If a Specials product is required Dermatologists in Fife have agreed to use only BAD approved Specials whenever possible.
|
|
|
- Julius Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 13 Skin Vehicles Both vehicle and active ingredients are important in the treatment of skin conditions. The vehicle affects the degree of hydration of the skin, has a mild anti-inflammatory effect, and aids the penetration of active drug. Creams are generally more cosmetically acceptable than ointments because they are less greasy and easier to apply. Gels are particularly suitable for application to the face and scalp. Lotions have a cooling effect and may be preferred for application over a hairy area. Lotions in alcoholic basis can sting if used on broken skin. Ointments are greasy preparations and are more occlusive than creams. They are particularly suitable for chronic, dry lesions. Pastes can be used to protect inflamed, lichenified, or excoriated skin. Unlicensed / Special Manufacture Preparations The British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) list of preferred unlicensed dermatological preparations ( Specials ) is available at Specially manufactured products can often be very expensive (often in excess of 100 per item). They should only be used when a suitable proprietary product is unavailable. If a Specials product is required Dermatologists in Fife have agreed to use only BAD approved Specials whenever possible Emollients Soap Substitutes (all choices below are fragrance free) 1st Choice Hydromol Ointment 2nd Choice Doublebase Emollient Wash Gel QV Gentle Wash R- Cetomacrogol Preparations containing Dermol Wash antimicrobials/antiseptics Soap substitutes can be used for hand washing and in the bath. The choice of emollient should be based on the severity of the condition, patient preference, site of application and preparation cost. Aqueous cream is no longer recommended as a soap substitute or emollient as it contains sodium lauryl sulphate which may damage the skin barrier. Fragrance free emollients are preferable in the management of eczema. R - Cetomacrogol may be used as soap substitute/leave on emollient in patients with genital dermatoses.
2 2 Preparations containing antimicrobials or antiseptics should only be used be used when treating patients with infected eczema or when antisepsis is required. Emollient Bath Additives (all choices below are fragrance free) 1st Choice 2nd Choice Preparations containing antimicrobials/antiseptics Hydromol Bath and Shower Emollient QV Bath Oil Oilatum Junior Dermol 600 Shower Preparations (all choices below are fragrance free) 1st Choice Hydromol Bath and Shower Emollient 2nd Choice Doublebase Emollient Shower Gel Oilatum Shower Emollient Gel Preparations containing Dermol 200 Shower Emollient antimicrobials/antiseptics Fragrance free emollients are preferable in the management of eczema. Preparations containing antimicrobials or antiseptics should only be used be used when treating patients with infected eczema or when antisepsis is required. Medium Weight Emollients preferable for use during the daytime 1st Choice Oilatum Cream QV Cream, Lotion 2nd Choice Aveeno Cream (ACBS) Cetraben Cream Doublebase Gel Doublebase Dayleve Gel E45 Cream R- Dermamist spray Heavy Weight Emollients - useful at night time or when using occlusive dressings 1st Choice Hydromol Ointment Hydrous Ointment Liquid Paraffin 50% and White Soft Paraffin 2nd Choice 50% Ointment QV Intensive Ointment White Soft Paraffin Yellow Soft Paraffin
3 3 Emollients soothe, smooth and hydrate the skin and are indicated for all dry or scaling disorders. They should be applied frequently (at least 3-4 times per day) even after improvement occurs. The choice of emollient should be based on the severity of the condition, patient preference, site of application and preparation cost. Aqueous cream is no longer recommended as a soap substitute or emollient as it contains sodium lauryl sulphate which may damage the skin barrier. Products that come in pump dispensers may be more suitable for long term use in order to reduce the risk of microbial contamination. Emollients should be applied in the direction of hair growth. Aveeno Cream should only be prescribed in line with ACBS recommendations (see BNF). R Dermamist Spray - Spray formulations of emollients are more expensive than creams / ointments but may be useful in patients unable to apply other formulations. Patients should be informed of the potential fire hazard when using paraffin based (See BNF). Preparations containing Urea Balneum Plus Cream (urea 5% + lauromacrogols 3%) Hydromol Intensive Cream (urea 10%) Dermatonics Once Heel Balm (urea 25%) Preparations containing urea are suitable for the treatment of dry, scaling conditions (including ichthyosis) Barrier preparations Dimeticone preparations 1st Choice Conotrane 2nd Choice Metanium Zinc preparations Sudocrem Zinc and castor oil ointment Nappy rash may clear if skin is left exposed to air. If fungal infection present then an antifungal preparation should be used Topical local anaesthetic and antipruritic preparations Crotamiton +/- hydrocortisone cream (Eurax, Eurax-HC ) Crotamiton lotion (Eurax )
4 4 Doxepin 5% cream (Xepin ) Further information on managing pruritus can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. Pruritus may be caused by systemic disease, skin disease or as a side-effect of medication. Where possible the underlying cause should be identified and treated. An emollient may be of value where the pruritus is associated with dry skin. Topical antihistamines and local anaesthetics are not recommended as they are only marginally effective and can cause sensitisation. Sedating oral antihistamines may be helpful in alleviating itch (see section ) Topical Corticosteroids For appropriate quantities of steroids to be prescribed for specific areas of the body see BNF. Topical corticosteroids are classified according to their potency: Mildly potent Moderately potent Potent Very Potent Hydrocortisone 1% Fluocinolone acetonide % (Synalar 1 in 10 ) Betamethasone (as valerate) 0.025% (Betnovate-RD ) Clobetasone butyrate 0.05% (Eumovate ) Fluocinolone acetonide % (Synalar 1 in 4 ) Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% (Diprosone ) Betamethasone valerate 0.1% Betamethasone diproprionate 0.05% + Salicylic acid 3% (Diprosalic ) Fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% (Synalar ) Hydrocortisone butyrate 0.1% (Locoid ) Mometasone furoate 0.1% Clobetasol propionate 0.05% (Dermovate ) R- Diflucortolone vaerate 0.3% (Nerisone Forte )
5 5 The choice of steroid will depend on the nature of the inflammatory condition being treated, the age of the patient and the site of application. In order to minimise the side-effects of a topical corticosteroid, it is important to apply once or twice daily to the affected areas only. Use the least potent formulation which is fully effective for the shortest duration of treatment. There is no benefit in increasing the strength of hydrocortisone. Instead, patients should be moved up the steroid potency ladder i.e. to a moderately potent steroid. The potency of the steroid should be stepped up or stepped down depending on the severity of symptoms. Potent corticosteroids should generally be avoided on the face and skin flexures. In general, the most potent topical corticosteroids should be reserved for recalcitrant dermatoses such as chronic discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen simplex chronicus, hypertrophic lichen planus, and palmoplantar pustulosis. Topical use of potent corticosteroids on widespread psoriasis can lead to systemic as well as to local side-effects. It is reasonable, however, to prescribe a mild to moderate topical corticosteroid for a short period (2 4 weeks) for flexural and facial psoriasis and to use a more potent corticosteroid such as betamethasone for psoriasis of the scalp, palms, or soles. Potent topical corticosteroids should be avoided or used only under specialist supervision in psoriasis because, although they may suppress the psoriasis in the short term, relapse or vigorous rebound occurs on withdrawal. Patients prescribed very potent topical corticosteroids should be reviewed regularly (at least monthly) and the preparation should not be prescribed on repeat prescription except on specialist advice. R Nerisone Forte is approved for restricted use in the management of genital dermatosis. Specialist initiation. Choice of formulation Water-miscible corticosteroid creams are suitable for moist areas e.g. axillae or groin or for weeping lesions. Ointments are generally chosen for dry, lichenified or scaly lesions or where a more occlusive effect is required. Gels / Lotions may be useful when minimal application to a large or hair-bearing area is required or for the treatment of exudative lesions. The inclusion of urea or salicylic acid increases the penetration of the corticosteroid. Mixing topical preparations (e.g. steroid, emollient) on the skin should be avoided where possible; several minutes should elapse between application of different preparations. Topical Corticosteroids with Antimicrobials/Antifungals Mildly potent Canesten HC
