Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves)
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Stevenson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
2 Objectives By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the deep origin of both Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves. Locate the exit of each nerve from the brain stem. Describe the course and distribution of each nerve. List the branches of both nerves.
3 Extra Slide: Mnemonics And Pictures To Help Memorise The Cranial Nerves 04:07 Big Brains Matter More
4 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve o It is principally a Sensory nerve with preganglionic parasympathetic and few motor fibers (it is a mixed nerve but most of the fibers are sensory). o It has no real nucleus to itself. Instead it shares nuclei with VII (facial) and X (vagus).
5 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Superficial Attachment o o It arises from the ventral aspect of the medulla by a linear series of small rootlets, in groove between olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle. It leaves the cranial cavity by passing through the jugular foramen in company with the Vagus (10), Acessory (11) nerves and the Internal jugular vein. Extra Extra Extra
6 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Course (extracranial) o It Passes forwards between Internal jugular vein and External carotid artery. o Lies Deep to Styloid process. o Passes between external and internal carotid arteries at the posterior border of Stylopharyngeus then lateral to it. Extra o It reaches the pharynx by passing between middle and inferior constrictors, deep to Hyoglossus, where it breaks into terminal branches. Extra
7 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Component of fibers & Deep origin (Deep origin = nuclei) Recall: SAME Sensory Afferent Motor Efferent SVE fibers: Special Visceral Efferent GVE fibers: General Visceral Efferent SVA fibers: Special Visceral Afferent GVA fibers: General Visceral Afferent originate from nucleus ambiguus (NA) arise from inferior salivatory nucleus (ISN) arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, their central processes terminate in nucleus of solitary tract (NST) end in nucleus of solitary tract. supply stylopharyngeus muscle relay in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland the peripheral processes supply the taste buds on posterior third of tongue. visceral sensation (pain and temp.) from mucosa of posterior third of tongue, pharynx, auditory tube and tympanic cavity, carotid sinus
8
9 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Ganglia & Communications It has two ganglia: o o Superior ganglion: Superior Small Small, with no branches. It is connected to the Superior Cervical sympathetic ganglion. Inferior ganglion: Large and carries general sensations from pharynx, soft palate and tonsil. It is connected to Auricular Branch of Vagus. The Trunk of the nerve is connected to the Facial nerve at the stylomastoid foramen
10 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Branches 1. Tympanic: relays in the otic ganglion and gives secretomotor to the parotid gland 2. Nerve to Stylopharyngeus muscle. (SVE fiber) 3. Pharyngeal: to the mucosa of pharynx. 4. Tonsillar. (GVE fiber) 5. Lingual : 6. carries sensory branches, general and special ( taste) from the posterior third of the tongue. (SVA fiber) o Sensory branches from the carotid sinus and body (pressoreceptors and chemoreceptors). Extra
11 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Nerve Lesions It produces: o Difficulty of swallowing; Impairment of taste and sensation over the posterior one-third of the tongue,palate and pharynx. o Absent gag reflex. Dysfunction of the parotid gland (it is salivary gland, dysfunction will lead to dry mouth). How to test for IX injury? o Have the patient open the mouth and inspect the palatal arch on each side for asymmetry. o Use a tongue blade to depress the base of the tongue gently if necessary. o Ask the patient to say "ahhh" as long as possible. Observe the palatal arches as they contract and the soft palate as it swings up and back in order to close off the nasopharynx from the oropharynx. o Normal palatal arches will constrict and elevate, and the uvula will remain in the midline as it is elevated. With paralysis there is no elevation or constriction of the affected side. o warn the patient that you are going to test the gag reflex. Gently touch first one and then the other palatal arch with a tongue blade, waiting each time for gagging.
12 Glossopharyngeal (IX) 9 th Cranial Nerve Summary
13 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve o It is a Mixed nerve. o Its name means wandering حائر it goes all the way to the abdomen) o So it is the longest and most widely distributed cranial nerve. o The principal role of the vagus is to provide parasympathetic supply to organs throughout the thorax and upper abdomen. o It also gives sensory and motor supply to the pharynx and larynx.
14 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Superficial Attachment & Course o Its rootlets exit from medulla between olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle. o Leaves the skull through jugular foramen. o It occupies the posterior aspect of the carotid sheath between the internal jugular vein laterally and the internal and common carotid arteries medially. o It has two ganglia: Superior ganglion in the jugular foramen Inferior ganglion, just below the jugular foramen Extra The sensory fibers end in the ganglion before continuing just like the dorsal root ganglion
15 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Communications o Superior ganglion with: Inferior ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve, Superior cervical sympathetic ganglion & Facial nerve. o Inferior ganglion with: Cranial part of accessory nerve, Hypoglossal nerve, Superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. 1 st cervical nerve.
