Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor accompanied by a dentigerous cyst: A case report
|
|
|
- Eugenia Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 14: , 2017 Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor accompanied by a dentigerous cyst: A case report SHOKO GAMOH 1, HIRONORI AKIYAMA 1, CHISATO FURUKAWA 2, YUKI MATSUSHIMA 2, TOMIO ISEKI 2, MASAHIRO WATO 3, AKIO TANAKA 3, SHOSUKE MORITA 2 and KIMISHIGE SHIMIZUTANI 1 1 Department of Oral Radiology; 2 First Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Osaka Dental University, Osaka ; 3 Department of Oral Pathology, Osaka Dental University, Osaka , Japan Received December 29, 2015; Accepted July 5, 2017 DOI /ol Abstract. A calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor (CCOT) is a proliferation of odontogenic epithelium and scattered nests of ghost cells and calcifications that may form the lining of a cyst, or present as a solid mass. It was previously described by Gorlin et al in 1962 as a calcifying odontogenic cyst. Dentigerous cysts are developmental odontogenic jaw cysts, commonly manifesting in the second and third decades of life. The present study reports an asymptomatic case in a 13 year old boy who was referred to the outpatient clinic of the Osaka Dental University Hospital (Osaka, Japan) for additional investigation of an area of radiolucency in the lower right jaw. X ray demonstrated a unilocular, well circumscribed, radiolucent lesion in the mandible, which measured 30x20 mm, with radiopaque structures within it. Enucleation of the lesion with tooth extraction was performed, which histopathologically revealed features of a CCOT and a cyst. To the best of our knowledge, the occurrence of such a lesion has not been previously identified. The present study examined the significance of the case with a brief review of the literature. Introduction Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor (CCOT) is a novel classification of calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) that was recommended by the 2005 classification of the World Health Organization (WHO) (1). COC was first described as a likely analogue of the calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe (also termed pilomatricoma or pilomatrixoma) in a study by Gorlin et al in 1962 (2); therefore, the eponym of Gorlin cyst is frequently used (3,4). The histopathological features Correspondence to: Dr Shoko Gamoh, Department of Oral Radiology, Osaka Dental University, Otemae, Chuo, Osaka , Japan E mail: gamo s@cc.osaka dent.ac.jp Key words: calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor, dentigerous cyst, simultaneous, septum, pediatric, panoramic radiography, computed tomography of this pathological entity are the most notable, including a cyst lining demonstrating characteristic ghost epithelial cells with a propensity to calcify, and the occasional association of this observation with certain odontogenic tumors, including odontoma and ameloblastoma (5). An association is often found between COC and impacted or displaced adjacent teeth. By contrast, dentigerous cysts (DC) are the second most common type of odontogenic cyst, following radicular cysts (6). DCs form at a frequency of 1.44/100 unerupted teeth, representing ~17.1% of all true jaw cysts (7). According to the WHO classification of jaw cysts, DC is defined as an epithelial developmental odontogenic cyst (8). As for CCOT and DC, certain studies have observed recurrent cases with subsequent malignant transformation (9,10). The present study describes the case of a 13 year old boy who exhibited CCOT and DC within the same cavity, an occurrence that, to the best of our knowledge, has not been previously identified in the literature. Although they may have arisen coincidentally, the presence of two odontogenic lesions in the same cavity in the same patient, one of which is categorized as a neoplasm and the other as a cyst, raises the question regarding their origin and growth process. These issues are investigated in the present study, with a brief review of the literature. Case report A 13 year old asymptomatic Japanese boy was referred to the outpatient clinic of the Osaka Dental University Hospital (Osaka, Japan) on March 23rd, 2015 by a dentist for additional investigation of an area of radiolucency in the lower right molar area. The lesions were first detected on conventional radiographs at a local dental clinic that the patient had visited for dental checkups. Clinical examination revealed slight facial asymmetry and no intra oral swelling (Fig. 1). The initial conventional radiograph was obtained using panoramic equipment (Super Veraview X500 AE; J Morita Manufacturing Corp., Kyoto, Japan) at 78 kv, 9 ma, and conventional equipment (UD150B 10; Shimadzu Corp., Kyoto, Japan) at 60 kv, 200 ma; this revealed the presence of a well defined, unilocular, radiolucent lesion with a smooth margin associated with impacted lower right second and third molars. The outline of the whole lesion encompassed an area of scalloping between the two impacted molars, although none of the observations
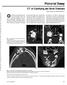
