CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
|
|
|
- Bryan Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute kidney injury cardiovascular disease (ischaemic heart disease, chronic heart failure, peripheral vascular disease or cerebral vascular disease) structural renal tract disease, recurrent renal calculi or prostatic hypertrophy multisystem disease eg.systemic lupus erythematosus family history of end-stage kidney disease (GFR category G5) or hereditary kidney disease Haematuria INTERPRETING egfr VALUES egfr is a less reliable marker of true GFR or kidney function when: egfr > 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 In extremes of body weight: egfr underestimates in patients with high BMI egfr overestimates in patients with low BMI Confirm an egfr result of less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 in a person not previously tested by repeating the test within 2 weeks. Allow for biological and analytical variability of serum creatinine (±5%) when interpreting changes in egfr CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES (egfr = estimated glomerular filtration rate; ACR = albumin creatinine ratio) GFR and ACR categories and risk of adverse outcomes ACR categories (mg/mmol) description and range <3 Normal to mildly increased 3-30 Moderately increased >30 Severely increased A1 A2 A TesTingG2for pro Teinuria Mild reduction related to normal range for a young Measure adult albumin:creatinine ration on a spot urine sample (preferably early morning) If the initial ACR G3a is >30 and <70 mg/mmol, confirm by Mild-moderate reduction a subsequent early morning sample. If the initial ACR is >70mg/mmol a repeat sample need not be tested In people without G3b Diabetes, clinically Moderate-severesignificant reduction proteinuria is present when ACR >30mg/mmol In people with Diabetes G4 microalbuminuria (ACR Severe reduction>2.5mg/ mmol in men and ACR >3.5mg/mmol in women) is clinically significant testing for haematuria 15 Use raegent strips G5rather than urine microscopy Kidney failure Evaluate further if there is a result of 1+ or more Do not use urine microscopy Starting toace confirm inhibitor a positive therapy Check result renal function and electrolytes 1-2 weeks after starting/dose change HAEMATURIA A fall in egfr of <25% is acceptable. PROTEINURIA If >25% stop ACEi or ARB and consider seeking specialist advice Use dipstick reagent If strips potassium rather >6mmol/l than urine and microscopy not on Spironolactone. Stop Proteinuria ACEi or ARB. is a useful Consider marker arranging of kidney low potassium damage and diet complication risk Evaluate further if there and re-instituting is a result of 1+ ACEi or more ARB (rpt once in 2 potassium weeks) normalised ACR is the recommended method for assessing proteinuria Dipstick haematuria If not egfr diagnostically falls by 5-25% useful recheck with in concurrent 2-3 weeks to ensure decline If initial is ACR not = progressive confirm with a subsequent early morning sample menstrual period, infection or in catheter samples If initial ACR > 70 mg/mmol, a repeat sample need not be tested Confirmed ACR 3 signifies clinically important proteinuria. V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July GFR categories, description and range 90 Normal and high G1 No CKD in the absence of markers of kidney damage*
2 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE REFERRAL ALGORITHM egfr<60 Is patient unwell? YES Manage acute illness Is this acute kidney injury (AKI)? Repeat egfr within 1 week, refer urgently if declining URGENT REFERRAL Suspected multisystem disease with evidence of renal involvement Urine dipstick Persistent haematuria ( 1+)? YES AND > 50 YRS Urology referral Acute kidney injury (without an obvious cause manageable in primary care) Newly diagnosed egfr < 15 YES AND < 50 YRS Is malignancy excluded? YES Nephrotic syndrome Accelerated hypertension ACR >70? YES Nephrology advice/referral Severe hyperkalaemia (>6.5mmol/L) STAGE G3a and G3b Monitor according to page 3 Repeat egfr stable? STAGE G4-5 Most patients with CKD 4/5 should be being followed in secondary care HOWEVER if RRT not indicated (eg. frail elderly), management of advanced CKD may be appropriate in primary care advice for primary care healthcare staff in North West London: ICHC-tr.ckdadvice@nhs.net Nephrology consultant response within 24 hours Mon - Fri Nephrology advice/referral if declining Sustained decrease in GFR of 25% within 12 months Sustained decrease in GFR of 15ml/min within 12 months What is cause for CKD? Seek nephrology guidance if this is uncertain ( advice below) Minimum information for referral Dates and results of previous creatinine/egfr measurement Medical history Drug history Current BP Urine dipstick and ACR if dipstick positive Renal Ultrasound if: accelerated progression of CKD visible or persistent invisible haematuria symptoms of urinary tract obstruction family history of polycystic kidney disease and are aged over 20 years egfr of <30 ml/min/1.73 m2 (GFR category G4 or G5) V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July
