IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
|
|
|
- Norah Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent structure. Cysts occur more commonly in the jaws than in any other bone. Almost 25 % of all cysts are found in the jaws. Definition: A cyst is an epithelial lined, pathological cavity having fluid, semi-fluid or gaseous contents: and surrounded by connective tissue. TECHNICAL ASPECTS. 1. Occlusal view 2. Pan 3. PA, OM, lateral oblique 4. CT - for bony lesions. 5. MRI - for soft tissue lesions ETIOLOGY. Developmental Inflammatory Traumatic Neoplastic As the cyst enlarges it is more likely to cause cortical expansion ( and thinning) but the margins tend to remain intact. Numerous classifications have been published of cysts of the jaws and most of them are satisfactory. CLASSIFICATION. N = asked on NERB B = asked on Nat Boards I. BONE A. EPITHELIAL 1. Developmental a. Odontogenic i. Dentigerous (follicular) B. N. ii. Eruption N iii. Lateral periodontal B. N. Gingival cyst of adult N iv. Keratocyst (primordial) B.N v. Calcifying Odontogenic B.N vi. Gingival cyst of newborn - 1 -
2 b. Non-Odontogenic. i. Nasopalatine duct cyst B.N. Cyst of incisive papilla B. ii. Globulomaxillary?? B.N. iii. Median palatine. (mandibular) 2. Inflammatory i. Radicular B. N. ii. Paradental iii. Residual. B. N. iv. Collateral B. N. B. NON-EPITHELIAL i. Latent bone cyst/ lingual mandibular salivary gland depression (defect) / Stafne cyst B.N. ii. Simple/unicameral / traumatic/ hemorrhagic B.N. iii. Aneurysmal bone cyst iv. Mucosal cyst of maxillary antrum B.N. v. Extravacation cyst and ranula BN C. GORLIN GOLTZ / Basal cell nevus syndrome B.N. II. SOFT TISSUE. i. Nasolabial / naso-extra alveolar N. B ii. Dermoid N. B iii. Thyroglossal N. iv. Branchial cleft N [Also called Lympho-epithelial] A. EPITHELIAL. 1. DEVELOPMENTAL Clinically, cysts may achieve extreme size before they are discovered clinically; especially true in the mandible. a. ODONTOGENIC CYSTS i. Dentigerous Cyst A follicular cyst, or dentigerous cyst is a developmental odontogenic cyst which develops around the fully-formed crown of an unerupted tooth. Most are discovered on routine radiographs, when a tooth has failed to erupt, a tooth is missing, teeth are tilted or are otherwise out of alignment. The dentigerous cyst is most frequently found in the age group years. The most prevalent areas for dentigerous cysts are, in order of frequency, the mandibular third molar, maxillary third molar, maxillary canine and mandibular second premolar. i.e. teeth that are prone to impaction. About 75% are located in the mandible. This is the most common pericoronal cyst - 2 -
3 Radiographically. There is no sharp borderline between a normal enlarged pericoronal space and a cyst; if the width of this lucency has reached more than 2.5 mm [and has an irregular outline] it is probably a dentigerous cyst. Dentigerous cysts may be classified according to the site at which the cyst develops in relation to the crown of the tooth. It may be of the central or lateral type. Impacted supernumerary teeth often develop dentigerous cysts. Dentigerous cysts have a greater tendency than other jaw cysts to produce root resorption of adjacent teeth i.e. they are the most aggressive of the cysts. Found after the age at which the tooth should have erupted. In younger patients consider a differential diagnosis of ameloblastic fibroma. ii. Eruption Cyst Is a variation of a dentigerous cyst and occurs partly in the soft tissue. The eruption cyst may impede a tooth in its eruption within soft tissues overlying the bone. The eruption cyst produces a smooth, fluctuant swelling over the erupting tooth which may be either the color of normal gingiva, or pale blue. It is usually painless unless infected. Radiographically - The cyst may throw a soft-tissue peri-coronal shadow, but there is little bone involvement except that the dilated and open tooth crypt around the unerupted crown, may be seen on the radiograph. iii. Lateral Periodontal Cyst / Gingival Cyst of Adult Lateral periodontal cysts occur most frequently in the mandibular canine premolar area in young adults. They are usually symptomless and are discovered during routine radiological examination of the teeth. Radiographically - shows a well-defined, unilocular, round or avoid lucent area. The cyst lies somewhere between the apex and the cervical margin of vital teeth. They vary in size from as small as 1 mm to larger lesions which may involve the length of the root. The Botyroid cyst is a multilocular variation iv. Odontogenic Keratocyst and (Primordial Cyst) Keratocyst or primordial is a cyst with keratinized epithelium. A primordial cyst forms from the tooth bud and forms instead of a tooth. All primordial cysts are keratocysts but all keratocysts are NOT primordial cysts. The keratocyst arises directly from the dental lamina or remnants thereof. Often contains cheesy material that is produced by the epithelium. Some