Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with a Prominent Anterior Spinal Artery Mimicking a Spinal Dural AV Fistula at MRI
|
|
|
- Ami Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report pissn eissn Korean J Radiol 2011;12(6): Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with a Prominent Anterior Spinal Artery Mimicking a Spinal Dural AV Fistula at MRI Seung Young Lee, MD, Sang-Hoon Cha, MD All authors: Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Chungbuk , Korea Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile (CVRM) is a very rare condition. We report a new case of CVRM initially detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spine. MRI demonstrated tortuous vascular signal voids limited to the anterior cerebrospinal fluid space mimicking spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. A diagnosis of CVRM was confirmed on the basis of angiographic findings of rete formation associated with bilateral aplasia of the cavernous internal carotid and vertebral arteries without abnormal arteriovenous connection. Index terms: Carotid and vertebral rete mirabile; MRI INTRODUCTION Rete mirabile (RM) is an arterial or arteriolar meshwork formed by branches from one or more arteries that converge into a single artery. Carotid rete mirabile (CRM) is a physiological network between the external and internal carotid systems that are usually located around the cavernous sinus in lower mammals, such as goats, sheep, and pigs (1). CRM is a very rare pathological condition in humans and is associated with aplasia or hypoplasia of the internal carotid artery (ICA), and carotid and vertebrobasilar RM (CVBRM) is even rarer. To the best of our knowledge, only nine cases, including six of vertebral rete (VR) and three of basilar rete (BR), have been reported. Some of the patients with CVBRM presented with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), intracerebral hemorrhage, or ischemia, Received January 6, 2011; accepted after revision April 8, Corresponding author: Sang-Hoon Cha, MD, Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, 410 Seongbong-ro, Cheongju, Chungbuk , Korea. Tel: (8243) Fax: (8243) shcha@chungbuk.ac.kr This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. but others were asymptomatic. When asymptomatic, the conditions were detected only incidentally on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain. We report the case of a patient with carotid and vertebral RM (CVRM) that was initially detected on MRI of the cervical spine. CASE REPORT A 28-year-old man presented with non-specific posterior neck pain radiating to the shoulder and arm, but not accompanied by sensory or motor changes. The patient was previously healthy with an unremarkable past medical history and no history of trauma. A neurological examination revealed no abnormal features. Non-contrast cervical MRI demonstrated tortuous vascular signal voids limited to the anterior cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) space on T2-weighted images (Fig. 1A). Neither abnormal intramedullary signal intensity, nor spinal cord swelling was observed by MRI. The CT angiography (CTA) performed to evaluate for abnormal vasculature showed a dilated and tortuous anterior spinal artery, focal interruption, and fusiform dilatation at the V4 segment of the vertebral artery (Fig. 1B). CTA demonstrated hypoplastic cervical ICA on the right side and relatively normal cervical ICA on the left side. The carotid canals 740 Korean J Radiol 12(6), Nov/Dec 2011 kjronline.org
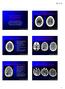
2 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Mimicking Spinal Dural AV Fistula A B C D E F G H Fig. 1. Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile in 28-year-old man. A. T2-weighted images of cervical spine MRI showing tortuous and dilated vascular signal voids (arrows) limited to anterior portion of spinal cord. B. Sagittal reconstructed maximum-intensity-projection image of CT angiography demonstrating dilated anterior spinal artery in spinal canal (black arrow) and fusiform dilatation of right distal vertebral artery (white arrow). C. Coronal reconstructed maximum-intensity-projection image and volume rendering image of CT angiography show hypoplastic cervical internal carotid artery and small carotid canal on right side (white open arrows) compared with normal cervical internal carotid artery and normal carotid canal on left side (black open arrows). D, E. Right common carotid artery angiography demonstrates diffuse narrowing of right internal carotid artery (thin arrows) and occlusion at level of cavernous internal carotid artery (thick arrow) accompanying transdural rete formation (open arrow) through external carotid artery branches. F. Left ICA angiography demonstrates segmental absence of cavernous ICA (white long arrow) with surrounding rete formation (open arrows). Distal basilar and posterior cerebral arteries (white short arrows) are being filled by posterior communicating artery (double arrowheads) and persistent