International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research Vol. 3, Issue 02, pp , June, 2018 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research Vol. 3, Issue 02, pp , June, 2018 DOI: /IJHMCR Article can be accessed online on: ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH MEDICINE AND CURRENT RESEARCH EPITHELIAL CELL REGENERATION OF GASTRIC MUCOSA IN RAT (Rattus novergicus) CAUSED BY A TRADITIONAL ALCOHOLIC DRINK, SOPI TREATED WITH RED FRUIT (Pandanus conoideus Lam) Michavel Moniharapon 1, Jantje Wiliem Souhaly 2, Pieter Kakisina 1,2,3* 1 Jurusan Biologi, FMIPA, Universitas Pattimura, Jl. Ir. Martinus Putuhena, Poka, Ambon, Indonesia Laboratorium Zoologi Jurusan Biologi, FMIPA, Universitas Pattimura, Ambon, Indonesia Laboratorium Ilmu Faal Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, East Java Province, Indonesia ARTICLE INFO Article History: Received 26th March, 2018 Received in revised form 30th April, 2018 Accepted 31th Mei, 2018 Published online 30th June, 2018 Key words: Red Fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam), tocoferol, sopi, gastric mucosa. *Correspondence to Author: Pieter Kakisina Jurusan Biologi, FMIPA, Universitas Pattimura, Jl. Ir. Martinus Putuhena, Poka, Ambon, Indonesia paet_kakisina@yahoo.com ABSTRACT Red Fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam) is one type of plant that contains antioxidant of tocoferol, alfatocoferol, and betacaroten, which supposedly netralizise free radical and heal gastric mucosa damaged in white rat (Rattus novergicus) which induced by a Maluku alcoholic drink called as sopi. This research was perfomed to investigate the effect of red fruit in gastric mucosa of rat which is induced by sopi. Mice with an average weight of 200 grams were given a dose of 2.5 ml/200g BB twice daily for 60 days. Then the Rattus novergicus was given the red fruit at a dose of 0.2 ml/200g BB, 0.4 ml/200g BB, and 0.6 ml/200g BB twice daily for 30 days, respectively. The results of this study indi`cate that the effect of red fruit was found to histology of the mucosal gastric of the mice. Provision of the Pandanus conoideus Lam with an effective dose of 0.6 ml/200g BB of mucosal gastric was repaired. While ulcer gastric of the Rattus novergicus were exposed to the type of sopi. Copyright 2018, Pieter Kakisina. This is an open access article distributed under the creative commons attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Citation: Michavel Moniharapon 1, Jantje Wiliem Souhaly 2, Pieter Kakisina 1,2,3*, 2018 Epithelial Cell Regeneration Of Gastric Mucosa In Mice (Rattus Novergicus) Caused By A Traditional Alcoholic Drink, Sopi Treated With Red Fruit (Pandanus Conoideus Lam), International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research, 3, (02), INTRODUCTION In Indonesia, there are few regional alcoholic drinks such as liquid brem, tuak, saguer, and ciu [1]. One of Maluku province local alcoholic drink International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 882
2 fabricated traditionally was sopi. This sopi was produced by people living on the hills part of Ambon island, the capital city of Maluku province, Seram island,and South west of Maluku, respectively. In Maluku, sopi was normally produced for the traditional culture celebrations and parties in almost all part of Maluku areas. A long term consuming of alcoholic drink will cause a heart failure, hypertency, stroke, liver failure, stomach aches, gastric failures, and a decreased of reproducity system. Furthermore, the overdoses of alcohol consumption can damage brain system as a result of the decreasing of the ability to memorize something, and to concentrate [2]. It is wel-known that the fast absorption of alcohol was happened through gastric and smooth intestine to the blood flow, and then the whole body [3]. In addition, alcohol can damage mucosa gastric due to its fast penetration in it by relasing free radial substance so that there is a network broken of the gastric especially on blood vein and parietal cell inside the gastric with an indicator of damaging cell [4-6]. Gastric is an important organ to react with HCL, and protein enzymes. Not all free radial substances in the body are bad. During a certain conditions, such free radials are needed, for example: in killing bacteria. Therefore, the free radials must be controlled by an antioxidant of the body. Antioxidant is a wanted substance to the body to neutralize the free radials, and protect the broken cells in the body. The antioxidant could be an enzyme such as catalace. Beside