2 5786 GAMOH et al: CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH A DENTIGEROUS CYST were indicative of the presence of a septum inside the lesion. Large and small radio opaque bodies formed a perimeter in the lesion around the impacted lower right second molar, which are characteristics specifically observed in CCOT. Radio opaque bodies were thinly spaced in the distal portion of the lesion. Root resorption or displacement of the lower right first molar was indistinct, although the lesion was located close to the distal side of the first molar. The mandibular canal was shifted downward due to pressure from the lesion (Fig. 2). The quality of the intraoral radiograph was poor as the X ray sensor induced the patient's gag reflex. Computed tomography (CT) images were obtained using a CT scanner (BrightSpeed Elite; GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) at 120 kv. The electrical current was automatically optimized for the object thickness (maximum, 120 ma). In addition, the CT was performed according to the following parameters: Slice thickness, 0.65 mm; pitch and tube voltage, 0.625:1; and field of view, 16.8 cm 2. CT images revealed a 20 mm sized, elliptical, well defined, unilocular expanding lesion with thinned buccolingual cortical plates in the right mandible molar area (Fig. 3). Lower right second and third molars were impacted underneath the bulk of the lesion, near the inferior margin of the mandible. Large and small radio opaque bodies lined the margin of the mesial lesion around the impacted lower right second molar. Radio opaque bodies were poorly detected in the distal portion around the impacted third molar. The mandibular canal near the lesion was shifted downward. There were no observations that indicated the existence of a septum. These results were consistent with those of the panoramic radiograph, providing additional information concerning buccolingual bony expansion. The CT value of the radiolucency inside the lesion was 30 HU, representing fluid, and that of the radio opaque bodies was ~1,200 Hounsfield units, suggesting that they were tooth like masses. Overall, the imaging diagnosis was of a CCOT. The lesion was judged to be a single mass due to the absence of a septum. It was hypothesized that the CCOT had displaced or prevented the eruption of molars, as the development of CCOT and tooth eruptions occurred concurrently. Following fenestration and incisional biopsy, histopathological examinations were performed. The specimens were fixed in 10% formalin solution and embedded in paraffin at room temperature for 24 h. Samples were sliced into 2 µm thick sections, deparaffinized in l limonene (Hemo D, FALMA Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and dehydrated through a graded ethanol series (80, 90, 95 and 100%). Antigen retrieval was performed by autoclaving at 121 C for 15 min in retrieval buffer (ph 6.0; Mitsubisi Kagaku Yatoron, Tokyo, Japan). Subsequent to autoclaving, slides were allowed to cool down to room temperature. The endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxidase, and non specific reactions were blocked with 2% normal horse serum (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA). The section was incubated with anti human B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl 2) oncoprotein mouse monoclonal antibody (1:100, clone 124, cat. no. M0887, lot no , Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). This antibody was incubated for 60 min at room temperature. Subsequently, the section was incubated with peroxidase conjugated anti mouse antibody Figure 1. Images at initial clinical examination. (A) Front face view and (B) intra oral view demonstrating no extra oral asymmetry or intra oral swelling, respectively. Figure 2. Initial conventional radiographs. (A) Panoramic and (B) posteroanterior radiographs revealing the presence of a well defined, unilocular, radiolucent lesion with a smooth margin associated with impacted lower right second and third molars. L, left side. (1:1, cat. no , Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.) for 30 min at room temperature. The section was visualized by 3,3' diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride and counterstained with 1% hematoxylin at room temperature for 60 min. As a negative control, a non immunized antibody [mouse immunoglobulin G (cat. no. X0943, lot no. 012C013; dilution, 1:1,000 Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.)] was used instead of primary antibodies. The specimen was independently interpreted by two pathologists without using any software. If decisions