6 6 (hydrocortisone 1% + Clotrimazole 1%) Daktacort (hydrocortisone 1% + miconazole 2%) Fucidin H (hydrocortisone 1% + Fusidic acid 2%) Terra-Cortril (hydrocortisone 1% + oxytetracycline 3%) Timodine (hydrocortisone 0.5% + nystatin units/g +benzalkonium chloride + dimeticone) Trimovate Moderately Potent (clobetasone 0.05% + oxytetracycline 3% + nystatin units/g) Potent Betamethasone 0.1% and clioquinol 3% FuciBet (betametasone valerate 0.1% + fusidic acid 2%) Synalar C (fluocinolone 0.025% + clioquinol 3%) Very Potent Clobetasol with neomycin and nysytatin The advantages of including antibacterials or antifungals with corticosteroids in topical preparations are uncertain, but such combinations may have a place where inflammatory skin conditions are associated with bacterial or fungal infection, such as infected eczema. Long term use of products containing antibacterials and antifungals increases the likelihood of resistance and sensitisation. Normally products should be used on a regular basis but for a short period only, usually 7 days. Terra Cortril contains oxytetracycline and is therefore contraindicated for use in children aged under 12 years Preparations for Psoriasis and Eczema Preparations for eczema Also see SIGN 125 Management of Atopic Eczema in Primary Care (March 2011) Emollients see section Topical corticosteroids see section 13.4 Ichthammol preparations (for chronic lichenified eczema) - Systemic drugs Methotrexate, Ciclosporin, Azathioprine (off label use) H - Alitretinoin (Toctino )
7 7 Further information on managing atopic eczema can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. The use of emollients should continue even if the eczema improves or if other treatment is being used. Bandages (including those containing zinc and ichthammol) are sometimes applied over topical corticosteroids or emollients to treat eczema of the limbs. Bacterial infection (commonly with Staphylococcus aureus) can exacerbate eczema and may require treatment with topical or systemic antibacterial drugs. See section and NHS Fife Guidance on Management of Common Infections Antihistamines (see section 3.4.1) may be helpful short-term for the management of itch. In severe refractory eczema, systemic immunosupressants e.g. methotrexate, ciclosporin, azathioprine may be prescribed after specialist initiation. Alitretinoin is accepted for use in adults with severe hand eczema unresponsive to treatment with potent topical corticosteroids. It should be prescribed only by, or under the supervision of, a consultant dermatologist and be dispensed by a hospital-based pharmacy. Topical immunomodulator preparations - Pimecrolimus 1% Cream (Elidel ) - Tacrolimus 0.03%, 0.1% ointment (Protopic ) Topical pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are options for atopic dermatitis not controlled by maximal topical corticosteroid treatment or if there is a risk of important corticosteroid side-effects (particularly skin atrophy). They can cause a transient sensation of warmth or burning. Pimecrolimus is recommended for moderate atopic eczema on the face and neck of children aged 2 16 years. Tacrolimus is recommended for moderate to severe atopic eczema in adults and children over 2 years. The 0.03% strength should be used in children aged 2-16 years. The 0.1% strength in those over 16 years of age. Tacrolimus ointment may be used twice weekly for the maintenance treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients experiencing a high frequency of disease exacerbations (i.e. occurring 4 or more times per year) who have had an initial response to a maximum of 6 weeks treatment of twice daily tacrolimus ointment (lesions cleared, almost cleared or mildly affected).
8 Preparations for Psoriasis Also see SIGN 121 Diagnosis and Management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Adults (Oct. 2010) Also see British Association of Dermatologists Guidelines for Biologic Interventions for Psoriasis 2009 Topical preparations Coal tar based preparations Dithranol Emollients see section Topical corticosteroids see section 13.4 Carbo-Dome (coal tar solution 10%) Exorex lotion (coal tar 1%) Psoriderm cream (coal tar 6%) Further information on managing psoriasis can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. Emollients are useful in softening scaling and reducing irritation in inflammatory / plaque psoriasis. It may be appropriate to treat psoriasis in specific sites, such as the face and flexures, usually with a mild corticosteroid, and psoriasis of the scalp, palms, and soles with a potent corticosteroid. Potent topical corticosteroids should be avoided or used only under specialist supervision in psoriasis because, although they may suppress the psoriasis in the short term, relapse or vigorous rebound occurs on withdrawal. Dithranol (Micanol, Dithrocream ) Dithranol is effective for chronic plaque psoriasis. Its major disadvantages are irritation (for which individual susceptibility varies) and staining of skin and of clothing. Dithranol should be applied to chronic extensor plaques only, carefully avoiding normal skin. Dithranol is not generally suitable for widespread small lesions nor should it be used in the flexures or on the face. Treatment should be started with a low concentration such as dithranol 0.1%, and the strength increased gradually every few days up to 3%, according to tolerance. Preparations are usually washed off after 30 to 60 minutes ( short contact ).
9 9 Vitamin D analogues Vitamin D analogue + steroid 1st Choice Calcipotriol ointment 2nd Choice Tacalcitol (Curatoderm ) ointment or lotion Calcitriol (Silkis ) Dovobet ointment or gel (calcipotriol 50mcg/g and betamethasone 0.05%) Vitamin D analogues are used as first-line treatment for plaque psoriasis; they do not smell or stain and they may be more acceptable than tar or dithranol products. Tacalcitol is less likely to irritate. Local skin reactions (itching, erythema, burning, paraesthesia, dermatitis) are common. Hands should be washed thoroughly after application to avoid inadvertent transfer to other body areas. Aggravation of psoriasis has also been reported. Dovobet contains betamethasone (a potent steroid). It should not be used on the face or flexures. Dovobet can be used once daily with a maximum 15g daily or 100g weekly. The recommended treatment period is 4 weeks. Treatment should only be continued beyond 4 weeks or repeated if recommended by a specialist. The use of Dovobet may lead to rebound exacerbation of the psoriasis when treatment is discontinued. When different preparations containing calcipotriol are used e.g. cream and scalp solution, the total maximum weekly dose should not be exceeded e.g. 60g cream or ointment with 30ml of scalp solution or 60ml of scalp solution with 30g of cream or ointment. Tacalcitol is of use for face and flexures. It should be used once daily with a maximum of 10g per day. Scalp Psoriasis Vitamin D analogues Calcipotriol scalp solution Vitamin D analogue + steroid Dovobet gel (calcipotriol 50mcg/g and betamethasone 0.05%) Topical Corticosteroid Preparations Potent Betamethasone valerate 0.1% lotion (Betacap, alcohol based) Betamethasone valerate 0.1% foam (Bettamousse, alcohol Based)
10 10 Very Potent Coal Tar preparations Shampoos "Leave on" products Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%, salicylic acid 2% scalp application (Diprosalic, alcohol based) Hydrocortisone butyrate 0.1% liquid emulsion (Locoid Crelo, aqueous based) Fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% gel (Synalar Gel ) Clobetasol propionate 0.05% scalp application (Dermovate ) Clobetasol propionate 0.05% foam (Clarelux ), shampoo (Etrivex ) Alphosyl 2 in 1 shampoo (coal tar extract 5%) Capasal (coal tar 1%, coconut oil 1%, salicylic acid 0.5%) T/Gel (coal tar extract 2%) Mild scalp psoriasis should be treated with a tar based shampoo. Sebco (Coal tar solution 12 %, salicylic acid 2%, sulphur 4% in a coconut oil base) For moderate scalp psoriasis or for itchy scalps a steroid scalp application can be used shortterm. Normally applied in the morning. Mousse/foam formulations of steroids can be used in patients with sensitive skin or where there is local scalp irritation. Calcipotriol scalp application can provide a safe maintenance treatment when long-term therapy is required. Scalp psoriasis is usually scaly, and the scale may be thick and adherent. This requires softening with an ointment, cream, or oil and usually combined with salicylic acid as a keratolytic. Salicyclic acid preparations may be useful where there is a marked scaling of the skin or scalp. Sebco should be left on for at least an hour, often more conveniently overnight, before washing it off. Oral retinoids for psoriasis H - Acitretin (Neotigason )
11 11 Acitretin is teratogenic and must not be given to women of child-bearing age unless they practice effective contraception. Women must also be registered with a pregnancy prevention programme Drugs affecting immune response Also see Appendix 10B Guidance on the Safe Use Of Oral Methotrexate In Non- Malignant Conditions Also see British Association of Dermatologists Guidelines for Biologic Interventions for Psoriasis 2009 Systemic Drugs 1st Choice 2nd Choice Methotrexate 2.5mg tablets H Ciclosporin (Capimune ) ) H Apremilast (Otezla ) 3rd Choice H Adalimumab (Humira ) H Etanercept (Enbrel ) H Infliximab (Remicade ) H Secukinumab (Cosentyx ) H Ustekinumab (Stelara ) Methotrexate can be used for severe psoriasis. The usual dose is methotrexate 10 to 25 mg once weekly. To avoid prescribing, dispensing and administration errors only the 2.5mg strength of methotrexate should be prescribed and dispensed. The patient should be advised on the dose and frequency for taking methotrexate. The patient should be advised to report immediately any signs of methotrexate toxicity. Regular monitoring of full blood count, renal function and liver function should be undertaken in line with local protocols. Ciclosporin preparations should be prescribed by brand name only due to differences in bioavailability. The formulary choice for ciclosporin is Capimune (10mg capsules and liquid formulation must be prescribed as Neoral ). Patients on ciclosporin should be regularly monitored for adverse effects including hypertension and renal impairment. Apremilast is approved for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis when other systemic treatments e.g. methotrexate, ciclosporin, PUVA have failed or are unsuitable, prior to the use of biologics.
