Diabetes Mellitus. Eiman Ali Basheir. Mob: /1/2019
|
|
|
- Baldric Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: /1/2019
2 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss HbA1C and its significance. Discuss Laboratory tests to prevent and delay complications of diabetes mellitus.
3 Diagnosis of Diabetes Diagnosis cannot be made from: Blood glucose strips read visually or by a meter. Urine testing Glycosalated Haemoglobin - HbA1c
4 Diagnosis of Diabetes Two pieces of evidence required Symptoms Random Venous Plasma Glucose > 11.1 Fasting Venous Plasma Glucose > Hour Venous Plasma Glucose > 11.1 WHO 1999
5 Action following fasting venous plasma glucose Criteria have been recommended by NZGG for the diagnosis of diabetes, IGT and IFG. Normal Diabetes Fasting glucose result < Interpretation Normal result Borderline result IFG Diabetic Action Retest in five years or three years for those at risk. OGTT for those at increased risk of diabetes. Re-test annually those with IFG or IGT. Assess with OGTT. Re-test annually Two results > 7 on two different days are diagnostic of diabetes. OGTT is not required. Critieria for the diagnosis of diabetes, IGT and IFG (NZGG, 2003)
6 Glucose Tolerance Test 3 days of unrestricted diet and exercise Evening meal as normal the night before Overnight fast of 8-14 hours TEST Fasting blood on the morning Drink 75g of anhydrous glucose in ml water over 5 mins Blood sample 2 hours later No smoking during the test
7 (WHO,2006) DIAGNOSIS AFTER AN OGTT Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) Diabetes Fasting Venous Plasma Glucose 6.1 mmol/l to 6.9 mmol/l <7.0 mmol/l > 7.0 mmol/l 2 hr post < 7.8 mmo/l >7.8 mmol/l up to 11.1 mmol/l >11.1 mmol/l
8 Interpretation of the glucose tolerance test A 75 gram oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is used to follow up people with equivocal results who may have diabetes, IFG or IGT. Fasting mmol/l 2 hours post load mmol/l Normal < 5.5 and < 7.8 IFG and < 7.8 IGT < 7.0 and Diabetes mellitus 7.0 and/or 11.1 GDM 5.5 and/or 9.0 Diagnosis of diabetes, IGT and IFG
9 Gestational diabetes mellitus Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) increases the risk of many foetal and maternal complications in pregnancy and the development of type 2 diabetes later in life. Screening is currently recommended for all women between weeks gestation. Screening for GDM using 50 gram load If the one hour blood glucose is 7.8 mmol/l, a two hour OGTT is performed. OGTT for diagnosis of GDM A fasting glucose 5.5 and/or a 2 hour value 9.0 mmol/l is diagnostic of GDM.
10 Impaired Glucose Regulation Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) - Abnormalities in glucose regulation in the postprandial state. - More common in women Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) - Elevated fasting glucose concentrations, but lower than those required to diagnose diabetes - More common in men
11 Impaired Glucose Regulation IFG and IGT are not interchangeable. Both can lead to diabetes or revert to normoglycaemia Both are associated with an increased risk of Cardiovascular disease Identify & Read Code Adhere to local guidelines regarding follow up
12 HbA1c Criteria Recently agreed by WHO & Diabetes UK Provides positive identification (ie specific) - If Hba1c > 48mmol/mol, twice or once in prescence of osmotic symptoms, and - if no confounding clinical problems Fails to rule out normality - Hba1c <48mmol/mol does not rule out diabetes - glucose criteria then remain essential Algorithm not widely agreed. Awaiting WEDS approval.
