Neuronal-glial chemical transmission mediated by glutamate and ATP Prof. Alexei Verkhratsky
|
|
|
- Josephine Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MD, PhD, DSc Professor of Neurophysiology, The University of Manchester, Faculty of Life Sciences, Manchester, UK 1 Experiments on glial cells in tissue culture demonstrated expression of neurotransmitter receptors Verkhratsky & Kettenmann (1996) Trends Neurosci.,19: Bergmann glial cells in situ express restricted receptor pattern which matches that of neuronal partners Experiments on glial cells in situ showed that receptors patterns are restricted to match neurotransmitters released in a particular brain region NT LC CF PF Bergmann glial cell AMPA mglur1,5 PLC P 2Y H 1 PLC H 1 PLC ET B NA, Glu, Hist Glutamate receptors Purinoreceptors Histamine receptors Adrenoreceptors Endotheline receptors AMPA mglur1 PLC P 2Y P 2X PLC H 1 H 1 ET B(?) Purkinje neurone GABA A GABA receptors GABA GABA A CF Verkhratsky, Orkand & Kettenmann (1998) Physiol Rev.,78: BA ST 3 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
2 Astrocytes form communication channels with nearby neurones Verkhratsky & Kirchhoff (2007) Neuroscientist, 13: Neurotransmission by glutamate: glutamate sensors Neurotransmission by glutamate: glutamate sensors Verkhratsky & Kirchhoff (2007) Neuroscientist, 13: mediated through glutamate Ionotropic glutamate receptors 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
3 Identification of neurotransmitter receptors in cultured astrocytes V m (mv) GABA Aspartate Glutamate Glycine Kettenmann, Backus, Schachner (1984) Neurosci Lett,52: (IF~2) L-glutamate D-glutamate Kainic acid L-aspartate D-aspartate NMDA Quinquialate Bowman, Kimelberg (1984) Nature, 311: (IF ~20) 7 Kainate induces massive calcium influx mediated by AMPA receptors into Bergmann glial cells in cerebellar slice preparations A Control Kainate Patch pipette loaded with Fura-2 Bergmann glial cell Purkinje cell layer F 340/380 Verkhratsky, A., Orkand, RK & Kettenmann., H. (1998) Physiol. Rev.,78: NMDA receptors in astroglial cells The NMDA receptor was, for a long time, believed to have exclusively neuronal localisation The NMDA receptors possess an important property of Mg 2+ block that precludes their opening at hyperpolarised membrane potentials The astroglial resting potential is set at -80 to -90 mv and therefore it was assumed that NMDA receptors can not function in glial cells Vorobjev VS. (1991) J Neurosci. Methods, 38: Pankratov Y, Lalo U, Krishtal O, & Verkhratsky A. (2002) J. Physiol.,542: Akaike N & Moorhouse AJ. (2003) Trends Pharmacol. Sci.,24: I norm V m (mv) The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 3
4 Glutamate induces a complex current response sensitive to inhibitors of AMPA and NMDA receptors and glutamate/na + transporters Lalo, Pankratov, Kirchhoff, North & Verkhratsky (2006) Journal of Neuroscience, 26: NMDA induces glycine-sensitive current response in isolated astrocytes I norm N A [NMDA], mm Lalo, Pankratov, Kirchhoff, North & Verkhratsky (2006) Journal of Neuroscience,26: Astroglial NMDA receptors are magnesium insensitive D I norm V m (mv) mm Mg 2+ 5 mm Mg mm Mg 2+ Lalo, Pankratov, Kirchhoff, North & Verkhratsky (2006) Journal of Neuroscience,26: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 4
5 mediated through glutamate Ionotropic receptors Metabotropic receptors 13 A Parallel fibers stimulation triggers calcium signals in Bergmann glial cell microdomains Pia PF STIM 200 mm B 1 2 C s PCL D 255 BG 10 mm 4 mm F/F 1.0 F/F 0 2 s Grosche, Matyash, Moller, Verkhratsky, Reichenbach & Kettenmann (1999) Nat. Neurosci., 2: mediated through glutamate Ionotropic receptors Metabotropic receptors Glutamate transporters 15 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 5
6 Astrocytes form the main glutamate-uptake system in the CNS 80% 20% Verkhratsky & Butt, (2007) Glial Neurobiology A Textbook, Wiley & Sons 16 Voltage-dependence of GluT- and AMPAR-mediated currents I norm Kirischuk, Kettenmann & Verkhratsky (2007) Pflugers Arch.,454: Application of glutamate triggers inward current and sodium influx Kirischuk, Kettenmann & Verkhratsky (2007) Pflugers Arch.,454: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 6