trigeminal artery (arrowhead). All segments of left ICA except for cavernous segment and cerebral arteries appear normal. G, H. Left external carotid artery angiography demonstrates transdural rete formation (arrows) between internal maxillary artery and enlarged ophthalmic artery (arrowhead). were asymmetrically small on the right side (Fig. 1C). A catheter angiography was performed to investigate a spinal arteriovenous fistula (AVF) or arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Angiography of the right common carotid artery (RCCA) demonstrated long segmental narrowing of the right ICA (RICA) from the proximal cervical portion and occlusion at the cavernous segment with trans-dural rete formation through the external carotid artery (ECA) branches (Fig. 1D, E). Selective angiography of the RICA was not attempted due to narrowing of the proximal ICA. Angiography of the left ICA (LICA) demonstrated segmental absence of the cavernous ICA with surrounding rete formation, while all segments of the LICA except for the cavernous portion, middle cerebral artery (MCA), and anterior cerebral artery (ACA) showed normal features. The distal basilar and posterior cerebral arteries are being filled by the posterior communicating artery and the persistent trigeminal artery (Fig. 1F). A left ECA angiography demonstrated transdural rete formation between the internal maxillary artery and the enlarged ophthalmic artery (Fig. 1G, H). A right vertebral artery (RVA) angiography showed segmental absence at the V3 segment of the RVA with surrounding tortuous dilated rete formation. A saccular aneurysm at the distal portion of the rete and fusiform dilatation of the V4 segment of kjronline.org Korean J Radiol 12(6), Nov/Dec
3 Lee et al. I J K L Fig. 1. Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile in 28-year-old man. I-L. Right (I, K, AP views; J, lateral view) and left vertebral artery angiography (L, AP view) show segmental agenesis at V3 segment (white arrow) with surrounding rete formation (black, open arrow). Saccular aneurysm (black arrowhead) at distal portion of rete and fusiform dilatation of V4 segment (black arrow) are demonstrated on right vertebral artery angiography. Enlarged radiculomedullary arteries (white arrowheads) are connected by dilated anterior spinal artery (double arrowheads) that is developed as collateral to asplastic segment. Right distal internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries supplied by posterior communicating artery (white, open arrows), appear normal. the RVA was demonstrated. The distal RICA and right MCA supplied by the posterior communicating artery (P-com) on RVA angiography had a normal configuration (Fig. 1I, J). The radiculomedullary artery (RMA) originating at the proximal RVA (at the level of the seventh cervical vertebra) was enlarged and connected via a prominent anterior spinal artery (Fig. 1K). A left vertebral artery (LVA) angiography revealed similar findings to those of the RVA angiography, with less prominent rete formation at the V3 segment level and RMA origination at the proximal LVA (at the level of the fifth cervical vertebra) (Fig. 1L). Other selective angiographies never showed abnormal arteriovenous connections suggestive of AVF or AVM. Bypass surgery was not attempted because symptoms were mild and the brain perfusion status was relatively normal. DISCUSSION Agenesis, aplasia, and hypoplasia of the ICA are rare. Agenesis is defined as the complete failure of development of an organ; aplasia, lack of development; and hypoplasia, incomplete development (2). Segments of the fully developed ICA correspond to embryonic structures. In segmental agenesis of the ICA, each of these embryonic arteries is a potential source of reconstitution of distal flow in the ICA (3). In the pathogenesis of CRM formation, the most accepted theory is the late (fetal or perinatal) regression of the artery (2, 3). Mahadevan et al. (3) postulated that if agenesis is the primary deficit, the embryonic vessels should be the primary source of recruitment for collateral circulation. If the absence of the ICA occur by regression after its development, the embryonic vessels are already regressed and no longer available for collateral circulation. As the CRM is not present in any human developmental state (3-6), it is probably a secondary change to ICA regression in early development (6). Evaluation of the skull base for presence or absence of the carotid canal is required for distinguishing aplasia from agenesis, since the presence of the ICA precursor is a prerequisite for the development of the carotid canal at 5-6 weeks of gestation. Demonstration of a small carotid canal by CT is helpful for excluding acquired etiologies; the thin and hypoplastic carotid canal demonstrated on CT supports this theory (6). In our case, both carotid canals were demonstrated on CT even though it was very small on the right side and relatively normal on the left side. This CT finding supports the theory that the pathogenesis of CRM is not agenesis, but the later regression of the artery. In this case, we could rule out the pseudorete by acquired atherosclerotic occlusion for several reasons; 1) 742 Korean J Radiol 12(6), Nov/Dec 2011 kjronline.org