12 12 Adalimumab is recommended for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis in adults which has failed to respond to standard systemic treatments (including ciclosporin and methotrexate) or to PUVA therapy, or when standard treatments cannot be used because of intolerance or contraindications. Its use should be restricted to severe disease (PASI score > or equal to 10 and a DLQI score of >10). Adalimumab should be withdrawn if the response is not adequate after 16 weeks (PASI 75 response from baseline). Etanercept is recommended for the treatment of severe plaque psoriasis which has failed to respond to standard systemic treatments (including ciclosporin and methotrexate) or to PUVA therapy, or when standard treatments cannot be used because of intolerance or contraindications. Etanercept should be withdrawn if the response is not adequate after 12 weeks. Infliximab is recommended for the treatment of severe plaque psoriasis in adults which has failed to respond to standard systemic treatments (including ciclosporin and methotrexate) or to PUVA therapy, or when standard treatments cannot be used because of intolerance or contraindications. Infliximab should be withdrawn if the response is not adequate after 10 weeks (PASI 75 response from baseline or a 50% reduction and a 5 point reduction in DLQI from baseline). Secukinumab has a different mode of action to other biologics, approved for use in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis when other biologics are ineffective or considered unsuitable. Ustekinumab is approved as a 3 rd choice treatment option for the treatment of severe plaque psoriasis (for treatment of psoriatic arthritis see section ) Acne and Rosacea Mild to moderate papulopustular rosacea prescribe a topical agent 1st Choice Metronidazole 0.75% cream or gel (Rozex ) 2nd Choice Azelaic Acid 15% gel (Finacea ) Moderate to severe papulopustular rosacea prescribe an oral agent 1st Choice Oxytetracycline or Tetracycline 2nd Choice Erythromycin Doxycycline (off label use) Lymecycline (off label use) Moderate to severe facial erythema predominant rosacea Brimonidine 0.3% gel (Mirvaso ) Acne Further information on managing rosacea can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. The pustules and papules of rosacea respond to topical metronidazole or to topical azelaic acid. Courses of oral antibiotics usually last for 12 weeks and are repeated intermittently. Brimonidine gel should only be used in patients with moderate severe erythema predominant rosacea. Patients should be reviewed after 1 month to determine benefits of ongoing treatment.
13 13 General Points The choice of treatment depends on whether the acne is predominantly inflammatory or comedonal and its severity. Acne can be broadly classified as mild, moderate and severe. Mild to moderate acne is generally treated with topical preparations. Systemic treatment with oral antibacterials is generally used for moderate to severe acne or where topical preparations are not tolerated or are ineffective or where application to the site is difficult Topical preparations for acne 1st Choice Benzoyl Peroxide 2.5% - 10% 2nd Choice Azelaic acid 20% cream (Skinoren ) Further information on managing acne can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. In mild to moderate acne, comedones and inflamed lesions respond well to benzoyl peroxide. The lower concentrations seem to be as effective as higher concentrations in reducing inflammation. It is usual to start with a lower strength and to increase the concentration of benzoyl peroxide gradually. Adverse effects include local skin irritation, particularly when therapy is initiated, but the scaling and redness often subside with treatment continued at a reduced frequency of application. If the acne does not respond after 2 months then use of a topical antibacterial should be considered. Azelaic acid has antimicrobial and anticomedonal properties. It can be used as an alternative to benzoyl peroxide for treating mild to moderate comedonal acne, particularly of the face. Some patients prefer azelaic acid because it is less likely to cause local irritation than benzoyl peroxide. Topical antibacterials for acne Clindamycin 1% (gel, lotion or solution) Duac (clindamycin 1% + benzoyl peroxide 5%) Zineryt (erythromycin 40mg + zinc acetate 12mg/ml) Topical antibacterials are effective in inflammatory acne and are probably best reserved for patients who wish to avoid oral antibacterials or who cannot tolerate them. Topical antibacterials are as effective as oral antibiotics but encourage resistance and are more expensive. Clindamycin solution (alcohol base) should be replaced with clindamycin lotion (aqueous base) or
14 14 clindamycin gel if skin irritation or drying out develops with the solution. Erythromycin topical solution on its own is not recommended due to antibiotic resistance. Duac Gel may be considered if benzoyl peroxide on its own is ineffective. Treclin may be considered in patients where monotherapy with clindamycin or tretinoin has been ineffective. Alcohol based antibacterials can produce mild irritation of the skin. Topical retinoids and related preparations for acne Combination Products Useful for treating comedones and inflammatory lesions in mild to moderate acne. Patients should be warned that some redness and skin peeling may occur initially but settles with time. Exposure to sunlight of areas treated with retinoids should be avoided or minimised. Topical retinoids are best applied at night. Several months of treatment may be needed to achieve an optimal response and the treatment should be continued until no new lesions develop. Adapalene is less irritant than other topical retinoids. Topical retinoids should be avoided in severe acne involving large areas. Topical retinoids are contra-indicated in pregnancy; women of child bearing age must use effective contraception (oral progestogen-only contraceptives are not considered effective in this scenario). Combination products are approved for use in patients with mild to moderate facial acne when monotherapy has been ineffective Oral preparations for acne 1st Choice Lymecycline 2nd Choice Doxycycline Erythromycin Oxytetracycline Systemic antibacterial treatment is useful for inflammatory acne if topical treatment is not adequately effective or if it is inappropriate. Anticomedonal treatment (e.g. with topical benzoyl Adapalene (Differin ) Isotretinoin gel Aknemycin Plus (tretinoin 0.025% + erythromycin 4%) Epiduo (adapalene 0.1% +benzoyl peroxide 2.5%) Treclin (tretinoin 0.025% + clindamycin 1%)
15 15 peroxide) may also be required. Oxytetracycline is usually given at a dose of 500 mg twice daily. Maximum improvement usually occurs after 4 to 6 months but in more severe cases treatment may need to be continued for 2 years or longer. Erythromycin at a dose of 500 mg twice daily is suitable for those under 12 or in pregnant women. Oral antibiotics may require up to 6 months of compliant use to achieve maximum benefit. Switch to an alternative antibiotic if no response after 6 months. Hormone Treatment for Acne Co-cyprindiol 2000/35 Co-cyprindiol (cyproterone acetate with ethinylestradiol) is no more effective than an oral broadspectrum antibacterial but is useful in women who also wish to also receive oral contraception. Co-cyprindiol should be stopped 3-4 months after the acne has completely resolved. Courses may be repeated if there is a recurrence of the acne. Co-cyprindiol is licensed for women with severe acne which has not responded to oral antibacterials and should not be used solely for contraception due to a higher risk of venous thromboembolism than low-dose combined oral contraceptives. The risk of VTE is rare but this remains an important side effect. Healthcare professionals should be vigilant for signs of DVT or PE in patients prescribed co-cyprindiol. Oral Retinoid for Acne Also see British Association of Dermatology Advice on the safe introduction and continued use of isotretinoin in acne in the U.K Isotretinoin is used in severe acne, acne unresponsive to prolonged courses of oral antibacterials, scarring, or acne associated with psychological problems. Isotretinoin is a toxic drug that should be prescribed only by, or under the supervision of, a consultant dermatologist. It is given for at least 16 weeks; repeat courses are not normally required. The drug is teratogenic and must not be given to women of child-bearing age unless they practice effective contraception. Women must also be registered with a pregnancy prevention programme Warts and calluses H Isotretinoin Occlusal (salicylic acid 26%) Salactol (salicylic acid 16.7% +lactic acid 16.7%) Verrugon (salicylic acid 50%)
