Daisuke; Shimizu, Hiroshi. Citation Journal of Investigative Dermatolog
|
|
|
- Kelley Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title Keratin 1 Gene Mutation Detected in Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis Tsubota, Akiko; Akiyama, Masashi; S Author(s) Nomura, Yukiko; Ando, Satomi; Abe, Daisuke; Shimizu, Hiroshi Citation Journal of Investigative Dermatolog Issue Date Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/30282 Right Nature Publishing Group, JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY, 127(6), 2007, pp Type article (author version) Additional Information Instructions for use Hokkaido University Collection of Scholarly and
2 Journal of Investigative Dermatology MS# JID Revised Version Mutation Report Keratin 1 Gene Mutation Detected in Epidermal Nevus with Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis Akiko Tsubota, Masashi Akiyama *, Kaori Sakai, Maki Goto, Yukiko Nomura, Satomi Ando, Masataka Abe, Daisuke Sawamura, Hiroshi Shimizu * Department of Dermatology, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan. *Co-corresponding authors: Masashi Akiyama and Hiroshi Shimizu Department of Dermatology Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine North 15 West 7, Kita-ku, Sapporo , Japan Telephone: , ext Fax: akiyama@med.hokudai.ac.jp shimizu@med.hokudai.ac.jp Short title: Keratin 1 mutation in epidermal nevus Key words: bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma / epidermolytic hyperkeratosis / granular degeneration / mosaicism / palmoplantar keratoderma Abbreviations: BCIE, bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma; EH, epidermolytic hyperkeratosis; K1, keratin 1; K10, keratin 10; LA-PCR, long and accurate PCR 1
3 Abstract Since 1994, four cases of epidermal nevus with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EH) caused by K10 gene mutations have been reported, although no K1 gene mutation has yet been reported. We detected a K1 gene (KRT1) mutation in epidermal nevus with EH in a 10-year-old Japanese male. The patient showed well-demarcated verrucous, hyperkeratotic plaques mainly on the trunk, covering 15 % of the entire body surface. No hyperkeratosis was seen on the palms or soles. He had no family history of skin disorders. His lesional skin showed typical granular degeneration and, ultrastructurally, clumped keratin filaments were observed in the upper epidermis. Direct sequence analysis of genomic DNA extracted from lesional skin revealed a heterozygous 5 donor splice site mutation c.591+2t>a in KRT1. This mutation was not detected in genomic DNA samples from patient s peripheral blood leukocytes or those of other family members. The identical splice mutation was previously reported in a family with palmoplantar keratoderma and mild ichthyosis, and was demonstrated to result in a 22 amino acid deletion p.val175_lys196del in the H1 and 1A domains of K1. The present patient is the first reported case of epidermal nevus associated with EH caused by a K1 gene mutation in a mosaic pattern. 2
4 INTRODUCTION Epidermal nevi are skin hamartomatous lesions comprised of keratinocytes. Their clinical features include circumscribed verrucous lesions of any size, single or multiple in nature, and they can occur at any site, frequently following Blaschko s lines. Epidermal nevi are thought to reflect a genetic mosaicism and, it has been often hypothesized that epidermal nevi with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (EH) reflect differentiation specific, suprabasal keratin gene mutations. The term EH in this case means pathological changes seen in bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (BCIE), a keratin 1 (K1)/keratin 10 (K10) disease, although EH is a histological feature of more than one disease. Indeed, K10 gene mutations were reported in four cases of epidermal nevi with EH (Paller et al., 1994; Moss et al., 1995), although no K1 gene mutation has yet been reported. A mosaic mutation in the V1 domain of keratin 16 was reported to underlie unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus with vacuolar degeneration of keratinocytes in the upper epidermis (Terrinoni et al., 2000). A diverse range of subtly different phenotypes including classical BCIE has been described with mutations in K1 (reviewed in Lane and McLean, 2004). Splice site mutations affecting the K1 peptide 1A or 2B domain caused epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) (reviewed in Terron-Kwiatkowski et al., 2002). Now a total of 47 different mutations have been reported in K1 (The Human Intermediate Filament Database). Here we report that a splice site mutation in the K1 gene, previously reported in a case of PPK and mild ichthyosis, was associated with the epidermal nevus with EH disease phentoype. As far as we know, the 3
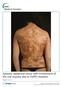
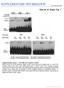
5 present case is the first reported patient of epidermal nevus with EH associated with a K1 gene mutation. RESULTS Clinical features A 10-year-old Japanese male showed well-demarcated verrucous, hyperkeratotic plaques mainly on the trunk, covering 15 % of his entire body surface. They distributed following the Blaschko s lines (Figure 1). No hyperkeratosis was seen on the palms and soles. The other family members including his parents and elder brother had neither BCIE nor epidermal nevus. Typical granular degeneration and clumped keratin filaments were seen in the epidermal nevus Light microscopy of the skin samples from the nevus on the trunk revealed typical granular degeneration with large keratohyalin granules in the upper epidermis (data not shown). Electron microscopy showed clumped keratin filaments in the upper epidermal keratinocytes (data not shown). Some of those keratinocytes with abnormal keratin clumps were undergoing degeneration. A splice site mutation in K1 gene (KRT1) was identified in lesional skin but not in peripheral blood Mutation analysis of the entire 1-9 exons including the intron-exon boundaries of the K1 gene (KRT1) revealed a heterozygous T>A substitution at base position 591+2, in intron 1 (c.591+2t>a) (Figure 2). 4