4 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Mimicking Spinal Dural AV Fistula the level of segmental agenesis is bilaterally symmetrical; 2) all cervical and cerebral arteries except hypoplastic right cervical ICA showed normal features without stenosis or luminal irregularity; 3) the patient was very young and had no risk factors for atherosclerosis such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and smoking. Sahin et al. (2) described six pathways of collateral circulation in association with ICA absence. Type F refers to collateral flow to the distal ICA via transcranial anastomoses from the maxillary branches of the ECA as well as tiny ICA collaterals, which are called rete mirabile (in Latin, wonderful net ). Carotid rete mirabile has the following characteristic features on angiogram: (i) hypoplastic ICA, (ii) arterial plexus between the maxillary artery and cavernous portion of the ICA, (iii) dilated ophthalmic artery, (iv) supraclinoid ICA that is not hypoplastic and is fed by the arterial plexus and ophthalmic artery, (v) bilateral lesions, and (vi) no abnormal vessels such as moyamoya in the intradural circulation (2, 7). In our case, all of these features were identified on angiography. Agenesis of the vertebral artery with associated rete compensation is even rarer than ICA agenesis. Most VRM occurs at the transdural segment with collateral circulation from the muscular and meningeal branches. To our knowledge, there are nine cases in the literature of carotid and vertebrobasilar rete mirabile in the literature (Table 1). Transdural rete formation was associated with vertebral agenesis in six cases (3, 4, 7-10), while intradural rete formation associated with basilar agenesis occurred in two cases (2, 6), and vertebrobasilar agenesis occurred in one (5). In only two of these cases, angiography demonstrated both transdural anastomosis via dilated anterior spinal or medullary arteries and intradural rete formation (3, 7). In our case, MRI of the cervical spine was performed as an initial examination, and we suspected spinal dural AVF. However, unlike typical AVF, MRI showed multiple vascular signal voids in only the anterior aspect of the spinal cord, and the dilated vessels were larger in our case than in spinal AVF. CRM can appear as moyamoya disease on brain MRI because it demonstrates dot-like signal voids at the basal cistern; however, the important difference between CRM and moyamoya disease is that MRI reveals normal supraclinoid ICA, MCA, and ACA signal voids in CRM. Some mammals, such as cats, sheep, goats, oxen, and pigs, have well-developed CRM as a part of their normal physiology (to prevent overheating of the brain and regulate the pressure and flow of the cerebral blood circulation). In humans, however, CVBRM can be a clinically significant condition because it frequently presents with hemorrhagic and ischemic manifestations at a relatively young age. According to Li et al. (7), 27 patients with CRM had variable presentations: 12 with ischemic stroke, 11 with SAH, and four with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Of the nine patients with CVBRM, three presented with ischemic events including ischemic stroke in two (a 40-year-old man and 34-year-old woman) and temporary blindness in one (a 29-year-old woman). In addition, one patient presented with carotid-cavernous fistula (a 20-year-old man), one patient presented with subarachnoid hemorrhage Table 1. Reported Cases of Bilateral Carotid and Vertebrobasilar Rete Mirabile Authors (Ref. No.) Age/Sex Presenting Symptom ICA VA BA Initial Detection/Associated Lesion Jones and Wetzel, 1970 (8) 43/M None Both Both Incidentally in AVM workup/avm Koo and Newton, 1972 (9) 20/M CCF Both Both Angiography/pseudoxanthoma elasticum Itoyama et al., 1993 (4) 40/M Ischemic stroke Both Both Multiple cerebral infarctions on CT Hyogo et al., 1996 (10) 37/F SAH Both Right Angiography Mahadevan et al., 2004 (3) 29/F Temporary blindness History of SAH Both Both Angiography Kim et al., 2006 (5) 38/M None Both VBA Vascular calcification on brain CT performed for post-traumatic headache Li et al., 2006 (7) 57/F ICH Both Both CTA Sahin et al., 2010 (2) 32/F None Both Incidentally in preoperative embolization BA of maxillary sinus cancer Castro et al., 2010 (6) 34/F Ischemic stroke Both BA Brain MRI and MRA Present case 28/M None Both Both Cervical spine MRI Note. AVM = arteriovenous malformation, BA = basilar artery, CCF = carotid cavernous fistula, CTA = CT angiography, ICA = internal carotid artery, ICH = intracerebral hemorrhage, MRA = MR angiography, Ref. No. = reference number, SAH = subarachnoid hemorrhage, VA = vertebral artery, VBA = vertebrobasilar arteries kjronline.org Korean J Radiol 12(6), Nov/Dec
