Subcellular segregation of kainate receptors and temporal lobe epilepsy
|
|
|
- Darren Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subcellular segregation of kainate receptors and temporal lobe epilepsy Christophe Mulle Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuroscience CNRS University of Bordeaux
2 Kainate receptors: a family of ionotropic glutamate receptors Glutamate receptor ion channels Five genes GluK1 to GluK5 Heterotetrameric receptors CA3 DG from Contractor, Mulle, Swanson, TINS 2011
3 Kainate receptors in the hippocampus Carta et al, EJN 2014
4 TLE: recurrent synapses in DG operate via aberrant KARs Epilepsy 100 µm oml PP AMPA-R Epilepsy iml gl rmf rmf KA-R G rmf MF CA3 h Valérie Crépel, INSERM, Marseille EPSP KA Epsztein et al., 2005, 2010 Artinian et al., 2011 Pinheiro et al., 2013
5 Recurrent Mf synapses on DG cells operate via KARs in TLE: implication for epilepsy? Control AMPA-R EPSP AMPA Role of aberrant KARs in Chronic Epilepsy Epileptic KA-R? EPSP KA
6 Reduced Number of Ictal Discharges in GluK2 KO Mice and in Presence of KAR Blockers
7 Aberrant postsynaptic KARs essential contributor to temporal lobe epilepsy Chronic models of temporal lobe epilepsy Peret et al - Cell Reports 2014
8 Subcellular segregation of KARs in control conditions and TLE
9 Mechanism for (recruitment and) stabilization of synaptic KARs: role of N-Cadherins CTD Δ 14 destabilization of KARs at MF-CA3 synapse Alteration of N-cadherins reduction of KAR-EPSCs 14 last aa interaction N-Cadherin/βcatenin complexes N-Cadherin/β-catenin complexes play a crucial role in stabilization of KARs Fièvre, Carta et al Nature Communications, 2016
10 Mechanisms for recruitment of aberrant postsynaptic KARs? Cadherin 9 labeling
11 What next? a translational approach Fact: >30% of TLE patients are intractable to pharmacological treatments they undergo surgical removal of the temporal lobe. Reduce the expression or activity of pathological KARs at ectopic synapses: a gene therapy approach, develop micrornas to invalidate KARs under the control of a DG specific promoter. develop GluK2/GluK5 antagonists prevent or disrupt the stabilization of ectopic KARs an interacting peptide approach. Disrupt Cadherin/KAR interactions (FFRE/FRC project). Collaboration with Valérie Crépel, INSERM Marseille, Support from AST Aquitaine and INSERM transfer
12 What next? a translational approach Tests on resected hippocampus from patients with TLE organotypic cultures collab Valérie Crépel, NSERM Fabrice Bartholoméi, Didier Scavarda, Service de Neurophysiologie Clinique - La Timone, APHM Eugène et al, J. Neurosci Meth, 2014
13 Funding ANR, FRC, FFRE Mario Carta Adam Gorlewicz Sabine Fièvre Collaboration Valérie Crépel, INSERM Marseille
14 Subcellular segregation of KARs at Mf-CA3 synapses GluK2 GluK2 -/- GluK5 -/- GluK5 st radiatum st lucidum st pyramidale Ruiz et al, J Neurosci 2005
15 Mechanism for recruitment and stabilization of synaptic KARs: Cadherin 9 could explain synapse specifity CA3 DG
16 CA3 synaptic circuits operation and plasticity role in memory Rebola, Carta and Mulle, Nature Rev Neuro, 2017
17 Functional mapping of GluRs: focal uncaging of glutamate CA3 pyramidal cell / GFP Distinct behaviour of AMPAR and KAR: strict subcellular segregation of KARs