investigators use the noncommittal term odontogenic keratocyst regarding the pathogenesis and only state that the cyst lining is keratinized. Keratocysts have characteristic locations, the ramus of the mandible, the canine region in the maxilla and mandible, and the mandibular third molar region. In many instances, patients are free of symptoms until the cysts have reached a large size. Patients may complain of either pain, swelling or discharge. The primordial cyst tends to extend in the medullary cavity and expansion of the cortex occurs late. The enlarging cyst may produce displacement of the teeth Radiographically. Primordial cysts may appear as unilocular, round or avoid radiolucent areas. Often the lesions are extensive. Most are well demarcated with a distinct sclerotic margins as expected from a slowly enlarging lesion. If multilocular, the locules are well - 3 -
4 demarcated and may be misinterpreted as an ameloblastoma but the locules are fewer and well demarcarted. The scalloped margins suggest that unequal growth activity may be taking place in different parts of the cyst. Primordial cysts may impede the eruption of adjacent teeth and this results in a "dentigerous" appearance radiologically. The mandibular canal is often displaced and highlighted. Keratocysts have a pronounced tendency to recur. Most common distal to the canine tooth. Primordial cysts form in place of a tooth; most commonly found in the mandibular third molar region. v. Calcifying Odontogenic (EPITHELIAL) Cyst GORLIN The calcifying odontogenic cyst has many features of an odontogenic cyst and tumor epithelial proliferation and continuous growth. It originates from developmental odontogenic epithelial tissue. The lesion usually occurs as a slowly enlarging, frequently painless and non-tender swelling of the jaw. Intraosseous lesions may produce a bony expansion and may be fairly extensive. Often associated with en unerupted tooth. Affects females under 40 and males over age 40. Radiographically The lesion appears as a well defined, uni-or multilocular radiolucent, cystic area. Initially there are no calcifications and thus appears as a non-specific cyst. Later, small irregular calcified [opaque] bodies may be seen in the radiolucent area and in some cases the calcification may be substantial and occupy the greater part of the lesion. This is the only cystic lesion with opacities. Differential Diagnosis partially calcified odontoma, adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, ossifying fibroma; ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor. vi. Gingival Cyst of newborn or adult. Not seen radiologically. Not to be mistaken with Epstein s Pearl (on median palatal raphe) and Bhon s nodule - seen on alveolar ridge of the newborn. b. NON-ODONTOGENIC CYSTS. i. Nasopalatine Duct Cyst / Cyst of the Incisal canal (Incisive papilla cyst) Is a non-odontogenic developmental cyst located in the incisive canal or in the anterior palatine papilla and develops from the embryonic ducts of Scarpa and Stenson. (primitive organs of smell) Etiologically when the incisive canals are formed, the nasopalatine ducts are enclosed within the canals, as a regular duct, an epithelial cord or as interrupted epithelial islands. Clinically - the most common signs are palatal swelling and displacement of vital central incisor teeth. Swelling may occur in the midline on the labial aspects of the alveolar ridge. Found in older patient (40) who may complain of a salty taste. Radiographically the nasopalatine duct cyst is a well-demarcated radiolucency in the midline of the palate, apical to the central incisor teeth. The lucency varies from round to oval or heartshaped
5 Cysts may develop bilaterally in both Stenson canals and in some instances the radiolucency may be seen laterally if a single cyst develops in one of the major lateral canals of Stenson. Very large cysts extend posteriorly and superiorly. The margins of nasopalatine duct cysts are well-corticated unless they become infected. Root resorption rarely occurs. Teeth are vital. Differentiating between cyst and large incisal foramen. The cyst has well defined borders all the way around the cyst. As it enlarges it becomes heart-shaped and pushes the apices of the centrals apart. Usually larger than 1 cm. Foramen well defined along lateral borders only and has an irregular shape with indistinct borders. According to S. White, the median palatine cyst is an extension of the incisive canal cyst. ii. Nasolabial / Naso-[extra] alveolar Cyst The nasolabial cyst occurs outside the bone in the nasolabial folds below the ala nasi. It is classified as a soft tissue cyst. The most frequent symptom is swelling and difficulty in nasal breathing. Rarely patients complain of pain. In most cases the cysts are unilateral, grow slowly. They fill out the nasolabial fold and may lift the ala nasi, distort the nostril and produce a swelling of the floor of the nose. Intra-orally they form a bulge in the labial sulcus. The majority of cases appear in adults with a predominance in females. Radiographically -The cyst can be seen radiographically only if the kvp is reduced and the correct angle used. Otherwise, nothing is seen, unless opacifier is injected. It is then seen as a spherical radiopacity lying against the inferior and lateral borders of the anterior bony aperture of the nose, extending from near the midline to the canine fossa. iii. Globulomaxillary cyst. Clinically: Usually nothing until it becomes very large. Many authorities feel it is either a radicular or a keratocyst. Radiographically: Seen between the vital maxillary lateral incisor and canine as a well demarcated, unilocular, pear-shaped lucency. 