6 This mutation disrupts the KRT1 exon 1 donor splice site. This mutation was not detected in genomic DNA samples from patient s peripheral blood leukocytes (Figure 2a) or those of his family members. No other mutation was found in the entire exon and intron/exon borders of the K1 and K10 genes. The mutation was not found in 100 normal, unrelated Japanese alleles (50 healthy unrelated Japanese individuals) by sequence analysis, and was unlikely to be a polymorphism (data not shown). By mutant allele specific amplification analysis (Hasegawa et al., 1995; Xu et al., 2003), a 102 bp fragment derived from the mutant allele was amplified from the genomic DNA sample extracted from the lesional skin (Figure 2b). The 102 bp fragment was sequenced and it was confirmed that the fragment was derived from the targeted region of K1 gene, KRT1. The mutant allele specific amplification showed no PCR product bands from the peripheral blood cell DNA samples from the patient, any other family members or controls. K1 expression was weak and keratin 2e (K2e) expression was upregulated in the epidermal nevus lesion Immunofluorescence studies revealed that K1 and K10 were present in the lesional epidermal suprabasal layers, although K1 expression was weaker than that in the normal control skin (Figure S1a-d). In the regions showing granular degeneration, abnormal, large granules in the degenerated keratinocytes were positive for K1 and K10. K2e was expressed only in the uppermost spinous and the granular layers of epidermis in normal control skin (Figure S1f). In the patient s lesional skin, K2e expression was seen in the almost all suprabasal epidermal 5
7 layers, suggesting an upregulated expression of K2e in the lesional epidermis (Figure S1e). DISCUSSION All the reported causative mutations underlying epidermal nevus with EH affected the K10 gene (Paller et al., 1994; Moss et al., 1995). As far as we know, the present case is the first reported case of epidermal nevus with EH caused by a K1 gene mutation. K2e expression increased in the lesional epidermis of the present case. Although we do not have any direct evidence, K2e expression might be upregulated compensatively in the epidermis with disrupted keratin network. Indeed, increased K2e expression was also observed in the lesional epidermis with disturbed keratin network of ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens patients (Akiyama et al., 2005). In our case, the causative K1 mutation was detected only in the lesional skin, but not in the peripheral blood cells, as previously reported in K10 mutations in epidermal nevus with EH (Paller et al., 1994; Moss et al., 1995). Our findings further support that the mutation detection of K1 as well as K10 in epidermal nevus can be reliably performed only from direct examination of lesional skin, not from analysis of other tissue or peripheral blood cells. As epidermal nevus is a disease caused by somatic mosaicism, widespread 6
8 skin lesions increase the risk of germ-line transmission (Paller et al., 1994). In case causative K1 or K10 mutations are transmitted in germ-line, a half of the children from patients with epidermal nevus with EH are expected to be affected with ichthyosis on the whole body. Mutation analysis using a patient's sperm gives us information on germ-line transmission (Zlotogora, 1998; Rantamaki et al., 1999). If the germ-line transmission is confirmed, prenatal genetic screening may be applied for the offspring of the patient as previously reported in the prenatal diagnosis of BCIE by molecular analysis (Rothnagel et al., 1994; Tsuji-Abe et al., 2004). The K1 gene mutation detected in the present case was a splice donor site mutation c.591+2t>a. According to Splice Site Prediction by Neural Network software ( (Tal et al., 2005; Wessagowit et al., 2005; Wessagowit et al., 2006), a consequence of this mutation is predicted with the highest probability, we can expect a splice variant with an upstream cryptic splice donor site resulting in a 66 bp deletion (22 amino acid deletion; p.val175-lys196del). The second highest probability, an alternative splice pattern activating a cryptic donor site 22 bp downstream of the mutation with the subsequent insertion of 8 amino acids into the 1A rod domain was predicted. Indeed, in a patient with PPK with the same K1 gene mutation as in the present case, mrna expression analysis by in vitro splicing assay clearly indicated that the splice site mutation c.591+2t>a results in a partial deletion of the H1 and 1A domains of K1 (p.val175_lys196del) (Terron-Kwiatkowski et al., 2002), as predicted by the highest probability using the software model. Concerning reported mutations in the adjacent nucleotide as our mutation 7
