|
|
|
- Melanie Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS People are fascinated by the exceptional, the unusual, and the abnormal. This fascination may be caused by two reasons: 1. During various moments we feel, think, and act like an abnormal individual. 2. Psychological disorders may bring unexplained physical symptoms, irrational fears, and suicidal thoughts.
3 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS To study the abnormal is the best way of understanding the normal. William James ( ) 1. There are 450 million people suffering from psychological disorders (WHO, 2004). 2. Depression and schizophrenia exist in all cultures of the world.
4 DEFINING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Mental health workers view psychological disorders as persistently harmful thoughts, feelings, and actions. When behavior is deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional psychiatrists and psychologists label it as disordered (Comer, 2004).
5 DEVIANT, DISTRESSFUL & DYSFUNCTIONAL 1. Deviant behavior (going naked) in one culture may be considered normal, while in others it may lead to arrest. 2. Deviant behavior must accompany distress. 3. If a behavior is dysfunctional it is clearly a disorder. In the Wodaabe tribe men wear costumes to attract women. In Western society this would be considered abnormal. Carol Beckwith
6 UNDERSTANDING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Ancient Treatments of psychological disorders include trephination, exorcism, being caged like animals, being beaten, burned, castrated, mutilated, or transfused with animal s blood. John W. Verano Trephination (boring holes in the skull to remove evil forces)
7 THE MEDICAL MODEL Philippe Pinel ( ) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. George Wesley Bellows, Dancer in a Madhouse, The Art Institute of Chicago Dance in the madhouse.
8 MEDICAL MODEL When physicians discovered that syphilis led to mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. 1. Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. 2. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. 3. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. 4. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. *Fails to recognize the effect of social and psychological factors!
9 THE BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL APPROACH Assumes that biological, socio-cultural, and psychological factors combine and interact to produce psychological disorders.
10 CLASSIFYING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS The American Psychiatric Association rendered a Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) to describe psychological disorders. The most recent edition, DSM-IV-TR (Text Revision, 2000), describes 400 psychological disorders compared to 60 in the 1950s.
11 GOALS OF DSM 1. Describe (400) disorders so they may be identified in affected individuals. 2. Determine how prevalent the disorder is. Disorders outlined by DSM-IV are reliable. Therefore, diagnoses by different professionals are similar. Others criticize DSM-IV for putting any kind of behavior within the compass of psychiatry.
12 MULTIAXIAL CLASSIFICATION Axis I Axis II Axis III Axis IV Axis V Is a Clinical Syndrome (cognitive, anxiety, mood disorders [16 syndromes]) present? Is a Personality Disorder or Mental Retardation present? Is a General Medical Condition (diabetes, hypertension or arthritis etc) also present? Are Psychosocial or Environmental Problems (school or housing issues) also present? What is the Global Assessment of the person s functioning?
13 MULTIAXIAL CLASSIFICATION Note 16 syndromes in Axis I
14 MULTIAXIAL CLASSIFICATION Note Global Assessment for Axis V
15 Fig. 14-3, p. 555
16 Fig. 14-4, p. 556
17 LABELING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS: SOME PSYCHOLOGISTS CRITICIZE THE USE OF LABELING. Critics of the DSM-IV argue that labels may stigmatize individuals. Labels may become self-fulfilling. Some psychologists find diagnostic labels useful. Labels may be helpful for healthcare professionals when communicating with one another and establishing therapy.
18 LABELING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Insanity labels raise moral and ethical questions about how society should treat people who have disorders and have committed crimes. Elaine Thompson/ AP Photo Theodore Kaczynski (Unabomber)
19 ANXIETY DISORDERS Feelings of excessive apprehension and anxiety. 1. Generalized anxiety disorder 2. Panic disorder 3. Phobias 4. Obsessive-compulsive disorder 5. Post-traumatic stress disorder
20 GENERALIZED ANXIETY DISORDER Symptoms 1. Persistent and uncontrollable tenseness and apprehension. 2. Autonomic arousal. 3. Inability to identify or avoid the cause of certain feelings, this is an anxiety which Freud labeled free floating.
21 PANIC DISORDER Symptoms Minutes-long episodes of intense dread which may include feelings of terror, chest pains, choking, or other frightening sensations. Anxiety is a component of both disorders. It occurs more in the panic disorder, making people avoid situations that cause it. Smokers have at least doubled risk of panic disorder.
22 PHOBIAS Marked by a persistent and irrational fear of an object or situation that disrupts behavior.
23 KINDS OF PHOBIAS Agoraphobia Acrophobia Claustrophobia Hemophobia Social phobia Phobia of open places. Phobia of heights. Phobia of closed spaces. Phobia of blood. Shyness to an extreme
24 OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE DISORDER Persistence of unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and urges to engage in senseless rituals (compulsions) that cause distress.
25 BRAIN IMAGING A PET scan of the brain of a person with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). High metabolic activity (red) in the frontal lobe areas are involved with directing attention.