of that, there are another non-enzymatic antioxidants. These antioxidants can be vitamins C, E, A, and beta-carotene. Most of these substances are exist in red fruit (Pandanus conoideus). The red fruit contains chemical active substances such as β-carotene, tocopherol, oleat acid, linoleat acid of Omega-9, linoleat acid of Omega-3, and decanoat [7]. Such active substances are important in improving the immune system of the body, intelligential memory, and cell repaired. Based on the major active substances of tocopherol, alpha-tocopherol, and β-carotene in red fruit, the fruit can function as cell regeneration. While its antioxidant can protect the attack of free radial subtances. By giving the extraction of red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam) to the body, it can regenerate epithelial cell of mucosa gastric in the white rat (Rattus novergicus) under sopi problem. METHODS with the weight of 70 kg, then the dose was calculated as folows 70/ ml = 140 ml. The conversion from human weight to that in mouse (20 g) is [9], so that rat dose is 0, ml = 2,5 ml. Therefore, from such results, the used dose was chosen to be 2.5 ml/200g BB. The content dose decision of Red Fruit As initial dose, a common used dose in society was taken ~8 ml (with a weight body of 50 kg). For human kind with the weight of (with a weight body of 50 kg), the dose was obtained as 70/50 8 ml = 11.2 ml. While the conversion factor from human being (70 kg) to be rat (200 gr) was 0.018, so that the rat dose was ml = 0.2 ml. Based on the above mentioned calculations, the first used dose (dose I) was 0.2 ml/200gr BB. While the use of dose I, and dose III were 0.4 ml/200gr BB, and 0.6 ml/200gr BB, respectively. Acording to Revianti, et al. [10], they found the treated dose of 0.3 ml/bb had already give the protection effect to the increase of the SGPT level. Treatment to tested animal 30 white male rats were divided into 5 groups randomly, and each test was consisted on 6 male white rats. While 20 of the rats were orally given 2.5 ml/200gr BB sopi every 2 days during 4 weeks (1 month). The following are the details of the whole 5 groups: (1). Group I (negative control) is male white rats with only aquades treatment for 8 weeks as a normal control. (2). Group II (possitive control) is male white rats with 2.5 ml/200gr BB sopi treatment every 2 days for 8 weeks. (3). Group III is male white rats with 0.2 ml/200gr BB red fruit juice treatment every 2 days for 4 weeks. (4). Group IV is male white rats with 0.4 ml/200gr BB red fruit juice treatment every 2 days for 4 weeks. (5). Group V is male white rats with 0.6 ml/200gr BB red fruit juice treatment every 2 days for 4 weeks. Fabrication of gastric preparate histology Handari (1983) [11] stated that a condition of fixation gastric with 4% formaline, after washed with 5 minutes aquades, there was an increase of dehydration every 30 minutes from 30%, 50%, 70%, 80%, 90% to 100%. The remind alcohol was cleansed by clearing process. Gastric was put inside xylol I, and xylol II for 1 The content dose decision of sopi According to Louhenapessy [8], an initial dose used to a chronical sociaety decease is 100 ml (with a weight body of 50 kg). If it was used to human being hour, respectively. Furthermore, infiltration process was International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 883
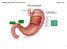
3 conducted by inserting the organ in the paraffin I, paraffin II, and paraffin III at 60 0 C for 1 hour, respectively. Moreover, embedding process was carried out by putting gastric inside paraffin box for 24 hours, and then sectioning or cutting through few minutes waiting process inside the paraffin ox by using microtom with the thickness of 6 μm. The slicing result was put down on objective glass which has been lubricated with albumin gliserine, and then was heated up on hot plate at 40 0 C. Stanning process in xylol I, and xylol II, for 15 to 30 minutes each, and following by inserting the preparate in alcohol 100%, 90%, 80%, 70%, and 30% for 3 minutes, respectively. In addition, the preparate was inserted inside hematoxilin 1% in aquades for 2 to 10 minutes, washed with water for 3 minutes, and then such preparate was put inside eosin I alcohol 50%, eosin II alcohol 100 % for 3 minutes each. Finally, the treated preparate was diluted inside xylol I, and xylol II for 3 minutes each, and then dried. In the last step, the preparate was closed with glass substrate, and observed under microscope. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION From the results as shown both in Figure 1 and Table 1, the descriptive analyzation can be obtained from the gastric of micrograph photo. By giving sopi for 60 days to white rat (Rattus novergicus), her mucosa gastric may have been broken. However, after its treatment with red fruit for 30 days, we found there was a regeneration or repair of mucosa gastric. These indications are seen obviously in the micrograph photo of mucosa gastric in Fig. 1. According to Fig. 1(A1), Fig. 1(A2), Fig. 1(B1), Fig. 1(B2), and Fig. 1(C1) provided the observation data of the 30 days treatment of red fruit juice with dose of 0.6 ml/200g BB into white rat addicted due to sopi with dose of 2.5 ml/200g BB, there were regenerated of mucosa gastric indicated with more observed epithial cells in the gastric. Such regenerated cells were because of the content of tocopherol (natural vitamin E) with its ability to repair broken cells, and alpha-tocopherol, and beta-carotene with their functions as antioxidant to handle free radials sourced by sopi. Figure 1. Micrograph photo of a controlled gastric mucosa of rat and its treatment. The folowing are the explanation of figure captures: A1 (SE) is the mucosal gastric histology of controlled white rat with 40x enlargement; (A2) is the mucosal gastric histology of controlled white rat with 100x enlargement in which SE, M, MM, and SP are epithelial cell, gastric mucosa, muscularis mucosa (lamina of muscle), and parietal cell, respectively. In (A2), there is no damage of mucosa gastric; (B1) is 100x enlargement histology of white rat given by sopi with dose of 2.5 ml/200g BB for 60 days in which N, UL and LP are necrosis cell, ulcer (wound) gastric, and lamina propria (a part of mucosa), respectively; (B2) is 100x enlargement histology of white rat given by sopi with dose of 2,5 ml/200g BB for 60 days; (C1) White rats treated with sopi for 30 days plus the red fruit juice with 0.2 ml/200g BB dose for 60 days (the picture with 40 x magnification), and (C2) White rats treated with sopi for 30 days plus the red fruit juice with 0.2 ml/200g BB dose for 60 days (the picture with 100 x magnification); (D1) is 40x enlargement histology of white rat given by sopi with dose of 0.4 ml/200g BB for 30 days; (D2) is is 100x enlargement histology of white rat given by sopi with dose of 0.4 ml/200g BB for 30 days; (E1) is is 40x enlargement mucosa gastric histology of white rat given by red fruit juice with dose of 0.6 ml/200g BB for 30 days; and (E2) is is 100x enlargement mucosa gastric histology of white rat given by red fruit juice with dose of 0.6 ml/200g BB for 30 days. International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 884
4 Table 1. The observation results of controlled white rat with its mucosal gastric micrograph photos treated with sopi plus red fruit. Normal Type of Treatment Sopi with dose of 2,5 ml/200g BB Red fruit juice with dose of 0,2 ml/200g BB Red fruit juice with dose of 0,4 ml/200g BB Red fruit juice with dose of 0,6 ml/200g BB Result of observation No damage of mucosa gastric (epihtesial cell, parietal cell) Mocosa gastric (epihtesial cell, parietal cell) experienced necrosis (injured cell), and ulcer (wound) in gastric. Mucosa gastric regeneration (epihtesial cell, parietal cell) Mucosa gastric regeneration in which it looks like more epihtesial cell and parietal cell in the mucosa. Mucosa gastric regeneration (epihtesial cell, parietal cell) until the same as a normal mucosa gastric. The observation of gastric histology preparate in the controlled white rat group which was only treated with aquades shows no changing in mucosa gastric (Fig. 1 A1 (SE) and Fig. 1(A2)). While the white rat group treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose shows a big broken part of gastric histology structure as depicted in their microscopic picture of mucosa gastric (Fig. 1(B1) and Fig. 1(B2)). The mechanism behind such broken parts can be explained into the following few manners such as the irritation of mucosa gastric due to alcohol effect from sopi, and the blocking of prostlagandin synthesis related to the mucosa gastric defending besides of bikarbonat, mucosa resistancy, and blood circulation in mucosa [14]. Mucosa gastric needs a strong blood flow to protect its existancy. If the blood supply is decreased, mucosa gastric will tend to experience necrosis and ulcus problem. The irritation due to sopi results the increase of permeability of mucosa gastric. By the increase of mucosa permeability, a reversed diffusion of HCl happened in the mucosa gastric because of the local