1 Q Fever: the disease First recognised as a new infection in Brisbane
Q FEVER: what the meat industry needs to know Prof Stephen R. Graves Medical Director, Australian Rickettsial Reference Laboratory 1 Q Fever: the disease First recognised as a new infection in Brisbane
Q Fever. Coxiella Burnetii. (Also Known as Query Fever) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS
 Q Fever Coxiella Burnetii (Also Known as Query Fever) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic reporting
Q Fever Coxiella Burnetii (Also Known as Query Fever) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic reporting
Outbreak Scenario Based on an outbreak that occurred in the Netherlands
 Outbreak Scenario Outbreak Scenario Based on an outbreak that occurred in the Netherlands Section Logistics 1 Background Scenario Investigation Response Objectives Identify the initial steps and sequence
Outbreak Scenario Outbreak Scenario Based on an outbreak that occurred in the Netherlands Section Logistics 1 Background Scenario Investigation Response Objectives Identify the initial steps and sequence
Q Fever Guidance Document NASPHV/NASAHO
 Q Fever Guidance Document NASPHV/NASAHO Q Fever Committee Q Fever Committee Formed in January 2012 Joint leadership of the National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) and the National
Q Fever Guidance Document NASPHV/NASAHO Q Fever Committee Q Fever Committee Formed in January 2012 Joint leadership of the National Association of State Public Health Veterinarians (NASPHV) and the National
Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study
 Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study Pranee Rodtian 1, *, Nuamjit M 1, Srijan M 2, Opaschaitat P 3, Ekgatat M 3 1 Fifth Regional Livestock Office, Chiang
Q Fever among Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, 2012: A Preliminary Study Pranee Rodtian 1, *, Nuamjit M 1, Srijan M 2, Opaschaitat P 3, Ekgatat M 3 1 Fifth Regional Livestock Office, Chiang
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality rev Jan 2018
 rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
ALAT - Chapter 4. Occupational Health and Safety. Dr. Carrie Freed, DACLAM, DVM, MLAS
 ALAT - Chapter 4 Occupational Health and Safety Dr. Carrie Freed, DACLAM, DVM, MLAS Freed.36@osu.edu, 292-7319 OSHA Every institution with an animal research program must have an occupational health and
ALAT - Chapter 4 Occupational Health and Safety Dr. Carrie Freed, DACLAM, DVM, MLAS Freed.36@osu.edu, 292-7319 OSHA Every institution with an animal research program must have an occupational health and
Q Fever Herd Management Plan
 Q Fever Herd Management Plan The purpose of this herd plan is to outline appropriate actions and management practices to protect public health by reducing exposure to Coxiella burnetii (the bacteria that
Q Fever Herd Management Plan The purpose of this herd plan is to outline appropriate actions and management practices to protect public health by reducing exposure to Coxiella burnetii (the bacteria that
Q Fever. Experiences in the Wheatbelt
 Q Fever Experiences in the Wheatbelt Introduction I will discuss 2 cases of a cluster of 5 cases in 2016 There was another cluster of 3-5 in 2013 Which will show the difficulty of treatment and management
Q Fever Experiences in the Wheatbelt Introduction I will discuss 2 cases of a cluster of 5 cases in 2016 There was another cluster of 3-5 in 2013 Which will show the difficulty of treatment and management
Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL
 Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate providers and laboratories to report stool cultures positive for Campylobacter jejuni or Campylobacter coli from patients within
Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate providers and laboratories to report stool cultures positive for Campylobacter jejuni or Campylobacter coli from patients within
Guidelines for Reducing the Risk of Exposure to the Q Fever Agent (Coxiella burnetii) for the University of Wisconsin- Madison
 Guidelines for Reducing the Risk of Exposure to the Q Fever Agent (Coxiella burnetii) for the University of Wisconsin- Madison 1.0 Objective In order to protect University of Wisconsin Madison faculty,
Guidelines for Reducing the Risk of Exposure to the Q Fever Agent (Coxiella burnetii) for the University of Wisconsin- Madison 1.0 Objective In order to protect University of Wisconsin Madison faculty,