26 POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER Four or more weeks of the following symptoms constitute post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): 1. Haunting memories 2. Nightmares 3. Social withdrawal 4. Jumpy anxiety 5. Sleep problems Bettmann/ Corbis
27 RESILIENCE TO PTSD Only about 10% of women and 20% of men react to traumatic situations and develop PTSD. Holocaust survivors show remarkable resilience against traumatic situations. All major religions of the world suggest that surviving a trauma leads to the growth of an individual. Post-traumatic growth is a theory in which challenging crises or traumatic experiences increases personal strength, positively shifts priorities and promotes spirituality.
28 EXPLAINING ANXIETY DISORDERS Freud suggested that we repress our painful and intolerable ideas, feelings, and thoughts, resulting in anxiety.
29 THE LEARNING PERSPECTIVE Learning theorists suggest two specific learning processes which contribute to anxiety: 1. Fear conditioning leads to anxiety. This anxiety then becomes associated with other objects or events (stimulus generalization). 2. Reinforcement maintains our phobias and compulsions when we avoid or escape the feared situation to reduce anxiety.
30 THE LEARNING PERSPECTIVE Investigators believe that fear responses are reinforced through observational learning. Young monkeys develop fear when they watch other monkeys who are afraid of snakes.
31 THE BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Natural Selection has led our ancestors to learn to fear snakes, spiders, and other animals. Therefore, fear preserves the species. Twin studies suggest that our genes may be partly responsible for developing fears and anxiety. Twins are more likely to share phobias.
32 THE BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Generalized anxiety, panic attacks, and even OCD are linked with brain circuits like the anterior cingulate cortex. When given challenging, cognitive tasks, these patients show elevated activity in the anterior cingulate cortex. Anterior Cingulate Cortex of an OCD patient. S. Ursu, V.A. Stenger, M.K. Shear, M.R. Jones, & C.S. Carter (2003). Overactive action monitoring in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychological Science, 14,
33 SOMATOFORM DISORDERS Symptoms mimic a physical disease or injury. Medical test results are either normal or do not explain the person s symptoms. One type of somatoform disorder is conversion disorder in which very specific genuine physical symptoms exist for which no physiological basis can be found. Hypochondriasis is a somatoform disorder in which a person interprets normal physical sensations as symptoms of a disease.
34 DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS Conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. Symptoms 1. Having a sense of being unreal. 2. Being separated from the body. 3. Watching yourself as if in a movie.
35 DISSOCIATIVE IDENTITY DISORDER (DID) A disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities, formerly called multiple personality disorder. Chris Sizemore (DID) Lois Bernstein/ Gamma Liason
36 DID CRITICS Critics argue that the diagnosis of DID increased in the late 20 th century. DID has not been found in other countries. Critics Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to a therapist s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety.
37 MOOD DISORDERS Emotional extremes of mood disorders come in two principal forms. 1. Major depressive disorder 2. Bipolar disorder
38 MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER Depression is the common cold of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). Blue mood Gasping for air after a hard run Major Depressive Disorder Chronic shortness of breath
39 MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. Signs include: 1. Lethargy and fatigue 2. Feelings of worthlessness 3. Loss of interest in family & friends 4. Loss of interest in activities
40 BIPOLAR DISORDER Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Gloomy Withdrawn Inability to make decisions Tired Slowness of thought Manic Symptoms Elation Euphoria Desire for action Hyperactive Multiple ideas
41 BIPOLAR DISORDER Many great writers, poets, and composers suffered from bipolar disorder. During their manic phase creativity surged, but not during their depressed phase. Bettmann/ Corbis George C. Beresford/ Hulton Getty Pictures Library Whitman Wolfe Clemens Hemingway The Granger Collection Earl Theissen/ Hulton Getty Pictures Library
42 EXPLAINING MOOD DISORDERS Since depression is so prevalent worldwide, investigators want to develop a theory of depression that will suggest ways to treat it. Lewinsohn et al., (1985, 1998) note that a theory of depression should explain the following: 1. Behavioral and cognitive changes 2. Common causes of depression
43 THEORY OF DEPRESSION 3. Gender differences
44 THEORY OF DEPRESSION 4. Depressive episodes self-terminate. 5. Stressful events often precede depression. 6. Depression is increasing, especially in the teens. Desiree Navarro/ Getty Images Post-partum depression
45 SUICIDE The most severe form of behavioral response to depression is suicide. Each year some 1 million people commit suicide worldwide. Suicide Statistics 1. National differences 2. Racial differences 3. Gender differences 4. Age differences 5. Other differences
46 COMPARATIVE SUICIDE RATES National Differences: Britain, Italy & Spain s rates are little more than half that of the US, Canada and Australia. Austria & Finland are double. Racial Differences: In the US, whites are 2x as likely than blacks. Gender Differences: Women are more likely to attempt, men are more likely to succeed. Age Differences: Rates increase dramatically in late adulthood, especially among men. Other: Rates are higher among the rich, nonreligious and those who are single, widowed or divorced. In the last 60 years, the global rate of annual suicide rose from 10 to 18 per 100,000. In 2006 in the US, suicide per 100,000: 11.1 (or 33,300 people).
