Cherubism: Clinicoradiographic Features, Treatment, and Long-Term Follow-Up of 8 Cases
|
|
|
- Madlyn Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65: , 2007 Cherubism: Clinicoradiographic Features, Treatment, and Long-Term Follow-Up of 8 Cases Edgard Carvalho Silva, DDS, PhD,* Guilherme Costa Carvalho Silva, DDS, and Tainah Couto Vieira, DDS Received from the School of Dentistry, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brasil. *Emeritus and Titular Professor, Department of Oral Surgery and Pathology. Resident, Department of Oral Surgery and Pathology. Resident, Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr G. Carvalho Silva: Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Faculdade de Odontologia, Departamento de Clínica, Patologia e Cirurgia, Av Antônio Carlos 6627, , Belo Horizonte, MG, Brasil; oguila@terra.com.br 2007 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons /07/ $32.00/0 doi: /j.joms Cherubism is a rare non-neoplastic hereditary disease related to genetic mutations characterized by bilateral bone enlargement of the jaws in childhood. Documented long-term follow-up of a series of cases is presented. Four familial and 4 sporadic cases of cherubism have been treated and followed for a mean of 18 years (range, 5 to 32 years). Four of the patients were subjected to cosmetic surgical correction justified by extreme size of the jaws, whereas the other 4 underwent just biopsy or ectopic and impacted teeth removal. Fibro-osseous lesions spontaneously regressed at different levels at variable time intervals. Apparent radiographic osseous repair occurred routinely. In adult life, the patients exhibited normal facial appearance, and radiographs showed almost complete involution of the lesions. Long-term follow-up of these patients is desirable to evaluate progression or involution of the lesions. Apparently, surgical intervention is unnecessary unless significant functional, esthetic, or emotional disturbances develop. Cherubism, first described by Jones, 1 is a benign, self-limiting fibro-osseous disorder characterized by bilateral expansion of the mandible, maxilla, or both. The lesions are usually symmetrical and painless. Frequently, cherubism is accompanied by dental arch and dental eruption abnormalities. Extragnathic skeletal involvement is rare. The rounded facies and occasional upward cast of the eyes with exposure of the sclerae below the pupil give the patient an appearance reminiscent of the cherubs portrayed in Renaissance paintings. Affected children appear normal at birth and are mentally normal. Jaw expansion is noticed within the first years of life, becoming progressively larger until puberty. Lesion regression is expected to occur spontaneously by the end of adolescence, resolving by middle age. 1 Radiographically, lesions appear as cystic multilocular radiolucencies, often beginning near the angle of the mandible and spreading to the mandibular ramus and body. Maxillary lesions may occur at the same time. Frequently, ectopic unerupted teeth are involved by lesions The histology is limited for diagnosis, showing fibrous hyperplasia and multinucleated giant cells. These features are similar to those other bone diseases such as brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism, giant cell tumor, and central and peripheral giant cell granuloma. 2-6,8-10,13 Cherubism is a familial disease 1-9 in which the trait is transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion with 100% penetrance in males and 50% to 70% penetrance in females. 4 However, several isolated cases have been reported in the literature. 7,9,11-13 Novel mutations in the gene encoding the binding protein SH3BP2 on chromosome 4p16.3 have been reported to cause cherubism Studies of cherubism with long-term follow-up presenting with clinicoradiographic documentation clearly demonstrating spontaneous resolution of bone lesions are extremely rare in the literature. Here we report 8 cases of cherubism, 4 cases from the same family and 4 nonfamilial sporadic cases, followed up for a mean of 18 years. We discuss disease behavior, treatment approaches, and clinicoradiographic aspects. 517
2 518 CHERUBISM Report of Cases CASE 1 Patient 1, a boy, presented with painless facial swelling at age 6 years. Extraoral radiographs showed transparent multilocular lesions completely involving the maxilla and mandible. Maxillary sinuses were not visible. Medical and family histories were unremarkable. With a clinicoradiographic diagnosis of cherubism, the patient was scheduled for regular FIGURE 2. Patient 2. A, At age 15 years, the patient showed follow-up. By age 10, mandibular enlargement became more mandibular bilateral enlargement. B, A panoramic radiograph noticeable; this persisted until age 12, when the lesions began showed the mandible filled with multilocular transparent lesions. C, to decrease. At age 16, mandibular enlargement was minor, Mandibular occlusal radiographs showed evident bone filling in the with swelling more noticeable in