16 16 Further information on the management of warts can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. Warts may regress on their own and treatment is required only if the warts are painful, unsightly, persistent, or cause distress. Wart removing preparations are keratolytic. They can cause irritation and application to normal or broken skin should be avoided. Surrounding skin to the wart can be protected by applying soft paraffin. Anogenital warts Podophyllotoxin 0.15% cream (Warticon ) 1st Choice or 0.5% solution Cryotherapy 2nd Choice S - Imiquimod 5% cream (Aldara ) Podophyllotoxin and cryotherapy are appropriate first line therapies in most instances. Patients with a limited number of external warts or keratinised lesions may be better treated with cryotherapy rather than using podophyllotoxin. Podophyllotoxin cream is recommended for use by women and the solution for use by men. Surrounding skin should be protected when treating anogenital warts. Treatment of warts should also be accompanied by screening for other sexually transmitted infections and counselling on various sexual health issues. Consider referral to GU Medicine when there are extensive warts, perianal warts, keratinised warts, recalcitrant warts and if warts are in immunocompromised/hiv patients, in men who have sex with men or pregnant patients. Imiquimod is relatively expensive and should be used only when other treatments have failed. Podophyllotoxin and imiquimod should not be used during pregnancy. Imiquimod is the only drug licensed for perianal warts. Imiquimod 3.75% cream (Zyclara ) is not approved for use by the SMC due to a nonsubmission. Requires submission and approval of an Individual Patient Treatment Request (IPTR) before prescribing Sunscreens and Camouflagers Sunscreen Preparations (ACBS) Sunsense Ultra lotion (UVB-SPF50+) Uvistat cream (UVB-SPF50) Sunscreen preparations may rarely cause allergic reactions.
17 17 For optimum photoprotection, sunscreen preparations should be applied thickly. Preparations with SPF less than 30 should not normally be prescribed. Sunscreen preparations should only be prescribed in line with ACBS recommendations. See BNF. Photodamage Lesional Small Field Large Field Actikerall (Fluorouracil 0.5%, salicylic acid 10% solution) Cryotherapy 1 st Choice Solaraze (Diclofenac 3% gel) 2 nd Choice Fluorouracil 5% cream (Efudix ) Ingenol mebutate gel (Picato ) 3 rd Choice S - Imiquimod 5% cream ( Aldara ) Solaraze (Diclofenac 3% gel) Fluorouracil 5% cream (Efudix ) Further information on managing actinic keratosis can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices. Actinic keratosis are pre-malignant but transformation to squamous cell carcinoma is rare. Patients must be referred if diagnosis is uncertain or if lesions become thickened or tender. Skin inflammation is common with topical fluorouracil and the concomitant use of a moderate/potent topical corticosteroid can be used. Fluorouracil 0.5% / salicylic acid 10% cutaneous solution (Actikerall ) can be used in immunocompetent patients with slightly palpable and/or moderately thick hyperkeratotic actinic keratosis (grade I/II). For use in patients with <10 isolated lesions of actinic keratoses where cryotherapy is unsuitable. Care should be taken when prescribing diclofenac gel. Only the 3% strength (Solaraze ) is licensed for use in actinic keratosis. Ingenol mebutate may improve adherence as it is only applied for 2-3 days. Local skin reactions peak at day 4 and tend to resolve by day 14. Imiquimod 5% cream (Aldara ) can be used on specialist advice based on the size or number of lesions Camouflagers (ACBS)
18 18 Should only be prescribed in line with ACBS recommendations. See BNF Shampoos and other preparations for scalp and hair conditions Shampoos Benzalkonium chloride 0.5% (Dermax ) Ketoconazole Selenium sulphide (Selsun ) Tar preparations Alphosyl 2 in 1 shampoo (coal tar extract 5%) Capasal (coal tar 1%, coconut oil 1%, salicylic acid 0.5%) T/Gel (coal tar extract 2%) Other Scalp preparations Sebco (Coal tar solution 12 %, salicylic acid 2%, sulphur 4% in a coconut oil base) Ketoconazole shampoo should be considered for persistent or severe dandruff or for seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp. Shampoo formulations are preferred for moderate scaly scalp conditions whereas more severe conditions require the use of an ointment. Hirsutism Dermacolor Veil 1st Choice Co-cyprindiol 2000/35 2nd Choice Eflornithine (Vaniqa ) Co-cyprindiol may be effective for moderately severe hirsutism. Treatment is required for 6 12 months before benefit is seen. Co-cyprindiol should be stopped 3-4 months after the hirsutism has completely resolved. Courses may be repeated if there is a recurrence. For further information on the safe prescribing of co-cyprindiol see section Eflornithine is relatively expensive and should only be used when co-cyprindiol can not be used. It should be discontinued if there is no improvement after 4 months of treatment Anti-infective skin preparations Antibacterial preparations Fusidic acid
19 19 Hydrogen peroxide cream (Crystacide ) Metronidazole R- Mupirocin (Bactroban ) Silver sulfadiazine (Flamazine ) Topical antibiotics should only be used for localised skin infections and for a short duration to minimise the risk of bacterial resistance. Hydrogen peroxide cream (Crystacide ) may be used as an alternative agent to topical antibiotics. Hydrogen peroxide cream may also be used in the management of molluscum contagiosom. Further information on managing molluscum contagiosom can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. In the community, for acute impetigo systematic review indicates topical and oral treatment produce similar results. As resistance is increasing topical antibiotics should be reserved for very localised lesions. Small areas of the skin may be treated by short-term topical application of fusidic acid three to four times daily for 5 days. Mupirocin should be used only to treat Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA). To avoid the development of resistance, topical mupirocin or fusidic acid should not be used for longer than 7 days and local microbiology advice should be sought before using in hospital. If the impetigo is extensive or longstanding, an oral antibacterial such as flucloxacillin (or erythromycin in penicillin-allergy) should be used. Topical antibacterials should be avoided on leg ulcers unless used in short courses for defined infections; treatment of bacterial colonisation is generally inappropriate. Silver sulfadiazine is used in the treatment of infected burns Antifungal Preparations Amorolfine Clotrimazole Miconazole Nystatin Terbinafine Tioconazole 3% Combination products with corticosteroids see section 13.4 Further information on managing fungal nail infections can be found at Dermatology Referral and Management Pathways. Medicines prescribed should be in line with Fife Formulary choices.