18 CA3 pyramidal cells: Anatomy and structure 3D reconstruction MFB A/C PP 1µm 1µm 3D reconstruction 10µm 10µm CA3 MF 50µm myfp, injected in vivo at P2 and collected at P24. Confocal microscopy, 100x. thorny excrescences
19 Mossy fiber synapses: short term plasticity dynamics frequency facilitation paired pulse facilitation MPFA: quantal analysis Lanore et al, J Neuroscience 2012
20 Mf-CA3 short term plasticity and spike transfer -80 mv Feedforward inhibition 0 mv -30 mv -60 mv current-clamp minimal stimulation, 20Hz Sachidhanandam et al, J Neurosci 2009 Torborg et al, J Neuroscience 2011
21 Properties of CA3-CA3 (A/C) synapses paired-pulse facilitation PP A/C long-term potentiation associative pairing Mf Silva et al, Nature Communications 2016
22 Mossy fiber synapses: short term plasticity and spike transfer current-clamp recording Mf-EPSPs 20 Hz burst stimulation 20 Hz 0 mv -30 mv -60 mv GluK2 -/- wild-type GluK2 -/- spikes s Sachidhanadam et al, J Neuroscience s
23 Kainate receptors in the hippocampus Carta et al, EJN 2014
24 Postsynaptic KARs at Mf-CA3 synapses mv CA1 Mf-EPSP -62 wt vs GluK2 -/- Sch. -64 CA3 fm pp DG wt -66 vs GluK3-/ s Sachidhanandam et al J Neurosci 2009
25 Postsynaptic KARs at Mf-CA3 synapses and synaptic integration KAR-EPSCs UPB 310 Mf-EPSP (AMPAR+ KAR) GYKI µM Postsynaptic KARs shape the EPSP waveform important for excitability Pinheiro et al, Cerebral Cortex 2013
26 Recombinant KARs: GluK2 vs GluK2/GluK5 GluK2 GluK2/GluK5 UBP 310 an antagonist with selectivity GluK2/GluK5 but not GluK2 Barberis et al, J. Neuroscience 2008 Pinheiro et al, Cer Cortex, 2013
27 Functional diversity of excitatory synapses Cellular mechanisms and functional consequences Glu Glu Structure/spine architecture Position along dendrite Glu Receptor equipment Presynaptic properties Types and extent of synaptic plasticity
28 Single-unit recordings from CA3 cells in freely moving mice wild-type GluK2 -/- collab Y. Cho
29 KARs and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE) A chronic Disease % of Adult Epilepsy Pharmaco-resistant Associated with Comorbidity Distresses: - Social - Emotional - Attention - Memory - Language
30 An unexpected link between KARs and Alzheimer disease? (on-going work) Pei Zhang Gaël Barthet
31 Early synaptic deficits with chronic elevation of Aß in APP/PS1 mice Amyloid deposits in DG - CA3 Region Silvia Viana da Silva APP/PS1 transgenic mice: Overexpression of APP swedish mutation + PS1 with deletion of exon 9 accumulation of Ab peptides acceleration of plaque deposits Immunolabeling by Adam Gorlewicz
32 Properties of CA3-CA3 (A/C) synapses in APP/PS1 mice paired-pulse facilitation PP A/C long-term potentiation associative pairing Mf Silva et al, Nat Comm 2016
33 No plasticity impairment at hippocampal Mf-CA3 synapses APP/PS1 at 6 months paired pulse facilitation PP A/C CA3 Mf TRAIN: 3 x 10s apart
34 Decreased KAR-EPSCs at Mf-CA3 synapses in APP/PS1 mice Wt APP/PS1 *Barthet, *Zhang et al, unpublished
35 Proteolysis of N-Cadherin Loss or reduction of g-secretase cleavage leads to increase in N-Cadh CTF1 Barthet et al, FASEB J 201
36 Molecular determinants: role of N-Cadherins Overexpression of dominant negative form of N-Cadh
37 Reduced KAR-EPSCs in PS-KO CA3 pyramidal cells AAV-cre in CA3 Ps1fl/fl mice AMPAR-EPSCs control PS KO KAR-EPSCs *** PS is involved in subcellular targeting of KARs Possible involvement of N-Cdh cleavage by g-secretase.