histamine (by mast cell in the lamina propia of mucosa gastric). This histamine then links with its receptor in the parietal gastric cell, and finally increases gastric acid secration from parietal cell [13]. The decrease of prostlagandin synthesis causes a distruption of gastric protection factor due to its function as defensive factor which can enhance mucus secretion and bicarbonate ion, mucosa blood circulation, mocosa resistancy, as well as fasten the grow and separation of cell [12]. In this research, mucosa gastric was observed to be broken in epihtesial cells of gastric and parietal cell experienced necrocis as well as the presence of ulcus gastric. Necrocis is a death cell that caused the gastric network not fully perfect. While ulcus in gastric is a wound in gastric. However, ulcus histology is a vanishing of epihtesial cell which reaches or passes through muskularis mukosa so that it looks like an erossion. Such opinion is in agreement with Ref. [4-6] mentioned that alcohol can break mucosa gastric because it can release free radicals. This broken part is usually happened in blood cell, and parietal cell located in the gastric wall that caused ulcus/ wound. Gastric has its own self defence to protect her self from an irritation. In gastric, there is a defence of mukosa gastro duodenal which protects the whole gastric and repair mukosa gastric if there is a damage. This system consisted of three layers of pre-epihtesial, epihtesial, and post-epihtesial. The pre-epihtesial layer contains muccus-bikarbonat working as a protection of physiochemical into a molecule such as hydrogen ion. The secretion muccus on the surface epihtesial cell consists of 95% water, and a mixture between lipid and glikoprotein. The mucus secretion was at least stimulated by prostaglandin E (PGE). PGE improves mucus production, and reduces the production of gastric acid. This effect helps to protect mucosa gastric. Beside its function to realese free radicals, alcohol can destroy mucus gel, and fosfolipid layer that causes a reversed acid and damage in mucosa gastric. Bikarbonat mucus layer is the protected part of the main pre-epihtesial. However, such protection is not always protecting the gastric from its broken. If released free radicals have a large number more than its ability of protective function, then gastric will have a slightly damage, so that an additional antioxidant from the outter food of the body is necessary. In this work, the juice of red fruit is the antioxidant source for the body. By injecting the red fruit International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 885
5 juice with 0.2 ml/200g BB dose for 30 days to a group of white rats treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose, one can see a repair process on mucosa gastric cells (Fig. 1(C1) and Fig. 1.(C2)). Therefore, the treatment with red fruit juice could reduce the damage of mucosa gastric of white rat due to sopi treatment. This is because of the antioksidant contents in red fruit juice such as tocopherol, alpha-tocopherol, and beta-carotene have ability to neutralize free radical, and repair broken cells so that it can handle the broken of mucosa gastric, and ulcus gastric. Tocopherol (natural Vitamin E) that improves prolifersai / cell multiplication is a healing mechanism process of ulcus in gastric. Such prolifersai is important in the ulcus healing because this process supplies epihtesial cells which is very useful to reepihtesialisation of mucosa surface, and the repair of gastric digestive cells. By giving red fruit juice with 0.4 ml/200g BB dose for 30 days to the group of white rats damaged due to sopi with 2.5 ml/200g BB dose, there is a little 886onsume886t due to not only a repair of mucosa gastric cells, but also more mucosa gastric cells observed in comparison with that for such treatment with 0.2 ml/200g BB dose (Fig. 1(D1) and Fig. 1(D2)). This reason is because of more concentrated of dose (2 times higher) in red fruit juice to the white rats realated to more antioxidant content in the treatment. While by increasing the red fruit juice to be 0.6 ml/200g BB dose for 30 days to the treated white rats with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose, the mucosa gastric has been fixed the same as the gastric histology of controlled white rats as depicted in Fig. 1(E1), and Fig. 1(E2). Therefore, there are obvious differences in gastric histology from those five groups of white rats: (1). Controlled white rats, (2). White rats treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose, (3). White rats treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose plus the injection of 0.2 ml/200g BB dose of red fruit juice. (4). White rats treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose plus the injection of 0.4 ml/200g BB dose of red fruit juice, and (5). White rats treated with sopi of 2.5 ml/200g BB dose plus the injection of 0.6 ml/200g BB dose of red fruit juice. CONCLUSION effective healing of mocosa gastric in the rat was observed. The following are our two suggestions to extend this research: 1. People in society please do not 886onsume an alcoholic drink of sopi type due to its effect to mucosa gastric damage. 