7 Different sensitivities of glial glutamate sensors allow precise determination of extracellular glutamate concentration NMDAR K D ~2 mm K D ~50 mm K D ~3-100 mm K D ~130 mm AMPAR GluNa + T mglur1/5 Verkhratsky & Kirchhoff (2007) Neuroscientist, 13: principal transmitter in neuronal-glial networks 20 -mediated transmission: the beginning was discovered in 1929 Extracellular signalling role of purines was suggested in 1929 Geoffrey Burnstock was born on May 10, 1929 Burnstock G., (1972) Purinergic nerves, Pharmacol. Rev., 24: GB: I came up with this concept in Pharmacological Reviews in 1972, and nobody believed it At the first Purines Meeting in Canada way back in the late 70s, probably 95% of the science concentrated on adenosine. And my stuff [on signaling through ] was very much frowned on. There were certain very strong figures very influential figures, and gifted and one of them was Robert Berne, who had early on claimed that adenosine was the physiological regulator of blood flow during hypoxia and ischemia in the heart and other organs. He was charming and he was clever, and although he collected adenosine from the hypoxic heart, he was totally opposed to the fact that it might be originating as. At the opening party of the second Purines Meeting a while later, I was suddenly trapped in the corner by several scientists who were also very opposed to the idea of as an extracellular regulator, and being an ex-boxer, I got very worried because I had the sense that it was going to become physical. People were very passionately against this! Geoffrey Burnstock: most highly cited scientist Molecular Interventions(2004) 4: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 7
8 : the primordial signalling molecule The purines were a part of very early signalling evolution Indeed the purines in the form of adenine and guanine phosphates occurred in the prebiotic period (as a result of purely thermal synthetic processes) and rapidly acquired high importance Purines and pyrimidines were essential for construction of both RNA and DNA, and hence their intracellular concentration was high Furthermore, was selected very early as the main source of biological energy, and thus became an indispensable feature of life The prominent roles of adenine-phosphates in energy metabolism in the most primitive life forms and ancient origin of adenine-binding sites are widely recognised This was a critical evolutionary choice as it immediately resulted in birth of the universal intracellular signalling system based on calcium ions, as keeping cytosolic Ca 2+ extremely low became vitally important, since otherwise insoluble Ca 2+ -phopshates would preclude the cell energetics Thus even the most primitive ancient cell had high cytosolic concentrations of (or GTP) and upon cell disintegration gradients of both would be present in the surrounding water This may have been the initial form of chemical transmission, which remained throughout evolution Indeed every known cell or single cell organism does display some form of sensitivity to, and moreover the transmission is unique in a sense that it is not confined to a particular tissue or organ of higher organisms it exists everywhere; Indeed it is difficult to find a cell type, which does not show sensitivity to Bursntock& Verkhratsky (2009) Acta Physiologica,195: Mechanisms of release in the central nervous system 23 release and degradation in the CNS Exocytosis in presynaptic terminals Exocytotic and non-exocytotic release in astrocytes Maxi channels Ca 2+ Ca 2+ Transporter-mediated release in axons Damaged cells Ca 2+ Ca 2+ ADP AMP Adenosine NTPDases, NPPs, Alk Phosp, 5 -Nuc, Myok, NDK Abbracchio, Burnstock, Verkhratsky & Zimmermann (2009) TINS, 32: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 8
9 Exocytotic release from synaptic terminals Dissection of GLUR/P2X-mediated mepscs in cortical neurones P2X antagonists selectively inhibit small amplitude mepscs Pankratov, Lalo, Verkhratsky, North (2007) J. Gen. Physiol., 129: Quantal release of from acutely isolated cortical astrocytes A B TFLLR 10 mm HEK293-P2X 2 cell Astrocyte [Ca 2+ ] i DF/F 0 (100%) HEK293 I m 8 pa Isolated astrocyte PPADS 10 mm TFLLR 10 mm 5 s Astrocyte [Ca 2+ ] i Lalo, Verkhratsky, Pankratov (2011) Semin Cell Dev Biol 22: HEK293 I m 26 Purinoceptors: an overview Abbracchio, Burnstock, Verkhratsky & Zimmermann (2009) TINS, 32: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 9
10 as a universal transmitter in neuronal-glial circuits Verkhratsky, Krishtal, & Burnstock (2009) Mol. Neurobiol., 39: Iono- and metabotropic receptors expressed in astroglia trigger calcium signals in the optic nerve DF/F 0 Thapsigargin 30s Zero-Ca 2+ Hamilton, Vayro, Kirchhoff, Verkhratsky, Robbins, Gorecki & Butt (2008) Glia,56: as a universal glial transmitter: oligodendrocytes A D B 10 mm 25 mm E C Kirischuk S, Scherer J, Kettenmann H, Verkhratsky A., (1995) J. Physiol., (London) 483: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 10