13 HbA1c > 48mmol/mol Symptomatic Asymptomatic Repeat within 2 weeks HbA1c > 48mmol/mol Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
14 HbA1c < 47mmol/mol Does not exclude Diabetes Hba1c 42 47mmol/mol Lifestyle changes & monitor at least annually Symptoms present exclude diabetes using conventional glucose tests
15 Under 18yrs Do not use HbA1c Possible Type 1 Where glucose may rise rapidly e.g.: steroids, antipsychotics. Reduced red cell survival e.g. haemolytic anaemia Gestational Diabetes Pancreatic damage/surgery Anaemia/Haemoglobinopathy
16 Use HbA1c for patients under investigation, or annual assessment of at risk groups including IFG / IGT Metabolic syndrome PMH Gestational Diabetes or large for dates baby (>4kg) Established Vascular disease CVA, IHD, PVD Age > 45 plus +ve Family history Age > 40 (or >30 if Asian or Pacific island descent) with hypertension & BMI>30 PCOS
17 Do Not Use HbA1c as it is unreliable as a screening tool in: Anyone under age 18 Possible Type 1 Diabetes, e.g. Symptoms of Diabetes for under 2 months or clinically unwell Situations where glucose may rise rapidly e.g. patient on atypical antipsychotics, steroids Patients known to have reduced red cell survival e.g. haemolytic anaemia Gestational diabetes Acute pancreatic damage / pancreatic surgery Anaemia / Haemoglobinopathy
18 WHO recommendation HbA1c can be used as a diagnostic test for diagnosing diabetes providing Stringent quality assurance tests are in place Assays are standardised to criteria aligned to the international reference values There are no conditions present which precludes its accurate measurement An Hba1c of 48mmol/mol (6.5%) is recommended as the cut point for diagnosing Diabetes. A value of less than 48 mmol/mol (6.5%) does not exclude diabetes, which can still be diagnosed using glucose tests.
19 Notes Caution: HbA1c should not be used to assess glycaemic status 6 weeks post partum use OGTT HbA1c can also be elevated by: Age. HbA1c is 4.5 mmol/mol higher at 70 than 40 years of age, Ethnicity. Afro-Caribbean and South Asians HbA1c is 4.5 mmol/mol higher than comparable Caucasians
20 Self monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) People who take insulin should regularly self monitor blood glucose. For people with non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes testing is most useful if patients use the results to learn and alter behaviour, or medication....smbg is most useful if patients use the results to learn, as part of an overall diabetes education package.
21 Laboratory tests to prevent and delay complications of diabetes People with diabetes usually die from macrovascular complications of their diabetes; namely cardiovascular disease. This is influenced by all of the commonly recognised risk factors for cardiovascular disease as well as glycaemic control. Fasting lipid levels are measured three monthly until stable and then 6-12 monthly thereafter. Parameter Total cholesterol LDL cholesterol HDL cholesterol Optimal value < 4 mmol/l < 2.5 mmol/l > 1 mmol/l It is important that management should be individualised TC:HDL ratio < 4.5 Triglycerides < 1.7 mmol/l HbA 1C < 7 mmol/l
22 Diabetic renal disease The best way of testing for diabetic renal disease is by urinary albumin:creatinine ratio (ACR) and serum creatinine with estimated glomerular filtration rate (egfr). These tests are performed on everyone with diabetes at diagnosis and repeated at least annually more frequently if there is proteinuria, microalbuminuria or reduced egfr.
23 Albumin:creatinine ratio ACR provides an estimate of daily urinary albumin excretion. Microalbuminuria cannot be detected on a conventional urinary protein dip stick. Microalbuminuria is urinary albumin excretion between 30 and 300 mg/day; above 300mg/day represents proteinuria. ACR is best measured in the laboratory using a first morning urine sample where possible when the patient is well. An abnormal initial test requires confirmation by testing on two further occasions. If at least one of these tests is positive microalbuminuria has been confirmed.
24 Renal testing in diabetes ACR mg/mmol (confirmed) egfr ml/min/ Risk Management men < 2.5 women < 3.5 and > % per year progress to microalbuminuria. Annual ACR and egfr. Good diabetes & BP management. men 2.5 women 3.5 or < 60 One third progress to overt nephropathy. CVD risk doubled. Review ACR and egfr at each visit. Intensive management of glycaemia and CVD risk factors. Use ACE inhibitor and low-dose aspirin. Avoid nephrotoxic drugs. Investigate if suspicious of causes other than diabetes* > 30 or < 30 Almost all proceed to end stage renal disease or die prematurely of CVD. Overt nephropathy Refer specialist *Non-diabetic renal disease is suspected when there is absence of diabetic retinopathy in a person with renal disease, there are urinary abnormalities such as haematuria or casts, or when there is renal disease without microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
25 Other Tests Testing of LFTs is recommended for people with diabetes: at diagnosis, at the start of antidiabetic drug therapy, and at any other time indicated by clinical judgement Other laboratory tests In patients with type 1 diabetes, intermittent checks for other autoimmune conditions may be useful. This could include testing for thyroid dysfunction or coeliac disease.
26 Key points Fasting morning venous glucose is the best initial test for diagnosing diabetes. An oral glucose tolerance test is reserved for people with equivocal fasting glucose results. Patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose benefit from lifestyle intervention and annual review. HbA 1C is the best test of glycaemic control in diabetes. Patients with diabetes benefit from aggressive monitoring and management of all cardiovascular risk factors.