3 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 14: , Figure 3. Initial computed tomography images. (A) Axial view and (B) coronal view demonstrating an impacted lower right second molar. (C) Coronal view illustrating the radio opaque bodies lined up along the margin of the mesial lesion. (D) Coronal view demonstrating the impacted lower right third molar. Images revealed a 20 mm, elliptic, well defined, unilocular expanding lesion with thinned buccolingual cortical plates in the right mandible molar area. between the pathologists differed, agreement was reached by consensus decision making. The histopathological results demonstrated that the lesion may have been an odontogenic fibroma with odontogenic epithelium. CT was performed 3.5 months after the initial CT and it was observed that the calcification inside the lesion had increased in the interval between the fenestration and the tumor excision (Fig. 4). With a tentative diagnosis of a benign odontogenic tumor of the mandible, surgical enucleation under general anesthesia was performed. The patient underwent surgical treatment with extensive bone curettage and extraction of the lower right second and third molars 4 months after the fenestration. Histopathological examination of the whole mount section of the excisional biopsy specimens, sectioned in a mesiodistal direction, demonstrated that the lesion exhibited two distinctive features (Fig. 5A). In the mesial portion around the lower right second molar, the cystic wall was lined by an ameloblastomatous epithelium with dentin like structures, ghost cells and numerous calcified particles (Fig. 5B). Only this portion of the specimen was stained by an antibody against Bcl 2 protein, the presence of which distinguishes tumors from other pathologies and is associated with the mechanism of apoptosis (11,12), which confirmed the existence of tumor cells (Fig. 5C). Conversely, in the distal portion around the third molar, the cystic lesion was lined by unkeratinized stratified squamous epithelia that Figure 4. Computed tomography image obtained subsequent to fenestration. Calcification inside the lesion was noted to be increased 3.5 months after the procedure. included an area of proliferation due to inflammation caused by the fenestration (Fig. 5D). This portion did not demonstrate any expression of Bcl 2 protein (Fig. 5E). These histopathological results supported the diagnoses of a CCOT and DC. A thick layer of collagen fiber was also observed between the two different histopathological entities.
4 5788 GAMOH et al: CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH A DENTIGEROUS CYST Figure 5. Histopathological data. (A) Image demonstrating the synchronism of the two aspects of the lesion. Hematoxylin and eosin staining; *, the mesial portion indicating calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor; **, the distal portion indicating a dentigerous cyst; ***, a thick layer of collagen fibers. Granulation tissue accompanied by cholesterol gap occupies the ex cystic space due to inflammation potentially caused by fenestration. However, a remaining cyst cavity may be observed near to the cyst wall surrounding the granulation tissue. (B) Image obtained from the mesial portion of the specimen. The cystic wall was lined by an ameloblastomatous epithelium with ghost cells and numerous calcified particles. The dentin like hard tissue was visible (scale bar, 50 µm; original magnification, x100). (C) The same tissue portion as (B) was stained by an antibody against Bcl 2 protein, which confirmed that this portion consisted of tumor cells (scale bar, 50 µm; original magnification, x100). (D) Image obtained from the distal portion of the specimen. The cystic lesion was lined by unkeratinized stratified squamous epithelia (scale bar, 50 µm; original magnification, x100). (E) The same portion as (D) was stained by an antibody against Bcl 2 protein (original magnification, x100). Bcl 2, B cell lymphoma 2. The results of the surgery were consistent with the radiological data (Fig. 6A) and the mandibular canal existed just underneath the impacted teeth (Fig. 6B). The enucleated material exhibited a solid structure with calcification in the thick wall. No recurrence or postoperative complications were observed during a 2 year follow up period. Written informed patient consent was obtained for the publication of this study. Discussion The current case presents two important clinical points, namely that CCOT and DC may occur simultaneously and adjacently in a single cavity of the same jaw, and that CT is useful in evaluating the result of the fenestration by visualizing the change in the total size of the tumor. The present study reports a case of the simultaneous occurrence of CCOT and DC in the mandible of a patient. To the best of our knowledge, the synchronous occurrence of CCOT and DC as distinct lesions has not been previously identified. In the present case, the diagnoses reached from the imaging and histopathological studies were inconsistent. The presence of a single mandibular radiolucent lesion led to the suspected diagnosis of a CCOT. However, the definitive diagnosis of the two pathologically distinct entities of CCOT and DC was made by pathologists based on the excisional biopsies. CCOT may occasionally be an aggressive and recurrent tumor (1,13), therefore close post surgical follow up is preferable. In general, odontogenic lesions containing calcifications are particularly difficult to diagnose based only on histopathological data. X rays are occasionally crucial to reach
