Overview of the Digestive System Organs are divided into two groups
|
|
|
- Curtis Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
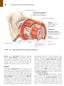
1 C H A P T E R 23 The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive System Organs are divided into two groups The alimentary canal Mouth, pharynx, and esophagus Stomach, small intestine, and large intestine (colon) Accessory digestive organs Teeth and tongue Gallbladder, salivary glands, liver, and pancreas The Alimentary Canal and Accessory Digestive Organs Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue Parotid gland Sublingual gland Salivary glands Submandibular gland Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Duodenum Small intestine Jejunum Ileum Anus Pharynx Stomach Pancreas (Spleen) Transverse colon Descending colon Ascending colon Cecum Large intestine Sigmoid colon Rectum Vermiform appendix Anal canal Figure
2 Digestive Processes Ingestion Propulsion Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion Absorption Defecation Peristalsis Major means of propulsion Adjacent segments of the alimentary canal relax and contract Figure 23.3a Segmentation Rhythmic local contractions of the intestine Mixes food with digestive juices Figure 23.3b 2
3 The Peritoneal Cavity and Peritoneum Peritoneum a serous membrane Visceral peritoneum surrounds digestive organs Parietal peritoneum lines the body wall Peritoneal cavity a slit-like potential space Falciform ligament Liver Parietal peritoneum Anterior Posterior Visceral peritoneum Peritoneal cavity (with serous fluid) Stomach Kidney (retroperitoneal) Wall of body trunk Figure 23.5 Mesenteries Lesser omentum attaches to lesser curvature of stomach Liver Gallbladder Lesser omentum Stomach Duodenum Transverse colon Small intestine Cecum Urinary bladder (b) Figure 23.6b Mesenteries Greater omentum a fatty apron of peritoneum Greater omentum and transverse colon reflected Greater omentum Transverse colon Transverse mesocolon Descending colon Jejunum Mesentery Sigmoid mesocolon Sigmoid colon Ileum (c) Figure 23.6c 3
4 Mesenteries Sagittal section through the abdominopelvic cavity Mesenteries attach to posterior abdominal wall Liver Lesser omentum Pancreas Stomach Duodenum Transverse mesocolon Transverse colon Mesentery Greater omentum Jejunum Ileum Visceral peritoneum Parietal peritoneum Urinary bladder Rectum (d) Figure 23.6d Histology of the Alimentary Canal Wall Same four layers from esophagus to anus The mucosa innermost layer Consists of: Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosae The submucosa external to the mucosa Contains blood and dlymphatic vessels, nerve fibers The muscularis externa external to the submucosa Two layers Circular muscularis Longitudinal muscularis The serosa the outermost layer The visceral peritoneum Nerve plexuses Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Histology of the Alimentary Canal Intrinsic nerve plexuses Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Glands in submucosa Mucosa Epithelium Lamina propria Muscularis mucosae Submucosa Muscularis externa Longitudinal muscle Circular muscle Serosa Epithelium Connective tissue Nerve Artery Gland in mucosa Lumen Vein Duct of gland outside Mucosa-associated Mesentery Lymphatic vessel alimentary canal lymphoid tissue (a) Longitudinal and cross-sectional views through the small intestine Figure 23.7a 4
5 Histology of the Alimentary Canal Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis externa Serosa (b) Light micrograph cross section through the small intestine (30 ) Figure 23.7b Smooth Muscle Longitudinal layer of smooth muscle (shows smooth muscle fibers in cross section, 145 ) (a) Location and plane of section shown in (b) Small intestine Mucosa (b) Cross section of the intestine showing the smooth muscle layers (one circular and the other longitudinal) running at right angles to each other Circular layer of smooth muscle (shows longitudinal views of smooth muscle fibers, 145 ) Figure 23.8a, b The Mouth and Associated Organs The mouth oral cavity Mucosal layer Stratified squamous epithelium Lamina propria The lips and cheeks Formed from orbicularis oris and buccinator muscles, respectively 5