5 Lee et al. (a 37-year-old woman), and one patient presented with intracerebral hemorrhage (a 57-year-old woman). The remaining three patients were asymptomatic, and CVBRM was incidentally detected in a brain CT performed after a traffic accident, or in an angiography performed for tumor embolization, or during diagnosis of AVM. Our patient presented with nonspecific posterior neck pain with no accompanying neurological symptoms or signs. His neck pain may bear no relation with CVBRM. Associated lesions in patients with CRM include intracranial aneurysm, AVM, carotid-cavernous fistula, Dieulafoy s ulcer, pseudoxanthoma elasticum, and posterior fossa malformations, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, coarctation of the aorta, and cardiac defects and eye abnormalities (PHACE) syndrome. However, only two patients with CVBRM had associated lesions including AVM and pseudoxanthoma elasticum (8, 9). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case where an aneurysm was demonstrated on angiography even though some cases presenting with SAH or ICH have been reported. Rupture of an aneurysm or anastomosing vessel and hemodynamic stress may cause SAH; however, endovascular or surgical treatment is almost impossible because of tortuous and fragile collateral vessels (2). We must recognize that CVBRM, although rare, is an important cause of strokes in young adults. An ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is a major presentation, and can be accompanied by non-specific symptoms such as dizziness or blindness. We could also incidentally encounter this condition on MRI-MRA or CT-CTA performed for another reason. As a result, we need to be aware of the specific MRI or CT imaging and angiographic findings for this condition. REFERENCES 1. Fukuta K, Kudo H, Sasaki M, Kimura J, bin Ismail D, Endo H. Absence of carotid rete mirabile in small tropical ruminants: implications for the evolution of the arterial system in artiodactyls. J Anat 2007;210: Sahin H, Cinar C, Oran I. Carotid and vertebrobasilar rete mirabile: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 2010;32: Mahadevan J, Batista L, Alvarez H, Bravo-Castro E, Lasjaunias P. Bilateral segmental regression of the carotid and vertebral arteries with rete compensation in a Western patient. Neuroradiology 2004;46: Itoyama Y, Kitano I, Ushio Y. Carotid and vertebral rete mirabile in man--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1993;33: Kim MS, Lee SJ, Lee CH, Park HI. Bilateral segmental absence of the internal carotid artery with rete compensation associated with absence of basilar artery: case report. Surg Neurol 2006;65: ; discussion 619; author reply Castro S, Abreu P, Azevedo E, Silva ML. A new pattern of arterial rete compensation of segmental basilar agenesis associated with carotid retia mirabilia: a case report (2010: 1b). Eur Radiol 2010;20: Li G, Jayaraman MV, Lad SP, Adler J, Do H, Steinberg GK. Carotid and vertebral rete mirabile in man presenting with intraparenchymal hemorrhage: a case report. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2006;15: Jones RR, Wetzel N. Bilateral carotid vertebrobasilar rete mirabile. Case report. J Neurosurg 1970;33: Koo AH, Newton TH. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum associated with carotid rete mirabile. Case report. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1972;116: Hyogo T, Nakagawara J, Nakamura J, Suematsu K. Multiple segmental agenesis of the cerebral arteries: case report. Neuroradiology 1996;38: Korean J Radiol 12(6), Nov/Dec 2011 kjronline.org
Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture of Spinal Artery Aneurysm
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 230, 205-209 Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with SAH 205 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 230, 205-209 Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with SAH 205 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture
Case Report Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile associated with intracranial multiple hemorrhages: a case report and literature review
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):12153-12162 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022787 Case Report Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile associated with intracranial multiple hemorrhages: a case report
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):12153-12162 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022787 Case Report Bilateral carotid and vertebral rete mirabile associated with intracranial multiple hemorrhages: a case report
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Rete Mirabile in Humans. Case Report
 Rete Mirabile in Humans Case Report Jun KARASAWA, Hajime TOUHO, Hideyuki OHNISHI, and Masahiko KAWAGUCHI* Departments of Neurosurgery and *Anesthesiology, Osaka Neurological Institute, Toyonaka, Osaka
Rete Mirabile in Humans Case Report Jun KARASAWA, Hajime TOUHO, Hideyuki OHNISHI, and Masahiko KAWAGUCHI* Departments of Neurosurgery and *Anesthesiology, Osaka Neurological Institute, Toyonaka, Osaka
Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No.