2. Red fruit can be used as an alternative medicine to heal a cronic decease in gastric. REFERENCES 1. Alex Paton, Alkohol in the body, BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, MC555673/, access 02 Agustus Woteki, Eat for Life : The Food and Nutrition Board s Guide to Reducing your Risk of Chronic Disease. Hardcover Fleming, M., S, J. Mihic, dan R.A. Harris Etanol. Dasar Farmakolgi. EGC: Jakarta; Suleyman, H., E.B. Mehmet, and M. Koruk., The Effects of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Extract on Ethanol Induced Gastric Lesion and Gastric Tissue Glutathione Level in Rats : A Comparative Study with Melatonin and Omeprazole, Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 2001; 33: Narayan, S., R.S. Devi, M. Jainu, K.E. Sabitha, and C.S.S. Devi, Protective Effect of a Polyherbal Drug, Ambrex in Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Lesions in Experimental Rats, Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 2004; 36(1): Khazaei, M., and S. Hussein, Protective Effect of Falacaria vulgaris Extract on ethanol Induced Gastric Ulcer in Rat, Iranian Jurnal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2006; 5: Budi, I made., Paimin, F. R. Buah merah. Jakarta: Penebar Swadaya; Louhenapessy R. J. Efek minuman keras tradisional masyarakat Maluku jenis sopi terhadap apoptosis sel hati serta kadar enzim GPT dan GOT: upaya pencegahan masyarakat Maluku dalam mengkonsumsi minuman keras tradisional. (studi in vivo pada mencit (Mus musculus): PKM-Penelitian. FMIPA UNPATTI: AMBON Ngatidjan, Metode Laboratorium dalam Toksikologi. Yogyakarta: pusat Antar Universitas Bioteknologi UGM; Revianti, S., W. Praningrum, dan R.P. Sari. Peran antioksidan ekstrak buah merah (Pandanus coneideus Lam) sebagai We conclude that there are 2 main findings as follows 1. With the treatment of red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam), mucosa gastric of white rat (Rattus novergicus) damaged due to sopi could be repaired. 2. By using the red fruit juice (Pandanus conoideus Lam) with dose of 0.6 ml/200g BB, an International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 886
6 hepatoprotektor. Jurnal Fakultas Kedokteran Gigi Universitas Hang Tuah Handari, S. Metode Pewarnaan. Bhatara Karya Aksara, Jakarta Amiruddin, R. Perkembangan Baru Dalam Klasifikasi Dan Peranan Sitoproteksi Pada Gastritis. Med Nus. 1998; 19(2). 13. Price, S.A. & Wilson, L.M. Patofisiologi. Jakarta: EGC. 1995: Khazaei, M and S. Hussein. Protective Effect of Falacaria Vulgaris Extract on Ethanol Induced Gastric Uclear in Rat. Iranian Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2006; 5: ******** International Journal of Health Medicine and Current Research 887
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
Snakehead (Channa striata) Extracts Treatment towards Hyperglycemic Mice (Mus musculus) Blood Glucose Levelsand Pancreatic Histology Structure
 J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., 4(5)1-6, 2014 2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4274 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Snakehead (Channa striata) Extracts Treatment
J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., 4(5)1-6, 2014 2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4274 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Snakehead (Channa striata) Extracts Treatment
) OIL ON MALONDIALDEHYDE LEVEL AND SPERMATOZOA QUALITY IN MICE
 EFFECTS OF RED FRUIT (Pandanus conoideus Lam) OIL ON MALONDIALDEHYDE LEVEL AND SPERMATOZOA QUALITY IN MICE (Mus musculus) EXPOSED TO MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE Agustina Widayati 1, Widjiati 2, Alfiah Hayati
EFFECTS OF RED FRUIT (Pandanus conoideus Lam) OIL ON MALONDIALDEHYDE LEVEL AND SPERMATOZOA QUALITY IN MICE (Mus musculus) EXPOSED TO MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE Agustina Widayati 1, Widjiati 2, Alfiah Hayati
Human Digestive System