9 in the K1 gene, i.e. splice donor site mutations c.591+1t>a and c.591+3t>a were reported to lead to the same 22 amino acid deletions (Vitanen et al., 2003; Tal et al., 2005). Thus, we may expect an identical 22 amino acid deletion p.val175_lys196del in K1 peptides as a consequence of the KRT1 mutation c.591+2t>a in lesional keratinocytes from the present patient. Interestingly, the KRT1 mutation that had been reported to cause PPK (Terron-Kwiatkowski et al., 2002) led to an epidermal nevus with EH phenotype distributed on the trunk and the extremities in our case. In the previous PPK patient with an identical mutation, only mild hyperkeratosis was found over limited body areas and it was speculated that loss of the protein motif in the helix boundary that is essential for the interaction of keratin filaments (Steinert et al., 1993) have a less disruptive effect on normal keratin filament assembly (Terron-Kwiatkowski et al., 2002). A similar mechanism can be expected in deletions at either end of the K1 rod domain. Indeed, a splice site mutation in K1 that leads to the insertion of 18 amino acids into the 2B domain led to a mild epidermolytic PPK phenotype (reviewed in Terron-Kwiatkowski et al., 2002). However, in our case, the mosaicism of the mutation showed an epidermal nevus phenotype even on the trunk and the extremities. The precise mechanism of how identical splice site mutations can result in a different severity of the lesions on the trunk remains unclear. Until the present report, all the reported mosaic mutations causing 8
10 epidermal nevus with EH had been due to K10 mutations that would have resulted in BCIE if every cell in the body were affected (Paller et al., 1994; Moss et al., 1995). In conclusion, the present case clearly indicated that K1 mutations with genetic mosaicism also cause epidermal nevus with EH. The present K1 mosaicism might have led to PPK with mild hyperkeratotic lesions if all the epidermal cells were affected over the entire body surface (Terron-Kwitkowski et al., 2002). MATERIALS AND METHODS Mutation detection Mutation analysis was performed using genomic DNA extracted from the lesional epidermal nevus skin and peripheral blood leukocytes from the patient. In the other family members and normal controls, genomic DNA isolated from peripheral blood leukocytes was used for the analysis. Briefly, genomic DNA samples were subjected to PCR amplification, followed by direct automated sequencing using an ABI PRISM 3100 genetic analyzer (ABI Advanced Biotechnologies, Columbia, MD, U.S.A.). The oligonucleotide primers were designed using the website program (primer3_www.cgi v 0.2). The primers used for amplification of exon 1 were as follows; forward, gtggacgtggtagtggcttt; reverse, ctttaggtcgaccaccaacc. The entire coding region including the intron/exon boundaries for both forward and reverse strands were sequenced. For normal controls, 50 healthy unrelated Japanese individuals (100 normal alleles) were studied. Mutant allele specific amplification analysis Long and accurate (LA)-PCR was done using primers, forward primer ex1f1; 9
11 aggaggtgggagatttt and a reverse primer ex2r; catgctgcttcatgatcttagc. For the verification of the mutation, using LA-PCR products as a template, mutant allele specific amplification analysis was performed with mutant allele specific primers carrying the substitution of two bases at the 3 -end (Linard et al., 2002; Sapio et al., 2006), as follows; forward, gcctccttcattgacaagaa; reverse, ttcaaacctgcgtgtgttttgactgcaccgatccc. PCR conditions were as follows; 94 for 5 min after (hot-start procedure) and then 94 for 1 min, 56 for 1 min, 72 for 1 min during 35 cycles, followed by 72 for 7 min. Only the 102 bp fragment derived from the mutant allele was amplified with these primers and the PCR condition. Ultrastructural observations Epidermal nevus on the trunk was biopsied for morphological observation. Skin biopsy samples were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde solution, post-fixed in 1% OsO4, dehydrated, and embedded in Epon 812. The samples were sectioned at 1 µm thickness for light microscopy and thin sectioned for electron microscopy (70 nm thick). The thin sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate and examined in a transmission electron microscope. Antibodies Polyclonal anti-k1 antiserum (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark), anti-k2e antibody (Progen Biotechnick, Heidelberg, Germany) and anti-k10 antiserum (Novocastra, New Castle upon Tyne, England) were used in the present study. Immunofluorescent labeling Immunofluorescent labeling was performed as described previously (Akiyama et al., 2000). Briefly, 0
12 6-µm-thick sections of freshly frozen patient s skin was cut using a cryostat. The sections were incubated in primary antibody solution for 30 min at 37 C. Antibody dilutions were as follows; 1/10 for anti-k1 antiserum, 1/50 for anti-k2e antibody and 1/100 for anti-k10 antibody. The sections were then incubated in fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated to rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulins and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulins diluted 1:100 (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) for 30 min at 37. The sections were extensively washed with phosphate-buffered saline between incubations. The stained sections were then mounted with a cover slip and observed using a confocal laser scanning microscope. The medical ethical committee at Hokkaido University and Hokkaido Cancer Institute approved all described studies. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki Principles. Participants gave their written, informed consent. Conflict of Interest The authors state no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Ms. Megumi Sato and Ms. Akari Nagasaki for their technical assistance on this project. We also thank Prof. James R. McMillan for proofreading this manuscript. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan to M. Akiyama (Kiban B ) and to H. Shimzu (Kiban A 1
13 ). 2
14 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Figure S1. Immunofluorescent staining for K1 was weak, although K2e expression was upregulated in the epidermal nevus. 3