11 -induced currents in cortical astrocytes Lalo, Pankratov, Wichert, Rossner, North, Kirchhoff & Verkhratsky (2008) Journal of Neuroscience, 28: Concentration-dependence of -induced currents Lalo, Pankratov, Wichert, Rossner, North, Kirchhoff & Verkhratsky (2008) Journal of Neuroscience, 28: A Pharmacology of -induced currents B * TNP-: 2,3 -O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) adenosine 5 -triphosphate Lalo, Pankratov, Wichert, Rossner, North, Kirchhoff & Verkhratsky (2008) Journal of Neuroscience, 28: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 11
12 Subunit composition of the astroglial P2X receptor Sensitivity to Sensitivity to abme Kinetics Rebound upon washout Ca 0-dependence Desensitization Inhibition by PPADS TNP- P2X 1/5 receptor expressed in artificial systems Exceptionally High, EC50 ~ 50 nm Yes Biphasic: rapid peak and steady-state Yes No No 100% inhibition Astroglial P2X receptor Exceptionally High, EC50 ~ 40 nm Yes Biphasic: rapid peak and steady-state Yes No No 100% inhibition Lalo, Pankratov, Wichert, Rossner, North, Kirchhoff & Verkhratsky (2008) Journal of Neuroscience, 28: Cortical astrocytes express P2X 1 and P2X 5 subunits Lalo, Pankratov, Wichert, Rossner, North, Kirchhoff & Verkhratsky (2008) Journal of Neuroscience, 28: Synaptic stimulation triggers fast astroglial currents mediated by ionotropic receptors and glutamate transporters 36 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 12
13 Glial synaptic currents (GSC) in the neocortex Stimulus/TTX dependence of GSCs and EPSCs Stimulus-frequency dependence of GSCs Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: Ionotropic receptors and glutamate transporter mediate GSC in the neocortex Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: A Spontaneous glial synaptic currents B Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 13
14 Calcium permeability of astroglial NMDA and P2X 1/5 receptors 40 Calcium permeability of NMDA and P2X 1/5 receptors in cortical astrocytes P Ca /P mono ~ 3 P Ca /P mono ~ 2 Palygin, Lalo, North, Verkhratsky & Pankratov, (2010) Cell Calcium, 28: Stimulation of NMDA and P2X 1/5 receptors triggers Ca 2+ signals in isolated cortical astrocytes Palygin, Lalo, North, Verkhratsky & Pankratov, (2010) Cell Calcium, 28: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 14
15 Synaptic stimulation-induced Ca 2+ signals in cortical astrocytes in situ are sensitive to ionotropic receptors antagonists C Palygin, Lalo, North, Verkhratsky & Pankratov, (2010) Cell Calcium, 28: Age-dependent remodelling of ionotropic receptors expression in cortical astroglia 44 In situ recordings from ageing cortical astroglia B Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 15
16 Ageing changes the relative weight of GSCs components 3 months C Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: months 46 Ageing modifies expression of glutamate and purinergic receptors in astroglia Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: Ageing affects ionotropic Ca 2+ signalling in astroglia in situ Lalo, Palygin, North, Verkhratsky, Pankratov, (2011) Aging Cell10: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 16
17 Ionotropic receptors in neuronal-astroglial signalling: What is the role of excitable molecules in non-excitable cells? Fast local signalling in astroglial perisynaptic compartments? NCX iglurs P2XRs EAAT Na/K pump Direct mode Reverse mode Lactate shuttle Lalo, Pankratov, Parpura, Verkhratsky (2011) Biochim Biophys Acta 1813: Conclusions Astroglial cells express several classes of fast ionotropic receptors These receptors are activated by ongoing synaptic transmission and mediate local cytoplasmic signalling mediated through [Ca 2+ ] i and [Na + ] i transients Rapid activation of astroglial ionotropic receptors can be instrumental for highly localised neuronal-glial signalling at the synaptic level Age-dependent decrease in synaptic communication in neuronal-glial circuitry may signify the beginning of age-dependent decline in brain functions Alternatively however, the bell-shaped changes in glial synaptic transmission may reflect maturation of the CNS, pruning of functionally irrelevant synaptic contacts and manifest the attainment of wisdom which generally accompanies advanced age The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 17
Neuronal-glial chemical transmission mediated by glutamate and ATP
 1 Experiments on glial cells in tissue culture demonstrated expression of neurotransmitter receptors 2 Neuronal-glial chemical transmission mediated by glutamate and TP lexei Verkhratsky The University
1 Experiments on glial cells in tissue culture demonstrated expression of neurotransmitter receptors 2 Neuronal-glial chemical transmission mediated by glutamate and TP lexei Verkhratsky The University