 3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
3 9 5 Table 1.Summary of 12 Patients with Brain Death and Deep Coma: Clinical Findings Patients No. Age/Sex Underlying Cause Study No. Brain Stem Reflex EEG Clinical Diagnosis 01 40/M Trauma 01 ECS Brain
Cerebral aneurysms A case study
 August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
Variant of Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery Associated with Giant Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 173-178 173 CASE REPORT Variant of Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery Associated with Giant Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm WEI-CHEN LIN 1 KUO-LUON KUNG 2 WEN-YUH HSIEH
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 173-178 173 CASE REPORT Variant of Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery Associated with Giant Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm WEI-CHEN LIN 1 KUO-LUON KUNG 2 WEN-YUH HSIEH
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke. Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital Acute stroke intervention Number of stroke patients increasing day by
Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital Acute stroke intervention Number of stroke patients increasing day by
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine
 Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Absence or hypoplasia of the terminal portion of 1 vertebral
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.M. Burger F. Siclari L. Gregg P. Gailloud Bilateral Segmental Agenesis of the Vertebrobasilar Junction: Developmental and Angiographic Anatomy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Bilateral vertebrobasilar
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.M. Burger F. Siclari L. Gregg P. Gailloud Bilateral Segmental Agenesis of the Vertebrobasilar Junction: Developmental and Angiographic Anatomy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Bilateral vertebrobasilar
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Congenital Absence of the Internal Carotid Artery
 Journal of Soonchunhyang Medical Science 16(1) p.09~15 June 2010 9 Congenital bsence of the Internal Carotid rtery Sun Hye Jeong, Hyun Sook Hong, Sung-Il Park, Dae Ho Kim, Hae Kyung Lee Department of Radiology,
Journal of Soonchunhyang Medical Science 16(1) p.09~15 June 2010 9 Congenital bsence of the Internal Carotid rtery Sun Hye Jeong, Hyun Sook Hong, Sung-Il Park, Dae Ho Kim, Hae Kyung Lee Department of Radiology,
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
Segmental Agenesis of the Internal Carotid Artery Distal to the Posterior Communicating Artery Leading to the Definition of a New Embryologic Segment
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1189 1193, August 2004 Case Report Segmental Agenesis of the Internal Carotid Artery Distal to the Posterior Communicating Artery Leading to the Definition of a New Embryologic
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1189 1193, August 2004 Case Report Segmental Agenesis of the Internal Carotid Artery Distal to the Posterior Communicating Artery Leading to the Definition of a New Embryologic
TABLES. Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms. Table. Aneurysm location. Bypass flow** Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient. Age/ Sex.