15 REFERENCES Akiyama M, Smith LT, Shimizu H (2000) Changing patterns of localization of putative stem cells in developing human hair follicles. J Invest Dermatol 114: Akiyama M, Tsuji-Abe Y, Yanagihara M, Nakajima K, Kodama H, Yaosaka M, Abe M, Sawamura D, Shimizu H (2005) Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens: its correct diagnosis facilitated by molecular genetic testing. Br J Dermatol 152: Hasegawa Y, Takeda S, Ichii S, Koizumi K, Maruyama M, Fujii A, et al. (1995) Deletion of K-ras mutations in DNAs isolated from faces of patients with colorectal tumors by mutant-allele-specific-amplification (MASA). Oncogene 10: Lane EB, Mclean WHI (2004) Keratins and skin disorders. J Pathol 204: Linard B, Bezieau S, Benlalam H, Labarrire N, Guilloux Y, Diez E, et al. (2002) A ras-mutated peptide targeted by CTL infiltrating a human melanoma lesion. J Immunol 168: Moss C, Jones DO, Blight A, Bowden PE (1995) Birthmark due to cutaneous mosaicism for keratin 10 mutation. Lancet 345: 596 Paller AS, Syder AJ, Chan YM, Yu QC, Hutton E, Tadini G, et al. (1994) 4
16 Genetic and clinical mosaicism in a type of epidermal nevus. N Engl J Med 331: Rantamaki T, Kaitila I, Syvanen A-C. Lukka M, Peltonen L (1999) Recurrence of Marfan syndrome as a result of parental germ-line mosaicism for an FBN1 mutation. Am J Hum Genet 64: Rothnagel JA, Longley MA, Holder RA, Kuster W, Roop DR (1994) Prenatal diagnosis of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis by direct gene sequencing. J Invest Dermatol 102:13-6 Sapio MR, Posca SD, Trocone G, Pettinato G, Palombini L, Rossi G, et al. (2006) Detection of BRAF mutation in thyroid papillary carcinomas by mutant allele-specific PCR amplification (MASA). Eur J Endocrinol 154: Steinert PM, Yang JM, Bale SJ, Compton JG (1993) Concrrence between the molecular overlap regions in keratin intermediate filaments and the locations of keratin mutations in genodermatoses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197: Tal O, Bergman R, Alcalay J, Indelman M, Sprecher E (2005) Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis type PS-1 caused by aberrant splicing of KRT1. Clin exp dermatol 30:64-7 Terrinoni A, Puddu P, Didona B, De Laurenzi V, Candi E, Smith FJ, McLean WH, Melino G (2000) A mutation in the V1 domain of K16 is 5
17 responsible for unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus. J Invest Dermatol 114: Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Paller AS, Compton J, Atherton DJ, McLean WH, Irvine AD (2002) Two cases of primarily palmoplantar keratoderma associated with novel mutations in keratin 1. J Invest Dermatol 119: Tsuji-Abe Y, Akiyama M, Nakamura H, Takizawa Y, Sawamura D, Matsunaga K, et al. (2004) DNA-based prenatal exclusion of bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma at the early stage, weeks' of pregnancy in two consequent siblings. J Am Acad Dermatol 51: Vitanen M, Smith SK, Gedde-Dahl Jr T, Vahlquist A, Bowden PE (2003) Splice site and deletion mutations in keratin (KRT1 and KRT10) genes: Unusual phenotypic alterations in scandinavian patients with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. J Invest Dermatol 121: Wessagowit V, Kim SC, Woong OS, McGrath JA (2005) Genotype-phenotype correlation in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: when missense doesn't make sense. J Invest Dermatol 124 : Wessagowit V, Nalla VK, Rogan PK, McGrath JA (2006) Normal and abnormal mechanisms of gene splicing and relevane to inherited skin disease. J Dermatol Sci 40:
18 Xu X, Quiros RM, Gattuso P, Ain KB, Prinz RA (2003) High prevalence of BRAF gene mutation in papillary thyroid carcinomas and thyroid tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 63: Zlotogora J. Germ line mosaicism (1998) Hum Genet 102:
19 FIGURE LEGENDS Figure 1. Clinical features of epidermal nevi at the age of 10 Well-demarcated verrucous, hyperkeratotic plaques, light to dark brown in color, were seen on the back (a), axilla (b) and abdomen (c). Figure 2. A splice site mutation c.591+2t>a was detected in the lesional skin (a) Direct sequencing of KRT1 exon 1 PCR products derived from patient s lesional skin revealed heterozygous donor splice site mutation c.591+2t>a. This mutation was not detected in genomic DNA samples from the patient s peripheral blood leukocytes. (b) Mutant allele specific amplification analysis showed the amplification band from the mutant allele as a 102 bp fragment only from the DNA sample from the patient s lesional skin, confirming the presence of the mutation c.591+2t>a in the patient s epidermal nevus. 8
20
21
22
Corresponding author: Alan Irvine, Department of Dermatology, Our Lady s
 Congenital Reticular Ichthyosiform Erythroderma V. Dvorakova, 1 RM Watson, 1 A. Terron Kwiatkowski, 2 N. Andrew 2 and AD. Irvine 1,3,4 1 Department of Dermatology, Our Lady s Children s Hospital, Crumlin,
Congenital Reticular Ichthyosiform Erythroderma V. Dvorakova, 1 RM Watson, 1 A. Terron Kwiatkowski, 2 N. Andrew 2 and AD. Irvine 1,3,4 1 Department of Dermatology, Our Lady s Children s Hospital, Crumlin,
Generalized and Naevoid Epidermolytic Ichthyosis in Denmark: Clinical and Mutational Findings*
 Acta Derm Venereol 2013; 93: 309 313 CLINICAL REPORT Generalized and Naevoid Epidermolytic Ichthyosis in Denmark: Clinical and Mutational Findings* Anette Bygum 1, Marie Virtanen 2, Flemming Brandrup 1,
Acta Derm Venereol 2013; 93: 309 313 CLINICAL REPORT Generalized and Naevoid Epidermolytic Ichthyosis in Denmark: Clinical and Mutational Findings* Anette Bygum 1, Marie Virtanen 2, Flemming Brandrup 1,
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Akemi Ishida-Yamamoto
 Journal of Dermatological Science (2003) 31(1):3-8. Loricrin keratoderma: a novel disease entity characterized by nuclear accumulation of mutant loricrin Akemi Ishida-Yamamoto Loricrin Keratoderma. A novel
Journal of Dermatological Science (2003) 31(1):3-8. Loricrin keratoderma: a novel disease entity characterized by nuclear accumulation of mutant loricrin Akemi Ishida-Yamamoto Loricrin Keratoderma. A novel