2. INFLAMMATORY (ODONTOGENIC) i. Radicular Cyst Radicular cysts arise from epithelial residues in the periodontal ligament as a result of low grade irritation. (inflammation). The inflammation follows upon necrosis of the dental pulp and cysts arising in this way are found most commonly at the apices of non-vital teeth. In deciduous teeth the furcation area is initially involved. They may, however, also be found on the lateral aspects of the roots in relation to lateral accessory root canals - then called a collateral or accessory cyst. Radicular cysts are by far the most common cystic lesion in the jaw. They may be the result of trauma in which case no caries will be seen. Clinically, the radicular cyst is usually symptomless in its early stages and may cause rather extensive destruction before it is discovered. It may cause expansion of the affected area. Radicular cysts on maxillary lateral incisor, often cause an expansion of palatal bone and mucosa
6 Radiographically, the radicular cyst is a well circumscribed periapical, unilocular, radiolucency. The cyst may cause the neighboring structures to be displaced, especially in the maxillary sinus and the mandibular canal. Root resorption is occasionally seen. An acute exacerbation may result in the disappearance of the characteristic peripheral cortical rim. ii. Paradental Cyst The paradental cyst (Shear 1983) and the mandibular infected buccal cyst Stoneman and Worth 1983) may be the same entity. Both cysts appear on the lateral aspect of partially erupted vital mandibular molar teeth. The paradental cyst is seen in older patients in association with third mandibular molar and the mandibular infected buccal cyst usually around the first or second molar teeth in children or young adults. Radiographically A well demarcated radiolucency distal [and buccal] to a partially erupted tooth. A 90 degree occlusal view will show that it is more buccally situated than distally. iii. Residual Dental Cyst The residual dental cyst results where a collateral, lateral periodontal, radicular, or any other cyst or granuloma remains after the extraction of a tooth or a root. Radiographically - A round unilocular, radiolucency with well defined borders in an edentulous area. Differential diagnosis important iv. Collateral [accessory canal] Cyst Found on the lateral aspect of roots of non vital teeth. Following necrosis of the dental pulp the irritation follows the tract of the lateral accessory root canal. Should the tooth be removed this can also result in a residual dental cyst. Radiographically - Very similar to a lateral periodontal cyst but the associated tooth will be found clinically to be non vital. B. NON-EPITHELIAL i. Lingual Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect/ Latent Bone Cyst/ Defect (Stafne Cyst) The lesion is developmental but the pathogenesis of this entity is still unknown. Rarely found in young people. There is no epithelial lining and this is NOT a cyst Clinically there are no symptoms. The lesion is detected incidentally on radiographs of the mandible. They represent developmental defects, on the lingual aspects of the mandible and which are occupied by a lobe of normal submandibular salivary gland. The defects are not necessarily congenital. Tolman and Stafne (1967) have shown that radiological evidence of their development may first appear after the patients have reached middle age. Radiographically. The elliptical or ovoid radiolucency has a well- defined radiopaque border. Normally, it is situated, inferior to the mandibular canal in the molar area and is round to oval. Sialography will show that the defect contains healthy salivary tissue