20 20 Most localised fungal infections are treated with topical preparations. To prevent relapse, local antifungal treatment should be continued after the disappearance of all signs of infection. See individual products for treatment duration. Topical application of amorolfine or tioconazole may be useful for treating early onychomycosis when involvement is limited to mild distal disease in up to 2 nails, or for superficial white onychomycosis, or where there are contra-indications to systemic therapy. More extensive nail infections require oral treatment (see section 5.2). Skin scrapings should be examined if systemic therapy is being considered or where there is doubt about the diagnosis. Combination of an imidazole antifungal and a mild corticosteroid (see section 13.4) may be of value in the treatment of eczematous intertrigo and, in the first few days only, of a severely inflamed patch of ringworm. Combination of a mild corticosteroid with either an imidazole or nystatin may be of use in the treatment of intertrigo associated with candida (see section 13.4) Antiviral preparations Aciclovir cream can be used for the treatment of initial and recurrent labial herpes simplex infections (cold sores). It is best applied at the earliest possible stage, usually when prodromal changes of sensation are felt in the lip and before vesicles appear Parasiticidal preparations Head lice "Bug busting Kit" Dimeticone 4% lotion (Hedrin ) Malathion 0.5% aqueous liquid (Derbac-M ) Scabies 1st Choice Permethrin 5% cream 2nd Choice Malathion 0.5% aqueous liquid (Derbac-M ) Crab (Pubic) lice Malathion 0.5% aqueous liquid (Derbac-M ) Permethrin 5% cream Dimeticone coats head lice and interferes with water balance in lice by preventing the excretion of water; it is less active against eggs. Head lice can not become resistant to dimeticone due to its mode of action. Aciclovir cream
21 21 Head Lice Scabies Malathion is recommended for scabies, head lice and crab lice. Permethrin is effective for scabies and crab lice but permethrin crème rinse is unsuitable for treatment of head lice. Head lice must be seen before any insecticidal treatments are used. Nits (empty egg shells) do not constitute an infection. Treat only if head lice are found. There is no need to treat members of the family or close contacts that do not have head lice. The policy of rotating insecticides on a Fife-wide basis is now considered outmoded. To overcome the development of resistance, a mosaic strategy is required whereby, if a course of treatment fails to cure, a different insecticide is used for the next course. A Bug Busting Kit can be recommended / prescribed as an alternative to insecticides for the detection and treatment of head lice. Only one kit is required per family and it is reusable. Aqueous formulations (liquids) are preferred. Shampoos or mousses should not be used as they are diluted too much in use and have a limited contact time to be effective. A contact time of 12 hours or overnight treatment is recommended to ensure eggs are killed. In general, a course of treatment for head lice should be 2 applications of product 7 days apart to prevent lice emerging from any eggs that survive the first application. No more than 3 applications of insecticidal preparations per infection are recommended. Applied no more frequently than once per week. Wet combing can be used to mechanically remove head lice by combing wet hair meticulously with a detection comb (probably for at least 30 minutes each time) over the whole scalp at 3- day intervals for a minimum of 3 weeks; hair conditioner can be used to facilitate the process. All members of the affected household and close contacts should be treated simultaneously, even if symptom free. Permethrin 5% dermal cream is the recommended 1 st line treatment of scabies; malathion 0.5% aqueous liquid can be used if permethrin is inappropriate. Treatment should be applied to the whole body including the scalp, neck, face, and ears. Particular attention should be paid to the webs of the fingers and toes and lotion brushed under the ends of nails. Treatment should be left on the skin for 8-12 hours with permethrin and for 24 hours with malathion, before washing off. Malathion and permethrin should be applied on two occasions for treatment at least one week apart. It is important to warn users to reapply treatment to the hands if they are washed. The itch and eczema of scabies can persist for 4-6 weeks after the infestation has been eliminated and treatment for pruritus and eczema may be required. Crotamiton (see section 11.3), a topical corticosteroid (see section 11.4) or a sedating antihistamine (see section 3.4) at
22 22 Crab (Pubic) Lice night may be of benefit. Permethrin and malathion are used to eliminate crab lice. Preparation should be applied, allowed to dry naturally and washed off after 12 hours; a second treatment is needed after 7 days to kill lice emerging from surviving eggs. All surfaces of the body should be treated, including the scalp, neck, and face (paying particular attention to the eyebrows and other facial hair). A different insecticide should be used if a course of treatment fails Preparations for Minor Cuts and Abrasions Magnesium Sulfate Paste Oxidisers and Dyes Crystacide cream is applied 2-3 times daily on the affected skin area. The treatment period should not exceed 3 weeks. Crystacide cream may be used as an alternative agent to topical antibiotics in the treatment of impetigo and molluscum contagiosom Antiperspirants Hydrogen Peroxide cream (Crystacide ) Hydrogen peroxide solution Potassium Permanganate (Permitabs ) Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate (Anhydrol Forte, Driclor ) H Botulinum toxin type A (Botox ) Botulinum toxin may be used in severe hyperhidrosis of the axillae unresponsive to topical antiperspirants or other treatments.
Soap Substitutes (all choices below are fragrance free) 1st Choice
 1 13 Skin 13.1.1 Vehicles Both vehicle and active ingredients are important in the treatment of skin conditions. The vehicle affects the degree of hydration of the skin, has a mild anti-inflammatory effect,
1 13 Skin 13.1.1 Vehicles Both vehicle and active ingredients are important in the treatment of skin conditions. The vehicle affects the degree of hydration of the skin, has a mild anti-inflammatory effect,
Soap Substitutes (all choices below are fragrance free) 1st Choice
 1 13 Skin 13.1.1 Vehicles Both vehicle and active ingredients are important in the treatment of skin conditions. The vehicle affects the degree of hydration of the skin, has a mild anti-inflammatory effect,
1 13 Skin 13.1.1 Vehicles Both vehicle and active ingredients are important in the treatment of skin conditions. The vehicle affects the degree of hydration of the skin, has a mild anti-inflammatory effect,
Report generated from BNF with QVH Formulary provided by FormularyComplete ( Accessed TA Number
 Report generated from BNF with QVH Formulary provided by FormularyComplete (www.pharmpress.com). Accessed 09 10 2015 Title Formulary Status Section TA Number TA Link Annotation ABRASIVE AGENTS Acnecide
Report generated from BNF with QVH Formulary provided by FormularyComplete (www.pharmpress.com). Accessed 09 10 2015 Title Formulary Status Section TA Number TA Link Annotation ABRASIVE AGENTS Acnecide
KEY MESSAGES. Psoriasis patients are more prone to cardiovascular diseases, stroke, lymphoma and non-melanoma skin cancers, and increased mortality.
 KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
13 Skin. In alphabetical order Product Manufacturer. NHS Lothian decision. Condition being treated. Date of NHS Lothian decision
 Recommendations from the Lothian Formulary Committee (FC) following Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) advice, NICE MTA advice, (FAF3) unlicensed and off-label medicines and (FAF2) medicines not considered
Recommendations from the Lothian Formulary Committee (FC) following Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) advice, NICE MTA advice, (FAF3) unlicensed and off-label medicines and (FAF2) medicines not considered
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care
 The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
Acne, Eczema and Psoriasis. Dr Rebecca Clapham
 Acne, Eczema and Psoriasis Dr Rebecca Clapham Aims Classification of severity Management in primary care tips and tricks When to refer Any other aspects you may want to cover? Acne First important aspect
Acne, Eczema and Psoriasis Dr Rebecca Clapham Aims Classification of severity Management in primary care tips and tricks When to refer Any other aspects you may want to cover? Acne First important aspect
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
13 Skin. In alphabetical order Product Manufacturer. NHS Lothian decision. Condition being treated. Date of NHS Lothian decision
 Recommendations from the Lothian Formulary Committee (FC) following Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) advice, NICE MTA advice, (FAF3) unlicensed and off-label medicines and (FAF2) medicines not considered
Recommendations from the Lothian Formulary Committee (FC) following Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) advice, NICE MTA advice, (FAF3) unlicensed and off-label medicines and (FAF2) medicines not considered
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Dermatology Round Up
 Dermatology Round Up Journal of Family Health Care Live Conference 25 March 2014 Julie Van Onselen Independent Dermatology Nurse, Oxford And Rachael Fagg, Mother Introduction 10.00 10.30hrs: Julie Van
Dermatology Round Up Journal of Family Health Care Live Conference 25 March 2014 Julie Van Onselen Independent Dermatology Nurse, Oxford And Rachael Fagg, Mother Introduction 10.00 10.30hrs: Julie Van
Prescribing Information
 Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
Prescribing Information Pr DERMOVATE Cream (clobetasol propionate cream, USP) Pr DERMOVATE Ointment (clobetasol propionate ointment, USP) Topical corticosteroid TaroPharma Preparation Date: A Division
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps
 Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
New Medicine Report. Pimecrolimus. RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003
 New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
New Medicine Report Document Status Pimecrolimus Reviewed by Suffolk D&T RED- Hospital only Date of Last Revision 6 th March 2003 Approved Name Pimecrolimus Trade Name Elidel Manufacturer Novartis Legal
Dermatology. Women and Children s Services
 Women and Children s Services Dermatology Disclaimer: The recommendations contained in this guideline do not indicate an exclusive course of action, or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations,
Women and Children s Services Dermatology Disclaimer: The recommendations contained in this guideline do not indicate an exclusive course of action, or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations,
GROUP 15 TOPICAL PREPARATIONS
 - 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
- 105 - GROUP 15 15.1 DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS 15.1.1 TOPICAL ANTIFUNGALS CLOTRIMAZOLE Indication: Treatment of susceptible fungal infections, dermatophytoses, superficial mycoses, and cutaneous candidiasis
Psoriasis. What is Psoriasis? What causes psoriasis? Medical Topics Psoriasis
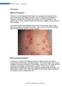 1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Recommended management of eczema in older patients
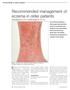 Recommended management of eczema in older patients Victoria Sherman MA, MRCP and Daniel Creamer BSc, MD, FRCP Our series Prescribing in older people gives practical advice for successful management of
Recommended management of eczema in older patients Victoria Sherman MA, MRCP and Daniel Creamer BSc, MD, FRCP Our series Prescribing in older people gives practical advice for successful management of
50 microgram/g Calcipotriol and 500 microgram/g betamethasone (as dipropionate).