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1. Basic agent information. Section I- Infectious Agent. Section II- Dissemination
 1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
1918 Influenza; Influenza A, H1N1 Basic agent information Section I- Infectious Agent Risk Group: - RG3 Synonym or Cross reference: - Spanish Flu - 1918 Flu - El Grippe Characteristics: - SELECT AGENT
UPDATE ON CANINE INFLUENZA IN TENNESSEE. Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice)
 UPDATE ON CANINE INFLUENZA IN TENNESSEE Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice) Headlines What is Canine Influenza? Highly contagious respiratory infection of dogs Caused by influenza
UPDATE ON CANINE INFLUENZA IN TENNESSEE Staci Cannon, DVM, MPH, DACVPM, DABVP (Shelter Medicine Practice) Headlines What is Canine Influenza? Highly contagious respiratory infection of dogs Caused by influenza
RESEARCH WITH HIGHLY PATHOGENIC AVIAN INFLUENZA H5N1
 Page 1 of 8 RESEARCH WITH HIGHLY PATHOGENIC AVIAN INFLUENZA H5N1 The University of Pittsburgh has developed guidelines to establish a system of education and safeguards to ensure compliance with both the
Page 1 of 8 RESEARCH WITH HIGHLY PATHOGENIC AVIAN INFLUENZA H5N1 The University of Pittsburgh has developed guidelines to establish a system of education and safeguards to ensure compliance with both the
Indiana State Board of Animal Health
 Indiana State Board of Animal Health Office of the State Veterinarian Marianne Ash, DVM, MVPH, DACVPM Animal Health Division Director BOAH s Charge the prevention, detection, control and eradication of
Indiana State Board of Animal Health Office of the State Veterinarian Marianne Ash, DVM, MVPH, DACVPM Animal Health Division Director BOAH s Charge the prevention, detection, control and eradication of
Public Health Responds to Avian Influenza Outbreaks in Commercial Poultry: Lessons from Nigeria
 Public Health Responds to Avian Influenza Outbreaks in Commercial Poultry: Lessons from Nigeria Lora Baker Davis, DVM, MPH Washington State Dept of Agriculture Avian Influenza Surveillance Activity Learning
Public Health Responds to Avian Influenza Outbreaks in Commercial Poultry: Lessons from Nigeria Lora Baker Davis, DVM, MPH Washington State Dept of Agriculture Avian Influenza Surveillance Activity Learning
Network for Prevention and Control of Leptospirosis in Asia
 Network for Prevention and Control of Leptospirosis in Asia JUN FUJII, SHIN-ICHI YOSHIDA Kyushu University, Japan XIAO-KUI GUO Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China SUBHASH C SEHGAL WHO Collaborating Centre
Network for Prevention and Control of Leptospirosis in Asia JUN FUJII, SHIN-ICHI YOSHIDA Kyushu University, Japan XIAO-KUI GUO Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China SUBHASH C SEHGAL WHO Collaborating Centre
SHORT REPORT Acute Q fever in northern Queensland: variation in incidence related to rainfall and geographical location
 Epidemiol. Infect. (213), 141, 134 138. f Cambridge University Press 212 doi:1.117/s952688121495 SHORT REPORT Acute Q fever in northern Queensland: variation in incidence related to rainfall and geographical
Epidemiol. Infect. (213), 141, 134 138. f Cambridge University Press 212 doi:1.117/s952688121495 SHORT REPORT Acute Q fever in northern Queensland: variation in incidence related to rainfall and geographical
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases)
 INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals.
 Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
MORE THAN JUST FOOTBATHS: PRACTICAL EQUINE BIOSECURITY
 MORE THAN JUST FOOTBATHS: PRACTICAL EQUINE BIOSECURITY Roberta M. Dwyer, DVM, MS, DACVPM Professor Department of Animal and Food Sciences 804 W.P. Garrigus Building University of Kentucky Lexington, KY
MORE THAN JUST FOOTBATHS: PRACTICAL EQUINE BIOSECURITY Roberta M. Dwyer, DVM, MS, DACVPM Professor Department of Animal and Food Sciences 804 W.P. Garrigus Building University of Kentucky Lexington, KY
Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii
 Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii 4. General overview of Coxiella burnetii and Q fever Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium, is the causative agent of Q fever. C.
Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii 4. General overview of Coxiella burnetii and Q fever Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium, is the causative agent of Q fever. C.