the maxilla; radiographs anterior region 1 year after the previous radiograph. exhibited significant remission of radiolucent areas, and the maxillary sinuses were clear. At age 25, the patient exhibited slight swelling of the maxilla, and a panoramic radiograph showed multilocular lesions almost totally filled in with bone (Fig 1). CASE 2 Patient 2, a girl, presented with bilateral painless swelling of the mandible at age 15. Her medical and family histories were unremarkable. Radiographs revealed multilocular areas involving the mandible. Biopsy findings confirmed a diagnosis of cherubism. Treatment involved regular follow-up visits. One year later, an occlusal radiograph showed outstanding osseous repair in the anterior portion of the mandible (Fig 2). Over the subsequent years, disease regression was observed. The patient was lost to follow-up at age 20. CASE 3 Patient 3, a boy, exhibited discrete painless growth of the face at age 6 years. A panoramic radiograph showed multilocular areas in mandibule and maxilla. No familial cases were reported. Biopsy findings confirmed a diagnosis of cherubism, and the patient was scheduled for regular follow-up. By age 12, the patient s condition began to regress. At age 21, he returned for extraction of ectopic and unerupted teeth, at which time swelling was found to be constricted to the maxilla. Two years later, his remaining teeth required extraction. At this time, minor residual enlargement in the maxilla was seen, and a radiograph showed significant bone filling over the multilocular areas (Fig 3). FIGURE 1. Patient 1. A, At age 6 years, the patient exhibited facial bilateral enlargement, and a lateral radiograph showed multilocular transparencies involving the jaws. The maxillary sinuses were not visible. Increased facial enlargement was seen at age 10 years (B) and also at 11 years (C). D, At 16 years, minor expansion of the mandibule and more maxillary enlargement were observed. A radiograph revealed clear maxillary sinuses and significant remission of the radiolucent areas, with a thin mandibular border. E, At age 25, the patient had only slight swelling of the maxilla, and a panoramic radiograph showed the jaws almost totally filled in with bone. The mandibular border was thicker and evident. CASE 4 In patient 4, a boy, facial alteration was first noted at age 4 years and progressively developed asymptomatically. At age 12, the patient showed enlargement of the jaws, most noticeable on the right side. Panoramic radiograph showed multilocular areas involving the jaws. Family history was negative for cherubism. In the subsequent year, the patient underwent minor surgeries for removal of the upper right second premolar and biopsy, which confirmed the clinical diagnosis of cherubism. At age 14, a small corrective approach was performed in the right body of the mandible, simultaneously with extraction of the lower right second premolar. At age 20, the patient had a harmonic face, and a panoramic radiograph showed bone filling into radiolucent areas (Fig 4). CASE 5 In patient 5, facial swelling noted at age 10 years was diagnosed as cherubism by a colleague. The patient was lost from follow-up. According to the patient, at age 18, resective surgery was performed in the right body of the mandible due to a misdiagnosis of ameloblastoma. At age 39, the
3 CARVALHO SILVA ET AL 519 patient had a normal face, and a panoramic radiograph showed only residual mandibular radiolucencies (Fig 5). CASE 6 Patient 6, the son of patient 5, was diagnosed with cherubism at age 6 years due to cheek enlargement and family history. A panoramic radiograph at age 9 showed multilocular transparencies completely occupying the mandible and maxilla. At age 13, painless bilateral jaw expansion was noted, and a radiograph showed remaining multilocular areas. Minor signs of osseous repair were observed in the mandibular ramus. Three minor surgeries were executed in the following 3 years for biopsy (which confirmed the diagnosis), for extraction of displaced and impacted teeth (upper right second molar and premolar; lower left canine and first and third molars; lower right canine, second premolar, and first and third molars), and in an attempt to provide orthodontically assisted eruption of unerupted upper left central incisor. At age 16, changes in cystic lesions were observed (Fig 6). CASE 7 Patient 7, a sister of patient 5, exhibited bilateral painless facial expansion at age 8 years. At age 11, the facial growth stopped, and corrective surgery was done in the left body of the mandible. No further enlargement was observed until age 15, when residual jaw expansion began to regress. At FIGURE 4. Patient 4. A, At age 12, the patient exhibited facial swelling, more pronounced on the right side. A radiograph showed a few well-delimited multilocular lesions involving the mandible and affecting only the tuberosities in the maxilla. A sclerotic area was seen below the lower right first molar, along with root resorption in this tooth. B, At age 20, facial