 DUPISOR Composition Gel 50 microgram/g Calcipotriol and 500 microgram/g betamethasone (as dipropionate). Action Calcipotriol is a non-steroidal antipsoriatic agent, derived from vitamin D. Calcipotriol
DUPISOR Composition Gel 50 microgram/g Calcipotriol and 500 microgram/g betamethasone (as dipropionate). Action Calcipotriol is a non-steroidal antipsoriatic agent, derived from vitamin D. Calcipotriol
Time to Learn. 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service
 Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Clinical Workshop on Dermatology. 3 Nov 2005 & 10 Nov 2005
 Clinical Workshop on Dermatology 3 Nov 2005 & 10 Nov 2005 Clinical Workshop on Dermatology Eczema Acne Psoriasis Highlights on commonly used dermatological products Eczema - Introduction The most common
Clinical Workshop on Dermatology 3 Nov 2005 & 10 Nov 2005 Clinical Workshop on Dermatology Eczema Acne Psoriasis Highlights on commonly used dermatological products Eczema - Introduction The most common
Paediatric Eczema. Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012
 Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Topical Calcipotriol Algorithm
 Topical Calcipotriol Algorithm Is this patient an adult previously diagnosed with psoriasis by a doctor? Do the skin patches look the same as those diagnosed as psoriasis? Is this psoriasis covering an
Topical Calcipotriol Algorithm Is this patient an adult previously diagnosed with psoriasis by a doctor? Do the skin patches look the same as those diagnosed as psoriasis? Is this psoriasis covering an
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals and Guidance Information Services Static List Review (SLR) report Title and TA publication number of static topic: Final decision:
PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT
 PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT Objectives Discuss pathology of psoriasis Review types of psoriasis Review triggers and factors affecting disease severity Common comorbidity review Review first and
PSORIASIS BEST PRACTICE IN MANAGEMENT Objectives Discuss pathology of psoriasis Review types of psoriasis Review triggers and factors affecting disease severity Common comorbidity review Review first and
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Flutarzole 0,05% w/w cream, Fluticasone propionate 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 1.1. Trade name Flutarzole 1.2. Composition Active substance: Fluticasone
PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER Christy Mary Sam
 PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER 2014-15 1 Christy Mary Sam COMMUNICATION SKILLS Communication is the process involved with the exchange of any kind of information between
PHARMACY PRACTICE I PHCY280 (2 CREDITS); PHCY280L (1CREDIT) SUMMER 2014-15 1 Christy Mary Sam COMMUNICATION SKILLS Communication is the process involved with the exchange of any kind of information between
LRI Children s Hospital
 Atopic Eczema Care LRI Children s Hospital Staff relevant to: Clinical staff working within the UHL Children s Hospital. Team approval date: May 2017 Version: V 4 Revision due: May 2020 Written by: K.
Atopic Eczema Care LRI Children s Hospital Staff relevant to: Clinical staff working within the UHL Children s Hospital. Team approval date: May 2017 Version: V 4 Revision due: May 2020 Written by: K.
3rd April Pearls and Pitfalls of Dermatology
 3rd April 2014 Pearls and Pitfalls of Dermatology The Basics AVOID SOAP Use Aqueous cream as a soap substitute, i.e. apply before bath/ shower and rinse off Bath oils Oilatum/Balneum LIBERAL EMOLLIENTS
3rd April 2014 Pearls and Pitfalls of Dermatology The Basics AVOID SOAP Use Aqueous cream as a soap substitute, i.e. apply before bath/ shower and rinse off Bath oils Oilatum/Balneum LIBERAL EMOLLIENTS
Prescribing Information. Taro-Clobetasol. Taro-Clobetasol
 Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
Prescribing Information Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Cream USP, 0.05% w/w Pr Taro-Clobetasol Clobetasol Propionate Ointment USP, 0.05% w/w Therapeutic Classification Topical corticosteroid
(5). (1, 5) Table 1:Appearance and location of dandruff, psoriasis and seborrhoeic dermatitis
 A-Dandruff(pityriasis capitis) 1-Dandruff is a chronic relapsing condition of the scalp which respond to treatment, but return when the treatment is stopped (1). Increased cell turnover rate (twice the
A-Dandruff(pityriasis capitis) 1-Dandruff is a chronic relapsing condition of the scalp which respond to treatment, but return when the treatment is stopped (1). Increased cell turnover rate (twice the
FACTSHEET ADULT SEBORRHOEIC DERMATITIS. What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Who gets and why? What does it look like?
 What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Sebhorrhoeic dermatitis is a common scaly rash that often affects the face, scalp and chest but it can affect other areas. Dermatitis is another word for eczema. Seborrhoeic
What is seborrhoeic dermatitis? Sebhorrhoeic dermatitis is a common scaly rash that often affects the face, scalp and chest but it can affect other areas. Dermatitis is another word for eczema. Seborrhoeic
MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS
 MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about male genital lichen sclerosus (also known as balanitis xerotica
MALE GENITAL (PENIS) LICHEN SCLEROSUS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about male genital lichen sclerosus (also known as balanitis xerotica
Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
 Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
Diagnosis: ATOPIC DERMATITIS (AD) Texas Children's Hospital Dermatology Service PCP Referral Guidelines- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) PATIENT ADVICE: Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, so
Common Skin Diseases. MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB
 Common Skin Diseases MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
Common Skin Diseases MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR PSORIASIS. Sandra Hanlon Dermatology Senior Charge Nurse NHS Ayrshire and Arran 07/03/17
 TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR PSORIASIS Sandra Hanlon Dermatology Senior Charge Nurse NHS Ayrshire and Arran 07/03/17 PSORIASIS A chronic, non-infectious inflammatory skin condition that has no cure Characterised
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR PSORIASIS Sandra Hanlon Dermatology Senior Charge Nurse NHS Ayrshire and Arran 07/03/17 PSORIASIS A chronic, non-infectious inflammatory skin condition that has no cure Characterised
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Psoriasis (excluding widespread plaque psoriasis) Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disorder. Estimates of the prevalence (proportion
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Psoriasis (excluding widespread plaque psoriasis) Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disorder. Estimates of the prevalence (proportion
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema
 Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE. Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio
 COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
15 minute eczema consultation
 THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
THERAPY WORKSHOP 15 minute eczema consultation History Current treatments Examination Treatment Plan Written action plan Soap substitute/bath oil Antiseptic baths Emollients Topical steroids Other treatments
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION. EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream. (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine
 RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine To Pharmacist Only Medicine NOVEMBER 2000 MEETING PART A 1. International non-proprietary
RECLASSIFICATION SUBMISSION EUMOVATE Eczema and Dermatitis Cream (Clobetasone butyrate 0.05%) From Prescription Only Medicine To Pharmacist Only Medicine NOVEMBER 2000 MEETING PART A 1. International non-proprietary
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema
 Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
Steroid use in managing your child s Atopic Eczema Clinical Nurse Specialist for Paediatric Dermatology (01284) 713575 Step up step down approach: Addressograph Severe Call your General Practitioner (GP)
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
 Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Buckinghamshire Dermatology Referral Guidance
 Buckinghamshire Dermatology Referral Guidance 1 of 29 CONTENTS PAGE Notes 3 Sub Specialities 1. Atopic Eczema in Children & Adults 4 2. Viral Warts & Molluscum Contaginosum 10 3. Hand Eczema 12 4. Acne
Buckinghamshire Dermatology Referral Guidance 1 of 29 CONTENTS PAGE Notes 3 Sub Specialities 1. Atopic Eczema in Children & Adults 4 2. Viral Warts & Molluscum Contaginosum 10 3. Hand Eczema 12 4. Acne
TCIs are only available on prescription and are usually started by a dermatology specialist.