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Campylobacteriosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case
August 2011 Campylobacteriosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case
Canine Influenza FAQ. Questions, Answers, and Interim Guidelines
 Page 1 of 5 https://www.avma.org/kb/resources/faqs/pages/control-of-canine-influenza-in-dogs.aspx?pf=1 Canine Influenza FAQ Questions, Answers, and Interim Guidelines Updated April 22, 2015 Q: What is
Page 1 of 5 https://www.avma.org/kb/resources/faqs/pages/control-of-canine-influenza-in-dogs.aspx?pf=1 Canine Influenza FAQ Questions, Answers, and Interim Guidelines Updated April 22, 2015 Q: What is
Polio (Paralytic and Non-paralytic
 Polio (Paralytic and Non-paralytic Infection) rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Poliovirus (genus Enterovirus) types, 1, 2, and 3. BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Poliovirus is transmitted by person-to-person
Polio (Paralytic and Non-paralytic Infection) rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Poliovirus (genus Enterovirus) types, 1, 2, and 3. BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Poliovirus is transmitted by person-to-person
Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade & Consumer Protection Division of Animal Health
 Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade & Consumer Protection Division of Animal Health Zoonotic Diseases Where Human and Veterinary Medicine Meet Darlene Konkle, DVM, MS, DACVIM Assistant State Veterinarian
Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade & Consumer Protection Division of Animal Health Zoonotic Diseases Where Human and Veterinary Medicine Meet Darlene Konkle, DVM, MS, DACVIM Assistant State Veterinarian
CDC Health Advisory 04/29/2009
 H1N1 (Swine Flu) is a sub-type of Influenza A. Wexford Labs disinfectants are effective against Influenza A. Current CDC Recommendations for Environmental Control in the Healthcare Setting: CDC Health
H1N1 (Swine Flu) is a sub-type of Influenza A. Wexford Labs disinfectants are effective against Influenza A. Current CDC Recommendations for Environmental Control in the Healthcare Setting: CDC Health
What is Legionnaires' disease?
 Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form
 Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
The duration of protective immunity following immunisation is unknown, but is believed to be in excess of five years.
 Q-VAX Q Fever Vaccine and Q-VAX Skin Test (AUST R 100517 & 100518) Page 1 of 6 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Q fever Vaccine AUST R 100517 Q fever Skin Test AUST R 100518 DESCRIPTION Q-VAX is a purified suspension
Q-VAX Q Fever Vaccine and Q-VAX Skin Test (AUST R 100517 & 100518) Page 1 of 6 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Q fever Vaccine AUST R 100517 Q fever Skin Test AUST R 100518 DESCRIPTION Q-VAX is a purified suspension
Avian Influenza: Worker Health and Safety
 Avian Influenza: Worker Health and Safety Lisa J. Delaney, M.S., C.I.H. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) The findings and conclusions in this presentation are those of the
Avian Influenza: Worker Health and Safety Lisa J. Delaney, M.S., C.I.H. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) The findings and conclusions in this presentation are those of the
Investigation of an Escherichia coli O111 Outbreak at a State-run Correctional Facility (Colorado, 2010)
 Investigation of an Escherichia coli O111 Outbreak at a State-run Correctional Facility (Colorado, 2010) S Reynolds, M Keifer, C Campbell, M Towle, A Warner, B Ray, N Comstock WestON September 2011 Investigation
Investigation of an Escherichia coli O111 Outbreak at a State-run Correctional Facility (Colorado, 2010) S Reynolds, M Keifer, C Campbell, M Towle, A Warner, B Ray, N Comstock WestON September 2011 Investigation
WYANDOT COUNTY 2016 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology
 California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Q FEVER, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Distance Learning Program Course # DL-005 Helen M. Sowers, MS, CLS Dept. of Biological Sciences (Retired) CSU
California Association for Medical Laboratory Technology Q FEVER, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Distance Learning Program Course # DL-005 Helen M. Sowers, MS, CLS Dept. of Biological Sciences (Retired) CSU
Q-FEVER Q FEVER. CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 EMEA 2002
 Q FEVER CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 General points on treatment Q fever is a zoonosis caused by Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium with high infectivity but with relatively
Q FEVER CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 General points on treatment Q fever is a zoonosis caused by Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium with high infectivity but with relatively
LEAD SAFETY PROGRAM. Purpose. Scope. Responsibilities. Southern Heat Exchanger Services Safety Program
 Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to identify the controls and actions necessary to prevent adverse health effects to employees from occupational exposure to lead, and to ensure
Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this procedure is to identify the controls and actions necessary to prevent adverse health effects to employees from occupational exposure to lead, and to ensure
Overview of Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) Stephen Munday, MD MPH Imperial County Public Health May 21, 2013
 Overview of Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) Stephen Munday, MD MPH Imperial County Public Health May 21, 2013 Objectives Assess the epidemiology of Coccidioidomycosis (aka Valley Fever) Describe the
Overview of Coccidioidomycosis (Valley Fever) Stephen Munday, MD MPH Imperial County Public Health May 21, 2013 Objectives Assess the epidemiology of Coccidioidomycosis (aka Valley Fever) Describe the
Biosecurity: Understanding its importance when working on livestock farms
 Biosecurity: Understanding its importance when working on livestock farms Kevin Janni, Extension Engineer Abby Neu, Extension Educator 1 2017 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved.