appearance was close to normal, and a panoramic radiograph showed remission of transparent lesions in all but the anterior portion of the mandible. No maxillary involvement was seen. Successful orthodontic treatment was carried out. Note the bone filling in the left coronoid process compared with the initial radiograph. age 40, the patient s face was normal. A radiograph revealed typical radiopacity of bone structures in the maxilla. In the mandible, a radiograph showed residual multilocular transparencies in the coronoid processes and in the mandibular ascending rami, along with some sclerotic areas in the mandibular body (Fig 7). CASE 8 Patient 8, a daughter of patient 7, was diagnosed with cherubism at age 5, based on painless facial enlargement and family history. A lateral extraoral radiograph showed multilocular radiolucencies in the jaws. Enlargement of the jaws persisted until age 9. Histological examination of an incisional biopsy specimen confirmed the diagnosis. At age 13, the patient demonstrated noticeable bilateral swelling of the jaws, and a radiograph showed persistent complete involvement of the jaws by the lesions, with a prominence in the right mandibular body. Four years later, involvement of the mandible and maxilla remained considerable, and FIGURE 3. Patient 3. A, At age 6, the patient exhibited facial enlargement. A panoramic radiograph showed multilocular radiolucencies with diffuse jaw involvement. Note the large radiolucency in the right mandibular body. B, At age 21, facial swelling was restricted to the maxilla, and a radiograph revealed impaction of the inferior anterior teeth, as well as teeth abnormalities. Regression of multilocular lesions was noticeable. C, At age 23, facial appearance was similar to the previous condition, and a radiograph showed almost complete regression of the lesions. Note the total bone filling in the large lesion observed at age 6 in the right body of the mandible. FIGURE 5. Patient 5. At age 39, facial appearance was normal. A panoramic radiograph showed normal maxilla and sclerotic areas near the apex of the lower left second molar. At age 18, a hemimandibulectomy was performed in the right side of the mandible due to an incorrect diagnosis of ameloblastoma.
4 520 CHERUBISM FIGURE 6. Patient 6. A, At age 9, a panoramic radiograph showed multilocular cystic lesions involving maxilla and mandibule. B, Atage 13, mandibular enlargement was evident, and a radiograph showed ectopic, unerupted teeth and complete filling of the mandible and maxilla by multilocular transparent lesions. C, At 16 years, mandibular swelling was persistent, and a panoramic radiograph revealed fewer but larger cystic lesions compared with previous findings. corrective surgery was executed in the right angle and body of the mandible. Three years after the operation, diminished right mandibular swelling was seen (Fig 8). Discussion Several family studies from different countries have postulated that cherubism is a hereditary condition, 1-10 transmitted in an autosomal dominant pattern. 4 A molecular pathogenesis of cherubism has been proposed: SH3BP2 gene mutations cause dysregulation of the Msx-1 gene, which is involved in FIGURE 7. Patient 7. At age 40, the face appears normal. A panoramic radiograph revealed residual radiolucencies in the coronoid processes and in the ascending rami, as well as sclerotic areas in the body of the mandible. FIGURE 8. Patient 8. A, At age 5, a lateral radiograph showed multilocular lesions occupying the jaws. B, At age 13, a panoramic radiograph showed diffuse, transparent multilocular lesions in the jaws. Ectopic, impacted, and missing teeth, as well as root resorption in the lower right first molar, were also observed. C, At age 17, facial enlargement was more pronounced on the right side. A radiograph showed persistent multilocular lesions, with some discrete sclerotic areas. D, At age 20, decreased facial enlargement on the right side was evident after corrective surgery. A radiograph still revealed multilocular lesions, however. Note the progression of bone filling in the left angle of the mandible, compared with previous radiographs. regulating mesenchymal interaction in craniofacial morphogenesis. In an affected individual, increased bone activity occurs between age 2.5 and 10 to 12 years, due to up-regulation of Msx-1. Dysfunction of Msx-1 stops at the end of molar development, leading to remineralization of lesions. 16 Isolated single cases of cherubism have been reported in the literature, 7,9,11-13 most of them based on historic reports of the affected family members, who had not noticed any facial alteration in other relatives. It is difficult to assess whether these cases represent spontaneous mutations, because of cherubism s variable expression and its tendency to resolve. In addition, the autosomal recessive pattern was suggested to occur in selected families. 8 In our nonfamilial cases, beyond the historic data provided by the patients parents, we observed close relatives for cherubic features; however, we cannot affirm that these cases are examples of pure mutations. In general, cherubism does not affect other parts of the skeleton or osseous metabolism; the bone markers phosphorous, serum calcium, and alkaline phos-