5 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 14: , Figure 6. Intraoperative images. (A) Image demonstrating the impaction of the lower third molar following the extraction of the lower second molar with calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor. (B) Image demonstrating the naked mandibular canal (arrow). The cystic lesion was easily separated from the surrounding bone. Figure 7. (A) X ray of the lesion. (B) Schematic view of the two lesions and the possible pressure (arrows) produced as a result of unequal growth. DC, dentigerous cyst; CCOT, calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor. the definite diagnosis. However, regarding the present case, it was important to consider potential explanations for the difficulty in achieving the diagnosis based on X ray images alone, which were not able to detect the existence of DC. Considering the X ray and histopathological data, two different types of soft tissues were estimated to be adjacent to each other in a single hard tissue cavity. Previous literature has described the simultaneous occurrence of odontogenic lesions as hybrid or distinct lesions (3,14 18). Among these studies, Chindasombatjaroen et al (17) described the case of a patient with CCOT associated with an odontoma, a supernumerary tooth, and DC that simultaneously occurred at varying maxillary locations. By contrast, the present study described the occurrence of two independent lesions that existed concomitantly in a single cavity. The characteristic feature of the case in the present study was that the CT images did not demonstrate any indication of the existence of a septum; only a bundle of collagen fibers separated the two lesions. It was also found that CT is useful not only for diagnosing the disease, but for evaluating the issue of fenestration. From a radiological viewpoint, the focus was directed towards the internal structure of the lesion. The CT images demonstrated that the calcification inside the lesion had increased in the interval between fenestration and enucleation. The following two assumptions about this observation could be made: The development of the CCOT was accelerated by stimulation caused by the fenestration, and the ossification as part of the healing process occurred inside the lesion. Neither assumption was correct in the present case. It was important to focus on the fact that the whole lesion had decreased in size following the fenestration, which indicated that sound healing was obtained subsequent to surgical intervention. According to the surgeon, additional development or ossification inside the CCOT may occur over the years following initial downsizing, due to surgical decompression or fenestration. This issue highlighted the unforeseen difference of viewpoints between radiologists and surgeons. CCOT generally appears as a unilocular lesion with a well defined margin (5,19). The tumor may resemble a calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor, odontoma, adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, ossifying fibroma or fibrous dysplasia. The lining of COC consists of ameloblastic epithelium and ghost cells, which undergo dystrophic calcification (20). In the early developmental stages, COCs will appear completely radiolucent. During maturation, calcifications develop that produce a well circumscribed, mixed radiolucent radiopaque appearance (4). In the case of the present study, well defined unilocular forms and regular margins were observed on conventional radiographs and CT images. Unexpectedly, the CT images did not demonstrate any indications of the slightly scalloped outline and septum like structure that was observed on the panoramic radiograph. The reason for this may be associated with the projection geometry peculiar to conventional radiographs, termed the eggshell effect. Conventional radiographs that project a three dimensional volume onto a two dimensional receptor may produce an eggshell effect of corticated structures. The septum like structure that was present only on the panoramic radiograph was a key result in the interpretation of the case, as it was present in a single lesion. It suggested that there was a difference in the potential doubling time between the two lesions. Considering the nature of tumors and cysts, the growth of the CCOT was potentially quicker compared with that of the DC, which could result in pressure from the CCOT on the side of the DC. Fig. 7 demonstrates the schematic view of the two lesions being exposed to an X ray beam. CCOT rarely presents in association with other odontogenic tumors, including ameloblastic fibro odontoma, ameloblastic fibroma, odontoameloblastoma and odontogenic myxofibroma (16,21,22). DC, ameloblastic fibro odontoma, adenomatoid odontogenic tumors and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors are all included in the differential diagnosis of a CCOT. A definitive diagnosis may be reached histologically (16,23). In the X ray investigation of the present case, ameloblastic fibro odontoma was ruled out, as radiopacity was not observed in the central region of the tumor, the density of which resembled that of dental hard tissue, as observed in odontomas (24). A calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor was also ruled out, as the radiolucent margin was clearly demarcated from the normal bone at the periphery.