3 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE ONGOING MANAGEMENT MANAGEMENT OF STABLE CKD Agree management plan with patient Lifestyle advice Smoking cessation advice Avoid NSAIDs (even topical) Vaccinate for influenza and pneumococcus BP: Encourage home BP monitoring Target BP: < 140/90 if ACR 70 < 130/80 if ACR > 70 Caution of BP targets in frailty (See page 7) Prioritise ACEi/ARB with associated sick day guidance Cardiovascular risk: Aspirin if CV risk at 10yrs >20% Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) esp. if higher risk of gastric irritation with aspirin. Observational data suggest PPIs may cause insidious inflammatory kidney injury switch to ranitidine if egfrfalling Statins all patients with CKD3b and beyond should be on unless contra-indicated Serum bicarbonate Consider sodium bicarbonate 500mg twice daily if acidotic (serum bicarbonate <22 mmol/l) RENAL ANAEMIA FREQUENCY OF MONITORING egfr (NUMBER OF TIMES PER YEAR) GFR and ACR categories and risk of adverse outcomes GFR categories, description and range 90 Normal and high Mild reduction related to normal range for a young adult Mild-moderate reduction Moderate-severe reduction Severe reduction 15 Kidney failure ACR categories (mg/mmol) description and range <3 Normal to mildly increased 3-30 Moderately increased >30 Severely increased A1 A2 A3 G G G3a G3b G G RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM INHIBITORS IN CKD (ACEI and ARB) Renal anaemia can start to develop from CKD stage 3b (egfr<45) and is common in advanced CKD5 (egfr<15). This may require treatment with intravenous iron and erythropoietin. Particularly in CKD stages 3b/4, renal anaemia should only be diagnosed after exclusion of other causes including iron deficiency, folate/b12 deficiency, haemolysis. ACEi and ARB prevent scarring in CKD and should be used preferentially in patients with proteinuria Assess kidney function and electrolytes. 1-2 weeks after initiating therapy, watch out for hyperkalemia Assess kidney function after any subsequent increase in dose A small rise in creatinine or a mild fall in egfr values is expected with therapy repeat the assessment of kidney function if the rise in creatinine is greater than 15% STOP therapy - If serum creatinine rises by >30% or egfr falls by >25%: seek specialist advice (to exclude possible renovascular disease) If K>6.0 stop ACEi/ARB and start low potassium diet if the patient has proteinuria and would benefit from an ACEi/ARB seek Nephrological advice as introduction of frusemide or bicarbonate can facilitate reintroduction of these agents Cautious use of ACEi/ARB with spironolactone and other potassium sparing diuretics, very close monitoring of potassium required. V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July
4 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE COMMON DRUGS Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) Should be considered if there is a higher risk of gastric irritation with aspirin or when the patient has more advanced CKD (egfr <20) Observational data suggest PPIs may cause insidious inflammatory kidney injury therefore stop or switch to ranitidine if acid suppression needed ANTIBIOTIC Issue in reduced kidney function Recommendation for use Trimethoprim Nitrofurantoin Temporarily raises serum potassium and creatinine ~20% (affects tubular function but not nephrotoxic per se) Requires filtration and tubular secretion. Reduced excretion in CKD and high levels cause peripheral neuritis Safe for use if egfr>30 but may transiently elevate K and creatinine repeat bloods 1-2 weeks later to ensure resolution Contraindicated if egfr less than 45 ml/ minute/1.73 m 2, except it may be used with caution if egfr ml/ minute/1.73 m 2 as a short-course only (3 to 7 days), to treat uncomplicated lower UTI caused by multidrug resistant bacteria only if the benefit is expected to outweigh the risks. Do not use nitrofurantoin in this situation if the infecting organism is sensitive to a safer antibiotic. Penicillin Risk of crystalluria Generally safe but avoid maximum doses if egfr<15 Macrolides (eg. Clarithromycin) Renally excreted, can cause neurotoxicity Reduce dose by 50% when egfr<30; AVOID in kidney transplants = interaction with tacroliums/ciclosporin Quinolones (eg. Ciprofloxacin) Renally excreted, risk of tendonopathy and potentially nephrotoxic Reduce dose by 50% when egfr <15 Tetracyclines Partly renally cleared; doxycycline safer Reduce dose when egfr<45 HYPOGLYCAEMIC AGENT egfr = (CKD stage 3a) egfr = (CKD stage 3b) egfr <30 (CKD stage 4-5) Metformin Reduce dose Stop Gliclazide Higher risk of hypoglycaemia use with caution; reduce dose DPP-4 inhibitors (eg. Linagliptin, Sitagliptin) (only Linagliptin unchanged = 5mg OD) (only Linagliptin unchanged = 5mg OD) SGLT-2 inhibitors (eg.canagliflozin, Empagliflozin) Reduce dose (Cana- and Empa-gliflozin) Stop Dapagliflozin Stop Stop GLP-1 inhibitors (eg. Liraglutide, Exanatide) Stop if egfr<15 (Liraglutide, Dulaglutide safe if egfr>15) Pioglitazone V6.0 Date of preparation: July (Updated Aug 2018) For review: July