6 Anatomy of the Mouth Soft palate Palatoglossal arch Uvula Hard palate Oral cavity Palatine tonsil Tongue Oropharynx Lingual tonsil Epiglottis Hyoid bone Laryngopharynx Esophagus Trachea (a) Sagittal section of the oral cavity and pharynx Figure 23.11a Anatomy of the Mouth The labial frenulum Connects lips to gum The palate Forms the roof of the mouth Gingivae (gums) Palatine raphe Hard palate Soft palate Uvula Palatine tonsil Sublingual fold with openings of sublingual ducts Vestibule Lower lip (b) Anterior view Upper lip Superior labial frenulum Palatoglossal arch Palatopharyngeal arch Posterior wall of oropharynx Tongue Lingual frenulum Opening of submandibular duct Gingivae (gums) Inferior labial frenulum Figure 23.11b The Tongue Interlacing fascicles of skeletal muscle Grips food and repositions it Helps form some consonants Intrinsic muscles within the tongue Extrinsic muscles external to the tongue 6
7 The Superior Surface of the Tongue Tongue papillae Filiform papillae Fungiform papillae Vallate papillae Figure The Teeth Dentition and dental formula Deciduous teeth 20 teeth First appear at 6 months of age Permanent teeth 32 teeth Most erupt by the end of adolescence Dental formula shorthand Way to indicate number and position of teeth The Teeth Incisors Central (7 yr) Lateral (8 yr) Incisors Central (6 8 mo) Lateral (8 10 mo) Canine (eyetooth) (16 20 mo) Molars First molar (10 15 mo) Second molar (about 2 yr) (a) Deciduous (milk) teeth Canine (eyetooth) (11 yr) Premolars (bicuspids) First premolar (11 yr) Second premolar (12 13 yr) Molars First molar (6 7 yr) Second molar (12 13 yr) Third molar (wisdom tooth) (17 25 yr) Permanent teeth Figure 23.13a 7
8 The Teeth (b) Deciduous teeth Permanent teeth Figure 23.13b Tooth Structure Enamel Longitudinal section of tooth in alveolus Crown Neck Dentin Dentinal tubules Pulp cavity (contains blood vessels and nerves) Gingiva (gum) Cementum Root Root canal Periodontal ligament Apical foramen Bone Figure The Salivary Glands Tongue Teeth Ducts of sublingual gland Frenulum of tongue Sublingual gland Mylohyoid muscle (cut) Anterior belly of digastric muscle (a) Parotid gland Parotid duct Masseter muscle Body of mandible (cut) Posterior belly of digastric muscle Submandibular duct Submandibular gland Mucous cells (b) Serous cells forming demilunes Figure
9 The Pharynx Oropharynx and laryngopharynx passages for air and food Lined with stratified squamous epithelium External muscle layer Consists of superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictors The Esophagus Gross anatomy muscular tube Begins as a continuation of the pharynx Joins the stomach inferior to the diaphragm Microscopic anatomy Epithelium is stratified squamous epithelium When empty mucosa and submucosa in longitudinal folds Mucous glands primarily compound tubuloalveolar glands Muscularis externa skeletal muscle first third of length Most external layer adventitia Microscopic Structure of the Esophagus Mucosa (contains a stratified squamous epithelium) Submucosa (areolar connective tissue) Lumen Muscularis externa Circular layer Longitudinal layer Adventitia (fibrous connective tissue) (a) Cross section through esophagus (5 ) (b) Gastroesophageal junction, longitudinal section (85 ) Figure
10 The Stomach Site where food is churned into chyme Protein digestion begins Secretes pepsin Functions under acidic conditions The Stomach Cardia Fundus Esophagus Muscularis externa Longitudinal layer Circular layer Oblique layer Lesser curvature Serosa Body Lumen Rugae of mucosa Greater curvature Duodenum (a) Pyloric canal Pyloric sphincter (valve) at pylorus Pyloric antrum Figure 23.17a The Stomach Microscopic Anatomy Gastric pits Surface epithelium (mucous cells) Surface epithelium Gastric pit Mucous neck cells Mucosa Lamina propria Muscularis Submucosa (contains mucosae submucosal plexus) Oblique layer Muscularis externa Circular layer (contains myenteric Longitudinal plexus) layer Serosa Stomach wall (a) Layers of the stomach wall, longitudinal section Parietal cell Gastric gland Chief cell Enteroendocrine cell (b) Enlarged view of gastric pits and gastric glands Pepsinogen HCl Pepsin Gastric pits Mucus-secreting cells Surface mucous cell Mitochondria Mucus neck cells Parietal cell Gastric gland HCl secreting parietal cells Chief cell Enteroendocrine cell (c) Location of the HCl-producing parietal cells and pepsin-secreting chief cells in a gastric gland Enzyme secreting chief cells Muscularis mucosae (d) Micrograph of the stomach mucosa, view similar to part (b) (115 ) Figure