27 Thank you
bpac better e m dicine
 bpac nz better medicin e bpac nz Development Team: Rachael Clarke Sonia Ross Dr Trevor Walker David Woods bpac nz Clinical Advisory Group (laboratory programme): Tracey Barron Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele
bpac nz better medicin e bpac nz Development Team: Rachael Clarke Sonia Ross Dr Trevor Walker David Woods bpac nz Clinical Advisory Group (laboratory programme): Tracey Barron Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele
NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde Managed Clinical Network for Diabetes
 Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde Managed Clinical Network for Diabetes Lead Authors: Dr Brian Kennon, Dr David Carty June 2015 Review due: December 2016 Diagnosis
Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde Managed Clinical Network for Diabetes Lead Authors: Dr Brian Kennon, Dr David Carty June 2015 Review due: December 2016 Diagnosis
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Over the years, high blood glucose damages nerves and blood vessels, which can
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Over the years, high blood glucose damages nerves and blood vessels, which can
CLINICAL AUDIT. Laboratory Testing in. Diabetes. in Primary Care
 CLINICAL AUDIT Laboratory Testing in Diabetes in Primary Care Valid to November 2013 bpac nz better medicin e Background Regular health checks are essential for people with diabetes to reduce the frequency
CLINICAL AUDIT Laboratory Testing in Diabetes in Primary Care Valid to November 2013 bpac nz better medicin e Background Regular health checks are essential for people with diabetes to reduce the frequency
Dr Aftab Ahmad Consultant Diabetologist at Royal Liverpool University Hospital Regional Diabetes Network Lead
 Dr Aftab Ahmad Consultant Diabetologist at Royal Liverpool University Hospital Regional Diabetes Network Lead Today s Presentation HbA1c & diagnosing Diabetes What is Impaired Glucose & IGR? Implications
Dr Aftab Ahmad Consultant Diabetologist at Royal Liverpool University Hospital Regional Diabetes Network Lead Today s Presentation HbA1c & diagnosing Diabetes What is Impaired Glucose & IGR? Implications
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS. Author: Josephine Davis
 DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES
 Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES Objectives u At conclusion of the lecture the participant will be able to: 1. Differentiate between the classifications of diabetes
Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES Objectives u At conclusion of the lecture the participant will be able to: 1. Differentiate between the classifications of diabetes
Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes?
 Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes? Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board Mercy Specialist Centre Case 1: A 24 year old stockcar driver presents
Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes? Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board Mercy Specialist Centre Case 1: A 24 year old stockcar driver presents
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose).
 DIABETES WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
DIABETES WHAT IS DIABETES? Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2016
 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2016 Care Delivery Systems 33-49% of patients still do not meet targets for A1C, blood pressure, or lipids. 14% meet targets for all A1C, BP, lipids, and nonsmoking
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2016 Care Delivery Systems 33-49% of patients still do not meet targets for A1C, blood pressure, or lipids. 14% meet targets for all A1C, BP, lipids, and nonsmoking
GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST: FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES MELLITUS
 Title of Document: Glucose tolerance test: For Diagnosis of Mellitus Authoriser: Leila Cornes Page 1 of 6 GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST: FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES MELLITUS Introduction In most cases mellitus
Title of Document: Glucose tolerance test: For Diagnosis of Mellitus Authoriser: Leila Cornes Page 1 of 6 GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST: FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES MELLITUS Introduction In most cases mellitus
American Academy of Insurance Medicine
 American Academy of Insurance Medicine October 2012 Dr. Alison Moy Liberty Mutual Dr. John Kirkpatrick Thrivent Financial for Lutherans 1 59 year old male, diagnosed with T2DM six months ago Nonsmoker
American Academy of Insurance Medicine October 2012 Dr. Alison Moy Liberty Mutual Dr. John Kirkpatrick Thrivent Financial for Lutherans 1 59 year old male, diagnosed with T2DM six months ago Nonsmoker
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
Diabetic Nephropathy Outline Introduction of diabetic nephropathy Manifestations of diabetic nephropathy Staging of diabetic nephropathy Microalbuminuria Diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy Treatment of
PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT
 PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT Conversion table for HbA1c% to mmol/mol Old DCCT aligned HbA1c(%) New IFCC HbA1c (mmol/mol) 4.0 20 5.0 31 6.0 42 6.5 48 7.0 53 7.5 59 8.0 64 9.0 75 10.0 86
PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT Conversion table for HbA1c% to mmol/mol Old DCCT aligned HbA1c(%) New IFCC HbA1c (mmol/mol) 4.0 20 5.0 31 6.0 42 6.5 48 7.0 53 7.5 59 8.0 64 9.0 75 10.0 86
DIABETES 20/02/2014 WHAT IS DIABETES? GLUCOSE WHAT IS DIABETES? GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS GLUCOSE METABOLISM
 WHAT IS DIABETES? DIABETES Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
WHAT IS DIABETES? DIABETES Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Chronic metabolic disorder with a predisposition of hyperglycaemia (increased blood glucose). Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Condition in which the body has lack
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
CLINICAL GUIDELINE. Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension.
 GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
GUIDELINE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Document No:CG38 *All Sites Management of adult patients referred to South Tees University Hospitals for hypertension. TITLE Management of adult patients referred to South
STANDARDS OF MEDICAL CARE IN DIABETES 2014
 STANDARDS OF MEDICAL CARE IN DIABETES 2014 I. CLASSIFICATION AND DIAGNOSIS Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes β-cell destruction Type 2 diabetes Progressive insulin secretory defect Other specific
STANDARDS OF MEDICAL CARE IN DIABETES 2014 I. CLASSIFICATION AND DIAGNOSIS Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes β-cell destruction Type 2 diabetes Progressive insulin secretory defect Other specific
Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents
 Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents Disclosures Paid consultant, Eli Lilly, Inc, Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Trials Outline The burden of diabetes Treatment and Prevention Youth Diabetes Prevention Clinic
Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents Disclosures Paid consultant, Eli Lilly, Inc, Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Trials Outline The burden of diabetes Treatment and Prevention Youth Diabetes Prevention Clinic
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital. New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty?
 Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) - Dr Hiren Patt
 Diabetes Mellitus (DM) - Dr Hiren Patt What is DM? FPG 2-Hour PG on OGTT Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus 126 mg/dl 100 mg/dl Impaired Fasting Glucose 200 mg/dl 140 mg/dl Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) - Dr Hiren Patt What is DM? FPG 2-Hour PG on OGTT Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus 126 mg/dl 100 mg/dl Impaired Fasting Glucose 200 mg/dl 140 mg/dl Impaired Glucose Tolerance
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
Case studies diabetes and complications. The role of the diabetes team.
 Case studies diabetes and complications The role of the diabetes team. This afternoon: Brief overview of diabetes: The size of the problem diagnosis type 1 and type 2 Brief overview of diabetic complications
Case studies diabetes and complications The role of the diabetes team. This afternoon: Brief overview of diabetes: The size of the problem diagnosis type 1 and type 2 Brief overview of diabetic complications
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
RCHC Clinical Guidelines Type 2 Diabetes; Adults
 RCHC Clinical Guidelines Type 2 Diabetes; Adults Screening for diabetes in asymptomatic adults 1 Population: Aged > 45 years; Aged < 45 years who are overweight (BMI> 25kg/m 2 ) and have an additional
RCHC Clinical Guidelines Type 2 Diabetes; Adults Screening for diabetes in asymptomatic adults 1 Population: Aged > 45 years; Aged < 45 years who are overweight (BMI> 25kg/m 2 ) and have an additional
Objectives. Objectives. Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015
 Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015 Presentation downloaded from http://ce.unthsc.edu Objectives Understand that the obesity epidemic is also affecting children and adolescents
Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015 Presentation downloaded from http://ce.unthsc.edu Objectives Understand that the obesity epidemic is also affecting children and adolescents
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Adolescent renal and cardiovascular disease protection in type 1 diabetes AdDIT Study
 Keystone, Colorado, July 2013 Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care Adolescent renal and cardiovascular disease protection in type 1 diabetes AdDIT Study Professor David Dunger Department
Keystone, Colorado, July 2013 Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care Adolescent renal and cardiovascular disease protection in type 1 diabetes AdDIT Study Professor David Dunger Department
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management
 Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES
 RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES Risk Factors or Complications Glycemic Control Fasting & Capillary Plasma Glucose Anti-platelet
RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES Risk Factors or Complications Glycemic Control Fasting & Capillary Plasma Glucose Anti-platelet
TUE Physician Guidelines Medical Information to Support the Decisions of TUE Committees Diabetes Mellitus DIABETES MELLITUS
 DIABETES MELLITUS 1. Introduction Diabetes is a global epidemic with 415 million people affected worldwide equivalent to the total population of the USA, Canada and Mexico. In recognition of this, the
DIABETES MELLITUS 1. Introduction Diabetes is a global epidemic with 415 million people affected worldwide equivalent to the total population of the USA, Canada and Mexico. In recognition of this, the
Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy
 Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy Sridhar Chitturi Consultant Endocrinologist Royal Darwin Hospital Outline of the talk Diabetes in Pregnancy Spectrum Diagnostic criteria Why bother about
Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy Sridhar Chitturi Consultant Endocrinologist Royal Darwin Hospital Outline of the talk Diabetes in Pregnancy Spectrum Diagnostic criteria Why bother about