38 Synaptic plasticity in CA3 pyramidal cells moderate short-term plasticity NMDA dependent LTP of AMPA EPSCs Perf. path A/C Stratum lucidum Mossy fiber Robust short-term plasticity presynaptic LTP, not dependent on NMDARs LTP of NMDA EPSCs Metaplastic switch to prime for LTP of AMPA EPSCs CA3 Pyramidal cell
39 KARs and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE) A chronic Disease % of Adult Epilepsy Pharmaco-resistant Timm's staining control Associated with Comorbidity Distresses - Social - Emotional - Attention - Memory - Language rmf chronic epilepsy Recurrent mossy fibers in the dentate gyrus in TLE
40 Recurrent MF onto DG Cells Operate via Aberrant KARs Epilepsy 100 µm oml PP AMPA-R Epilepsy iml gl rmf rmf KA-R G rmf MF CA3 h work of Valérie Crépel, INSERM, Marseille EPSP KA Epsztein et al., 2005, 2010 Artinian et al., 2011 Pinheiro et al., 2013
41 Organotypic hippocampal slices retain synaptic segregation of KARs P5-7 DIV 7-14 culture on insert CA3 CA1 DG Mf stimulation A/C stimulation WT GluK2 -/- WT LY LY LY Ctrl 60 pa 50 ms Ctrl 100 pa 50 ms Ctrl 100 pa 50 ms
42 Aberrant postsynaptic KARs are essential contributor to temporal lobe epilepsy Chronic models of temporal lobe epilepsy Mechanisms allowing recruitment of postsynaptic KARs should be better understood Peret et al - Cell Reports 2014
43 Quantitative reexpression of GluK2: kinetics Normalized traces
44 Subcellular distribution of SEP GluK2a in CA3 PCs Live staining for the SEP moiety using anti-gfp nanobody-atto647 (red) coll Ingrid Chamma, Olivier Thoumine
45 Molecular determinants: role of N-Cadherins Overexpression of dominant negative form of N-Cadh
46 High affinity Kainate binding in the human hippocampus control Temporal lobe epilepsy The autoradiography carried out with [ 3 H]kainate High Low Control Epileptic Represa et al Brines et al
47 In vitro model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Hippocampal Organotypic Slices organotypic slice culture treated with pilocarpine Synaptoporin staining EPSC KA EPSC AMPA Mossy fiber sprouting
48 Inter-ictal spikes in vivo in mouse model of TLE In vivo recording from pilocarpine-treated mice Local Field Potential
49 The slow kinetics of EPSCs are Important Determinants of Epileptiform Activity
50 Quantitative reexpression of GluK2: focal Glu uncaging GluK2 -/- slices, CA3 Pyramidal cells Single cell electroporation GluK2a + GFP
51 Quantitative reexpression of GluK2: kinetics Normalized traces WT GluK2 -/- Aberrant/ectopic KARs upon overexpression of GluK2 are homomeric GluK2 KARs
52 Synaptic KARs with GluK2a re-expression
53 Part I - Interim conclusions Distinct behaviour of AMPARs and KARs: strict subcellular segregation of KARs no extrasynaptic receptors Single cell electroporation necessary for quantitative replacement approach for study of receptor trafficking Synaptic KARs are heteromers containing GluK2 and GluK5 ectopic KARs following overexpression are likely homomers of GluK2. Synaptic KARs are readily rescued in amplitude and decay following GluK2 reexpression at Mf- but not A/C synapses. Data suggest limited amount of synaptic slots for KARs limited amount of GluK5 for heteromer formation strong transcriptional or post-transcriptional regulation of GluK2 What are molecular determinants of this subcellular segregation? Fièvre, Carta et al Nat Communications, 2016
54 Molecular determinants: Rexpression of mutated GluK2a HEK 293 cells Jaskolski et al J Neurosci 2004
55 Specific role of N-Cadherins for KARs: focal Glu uncaging focal Glu uncaging
56
57 Mechanism for recruitment and stabilization of synaptic KARs Transssynaptic Recruitment by C1ql2/3 Stabilization by Cadherins limited number of slots Regulated amount of GluK2 protein sumoylation, park2 interaction
58 Sprouting of recurrent mossy fibers in dentate gyrus in TLE Non epileptic Epileptic Rodents Human Timm/CV Golgi/CaBP rmf rmf rmf Tauck and Nadler, 1985 Represa et al., 1987 Hester and Danzer, 2013 Gabriel et al. 2004
59 Epileptiform discharges are strongly reduced in GluK2 -/- mice and in presence of KAR antagonists organotypic slice culture
60 Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Status epilepticus Latent period (several weeks) Chronic phase 1 w 2 w 3 w PILOCARPINE (ip)
61 Molecular determinants: Rexpression of mutated GluK2a HEK 293 cells Jaskolski et al J Neurosci 2004 KAR-EPSCs Mf stimulation
62 Molecular determinants: role of N-Cadherins Targeted expression of Cre in N-Cadh floxed mice single cell electroporation in organotypic slices
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Contribution of Aberrant GluK2-Containing Kainate Receptors to Chronic Seizures in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Cell Reports Report Contribution of Aberrant GluK2-Containing Kainate Receptors to Chronic Seizures in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Angélique Peret, 1,2,4 Louisa A. Christie, 1,2,4 David W. Ouedraogo, 1,2 Adam
Cell Reports Report Contribution of Aberrant GluK2-Containing Kainate Receptors to Chronic Seizures in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Angélique Peret, 1,2,4 Louisa A. Christie, 1,2,4 David W. Ouedraogo, 1,2 Adam