11 The Small Intestine Gross Anatomy Longest portion of the alimentary canal Site of most enzymatic digestion and absorption Three subdivisions Duodenum Brunner s glands Jejunum Ileum Peyer s patches The Small Intestine Structural Features Vein carrying blood to hepatic portal vessel Muscle layers Circular folds Villi Lumen Absorptive cells Microvilli (brush border) Lacteal Goblet cell (a) Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal (b) gland Vilus Enteroendocrine cells Venule Lymphatic vessel Submucosa Goblet cells Villi Absorptive cells (c) Intestinal crypt Figure The Duodenum Receives digestive enzymes and bile Main pancreatic duct and common bile duct enter duodenum Sphincters control entry of bile and pancreatic juices 11
12 The Duodenum and Related Organs Right and left hepatic ducts of liver Common hepatic duct Cystic duct Bile duct and sphincter Accessory pancreatic duct Mucosa with folds Gallbladder Major duodenal papilla Hepatopancreatic ampulla and sphincter Duodenum Tail of pancreas Pancreas Jejunum Main pancreatic duct and sphincter Head of pancreas Figure The Large Intestine Digested residue contains few nutrients Small amount of digestion by bacteria Main functions absorb water and electrolytes Mass peristaltic movements force feces toward the rectum Gross Anatomy of Large Intestine Subdivided into: Cecum, vermiform appendix, colon, rectum, anal canal Special features of large intestine Teniae coli, haustra, and epiploic appendages Cecum a blind pouch Vermiform appendix contains lymphoid tissue Neutralizes pathogens Colon divided into distinct segments Ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon Rectum descends along the inferior half of the sacrum Anal Canal the last subdivision of the large intestine 12
13 Gross Anatomy of Large Intestine Right colic (hepatic) flexure Transverse colon Superior mesenteric artery Haustrum Ascending colon IIeum IIeocecal valve Left colic (splenic) flexure Transverse mesocolon Epiploic appendages Descending colon Cut edge of mesentery Teniae coli Cecum Sigmoid colon Vermiform appendix (a) Rectum Anal canal External anal sphincter Figure 23.21a Gross Anatomy of Large Intestine Rectal valve Rectum Hemorrhoidal veins Levator ani muscle Anal canal External anal sphincter Internal anal sphincter Anal columns Anal valves Pectinate line Anal sinuses Anus (b) Figure 23.21b Microscopic Anatomy of Large Intestine Villi are absent Contains numerous goblet cells Intestinal crypts simple tubular glands Lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue Epithelium changes at anal canal Becomes stratified squamous epithelium 13
14 The Liver Largest gland in the body Performs over 500 functions Digestive function bile production Performs many metabolic functions Visceral Surface of the Liver Left lobe Ligamentum venosum in fissure Porta hepatis Left hepatic artery Hepatic portal vein Caudate lobe Hepatic veins Inferior vena cava Bare area Right hepatic artery Right hepatic duct Left hepatic duct (b) Common hepatic duct Fissure Falciform ligament Ligamentum teres Quadrate lobe Cystic duct Gallbladder Right lobe Figure 23.25b Microscopic Anatomy of Liver (a) Lobule (b) Central vein Connective tissue septum Interlobular veins (to hepatic vein) Central vein Sinusoids Plates of hepatocytes Bile canaliculi Bile duct (receives bile from bile canaliculi) Fenestrated lining (endothelial cells) of sinusoids Portal vein Hepatic macrophages in sinusoid walls Bile duct Portal venule Portal triad Portal arteriole (c) Figure
15 The Gallbladder Stores and concentrates bile Expels bile into duodenum Bile emulsifies fats Cholecystokinin released from enteroendocrine cells in response to fatty chyme The Gallbladder Right and left hepatic ducts of liver Common hepatic duct Cystic duct Bile duct and sphincter Accessory pancreatic duct Mucosa with folds Gallbladder Major duodenal papilla Hepatopancreatic ampulla and sphincter Duodenum Tail of pancreas Pancreas Jejunum Main pancreatic duct and sphincter Head of pancreas Figure The Pancreas Pancreatic duct penetrates duodenal wall Endocrine functions Insulin (beta cells) and glucagons (alpha cells) Exocrine functions Acinar cells make, store, and secrete pancreatic enzymes Majority of pancreatic secretions Pancreatic juice secreted into small intestine ti Carbohydrases Lipases Nucleases Proteolytic enzymes Figure