Living Well with Diabetes
 Living Well with Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes Overview Diabetes is a disorder of the way the body uses food for growth and energy. Most of the food people eat is broken down into glucose, the form
Living Well with Diabetes What is diabetes? Diabetes Overview Diabetes is a disorder of the way the body uses food for growth and energy. Most of the food people eat is broken down into glucose, the form
DIABETES WITH PREGNANCY
 DIABETES WITH PREGNANCY Prof. Aasem Saif MD,MRCP(UK),FRCP (Edinburgh) Maternal and Fetal Risks Diabetes in pregnancy is associated with risks to the woman and to the developing fetus. Maternal and Fetal
DIABETES WITH PREGNANCY Prof. Aasem Saif MD,MRCP(UK),FRCP (Edinburgh) Maternal and Fetal Risks Diabetes in pregnancy is associated with risks to the woman and to the developing fetus. Maternal and Fetal
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Personal Diabetes Passport
 Personal Diabetes Passport Contact information: Name: Physician: Diabetes Education Centre: Dietitian: Ophthalmologist: Chiropodist: Type of Diabetes: Type 1 (T1DM) Increased risk for diabetes Type 2(T2DM)
Personal Diabetes Passport Contact information: Name: Physician: Diabetes Education Centre: Dietitian: Ophthalmologist: Chiropodist: Type of Diabetes: Type 1 (T1DM) Increased risk for diabetes Type 2(T2DM)
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
 Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide NOVEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
HIHIM Clinical Cocepts for Managers 7/31/2009. Fernando Vega, MD 1
 Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 July 31, 2008 Hyperglycemia characterized by relative or absolute lack of insulin secretion Varying degrees of insulin resistance Often associated with symptoms: polyruia, polydipsia,
Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 July 31, 2008 Hyperglycemia characterized by relative or absolute lack of insulin secretion Varying degrees of insulin resistance Often associated with symptoms: polyruia, polydipsia,
CVD, diabetes renal disease
 Testing for CVD, diabetes renal disease and in elderly people As people age and their co-morbidities and medicine use increases, decisions about medical management change. There is limited evidence of
Testing for CVD, diabetes renal disease and in elderly people As people age and their co-morbidities and medicine use increases, decisions about medical management change. There is limited evidence of
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes is a chronic illness that requires
 P O S I T I O N S T A T E M E N T Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION Diabetes is a chronic illness that requires continuing medical care and patient
P O S I T I O N S T A T E M E N T Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION Diabetes is a chronic illness that requires continuing medical care and patient
Metabolic Syndrome. Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah
 Metabolic Syndrome Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah Objectives Be able to outline the pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome Be able to list diagnostic criteria for
Metabolic Syndrome Bill Roberts, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pathology University of Utah Objectives Be able to outline the pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome Be able to list diagnostic criteria for
MPharmProgramme. Hypertension (HTN)
 MPharmProgramme Hypertension (HTN) Slide 1 of 30 Overview Definition Prevalence Type Causes Diagnosis Management Patients perspective Slide 2 of 30 Definition It is not a disease! So what is it? What two
MPharmProgramme Hypertension (HTN) Slide 1 of 30 Overview Definition Prevalence Type Causes Diagnosis Management Patients perspective Slide 2 of 30 Definition It is not a disease! So what is it? What two
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
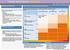 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes
 Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes. Learning Outcomes. Type 2 Diabetes. Senga Hunter Community Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes Senga Hunter Community Diabetes Specialist Nurse Learning Outcomes Understand why blood monitoring is necessary Understand the blood tests for monitoring diabetes Understand
Monitoring in Type 2 Diabetes Senga Hunter Community Diabetes Specialist Nurse Learning Outcomes Understand why blood monitoring is necessary Understand the blood tests for monitoring diabetes Understand
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes Routine cases and Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia adapted with permission from Royal Devon and Exeter
 Diagnostic criteria for diabetes Routine cases and Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia adapted with permission from Royal Devon and Exeter Diabetes may be diagnosed on any of the following criteria (WHO 2006,
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes Routine cases and Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia adapted with permission from Royal Devon and Exeter Diabetes may be diagnosed on any of the following criteria (WHO 2006,
Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better?
 Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010
 E X E C U T I V E S U M M A R Y Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Current criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes A1C 6.5%: The test should be performed in a laboratory using
E X E C U T I V E S U M M A R Y Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Current criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes A1C 6.5%: The test should be performed in a laboratory using
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES IN PREGNANCY
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES IN PREGNANCY Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Endocrine & Metabolic Society Perinatal Society of Malaysia Family Medicine Specialists Association of Malaysia Academy of Medicine
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES IN PREGNANCY Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Endocrine & Metabolic Society Perinatal Society of Malaysia Family Medicine Specialists Association of Malaysia Academy of Medicine
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
ATHLETES & PRESCRIBING PHYSICIANS PLEASE READ
 ATHLETES & PRESCRIBING PHYSICIANS PLEASE READ USADA can grant a Therapeutic Use Exemption (TUE) in compliance with the World Anti- Doping Agency International Standard for TUEs. The TUE application process
ATHLETES & PRESCRIBING PHYSICIANS PLEASE READ USADA can grant a Therapeutic Use Exemption (TUE) in compliance with the World Anti- Doping Agency International Standard for TUEs. The TUE application process
Information for people with diabetes. diabetes. glossary of. terms
 Information for people with diabetes i diabetes glossary of terms Diabetes is a common condition, which most people have some understanding of, but when you listen to people talk about it, you may feel
Information for people with diabetes i diabetes glossary of terms Diabetes is a common condition, which most people have some understanding of, but when you listen to people talk about it, you may feel
There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks.
 Diabetes Clinical update There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks. Changes in the diagnosis of diabetes a) HbA1C Since 2011, World Health Organisation
Diabetes Clinical update There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks. Changes in the diagnosis of diabetes a) HbA1C Since 2011, World Health Organisation
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management
 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management Michael King, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director University of Kentucky Dept. of Family & Community Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Review
Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management Michael King, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director University of Kentucky Dept. of Family & Community Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Review
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS
 IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) and Diabetes in Pregnancy: Diagnostic Recommendations, NSLHD
 Guideline Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) and Diabetes in Pregnancy: Diagnostic Document Number GE2017_003 Publication Date 31 January 2017 Intranet location/s Summary Author Department Contact (Details)
Guideline Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) and Diabetes in Pregnancy: Diagnostic Document Number GE2017_003 Publication Date 31 January 2017 Intranet location/s Summary Author Department Contact (Details)
Diabetes: Staying Two Steps Ahead. The prevalence of diabetes is increasing. What causes Type 2 diabetes?
 Focus on CME at the University of University Manitoba of Manitoba : Staying Two Steps Ahead By Shagufta Khan, MD; and Liam J. Murphy, MD The prevalence of diabetes is increasing worldwide and will double
Focus on CME at the University of University Manitoba of Manitoba : Staying Two Steps Ahead By Shagufta Khan, MD; and Liam J. Murphy, MD The prevalence of diabetes is increasing worldwide and will double
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
The York Diabetes Care Model
 This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
Pre-diabetes. Dr Neel Basudev. GPSI Lambeth DICT, Diabetes Lead Lambeth CCG
 Pre-diabetes Dr Neel Basudev GPSI Lambeth DICT, Diabetes Lead Lambeth CCG The Prevention of Diabetes Where has this come from? Pre-diabetes mellitus (PDM) Term introduced by Tommy G. Thompson (Health &
Pre-diabetes Dr Neel Basudev GPSI Lambeth DICT, Diabetes Lead Lambeth CCG The Prevention of Diabetes Where has this come from? Pre-diabetes mellitus (PDM) Term introduced by Tommy G. Thompson (Health &
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Blood Pressure Measurement (children> 3 yrs)
 Blood Pressure Measurement (children> 3 yrs) If initial BP elevated, repeat BP manually 2x and average, then classify Normal BP Systolic and diastolic
Blood Pressure Measurement (children> 3 yrs) If initial BP elevated, repeat BP manually 2x and average, then classify Normal BP Systolic and diastolic
Diabetes is a chronic illness that
 Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Originally approved 1988. Most recent review/revision, October 2001 Abridged from Diabetes Care 25:213 229, 2002. Full text of this position
Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Originally approved 1988. Most recent review/revision, October 2001 Abridged from Diabetes Care 25:213 229, 2002. Full text of this position
Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
 Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus American Diabetes Association Originally approved 1988. Most recent review/revision, October 2002. Abridged from Diabetes Care 26 (Suppl. 1):S33
Standards of Medical Care for Patients With Diabetes Mellitus American Diabetes Association Originally approved 1988. Most recent review/revision, October 2002. Abridged from Diabetes Care 26 (Suppl. 1):S33
WILL YOU USE HBA1C TO SCREEN & MONITOR DIABETES? Dr. Amany Mousa
 WILL YOU USE HBA1C TO SCREEN & MONITOR DIABETES? Dr. Amany Mousa Diabetes is clinically well defined by glycation of proteins 1. True 2. false So far, diabetes has been defined as a clinical condition
WILL YOU USE HBA1C TO SCREEN & MONITOR DIABETES? Dr. Amany Mousa Diabetes is clinically well defined by glycation of proteins 1. True 2. false So far, diabetes has been defined as a clinical condition
Clinical Practice Guideline Key Points
 Clinical Practice Guideline Key Points Clinical Practice Guideline 2008 Key Points Diabetes Mellitus Provided by: Highmark Endocrinology Clinical Quality Improvement Committee In accordance with Highmark
Clinical Practice Guideline Key Points Clinical Practice Guideline 2008 Key Points Diabetes Mellitus Provided by: Highmark Endocrinology Clinical Quality Improvement Committee In accordance with Highmark
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
Standard Operating Procedure 11. Completion of DAFNE Data Collection: Full Post Course Form F04.010, Version 8
 Standard Operating Procedure 11 Completion of DAFNE Data Collection: Full Post Course Form F04.010, Version 8 Date Version Issue Review Contact Approved Date Date Person October 2013 9 October 2013 March
Standard Operating Procedure 11 Completion of DAFNE Data Collection: Full Post Course Form F04.010, Version 8 Date Version Issue Review Contact Approved Date Date Person October 2013 9 October 2013 March
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Primary Prevention Patients aged 85yrs and over
 Rotherham Guideline for the management of Non-Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Type 1 Diabetes Offer lifestyle advice Over 40yrs of age? Diabetic for more than 10 years? Established nephropathy? Other CVD
Rotherham Guideline for the management of Non-Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Type 1 Diabetes Offer lifestyle advice Over 40yrs of age? Diabetic for more than 10 years? Established nephropathy? Other CVD
28-Aug-15. RACGP guidelines 2014/15. ADS guidelines Part 1 T2D Guidelines. Part 2 What comes after metformin?
 Part 1 T2D Guidelines Oral therapies in T2 diabetes Dr Gary Kilov T2D Guidelines - What s New? What comes after metformin? 1 RACGP guidelines 2014/15 ADA-EASD: Anti-Hyperglycaemic therapy 2015 3 4 Inzucchi
Part 1 T2D Guidelines Oral therapies in T2 diabetes Dr Gary Kilov T2D Guidelines - What s New? What comes after metformin? 1 RACGP guidelines 2014/15 ADA-EASD: Anti-Hyperglycaemic therapy 2015 3 4 Inzucchi
Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy)
 Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy) Patient information Oxford Kidney Unit If you have been told you have chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetic nephropathy this leaflet
Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy) Patient information Oxford Kidney Unit If you have been told you have chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetic nephropathy this leaflet
Metabolic Syndrome. Shon Meek MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Florida Endocrinology
 Metabolic Syndrome Shon Meek MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Florida Endocrinology Disclosure No conflict of interest No financial disclosure Does This Patient Have Metabolic Syndrome? 1. Yes 2. No Does This Patient
Metabolic Syndrome Shon Meek MD, PhD Mayo Clinic Florida Endocrinology Disclosure No conflict of interest No financial disclosure Does This Patient Have Metabolic Syndrome? 1. Yes 2. No Does This Patient
Management of diabetes
 116 Management of diabetes A national clinical guideline March 2010 Updated November 2017 KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND GRADES OF RECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High quality meta-analyses, systematic
116 Management of diabetes A national clinical guideline March 2010 Updated November 2017 KEY TO EVIDENCE STATEMENTS AND GRADES OF RECOMMENDATIONS LEVELS OF EVIDENCE High quality meta-analyses, systematic
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Standards of Medical Care In Diabetes
 Standards of Medical Care In Diabetes - 2017 Robert E. Ratner, MD, FACP, FACE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University School of Medicine Disclosed no conflict of interest Standards of Care Professional.diabetes.org/SOC
Standards of Medical Care In Diabetes - 2017 Robert E. Ratner, MD, FACP, FACE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University School of Medicine Disclosed no conflict of interest Standards of Care Professional.diabetes.org/SOC
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
NHS Highland Diabetes Managed Clinical Network Newsletter. Welcome to this issue of the NHS Highland Diabetes MCN Newsletter. (October 2016).