47 BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE Genetic Influences: Mood disorders run in families. The rate of depression is higher in identical (50%) than fraternal twins (20%). Linkage analysis and association studies link possible genes and dispositions for depression. Jerry Irwin Photography
48 THE DEPRESSED BRAIN PET scans show that brain energy consumption rises and falls with manic and depressive episodes. Courtesy of Lewis Baxter an Michael E. Phelps, UCLA School of Medicine
49 SOCIAL-COGNITIVE PERSPECTIVE The social-cognitive perspective suggests that depression arises partly from self-defeating beliefs and negative explanatory styles.
50 NEGATIVE THOUGHTS AND MOODS Explanatory style plays a major role in becoming depressed.
51 DEPRESSION CYCLE 1. Negative stressful events. 2. Pessimistic explanatory style. 3. Hopeless depressed state. 4. These hamper the way the individual thinks and acts, fueling personal rejection.
52 SCHIZOPHRENIA The literal translation is split mind which refers to a split from reality. A group of severe disorders characterized by the following: 1. Disorganized and delusional thinking. 2. Disturbed perceptions. 3. Inappropriate emotions and actions.
53 SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Positive symptoms: the presence of inappropriate behaviors (hallucinations, disorganized or delusional talking) Negative symptoms: the absence of appropriate behaviors (expressionless faces, rigid bodies)
54 DISORGANIZED & DELUSIONAL THINKING This morning when I was at Hillside [Hospital], I was making a movie. I was surrounded by movie stars I m Mary Poppins. Is this room painted blue to get me upset? My grandmother died four weeks after my eighteenth birthday. (Sheehan, 1982) This Other monologue forms of illustrates delusions fragmented, include, delusions bizarre of thinking persecution with distorted ( someone beliefs is following called delusions me ) or grandeur ( I m Mary ( I Poppins ). am a king ).
55 DISORGANIZED & DELUSIONAL THINKING Many psychologists believe disorganized thoughts occur because of selective attention failure (fragmented and bizarre thoughts).
56 DISTURBED PERCEPTIONS A schizophrenic person may perceive things that are not there (hallucinations). Frequently such hallucinations are auditory and lesser visual, somatosensory, olfactory, or gustatory. L. Berthold, Untitled. The Prinzhorn Collection, University of Heidelberg August Natter, Witches Head. The Prinzhorn Collection, University of Heidelberg Photos of paintings by Krannert Museum, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
57 INAPPROPRIATE EMOTIONS & ACTIONS A schizophrenic person may laugh at the news of someone dying or show no emotion at all (flat affect). Patients with schizophrenia may continually rub an arm, rock a chair, or remain motionless for hours (catatonia).
58 ONSET AND DEVELOPMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia, and throughout the world over 24 million people suffer from this disease (WHO, 2002). Schizophrenia strikes young people as they mature into adults. It affects men and women equally, but men suffer from it more severely than women.
59 CHRONIC AND ACUTE SCHIZOPHRENIA When schizophrenia is slow to develop (chronic/process) recovery is doubtful. Such schizophrenics usually display negative symptoms. When schizophrenia rapidly develops (acute/reactive) recovery is better. Such schizophrenics usually show positive symptoms.
60 UNDERSTANDING SCHIZOPHRENIA Schizophrenia is a disease of the brain exhibited by the symptoms of the mind. Brain Abnormalities Dopamine Overactivity: Researchers found that schizophrenic patients express higher levels of dopamine D4 receptors in the brain.
61 ABNORMAL BRAIN ACTIVITY Brain scans show abnormal activity in the frontal cortex, thalamus, and amygdala of schizophrenic patients. Paul Thompson and Arthur W. Toga, UCLA Laboratory of Neuro Imaging and Judith L. Rapport, National Institute of Mental Health
62 ABNORMAL BRAIN MORPHOLOGY Schizophrenia patients may exhibit morphological changes in the brain like enlargement of fluid-filled ventricles. Both Photos: Courtesy of Daniel R. Weinberger, M.D., NIH-NIMH/ NSC
63 VIRAL INFECTION Schizophrenia has also been observed in individuals who contracted a viral infection (flu) during the middle of their fetal development.
64 GENETIC FACTORS The likelihood of an individual suffering from schizophrenia is 50% if their identical twin has the disease (Gottesman, 2001). Identical Both parents Fraternal One parent Sibling Nephew or niece Unrelated
65 GENETIC FACTORS The following shows the prevalence of schizophrenia in identical twins as seen in different countries.
66 PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicol & Gottesman, 1983). Genain Sisters Courtesy of Genain Family The genetically identical Genain sisters suffer from schizophrenia. Two more than others, thus there are contributing environmental factors.
67 PERSONALITY DISORDERS Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually without anxiety, depression, or delusions.
68 ANTISOCIAL PERSONALITY DISORDER A disorder in which the person (usually men) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members. Formerly, this person was called a sociopath or psychopath. Symptoms May Include: Lack of empathy or affection. No regard for right and wrong. Using charm or wit to manipulate others. Intimidation of others. Violent or aggressive behavior.
69 ANTISOCIAL PERSONALITY DISORDER Some have trouble functioning normally in society: trouble with relationships and with the law. Others are very successful at mimicking emotion and general deception.