Recurrent Mossy Fibers Establish Aberrant Kainate Receptor-Operated Synapses on Granule Cells from Epileptic Rats
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 7, 2005 25(36):8229 8239 8229 Neurobiology of Disease Recurrent Mossy Fibers Establish Aberrant Kainate Receptor-Operated Synapses on Granule Cells from Epileptic
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 7, 2005 25(36):8229 8239 8229 Neurobiology of Disease Recurrent Mossy Fibers Establish Aberrant Kainate Receptor-Operated Synapses on Granule Cells from Epileptic
Synaptic Plasticity and Memory
 Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Properties and synaptic mechanisms underlying the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) The role of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII) in the induction,
Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Properties and synaptic mechanisms underlying the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) The role of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII) in the induction,
CONTEXT. LTP (long term potentiation) definition. LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory
 CONTEXT LTP (long term potentiation) definition LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory LTP is due primarily to a pre or post- synaptic modification? (Increased Glut release or increased
CONTEXT LTP (long term potentiation) definition LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory LTP is due primarily to a pre or post- synaptic modification? (Increased Glut release or increased
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA3 output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity
 Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Cellular mechanisms of information transfer: neuronal and synaptic plasticity
 Cellular mechanisms of information transfer: neuronal and synaptic plasticity Ivan Pavlov (UCL Institute of Neurology, UK) Anton Chizhov (Ioffe Physical Technical Institute) Pavel Zykin (St.-Petersburg
Cellular mechanisms of information transfer: neuronal and synaptic plasticity Ivan Pavlov (UCL Institute of Neurology, UK) Anton Chizhov (Ioffe Physical Technical Institute) Pavel Zykin (St.-Petersburg
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory. David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology
 Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
COMMENTARY THE MULTIFARIOUS HIPPOCAMPAL MOSSY FIBER PATHWAY: A REVIEW
 Pergamon www.elsevier.com/locate/neuroscience Hippocampal mossy fibers Neuroscience Vol. 98, No. 3, pp. 407 427, 2000 407 2000 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights
Pergamon www.elsevier.com/locate/neuroscience Hippocampal mossy fibers Neuroscience Vol. 98, No. 3, pp. 407 427, 2000 407 2000 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP. Reading: BCP Chapter 25
 Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs)
 Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
Adenosine A 2A Receptors Are Essential for Long-Term Potentiation of NMDA-EPSCs at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses
 Article Adenosine A 2A Receptors Are Essential for Long-Term Potentiation of NMDA-EPSCs at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses Nelson Rebola, 1,3 Rafael Lujan, 2 Rodrigo A. Cunha, 1 and Christophe Mulle 3,
Article Adenosine A 2A Receptors Are Essential for Long-Term Potentiation of NMDA-EPSCs at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses Nelson Rebola, 1,3 Rafael Lujan, 2 Rodrigo A. Cunha, 1 and Christophe Mulle 3,
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II)
 BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
A Selective Interplay between Aberrant EPSP KA and I NaP Reduces Spike Timing Precision in Dentate Granule Cells of Epileptic Rats
 Cerebral Cortex April 2010;20:898--911 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp156 Advance Access publication August 14, 2009 A Selective Interplay between Aberrant EPSP KA and I NaP Reduces Spike Timing Precision in Dentate
Cerebral Cortex April 2010;20:898--911 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp156 Advance Access publication August 14, 2009 A Selective Interplay between Aberrant EPSP KA and I NaP Reduces Spike Timing Precision in Dentate
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
Neurobiology of Disease. Julien Artinian, 1,2,3 Angélique Peret, 1,2,3 Geoffrey Marti, 1,2,3 Jérôme Epsztein, 1,2,3 and Valérie Crépel 1,2,3 1
 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 27, 211 31(3):1811 1818 1811 Neurobiology of Disease Synaptic Kainate Receptors in Interplay with I NaP Shift the Sparse Firing of Dentate Granule Cells to a Sustained
The Journal of Neuroscience, July 27, 211 31(3):1811 1818 1811 Neurobiology of Disease Synaptic Kainate Receptors in Interplay with I NaP Shift the Sparse Firing of Dentate Granule Cells to a Sustained
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
Synaptic plasticity. Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses.