 Human Digestive System Extension Independent Study Activity Article 1 The Human Microbiome, p2-p5 Article 2 Stomach Ulcers, p6-p12 Question Booklet Instructions: Read the above two articles and answer
Human Digestive System Extension Independent Study Activity Article 1 The Human Microbiome, p2-p5 Article 2 Stomach Ulcers, p6-p12 Question Booklet Instructions: Read the above two articles and answer
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8 10 Reasons to Drink Alkaline Ionized Every Day...10 #1 Hydration...11 #2 Detoxification (Cleansing)...13
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...5 What the Wrong Kind of Water...5 Benefits of Alkaline Water...8 10 Reasons to Drink Alkaline Ionized Every Day...10 #1 Hydration...11 #2 Detoxification (Cleansing)...13
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System: Basics. WedNesday October 24th All organisms need energy to survive. > Use energy to reproduce, grow, and repair
 WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
WedNesday October 24th 2012 QU: What would happen if an organism stopped eating? OBJ: Digestive System Notes All about hydrolysis and surface area Digestive System All organisms need energy to survive
Vitamin K & Antioxidants. NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018
 Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Vitamin K & Antioxidants NUT1602 E-Tutor 2018 Vitamin K O Can be obtained from non-food source O Bacteria in the GI tract O Acts primarily in blood clotting O Prothrombin O Metabolism of bone proteins
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion?
 Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
TODA Herbal International Inc.
 TODA Herbal International Inc. SEABUCKTHORN PRODUCTS Toda Herbal International Inc. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada Telephone: Vancouver, BC: (778) 838-7008 Toll Free Canada (only) 1-866-933-7008 International:
TODA Herbal International Inc. SEABUCKTHORN PRODUCTS Toda Herbal International Inc. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada Telephone: Vancouver, BC: (778) 838-7008 Toll Free Canada (only) 1-866-933-7008 International:
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: u food food u oxygen Animals build bodies using: u food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats,
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Sun Ancon total Enzymes
 Sun Ancon total Enzymes Enzymes Enzymes regulate the normal processes of digestion, absorption, detoxification, blood circulation, balance our body PH and waste removal all essential to the very functions
Sun Ancon total Enzymes Enzymes Enzymes regulate the normal processes of digestion, absorption, detoxification, blood circulation, balance our body PH and waste removal all essential to the very functions
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Nutritional Management of the Racehorse. Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky
 Nutritional Management of the Racehorse Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky Considerations Meet nutrient requirements Maintain normal GI tract Feeding the
Nutritional Management of the Racehorse Laurie Lawrence, Ph.D. Department of Animal and Food Sciences University of Kentucky Considerations Meet nutrient requirements Maintain normal GI tract Feeding the
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
Human Digestion. Junior Science
 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin
 Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
Augmentation of Cysteamine and Mepirizole-Induced Lesions in the Rat Duodenum and Stomach by Histamine or Indomethacin Hironori TANAKA, Yoshimi KUWAHARA and Susumu OKABE Department of Applied Pharmacology,
4th Asian Academic Society International Conference (AASIC) 2016 SCI-OR-007
 SCI-OR-007 THE EFFECTS OF RED FRUIT TREATMENT ON INFERTILITY MICE MODELS TO OVERVIEW FOLLICULOGENESIS, ESTROUS CYCLE AND PREGNANCY RATE Saiful Rizal, Gagang Ichwanul Akbar, Diana Nurjanah Veterinary Medicine
SCI-OR-007 THE EFFECTS OF RED FRUIT TREATMENT ON INFERTILITY MICE MODELS TO OVERVIEW FOLLICULOGENESIS, ESTROUS CYCLE AND PREGNANCY RATE Saiful Rizal, Gagang Ichwanul Akbar, Diana Nurjanah Veterinary Medicine
Structure and Function of Cells, Organs and Organ Systems 1
 I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
(*) (*) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. Uptake of nutrients by body cells (intestine)
 Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
Do Now #1. Name: Enzymes & ph. 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule?