70 UNDERSTANDING ANTISOCIAL PERSONALITY DISORDER Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters, before committing a crime, respond with lower levels of stress hormones than others do at their age.
71 UNDERSTANDING ANTISOCIAL PERSONALITY DISORDER PET scans of 41 murderers revealed reduced activity in the frontal lobes. In a follow-up study, repeat offenders had 11% less frontal lobe activity (Raine et al., 1999; 2000). Normal Murderer Courtesy of Adrian Raine, University of Southern California
72 RATES OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
73 RATES OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS The prevalence of psychological disorders during the previous year is shown below (WHO, 2004).
Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar Disorder. Theory of Depression. Explaining Mood Disorders. Theory of Depression. Suicide
 Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders 1 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Understanding Psychological Disorders Classifying Psychological Disorders Labeling
Psychological Disorders 1 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Understanding Psychological Disorders Classifying Psychological Disorders Labeling
Schizophrenia. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Psychological Disorders. Module 51. Schizophrenia
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 I felt the need to clean my room would spend four to five hours at it At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but
Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 I felt the need to clean my room would spend four to five hours at it At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but
Psychological Disorders
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Psychological Disorders Chapter 16 2 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Psychological Disorders Chapter 16 2 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 I felt the need to clean my room would spend four to five hours at it At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but
Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 I felt the need to clean my room would spend four to five hours at it At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Note: See my PinterestBoard for more articles and videos on Psychological Disorders: www.pinterest.com/carmcmurray Psychology 40S C. McMurray Source: PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David
Psychological Disorders Note: See my PinterestBoard for more articles and videos on Psychological Disorders: www.pinterest.com/carmcmurray Psychology 40S C. McMurray Source: PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David
Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy Spring, 2010 Rita Sampers
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2010 Rita Sampers 1 2 Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent four to five hour at it At the time I loved it but then didn't
Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2010 Rita Sampers 1 2 Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent four to five hour at it At the time I loved it but then didn't
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 16 Psy12000.003 Fall, 2010 Online Course Evaluations I felt the need to clean my room spent four to five hour at it At the time I loved it but then
Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders Chapter 16 Psy12000.003 Fall, 2010 Online Course Evaluations I felt the need to clean my room spent four to five hour at it At the time I loved it but then
Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy Fall, 2011
 Exam 4 N= 402 Mean: 37.2 Median: 38 Mode: 39 Standard Deviation: 6.14 Top score: 49 Top cumulative score to date: 190 Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy12000.003 Fall, 2011 Online Course Evaluations
Exam 4 N= 402 Mean: 37.2 Median: 38 Mode: 39 Standard Deviation: 6.14 Top score: 49 Top cumulative score to date: 190 Psychological Disorders Chapter 14 Psy12000.003 Fall, 2011 Online Course Evaluations
Psychological Disorders
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical--not enough in itself disturbing--varies with time and culture maladaptive--harmful unjustifiable--sometimes
Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical--not enough in itself disturbing--varies with time and culture maladaptive--harmful unjustifiable--sometimes
Disorders. Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality.
 Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain ( )
 Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain (1860-1939) onset of schizophrenia Nearly 1% of the population suffers from schizophrenia Schizophrenia strikes young people as they mature into adults. (18-24 years
Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain (1860-1939) onset of schizophrenia Nearly 1% of the population suffers from schizophrenia Schizophrenia strikes young people as they mature into adults. (18-24 years
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders On the post-it note(s) provided, write about your experience with mental illness. How has your life been affected by mental illness? 1 Defining Psychological Disorders Complete
Psychological Disorders On the post-it note(s) provided, write about your experience with mental illness. How has your life been affected by mental illness? 1 Defining Psychological Disorders Complete
A deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional pattern of thoughts, feelings, and actions.
 Chapter 13 A deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional pattern of thoughts, feelings, and actions. Deviant: diverging sharply from what is considered customary, traditional or generally accepted standard.
Chapter 13 A deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional pattern of thoughts, feelings, and actions. Deviant: diverging sharply from what is considered customary, traditional or generally accepted standard.