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Systemic epidermal nevus with involvement of the oral mucosa due to FGFR3 mutation
 Systemic epidermal nevus with involvement of the oral mucosa due to FGFR3 mutation Bygum et al. Bygum et al. BMC Medical Genetics 2011, 12:79 (5 June 2011) CASE REPORT Open Access Systemic epidermal nevus
Systemic epidermal nevus with involvement of the oral mucosa due to FGFR3 mutation Bygum et al. Bygum et al. BMC Medical Genetics 2011, 12:79 (5 June 2011) CASE REPORT Open Access Systemic epidermal nevus
Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography
 15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy
 Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
University of Dundee. Published in: British Journal of Dermatology. DOI: /bjd Publication date: 2015
 University of Dundee Novel autosomal dominant mutation in loricrin presenting as prominent ichthyosis Pohler, E.; Cunningham, F.; Sandilands, A.; Cole, C.; Digby, S.; McMillan, J. R.; Aristodemou, S.;
University of Dundee Novel autosomal dominant mutation in loricrin presenting as prominent ichthyosis Pohler, E.; Cunningham, F.; Sandilands, A.; Cole, C.; Digby, S.; McMillan, J. R.; Aristodemou, S.;
Keratin 17 Mutations in Four Families from India with Pachyonychia Congenita
 Indian J Dermatol. 2017 Jul Aug; 62(4): 422 426. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_321_16 PMCID: PMC5527726 Keratin 17 Mutations in Four Families from India with Pachyonychia Congenita 1 2 Manoj Agarwala, Pankaj Salphale,
Indian J Dermatol. 2017 Jul Aug; 62(4): 422 426. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_321_16 PMCID: PMC5527726 Keratin 17 Mutations in Four Families from India with Pachyonychia Congenita 1 2 Manoj Agarwala, Pankaj Salphale,
Cyclic Ichthyosis with Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis: A Phenotype Conferred by Mutations in the 2B Domain of Keratin K1
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:732 738, 1999 Cyclic Ichthyosis with Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis: A Phenotype Conferred by Mutations in the 2B Domain of Keratin K1 Virginia P. Sybert, 1,2,5 Julie S. Francis, 1,2,5
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:732 738, 1999 Cyclic Ichthyosis with Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis: A Phenotype Conferred by Mutations in the 2B Domain of Keratin K1 Virginia P. Sybert, 1,2,5 Julie S. Francis, 1,2,5
Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Gostynski, A. (2014). Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/83/87846749.jpg) University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Revertant cell therapy for epidermolysis bullosa Gostynski, Antoni IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma
 Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Mutations in lipid transporter ABCA12 in harlequin ichthyosis and functional recovery by corrective gene transfer
 Related Commentary, page 1708 Research article Mutations in lipid transporter ABCA12 in harlequin ichthyosis and functional recovery by corrective gene transfer Masashi Akiyama, 1 Yoriko Sugiyama-Nakagiri,
Related Commentary, page 1708 Research article Mutations in lipid transporter ABCA12 in harlequin ichthyosis and functional recovery by corrective gene transfer Masashi Akiyama, 1 Yoriko Sugiyama-Nakagiri,
Review. Lessons from disorders of epidermal differentiation-associated keratins. Histology and Histopathology
 Histol Histopathol (2002) 17: 331-338 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Review Lessons from disorders of epidermal differentiation-associated keratins A. Ishida-Yamamoto,
Histol Histopathol (2002) 17: 331-338 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Review Lessons from disorders of epidermal differentiation-associated keratins A. Ishida-Yamamoto,
Insights into Genotype Phenotype Correlation in Pachyonychia Congenita from the Human Intermediate Filament Mutation Database
 Insights into Genotype Phenotype Correlation in Pachyonychia Congenita from the Human Intermediate Filament Mutation Database W. H. Irwin McLean, Frances J. D. Smith, and Andrew J. Cassidy Epithelial Genetics
Insights into Genotype Phenotype Correlation in Pachyonychia Congenita from the Human Intermediate Filament Mutation Database W. H. Irwin McLean, Frances J. D. Smith, and Andrew J. Cassidy Epithelial Genetics
2) Disorders of Abnormal Keratinization - Dr. Ali
 2) Disorders of Abnormal Keratinization - Dr. Ali Disorder of Keratinization In the normal epidermis, as the keratinocytes move from the basal-cell layer to the surface, the process of terminal differentiation
2) Disorders of Abnormal Keratinization - Dr. Ali Disorder of Keratinization In the normal epidermis, as the keratinocytes move from the basal-cell layer to the surface, the process of terminal differentiation
Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa
 Case Report Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa K.J. Zhu*, C.Y. Zhu*, Y. Zhou and Y.M. Fan Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital
Case Report Novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chinese patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa K.J. Zhu*, C.Y. Zhu*, Y. Zhou and Y.M. Fan Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital
Keratin gene mutations in human skin disease
 Postgrad Med J (1994) 70, 775-779 i) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1994 Leading Article Keratin gene mutations in human skin disease H.P. Stevens and M.H.A. Rustin Departments ofdermatology,
Postgrad Med J (1994) 70, 775-779 i) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1994 Leading Article Keratin gene mutations in human skin disease H.P. Stevens and M.H.A. Rustin Departments ofdermatology,
Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva
 Pachyonychia congenita type 1- Jadassohn Lewandowsky syndrome Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Institute- Guru Gobind Singh medical
Pachyonychia congenita type 1- Jadassohn Lewandowsky syndrome Tejinder Kaur; Rajesh Rani Gupta; BB Mahajan; Rajiv Sachdeva Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Institute- Guru Gobind Singh medical
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex
 The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE UPDATED MOLECULAR GENETICS AND PATHOGENESIS OF ICHTHYOSES
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 79 ~ 90, 2011 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE UPDATED MOLECULAR GENETICS AND PATHOGENESIS OF ICHTHYOSES MASASHI AKIYAMA Department of Dermatology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 73. 79 ~ 90, 2011 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE UPDATED MOLECULAR GENETICS AND PATHOGENESIS OF ICHTHYOSES MASASHI AKIYAMA Department of Dermatology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yatsenko AN, Georgiadis AP, Röpke A, et al. X-linked TEX11
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yatsenko AN, Georgiadis AP, Röpke A, et al. X-linked TEX11
Disadhesion of epidermal keratinocytes: A histologic clue to palmoplantar keratodermas caused by DSG1 mutations
 DERMATOPATHOLOGY Disadhesion of epidermal keratinocytes: A histologic clue to palmoplantar keratodermas caused by DSG1 mutations Reuven Bergman, MD, a Dov Hershkovitz, MD, b Dana Fuchs, MSc, c Margarita
DERMATOPATHOLOGY Disadhesion of epidermal keratinocytes: A histologic clue to palmoplantar keratodermas caused by DSG1 mutations Reuven Bergman, MD, a Dov Hershkovitz, MD, b Dana Fuchs, MSc, c Margarita
University of Groningen. Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda
 University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
Progressive symmetrical Erythrokeratoderma: A case report and literature review.
 214 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2010 Progressive symmetrical Erythrokeratoderma: A case report and literature review. Pasu Piamphongsant MD, Kowit Kampirapap MD. ABSTRACT: PIAMPHONGSANT
214 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2010 Progressive symmetrical Erythrokeratoderma: A case report and literature review. Pasu Piamphongsant MD, Kowit Kampirapap MD. ABSTRACT: PIAMPHONGSANT
Transgrediens et progrediens palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert: Four cases in a single family
 Case Report Transgrediens et progrediens palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert: Four cases in a single family Anup Kumar Tiwary, MBBS, MD Dharmendra Kumar Mishra, MBBS, MD Department of Dermatology, Venereology
Case Report Transgrediens et progrediens palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert: Four cases in a single family Anup Kumar Tiwary, MBBS, MD Dharmendra Kumar Mishra, MBBS, MD Department of Dermatology, Venereology
Title. CitationJournal of Investigative Dermatology, 127(11): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information
 Title Novel ABCA12 mutations identified in two cases of no with multiple skin malignant neoplasia Natsuga, Ken; Akiyama, Masashi; Kato, Naoko; Sakai, Author(s) Hiroo; Abe, Masataka; Arita, Ken; Tsuji-Abe,
Title Novel ABCA12 mutations identified in two cases of no with multiple skin malignant neoplasia Natsuga, Ken; Akiyama, Masashi; Kato, Naoko; Sakai, Author(s) Hiroo; Abe, Masataka; Arita, Ken; Tsuji-Abe,
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography
 15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISEASE/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: London North East RGC GOSH Approved: September
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISEASE/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: London North East RGC GOSH Approved: September
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG)
 Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Mutation S233L in the 1B Domain of Keratin 1 Causes Epidermolytic Palmoplantar Keratoderma with Tonotubular Keratin
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mutation S233L in the 1B Domain of Keratin 1 Causes Epidermolytic Palmoplantar Keratoderma with Tonotubular Keratin Ana Terron-Kwiatkowski 1, Maurice A.M. van Steensel 2, Michel van Geel
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mutation S233L in the 1B Domain of Keratin 1 Causes Epidermolytic Palmoplantar Keratoderma with Tonotubular Keratin Ana Terron-Kwiatkowski 1, Maurice A.M. van Steensel 2, Michel van Geel
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29;
 SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
Title. Author(s)Onozuka, Takashi; Sawamura, Daisuke; Goto, Maki; Yok. CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 41(3): Issue Date
 Title Possible role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the Author(s)Onozuka, Takashi; Sawamura, Daisuke; Goto, Maki; Yok CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 41(3): 217-220 Issue Date 2006-03 Doc
Title Possible role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the Author(s)Onozuka, Takashi; Sawamura, Daisuke; Goto, Maki; Yok CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 41(3): 217-220 Issue Date 2006-03 Doc
Epidermolytic Ichthyosis Sine Epidermolysis
 ORIGINAL STUDY Marina Eskin-Schwartz, MD, PhD,* Marianna Drozhdina, PhD, Ofer Sarig, PhD,* Andrea Gat, MD, Tomer Jackman, PhD, Ofer Isakov, MSc, Noam Shomron, PhD, Liat Samuelov, MD,* Natalia Malchin,
ORIGINAL STUDY Marina Eskin-Schwartz, MD, PhD,* Marianna Drozhdina, PhD, Ofer Sarig, PhD,* Andrea Gat, MD, Tomer Jackman, PhD, Ofer Isakov, MSc, Noam Shomron, PhD, Liat Samuelov, MD,* Natalia Malchin,
What s already known about this topic? What does this study add?