5 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIABETES S DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY E Diabetic Nephropathy is characterised by the excretion of abnormal amounts of albumin in the urine, arterial hypertension or progressive decline in E kidney function K ALBUMINURIA MANAGEMENT OF INDIVIDUAL WITH DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY Albuminuria is the earliest sign of kidney involvement in Type 2 Diabetes. This is best assessed by laboratory measurement of the urinary albumin creatinine ratio (ACR). Albuminuria is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease and progression to end-stage kidney disease. All patients with albuminuria should be on maximal ACEi or ARB therapy and have BP controlled to target (see below) Patient education is an integral part of overall management Lifestyle changes, weight loss and smoking cessation should be advised Target HbA1c: Type 1 Diabetes - CKD stages 1 and 2 = mmol/mol - CKD stages 3 and 4 = mmol/mol - CKD stage 5 (incl on dialysis) = mmol/mol Type 2 Diabetes - CKD stages 1 and 2 = mmol/mol - CKD stages 3 and 4 on non-hypo inducing agents = mmol/mol - CKD stages 3, 4 and 5 (incl on dialysis) on hypo inducing agents = mmol/mol SEEK RENAL ADVICE IF Unexplained sudden increases in albuminuria Unexplained egfr decline in absence of albuminuria Maintain blood pressure below 140/90 (130/80 if ACR > 70) - Maximal doses of ACE inhibitors or Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are recommended first line drugs - Calcium channel blocker (non-dihydropyridine class) drugs and low dose thiazide diuretics are useful second line agents - Loop diuretics are useful in the presence of volume overload (e.g. leg oedema not caused by the side effects of calcium channel blockers) - Additional antihypertensive therapy may be required. Treat dyslipidaemia (serum cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and serum triglycerides to targets) Aspirin therapy if egfr <60 and ACR>70 All patients with Diabetes should be on a register and minimum data should include annual measures for microvascular disease. Please see Cardiovascular Risk for additional requirements. PROTEINURIA MEASUREMENTS AND BLOOD PRESSURE TARGETS (adjust in frailty) Ensure patient understands sick day guidance for relevant drugs eg ACE/ARBs/ Metformin ACR PCR BP target /90 > 70 > /80 V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July
6 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE HEART FAILURE Developed with Dr. C. Plymen, Cardiology Consultant, Imperial College NHS Trust BACKGROUND POINTS MANAGEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS WITH CKD AND HEART FAILURE Signs and symptoms of heart failure are often non- specific and can overlap with symptoms of CKD (e.g.dyspnoea, peripheral and pulmonary oedema). Heart failure is not a benign disease: there is a 10% inpatient mortality associated with diagnosis, and 50% mortality at 5 years follow-up. 1 The prognostic benefits of ACEi and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure are just as important in patients with concomitant CKD. (Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) in patients intolerant of ACEi). The risks/benefits of temporarily withholding or continuing these therapeutic agents during inter-current illness, or when predictive effects occur are different in patients with both heart failure and CKD compared to patients with CKD alone. PERMISSIBLE RISES IN CREATININE WITH ACEi / ARB Because of the need to reach adequate ACEi dosing to see a prognostic benefit in heart failure, a Cr increase of up to 50% above baseline, or 266μmol/L, or egfr <25 ml/min/1.73 m2, whichever is the smaller is acceptable in patients with concomitant CKD and heart failure 3. This is a larger increase than that which is considered acceptable for patients without heart failure. Patient education is an integral part of overall management Lifestyle changes; exercise, weight loss and smoking cessation should be advised ACEi/ARB Therapy: - Check renal function prior to initiation of therapy - Stop concomitant nephrotoxic drugs e.g. NSAIDS - Recheck 1-2 weeks after initiation and 1-2 weeks after final dose titration - Recheck renal function 4-monthly thereafter - Maximal tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or ARBs (unless contraindicated) - ACEi/ARBs should not be withheld if BP low unless significant symptomatic hypotension - If Cr >200μmol/L, egfr < 25 ml/min or K+ >5.5mmol/L, seek specialist help - Additional antihypertensive therapy may be required Monitor K+ : - A rise in potassium of up to 5.5 mmol/l is acceptable - Stop potassium supplements or potassium sparing drugs (e.g. amiloride) if high potassium an issue - Consider sodium bicarbonate 500mg twice daily if acidotic (serum bicarbonate <22 mmol/l) - Consider increasing loop diuretic if patient experiencing symptoms of overload Treat dyslipidaemia (serum cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and serum triglycerides to targets) Aspirin therapy if indicated (2⁰ prevention) Ensure prescribing is consistent with CKD Sick day rules: Consider withholding ACEi and seek early medical attention. Patients with heart failure often have multiple comorbidities: their care is not straight forward. Such patients are best managed in the context of a multidisciplinary team. References 1. National Heart Failure Audit NICOR Bakris GL, Weir MR. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated elevations in serum creatinine. Arch Intern Med (2000);160: ESC Guidelines for the treatment and management of acute and chronic heart failure. European Heart Journal (2016); 37: V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July