Unit 12 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following disorders is classified as a mood disorder? A) antisocial personality disorder B) agoraphobia C) catatonia D) generalized anxiety disorder E) bipolar disorder 2. Mania
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following disorders is classified as a mood disorder? A) antisocial personality disorder B) agoraphobia C) catatonia D) generalized anxiety disorder E) bipolar disorder 2. Mania
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent 4 to 5 hours at it At the time I loved it but then didn't want to do it any more, but could not stop The clothes hung two fingers apart I
Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent 4 to 5 hours at it At the time I loved it but then didn't want to do it any more, but could not stop The clothes hung two fingers apart I
Biopsychosocial Approach. considers combination of biological, psychological, and social factors as contributing to development of disorders
 Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out, godlike powers, movement of stars Treatments: institutionalized, castration, drilling holes in skull, transfusion of animal blood, and
Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil spirits trying to get out, godlike powers, movement of stars Treatments: institutionalized, castration, drilling holes in skull, transfusion of animal blood, and
Active listening. drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antianxiety drugs
 Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide
 Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide Psychological disorders patterns of thoughts feelings or actions that are deviant distressful of dysfunctional Disorder refers state of mental/behavioral ill health Patterns
Psychology Chapter 15 Study Guide Psychological disorders patterns of thoughts feelings or actions that are deviant distressful of dysfunctional Disorder refers state of mental/behavioral ill health Patterns
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3. By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin
 Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
True or False? Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders. What is Abnormal Behavior? 12/9/10. Characteristics of Abnormal Behavior
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormality Classifying Psychological Disorders Origins of Psychological Disorders True or False? Abnormal behaviors are always bizarre. A clear distinction
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormality Classifying Psychological Disorders Origins of Psychological Disorders True or False? Abnormal behaviors are always bizarre. A clear distinction
AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Abnormal Psychology At various moments, all of us feel, think or act the same way disturbed people do much of
AP PSYCH Unit 12.1 Abnormal Psychology Anxiety Disorders Defining Psychological Disorders Abnormal Psychology At various moments, all of us feel, think or act the same way disturbed people do much of
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
Chapter 18: Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 18: Case Study: Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity Section 1: Understanding Section 2: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Section 3: Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders Section 4: Schizophrenia Section
Chapter 18: Case Study: Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity Section 1: Understanding Section 2: Anxiety and Mood Disorders Section 3: Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders Section 4: Schizophrenia Section
 Psychopathology Psychopathy (con t) Psychopathy Characteristics High impulsivity Thrill seeking Low empathy Low anxiety What is the common factor? Callous Self-Centeredness N M P Dr. Robert Hare
Psychopathology Psychopathy (con t) Psychopathy Characteristics High impulsivity Thrill seeking Low empathy Low anxiety What is the common factor? Callous Self-Centeredness N M P Dr. Robert Hare
Bi-polar MDD. Repeated episodes of mania and depression
 MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
WHAT ARE PERSONALITY DISORDERS?
 CHAPTER 16 REVIEW WHAT ARE PERSONALITY DISORDERS? How is abnormal behaviour defined? Statistically infrequent Violates of social norms Personally distressful Disability or dysfunction Unexpected DSM-IV
CHAPTER 16 REVIEW WHAT ARE PERSONALITY DISORDERS? How is abnormal behaviour defined? Statistically infrequent Violates of social norms Personally distressful Disability or dysfunction Unexpected DSM-IV
General Psychology. Chapter Outline. Psychological Disorders 4/28/2013. Psychological Disorders: Maladaptive patterns of behavior that cause distress
 General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
Dr Rikaz Sheriff. Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital
 Dr Rikaz Sheriff MBBS Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital Transplant & Employee Counselor PGIM Trainee MSc in Biomedical Informatics PGIM Trainee Certificate in Medical Education Outline Psychological
Dr Rikaz Sheriff MBBS Senior Medical Officer, Western Hospital Transplant & Employee Counselor PGIM Trainee MSc in Biomedical Informatics PGIM Trainee Certificate in Medical Education Outline Psychological
UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY PERSPECTIVES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS OBJECTIVE 1: Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. 1. Psychological disorders are persistently
UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY PERSPECTIVES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS OBJECTIVE 1: Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. 1. Psychological disorders are persistently
Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments
 Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments 1. A person may have a strong fear of spiders, but it is not considered a disorder unless it is: A) not based in reality. B) the result of a traumatic
Chapter 14 & 15: Psychological Disorders and Treatments 1. A person may have a strong fear of spiders, but it is not considered a disorder unless it is: A) not based in reality. B) the result of a traumatic
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
Agoraphobia. An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible.
 Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
AP Psychology: Abnormal Quiz 1
 AP Psychology: Abnormal Quiz 1 1. Applying a medical model to identify and treat psychological disorders should be used: A) in every case. B) only in cases of suspected trauma. C) only in cases of suspected
AP Psychology: Abnormal Quiz 1 1. Applying a medical model to identify and treat psychological disorders should be used: A) in every case. B) only in cases of suspected trauma. C) only in cases of suspected
Psychological Factors
 Psychological Factors Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Genain Sisters The genetically identical
Psychological Factors Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Genain Sisters The genetically identical
Abnormal Psychology. Defining Abnormality
 Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 12 Psychological 12-1 Abnormal Behavior The most commonly used criteria for distinguishing between normal and abnormal behaviors are: 12-2 Abnormal Behavior We can define behaviors as abnormal
Chapter 12 Psychological 12-1 Abnormal Behavior The most commonly used criteria for distinguishing between normal and abnormal behaviors are: 12-2 Abnormal Behavior We can define behaviors as abnormal
Chapter 14. Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders We ve Come a Long Way Trepanning Ancient priests or medicine men cut holes into the skills of living persons, to release the demons. What is Abnormality Psychopathology
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders We ve Come a Long Way Trepanning Ancient priests or medicine men cut holes into the skills of living persons, to release the demons. What is Abnormality Psychopathology