 CASE REPORT BJD British Journal of Dermatology Mutations in desmoglein 1 cause diverse inherited palmoplantar keratoderma phenotypes: implications for genetic screening M.-L. Lovgren, 1 M.A. McAleer, 2,3
CASE REPORT BJD British Journal of Dermatology Mutations in desmoglein 1 cause diverse inherited palmoplantar keratoderma phenotypes: implications for genetic screening M.-L. Lovgren, 1 M.A. McAleer, 2,3
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Program First World Conference on Ichthyosis August 31 September 2, 2007 Münster, Germany
 Date: August 10, 2007 Program First World Conference on Ichthyosis August 31 September 2, 2007 Münster, Germany Organized by Network for Ichthyoses and related keratinization disorders (NIRK) together
Date: August 10, 2007 Program First World Conference on Ichthyosis August 31 September 2, 2007 Münster, Germany Organized by Network for Ichthyoses and related keratinization disorders (NIRK) together
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Germline mutation analysis in the CYLD gene in Chinese patients with multiple trichoepitheliomas
 Germline mutation analysis in the CYLD gene in Chinese patients with multiple trichoepitheliomas Z.L. Li 1,2, H.H. Guan 3, X.M. Xiao 1,2, Y. Hui 3, W.X. Jia 1,2, R.X. Yu 1,2, H. Chen 1,2 and C.R. Li 1,2
Germline mutation analysis in the CYLD gene in Chinese patients with multiple trichoepitheliomas Z.L. Li 1,2, H.H. Guan 3, X.M. Xiao 1,2, Y. Hui 3, W.X. Jia 1,2, R.X. Yu 1,2, H. Chen 1,2 and C.R. Li 1,2
Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 1 Number 2 Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance A Darjani, A Ramezanpour Citation A Darjani, A Ramezanpour.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 1 Number 2 Darier's Disease: Report Of A New Case With A Rare Clinical Appearance A Darjani, A Ramezanpour Citation A Darjani, A Ramezanpour.. The Internet
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 30; 06 June 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography
 15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
15 March 2005 Use of Articles in the Pachyonychia Congenita Bibliography The articles in the PC Bibliography may be restricted by copyright laws. These have been made available to you by PC Project for
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29; 31 July 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
Chapter 3. Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons. on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs bind protein factors to
 22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
Self assesment Case 21
 17-18 MAY 2018 London Dermatopathology Symposium 2018 Self assesment Case 21 MARC HASPESLAGH CASE 21 1802-50585 48 year old lady with eczematous lesions at ear helix and red patch on nose bridge since
17-18 MAY 2018 London Dermatopathology Symposium 2018 Self assesment Case 21 MARC HASPESLAGH CASE 21 1802-50585 48 year old lady with eczematous lesions at ear helix and red patch on nose bridge since
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3.
 Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies
 Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Faculty of Medicine) in Dermatology and Venereology presented at Uppsala University in 2001
 Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Faculty of Medicine) in Dermatology and Venereology presented at Uppsala University in 2001 ABSTRACT Virtanen, M. 2001. On Keratin Mutations in Epidermolytic
Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Faculty of Medicine) in Dermatology and Venereology presented at Uppsala University in 2001 ABSTRACT Virtanen, M. 2001. On Keratin Mutations in Epidermolytic
CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
 THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD
 Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD Avčin T, Debeljak M, Markelj G, Anderluh G*, Glavnik V, Kuhar M University Children s Hospital Ljubljana and *Biotechnical Faculty,
Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD Avčin T, Debeljak M, Markelj G, Anderluh G*, Glavnik V, Kuhar M University Children s Hospital Ljubljana and *Biotechnical Faculty,
Title. Author(s)Akiyama, Masashi. CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 42(2): Issue Date Doc URL. Type.