5 CARVALHO SILVA ET AL 521 Table 1. PATIENTS GENDER, AGE AT DIAGNOSIS, TYPE OF INTERVENTION, AND FOLLOW-UP PERIOD Patient Gender Age (yrs) Classification Intervention Follow-Up (yrs) 1(Fig 1) M 6 Grade 3 Biopsy and impacted teeth removal 19 2(Fig 2) F 15 Grade 1 Biopsy 5 3(Fig 3) M 6 Grade 3 Biopsy and impacted teeth removal 17 4(Fig 4) M 4 Grade 2 Biopsy, impacted teeth removal, and minor corrective surgery 16 in the right body of the mandible 5(Fig 5) F 10 Grade 3 Biopsy, impacted teeth removal, and resective surgery in the 29 right body of the mandible 6(Fig 6) M 6 Grade 3 Biopsy and impacted teeth removal 10 7(Fig 7) F 8 Grade 3 Biopsy, impacted teeth removal, and corrective surgery in the 32 right body of the mandible 8(Fig 8) F 4 Grade 3 Biopsy, impacted teeth removal, and corrective surgery in the right angle of the mandible 16 phatase are usually at normal levels with respect to age. 2,5,10,12,13,17,18 Significant ocular disturbances, such as proptosis, superior globe displacement, and visual loss, may occur, 19 although these were not observed in our cases. Patients 1, 6, and 8 showed exposure of the inferior part of the sclerae, confirming that this characteristic is occasional. 4,7-9 Some studies have suggested that cherubism may be associated with other genetic diseases, such as Noonan s syndrome 20,21 and Ramon syndrome. 22,23 An association with gingival fibromatosis also has been postulated. 24 Aggressive manifestations of cherubism have been reported, 6,12,25 including 1 extreme case that progressed rapidly, resulting in death due to gastrointestinal and pulmonary infections. 26 In cherubism, the initial facial alteration becomes apparent in the first years of life. 1-5,7-11,13 We cannot precisely affirm when facial swelling was first noticed in all of our patients, because they were first examined at different ages, ranging from 4 to 15 years. In the older patients, signs of cherubism likely were present well before the patients came to us. The clinical aspects and disease course observed in our patients were similar to those in previous studies, 1-5,7-11 as were the histological features. 1,2,4,5,8-11,13 All of the patients that we followed presented with painless bilateral lesions. Radiographically, these lesions appeared as multilocular cystic radiolucencies involving the jaws in all patients but patient 2, who exhibited mandibular association but no maxillary involvement. Because this patient was first seen at age 15, we cannot verify that she never had any maxillary alteration. Abnormal patterns of teeth eruption were noted in all cases, as well as teeth agenesis and the presence of ectopic or retained teeth. On average, the disease manifested in childhood, stabilized by age 12 years, and began to regress during puberty. Bone recontouring continued through the third decade of life, and the face alteration disappeared. This course was observed in all patients except patient 8, who at age 20 still manifested clinicoradiographic features of cherubism. The remission of facial bone enlargement seemed to occur later in the maxilla than in the mandible. Radiographic follow-up showed that multilocular radiolucent areas gradually filled in with osseous structure, sometimes within a short period, as seen in patient 2. Sclerotic areas replaced radiolucent multilocular regions even in the 2 familial cases (patients 5 and 7) in the fifth decade of life, in contrast to the conclusion of another study 7 asserting that sclerotic areas have been described only in single cases. The histological appearance was similar to that of brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism, giant cell tumor, and central and peripheral giant cell granuloma, consisting of proliferating vascular fibrous connective tissue with abundant multinucleated giant cells. In adult patients, this tissue showed an increase of bone matrix in fibrous stroma. Seward and Hankey 3 suggested a grading system for cherubism that has been since modified by other authors. 6,7,9 According to the classical grading system based on the radiographic location of the lesions, 6 of our 8 patients were grade 3 (both jaws diffusely affected); 1 patient (patient 2) was grade 1, with mandibular but no maxillary involvement at the time of examination; and 1 patient (patient 4) was grade 2, with full mandibular involvement and maxillary involvement only in the tuberosities. Remission of signs of cherubism occurs most rapidly in grade 1 (lesions restricted to posterior regions of the mandible). 7 We found that the lesions regressed progressively even in the patients with grade 3, both those who underwent surgery and those who did not, and in adulthood these patients had normal or close to normal facial and radiographic aspects, sometimes with minor residual marks.
6 522 CHERUBISM Conventional surgical procedures for biopsy or impacted teeth removal were used in all cases (Table 1). In the 4 patients who exhibited significant increase in the jaws, corrective osteoplasty was performed, producing marked reduction of facial deformities with no recurrence. Consider the case of patient 5, who was lost to follow-up and underwent a hemimandibulectomy due to an incorrect diagnosis of ameloblastoma but even so exhibited remission of cherubic characteristics in adulthood. Traditionally, the general approach to treating cherubism was to follow patients, perform biopsies, remove ectopic and impacted teeth, and provide surgical correction when appropriate. 3-5,7-9,11,17 Liposuction has been proposed to reduce the mass of the lesion in particular cases. 27 When discussing treatment, we must consider the psychological problems associated with an unattractive cherubic appearance in young patients. The 4 patients who underwent surgery for osseous contouring had deformities caused by large bone expansion, mainly in the mandible. Findings showed that the multinucleated cells in cherubic lesions were osteoclasts from a structural and biochemical standpoint, 10 raising the possibility of treatment with calcitonin, reducing the need for surgery in cases with significant expansion. Calcitonin has been used successfully for treatment of giant cell granuloma, 28,29 and it has reduced bone absorption of cherubic osteoclasts in vitro. 10 Based on the genetic mutations related to the disease, gene therapy is expected to play a role in future treatment. References 1. Jones WA: Familial multilocular cystic disease of the jaws. Am J Cancer 17:946, Jones WA, Gerrie J, Pritchard J: Cherubism: A familial fibrous dysplasia of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 5:292, Seward GR, Hankey GT: Cherubism. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 10:925, Peters WJ: Cherubism: A study of twenty cases from one family. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 47:307, Faircloth WJ Jr, Edwards RC, Farhood VW: Cherubism involving a mother and daughter: Case reports and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 49:535, Motamedi MHK: Treatment of cherubism with locally aggressive behavior presenting in adulthood: Report of four cases and a proposed new grading system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 56: 1336, Von Wowern N: Cherubism: A 36-year long-term follow-up of 2 generations in different families and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90:765, Kozakiewicz M, Perczynska-Partyka W, Kobos J: Cherubism: Clinical picture and treatment. Oral Dis 7:123, Meng XM, Yu SF, Yu GY: Clinicopathologic study of 24 cases of cherubism. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:350, Southgate J, Sarma U, Townend JV, et al: Study of the cell biology and biochemistry of cherubism. J Clin Pathol 51:831, Katz JO, Dunlap CL, Ennis RL: Cherubism: Report of a case showing regression without treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:301, Kaugars GE, Niamtu J 3rd, Svirsky JA: Cherubism: Diagnosis, treatment, and comparison with central giant cell granulomas and giant cell tumors. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 73:369, Ozkan Y, Varol A, Turker N, et al: Clinical and radiological evaluation of cherubism: A sporadic case report and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 67:1005, Mangion J, Rahman N, Edkins S, et al: The gene for cherubism maps to chromosome 4p16.3. Am J Hum Genet 65:151, Ueki Y, Tiziani V, Santanna C, et al: Mutations in the gene encoding c-abl binding protein SH3BP2 cause cherubism. Nat Genet 28:125, Lo B, Faiyaz-Ul-Haque M, Kennedy S, et al: Novel mutation in the gene encoding c-abl binding protein SH3BP2 causes cherubism. Am J Med Genet A 121:37, Hyckel P, Berndt A, Schleier P, et al: Cherubism: New hypotheses on pathogenesis and therapeutic consequences. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 33:61, Hitomi G, Nishide N, Mitsui K: Cherubism: Diagnostic imaging and review of the literature in Japan. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 81:623, Hawes MJ: Cherubism and its orbital manifestations. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 5:133, Dunlap C, Neville B, Vickers RA, et al: The Noonan syndrome/ cherubism association. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 67:698, Addante RR, Breen GH: Cherubism in a patient with Noonan s syndrome. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54:210, Ramon Y, Berman W, Bubis JJ: Gingival fibromatosis combined with cherubism. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 24:435, de Pina-Neto JM, de Souza NV, Velludo MA, et al: Retinal changes and tumorigenesis in Ramon syndrome: Follow-up of a Brazilian family. Am J Med Genet 77:43, Benazza D, Elmouadden M, Benjalloun A, et al: Gingival fibromatosis associated with cherubism. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 106:174, Lannon DA, Earley MJ: Cherubism and its charlatans. Br J Plast Surg 54:708, Silva EC, de Souza PE, Barreto DC, et al: An extreme case of cherubism. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40:45, Dubin B, Jackson IT: The use of liposuction to contour cherubism. Plast Reconstr Surg 86:996, Harris M: Central giant cell granulomas of the jaws regress with calcitonin therapy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31:89, Pogrel MA: Calcitonin therapy for central giant cell granuloma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:649, 2003
CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 Dysanoor Maxillofacial Sujatha, surgery Naik Shobha CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Prof. PhD, The Oxford Dental College
Dysanoor Maxillofacial Sujatha, surgery Naik Shobha CLINICO-RADIOLOGIC FEATURES OF BILATERAL MANDIBULAR SWELLING A CASE REPORT OF CHERUBISM AND LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Prof. PhD, The Oxford Dental College
Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic Features and Osseous-Dental Treatments
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic and histological features
 (2005) 34, 313 318 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic
(2005) 34, 313 318 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Aggressive behaviour of cherubism in a teenager: 4-years of clinical follow-up associated with radiographic
Ramon s Syndrome: A Rare Entity
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1039 CASE REPORT 1 Alexander, 2 Sherry Peter, 3 Sheela Nampoothiri, 4 Latha Rao, 5 Ajith Nambiar 4 Ravi Veeraraghavan, 4 Ushass Puthalath WJD 1 Professor, Department of Oral Medicine
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1039 CASE REPORT 1 Alexander, 2 Sherry Peter, 3 Sheela Nampoothiri, 4 Latha Rao, 5 Ajith Nambiar 4 Ravi Veeraraghavan, 4 Ushass Puthalath WJD 1 Professor, Department of Oral Medicine
Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 58-62 Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 58-62 Cherubism, a rare childhood disease with a brief review of literature
Cherubism with multiple dental abnormalities: a rare presentation
 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 3 Department of
1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Institute of Dental Sciences, Bhubaneswar, 3 Department of
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
A c.1244g>a (p.arg415gln) mutation in SH3BP2 gene causes cherubism in a Turkish family: Report of a family with review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19496 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19496 A c.1244g>a (p.arg415gln) mutation in in a Turkish family:
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19496 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19496 A c.1244g>a (p.arg415gln) mutation in in a Turkish family:
Cherubism in a 4-year-old boy managed with tumor curettage, mandibular osteotomies and repositioning
 Garlick et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:29 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.36 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Case Report Open Access Cherubism in a 4-year-old boy managed with tumor curettage, mandibular
Garlick et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:29 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.36 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Case Report Open Access Cherubism in a 4-year-old boy managed with tumor curettage, mandibular
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Reconstruction of large mandibular defects
 Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
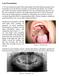 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
CHERUBISM: CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Querubismo: relato de caso e revisão da literatura
 Cherubism: case report and literature review CHERUBISM: CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Querubismo: relato de caso e revisão da literatura Victor Perez Teixeira 1 Rogério Aparecido Dedivitis 2 André
Cherubism: case report and literature review CHERUBISM: CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Querubismo: relato de caso e revisão da literatura Victor Perez Teixeira 1 Rogério Aparecido Dedivitis 2 André
Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems. in preadolescent children
 In the name of GOD Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 7 William R. Proffit,
In the name of GOD Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 7 William R. Proffit,
Partial Spontaneous Bone Regeneration Subsequent to Mandibulectomy
 Partial Spontaneous Bone Regeneration Subsequent to Mandibulectomy Abstract A case of spontaneus bone regeneration after mandibulectomy is presented. The patient was young and had a mandibular resection
Partial Spontaneous Bone Regeneration Subsequent to Mandibulectomy Abstract A case of spontaneus bone regeneration after mandibulectomy is presented. The patient was young and had a mandibular resection
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Case presentation. Central Giant Cell Granuloma. Case presentation
 Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
Jane Dahlstrom Anatomical Pathologist The Canberra Hospital Case presentation James, 15 year old boy Presented with a < 6 month history of a rapidly growing right sided palatal mass and loose teeth No
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Gorham Disease an Enigma
 Article ID: WMC002898 ISSN 2046-1690 Gorham Disease an Enigma Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashant Kothari, Asso Professor, ODMR MCDRC, 442301 - India Submitting Author: Dr. Prashant Kothari, Asso Professor,
Article ID: WMC002898 ISSN 2046-1690 Gorham Disease an Enigma Corresponding Author: Dr. Prashant Kothari, Asso Professor, ODMR MCDRC, 442301 - India Submitting Author: Dr. Prashant Kothari, Asso Professor,
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible
 Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report
 Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted Canines: Report of Five Cases Sulabha AN, Sachin Deshpande, Sameer C
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth
 Oral Science International, November 2008, p.150 154 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth Hiroyuki
Oral Science International, November 2008, p.150 154 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth Hiroyuki
Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari
 Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
Case Report Giant Cell Lesion of the Jaw: A Case Report in a Child MK Gupta, *SG Naidu, *VJ Maheshwari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, *Oral Medicine & Radiology, People s Dental Academy, Peoples
Dr Robert Drummond. BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho. Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015
 Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Tooth transplantation in cherubism and incontinentia pigmenti: report of two unusual cases
 Oral Surgery ISSN 1752-2471 CASE REPORT ors_1105 39..43 Tooth transplantation in cherubism and incontinentia pigmenti: report of two unusual cases J.L. Jensen 1,2 & B. Album 1 1 Department of Oral Surgery
Oral Surgery ISSN 1752-2471 CASE REPORT ors_1105 39..43 Tooth transplantation in cherubism and incontinentia pigmenti: report of two unusual cases J.L. Jensen 1,2 & B. Album 1 1 Department of Oral Surgery
Conservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
 SE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.s1.s1 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 onservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
SE REPORT https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.s1.s1 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 onservative management of a dentigerous cyst associated with eruption of teeth in a 7-year-old girl: a case report
Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage
 CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report
 J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
J. Oral Diag. 2017; 02:e20170031. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eight-year follow-up of central giant cell lesion treated with corticosteroid: Case report Tila Fortuna Costa 1,2 Juliana Borges de Lima Dantas 1 Daniel
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite
 BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
Sample Case #1. Disclaimer
 ABO Sample Cases Disclaimer Sample Case #1 The following sample questions and answers were composed and vetted by a panel of experts in orthodontics and are intended to provide an example of the types
ABO Sample Cases Disclaimer Sample Case #1 The following sample questions and answers were composed and vetted by a panel of experts in orthodontics and are intended to provide an example of the types
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report
 Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Coronoid Process of the Mandible: A Case Report Abstract A rare case of aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) located in the ramus of the mandible with involvement of the coronoid process
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Objective: There is little information regarding the mesiodistal angulation of permanent teeth
 www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation
 Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy
 Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Treatment of Long face / Open bite
 In the name of GOD Treatment of Long face / Open bite in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 13 William R. Proffit, Henry W.
In the name of GOD Treatment of Long face / Open bite in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 13 William R. Proffit, Henry W.