 (TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
(TCIs) What are topical calcineurin inhibitors? Topical calcineurin inhibitors are treatments that alter the immune system and have been developed for controlling eczema. There are two types available:
Childhood Eczema Flowchart
 Childhood Eczema Flowchart EXCLUSIONS -Over 15 years of age -Contact dermatitis -Seborrhoeic Eczema -Mild and Moderate Eczema Childhood Eczema Assess Eczema Severity RED FLAGS -Eczema Herpecitum -Severe
Childhood Eczema Flowchart EXCLUSIONS -Over 15 years of age -Contact dermatitis -Seborrhoeic Eczema -Mild and Moderate Eczema Childhood Eczema Assess Eczema Severity RED FLAGS -Eczema Herpecitum -Severe
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES ATOPIC DERMATITIS / ECZEMA MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory BETNOVATE - S
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory BETNOVATE - S Betamethasone Valerate and Salicylic Acid Skin Ointment QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION BETNOVATE
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory BETNOVATE - S Betamethasone Valerate and Salicylic Acid Skin Ointment QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION BETNOVATE
ECZEMA. Introduction. Differential diagnoses. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References See also Auckland Regional Clinical Pathways for Eczema (with
Introduction Differential Diagnoses Indications for Admission Inpatient Treatment Flow Chart for Inpatient Care Outpatient Treatment References See also Auckland Regional Clinical Pathways for Eczema (with
Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice)
 Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice) Patient Case Study in Psoriasis Patient Case Study in Psoriasis William Smith,
Using Your ESP* in Pharmacy: How to Improve Treatment Adherence and Patient Outcomes in Psoriasis (*Expanded Scope of Practice) Patient Case Study in Psoriasis Patient Case Study in Psoriasis William Smith,
Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference?
 Dermatology Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference? Dr Stephen Kownacki Executive chair, Primary Care Dermatology Society (PCDS) This session
Dermatology Psoriasis the latest recommendations for management: where can primary care make a real difference? Dr Stephen Kownacki Executive chair, Primary Care Dermatology Society (PCDS) This session
What you need to know about your child s PSORIASIS. Psoriasis
 What you need to know about your child s PSORIASIS Ps Psoriasis The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health
What you need to know about your child s PSORIASIS Ps Psoriasis The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health
MAS Formulary Products
 Ibuprofen Susp.100mg/5ml for pain and inflammation 100ml Care Ibuprofen Tabs 200mg for pain and inflammation 24 Care ( Added Jan 2016) Ibuprofen Tabs 400mg for pain and inflammation 24 Tariff price - P
Ibuprofen Susp.100mg/5ml for pain and inflammation 100ml Care Ibuprofen Tabs 200mg for pain and inflammation 24 Care ( Added Jan 2016) Ibuprofen Tabs 400mg for pain and inflammation 24 Tariff price - P
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
ATOPIC ECZEMA. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
Pediatric Dermatology. Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital
 Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
OTC PRODUCTS. 4 Gama Benzene HCL 0.1% + Proflavine Hermisulphate 0.1% + Cetrimide 0.45% Cream
 OTC PRODUCTS SR. No. COMPOSITION Allantoin 0.2% + Dimethicone 1% + Urea 10% + Propylene Glycol 5% + Glyserine 5% + 1 Light Liquid Paraffin 8% Cream (FOOT CREAM) 2 Aquous Cream 3 Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine
OTC PRODUCTS SR. No. COMPOSITION Allantoin 0.2% + Dimethicone 1% + Urea 10% + Propylene Glycol 5% + Glyserine 5% + 1 Light Liquid Paraffin 8% Cream (FOOT CREAM) 2 Aquous Cream 3 Cetrimide 0.5% + Chlorhexidine
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory, Prescribing in children
 Psoriasis in children: current approaches to management Laura Proudfoot BSc, MRCP, Elisabeth Higgins MA, FRCP and Judy Davids RGN Our series Prescribing in children gives practical advice for successful
Psoriasis in children: current approaches to management Laura Proudfoot BSc, MRCP, Elisabeth Higgins MA, FRCP and Judy Davids RGN Our series Prescribing in children gives practical advice for successful
Acne vulgaris is a disease of the pilosebaceous unit (i.e., the sebaceous glands and adjacent hair follicle).
 Dr. Ghassan Salah Acne is a common, chronic inflammatory disorder of the pilosebaceous unit in which a microcomedo develops as the initial condition. The most common form of acne is acne vulgaris. Other
Dr. Ghassan Salah Acne is a common, chronic inflammatory disorder of the pilosebaceous unit in which a microcomedo develops as the initial condition. The most common form of acne is acne vulgaris. Other
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Self-care aware When should you prescribe?
 Self-care aware When should you prescribe? Over-the-counter medicines can only be sold within their licensed indications and in limited quantities in some cases. Below are some examples of instances when
Self-care aware When should you prescribe? Over-the-counter medicines can only be sold within their licensed indications and in limited quantities in some cases. Below are some examples of instances when
Dermatology Pearls. Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018
 Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
(minutes for web publishing)
 Dermatology Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 20 October 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Dermatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance
Dermatology Subcommittee of the Pharmacology and Therapeutics Advisory Committee (PTAC) Meeting held on 20 October 2017 (minutes for web publishing) Dermatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, Committee Approval: March 10, 2017 Next Review Date: May 2018
 Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Independent licensees of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru493 Topic: Dupixent, dupilumab Date of Origin: March 10, 2017 Committee Approval: March 10, 2017
Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System
 Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System Chapter 25 1 Anatomy of the Skin Skin is made of various layers that contain nerves, glands, hair, and blood vessels Function is to protect the body against
Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System Chapter 25 1 Anatomy of the Skin Skin is made of various layers that contain nerves, glands, hair, and blood vessels Function is to protect the body against
PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE PSORIASIS. Plaque a raised lesion where the diameter is greater than the thickness. Number 2
 Number 2 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE AYERS ROCK, ULURU NATIONAL PARK, AUSTRALIA PSORIASIS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE 2011 Plaque a raised lesion
Number 2 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE AYERS ROCK, ULURU NATIONAL PARK, AUSTRALIA PSORIASIS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE 2011 Plaque a raised lesion
BETNOVATE Betamethasone 17-valerate
 BETNOVATE Betamethasone 17-valerate Betamethasone valerate is referred to as Betnovate throughout this information. PRESENTATION BETNOVATE Cream (non-greasy base) 0.1% betamethasone as 17-valerate in a
BETNOVATE Betamethasone 17-valerate Betamethasone valerate is referred to as Betnovate throughout this information. PRESENTATION BETNOVATE Cream (non-greasy base) 0.1% betamethasone as 17-valerate in a
84:00. Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents. 84:00 Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents
 Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents COMPOUND PRESCRIPTION 00000999119 00000999112 COMPOUND - RETINOIC ACID (TRETINOIN) () MISCELLANEOUS COMPOUND To be used when the compound
Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents Skin and Mucous Membrane Agents COMPOUND PRESCRIPTION 00000999119 00000999112 COMPOUND - RETINOIC ACID (TRETINOIN) () MISCELLANEOUS COMPOUND To be used when the compound
12.1 DRUGS ACTING ON THE EAR
 12.1 DRUGS ACTING ON THE EAR Anti-inflammatory/anti-infective preparations These preparations usually contain a corticosteroid either alone or with an antibacterial agent. Betamethasone 0.1% ear, eye,
12.1 DRUGS ACTING ON THE EAR Anti-inflammatory/anti-infective preparations These preparations usually contain a corticosteroid either alone or with an antibacterial agent. Betamethasone 0.1% ear, eye,
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Eczema and its Management. A Guide for Nurses
 Eczema and its Management A Guide for Nurses Contents Page Contents Introduction 1 What is eczema? 1 Types of Eczema 3 Atopic eczema 3 Seborrhoeic dermatitis 5 Contact dermatitis 6 Gravitational/stasis/varicose
Eczema and its Management A Guide for Nurses Contents Page Contents Introduction 1 What is eczema? 1 Types of Eczema 3 Atopic eczema 3 Seborrhoeic dermatitis 5 Contact dermatitis 6 Gravitational/stasis/varicose
過敏病科中心. Allergy Centre. Eczema. Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心. Allergy Centre. For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at:
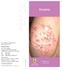 Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心 Eczema For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: Allergy Centre 9/F, Li Shu Pui Block Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital 2 Village Road, Happy Valley, Hong Kong Tel: 2835
Allergy Centre 過敏病科中心 Eczema For enquiries and appointments, please contact us at: Allergy Centre 9/F, Li Shu Pui Block Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital 2 Village Road, Happy Valley, Hong Kong Tel: 2835
Skin disorders. Seborrhoeic dermatitis Search date April 2010 Luigi Naldi ...