7 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE FRAILTY Developed with Medicine for The Elderly department Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust Management of CKD in the context of frailty requires a holistic approach Kidney Ageing Kidney function (GFR) declines with age: ~0.8 ml/min/year after 35 years old up to 2mL/min/year after 70 years old egfr >30mL/min in the absence of acute illness, proteinuria or uncontrolled HTN is unlikely to progress to end-stage kidney disease MANAGEMENT OF FRAIL PATIENTS WITH CKD Identify frailty and screen for cognitive impairment Calculate EFI score ( Screen cognition using GPCOG ( Medications Frail patients are more susceptible to harm from medications Refer to CKD - Common Drugs page 4 Blood pressure (BP) or HbA1c targets - individualise to patient: Be wary of falls risk check postural BPs Higher BP targets are appropriate eg. systolic BP mmhg / diastolic BP mmhg Be wary of hypoglycaemia risk with insulin and oral hypoglycaemic agents Higher HbA1c targets are appropriate eg mmol/mol Focus of Care in Frail Patients Should be patient and outcome centred View CKD in the context of an individual s comorbidities and personal priorities Renal replacement therapy (RRT) may not improve quality of life symptom control may be more appropriate Advance care planning should be a priority Further advice Diet avoid protein restriction / aggressive salt restriction Monitoring of renal function If renal replacement therapy (RRT) is considered - refer to page 3 If RRT is unlikely to improve quality of life, tailor frequency to clinical need In event of sudden egfr decline exclude common causes: UTIs dehydration obstructive uropathy Medications (eg. Diuretics, anti-hypertensives, NSAIDs) Consider nephrology advice if: Unexplained and sustained decline in renal function / new nephrotic range proteinuria Refractory and symptomatic anaemia (<100g/L) in advanced CKD (stages 3b 5) may require intravenous iron +/- erythropoietin supplementation Specialty advice is available to North West London primary care services: ICHC-tr.ckdadvice@nhs.net (consultant nephrologist advice) ICHC-tr.adviceelderlymedicine-imperial@nhs.net (consultant geriatrician advice) V6.0 Date of preparation: July For review: July
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
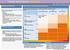 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway. 5 th April 2018
 Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease
 The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma. Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales
 Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
Bulletin Independent prescribing information for NHS Wales October 2017 Chronic kidney disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term irreversible deterioration in the function of the kidneys, often
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline
 CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD
 Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Doncaster & Bassetlaw. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
Doncaster & Bassetlaw AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH AKI DETECTED IN PRIMARY CARE... 2 FLOW DIAGRAM: MANAGEMENT OF HYPERKALAEMIA.... 3 FLOW DIAGRAM:
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Clinical guideline Published: 23 July 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg182
 Chronic kidney disease in adults: assessment and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 July 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg182 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Chronic kidney disease in adults: assessment and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 July 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg182 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD
 Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Screen annually for patients with any of the following risk factors:
 CASE DEFINITION Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is either of the following, persisting for at least three months, repeated on at least two occasions: 1. Markers of kidney damage (e.g. proteinuria, haematuria
CASE DEFINITION Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is either of the following, persisting for at least three months, repeated on at least two occasions: 1. Markers of kidney damage (e.g. proteinuria, haematuria
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. AKI guidelines for primary care
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines AKI guidelines for primary care Contents: Flow Diagram: Recommended response time to AKI warning stage test results for adults in primary care 2 Table
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care
 Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
UPDATE. Northern Ireland Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 UPDATE Northern Ireland Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Practical Points for Use of Estimated GFR and Albuminuria (ACR) in Assessing CKD Developed by GAIN and the Northern
UPDATE Northern Ireland Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Practical Points for Use of Estimated GFR and Albuminuria (ACR) in Assessing CKD Developed by GAIN and the Northern