 Synaptic plasticity Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses. Repair/changes in the nervous system after damage. MRC Centre
Synaptic plasticity Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses. Repair/changes in the nervous system after damage. MRC Centre
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11775 Supplementary Discussion Based on our data, we propose that LTP requires a large extrasynaptic pool of surface receptors regardless of their subunit composition.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11775 Supplementary Discussion Based on our data, we propose that LTP requires a large extrasynaptic pool of surface receptors regardless of their subunit composition.
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
Cellular Neurobiology / BIPN 140
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
Neuroscience 201A (2016) - Problems in Synaptic Physiology
 Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
CURRENT REVIEW IN BASIC SCIENCE
 CURRENT REVIEW IN BASIC SCIENCE SEIZURES BEGET SEIZURES IN TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSIES: THE BOOMERANG EFFECTS OF NEWLY FORMED ABERRANT KAINATERGIC SYNAPSES Yehezkel Ben-Ari, PhD, Valérie Crepel, PhD, and
CURRENT REVIEW IN BASIC SCIENCE SEIZURES BEGET SEIZURES IN TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSIES: THE BOOMERANG EFFECTS OF NEWLY FORMED ABERRANT KAINATERGIC SYNAPSES Yehezkel Ben-Ari, PhD, Valérie Crepel, PhD, and
Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor
 Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor Lecture 4.2 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Long Term Synaptic Plasticity Long Term Potentiation (LTP) Reversal of LTP Long Term Depression (LTD) Reversal of
Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor Lecture 4.2 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Long Term Synaptic Plasticity Long Term Potentiation (LTP) Reversal of LTP Long Term Depression (LTD) Reversal of
Kainate receptors and cognition enhancement
 D.I.Bink Supervisors: H. Hendriksen, R.S. Oosting, G. Ramakers 27-12-2010 Abstract The kainate (KA) receptor family is one of the three ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) families, consisting of five
D.I.Bink Supervisors: H. Hendriksen, R.S. Oosting, G. Ramakers 27-12-2010 Abstract The kainate (KA) receptor family is one of the three ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) families, consisting of five
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder
 AD Award Number: W81XW -12-1-0196 TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. David Sulzer, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XW -12-1-0196 TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. David Sulzer, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Sample Lab Report 1 from 1. Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties
 Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Annals of Neurology Research Article ANA R1. Impaired neuronal operation through aberrant intrinsic plasticity in epilepsy
 Research Article ANA-14-0581. R1 Impaired neuronal operation through aberrant intrinsic plasticity in epilepsy Julien Artinian 1,2, Angélique Peret 1,2, Yanina Mircheva 1,2, Geoffrey Marti 1,2, & Valérie
Research Article ANA-14-0581. R1 Impaired neuronal operation through aberrant intrinsic plasticity in epilepsy Julien Artinian 1,2, Angélique Peret 1,2, Yanina Mircheva 1,2, Geoffrey Marti 1,2, & Valérie
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks
 How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
epilepticus (SE) or trauma. Between this injury and the emergence of recurrent
 Introduction Epilepsy is one of the oldest medical disorders known. The word epilepsy derived from the Greek word epilamhanein, meaning to be seized or to be overwhelmed by surprise. Epilepsy is one of
Introduction Epilepsy is one of the oldest medical disorders known. The word epilepsy derived from the Greek word epilamhanein, meaning to be seized or to be overwhelmed by surprise. Epilepsy is one of
Synapses and synaptic plasticity. Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember
 Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam Ready for Pickup By the elevator on the 3 rd Floor of Pacific Hall (waiver) Exam Depot Window at the north entrance to Pacific Hall (no waiver) Mon-Fri, 10:00
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam Ready for Pickup By the elevator on the 3 rd Floor of Pacific Hall (waiver) Exam Depot Window at the north entrance to Pacific Hall (no waiver) Mon-Fri, 10:00
Zinc Dynamics and Action at Excitatory Synapses
 Neuron Article Zinc Dynamics and Action at Excitatory Synapses Angela Maria Vergnano, 1,2,3,8 Nelson Rebola, 4,5,8 Leonid P. Savtchenko, 6,8 Paulo S. Pinheiro, 4,5 Mariano Casado, 1,2,3 Brigitte L. Kieffer,
Neuron Article Zinc Dynamics and Action at Excitatory Synapses Angela Maria Vergnano, 1,2,3,8 Nelson Rebola, 4,5,8 Leonid P. Savtchenko, 6,8 Paulo S. Pinheiro, 4,5 Mariano Casado, 1,2,3 Brigitte L. Kieffer,
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse
 Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
TECHNICAL REVIEW REPORT
 TECHNICAL REVIEW REPORT Grant Agreement number: FP7 202167 Project Acronym: NeuroGLIA Project title: Molecular and cellular investigation of neuron-astroglia interactions: Understanding brain function
TECHNICAL REVIEW REPORT Grant Agreement number: FP7 202167 Project Acronym: NeuroGLIA Project title: Molecular and cellular investigation of neuron-astroglia interactions: Understanding brain function
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60
 Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Contribution of different classes of glutamate receptors in the corticostriatal polysynaptic responses from striatal direct
Vizcarra-Chacón et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:60 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Contribution of different classes of glutamate receptors in the corticostriatal polysynaptic responses from striatal direct
VS : Systemische Physiologie - Animalische Physiologie für Bioinformatiker. Neuronenmodelle III. Modelle synaptischer Kurz- und Langzeitplastizität
 Bachelor Program Bioinformatics, FU Berlin VS : Systemische Physiologie - Animalische Physiologie für Bioinformatiker Synaptische Übertragung Neuronenmodelle III Modelle synaptischer Kurz- und Langzeitplastizität
Bachelor Program Bioinformatics, FU Berlin VS : Systemische Physiologie - Animalische Physiologie für Bioinformatiker Synaptische Übertragung Neuronenmodelle III Modelle synaptischer Kurz- und Langzeitplastizität
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality
 The Study of Memory Has Two Parts: Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality (1) The Systems Problem of Memory: Where in the brain is memory stored? (2) The Molecular Problem
The Study of Memory Has Two Parts: Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality (1) The Systems Problem of Memory: Where in the brain is memory stored? (2) The Molecular Problem
Serotonergic Control of the Developing Cerebellum M. Oostland
 Serotonergic Control of the Developing Cerebellum M. Oostland Summary Brain development is a precise and crucial process, dependent on many factors. The neurotransmitter serotonin is one of the factors
Serotonergic Control of the Developing Cerebellum M. Oostland Summary Brain development is a precise and crucial process, dependent on many factors. The neurotransmitter serotonin is one of the factors
8 Epilepsy-Based Changes in Hippocampal Excitability: Causes and Effects
 8 Epilepsy-Based Changes in Hippocampal Excitability: Causes and Effects L. Stan Leung and Kun Wu * Departments of Physiology-Pharmacology and Clinical Neurological Sciences and Neuroscience Graduate Program,
8 Epilepsy-Based Changes in Hippocampal Excitability: Causes and Effects L. Stan Leung and Kun Wu * Departments of Physiology-Pharmacology and Clinical Neurological Sciences and Neuroscience Graduate Program,
Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous inhibitory networks
 Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Learning and Memory. The Case of H.M.
 Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki
 TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting
 Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded.