16 The Pancreas Figure Disorders of the Digestive System Intestinal obstruction Mechanical obstructions Adhesions, tumors, or foreign objects Nonmechanical obstruction Halt in peristalsis Trauma Intestines touched during surgery Disorders of the Digestive System Inflammatory bowel disease Inflammation of intestinal wall Crohn s disease Ulcerative colitis Viral hepatitis jaundice and flu-like symptoms Major types A, B, C, and G Cystic Fibrosis and the Pancreas 16
17 The Digestive System in Later Life Middle age gallstones and ulcers Old age activity of digestive organs decline Fewer digestive juices and enzymes produced Absorption is less efficient Dehydration of fecal mass leads to constipation Diverticulosis and cancer of digestive organs 17
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Chapter 25
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13
 Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
The Digestive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska
 25 The Digestive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The digestive system consists of: The digestive tract Accessory
25 The Digestive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The digestive system consists of: The digestive tract Accessory
Al s 202 study guide answers Answers Respiratory System 1 External nares (nostrils) 33 Carina 2 Vestibule 34 Left primary bronchus 3 Nasal cavity 35
 Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
BIOL& 253 Lab Manual for Practical #2 Page 1 Rausch. For all slides, know a function for structures marked with a single asterisk (*).
 BIOL& 253 Lab Manual for Practical #2 Page 1 Rausch Lab equipment: slides, models SLIDES For all slides, know a function for structures marked with a single asterisk (*). DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Layers of the
BIOL& 253 Lab Manual for Practical #2 Page 1 Rausch Lab equipment: slides, models SLIDES For all slides, know a function for structures marked with a single asterisk (*). DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Layers of the
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Nutrition and the Digestive System
 C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Chapter 25. The Digestive System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 25 The Digestive System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The digestive system consists of: The digestive tract Accessory organs of digestion Digestive
Chapter 25 The Digestive System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The digestive system consists of: The digestive tract Accessory organs of digestion Digestive
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
 Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System. Digestive Processes. The Digestive System. Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells
 The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
the serous membranes lining the peritoneal cavity continuously produce what?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
Lab 8: Digestive System
 BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
Lungs a. d. b. c. e.
 Lungs d. e. Lungs Right superior lobe Right middle lobe Right inferior lobe d. Left superior lobe e. Left inferior lobe Sinuses d. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. g. i. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. h. d. f. e.
Lungs d. e. Lungs Right superior lobe Right middle lobe Right inferior lobe d. Left superior lobe e. Left inferior lobe Sinuses d. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. g. i. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. h. d. f. e.
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 24 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 24 For this lab you will use
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Chapter 16. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Gastrointestinal System!
 Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology
 458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
Digestive System CHAPTER 14
 Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive system
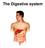 The Digestive system The GI tract (gastrointestinal tract) Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus The accessory digestive organs Supply secretions contributing to the breakdown
The Digestive system The GI tract (gastrointestinal tract) Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus The accessory digestive organs Supply secretions contributing to the breakdown
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. Digestive system organs fall into two main groups: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. (pp. 857 858; Fig. 23.1) 1. The
The Digestive System Outline PART 1: OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. Digestive system organs fall into two main groups: the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. (pp. 857 858; Fig. 23.1) 1. The
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Chapter 23: The Digestive System
 Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Introduction. Digestive System. Introduction. Introduction 5/14/2016. Every cell requires a constant energy source. Digestive processes
 Introduction Every cell requires a constant energy source Ingested food is complex Modification is needed to utilize Introduction Digestive system is a tube Gastrointestinal tract Specialized regions Mouth
Introduction Every cell requires a constant energy source Ingested food is complex Modification is needed to utilize Introduction Digestive system is a tube Gastrointestinal tract Specialized regions Mouth
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Digestive System Chapter 22. Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs
 13 Bio104 Lecture Outline Digestive System Chapter 22 Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs è Module 22.1: Overview of the Digestive System INTRODUCTION Digestive system
13 Bio104 Lecture Outline Digestive System Chapter 22 Digestive System = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract or plus Accessory organs è Module 22.1: Overview of the Digestive System INTRODUCTION Digestive system
Digestion Overview. I. Picture
 I. Picture II. Digestion Overview Organ grouping A. Alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract ( ) 1. continuous tube mouth to anus ( ) 2. breaks down food, nutrients and wastes 3. organs mouth, pharynx,
I. Picture II. Digestion Overview Organ grouping A. Alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract ( ) 1. continuous tube mouth to anus ( ) 2. breaks down food, nutrients and wastes 3. organs mouth, pharynx,
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Digestive System 1
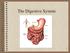 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
Overview of Digestion
 Digestive System Overview of Digestion 2 main groups of organs in the digestive system. 1. Alimentary Canal (nutrition) a. Mouth b. Pharynx c. Esophagus d. Stomach e. Small bowel f. Large bowel 2. Accessory
Digestive System Overview of Digestion 2 main groups of organs in the digestive system. 1. Alimentary Canal (nutrition) a. Mouth b. Pharynx c. Esophagus d. Stomach e. Small bowel f. Large bowel 2. Accessory
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition The Digestive System: Mouth and Pharynx The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Breakdown of ingested Absorption of nutrients into
Name: Date: Class: Unit 7 Outline: The Digestive System and Nutrition The Digestive System: Mouth and Pharynx The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Breakdown of ingested Absorption of nutrients into
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Overview of the Digestive
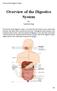 Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking
The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract Overview of the Digestive Tract
 16 The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract The Digestive System Consists of the muscular digestive tract assisted by various accessory organs Digestive functions include: Ingestion Mechanical
16 The Digestive System Overview of the Digestive Tract The Digestive System Consists of the muscular digestive tract assisted by various accessory organs Digestive functions include: Ingestion Mechanical
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
Functions. Digestive System. Chapter 24
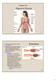 Chapter 24 Digestive System 24-1 1. Ingestion: introduction of food into stomach 2. Mastication: chewing. Chemical digestion requires large surface area so breaking down large particles mechanically facilitates
Chapter 24 Digestive System 24-1 1. Ingestion: introduction of food into stomach 2. Mastication: chewing. Chemical digestion requires large surface area so breaking down large particles mechanically facilitates
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
 Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
The Digestive System. Part B. From the mouth, the oro- and laryngopharynx allow passage of: Lined with stratified squamous epithelium and mucus glands
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, University of Kentucky The Digestive System Part B 23 Pharynx From the mouth, the oro- and laryngopharynx allow passage of: Food and fluids to the esophagus
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, University of Kentucky The Digestive System Part B 23 Pharynx From the mouth, the oro- and laryngopharynx allow passage of: Food and fluids to the esophagus
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) DIGESTIVE P1 OF 8
 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) DIGESTIVE P1 OF 8 I. Function of the digestive system a. Take in food b. Break it down to nutrient molecules c. Absorb nutrient molecules into the bloodstream
LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) DIGESTIVE P1 OF 8 I. Function of the digestive system a. Take in food b. Break it down to nutrient molecules c. Absorb nutrient molecules into the bloodstream
Chapter 15 The Digestive System
 Chapter 15 The Digestive System 3 major macromolecules are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Carbohydrates are polymers of simple monosacharides. Fats are polymers of glycerol and fatty acids. Proteins
Chapter 15 The Digestive System 3 major macromolecules are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Carbohydrates are polymers of simple monosacharides. Fats are polymers of glycerol and fatty acids. Proteins
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Chapter 23 The Digestive System
 Chapter 23 The Digestive System Functions of Digestive System 1. Take in food 2. Break it down into food molecules 3. Absorb molecules into the bloodstream 4. Rid body of any indigestible remains Organs
Chapter 23 The Digestive System Functions of Digestive System 1. Take in food 2. Break it down into food molecules 3. Absorb molecules into the bloodstream 4. Rid body of any indigestible remains Organs
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