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
TA Review. Neuronal Synapses. Steve-Felix Belinga Neuronal synapse & Muscle
 TA Review Steve-Felix Belinga sbelinga@wustl.edu Neuronal synapse & Muscle Neuronal Synapses 1 Things you should know beyond the obvious stuff 1. Differences between ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
TA Review Steve-Felix Belinga sbelinga@wustl.edu Neuronal synapse & Muscle Neuronal Synapses 1 Things you should know beyond the obvious stuff 1. Differences between ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
University of Warwick institutional repository:
 University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
How neurons talk. Nivedita Chatterjee Vision Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai
 How neurons talk Nivedita Chatterjee Vision Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai The Synaptic Bouton of a chemical synapse Chemical synapse with synaptic cleft The Electrical synapse works
How neurons talk Nivedita Chatterjee Vision Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai The Synaptic Bouton of a chemical synapse Chemical synapse with synaptic cleft The Electrical synapse works
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY SYNAPTIC COMMUNICATION ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NERVE ENDINGS II. Interneuronal communication 2 INTERNEURONAL COMMUNICATION I. ELECTRONIC SYNAPSE GAP JUNCTION II. CHEMICAL SYNAPSE SYNAPSES
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs)
 Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse
 Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
Applied Neuroscience. Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017
 Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
The wufless-ness of glutamate!
 The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Human Brain and Senses
 Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Human Brain and Senses Outline for today Levels of analysis Basic structure of neurons How neurons communicate Basic structure of the nervous system Levels of analysis Organism Brain Cell Synapses Membrane
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded.
 When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
When cells are already maximally potentiated LTP is occluded. Stein, V et al., (2003) J Neurosci, 23:5503-6606. Also found in Rat Barrel Cortex Ehrlich & Malinow (2004) J. Neurosci. 24:916-927 Over-expression
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses
 M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
Changes in Extracellular Ionic Composition q
 Changes in Extracellular Ionic Composition q JL Stringer, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, United States Ó 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction 1 Background 1 Methods 2 Recent Results
Changes in Extracellular Ionic Composition q JL Stringer, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, United States Ó 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction 1 Background 1 Methods 2 Recent Results
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission.
 The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission Mitesh Shrestha Structure of the neuron the neuron consists of: the cell body, or
The axon and the nerve impulse, Generation and propagation of the nerve impulse, Ionic channels, Synaptic transmission Mitesh Shrestha Structure of the neuron the neuron consists of: the cell body, or
Neuroscience 201A (2016) - Problems in Synaptic Physiology
 Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 5. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GABAERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 5-1: GABA A receptor-mediated current and potential changes GABAergic synaptic transmission 1 Constance
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 5. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GABAERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 5-1: GABA A receptor-mediated current and potential changes GABAergic synaptic transmission 1 Constance
Problem Set 3 - Answers. -70mV TBOA
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience Course Director: Dr. David Corey HST 131/ Neuro 200 18 September 05 Explanation in text below graphs. Problem
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience Course Director: Dr. David Corey HST 131/ Neuro 200 18 September 05 Explanation in text below graphs. Problem
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Neuropharmacology NOTES
 Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
de Montpellier, Montpellier, France and Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes Sorbonne, Paris, France.