 When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
O Brother, Wherefore Are Thou? Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Make an Appearance in Adult Status Epilepticus
 Current Literature In Basic Science O Brother, Wherefore Are Thou? Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Make an Appearance in Adult Status Epilepticus Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Are Expressed in a Rodent
Current Literature In Basic Science O Brother, Wherefore Are Thou? Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Make an Appearance in Adult Status Epilepticus Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Are Expressed in a Rodent
Quantal Release of Glutamate Generates Pure Kainate and Mixed AMPA/Kainate EPSCs in Hippocampal Neurons
 Neuron, Vol. 35, 147 159, July 3, 2002, Copyright 2002 by Cell Press Quantal Release of Glutamate Generates Pure Kainate and Mixed AMPA/Kainate EPSCs in Hippocampal Neurons Rosa Cossart, 2 Jérôme Epsztein,
Neuron, Vol. 35, 147 159, July 3, 2002, Copyright 2002 by Cell Press Quantal Release of Glutamate Generates Pure Kainate and Mixed AMPA/Kainate EPSCs in Hippocampal Neurons Rosa Cossart, 2 Jérôme Epsztein,
TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0196 TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. David Sulzer, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0196 TITLE: Altered Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions and Epileptogenesis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Disorder PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. David Sulzer, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013
 NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
Thalamo-Cortical Relationships Ultrastructure of Thalamic Synaptic Glomerulus
 Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
Central Visual Pathways V1/2 NEUR 3001 dvanced Visual Neuroscience The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus () is more than a relay station LP SC Professor Tom Salt UCL Institute of Ophthalmology Retina t.salt@ucl.ac.uk
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks
 Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
Astrocytes regulate heterogeneity of presynaptic strengths in hippocampal networks
 Astrocytes regulate heterogeneity of presynaptic strengths in hippocampal networks Mathieu Letellier a,1,2,3, Yun Kyung Park a, Thomas E. Chater a,4, Peter H. Chipman a,4, Sunita Ghimire Gautam a, Tomoko
Astrocytes regulate heterogeneity of presynaptic strengths in hippocampal networks Mathieu Letellier a,1,2,3, Yun Kyung Park a, Thomas E. Chater a,4, Peter H. Chipman a,4, Sunita Ghimire Gautam a, Tomoko
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory
 Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory Tobias Bast School of Psychology, University of Nottingham tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk Synaptic plasticity as the neurophysiological substrate of learning Hebb
Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory Tobias Bast School of Psychology, University of Nottingham tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk Synaptic plasticity as the neurophysiological substrate of learning Hebb
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Hippocampus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP
 Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP 9.013 04 Po st -S yn ap (P ti SD c ) De ns it y PSD site en face.25 µm From: Kennedy (2000) Science MEMBRANE ASSOCIATED GUANYLATE KINASES
Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP 9.013 04 Po st -S yn ap (P ti SD c ) De ns it y PSD site en face.25 µm From: Kennedy (2000) Science MEMBRANE ASSOCIATED GUANYLATE KINASES
Neurobiology of Epileptogenesis
 Neurobiology of Epileptogenesis Michael C. Smith, MD Director, Rush Epilepsy Center Professor and Senior Attending Neurologist Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL Network Milieu Cellular Milieu
Neurobiology of Epileptogenesis Michael C. Smith, MD Director, Rush Epilepsy Center Professor and Senior Attending Neurologist Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL Network Milieu Cellular Milieu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
MCB MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY
 MCB 160 - MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY Name ID# Instructions: -Only tests written in pen will be regarded -Please submit a written request indicating where and why you deserve more points
MCB 160 - MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY Name ID# Instructions: -Only tests written in pen will be regarded -Please submit a written request indicating where and why you deserve more points
Beyond Vanilla LTP. Spike-timing-dependent-plasticity or STDP
 Beyond Vanilla LTP Spike-timing-dependent-plasticity or STDP Hebbian learning rule asn W MN,aSN MN Δw ij = μ x j (v i - φ) learning threshold under which LTD can occur Stimulation electrode Recording electrode
Beyond Vanilla LTP Spike-timing-dependent-plasticity or STDP Hebbian learning rule asn W MN,aSN MN Δw ij = μ x j (v i - φ) learning threshold under which LTD can occur Stimulation electrode Recording electrode
Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Janice R. Naegele, Ph.D. Department of Biology Program in Neuroscience Wesleyan University Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds
Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Janice R. Naegele, Ph.D. Department of Biology Program in Neuroscience Wesleyan University Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds
serotonin in learning and plasticity
 serotonin in learning and plasticity pt.1 immediate action L P H N NRX N N R X N CDH RhoA/ROCK RAC1 DAG [Ca2+] camp GIRK2 P11 Gq CASK PICK1 VELI MINT-1 CaMK Ca2+ channel AC Gi mglur7 mglur5 Glutamate NMDAR
serotonin in learning and plasticity pt.1 immediate action L P H N NRX N N R X N CDH RhoA/ROCK RAC1 DAG [Ca2+] camp GIRK2 P11 Gq CASK PICK1 VELI MINT-1 CaMK Ca2+ channel AC Gi mglur7 mglur5 Glutamate NMDAR
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Glutamate Overview. How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions?