 Seborrhoeic Search date April 21 Luigi Naldi.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Seborrhoeic affects at least 1% of the population. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) ovale
Seborrhoeic Search date April 21 Luigi Naldi.................................................. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Seborrhoeic affects at least 1% of the population. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) ovale
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1 LOCOID 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSTION 3 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM 4 CLINICAL PARTICULARS
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1 LOCOID Lipocream Ointment Topical Emulsion (Locoid Crelo ) Scalp Lotion hydrocortisone butyrate 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSTION Each formulation contains active ingredient
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1 LOCOID Lipocream Ointment Topical Emulsion (Locoid Crelo ) Scalp Lotion hydrocortisone butyrate 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSTION Each formulation contains active ingredient
Package leaflet: Information for the patient. Mometasone furoate 0.1%w/w Ointment (mometasone furoate)
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient Mometasone furoate 0.1%w/w Ointment (mometasone furoate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important
Package leaflet: Information for the patient Mometasone furoate 0.1%w/w Ointment (mometasone furoate) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important
Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57
 Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 12 December 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg57 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin. 1. ECZEMA Atopic Dermatitis- specific form of eczema starting in childhood
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
Specials Recommended by the British Association of Dermatologists for Skin Disease DEIRDRE BUCKLEY, TIM ROOT AND SIMON BATH
 Specials Recommended by the British Association of Dermatologists for Skin Disease DEIRDRE BUCKLEY, TIM ROOT AND SIMON BATH On behalf of the BAD Specials Working Group 2018 Specials Recommended by the
Specials Recommended by the British Association of Dermatologists for Skin Disease DEIRDRE BUCKLEY, TIM ROOT AND SIMON BATH On behalf of the BAD Specials Working Group 2018 Specials Recommended by the
Bradford Contraception and Sexual Health Services FORMULARY
 Bradford Contraception and Sexual Health Services FORMULARY Medication Stock Item Strength Form Pack Size Indication Acetone Liquid 50ml For lab use Aciclovir TTO (PGD) 400mg Tablets 15 Herpes Treatment
Bradford Contraception and Sexual Health Services FORMULARY Medication Stock Item Strength Form Pack Size Indication Acetone Liquid 50ml For lab use Aciclovir TTO (PGD) 400mg Tablets 15 Herpes Treatment
ACNE. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ACNE What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about acne - what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it and where you can find out more about
ACNE What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about acne - what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it and where you can find out more about
What are the symptoms of a vulval skin condition?
 Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
Information for you Published in December 2013 Skin conditions of the vulva About this information This information is for you if you want to know about skin conditions affecting the vulva. If you are
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018 DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO RELEVANT FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Structure and function of the skin IBD
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018 DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO RELEVANT FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Structure and function of the skin IBD
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 18 January 2012
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 January 2012 EPIDUO, gel Tube of 30 g (CIP code: 383 814-6) Tube of 60 g (CIP code: 383 816-9) Applicant: GALDERMA
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 January 2012 EPIDUO, gel Tube of 30 g (CIP code: 383 814-6) Tube of 60 g (CIP code: 383 816-9) Applicant: GALDERMA
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Treatment of Acne and Rosacea in Canada. Catherine Zip Nov 10, 2016
 Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Treatment of Acne and Rosacea in Canada Catherine Zip Nov 10, 2016 Acne Acne Classification Type Comedonal Mild-to-moderate papulopustular acne Severe Description
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Treatment of Acne and Rosacea in Canada Catherine Zip Nov 10, 2016 Acne Acne Classification Type Comedonal Mild-to-moderate papulopustular acne Severe Description
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology
 Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Managing and Minimizing Flare-ups in Atopic Dermatitis
 Managing and Minimizing Flare-ups in Atopic Dermatitis Importance of the skin barrier & how commonly used drugs are impacting it Dr. Benjamin Barankin, MD FRCPC Medical Director & Founder of Toronto Dermatology
Managing and Minimizing Flare-ups in Atopic Dermatitis Importance of the skin barrier & how commonly used drugs are impacting it Dr. Benjamin Barankin, MD FRCPC Medical Director & Founder of Toronto Dermatology
fluorouracil 0.5% / salicylic acid 10% cutaneous solution (Actikerall ) SMC No. (728/11) Almirall S.A.
 fluorouracil 0.5% / salicylic acid 10% cutaneous solution (Actikerall ) SMC No. (728/11) Almirall S.A. 09 September 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above
fluorouracil 0.5% / salicylic acid 10% cutaneous solution (Actikerall ) SMC No. (728/11) Almirall S.A. 09 September 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above
ICHTHYOSIS. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
ICHTHYOSIS What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about ichthyosis. It will tell you what it is, the types of ichthyosis, what can be done about it,
Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100
 4 4 w Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES Primary care manages by far the largest number of patients with atopic eczema, the vast majority
4 4 w Primary Care Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Eczema 10/07100 1.0 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES Primary care manages by far the largest number of patients with atopic eczema, the vast majority
Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
 Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
DATA SHEET. Betamethasone dipropionate equivalent to betamethasone 0.5mg/g (0.05% w/w).
 DATA SHEET 1. DIPROSONE DIPROSONE (0.05% w/w) cream DIPROSONE (0.05% w/w) ointment 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Betamethasone dipropionate equivalent to betamethasone 0.5mg/g (0.05% w/w).
DATA SHEET 1. DIPROSONE DIPROSONE (0.05% w/w) cream DIPROSONE (0.05% w/w) ointment 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Betamethasone dipropionate equivalent to betamethasone 0.5mg/g (0.05% w/w).
ACNE. Jason M Cheyney, MPAS, PA-C Dermatologic Surgery Specialists Macon, Ga 31211
 ACNE Jason M Cheyney, MPAS, PA-C Dermatologic Surgery Specialists Macon, Ga 31211 Pathogenesis of Acne Causative Factors Therapy On the horizon Approximately 45 million Americans have acne It is often
ACNE Jason M Cheyney, MPAS, PA-C Dermatologic Surgery Specialists Macon, Ga 31211 Pathogenesis of Acne Causative Factors Therapy On the horizon Approximately 45 million Americans have acne It is often
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies. Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017
 Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
Common Skin Diseases. Md Ahad Ali Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB
 Common Skin Diseases Md Ahad Ali Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
Common Skin Diseases Md Ahad Ali Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