Biosecurity: Understanding its importance when working on livestock farms Kevin Janni, Extension Engineer Abby Neu, Extension Educator 1 2017 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved.
Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza
 PAGE 1 TechUpdate Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza Frequently asked Questions The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have recently issued
PAGE 1 TechUpdate Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza Frequently asked Questions The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have recently issued
Guidance for Influenza in Long-Term Care Facilities
 Guidance for Influenza in Long-Term Care Facilities DSHS Region 2/3 Epidemiology Team January 2018 1. Introduction Every year, the flu affects people around the world, regardless of age. However, residents
Guidance for Influenza in Long-Term Care Facilities DSHS Region 2/3 Epidemiology Team January 2018 1. Introduction Every year, the flu affects people around the world, regardless of age. However, residents
The Basics of Grow-Finish Biosecurity
 The Basics of Grow-Finish Biosecurity PorkBridge Alex Ramirez, DVM, MPH Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic and Production Animal Medicine August 3, 2006 Goals Discuss the foundations for biosecurity
The Basics of Grow-Finish Biosecurity PorkBridge Alex Ramirez, DVM, MPH Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic and Production Animal Medicine August 3, 2006 Goals Discuss the foundations for biosecurity
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease)
 ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October Main conclusions and options for response
 RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Zika. Nicole Evert, MS Zoonosis Control Branch Department of State Health Services Austin, Texas
 Zika Nicole Evert, MS Zoonosis Control Branch Department of State Health Services Austin, Texas Family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus Vectors: Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus Maintained in a human-mosquito-human
Zika Nicole Evert, MS Zoonosis Control Branch Department of State Health Services Austin, Texas Family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus Vectors: Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus Maintained in a human-mosquito-human
Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC)
 Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC) September 7, 2012 Attention Swine Exhibitors: The 2012 Texas fair and rodeo season is right around the corner. The Texas Pork Producers Association, the Texas Animal
Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC) September 7, 2012 Attention Swine Exhibitors: The 2012 Texas fair and rodeo season is right around the corner. The Texas Pork Producers Association, the Texas Animal
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
Q FEVER. By Theresa Deike. Disease Etiologic Agent. Disease Transmission and Reservoirs
 Q FEVER By Theresa Deike Disease Etiologic Agent Q fever is a zoonosis disease caused by the gram-negative bacterium Coxiella burnetii. The causative microbe, C. burnetii, is an obligate parasitic coccobacillus
Q FEVER By Theresa Deike Disease Etiologic Agent Q fever is a zoonosis disease caused by the gram-negative bacterium Coxiella burnetii. The causative microbe, C. burnetii, is an obligate parasitic coccobacillus
WYANDOT COUNTY 2016 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
WYANDOT COUNTY 216 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT February 217 Wyandot County saw a.87% increase in communicable disease cases from 21 to 216 (11 cases and 116 cases respectively). Numerous infectious diseases
McHenry County Norovirus Outbreaks November McHenry County Department of Health November 29,2010
 McHenry County Norovirus Outbreaks November 2010 McHenry County Department of Health November 29,2010 What is Norovirus The most common cause of gastrointestinal illness resulting from an inflammation
McHenry County Norovirus Outbreaks November 2010 McHenry County Department of Health November 29,2010 What is Norovirus The most common cause of gastrointestinal illness resulting from an inflammation
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
Rift Valley Fever RVF. Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011
 Rift Valley Fever RVF Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011 Definition Rift valley fever (RVF) is an acute febrile arthropod-borne zoonotic disease.
Rift Valley Fever RVF Enhancing Safe Inter-Regional Livestock Trade Dubai, United Arab Emirates June 13-16, 2011 Definition Rift valley fever (RVF) is an acute febrile arthropod-borne zoonotic disease.
Western Veterinary Conference 2013
 Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH IMPLICATIONS: FROM LABORATORY TO FIELD
 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH IMPLICATIONS: FROM LABORATORY TO FIELD USDA ARS 5 TH INTERNATIONAL BIOSAFETY & BIOCONTAINMENT SYMPOSIUM February 13 th, 2019 Lee Wugofski MD,MPH Deputy Medical Director, CHS, FOH ASSESSING
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH IMPLICATIONS: FROM LABORATORY TO FIELD USDA ARS 5 TH INTERNATIONAL BIOSAFETY & BIOCONTAINMENT SYMPOSIUM February 13 th, 2019 Lee Wugofski MD,MPH Deputy Medical Director, CHS, FOH ASSESSING
FACT SHEET Q Fever and the Australian Q Fever Register
 FACT SHEET Q Fever and the The Bare Facts Q Fever Protection Q Fever is an infectious disease that can cause severe illness in some people. People usually get Q Fever from farm animals (cattle, sheep and
FACT SHEET Q Fever and the The Bare Facts Q Fever Protection Q Fever is an infectious disease that can cause severe illness in some people. People usually get Q Fever from farm animals (cattle, sheep and
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians
 MEMORANDUM DATE: October 1, 2009 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians Michael
MEMORANDUM DATE: October 1, 2009 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians Michael
UNION COUNTY 2017 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
UNION COUNTY 7 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious disease for January 7 December 7. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
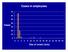 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES EMERGING NONE
 EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT. The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018.
 WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
CONTROL OF VIRAL GASTROENTERITIS OUTBREAKS IN CALIFORNIA LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES
 CONTROL OF VIRAL GASTROENTERITIS OUTBREAKS IN CALIFORNIA LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES California Department of Health Services Division of Communicable Disease Control In Conjunction with Licensing and Certification
CONTROL OF VIRAL GASTROENTERITIS OUTBREAKS IN CALIFORNIA LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES California Department of Health Services Division of Communicable Disease Control In Conjunction with Licensing and Certification
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza:
 United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Program Aid No. 1704 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: A Threat to U.S. Poultry A Threat to U.S. Poultry Worldwide, there
United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Program Aid No. 1704 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: A Threat to U.S. Poultry A Threat to U.S. Poultry Worldwide, there
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
 Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Salt Lake County Annual Influenza Report Season Bureau of Epidemiology
 Number of Cases Salt Lake County Annual Influenza Report 6-7 Season Bureau of Epidemiology Introduction Table of Contents Introduction The 6-7 influenza season saw 6 confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations
Number of Cases Salt Lake County Annual Influenza Report 6-7 Season Bureau of Epidemiology Introduction Table of Contents Introduction The 6-7 influenza season saw 6 confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations
CFIA Animal Health, Welfare and Biosecurity Division Biosecurity Recommendations for Travellers to Keep African Swine Fever Out of Canada
 CFIA Animal Health, Welfare and Biosecurity Division Biosecurity Recommendations for Travellers to Keep African Swine Fever Out of Canada Re: Travellers to Canada - Visitors or returning Canadian residents
CFIA Animal Health, Welfare and Biosecurity Division Biosecurity Recommendations for Travellers to Keep African Swine Fever Out of Canada Re: Travellers to Canada - Visitors or returning Canadian residents
Leptospirosis - a global disease but a local phenomenon
 Leptospirosis - a global disease but a local phenomenon Jackie Benschop, Julie Collins-Emerson, Neville Haack, Shaan Mocke, Juan Sanhueza, Yuni Yupiana, Jenny Weston, Cord Heuer and Peter Wilson. 22 and
Leptospirosis - a global disease but a local phenomenon Jackie Benschop, Julie Collins-Emerson, Neville Haack, Shaan Mocke, Juan Sanhueza, Yuni Yupiana, Jenny Weston, Cord Heuer and Peter Wilson. 22 and
Hepatitis Case Investigation
 * indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
* indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
Texas Influenza Summary Report, Season (September 28, 2008 April 11, 2009)
 Texas Influenza Summary Report, 2008 2009 Season (September 28, 2008 April 11, 2009) Background Influenza and influenza-like illnesses (ILI) were last reportable by law in any county in Texas in 1993 (1).
Texas Influenza Summary Report, 2008 2009 Season (September 28, 2008 April 11, 2009) Background Influenza and influenza-like illnesses (ILI) were last reportable by law in any county in Texas in 1993 (1).
Now Is the Time To Prepare.
 Now Is the Time To Prepare. If a natural disaster shuts down your local electricity service, could you keep your manufacturing lines running? How about the interior lights, phone lines and cash registers
Now Is the Time To Prepare. If a natural disaster shuts down your local electricity service, could you keep your manufacturing lines running? How about the interior lights, phone lines and cash registers
FMD Summary Epidemiology Report Situation as at 10:00 Thursday 09 August
 FMD 2007. Summary Epidemiology Report Situation as at 10:00 Thursday 09 August Executive summary 1. Two confirmed cases and one highly probable case of Foot and Mouth Disease have been confirmed in Surrey
FMD 2007. Summary Epidemiology Report Situation as at 10:00 Thursday 09 August Executive summary 1. Two confirmed cases and one highly probable case of Foot and Mouth Disease have been confirmed in Surrey
TID-16-C-142.R1, Received: 8 November 2016, Revised: 23 February 2017, Accepted: 26 March 2017
 DR. LINDSAY PETTY (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8731-105X) Article type : Case Report TID-16-C-142.R1, Received: 8 November 2016, Revised: 23 February 2017, Accepted: 26 March 2017 CASE REPORT A case of Q fever
DR. LINDSAY PETTY (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8731-105X) Article type : Case Report TID-16-C-142.R1, Received: 8 November 2016, Revised: 23 February 2017, Accepted: 26 March 2017 CASE REPORT A case of Q fever
Swine Flu; Symptoms, Precautions & Treatments
 Swine Flu; Symptoms, Precautions & Treatments What is the swine flu? Swine flu, also known as the H1N1 virus, is a relatively new strain of an influenza virus that causes symptoms similar to the regular
Swine Flu; Symptoms, Precautions & Treatments What is the swine flu? Swine flu, also known as the H1N1 virus, is a relatively new strain of an influenza virus that causes symptoms similar to the regular
Anthrax. Department of Child Health Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara
 Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study
 Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Bryce Spiker, MPH Legionellosis Epidemiologist Mike Wesenberg Environmental Health Specialist
Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Bryce Spiker, MPH Legionellosis Epidemiologist Mike Wesenberg Environmental Health Specialist
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October EMS TB Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
 UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
RESEARCH WITH MIDDLE EAST RESPIRATORY SYNDROME CORONAVIRUS (MERS-CoV)
 Page 1 of 5 RESEARCH WITH SYNDROME CORONAVIRUS (MERS-CoV) The University of Pittsburgh has developed guidelines to establish a system of education and safeguards to ensure that all Federal, State, and
Page 1 of 5 RESEARCH WITH SYNDROME CORONAVIRUS (MERS-CoV) The University of Pittsburgh has developed guidelines to establish a system of education and safeguards to ensure that all Federal, State, and
EBOLA 101. Update for EMS System Stakeholders. Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014
 EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
2009 H1N1 (Pandemic) virus IPMA September 30, 2009 Anthony A Marfin
 2009 H1N1 (Pandemic) virus IPMA September 30, 2009 Anthony A Marfin Introduction to Influenza What is influenza? What is pandemic influenza? What is 2009 H1N1 influenza? Current situation & predictions
2009 H1N1 (Pandemic) virus IPMA September 30, 2009 Anthony A Marfin Introduction to Influenza What is influenza? What is pandemic influenza? What is 2009 H1N1 influenza? Current situation & predictions
Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers
 EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers VERSION 2 Interim Guidelines for Evaluation of US Patients Suspected of Having Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) This is a rapidly
EBOLA VIRUS Guidance for Michigan local health departments and healthcare providers VERSION 2 Interim Guidelines for Evaluation of US Patients Suspected of Having Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) This is a rapidly
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Influenza H3N2
 Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Influenza H3N2 1. How was H3N2 first discovered in North America? In March 2015, veterinarians in and around the Chicago area began to notice an increase in the
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Influenza H3N2 1. How was H3N2 first discovered in North America? In March 2015, veterinarians in and around the Chicago area began to notice an increase in the