 Title Harlequin ichthyosis and other autosomal recessive c pathomechanisms Author(s)Akiyama, Masashi CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 42(2): 83-89 Issue Date 2006-05 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/13466
Title Harlequin ichthyosis and other autosomal recessive c pathomechanisms Author(s)Akiyama, Masashi CitationJournal of Dermatological Science, 42(2): 83-89 Issue Date 2006-05 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/13466
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR
 SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
Autoimmune retinopathy associated with colonic adeno. The original publication is available at Instructions for use
 Title Autoimmune retinopathy associated with colonic adeno Author(s)Saito, Wataru; Kase, Satoru; Ohguro, Hiroshi; Ishida CitationGraefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophth Issue Date 2013-05
Title Autoimmune retinopathy associated with colonic adeno Author(s)Saito, Wataru; Kase, Satoru; Ohguro, Hiroshi; Ishida CitationGraefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophth Issue Date 2013-05
Clinical Manifestation and Classification of Japanese Patients with Inherited Keratinizing Disorders
 Original Articles Juntendo Medical Journal 2012. 58(2), 135 142 Clinical Manifestation and Classification of Japanese Patients with Inherited Keratinizing Disorders Aya k o IKEJIMA *1) Ya s u s h i SUGA
Original Articles Juntendo Medical Journal 2012. 58(2), 135 142 Clinical Manifestation and Classification of Japanese Patients with Inherited Keratinizing Disorders Aya k o IKEJIMA *1) Ya s u s h i SUGA
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Visualization of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interaction by in situ proximity ligation assay. A) Illustration of targeted proteins in mitochondria (M), endoplasmic reticulum
Supplementary Figure 1. Visualization of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interaction by in situ proximity ligation assay. A) Illustration of targeted proteins in mitochondria (M), endoplasmic reticulum
Porokeratosis: Introduction
 Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
Porokeratosis: Introduction Benign epidermal proliferation Distinct clinical & histologic features 5 clinical subtypes Erroneously named porokeratosis CLINICAL SUBTYPES 1. Porokeratosis of Mibelli 2. Disseminated
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections
 Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Keratin disorders: from gene to therapy
 HMG Advance Access published September 10, 2011 Human Molecular Genetics, 2011 doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr379 R1 R9 Keratin disorders: from gene to therapy W.H. Irwin McLean 1, and C.B. Tara Moore 1,2 1 Division
HMG Advance Access published September 10, 2011 Human Molecular Genetics, 2011 doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr379 R1 R9 Keratin disorders: from gene to therapy W.H. Irwin McLean 1, and C.B. Tara Moore 1,2 1 Division
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers).
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
 Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: EPHB2 germline variants in patients with colorectal cancer or hyperplastic polyposis Authors: Antti Kokko (antti.kokko@helsinki.fi) Paivi Laiho (paivi.laiho@helsinki.fi)
Author's response to reviews Title: EPHB2 germline variants in patients with colorectal cancer or hyperplastic polyposis Authors: Antti Kokko (antti.kokko@helsinki.fi) Paivi Laiho (paivi.laiho@helsinki.fi)
RNA based high-resolution HLA sequencing based typing
 Chapter 2 RNA based high-resolution HLA sequencing based typing Judith Reinders, Anna Houben, Alain van Mill, Erik Rozemuller, Jan van den Tweel and Marcel Tilanus Department of Pathology, University Medical
Chapter 2 RNA based high-resolution HLA sequencing based typing Judith Reinders, Anna Houben, Alain van Mill, Erik Rozemuller, Jan van den Tweel and Marcel Tilanus Department of Pathology, University Medical
Product Datasheet. HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB Unit Size: 0.25 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22
 Product Datasheet HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB100-64775 Unit Size: 0.25 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research
Product Datasheet HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB100-64775 Unit Size: 0.25 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Progressive Symmetric Erythrokeratodermia
 * * Progressive Symmetric Erythrokeratodermia A Case Report Shu-Feng Kan Chung-Hong Hu Woan-Ruoh Lee* Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia (PSEK) is a rare disorder of cornification characterized
* * Progressive Symmetric Erythrokeratodermia A Case Report Shu-Feng Kan Chung-Hong Hu Woan-Ruoh Lee* Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia (PSEK) is a rare disorder of cornification characterized
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study
 Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study Investigators: Department of Dermatology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study Investigators: Department of Dermatology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
ANALYSIS OF IL17 AND IL17RA POLYMORPHISMS IN SPANISH PSORIASIS PATIENTS: ASSOCIATION WITH RISK FOR DISEASE.
 ANALYSIS OF IL17 AND IL17RA POLYMORPHISMS IN SPANISH PSORIASIS PATIENTS: ASSOCIATION WITH RISK FOR DISEASE. Batalla A, Coto E*, González-Lara L, González- Fernández D, Maldonado-Seral C, García-García
ANALYSIS OF IL17 AND IL17RA POLYMORPHISMS IN SPANISH PSORIASIS PATIENTS: ASSOCIATION WITH RISK FOR DISEASE. Batalla A, Coto E*, González-Lara L, González- Fernández D, Maldonado-Seral C, García-García
6/12/2018. Disclosures. Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective. Outline. COH HopeSeq Heme Panels
 Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma
 Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Introduction to genetic variation. He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016
 Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
Introduction to genetic variation He Zhang Bioinformatics Core Facility 6/22/2016 Outline Basic concepts of genetic variation Genetic variation in human populations Variation and genetic disorders Databases
