Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Alyson Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D.
2 Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26
3 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26
4 Skull Pg. 26
5 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26
6 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26
7 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26
8 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26
9 An elderly woman complains of a slow onset of headache, dizziness, and nausea. Upon physical examination, it is noted that 5 days previous she fell and hit her head on the pavement. She still has a nice goose egg. A head CT show diffuse bleeding outside the brain. What type of hematoma/hemmorhage would you suspect in this patient? A. Epidural hematoma due to a ruptured berry aneurysm (small sac-like ballooning of the vessel wall) of the anterior communicating artery B. Epidural hematoma due to a torn middle meningeal artery C. Subarachnoid hematoma due to a ruptured berry aneurism (small sac-like ballooning of the vessel wall) of the anterior communicating artery D. Subarachnoid hematoma due to a torn emissary vein coursing from the scalp to a dural sinus E. Subdural hematoma due to a torn bridging vein coursing from the cerebrum to a dural sinus F. Subdural hematoma due to a torn middle meningeal artery
10 One aspect of the cardio-physical exam is measuring the jugular venous pressure (JVP). The JVP appears as a pulse seen in the neck, but it is actually occurring in the venous system, not the arterial. This is due to right atrial contraction, where some blood is pushed back out of the chamber and up the superior vena cava all the way to the jugular vein in a pulsating fashion. The IJV lacks valves. There is usually two pulses seen for the JVP and only one for the carotid pulse. Describe what is responsible for this observation.
11 One aspect of the cardio-physical exam is measuring the jugular venous pressure (JVP). The JVP appears as a pulse seen in the neck, but it is actually occurring in the venous system, not the arterial. This is due to right atrial contraction, where some blood is pushed back out of the chamber and up the superior vena cava all the way to the jugular vein in a pulsating fashion. The JVP is only pathologic if the pulse is seen too high up the neck, indicating an overload or back up of blood entering the heart.
12 The JVP is only pathologic if the pulse is seen too high up the neck, indicating an overload or back up of blood entering the heart. The JVP can be caused by a number of conditions. Which of the following would NOT cause an abnormally high JVP? A. Abnormal tricuspid valve (prolapsed or stenotic) B. Fluid overload (renal failure causing an increased blood volume) C. Right atrial fibrillation (uncoordinated contraction or quivering) D. Right-sided heart failure (due to pulmonary hypertension)
13 A 2-year-old boy is brought to see a neurologist for a 3-month history of vomiting, irritability, and excessive sleepiness. On examination, he is noted to have papilledema, prompting the neurologist to order a head CT, which reveals greatly dilated lateral and third ventricles, but a normal-appearing fourth ventricle and cerebral aqueduct. What is the location of this infant s occlusions? A. Cerebra aqueduct B. Lateral aperature C. Median aperature D. Foreman of Monro (interventricular foramen) E. Fourth ventricle
14 A 2-year-old boy is brought to see a neurologist for a 3-month history of vomiting, irritability, and excessive sleepiness. On examination, he is noted to have papilledema, prompting the neurologist to order a head CT, which reveals greatly dilated lateral and third ventricles, but a normal-appearing fourth ventricle and cerebral aqueduct. What is the location of this infant s occlusions?
15 You conduct a post-operative check-up on a patient that has underwent the removal of an atherosclerotic plaque in the right common carotid artery. During the check-up you observe large fluctuations in blood pressure. Damage to which cranial nerve may be associated with this blood pressure instability? A. CN V-3 B. CN VI C. CN VII D. CN VIII E. CN IX F. CN XII
16 Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) VS: carotid sinus and body
17 A surgeon is performing a carotid endarterectomy in a 64-year-old man who has a carotid artery occlusion. While approaching the internal carotid artery, a nerve embedded within the fascia of the carotid sheath is severed. Describe what effect may occur as a result of this nerve lesion. Sensory (dermatomal, cutaneous field)? Motor (suprahyoid, infrahyoid, etc )?
18 Carotid sheath - Ansa cervicalis
19 In the case of peritonitis in the parietal peritoneum on the inferior surface of the diaphragm, pain my be referred through each of the following nerves EXCEPT: a) Great auricular b) Lesser occipital c) Supraclavicular d) Transverse cervical
20
21 THANK-YOU
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
What Are We Going to Do? Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy. Hydrocephalus and Effects of Interruption of CSF Flow. Tube Blockage Doctrine
 Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination - November 4, 2013
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination - November 4, 2013 NOTE 1: Whenever your answer refers to a cranial nerve, give both its number and its name. In the case of the trigeminal nerve, give
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination - November 4, 2013 NOTE 1: Whenever your answer refers to a cranial nerve, give both its number and its name. In the case of the trigeminal nerve, give
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
8th Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/28/2014
 Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Quality Metrics. Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes
 Quality Metrics Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes Below is a description of some of the stroke-related procedures performed at St. Dominic Hospital in Jackson, with quality information on the complication
Quality Metrics Stroke Related Procedure Outcomes Below is a description of some of the stroke-related procedures performed at St. Dominic Hospital in Jackson, with quality information on the complication
Tutorials. By Dr Sharon Truter
 Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
The SCALP. Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
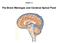 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Blood Supply. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Papilledema. Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D.
 Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Stroke Awareness. Presented by: Duane Anderson, MD Snoqualmie Valley Hospital Emergency Department Medical Director
 Stroke Awareness Presented by: Duane Anderson, MD Snoqualmie Valley Hospital Emergency Department Medical Director What is a stroke? Stroke can happen to anyone. Stroke is the fourth leading cause of death
Stroke Awareness Presented by: Duane Anderson, MD Snoqualmie Valley Hospital Emergency Department Medical Director What is a stroke? Stroke can happen to anyone. Stroke is the fourth leading cause of death
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8. Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet.
 Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8 Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet. Interactive Physiology o Open Internet Explorer and go to the Health
Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8 Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet. Interactive Physiology o Open Internet Explorer and go to the Health
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Lab CT scan. Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali
 Lab CT scan Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali Some rules to read The CT Scan : 1. Remember that it s a transverse section across the body and we are looking at the inferior part of the section (not the superior),
Lab CT scan Murad Kharabsheh Yaman Alali Some rules to read The CT Scan : 1. Remember that it s a transverse section across the body and we are looking at the inferior part of the section (not the superior),
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Anatomy #9. Rashed AL-Jomared. The Cranial Nerves IX. Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji
 Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Injuries to the head and spine
 Injuries to the head and spine Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Nervous System Two sub-systems Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 cranial
Injuries to the head and spine Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Nervous System Two sub-systems Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 cranial
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE
 REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
Head Trauma Inservice (October)
 John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