 Name: Do Now #1 Enzymes & ph 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule? 2. What do you think enzymes do for the body? Chemical reactions with enzymes are used
Name: Do Now #1 Enzymes & ph 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule? 2. What do you think enzymes do for the body? Chemical reactions with enzymes are used
Ch 5 Metabolism and enzymes
 Ch 5 Metabolism and enzymes Think about (Ch 5, p.2) 1. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up metabolic reactions. 2. Enzymes catalyse the breakdown of cellulose fibres of the
Ch 5 Metabolism and enzymes Think about (Ch 5, p.2) 1. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts to speed up metabolic reactions. 2. Enzymes catalyse the breakdown of cellulose fibres of the
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
High-Absorbable Ferric Pyrophosphate for Iron Supplement. Ferrsorb
 High-Absorbable Ferric Pyrophosphate for Iron Supplement R Ferrsorb Ferrsorb is iron supplement which is absorbed efficiently into the body without impairing taste and texture of various foods. It can
High-Absorbable Ferric Pyrophosphate for Iron Supplement R Ferrsorb Ferrsorb is iron supplement which is absorbed efficiently into the body without impairing taste and texture of various foods. It can
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Digestion: An Absorbing Tale
 8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Gastric and Intestinal secretion
 Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Gastric and Intestinal secretion OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the various types of gastric cells and the secretion of each cell type. 2. Mention the components of gastric juice and the function of each component.
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
4. Which sentence is a
 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
The Digestive Process Begins
 Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
Name Date Class The Digestive Process Begins This section explains what the digestive system does and describes the functions of the mouth, the esophagus, and the stomach. Use Target Reading Skills Before
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion. Regents Biology
 38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
38.2 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion Objectives Distinguish intracellular from extracellular digestion Examine how the digestive system evolves across the phyla Identify the components of the human digestive
Lipid Digestion. An Introduction to Lipid Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins.