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of Ca 2+ Signaling Mechanisms Our Experience on the Intercellular Communication in Muscle Remodeling S. Filip 1, J. Mokrý 2, O. Forostyak 3, G. Dayanithi 4,5 1 Charles University,
SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of Ca 2+ Signaling Mechanisms Our Experience on the Intercellular Communication in Muscle Remodeling S. Filip 1, J. Mokrý 2, O. Forostyak 3, G. Dayanithi 4,5 1 Charles University,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Physiology of synapses and receptors
 Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
Department of medical physiology 1 st week
 Department of medical physiology 1 st week Semester: summer Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology 1 st week 1. General neurophysiology 2. Central
Department of medical physiology 1 st week Semester: summer Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology 1 st week 1. General neurophysiology 2. Central
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Neuroscience, synapses, and the most potent toxin known to man. Dr. Katie Hoffman Lehigh University Biological Sciences Department
 Neuroscience, synapses, and the most potent toxin known to man Dr. Katie Hoffman Lehigh University Biological Sciences Department Mouse stem cell derived neuron Mouse hippocampal slice What makes us who
Neuroscience, synapses, and the most potent toxin known to man Dr. Katie Hoffman Lehigh University Biological Sciences Department Mouse stem cell derived neuron Mouse hippocampal slice What makes us who
Chapter 2 Ex uno plures: Out of One, Many
 Chapter 2 Ex uno plures: Out of One, Many R. Gutie rrez Abstract Ex uno plures, out of one (cell) many (neurotransmitters), seems to be a principle that applies to many, if not all, neuronal types. The
Chapter 2 Ex uno plures: Out of One, Many R. Gutie rrez Abstract Ex uno plures, out of one (cell) many (neurotransmitters), seems to be a principle that applies to many, if not all, neuronal types. The
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 18, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Nervous System Communication. Nervous System Communication. The First Nerve Cells 1/2/11
 Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels. Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker
 Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013
 NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body
 The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3
 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES. Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I.
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
PRESYNAPTIC IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS AND CONTROL OF TRANSMITTER RELEASE
 PRESYNAPTIC IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS AND CONTROL OF TRANSMITTER RELEASE Holly S. Engelman and Amy B. MacDermott Presynaptic nerve terminals are dynamic structures that release vesicular packages of neurotransmitter,
PRESYNAPTIC IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS AND CONTROL OF TRANSMITTER RELEASE Holly S. Engelman and Amy B. MacDermott Presynaptic nerve terminals are dynamic structures that release vesicular packages of neurotransmitter,
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
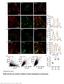 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems
 CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Synapses and synaptic plasticity. Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember
 Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Glial calcium and sodium signalling
 Glial calcium and sodium signalling How calcium signalling was discovered Principles of calcium signalling Calcium signalling in neuroglia Voltage- and ligand-gated channels Endoplasmic reticulum calcium
Glial calcium and sodium signalling How calcium signalling was discovered Principles of calcium signalling Calcium signalling in neuroglia Voltage- and ligand-gated channels Endoplasmic reticulum calcium
Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Mohammad Tarek. Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology
 Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Dania Ahmad. Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad. Faisal I. Mohammed
 16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
Introduction to CNS 1
 Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
Notes: Synapse. Overview. PSYC Summer Professor Claffey PDF. Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the
 PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
CONTEXT. LTP (long term potentiation) definition. LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory
 CONTEXT LTP (long term potentiation) definition LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory LTP is due primarily to a pre or post- synaptic modification? (Increased Glut release or increased
CONTEXT LTP (long term potentiation) definition LTP as a interesting mechanism for learning and memory LTP is due primarily to a pre or post- synaptic modification? (Increased Glut release or increased
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Structure of a Neuron:
 Structure of a Neuron: At the dendrite the incoming signals arrive (incoming currents) At the soma current are finally integrated. At the axon hillock action potential are generated if the potential crosses
Structure of a Neuron: At the dendrite the incoming signals arrive (incoming currents) At the soma current are finally integrated. At the axon hillock action potential are generated if the potential crosses
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