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented as Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Jaw Bones. A Report of Three Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Hyperparathyroidism Presented
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
The incidence of mandibular third molar impactions in different skeletal face types
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2008; 53: 320 324 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2008.00073.x The incidence of mandibular third molar impactions in different skeletal face types O Breik,* D Grubor*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2008; 53: 320 324 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2008.00073.x The incidence of mandibular third molar impactions in different skeletal face types O Breik,* D Grubor*
Objective: There is little information regarding the mesiodistal angulation of permanent teeth
 www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
www.scielo.br/jaos Mesiodistal root angulation of permanent teeth in children with mixed dentition and normal occlusion Flávia A. S. JESUINO 1, Luciane R. COSTA 2, José VALLADARES-NETO 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD,
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Orthodontic Treatment of a Patient with an Impacted Maxillary Second Premolar and Odontogenic Keratocyst in the Maxillary Sinus
 Case Report Orthodontic Treatment of a Patient with an Impacted Maxillary Second Premolar and Odontogenic Keratocyst in the Maxillary Sinus Yuko Tanimoto a ; Shouichi Miyawaki b ; Mikako Imai c ; Ryoko
Case Report Orthodontic Treatment of a Patient with an Impacted Maxillary Second Premolar and Odontogenic Keratocyst in the Maxillary Sinus Yuko Tanimoto a ; Shouichi Miyawaki b ; Mikako Imai c ; Ryoko
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Case Report. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System.
 Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Patient information booklet Orthognathic Surgery
 Patient information booklet Orthognathic Surgery 2 Table of contents This patient information booklet contains all the answers to your questions regarding orthognathic surgery. + + + + + + What is Orthognathic
Patient information booklet Orthognathic Surgery 2 Table of contents This patient information booklet contains all the answers to your questions regarding orthognathic surgery. + + + + + + What is Orthognathic
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature
 Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy:
 Case Report Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy: Report of a Case A. Khodayari 1, A. Khojasteh 2, MT. Kiani 3, A. Nayebi 4, L. Mehrdad 5, M. Vahdatinia 6 1 DMD, MS. Associate
Case Report Spontaneous Regeneration of the Mandible after Hemimandibulectomy: Report of a Case A. Khodayari 1, A. Khojasteh 2, MT. Kiani 3, A. Nayebi 4, L. Mehrdad 5, M. Vahdatinia 6 1 DMD, MS. Associate
Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth
 Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth Cengiz Gadimli a Zafer Sari b Abstract The objective of this report is to describe combined orthodontic and endodontic treatment
Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth Cengiz Gadimli a Zafer Sari b Abstract The objective of this report is to describe combined orthodontic and endodontic treatment
Aneurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 35-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.35 neurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization Department
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 35-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.35 neurysmal bone cyst of the mandible managed by conservative surgical therapy with preoperative embolization Department
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1
 Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2017
 NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 42 No. 4 December 1987 CLINICAL STATISTICS OF THE ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR IN MALAYSIA (1968-1986) CH SIAR* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond), FDS RCPS (Glasg) K H NG* 80S (Mal), MSc (Lond),
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Lingual correction of a complex Class III malocclusion: Esthetic treatment without sacrificing quality results.
 SM 3M Health Care Academy Lingual correction of a complex Class III malocclusion: Esthetic treatment without sacrificing quality results. Christopher S. Riolo, DDS, M.S, Ph.D. Dr. Riolo received his DDS
SM 3M Health Care Academy Lingual correction of a complex Class III malocclusion: Esthetic treatment without sacrificing quality results. Christopher S. Riolo, DDS, M.S, Ph.D. Dr. Riolo received his DDS
Assessment of Relapse Following Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy Mandibular Setback and Short-term Immobilization
 Assessment of Relapse Following Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy Mandibular Setback and Short-term Immobilization Koroush Taheri Talesh, DDS, a Mohammad Hosein Kalantar Motamedi, DDS, b Mahdi Sazavar,
Assessment of Relapse Following Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy Mandibular Setback and Short-term Immobilization Koroush Taheri Talesh, DDS, a Mohammad Hosein Kalantar Motamedi, DDS, b Mahdi Sazavar,
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Intrabony Migration of Impacted Teeth
 Clinical Report Intrabony Migration of Impacted Teeth Yehoshua Shapira, DMD a ; Mladen M. Kuftinec, DMD, DStom, ScD b Abstract: Intrabony migration of impacted teeth is a rare dental anomaly, which occurs
Clinical Report Intrabony Migration of Impacted Teeth Yehoshua Shapira, DMD a ; Mladen M. Kuftinec, DMD, DStom, ScD b Abstract: Intrabony migration of impacted teeth is a rare dental anomaly, which occurs
Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
 Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report
 Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014
 NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014 The inclusion of a rate on this table does not guarantee
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014 The inclusion of a rate on this table does not guarantee
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
The ASE Example Case Report 2010
 The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