 tamate Overview How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions? Darryle Schoepp, Ph.D. Senior Vice President and Franchise Head, Neuroscience Control of Excitability via Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
tamate Overview How can one neurotransmitter have so many diverse functions? Darryle Schoepp, Ph.D. Senior Vice President and Franchise Head, Neuroscience Control of Excitability via Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
Wnt Signaling Mediates Experience-Related Regulation of Synapse Numbers and Mossy Fiber Connectivities in the Adult Hippocampus
 Article Wnt Signaling Mediates Experience-Related Regulation of Synapse Numbers and Mossy Fiber Connectivities in the Adult Hippocampus Nadine Gogolla, 1,2 Ivan Galimberti, 1 Yuichi Deguchi, 1 and Pico
Article Wnt Signaling Mediates Experience-Related Regulation of Synapse Numbers and Mossy Fiber Connectivities in the Adult Hippocampus Nadine Gogolla, 1,2 Ivan Galimberti, 1 Yuichi Deguchi, 1 and Pico
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Structure of a Neuron:
 Structure of a Neuron: At the dendrite the incoming signals arrive (incoming currents) At the soma current are finally integrated. At the axon hillock action potential are generated if the potential crosses
Structure of a Neuron: At the dendrite the incoming signals arrive (incoming currents) At the soma current are finally integrated. At the axon hillock action potential are generated if the potential crosses
Lisa M. Giocomo & Michael E. Hasselmo
 Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
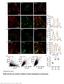 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplemental Information. Differential Regulation. of Evoked and Spontaneous Release. by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors
 Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
Problem Set 3 - Answers. -70mV TBOA
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience Course Director: Dr. David Corey HST 131/ Neuro 200 18 September 05 Explanation in text below graphs. Problem
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience Course Director: Dr. David Corey HST 131/ Neuro 200 18 September 05 Explanation in text below graphs. Problem
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior
 Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Postnatal maturation of mossy fibre excitatory transmission in mouse CA3 pyramidal cells: a potential role for kainate receptors
 J Physiol 561.1 (2) pp 27 37 27 Postnatal maturation of mossy fibre excitatory transmission in mouse C3 pyramidal cells: a potential role for kainate receptors Cécile Marchal and Christophe Mulle Laboratoire
J Physiol 561.1 (2) pp 27 37 27 Postnatal maturation of mossy fibre excitatory transmission in mouse C3 pyramidal cells: a potential role for kainate receptors Cécile Marchal and Christophe Mulle Laboratoire
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Control of CA3 Output by Feedforward Inhibition Despite Developmental Changes in the Excitation-Inhibition Balance
 Control of C Output by Feedforward Inhibition Despite Developmental Changes in the Excitation-Inhibition alance The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Control of C Output by Feedforward Inhibition Despite Developmental Changes in the Excitation-Inhibition alance The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development
 Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis
 Enrico Cherubini Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis SPACE PHYSICS and BIOLOGY Dubna, December 19-23, 2010 The construction of the brain relies on genetic
Enrico Cherubini Correlated network activity in the developing hippocampus: role in synaptogenesis SPACE PHYSICS and BIOLOGY Dubna, December 19-23, 2010 The construction of the brain relies on genetic
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0356 TITLE: New Treatments for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy that Target Presynaptic Transmitter Release PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Emilio R. Garrido Sanabria, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0356 TITLE: New Treatments for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy that Target Presynaptic Transmitter Release PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Emilio R. Garrido Sanabria, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
DOMINIQUE DEBANNE*, BEAT H. GÄHWILER, AND SCOTT M. THOMPSON MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 11225 11230, October 1996 Neurobiology Cooperative interactions in the induction of long-term potentiation and depression of synaptic excitation between hippocampal
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 11225 11230, October 1996 Neurobiology Cooperative interactions in the induction of long-term potentiation and depression of synaptic excitation between hippocampal
A tale of a thousand electrodes and one - Combining multielectrode array with patch clamp
 A tale of a thousand electrodes and one - Combining multielectrode array with patch clamp Technical Journal Club March 26 2018 Marc Emmenegger The brain Regulation of involuntary and voluntary internal
A tale of a thousand electrodes and one - Combining multielectrode array with patch clamp Technical Journal Club March 26 2018 Marc Emmenegger The brain Regulation of involuntary and voluntary internal