6 5790 GAMOH et al: CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH A DENTIGEROUS CYST By definition, a DC encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth as a result follicular expansion, and it is attached to the cement enamel tooth junction. The peak incidence for DCs is within the second and third decades of life, with the mandibular third molars being the most frequently involved teeth (24). The histological appearance of the lesion is of a thin myxoid appearing fibrous tissue wall, lined by non keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium, which is actually a derivative of reduced enamel epithelium (25). Radiologically, a well circumscribed cyst that contains the crown of the tooth is observed. As the cyst grows, it pulls the unerupted tooth with it. A small DC is unilocular. Large cysts may be multilocular, and the confined tooth may be displaced from its normal location (20,26). In the present case, achieving a diagnosis based on radiology was challenging for the following reasons: The suspected entities of CCOT and DC are occasionally associated with impacted or unerupted teeth (20) and no septum like structure was observed on the CT images. In this regard, it is possible that resorption of the septum occurred due to the skeletal growth of the patient. However, the amount of calcification was markedly different between the portions around the second and third molars. The existence of considerable differences between the two portions was confirmed by CT. In conclusion, the present case demonstrated that CCOT and DC may be present simultaneously in a single cavity. Additionally, CT was important in evaluating the healing process in detail. The present case may serve as a valuable warning that CCOT, which may recur and transform into malignancy if improperly treated, may be present in such lesions. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Dr Kaname Tsuji (First Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Osaka Dental University, Osaka, Japan) for providing support to the study, and ThinkSCIENCE Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) for providing language editing services. References 1. Utumi ER, Pedron IG, da Silva LP, Machado GG and Rocha AC: Different manifestations of calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 10: , 2012 (In English, Portuguese). 2. Gorlin RJ, Pindborg JJ, Odont, Clausen FP and Vickers RA: The calcifying odontogenic cyst a possible analogue of the cutaneous calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe. An analysis of fifteen cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 15: , Basile JR, Klene C and Lin YL: Calcifying odontogenic cyst with odontogenic keratocyst: A case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109: e40 e45, Menat S, Md S, Attur K and Goyal K: Ameloblastomatous CCOT: A case report of a rare variant of CCOT with a review of the literature on its diverse histopathologic presentation. Case Rep Dent 2013: , Iida S, Fukuda Y, Ueda T, Aikawa T, Arizpe JE and Okura M: Calcifying odontogenic cyst: Radiologic findings in 11 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101: , Son HJ, Jeong YJ, Jeong JS and Kang DY: An inflammatory dentigerous cyst shows rim uptake on bone scan: A case report. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48: 79 81, Narang RS, Manchanda AS, Arora P and Randhawa K: Dentigerous cyst of inflammatory origin a diagnostic dilemma. Ann Diagn Pathol 16: , Sumbh B, Sumbh SG, Jain P and Pagare J: Classification of odontogenic cysts: A review. IOSR J Dental Med Sci 16: 79 82, Mokhtari S, Mohsenifar Z and Ghorbanpour M: Predictive factors of potential malignant transformation in recurrent calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor: Review of the literature. Case Rep Pathol 2013: , Zapała Pośpiech A, Wyszyńska Pawelec G, Adamek D, Tomaszewska R, Zaleska M and Zapała J: Malignant transformation in the course of a dentigerous cyst: A problem for a clinician and a pathologist. Considerations based on a case report. Pol J Pathol 64: 64 68, Cheung TH, Chung TK, Lo KW, Yu MY, Krajewski S, Reed JC and Wong YF: Apotosis related proteins in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Gynecol Oncol 86: 14 18, Murakami M, Sakai H, Kodama A, Mori T, Maruo K, Yanai T and Masegi T: Expression of the anti apoptotic factors Bcl 2 and survivin in canine vascular tumours. J Comp Pathol 139: 1 7, Daniels JS: Recurrent calcifying odontogenic cyst involving the maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 98: , Hisatomi M, Asaumi J, Konouchi H, Yanagi Y and Kishi K: A case of glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Correlation of diagnostic imaging with histopathological features. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 29: , Shimamoto H, Kishino M, Okura M, Chindasombatjaroen J, Kakimoto N, Murakami S and Furukawa S: Radiographic features of a patient with both cemento ossifying fibroma and keratocystic odontogenic tumor in the mandible: A case report and review of literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 112: , Chindasombatjaroen J, Kakimoto N, Akiyama H, Kubo K, Murakami S, Furukawa S and Kishino M: Computerized tomography observation of a calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor with an odontoma: Case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 104: e52 e57, Chindasombatjaroen J, Poomsawat S and Klongnoi B: Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor associated with other lesions: Case report with cone beam computed tomography findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 113: , Fregnani ER, da Cruz Perez DE, Soares FA and Alves FA: Synchronous ameloblastoma and orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst of the mandible. J Oral Pathol Med 35: , Uchiyama Y, Akiyama H, Murakami S, Koseki T, Kishino M, Fukuda Y, Shimizutani K and Furukawa S: Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumour: CT imaging. Br J Radiol 85: , Som PM and Brandwein MS: Tumors and tumor like conditions. In: Head and Neck Imaging. Som PM and Curtin HD (eds). 4th edition. Mosby, St. Louis, pp , p352, p9385, Yoon JH, Kim HJ, Yook JI, Cha IH, Ellis GL and Kim J: Hybrid odontogenic tumor of calcifying odontogenic cyst and ameloblastic fibroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 98: 80 84, Lin CC, Chen CH, Lin LM, Chen YK, Wright JM, Kessler HP, Cheng YS and Ellis E III: Calcifying odontogenic cyst with ameloblastic fibroma: Report of three cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 98: , McGowan RH and Browne RM: The calcifying odontogenic cyst: A problem of preoperative diagnosis. Br J Oral Surg 20: , Koenig LJ: Mandible and maxilla. In: Diagnostic Imaging Oral and Maxillofacial. Koenig LJ, Tamimi D, Petrikowski CG, Harnsberger HR, Ruprecht A, Benson BW, Van Dis ML, Hatcher D and Perschbacher SE (eds). Amirsys, Milwaukee, WI, pp50 53, pp , Shephard M and Coleman H: Simultaneous adenomatoid odontogenic and keratocystic odontogenic tumours in a patient with Gorlin Goltz syndrome. Aust Dent J 59: , Verbin RS and Barnes L: Cysts and cystlike lesions of the oral cavity, jaws and neck. In: Surgical Pathology of the Head and Neck. 1st edition. Barns L (ed). Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY, pp , 1985.
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion
 DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy
 Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions.
 Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor A Case Report and Review on Diverse Presentation of the Tumor
 : J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
: J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
IMPACTED CANINE ASSOCIATED WITH COMPOUND ODONTOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Maxilo-facial surgery IMPACTED CANINE ASSOCIATED WITH COMPOUND ODONTOMA: A CASE REPORT Carmen Gabriela STELEA 1, Emilia DÎMBU 2, Alexandra Lorina STELEA 3, Alina BOTEZATU 4 1 Lecturer, Gr. T. Popa University
Maxilo-facial surgery IMPACTED CANINE ASSOCIATED WITH COMPOUND ODONTOMA: A CASE REPORT Carmen Gabriela STELEA 1, Emilia DÎMBU 2, Alexandra Lorina STELEA 3, Alina BOTEZATU 4 1 Lecturer, Gr. T. Popa University
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy
 Iranian Journal of Orthodontics Shirani, Arshad, Asefi 43 Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy Gholamreza Shirani a, Mahnaz Arshad
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics Shirani, Arshad, Asefi 43 Formation of supernumerary tooth one year after enucleation of adjacent dentigerous cyst in a 9-year-old boy Gholamreza Shirani a, Mahnaz Arshad
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature
 Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible
 114 J Meikai Dent Med 44 1, 114 118, 2015 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 46 A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible Nobuaki TAMURA 1, Hiroshi TAKESHIMA 1, Kentaro KIKUCHI
114 J Meikai Dent Med 44 1, 114 118, 2015 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 46 A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible Nobuaki TAMURA 1, Hiroshi TAKESHIMA 1, Kentaro KIKUCHI
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
Combined Benign Odontogenic Tumors: CT and MR Findings and Histomorphologic Evaluation
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:867 872, May 2001 Case Report Combined Benign Odontogenic Tumors: CT and MR Findings and Histomorphologic Evaluation Nadine Martin-Duverneuil, Marie-Hélène Roisin-Chausson, Anthony
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:867 872, May 2001 Case Report Combined Benign Odontogenic Tumors: CT and MR Findings and Histomorphologic Evaluation Nadine Martin-Duverneuil, Marie-Hélène Roisin-Chausson, Anthony
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Conservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
 SE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.s1.s1 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 onservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
SE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.s1.s1 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 onservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation
 European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of. the ethmoid sinus
 Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT
 May, 2012 INTERNATIONAL DENTAL JOURNAL OF STUDENT S RESEARCH: CASE REPORT Article Code: IDJSR 0002 EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT Authors Bouguezzi Adel, DDS, Resident 1
May, 2012 INTERNATIONAL DENTAL JOURNAL OF STUDENT S RESEARCH: CASE REPORT Article Code: IDJSR 0002 EXTENSIVE PERIAPICAL CYST IN THE MAXILLARY SINUS A CASE REPORT Authors Bouguezzi Adel, DDS, Resident 1
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology ISSN: Vol. 4 No. 4; April 2017
 Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions
 Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
Impacted third molars can be. Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report
 Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report Kevin E Lung, BSc, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C); Seema Ganatra, BSc, DDS, MSD, FRCD(C); Christopher
Multiple Multilocular Dentigerous Cysts with Intra-osseous and Extra-osseous Third Molar Displacement: A Case Report Kevin E Lung, BSc, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C); Seema Ganatra, BSc, DDS, MSD, FRCD(C); Christopher
Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle
 (2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
(2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of a Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1472 Manikkath Aparna et al case report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of A Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma Manikkath Aparna, Mukund Gupta,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1472 Manikkath Aparna et al case report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Rare Report of A Nonneoplastic Variant associated with Cholesterol Granuloma Manikkath Aparna, Mukund Gupta,
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Keywords: Mandible, Maxilla, Teeth, Cone Beam CT, Implants, Tumor and tumor-like conditions
 Dental Cone Beam CT: a primer for clinical radiologists e-poster: EP-1 Congress: ESHNR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Topic: ESHNR 2014 Authors: C. Vanhoenacker 1, F. Vanhoenacker 1, L. Vannitsen 1, A.
Dental Cone Beam CT: a primer for clinical radiologists e-poster: EP-1 Congress: ESHNR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Topic: ESHNR 2014 Authors: C. Vanhoenacker 1, F. Vanhoenacker 1, L. Vannitsen 1, A.
Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.04.40.5.5 pissn 34-550 eissn 34-5930 Characteristics of bony changes and tooth displacement in the mandibular cystic lesion involving the impacted third molar
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone
 Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst
 A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Shailesh Menat, 1 Shylaja MD, 2 Kailash Attur, 3 and Kaushal Goyal Introduction. 2. Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 407656, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/407656 Case Report Ameloblastomatous CCOT: A Case Report of a Rare Variant of CCOT with a Review of the Literature on
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 407656, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/407656 Case Report Ameloblastomatous CCOT: A Case Report of a Rare Variant of CCOT with a Review of the Literature on