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar College Lecture
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar College Lecture
16 Overview! 16 Mental disorder! Psychological disorders! Dilemmas of definition! Your turn!
 Psychological disorders! Overview! Defining and diagnosing disorder Anxiety disorders Mood disorders Personality disorders Drug abuse and addiction Dissociative identity disorder Schizophrenia Dilemmas
Psychological disorders! Overview! Defining and diagnosing disorder Anxiety disorders Mood disorders Personality disorders Drug abuse and addiction Dissociative identity disorder Schizophrenia Dilemmas
Copyright 2014 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill
 Copyright 2014 All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of CHAPTER PREVIEW Defining/Explaining Abnormal Behavior Anxiety-Related Disorders Mood-Related Disorders
Copyright 2014 All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of CHAPTER PREVIEW Defining/Explaining Abnormal Behavior Anxiety-Related Disorders Mood-Related Disorders
Examples of Cognitions that can Worsen Anxiety:
 Examples of Cognitions that can Worsen Anxiety: Cognitive errors, such as believing that we can predict that bad events will happen Irrational beliefs, such as bad things don t happen to good people, so
Examples of Cognitions that can Worsen Anxiety: Cognitive errors, such as believing that we can predict that bad events will happen Irrational beliefs, such as bad things don t happen to good people, so
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2
 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY
 Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO
 KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO Categories of Disorder: 1. Anxiety 2. Mood 3. Dissociative 4. Schizophrenia 5. Personality 6. Somatoform (Not in Book) 7. Facticious (Not in Book) Anxiety Disorders
KNOW WHAT CATEGORY ANY DISORDER FITS INTO Categories of Disorder: 1. Anxiety 2. Mood 3. Dissociative 4. Schizophrenia 5. Personality 6. Somatoform (Not in Book) 7. Facticious (Not in Book) Anxiety Disorders
A Guide to Mental Disorders
 A Guide to Mental Disorders Objectives 1. Identify at least 5 mental illnesses. 2. Describe the warning signs of various mental illnesses. 3. Share ways to promote mental health. Affective Disorders *These
A Guide to Mental Disorders Objectives 1. Identify at least 5 mental illnesses. 2. Describe the warning signs of various mental illnesses. 3. Share ways to promote mental health. Affective Disorders *These
Chapter 14. Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Deviant: represents a serious departure from social and cultural norms of behavior, not normal.
 Psychopathology: mental disorder Deviant: represents a serious departure from social and cultural norms of behavior, not normal. Maladaptive: dysfunctional behavior that interferes with a person s ability
Psychopathology: mental disorder Deviant: represents a serious departure from social and cultural norms of behavior, not normal. Maladaptive: dysfunctional behavior that interferes with a person s ability
Psychological Disorder. Abnormal Psychology 3/20/15. Early Theories. Perspectives and Disorders
 3/20/15 Abnormal Psychology Psychological Disorder How would you define a Psychological Disorder? Patterns of thoughts, feelings, or actions that are deviant, distressful, or dysfunctional. Early Theories
3/20/15 Abnormal Psychology Psychological Disorder How would you define a Psychological Disorder? Patterns of thoughts, feelings, or actions that are deviant, distressful, or dysfunctional. Early Theories
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 /
 Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
Chapter 10. Abnormal Psychology Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 10 Abnormal Psychology Psychological Disorders APPROACHES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Approaches Society Individuals Mental Health Professionals APPROACHES OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Approaches
Chapter 10 Abnormal Psychology Psychological Disorders APPROACHES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Approaches Society Individuals Mental Health Professionals APPROACHES OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Approaches
Psychological Disorders
 1 2 3 4 5 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Societal Does the behavior conform to existing social norms? Individual Personal sense of well-being Happy, satisfied, peaceful
1 2 3 4 5 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Societal Does the behavior conform to existing social norms? Individual Personal sense of well-being Happy, satisfied, peaceful
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology
 Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology Section 1: Abnormal Behaviour Section 2: Anxiety Disorders Section 3: Somatoform Disorders Section 4: Dissociative Disorders Section 5: Mood Disorders Section 6: Schizophrenic
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology Section 1: Abnormal Behaviour Section 2: Anxiety Disorders Section 3: Somatoform Disorders Section 4: Dissociative Disorders Section 5: Mood Disorders Section 6: Schizophrenic
3/9/2017. A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course. Our purpose
 A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
Chapter 29. Caring for Persons With Mental Health Disorders
 Chapter 29 Caring for Persons With Mental Health Disorders The Whole Person The whole person has physical, social, psychological, and spiritual parts. Mental relates to the mind. Mental health and mental
Chapter 29 Caring for Persons With Mental Health Disorders The Whole Person The whole person has physical, social, psychological, and spiritual parts. Mental relates to the mind. Mental health and mental
CHAPTER 12 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 CHAPTER 12 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Observing people s strange-seeming behaviors, we may wonder what is going on inside their heads. Most people would say these behaviors
CHAPTER 12 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Observing people s strange-seeming behaviors, we may wonder what is going on inside their heads. Most people would say these behaviors
Name. 1. Cultural expectations for "normal" behavior in a particular society influence the understanding of "abnormal behavior.
 Chapter 10 Quiz Name Psychological Disorders (Modules 33 & 34) True or False: 1. Cultural expectations for "normal" behavior in a particular society influence the understanding of "abnormal behavior."