 Digestion An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Suspension and Nutralization of Chyme ph Boli containing lipids enters
Digestion An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Suspension and Nutralization of Chyme ph Boli containing lipids enters
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus. Barbora Konečná
 Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
B17 instructions for 227. April 15, 2011
 Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals,
Microviewer 227: Comparative Digestive Systems Introduction This set is one of a series of lessons examining comparative life function systems. In these sets, you will examine slides of different animals,
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Holistic Healing Professional Practitioner Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates
 Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates I Types of Carbohydrates If someone told you "My carbohydrate intake is too high", what would you assume about what they're eating? A. SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES:
Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates I Types of Carbohydrates If someone told you "My carbohydrate intake is too high", what would you assume about what they're eating? A. SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES:
Effect Of Mixed Green Beans Essences And Red Guava Of Haemoglobin Levels In Young Women Ages Years Old
 Effect Of Mixed Green Beans Essences And Red Guava Of Haemoglobin Levels In Young Women Ages 13-16 Years Old Yuniasih Purwaningrum Abstract: In Indonesia, in 2013 the prevalence of anemia in adolescent
Effect Of Mixed Green Beans Essences And Red Guava Of Haemoglobin Levels In Young Women Ages 13-16 Years Old Yuniasih Purwaningrum Abstract: In Indonesia, in 2013 the prevalence of anemia in adolescent
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7
 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 Regeneration and Antioxidant Activity NanoVit oa is a nano-emulsion loaded with sea buckthorn pulp oil. Sea
NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 Regeneration and Antioxidant Activity NanoVit oa is a nano-emulsion loaded with sea buckthorn pulp oil. Sea
Immunity. Chapter 38 Part 1
 Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
UNIVERSITAS SEBELAS MARET PASCASARJANA
 CYTOTOXICITY OF COMBINATION EXTRACT Pandanus conoideus Lam. Var. YELLOW AND RED FRUIT ON MCF-7 CELL Disusun Oleh : Sutarno Okid Parama Astirin UNIVERSITAS SEBELAS MARET PASCASARJANA 2011 CYTOTOXICITY OF
CYTOTOXICITY OF COMBINATION EXTRACT Pandanus conoideus Lam. Var. YELLOW AND RED FRUIT ON MCF-7 CELL Disusun Oleh : Sutarno Okid Parama Astirin UNIVERSITAS SEBELAS MARET PASCASARJANA 2011 CYTOTOXICITY OF
Etiology, Assessment and Treatment
 Etiology, Assessment and Treatment Andrew Tinsley MD, MS Associate Director of IBD Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Abbvie Janssen Nestle 1 To review the prevalence
Etiology, Assessment and Treatment Andrew Tinsley MD, MS Associate Director of IBD Center Assistant Professor of Medicine Penn State College of Medicine Abbvie Janssen Nestle 1 To review the prevalence
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Modeling Tetanus Neonatorum case using the regression of negative binomial and zero-inflated negative binomial
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Modeling Tetanus Neonatorum case using the regression of negative binomial and zero-inflated negative binomial To cite this article: Luthfatul Amaliana
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Modeling Tetanus Neonatorum case using the regression of negative binomial and zero-inflated negative binomial To cite this article: Luthfatul Amaliana
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
THE EFFECT OF GIVING DATE PALM EXTRACT TO AGAINTS CONSTIPATION THAT HAPPEN TO POSTPARTUM MOTHER. Ninik Azizah 1 dan Suyati 2
 THE EFFECT OF GIVING DATE PALM EXTRACT TO AGAINTS CONSTIPATION THAT HAPPEN TO POSTPARTUM MOTHER Ninik Azizah 1 dan Suyati 2 Diploma III Kebidanan Faculty of Health Science Universitas Pesantren Tinggi
THE EFFECT OF GIVING DATE PALM EXTRACT TO AGAINTS CONSTIPATION THAT HAPPEN TO POSTPARTUM MOTHER Ninik Azizah 1 dan Suyati 2 Diploma III Kebidanan Faculty of Health Science Universitas Pesantren Tinggi
Enzymes. Biology Gr10. Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Act as. They Are. Examples are. They cause.
 Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Enzymes Biology Gr10 Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Are They Act as They cause Examples are Affected by
Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Enzymes Biology Gr10 Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Are They Act as They cause Examples are Affected by
Digestion Review V1 /36
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Digestion Review V1 /36 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the above parts of the digestive system would be
Different diets; different lives All animals eat other organisms. Mouth
 Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
Digestive and Excretory System TOC #4 Digestive System *3) Digestive System: Mouth, Saliva, Esophagus, Peristalsis, Chyme, Stomach, Small Intestine, Pancreas, Liver, Villi, Large Intestine, Excretory System:
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
There are four classes of biological macromolecules: Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
 There are four classes of biological macromolecules: Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids Before you can understand the topics in this unit there are some key vocabulary terms you need to
There are four classes of biological macromolecules: Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids Before you can understand the topics in this unit there are some key vocabulary terms you need to
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Chemical Level Of Organization
 Chemical Level Of Organization List the Four Chemical Elements that Make Up Most of the Body s Mass Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Distinguish Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds Organic Compounds:
Chemical Level Of Organization List the Four Chemical Elements that Make Up Most of the Body s Mass Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Distinguish Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds Organic Compounds:
