Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 8 Cases and Comparison with Craniofacial Fibro-osseous Lesions
|
|
|
- Clifton Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: linicopathologic Study of 8 ases and omparison with raniofacial Fibro-osseous Lesions Sohyung Park ong-jae Lee 1 Jeong Hyun Lee 2 Kyung-Ja ho Departments of Pathology, 1 Otorhinolaryngology and 2 Radiology, University of Ulsan ollege of Medicine, san Medical enter, Seoul, Korea Received : September 10, 2007 ccepted : October 24, 2007 orresponding uthor Kyung-Ja ho, M.D. Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan ollege of Medicine, san Medical enter, Pungnap-dong, Songpa-gu, Seoul , Korea Tel: Fax: kjc@amc.seoul.kr ackground : Juvenile ossifying fibroma (JOF) is defined as a variant of the ossifying fibroma, and the latter includes juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma (JTOF) and juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma (JPOF). JOF can be distinguished from other craniofacial fibroosseous lesions by its tendency to recur and its clinical mimicry of malignant bone tumors, but some clinical and histological features of JOF overlap with the other fibro-osseous lesions as well. We aimed to identify the clinicopathologic definition of JOF. Methods : Forty-two cases of fibro-osseous lesions were reviewed and they were classified into JOF, fibrous dysplasia (FD) and ossifying fibroma (OF). Results : JTOF had long, slender and anastomosing trabeculae of osteoid in a fibrocellular stroma, and JPOF had small ossicles resembling psammoma bodies with a thick collagenous rim in the fibrous stroma, which are features that differ from those of FD and OF. Radiologically, JOF and OF showed a well-defined lesion but FD exhibited an ill-defined lesion. linically, the average age of the JOF patients was the youngest, followed by OF and FD. For JOF, three cases had rapid growth and two others showed recurrences. JOF mainly occurred in the paranasal sinuses, OF in the mandible and FD in any craniofacial bone. onclusion : We demonstrated the distinct characteristics of JOF and these features may be helpful for the diagnosis and management of this malady. Key Words : Fibroma, Ossifying; Juvenile Juvenile ossifying fibroma (JOF) is a benign bone-forming neoplasm, and it is defined as a variant of the ossifying fibroma in the craniofacial skeleton of young age patients. 1,2 It is known to have two distinct histological subtypes, that is, juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma (JTOF) and juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma (JPOF). 2,3 JOF has been considered as a distinct disease entity from conventional ossifying fibroma (OF) and the other fibro-osseous lesions because of its tendency to occur at a young age and its locally aggressive behavior. 1 Moreover, JOF may clinically manifest with rapid painless expansion of the affected bone as an aggressive lesion mimicking malignancy such as osteosarcoma. 4 So, it is important to accurately recognize JOF for making the diagnosis and managing this disease. Yet there also has been some controversy about the recognition of this entity because some features of JOF overlap, to some extent, with those of other fibro-osseous lesions. 1-3 In this paper, we define the specific, precise clinicopathologic features of JOF conducting a review of the fibro-osseous lesions of the craniofacial bone. MTERILS ND METHODS Forty-two surgically resected fibro-osseous lesions of the craniofacial bones were retrieved from the surgical pathology files of san Medical enter (M) from 1997 to The clinical histories and radiological findings were available for all the cases. The pathological materials were reviewed by two pathologists. The histology of fibro-osseous lesions usually consisted of three parts, which were osseous components, fibrous components and the secondary changes. We analyzed our cases according to the former two components and we set the criteria for the classification as the following: fibrous dysplasia (FD), curvilinear bony trabeculae without osteoblastic rimming in fibrous stroma; ossifying fibroma (OF), irregular and short osteoid with osteoblastic rimming in a fibrous stroma; JPOF displays psammomatoid or spherical osteoid with or without osteoblastic rimming in a fibrous stroma, and JTOF displays long, slender anastomosing bony trabeculae with or without osteoblastic rimming in a fibrous stroma. The secondary changes included aneurysmal bone cyst ()-like changes, myxoid changes and hemorrhage. 373
2 374 Sohyung Park ong-jae Lee Jeong Hyun Lee, et al. RESULTS Eight cases of JOF (two cases of JTOF and six cases of JPOF), seven cases of OF and 27 cases of FD could be classified after analysis of the histological findings. Microscopically, for the osseous components, JTOF showed a mixture of cellular osteoids without osteoblastic rimming, and there were trabeculae of immature bone with osteoblastic rimming (Fig. 1). OF also showed irregular trabeculae (Fig. 1), similar to those of JTOF, but the trabeculae in JTOF were longer and slenderer, with an anastomosing pattern resembling paintbrush strokes. It was occasionally difficult to distinguish the cellular osteoid from the cellular fibrous stroma, and the latter was reminiscent of adamantinoma (Fig. 1). FD also exhibited similar irregular immature bone trabeculae, but the FD cases had no or scant osteoblastic rimming and the trabeculae were curvilinear woven bones (Fig. 1). JPOF exhibited spherical or ovoid ossicles that resembled psammoma bodies with or without osteoblastic rimming and some ossicles were calcified with a basophilic center and an eosinophilic fringe with lamellation. The ossicles of JPOF were surrounded by a thick irregular collagenous rim and the ossicles were occasionally fused together (Fig. 2). OF sometimes partly showed cellular or acellular spherical ossicles of immature bone, but the ossicles of OF were more uniform with a thinner and less conspicuous collagenous rim (Fig. 2) and they showed the transition with irregular bony trabeculae. The fibrous components of JOF, OF and FD exhibited similar features. The stroma consisted of cohesive or loosely packed fibroblasts around the osseous components. In JOF, the cellularity of the fibrocellular stroma tended to be variable, ranging from a scanty fibroblastic stroma that was due to closely packed ossicles to a highly cellular stroma. The stroma of FD consistently showed relatively low cellularity. Secondary changes were commonly encountered in JOF, including -like changes such as multinucleated giant cell infiltration and hemorrhage in JTOF (Fig. 3), and myxoid (Fig. 3) and hemorrhagic cystic changes in JPOF (Fig. 3). Such findings were uncommon in OF and FD. When the radiological findings were compared after histo- Fig. 1. Juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma (JTOF) shows mixed cellular osteoids without an osteoblastic rimming and trabeculae of immature bone with a osteoblastic rimming in a cellular fibrous stroma (ase 1) (). Ossifying fibroma (OF) exhibits similar osteoids with an osteoblastic rimming, but the osteoids were more irregular and shorter than those of JTOF (). Fibrous dysplasia (FD) reveals irregular curvilinear woven bone trabeculae with no or scant osteoblastic rimming ().
3 Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: a linicopathologic Study of 8 ases and omparison with raniofacial Fibro-osseous Lesions 375 logical classification, JOF and OF showed similar well defined, radiolucent bone expansions with soft tissue density (Fig. 4-). JOF showed a more aggressive mass (Fig. 4) than OF (Fig. 4). In contrast to OF and JOF, FD exhibited a poorly defined lesion with a ground-glass appearance, with expansion of the involved bone throughout its length (Fig. 4D). linically, some differences were found between the different patients. lthough the patients with JTOF (7 and 26 years old) and JPOF (from 8 to 58 years old) were not always young, the patients with JOF had the youngest average age (20.5 years), followed by OF (25.1 years) and FD (29.6 years). gender preponderance was absent for all the entities. JTOF occurred in the maxilla and skull bone, and the sites of JPOF were the paranasal sinuses, maxilla, and skull bone. The mandible and maxilla were favorable sites of OF. FD was found in any craniofacial bone, such as the maxilla, followed by the mandible, skull so on. One patient with JTOF and two patients with JPOF had been admitted, complaining of the rapid growth of the lesions for three weeks to three months. The above JTOF patient with rapid growth experienced a recurrence 17 months after the surgery, and the patient received reoperation. The resected tumor showed the same features of JTOF without any evidence of malignancy. nother patient with JPOF manifested radiological changes that were suspicious for a local recurrence and further management is being planned. The remaining six patients with JOF have been well at 4 to 65 months of follow-up. There has been no recurrence in the patients with OF during follow-up. Two patients with FD received surgeries twice because of the incomplete initial surgery (Table 1). DISUSSION The fibro-osseous lesions are thought to be the result of diverse processes in which the normal bone architecture is replaced by fibroblasts and collagen fibers that contain various amounts of mineralized material, and these lesions include a broad group of several entities like OF, JOF, FD and so on. 5 Most of them have been considered as benign lesions, but JOF has been classified as a different disease because of its local aggressive behavior Fig. 2. The ossicles in JPOF have a thick irregular collagenous rim with several ossicles (ase 5) (). Ossifying fibroma exhibits similar cementum-like deposits but showing a smooth contour and a thin fringe of collagen fibers (). JPOF shows a zonal pattern with central cementum-like ossicles and peripheral mature bony trabeculae (ase 4) ().
4 376 Sohyung Park ong-jae Lee Jeong Hyun Lee, et al. Fig. 3. JTOF shows several multinucleated giant cells in the stroma with hemorrhage (ase 1) (). The JPOF reveals mild myxoid change in the fibrocelluar area (ase 3) (), and hemorrhagic cystic change resembling an aneurysmal cyst (ase 3) (). and its tendency to predominantly occur in children and adolescents. 1,6,7 JOF needs to be distinguished from malignant bone tumors in that there is a similarity of clinical manifestations, 4,6-8 but JOF can be easily excluded from malignant bone tumors on the routine histological examination. dditionally, it may be difficult to distinguish JOF from other fibro-osseous lesions because of the overlapping features. 1,6,7 We analyzed 42 fibroosseous lesions of the craniofacial bone based on the descriptions in the literature 1-6,9-20 and on our own experience. ccording to the WHO classification, the cementum-like deposits seen in OF show a smooth contour with a radiating fringe of collagen fibers, but the ossicles in JPOF have a thick irregular collagenous rim. 2 This description was confirmed in our cases (Fig. 2, ). Moreover, JOF may show a zonal pattern with central cementum-like ossicles and peripheral mature bony trabeculae (Fig. 2), but OF seemed to show a mixed, random pattern. These features of osseous components were unique histological features and they could be clues for the diagnosis of JOF. 1-4,9 No or scant osteoblastic rimming in osseous components suggested FD. 1-4 lthough the fibrous components were relatively similar between JOF, OF and FD, an extremely cellular fibrous stroma tended to be observed in JOF, which may be attributed to the aggressiveness of JOF according to other reports. 1,9,10 The secondary -like changes that were present in some cases of JOF, and not in OF and FD may suggest JOF 1-3, but these features may not be very specific since many fast growing bone lesions may develop -like changes. 1,11,12 Therefore, the characteristic osseous components of JOF that were described as above, and the highly cellular fibrous stroma with or without secondary changes are best recognizable as features of JOF. Fibro-osseous lesions also have relatively distinct radiological features. JOF and OF both displayed well-demarcated, round or oval lesions. dditionally, JOF often revealed aggressive lesions with cortical destruction, which can be used to discriminate JOF from OF. FD manifested ill-defined contiguous lesions because of their blending with normal bone, with expanding of the involved bone throughout its overall length over several years, which demonstrates a slow growth pattern. The area of the involved bone adjacent to the lesion showed a transitional thickened area that histologically demonstrated a blending region
5 Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: a linicopathologic Study of 8 ases and omparison with raniofacial Fibro-osseous Lesions 377 D Fig. 4. On the computer tomography, JTOF shows a relatively well defined, radiolucent mass-like lesion with soft tissue density in the right maxilla (ase 1), (). JPOF exhibits a relatively well defined, mixed radiolucent and radiodense mass-like lesion with an aggressive pattern in the left maxilla (ase 3), (). Ossifying fibroma also shows a similar well demarcated lesion frequently affecting the mandible (). Fibrous dysplasia shows a poorly defined, asymmetrical ground-glass lesion blending into the normal bone (D). Table 1. linical findings of juvenile trabecular ossifying fibromas and juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibromas ase ge/sex Site Dx. Management Follow-up period/ outcome 1 7/F Right maxilla JTOF Resections (x2) 23Mo/Recurrence 2 26/F Skull JTOF Resection 4Mo/NED 3 10/F Left maxilla JPOF Resection 12Mo/Recurrence 4 9/M Left ethmoid sinus JPOF Resection 10Mo/NED, F/U loss 5 23/M Right frontal sinus JPOF Resection 11Mo 6 8/M Mandible JPOF Resection 15Mo/NED 7 23/F Right zygomus JPOF Resection F/U loss 8 58/M Inferior turbinate JPOF Resection 65Mo/NED, F/U loss Dx, Diagnosis; JTOF, Juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma; JPOF, Juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma; Mo, Month; NED, no evidence of disease; F/U, Follow-up. between the lesion and normal bone, and the boundary of the lesion was ill defined and not clear. In one case of JOF, it appeared as a relatively ill-defined confluent lesion that mimicked FD due to the extension of lesion to several adjacent bones. Yet the lesion still suggested JOF, because it partly showed a well-defined and localized mass-like area with a clinically rapid growth pattern, which was unusual for FD. Moreover, the area between the lesion and the normal adjacent bone was abrupt, in contrast to those