Chapter 10 Quiz Name Psychological Disorders (Modules 33 & 34) True or False: 1. Cultural expectations for "normal" behavior in a particular society influence the understanding of "abnormal behavior."
Psychological Disorders.notebook. March 25, Feb 13 10:03 AM. Apr 13 12:46 PM. Apr 13 12:57 PM. Psychological Disorders
 Feb 13 10:03 AM Psychological Disorders Psychological disorders are conditions where behaviour is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive (harmful) and unjustifiable. Terminology: Organic disorders:
Feb 13 10:03 AM Psychological Disorders Psychological disorders are conditions where behaviour is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive (harmful) and unjustifiable. Terminology: Organic disorders:
Average? Anyone at the extremes is? Violating social norms? Cultural Norms? Experiencing subjective discomfort? Maladaptive Behavior?
 Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
Rates of Psychological Disorders (pp ) PROGRESS TEST Multiple-Choice Questions
 Progress Test 1 419 6. PET scans of murderers' brains reveal reduced activity in the 7. As in other disorders, in antisocial personality, genetics whole story. Rates of Psychological Disorders (pp. 680-682)
Progress Test 1 419 6. PET scans of murderers' brains reveal reduced activity in the 7. As in other disorders, in antisocial personality, genetics whole story. Rates of Psychological Disorders (pp. 680-682)
Behavioral Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Behavioral Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess, & treat patients with behavioral emergencies, including patients with psychiatric history & substance abuse Lesson Objectives Define these terms: Suicide
Behavioral Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess, & treat patients with behavioral emergencies, including patients with psychiatric history & substance abuse Lesson Objectives Define these terms: Suicide
Introduction to Psychology. Lecture No: 37
 Lecture No: 37 Causes of Phobias may include: Result of some traumatic event or disaster Hereditary component, Prevalent equally in men and women, Anxiety, Panic attacks. SOME COMMON PHOBIAS Acrophobia
Lecture No: 37 Causes of Phobias may include: Result of some traumatic event or disaster Hereditary component, Prevalent equally in men and women, Anxiety, Panic attacks. SOME COMMON PHOBIAS Acrophobia
Who has Schizophrenia? What is Schizophrenia? 11/20/2013. Module 33. It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders!
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY PERSPECTIVES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS OBJECTIVE 1: Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. 1. Psychological disorders are persistently
UNIT 12: ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY PERSPECTIVES ON PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS OBJECTIVE 1: Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. 1. Psychological disorders are persistently
A. A diagnosis of anxiety disorder occurs when overwhelming anxiety disrupts social or occupational functioning or produces significant distress.
 1 TYPES OF DISORDERS 1. Anxiety Disorders and Somatoform Disorders I. Anxiety disorders in general A. A diagnosis of anxiety disorder occurs when overwhelming anxiety disrupts social or occupational functioning
1 TYPES OF DISORDERS 1. Anxiety Disorders and Somatoform Disorders I. Anxiety disorders in general A. A diagnosis of anxiety disorder occurs when overwhelming anxiety disrupts social or occupational functioning
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders
 How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
Abnormal Psychology. A.K.A. Psychological Disorders
 Abnormal Psychology A.K.A. Psychological Disorders A harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil
Abnormal Psychology A.K.A. Psychological Disorders A harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil
Mood Disorders. Tara Khanna, David Power, Alexandra Wen, Shania Yang, Kelly Zhan
 Mood Disorders Tara Khanna, David Power, Alexandra Wen, Shania Yang, Kelly Zhan Mood Disorders Generally, mood disorders are psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes. They come in 2
Mood Disorders Tara Khanna, David Power, Alexandra Wen, Shania Yang, Kelly Zhan Mood Disorders Generally, mood disorders are psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes. They come in 2
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
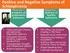 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Study Guide Chapter 16
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following is true concerning abnormal behavior? A) Definitions of abnormal behavior are culture-dependent. B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following is true concerning abnormal behavior? A) Definitions of abnormal behavior are culture-dependent. B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Lecture notes available at http://www.cybersisman.com Dysfunctional Behavior Dysfunctional or abnormal behavior is any behavior judged to be disturbing, atypical, maladaptive or
Psychological Disorders Lecture notes available at http://www.cybersisman.com Dysfunctional Behavior Dysfunctional or abnormal behavior is any behavior judged to be disturbing, atypical, maladaptive or
Highs and Lows. Anxiety and Depression
 Highs and Lows Anxiety and Depression ANXIETY Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become excessive. However a
Highs and Lows Anxiety and Depression ANXIETY Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can actually be beneficial in some situations. For some people, however, anxiety can become excessive. However a
AP Psychology Ch. 16 Disorders Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following is true concerning abnormal behavior? A) Definitions of abnormal behavior are culture-dependent. B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following is true concerning abnormal behavior? A) Definitions of abnormal behavior are culture-dependent. B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered
Chapter 13 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions
 Chapter 13 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions As you review the various theories in this chapter, you might want to make notes on the tables at the end of this document to use as study aids for comparing