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) (Southampton pathway)
 Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
Background information Patient information Key messages for this pathway Definitions and abbreviations used in this pathway Classification of CKD Diagnosis of CKD Summary of referral criteria Screening
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012
 Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface. Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB
 CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
CKD at the primary and secondary care interface Paul Cockwell Consultant Nephrologist Clinical Service Lead Renal Medicine, QEHB The Health improvement Network (THIN): 6.7 million patients from 426 primary
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
What should you do next? Presenter Disclosure Information. Learning Objectives. Case: George
 2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach
 Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meetings 1 st and 2 nd September 2016 - London and Leeds Prof Sunil
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meetings 1 st and 2 nd September 2016 - London and Leeds Prof Sunil
Diabetes Mellitus. Eiman Ali Basheir. Mob: /1/2019
 Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi: /kisup
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions. Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist
 The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
The evidence base for interventions to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease: Medical interventions Jonathan Evans Paediatric Nephrologist CKD in adults Often unrecognised Preventable Major cardiovascular
keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: diuretics Drug monitoring Monitoring diuretics in primary care 2 March 2009 best tests Why do we monitor patients taking diuretics and what do we monitor? Monitoring a person on
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
CKD: An update on recent developments. Robert Lewis Wessex Kidney Centre
 CKD: An update on recent developments Robert Lewis Wessex Kidney Centre Anatomy and functions of the kidney Calyces Key functions of the kidney Renal artery Renal vein Ureter Cortex Renal pelvis Medulla
CKD: An update on recent developments Robert Lewis Wessex Kidney Centre Anatomy and functions of the kidney Calyces Key functions of the kidney Renal artery Renal vein Ureter Cortex Renal pelvis Medulla
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
Summary of recommendations
 Summary of recommendations Measuring blood pressure (BP) Use the recommended technique at every BP reading to ensure accurate measurements and avoid common errs. Pay particular attention to the following:
Summary of recommendations Measuring blood pressure (BP) Use the recommended technique at every BP reading to ensure accurate measurements and avoid common errs. Pay particular attention to the following:
Nephrology. 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan
 Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
Nephrology 3 rd Year Revision Session 06/05/17 Cathal Hannan Aims Acute Kidney Injury-recognition and management Sample OSCE Station Clinically relevant renal physiology Aetiology of Chronic Kidney Disease
Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance
 Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Fluid balance assessment (NICE CG 169) Assess the patient s likely fluid and electrolyte needs 1.History previous limited intake, thirst, abnormal
Acute Kidney Injury shared guidance Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Fluid balance assessment (NICE CG 169) Assess the patient s likely fluid and electrolyte needs 1.History previous limited intake, thirst, abnormal
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist
 Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care
 Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Patient details GP details Specialist details Name GP Name Dr Specialist Name Dr R. Horton
 Rationale for Initiation, Continuation and Discontinuation (RICaD) Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) For the treatment of symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (NICE TA388) This document
Rationale for Initiation, Continuation and Discontinuation (RICaD) Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto) For the treatment of symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (NICE TA388) This document
Management of Hypertension. M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine
 Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates January 2016 By Yunuo (Enora) Wu, PharmD Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as kidney damage (including structural or functional abnormalities) or glomerular filtration rate
Long-Term Care Updates January 2016 By Yunuo (Enora) Wu, PharmD Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as kidney damage (including structural or functional abnormalities) or glomerular filtration rate
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks
 Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
hypertension Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath
 hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 7/23/2013. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes
 Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes Paola Atallah, MD Lecturer of Clinical Medicine SGUMC EDL monthly meeting October 25,2016 Overview Physiopathology of hypertension Classification
Reframe the Paradigm of Hypertension treatment Focus on Diabetes Paola Atallah, MD Lecturer of Clinical Medicine SGUMC EDL monthly meeting October 25,2016 Overview Physiopathology of hypertension Classification
Transforming Diabetes Care
 Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care
 SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care Table of Contents Page 1 Key Messages 2 2 Introduction & Background 2 3 Relevant Guidelines & Standards 2 4 Scope of Service 3 5 Interdependencies
SERVICE SPECIFICATION 6 Conservative Management & End of Life Care Table of Contents Page 1 Key Messages 2 2 Introduction & Background 2 3 Relevant Guidelines & Standards 2 4 Scope of Service 3 5 Interdependencies
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression
 CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
Clinical guideline Published: 24 August 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg127
 Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 24 August 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg127 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 24 August 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg127 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital. New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty?
 Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD
 Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson
 The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT A NEW PARADIGM Aaron Cass, MD, FRCPC Nephrologist, Fraser Health January 22, 2014 Where Are We
The future is here. It s just not widely distributed yet. William Gibson CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE MANAGEMENT A NEW PARADIGM Aaron Cass, MD, FRCPC Nephrologist, Fraser Health January 22, 2014 Where Are We
in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease Summary of recommendations July 2017
 Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines
 Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines Abstract Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is often thought to be a relatively rare condition requiring specialist
Identification, management and referral of adults with chronic kidney disease: concise guidelines Abstract Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is often thought to be a relatively rare condition requiring specialist
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives
 Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives 1. Understand the impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) as a common condition of the adult US population.
Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives 1. Understand the impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) as a common condition of the adult US population.
DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES
 DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES 1 Dr.Mohamed Omar Shariff, 2 nd Year Post Graduate, Department of General Medicine. DR.B.R.Ambedkar Medical College & Hospital. 2 INTRODUCTION Leading cause of global
DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES 1 Dr.Mohamed Omar Shariff, 2 nd Year Post Graduate, Department of General Medicine. DR.B.R.Ambedkar Medical College & Hospital. 2 INTRODUCTION Leading cause of global
CLINICAL GUIDELINE. Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension.
 GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
DISCLOSURES OUTLINE OUTLINE 9/29/2014 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
JNC Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
 JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease
 Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease July 2017 Indranil Dasgupta DM FRCP, Debasish Banerjee MD
Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease July 2017 Indranil Dasgupta DM FRCP, Debasish Banerjee MD
Chronic Kidney Disease. Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic
 Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Outline. Outline 10/14/2014 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CKD IN THE CLINIC. Session Content. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD. CKD screening and referral
 CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
Factsheet Sacubitril valsartan (Entresto ) for chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 North Central London Joint Formulary Committee Factsheet Sacubitril valsartan (Entresto ) for chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Start date: July 2016 Review date: July 2019 Document
North Central London Joint Formulary Committee Factsheet Sacubitril valsartan (Entresto ) for chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Start date: July 2016 Review date: July 2019 Document
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points
 American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care
 Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