Introduction. Objectives. Risk Classification. Biologic Hazards
 Occupational Medicine Residency at WVU 2 Year program (after internship) AOA & ACGME Accredited Only AOA program in OEM Includes MPH (or soon MOH) degree Based in Morgantown, WV NIOSH (DRDS, DSR, and HELD)
Occupational Medicine Residency at WVU 2 Year program (after internship) AOA & ACGME Accredited Only AOA program in OEM Includes MPH (or soon MOH) degree Based in Morgantown, WV NIOSH (DRDS, DSR, and HELD)
Secure Food Supply Plans What s New? Danelle Bickett-Weddle, DVM, MPH, PhD, DACVPM Center for Food Security and Public Health Iowa State University
 Secure Food Supply Plans What s New? Danelle Bickett-Weddle, DVM, MPH, PhD, DACVPM Center for Food Security and Public Health Iowa State University Overview Secure Poultry Supply Plans What did HPAI teach
Secure Food Supply Plans What s New? Danelle Bickett-Weddle, DVM, MPH, PhD, DACVPM Center for Food Security and Public Health Iowa State University Overview Secure Poultry Supply Plans What did HPAI teach
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association
 Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Healthcare Professionals
 EMPLOYEE HEALTH Employee Health: Screening and immunization programs Counseling, follow up work restrictions Analysis and trending of occupational exposure incidents Assess risk for occupational exposure
EMPLOYEE HEALTH Employee Health: Screening and immunization programs Counseling, follow up work restrictions Analysis and trending of occupational exposure incidents Assess risk for occupational exposure
FMD Control Initiatives in Bangladesh
 FMD Control Initiatives in Bangladesh Dr. Md. Mohsin Ali Dr. Md. Ainul Haque Department of Livestock Services, Bangladesh Country Profile In Short Bangladesh is a Republic of South Asia It is bordered
FMD Control Initiatives in Bangladesh Dr. Md. Mohsin Ali Dr. Md. Ainul Haque Department of Livestock Services, Bangladesh Country Profile In Short Bangladesh is a Republic of South Asia It is bordered
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department
 Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING
 Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING Infection Control Principles for Preventing the Spread of Influenza The following infection control principles apply in any setting
Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING Infection Control Principles for Preventing the Spread of Influenza The following infection control principles apply in any setting
Swine Influenza 2009
 Swine Influenza 2009 A new strain of swine influenza virus (swh1n1) Large outbreak in Mexico 1324 suspect cases 81 deaths reported (26 confirmed swh1n1) Mexico City schools closed 91 U.S. cases so far
Swine Influenza 2009 A new strain of swine influenza virus (swh1n1) Large outbreak in Mexico 1324 suspect cases 81 deaths reported (26 confirmed swh1n1) Mexico City schools closed 91 U.S. cases so far
INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE
 Cough, Cough, Sneeze, Wheeze: Update on Respiratory Disease Lisa McHugh, MPH Infectious and Zoonotic Disease Program Communicable Disease Service New Jersey Department of Health INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE
Cough, Cough, Sneeze, Wheeze: Update on Respiratory Disease Lisa McHugh, MPH Infectious and Zoonotic Disease Program Communicable Disease Service New Jersey Department of Health INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE
Cough, Cough, Sneeze, Wheeze: Update on Respiratory Disease
 Cough, Cough, Sneeze, Wheeze: Update on Respiratory Disease Lisa McHugh, MPH Infectious and Zoonotic Disease Program Communicable Disease Service New Jersey Department of Health INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE
Cough, Cough, Sneeze, Wheeze: Update on Respiratory Disease Lisa McHugh, MPH Infectious and Zoonotic Disease Program Communicable Disease Service New Jersey Department of Health INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard
 Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
(and what you can do about them)
 (and what you can do about them) What s an outbreak? In general, more cases than expected (baseline) More cases clustered in a specific unit or facility than you d expect at a particular time of year Some
(and what you can do about them) What s an outbreak? In general, more cases than expected (baseline) More cases clustered in a specific unit or facility than you d expect at a particular time of year Some
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018
 Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
Haemophilus influenzae, Invasive Disease rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) is a small, Gram-negative bacillus, a bacterium capable of causing a range
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about the
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about the