Chapter 13 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions As you review the various theories in this chapter, you might want to make notes on the tables at the end of this document to use as study aids for comparing
Critics of dissociative identity disorder, 657
 Critics of dissociative identity disorder, 657 They argue it doesn t really exist. Movies and books increased the diagnosis, not actual patient symptoms. DID has not been found in other countries 1. Those
Critics of dissociative identity disorder, 657 They argue it doesn t really exist. Movies and books increased the diagnosis, not actual patient symptoms. DID has not been found in other countries 1. Those
Psychological Disorders
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 16 Psychological C16:1 Psychological C16:2 Widespread and debilitating effects WHO (2001) Estimated 450 million people worldwide suffer psychological disorders Account for 15.4%
Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 16 Psychological C16:1 Psychological C16:2 Widespread and debilitating effects WHO (2001) Estimated 450 million people worldwide suffer psychological disorders Account for 15.4%
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 14.1 What Is a Psychological Psychopathology
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 14.1 What Is a Psychological Psychopathology
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology. Lecture Series: Chapter 15 Psychological Disorders Pages: 26
 Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 15 Psychological Disorders Pages: 26 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 15 Psychological Disorders Pages: 26 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Psyhcological Disorders Ch. 16
 Important Dates to remember Psyhcological Disorders Ch. 16 1. Journals 2/26 2. Homework 3/3 3. Test 3/4 Defining Psychological Disorders What's normal and what's abnormal? Psychological Disorders a harmful
Important Dates to remember Psyhcological Disorders Ch. 16 1. Journals 2/26 2. Homework 3/3 3. Test 3/4 Defining Psychological Disorders What's normal and what's abnormal? Psychological Disorders a harmful
Anxiety, Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders. Chapter 16, Sections 2-3
 Anxiety, Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders Chapter 16, Sections 2-3 Anxiety Disorders Do Now (Discussion) What is anxiety? How is it different from worry or fear? Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders
Anxiety, Somatoform & Dissociative Disorders Chapter 16, Sections 2-3 Anxiety Disorders Do Now (Discussion) What is anxiety? How is it different from worry or fear? Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders
What is Abnormal anyway?
 What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
Research suggests that the stigma and stress associated with being gay increase the risk of mental health problems.
 1 Research suggests that the stigma and stress associated with being gay increase the risk of mental health problems. 2 In some cultures, depression and schizophrenia are nonexistent. 3 Research indicates
1 Research suggests that the stigma and stress associated with being gay increase the risk of mental health problems. 2 In some cultures, depression and schizophrenia are nonexistent. 3 Research indicates
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
Psychology Session 11 Psychological Disorders
 Psychology Session 11 Psychological Disorders Date: November 18th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Normal vs. Abnormal 2. Communication disorders 3. Anxiety disorders
Psychology Session 11 Psychological Disorders Date: November 18th, 2016 Course instructor: Cherry Chan Mothercraft College Agenda 1. Normal vs. Abnormal 2. Communication disorders 3. Anxiety disorders
Sec 1: What are Psychological Disorders?
 Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders Sec 1: What are Psychological Disorders? Defining & Identifying Psychological Disorders 1. Deviation from Normality abnormality is any deviation from the average or from
Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders Sec 1: What are Psychological Disorders? Defining & Identifying Psychological Disorders 1. Deviation from Normality abnormality is any deviation from the average or from
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY. Psychological Disorders. Fast Track Chapter 11 (Bernstein Chapter 15)
 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY Psychological Disorders Fast Track Chapter 11 (Bernstein Chapter 15) Introduction to Abnormal Psychology PSYCHOPATHOLOGY the study of the causes, symptoms, and development of psychological
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY Psychological Disorders Fast Track Chapter 11 (Bernstein Chapter 15) Introduction to Abnormal Psychology PSYCHOPATHOLOGY the study of the causes, symptoms, and development of psychological
Psychological Definition of a Mental Disorder
 Mental Illness Disclaimer Please do not start diagnosing yourself, friends, family, or school mates. This section will provide common traits of certain Mental Illnesses, it will not enable you to make
Mental Illness Disclaimer Please do not start diagnosing yourself, friends, family, or school mates. This section will provide common traits of certain Mental Illnesses, it will not enable you to make
PSYCHOLOGY PRACTICE FOR FUN
 PSYCHOLOGY PRACTICE FOR FUN Abnormal Behavior Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each
PSYCHOLOGY PRACTICE FOR FUN Abnormal Behavior Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each
Mental Health and Stress
 Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
Psych Grand Rounds. Disclosure. My books
 for Asperger Syndrome and Other Related Disorders Practical Strategies for Assessment Practical Strategies and for Treatment Assessment and Treatment Illustrated by Laura S. Kowalski A Simple Technique
for Asperger Syndrome and Other Related Disorders Practical Strategies for Assessment Practical Strategies and for Treatment Assessment and Treatment Illustrated by Laura S. Kowalski A Simple Technique
Crisis Management. Crisis Management Goals. Emotionally Disturbed Persons 10/29/2009
 Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
Mental Health and Stress Management
 Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
Mental Health and Stress Management In recent years, psychologists have become more interested in positive psychology Focus on positive emotions, characteristics, strengths, and conditions that create
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