6 378 Sohyung Park ong-jae Lee Jeong Hyun Lee, et al. areas of FD. In addition, the lesion of FD showed a typical ground glass appearance but JOF or OF displayed focal or heterogeneous opacity in the lesion. These image findings could discriminate JOF from FD and OF, the same as in other reports. 1,2,13-17 Regarding the clinical features, the lesion location and patient age may not be helpful as differential points due to the overlapped features of these diseases. Nevertheless, each entity had some distinct features. The sites of JOF in our cases were consistent with other reports 1,18-20 in that JTOF mainly occur in the maxilla, mandible, and fronto-ethmoid complex, and JPOF occurred in the paranasal sinus, calvarium, maxilla and mandible, as well as in the sites frequented by OF and FD. JOF mainly occurred at young ages (JPOF, mean age: 21.8 years; JTOF, mean age: 16.5 years), but the age range of JPOF has been described to be quite wider (3 months to 72 years old). 1,2,18-20 These features were similarly observed in our cases that the JTOF patients were 6 and 26 years old, and JPOF showed more variable ages that ranged from 8 to 58 years old. The clinical behavior of JOF has been reported to be more aggressive than the other fibro-osseous lesions, and certain histological features, including hypercellular stroma, psammomatoid ossicles, garland-like strands of cellular osteoid and myxoid change, have been previously mentioned to be related with JOF aggressiveness. 1 These secondary changes were observed in our recurred cases of JOF and also in our other cases of JOF. lthough some of our patients with JOF in our cases showed rapid growth and recurrences, we need more follow-up data to determine the clinical significance of JOF. The genetic differences in cranial fibro-osseous lesions are not well established, but some genetic studies had been done. Nonrandom chromosome break points at Xq26 and 2q33, resulting in (X;2) translocation, were identified in some cases of JPOF. 21 For OF, alterations in the tumor suppressor gene HPRT2 were identified in two out of four cases. 22 In FD, an activating point mutation of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein gene (GNS) at the rg 201 codon was identified in extragnathic FD, and this was recognized as a molecular maker, but this gene has not been examined for gnathic FD So far, the results of these early studies are not be helpful for practical diagnosis. Progressive molecular research in the future may make the definition of JOF clear and explain the biological behavior of JOF. In summary, we reviewed 42 craniofacial fibro-osseous lesions and we could identify JOF as a distinct clinicopathologic entity. If a patient has the characteristics of JOF as mentioned above such as distinct histological features, occurrence sites and radiological features etc, then the possibility of JOF should be in mind and the informed clinicians should perform appropriate management and watchful follow-up. REFERENES 1. rannon R, Fowler. enign fibro-osseous lesions: a review of current concepts. dv nat Pathol 2001; 8: arnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology & genetics of head and neck tumours. Lyon: IR Press 2005; El-Mofty S. Psammomatoid and trabecular juvenile ossifying fibroma of the craniofacial skeleton: two distinct clinicopathologic entities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002; 93: Rinaggio J, Land M, leveland D. Juvenile ossifying fibroma of the mandible. J Pediatr Surg 2003; 38: Su L, Weathers DR, Waldron. Distinguishing features of focal cemento-osseous dysplasia and cemento-ossifying fibromas: I. a pathologic spectrum of 316 cases. Oral surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1997; 84: Waldron. Fibro-osseous lesions of the jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1985; 43: Waldron. Fibro-osseous lesions of the jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993; 51: Mehta D, lifton N, Mclelland L, Jones NS. Paediatric fibro-osseous lesions of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2006; 70: Pilch Z. Head and neck surgical pathology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2001; Margo E, Ragsdale D, Perman KI, Zimmerman LE, Sweet DE. Psammomatoid (juvenile) ossifying fibroma of the orbit. Ophthalmology 1985; 92: Eversole LR, Leider S, Nelson K. Ossifying fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of sixty-four cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1985; 60: Slootweg PJ. Maxillofacial fibro-osseous lesions: classification and differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol 1996; 13: Macdonald-Jankowsky DS. Fibro-osseous lesions of the face and jaws. lin Radiol 2004; 59: Daffner RH, Kirks DR, Gehweiler J Jr, Heaston DK. omputed tomography of fibrous dysplasia. m J Roentgenol 1982; 139: Khoury NJ, Naffaa LN, Shabb NS, Haddad M. Juvenile ossifying fibroma: T and MR findings. Eur Radiol 2002; 12: S Kuta J, Worley M, Kaugars GE. entral cementoossifying fibroma of the maxillary sinus: a review of six cases. m J Neuroradiol
7 Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: a linicopathologic Study of 8 ases and omparison with raniofacial Fibro-osseous Lesions ; 16: Yonetsu K, Nakamura T. T of calcifying jaw bone diseases. m J Roentgenol 2001; 177: Johnson L, Yousefi M. Vinh TN, Heffener DK, Hyams VJ. Hartman KS. Juvenile active ossifying fibroma: its nature, dynamics and origin. cta Otolaryngol Suppl 1991; 488: Slootweg PJ, Panders K, Koopmans R, Nikkels PG. Juvenile ossifying fibroma: an analysis of 33 cases with emphasis on histological aspects. J Oral Pathol Med 1994; 23: Williams HK. Mangham, Speight PM. Juvenile ossifying fibroma. an analysis of eight cases and a comparison with other fibro-osseous lesions. J Oral Pathol Med 2000; 29: Sawyer JR, Tryka F, ell JM, oop F. Nonrandom chromosome breakpoints at Xq26, and 2q33 characterize cemento-ossifying fibromas of the orbit. ancer 1995; 76: Pimenta FJ, Gontijo Silveira LF, Tavares G, et al. HRPT2 gene alterations in ossifying fibroma of the jaws. Oral Oncol 2006; 42: Toyosawa S, Yuki M, Kishino M, et al. Ossifying fibroma vs fibrous dysplasia of the jaw: molecular and immunological characterization. Mod Pathol 2007; 20: lman, Greel D, Wolfe HJ. ctivating mutations of Gs protein in monostotic fibrous lesions of bone. J Orthop Res 1996; 14: ianco P, Riminucci M, Majolagbe, et al. Mutations of the GNS1 gene, stromal cell dysfunction, and osteomalacic changes in non- Mcune-lbright fibrous dysplasia of bone. J one Miner Res 2000; 15:
Juvenile Trabecular And Psammomatoid Variant Of Ossifying Fibroma Of The Maxilla With Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Juvenile Trabecular And Psammomatoid Variant Of Ossifying Fibroma Of The Maxilla With Secondary L Emerson., M Alexander, A Job Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 1 Juvenile Trabecular And Psammomatoid Variant Of Ossifying Fibroma Of The Maxilla With Secondary L Emerson., M Alexander, A Job Citation
Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible
 Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of. the ethmoid sinus
 Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Original Article. Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study
 Original Article Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study Sajitha K*, Kishan Prasad H L, Netra Sajjan and Jayaprakash Shetty K Dept of Pathology, K S Hegde Medical Academy, Mangalore, India
Original Article Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study Sajitha K*, Kishan Prasad H L, Netra Sajjan and Jayaprakash Shetty K Dept of Pathology, K S Hegde Medical Academy, Mangalore, India
Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle
 (2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
(2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Benign Fibro-Osteo-Cemental Lesions of the Craniofacial Complex A Review
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. I. (Feb. 2014), PP 74-78 Benign Fibro-Osteo-Cemental Lesions of the Craniofacial Complex
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. I. (Feb. 2014), PP 74-78 Benign Fibro-Osteo-Cemental Lesions of the Craniofacial Complex
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
PRIMARY LESIONS OF THE BONY ORBIT
 USCAP 2016 Companion Meeting Primary Lesions of the Bony Orbit Milman 1 Tatyana Milman, MD Pathology Department Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania milmant@uphs.upenn.edu PRIMARY LESIONS OF THE
USCAP 2016 Companion Meeting Primary Lesions of the Bony Orbit Milman 1 Tatyana Milman, MD Pathology Department Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania milmant@uphs.upenn.edu PRIMARY LESIONS OF THE
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Psammomatoid Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report with Literature Review
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1071 JIAOMR Psammomatoid Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report with Literature Review CASE REPORT Psammomatoid Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report with Literature Review
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1071 JIAOMR Psammomatoid Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report with Literature Review CASE REPORT Psammomatoid Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report with Literature Review
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions
 Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Chapter 2 Bone/Osteoid Producing Lesions Introduction There are many lesions that are associated with reactive new bone formation; this chapter predominantly covers those in which deposition of osteoid/bone
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN A CASE REPORT
 www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6439026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6439026 Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma Sreelakshmi N. Nair,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6439026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6439026 Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma Sreelakshmi N. Nair,
Case I Fibrous dysplasia ( FD)
 SLIDE SEMINAR - PART I: BENIGN BONE TUMORS Case I Fibrous dysplasia ( FD) Introduction and definition: Definition by WHO Benign medullary fibro-osseous lesion wich may involve one or more bones. Fibrous
SLIDE SEMINAR - PART I: BENIGN BONE TUMORS Case I Fibrous dysplasia ( FD) Introduction and definition: Definition by WHO Benign medullary fibro-osseous lesion wich may involve one or more bones. Fibrous
Diagnosis and Management of Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Jaws -
 Diagnosis and Management of Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Jaws - A Current Review for the Dental Clinician Gisele N. Mainville, DMD, MSc, FRCD(C), Dipl. ABOMP 1 Daniel P. Turgeon, DMD, MSc, FRCD(C),
Diagnosis and Management of Benign Fibro-Osseous Lesions of the Jaws - A Current Review for the Dental Clinician Gisele N. Mainville, DMD, MSc, FRCD(C), Dipl. ABOMP 1 Daniel P. Turgeon, DMD, MSc, FRCD(C),
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Osteomas of the craniofacial region
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2011; 41 : 107-13 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.3.107 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, usan, Korea STRCT
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2011; 41 : 107-13 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2011.41.3.107 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, usan, Korea STRCT
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report. A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Juvenile ossifying fibroma: case report and literature review. Management and differential diagnosis
 The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2017023 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Juvenile ossifying fibroma: case report and literature review. Management and differential
The authors, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/mbcb/2017023 https://www.jomos.org Up-to Date Review And Case Report Juvenile ossifying fibroma: case report and literature review. Management and differential
Modern Pathology (2014), 1 9. & 2014 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved /14 $
 & 2014 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/14 $32.00 1 Chromosome 12 long arm rearrangement covering MDM2 and RASAL1 is associated with aggressive craniofacial juvenile ossifying fibroma and extracranial
& 2014 USCAP, Inc. All rights reserved 0893-3952/14 $32.00 1 Chromosome 12 long arm rearrangement covering MDM2 and RASAL1 is associated with aggressive craniofacial juvenile ossifying fibroma and extracranial
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases
 Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IV (November. 2016), PP 110-114 www.iosrjournals.org Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IV (November. 2016), PP 110-114 www.iosrjournals.org Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia
Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2018; 48: 131-7 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2018.48.2.131 Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report Chang-Ki Min 1, Kwang-Joon Koh 1, Kyoung-A Kim 1, *
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2018; 48: 131-7 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2018.48.2.131 Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report Chang-Ki Min 1, Kwang-Joon Koh 1, Kyoung-A Kim 1, *
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Myositis Ossificans Mimicking Sarcoma, the Importance of Diagnostic Imaging Case Report
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2014; 79: 228-232 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.890209 CASE REPORT Received: 2013.12.18 Accepted: 2014.01.27 Published: 2014.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2014; 79: 228-232 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.890209 CASE REPORT Received: 2013.12.18 Accepted: 2014.01.27 Published: 2014.07.28 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C
Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
Fibro Osseous Lesions Classifications, Pathophysiology and Importance of Radiology: a Short Review
 IBBJ Winter 2016, Vol 2, No 1 Mini Review Fibro Osseous Lesions Classifications, Pathophysiology and Importance of Radiology: a Short Review Kenniyan Kumar Srichinthu 1, Thukanayakanpalayam Ragunathan
IBBJ Winter 2016, Vol 2, No 1 Mini Review Fibro Osseous Lesions Classifications, Pathophysiology and Importance of Radiology: a Short Review Kenniyan Kumar Srichinthu 1, Thukanayakanpalayam Ragunathan
Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report
 DOI 10.1007/s12105-017-0832-z CASE REPORT Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report Hui Jeong Jeong 1 Jin Roh 1 Bong Jae Lee 2 Kyung Ja Cho 1 Received: 13 March 2017 / Accepted: 13 June
DOI 10.1007/s12105-017-0832-z CASE REPORT Low-Grade Papillary Schneiderian Carcinoma: A Case Report Hui Jeong Jeong 1 Jin Roh 1 Bong Jae Lee 2 Kyung Ja Cho 1 Received: 13 March 2017 / Accepted: 13 June
Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage
 Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Accepted February 13th, 2004 Iliac aneurysmal bone cyst treated by cystoscopic controlled curettage Ludwig Schwering¹, Markus Uhl² and Georg W. Herget( )¹ ¹ Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pleomorphic adenoma of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari
 of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
of breast - a case report and distinction with metaplastic carcinoma D Gupta, S Agrawal, N Trivedi, A Tewari Introduction, also known as mixed tumour, is a benign tumour which typically presents as a painless,
Case report. Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma. Open Access
 Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
Case report Open Access Giant cell reparative granuloma of the hallux following enchondroma Khaled Kamoun 1,&, Tarak Sellami 1, Zied Jlailia 1, Layla Abid 2, Mourad Jenzri 1, Mouna Bouaziz 3, Omar Zouar
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Disclosures. Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone. Outline. The osteoclast. Giant cell rich tumors 5/21/11
 Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Disclosures Giant Cell Rich Tumors of Bone Andrew Horvai, MD, PhD Associate Clinical Professor, Pathology This lecture discusses "off label" uses of a number of pharmaceutical agents. The speaker is describing
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2013; 47: 481-485 CASE STUDY Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland Ji Yun Jeong Dongbin
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2013; 47: 481-485 CASE STUDY Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland Ji Yun Jeong Dongbin
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Case Report
 Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Brown tumor of the rib as a first presentation of primary hyperparathyroidism: Report of three cases and literature review
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 CASE REPORT Brown tumor of the rib as a first presentation of primary hyperparathyroidism: Report of three cases and literature review Jie Zhang 1, Hao Wang 2, Weijun Tian
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 CASE REPORT Brown tumor of the rib as a first presentation of primary hyperparathyroidism: Report of three cases and literature review Jie Zhang 1, Hao Wang 2, Weijun Tian
PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT
 PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT Dr.V.Gopinath, 1 Dr.V.Krishna, 2 Dr.Pramod kumar 3 1. Professor and Head, Department Of Periodontology, Department Of Periodontology, Rungta College
PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT Dr.V.Gopinath, 1 Dr.V.Krishna, 2 Dr.Pramod kumar 3 1. Professor and Head, Department Of Periodontology, Department Of Periodontology, Rungta College
Case Report Concurrent Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia and Osteogenic Sarcoma: Report of Two Cases
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 180561, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/180561 Case Report Concurrent Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia and Osteogenic Sarcoma: Report of Two Cases A. A. Olusanya, 1 B.
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 180561, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/180561 Case Report Concurrent Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia and Osteogenic Sarcoma: Report of Two Cases A. A. Olusanya, 1 B.
ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT
 Case Report Received : 23-07-2013 Review completed : 29-08-2013 Accepted : 04-09-2013 ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT V. V. N Pavan Kumar,* Madhumati Singh,** Sandeep Kashyap,*** Madan
Case Report Received : 23-07-2013 Review completed : 29-08-2013 Accepted : 04-09-2013 ANEURYSMAL BONE CYST OF MANDIBLE - A CASE REPORT V. V. N Pavan Kumar,* Madhumati Singh,** Sandeep Kashyap,*** Madan
Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases
 Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report 1
 Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:264-268 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.264 Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report Jung Ah Park, Sung Gyu Moon,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:264-268 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.264 Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma with Cystic Change of the Femur: a Case Report Jung Ah Park, Sung Gyu Moon,
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report
 Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a
 G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 46/Sep 22, 2014 Page 11296
 CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association
 218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
Osteosarcoma of the maxilla
 case report Osteosarcoma of the maxilla Bige Sayin, Nilgün Yildirim, Murat Vural, Doǧan Dede Department of Radiology, Ankara Numune State Hospital, Ankara, Turkey Background. Maxillofacial sarcomas are
case report Osteosarcoma of the maxilla Bige Sayin, Nilgün Yildirim, Murat Vural, Doǧan Dede Department of Radiology, Ankara Numune State Hospital, Ankara, Turkey Background. Maxillofacial sarcomas are
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
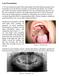 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3
 SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
SPECIAL SLIDE SEMINAR CASE 3 Tihana Džombeta, MD Leo Pažanin, MD, PhD Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Centre Sestre milosrdnice
Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment
 The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment Katie L. Dennis * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology
The Open Pathology Journal, 2009, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Evaluating and Reporting Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Imatinib Mesylate Treatment Katie L. Dennis * and Ivan Damjanov Department of Pathology
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2016; 34(2): 123-8 Original Article Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report Sedigheh Bakhtiari 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas 2 Seyyed Hasan
Journal of Dental School 2016; 34(2): 123-8 Original Article Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report Sedigheh Bakhtiari 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas 2 Seyyed Hasan
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: ABSTRACT
 Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case Report Extensive Presentation of Central Ossifying Fibroma Treated with Conservative Surgical Excision
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 204258, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/204258 Case Report Extensive Presentation of Central Ossifying Fibroma Treated with Conservative Surgical Excision Matheus
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 204258, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/204258 Case Report Extensive Presentation of Central Ossifying Fibroma Treated with Conservative Surgical Excision Matheus
Huge Central Ossifying Fibroma on the Anterior Mandible : A Case Report
 Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(4):243-250 하악전방부에발생한거대중심성골화성섬유종 문성용 1) *, 김수관 1), 김학균 2), 윤정훈 3) ** 조선대학교치과대학구강악안면외과학교실 1), 충남대학교의과대학치과학교실구강악안면외과 2) 원광대학교치과대학대전치과병원구강병리과 3) Huge Central
Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(4):243-250 하악전방부에발생한거대중심성골화성섬유종 문성용 1) *, 김수관 1), 김학균 2), 윤정훈 3) ** 조선대학교치과대학구강악안면외과학교실 1), 충남대학교의과대학치과학교실구강악안면외과 2) 원광대학교치과대학대전치과병원구강병리과 3) Huge Central
9990 East Cent. Afr. J. surg
 Management of Giant Craniofacial Ossifying Fibroma Case Series Report. J. Moshy. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, Muhimbili University and Allied Health Sciences, P.O.Box 65014, Dar-Es-Salaam,
Management of Giant Craniofacial Ossifying Fibroma Case Series Report. J. Moshy. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery, Muhimbili University and Allied Health Sciences, P.O.Box 65014, Dar-Es-Salaam,
(CYLINDROMA) ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA
 (CYLINDROMA) This malignant tumor is poorly encapsulated and while seemingly well defined within the affected gland, there is usually infiltration of surrounding tissue on closer examination. The cut surface
(CYLINDROMA) This malignant tumor is poorly encapsulated and while seemingly well defined within the affected gland, there is usually infiltration of surrounding tissue on closer examination. The cut surface
04/09/2018. Follicular Thyroid Tumors Updates in Classification & Practical Tips. Dissecting Indeterminants. In pursuit of the low grade malignancy
 Follicular Thyroid Tumors Updates in Classification & Practical Tips Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Follicular Thyroid Tumors Updates in Classification & Practical Tips Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p
 Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
LAC + USC.
 Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
ISSN Supplement 2011
 ISSN 2250-0359 Supplement 2011 Fibrous dysplasia of Faciomaxillary region case reports and review of literature Dr T Balasubramanian Abstract: This article discusses the author's experience in managing
ISSN 2250-0359 Supplement 2011 Fibrous dysplasia of Faciomaxillary region case reports and review of literature Dr T Balasubramanian Abstract: This article discusses the author's experience in managing
Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses:
 Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses: Approaches to Diagnostic Imaging Nir J. Harish September 2007 Head and Neck Cancers Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Salivary glands Incidence
Tumors of the Paranasal Sinuses: Approaches to Diagnostic Imaging Nir J. Harish September 2007 Head and Neck Cancers Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Salivary glands Incidence
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP. Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest
 USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING OSTEOSARCOMA
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