 Welcome to this issue of the NHS Highland Diabetes MCN Newsletter In this issue: (October 2016). 1. Local Diabetes MCN Update 2. SCI Diabetes 3. Education Sessions for 2016 4. HbA1c for Diagnosis Agreed
Welcome to this issue of the NHS Highland Diabetes MCN Newsletter In this issue: (October 2016). 1. Local Diabetes MCN Update 2. SCI Diabetes 3. Education Sessions for 2016 4. HbA1c for Diagnosis Agreed
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Type 2 diabetes. Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Type 2 diabetes Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline NOTE: NICE is unable to accept comments from non-registered organisations or individuals. If you wish
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Type 2 diabetes Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline NOTE: NICE is unable to accept comments from non-registered organisations or individuals. If you wish
HbA1c for Diagnosis (including pregnancy and in children). Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney
 HbA1c for Diagnosis (including pregnancy and in children). Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney DECLARATION OF INTEREST/DISCLOSURES Nil I acknowledge and thank Prof David
HbA1c for Diagnosis (including pregnancy and in children). Aidan McElduff The Discipline of Medicine, The University of Sydney DECLARATION OF INTEREST/DISCLOSURES Nil I acknowledge and thank Prof David
GESTATIONAL DIABETES for GP Obstetric Shared Care Accreditation Seminar. Simon Kane March 2016
 GESTATIONAL DIABETES for GP Obstetric Shared Care Accreditation Seminar Simon Kane March 2016 Objectives History and definitions Definition and Australian data Pathophysiology and prevalence Rationale
GESTATIONAL DIABETES for GP Obstetric Shared Care Accreditation Seminar Simon Kane March 2016 Objectives History and definitions Definition and Australian data Pathophysiology and prevalence Rationale
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral
 Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient
 Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Diabetic Retinopathy: a case study David Garland NP
 Diabetic Retinopathy: a case study David Garland NP Financial disclosure With 3 daughters I don t have any finances The patient Joe 45 year old Polynesian man with hx of diabetic retinopathy Routine f/up
Diabetic Retinopathy: a case study David Garland NP Financial disclosure With 3 daughters I don t have any finances The patient Joe 45 year old Polynesian man with hx of diabetic retinopathy Routine f/up
Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain
 control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome. Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group
 Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group Conflict of interest regarding this presentation: I have no conflict of interest to
Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group Conflict of interest regarding this presentation: I have no conflict of interest to
Diabetes. Ref HSCW 024
 Diabetes Ref HSCW 024 Why is it important? Diabetes is an increasingly common, life-long, progressive but largely preventable health condition affecting children and adults, causing a heavy burden on health
Diabetes Ref HSCW 024 Why is it important? Diabetes is an increasingly common, life-long, progressive but largely preventable health condition affecting children and adults, causing a heavy burden on health
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Guiding Principles. for Diabetes Care: For Health Care. Providers
 Guiding Principles N A T I O N A L for Diabetes Care: D I A B E T E S For Health Care E D U C A T I O N Providers P R O G R A M The National Diabetes Education Program (NDEP) has developed these Guiding
Guiding Principles N A T I O N A L for Diabetes Care: D I A B E T E S For Health Care E D U C A T I O N Providers P R O G R A M The National Diabetes Education Program (NDEP) has developed these Guiding
Diabetes Summary of Medical Guidelines
 Diabetes Summary of Medical Guidelines Key concepts in setting glycemic controls: goals should be individualized; certain populations (children, pregnant women, and elderly) require special considerations;
Diabetes Summary of Medical Guidelines Key concepts in setting glycemic controls: goals should be individualized; certain populations (children, pregnant women, and elderly) require special considerations;
Indicator Points Payment stages. HF 1: The practice can produce a register of patients with 4 heart failure
 Heart failure Indicator Points Payment stages Records HF 1: The practice can produce a register of patients with 4 heart failure Initial diagnosis HF 2: The percentage of patients with a diagnosis of heart
Heart failure Indicator Points Payment stages Records HF 1: The practice can produce a register of patients with 4 heart failure Initial diagnosis HF 2: The percentage of patients with a diagnosis of heart