7 ii. Simple/ Unicameral/ Hemorrhagic/ Traumatic Bone Cyst The simple bone cyst, which occurs in the mandible and never in the maxilla, is a unicameral cavity, empty or partly filled with a clear or a sero-sanguinous fluid. Does not have an epithelial lining. The lesion has been described under a variety of names, such as solitary bone cyst, hemorrhagic bone cyst, traumatic bone cyst, etc. Seen in young individuals. Clinically, more than 50 per cent of the reported cases present a definite history of trauma, which also is the most favored theory of origin. The simple bone cyst is often discovered incidentally, but swelling due to lateral expansion of the mandible and pain is present in more than 30 per cent of the cases. The mandibular premolar / molar area of young adults is the most frequent site. Teeth are vital. By definition this too is NOT a cyst. Radiographically, the lesion appears as a radiolucency with an irregular but fairly well demarcated outline. Often the lesion extends upward between the roots, producing the characteristic scalloped outline. The lamina dura of the teeth is identifiable in most cases. NO tilting of teeth and NO root resorption occurs. iii. Aneurysamal Bone Cyst The aneurysmal bone cyst is a benign intra-osseous lesion characterized by blood filled spaces of varying size. The cyst occurs almost exclusively in children and young adults. There are 3 stages of development; an initial stage due to a lytic reaction; a growth stage with an enlarged area of bone destruction and peripheral cortication; and a mature stage with bony expansion, cortication of the margins and septae formation [which often appears multilocular similar to an ameloblastoma] Clinically, the lesion is found most often in the mandible. It is unilateral, and often is asymptomatic except for tension; characterized as a fast growing expansive lesion that asists in differentiating it from an ameloblastoma. Radiographically, the aneurysmal bone cyst is characterized by irregular cyst-like radiolucencies intermingled with thin bony trabeculae giving a honeycomb or soap-bubble appearance. Laterally, the lesion is usually covered by a thin cortical layer. Is this a cyst? iv. Mucosal cyst of the Maxillary Antrum / Mucocele / Pseudocyst The mucosal cyst of the maxillary antrum, referred to as a mucocele or mucous retention cyst, probably occurs more commonly than was previously thought. See lecture on maxillary sinus. The mucosal cyst is characterized by the absence of symptoms in most cases and is usually discovered in the course of radiological examination. The cysts appear as dome-shaped radiopacities on the floor of the sinus and which have smooth and uniform outline. They vary in size from minute to very large and may occupy the entire maxillary sinus. The smooth curved borders are well-defined but not corticated. There is no resorption of adjacent bone and of particular importance is the persistence of the thin radio-opaque line of the antral cortex itself
8 C. Multiple Cysts and Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome / Gorlin-Goltz Syndrome This syndrome consists of a number of changes, of which multiple kerato and dentigerous cysts, multiple basal cell nevi on the skin of young people and skeletal abnormalities are among the most frequent. It is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but with a varying, often poor, penatrance. The cysts appear early in adolescence. Clinically, frontal bossing, hypertelorism with a broad nasal root and occasionally a slight mandibular prognathism gives patients with this syndrome a rather characteristic face. Numerous small, flattened, brownish / red basal cell tumors in young people are found in the skin, especially on the face, trunk, neck and arms. Radiographically, cystic radiolucencies in the mandible and the maxilla. The impacted teeth, NOT supernumary teeth, often with kerato and dentigerous cysts, are displaced and may have malformed roots. Calcification of falx cerebri occurs. Bifid ribs II. SOFT TISSUE CYSTS I. Nasolabial discussed above Nerb II. Dermoid III. Thyroglossal Nerb IV. Branchial cleft Nerb V. Sebaceous VI. Extravasation cyst. / ranula Nerb Remember the cyst of the incisal papilla is also soft tissue cysts. Also extravacation cyst, and the cyst-like lesions seen in early herpes and herpes zoster [shingles] - 8 -
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
CYSTS OF THE JAW AND SOFT TISSUES
 CYSTS OF THE JAW AND SOFT TISSUES Definition: it is a pathological cavity lined by epithelium containing fluid or semifluid (true cyst). If the cyst not lined by epithelium it is pseudo- cyst. Classification
CYSTS OF THE JAW AND SOFT TISSUES Definition: it is a pathological cavity lined by epithelium containing fluid or semifluid (true cyst). If the cyst not lined by epithelium it is pseudo- cyst. Classification
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Chapter 5. Developmental Disorders. Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1
 Chapter 5 Developmental Disorders Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1 Outline Ø Embryonic Development of the Face, Oral Cavity, and Teeth Ø Developmental
Chapter 5 Developmental Disorders Copyright 2014, 2009, 2004, 2000, 1996, 1992 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc 1 Outline Ø Embryonic Development of the Face, Oral Cavity, and Teeth Ø Developmental
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions
 Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area
 VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions.
 Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Only 40% of the Story
 X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
Oral Surgery. Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia. A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia:
 Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
INTERPRETATION RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION. Law of Symmetry. We will be reviewing: 7/30/16
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview
 Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
University of Palestine. Final Exam 2 ed Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone
 Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible
 Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Dental panoramic tomography: An approach for the general radiologist
 Pictorial Essay Australasian Radiology (2006) 50, 526 533 Dental panoramic tomography: An approach for the general radiologist R Boeddinghaus and A Whyte Perth Radiological Clinic, Perth, Western Australia,
Pictorial Essay Australasian Radiology (2006) 50, 526 533 Dental panoramic tomography: An approach for the general radiologist R Boeddinghaus and A Whyte Perth Radiological Clinic, Perth, Western Australia,
Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted Canines: Report of Five Cases Sulabha AN, Sachin Deshpande, Sameer C
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
IMAGING NONODONTOGENIC TUMORS OF THE JAWBONES
 IMAGING NONODONTOGENIC TUMORS OF THE JAWBONES N. Serman. Sept, 2002 W. & P Ch. 20 + 21. Stafne & Gibilisco Ch 15 Oral and Maxillofacial diagnostic Imaging Ch. 8 Non agenesis or non eruption of teeth often
IMAGING NONODONTOGENIC TUMORS OF THE JAWBONES N. Serman. Sept, 2002 W. & P Ch. 20 + 21. Stafne & Gibilisco Ch 15 Oral and Maxillofacial diagnostic Imaging Ch. 8 Non agenesis or non eruption of teeth often
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
10/23/2014. features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means. interpretation vs. diagnosis. science or art? image investigation
 features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud
 Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series.
 This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series. Radiology: Back to the Classroom! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate
This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series. Radiology: Back to the Classroom! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion
 DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
DOI 10.7603/s40782-014-0006-9 GST International Journal of Advances in edical Research (JAR) Vol.1.1, ay 2014 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review with Discussion Dr. Ritika Jindal BDS, 1 Dr. Ravikiran
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA. Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor
 DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 doi: 10.5958/0976-156X.2014.00005.7 LARGE RADICULAR CYST OF THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA A CASE REPORT 1 Manoj Meena 2 Nigel R Figueiredo 3 Ajit D Dinkar 4 Ena Mathur 5 Arum Khatkar 6 Sonam Malik 1 Senior lecturer
doi: 10.5958/0976-156X.2014.00005.7 LARGE RADICULAR CYST OF THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA A CASE REPORT 1 Manoj Meena 2 Nigel R Figueiredo 3 Ajit D Dinkar 4 Ena Mathur 5 Arum Khatkar 6 Sonam Malik 1 Senior lecturer
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
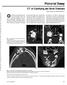 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS
 Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL AND ORAL CARE UNDER MEDICAL PLANS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL AND ORAL CARE UNDER PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL AND ORAL CARE UNDER PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Tapping the teeth with a tongue depressor will cause tingling sensation because of involvement of the root of the teeth.
 Odontogenic Cysts of upper jaw an analysis March 26, 2013 Rhinology 1 Professor Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Stanley Medical College Thiagarajan B. Odontogenic Cysts of upper
Odontogenic Cysts of upper jaw an analysis March 26, 2013 Rhinology 1 Professor Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Stanley Medical College Thiagarajan B. Odontogenic Cysts of upper
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