16 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Course (extracranial) o The vagus runs down the neck on the prevertebral muscles and fascia. o The internal jugular vein lies behind it, and the internal and common carotid arteries are in front of it, all the way down to the superior thoracic aperture. o It lies on the prevertebral muscles and fascia. o Enters thorax through its inlet: Right Vagus descends in front of the right subclavian artery. Left Vagus descends between the left common carotid and subclavian arteries.
17 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Components of fibers & Deep origin Recall: SAME Sensory Afferent Motor Efferent SVE fibers: Special Visceral Efferent (Motor) GVE fibers: General Visceral Efferent (Preganglionic parasympathetic) SVA fibers: Special Visceral Afferent GVA fibers: General Visceral Afferent (sensory) originate from Nucleus Ambiguus, originate from Dorsal Nucleus of Vagus synapses in parasympathetic ganglia, to Spinal Tract & Nucleus of Trigeminal to Nucleus of Solitary Tract to muscles of pharynx and larynx short postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands of viscera. sensation from auricle, external acoustic meatus and cerebral dura mater*, carry impulse from viscera in neck, thoracic and abdominal cavities When stretches causes headache*
18 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Branches (The fibers will give branches) stimulation of auricular will also stimulate cardiac branch to heart so trauma to the ear may lead to tachycardia and cardiac arrest 1. Meningeal Dura (SVA) 2. Auricular nerve external acoustic meatus, and tympanic membrane. 3. Pharyngeal (enters the wall of the pharynx) 4. To carotid body 5. Superior Laryngeal: It divides into: (1) Internal Laryngeal : mucous membrane of the pharynx, superior and middle constrictor muscles, all the muscles of the palate except the tensor palate. provides sensation to the hypopharynx(back), the epiglottis, and the part of the larynx that lies above the vocal folds (2) External Laryngeal : supplies the cricothyroid muscle
19 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Branches 6. Recurrent Laryngeal : it goes round the subclavian artery on the right, and round the arch of the aorta on the left It runs upwards and medially alongside the trachea, and passes behind the lower pole of the thyroid gland. motor supply to all the muscles of the larynx, except the cricothyroid. It also provides sensation to the larynx below the vocal folds. Injury will in thyroidectomy will lead to hoarseness of voice or complete loss of voice
20 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Lesions o Vagus nerve lesions produce palatal and pharyngeal and laryngeal paralysis. o Abnormalities of esophageal motility, gastric acid secretion, gallbladder emptying, and heart rate; and other autonomic dysfunction. How to diagnose X nerve Injury? o o o o Listen to the patient talk as you are taking the history. Hoarseness, whispering, nasal speech, or the complaint of aspiration or regurgitation of liquids through the nose (since soft palate is not working) should make you especially mindful of abnormality. Give the patient a glass of water to see if there is choking or any complaints as it is swallowed. Laryngoscopy is necessary to evaluate the vocal cord (to assess movement).
21 Vagus (X) 10 th Cranial Nerve Summary o X is a mixed nerve. o It contains afferent, motor, and parasympathetic fibers. o The afferent fibers convey information from: esophagus, tympanic membrane, external auditory meatus and part of chonca of the middle ear. End in trigeminal sensory nucleus. o Chemoreseptors in aortic bodies and baroreseptors in aortic arch. o Receptors from thoracic & abdominal viscera, end in nucleus solitarius. o The motor fibers arise from nucleus ambiguus of medulla to innervate muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, and upper part of esophagus. o The parasympathetic fibers originate from dorsal motor nucleus of vagus in medulla distributed to cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems (up to right 2/3 the rest is from sacral fibers s2-s4).
22 Causes of both IX & X nerve lesions: 1. Lateral medullary syndrome: A degenerative disorder seen over age of 50 mostly due to Thrombosis of the Inferior Cerebellar Artery. 2. Tumors compressing the cranial nerves in their exiting foramina from the cranium via the skull base Extra Manifested by: Ipsilateral* paralysis of the muscles of the Palate, Pharynx and Larynx. Ipsilateral loss of Taste from the Posterior Third of tongue. *the same side of the body Extra
23 Nerve Glossopharyngeal (9th) Vagus (10th) Type Sensory (mainly) Mixed Exits from Ventral medulla (b/w olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle) Leaves cranial cavity via Jugular foramen Jugular foramen Nuclei 1. Nucleus ambiguous 2. Inferior salivatory nucleus 3. Nucleus of solitary tract Branches 1. Tympanic 2. Nerve to stylopharyngeus muscle 3. Pharyngeal 4. Tonsillar 5. Lingual 6. Sensory (from carotid sinus and body) Nerve lesion manifestation 1. Difficulty swallowing 2. Impairment of taste and sensation of posterior 1/3 of the tongue, palate and pharynx. 3. Absent gag reflex 4. Dysfunction of parotid gland Ventral medulla (b/w olive and inferior cerebellar peduncle) 1. Nucleus ambiguous 2. Dorsal nucleus of vagus 3. Spinal tract & nucleus of trigeminal 4. Nucleus of solitary tract 1. Meningeal 2. Auricular nerve 3. Pharyngeal 4. To carotid body 5. Superior laryngeal (internal and external laryngeal) 6. Recurrent laryngeal 1. Palatal, pharyngeal, and laryngeal paralysis. 2. Abnormalities of: esophageal motility gastric acid secretion gall bladder emptying heart rate 3. Other autonomic dysfunction Cause of nerve lesion 1. Lateral medullary syndrome 2. Tumors compressing the cranial nerves in their exit
24 1. Glossopharyngeal shares its nuclei with: A- CN 7 & 8 B- CN 7 & 10 C- CN 8 & 10 D- CN 11 Answer: B MCQs 5. The right vagus nerve descends: A- in front right subclavian artery. B- in front of right subclavian vein. C- between left common carotid and subclavian arteries. D- between right common carotid and subclavian arteries. Answer: A 2. Cranial nerves 9 and 10 exit the cranial cavity through: A- foramen magnum B- foramen ovale C- jugular foramen D- carotid foramen Answer: C 3. The tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal supplies: A- parotid gland B- pineal gland C- pituitary gland D- sublingual gland Answer: A 4. A patient was shown to have absent gag reflex. Which nerve is most likely affected: A- facial B- vagus C- glossopharyngeal Answer: C 6. Which of the following nuclei give fibers to muscles of pharynx and larynx? A- nucleus solitarus B- nucleus ambiguus C- nucleus of trigeminal Answer: B 7. Cricothyroid is supplied by which branch of the vagus nerve: A- internal laryngeal B- external laryngeal C- recurrent laryngeal Answer: B 8. CN 9 & 10 lesions can be caused by: A- lateral medullary syndrome B- medial medullary syndrome C- anterior medullary syndrome D- posterior medullary syndrome Answer: A
25 Leaders: Nawaf AlKhudairy Jawaher Abanumy Members: Hamad alkhudairy Abdulaziz alsalman Anatomy Team References: 1- Girls & Boys Slides 2- Greys Anatomy for Students 3- TeachMeAnatomy.com
Anatomy #9. Rashed AL-Jomared. The Cranial Nerves IX. Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji
 Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben
 lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
Lec#10 Part 2. Dawood Alatefi. Mariam Hassouneh. Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem
 Lec#10 Part 2 Dawood Alatefi Mariam Hassouneh Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem This part s record is found on the Batch s channel as LabA.3, starting from 0.00min until 26.20min. Hope this ll be an easy part on you;
Lec#10 Part 2 Dawood Alatefi Mariam Hassouneh Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem This part s record is found on the Batch s channel as LabA.3, starting from 0.00min until 26.20min. Hope this ll be an easy part on you;
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II. Nerves covered in other lectures. A reminder about embryology. Prof. Stuart Bunt
 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
Brain Stem. 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata
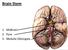 Brain Stem 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata 1 Ext. features Medulla Oblongata *Direct continuation of Spinal Cord *Extend from foramen magnum to lower Pons *More than 2.5 cm in length. *Lower part
Brain Stem 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata 1 Ext. features Medulla Oblongata *Direct continuation of Spinal Cord *Extend from foramen magnum to lower Pons *More than 2.5 cm in length. *Lower part
Cranial Nerves VII to XII
 Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Jolanta Marszalek CN 1,9-12
 Jolanta Marszalek CN 1,9-12 Olfactory SVA, special visceral afferent, which carries the modality of smell Shortest of the CNs Does not emanate from brainstem (CN II) The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory
Jolanta Marszalek CN 1,9-12 Olfactory SVA, special visceral afferent, which carries the modality of smell Shortest of the CNs Does not emanate from brainstem (CN II) The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
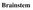 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES. Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa
 MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa SENR 2014 CRANIAL NERVES Olfactory: I Optic: II Oculomotor nerves: III, IV, VI Trigeminal nerve:
MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa SENR 2014 CRANIAL NERVES Olfactory: I Optic: II Oculomotor nerves: III, IV, VI Trigeminal nerve:
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System. Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24
 Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM In the last episode we have seen the structures and function of the components of central nervous system. In this episode we shall examine the peripheral
CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM In the last episode we have seen the structures and function of the components of central nervous system. In this episode we shall examine the peripheral
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
CN I Olfactory. CN II Optic. CN III Oculomotor. Special Sensory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb. Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid
 CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Stimulatory
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