 Table TABLES Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms Age/ Sex Aneurysm location Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient Recipient territory Recipient territory flow* Cut flow Bypass flow** Graft Patent postop F/U
Table TABLES Table 1 Terminal vessel aneurysms Age/ Sex Aneurysm location Symptoms Strategy Bypass recipient Recipient territory Recipient territory flow* Cut flow Bypass flow** Graft Patent postop F/U
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Overview Blood supply of the brain What is moyamoya disease? > 1
 Moyamoya Disease Overview Moyamoya disease is caused by blocked arteries at the base of the brain. The name "moyamoya" means "puff of smoke" in Japanese and describes the appearance of tiny vessels that
Moyamoya Disease Overview Moyamoya disease is caused by blocked arteries at the base of the brain. The name "moyamoya" means "puff of smoke" in Japanese and describes the appearance of tiny vessels that
Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.201 Original Article Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Vertebral
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.201 Original Article Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Vertebral
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms
 Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Fenestration of Intracranial Arteries with Special Attention to Associated Aneurysms and Other Anomalies
 Fenestration of Intracranial Arteries with Special Attention to Associated Aneurysms and Other Anomalies William P. Sanders, 1 Patrick A. Sorek, 1 and Bharat A. Mehta 1 PURPOSE: To determine the association
Fenestration of Intracranial Arteries with Special Attention to Associated Aneurysms and Other Anomalies William P. Sanders, 1 Patrick A. Sorek, 1 and Bharat A. Mehta 1 PURPOSE: To determine the association
Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms
 33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Bilateral blunt carotid artery injury: A case report and review of the literature
 CASE REPORT Bilateral blunt carotid artery injury: A case report and review of the literature S Cheddie, 1 MMed (Surg), FCS (SA); B Pillay, 2 FCS (SA), Cert Vascular Surgery; R Goga, 2 FCS (SA) 1 Department
CASE REPORT Bilateral blunt carotid artery injury: A case report and review of the literature S Cheddie, 1 MMed (Surg), FCS (SA); B Pillay, 2 FCS (SA), Cert Vascular Surgery; R Goga, 2 FCS (SA) 1 Department
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION
 TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION ---Rune Aaslid First TCD Publication 1982 WHAT IS TCD? Uses 2 MHz pulsed Doppler ultrasound Passes through cranial windows Provides information
TRANSCRANIAL DOPPLER ULTRASOUND INTRODUCTION TO TCD INTERPRETATION ---Rune Aaslid First TCD Publication 1982 WHAT IS TCD? Uses 2 MHz pulsed Doppler ultrasound Passes through cranial windows Provides information
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Ruptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report
 Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment
 Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment Arthur G. Kane, William P. Dillon, A. James Barkovich, David Norman, Christopher
Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment Arthur G. Kane, William P. Dillon, A. James Barkovich, David Norman, Christopher
Sciences, Sri Ramachandra Medical College and Research Institute, Chennai, India.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Devara K V A, 1 Joseph S, 2 Uppu S C. 3 Spontaneous Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Due to Coarctation of Aorta and 1 Department of Radiology, Medall Healthcare Private Ltd, King
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Devara K V A, 1 Joseph S, 2 Uppu S C. 3 Spontaneous Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Due to Coarctation of Aorta and 1 Department of Radiology, Medall Healthcare Private Ltd, King
TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH
 CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
Multidetector computed tomographic (CT) angiography : FREQUENTLY ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE CIRCLE WILLIS ICONOGRAPHIC REVIEW
 Multidetector computed tomographic (CT) angiography : FREQUENTLY ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE CIRCLE WILLIS ICONOGRAPHIC REVIEW Dra. Ximena González Larramendi Dr. Fernando Landó Baison ABSTRACT: Objetives:
Multidetector computed tomographic (CT) angiography : FREQUENTLY ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE CIRCLE WILLIS ICONOGRAPHIC REVIEW Dra. Ximena González Larramendi Dr. Fernando Landó Baison ABSTRACT: Objetives:
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al.
 ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case report
 Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Although moyamoya disease, a rare cerebrovascular occlusive
 Renal Artery Lesions in Patients With Moyamoya Disease Angiographic Findings Ichiro Yamada, MD; Yoshiro Himeno, MD; Yoshiharu Matsushima, MD; Hitoshi Shibuya, MD Background and Purpose Renal artery lesions
Renal Artery Lesions in Patients With Moyamoya Disease Angiographic Findings Ichiro Yamada, MD; Yoshiro Himeno, MD; Yoshiharu Matsushima, MD; Hitoshi Shibuya, MD Background and Purpose Renal artery lesions
10/19/12. Uncommon Causes of Stroke. José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures. Dr. Biller has no disclosures to report
 10/19/12 Uncommon Causes of Stroke José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Chicago, IL José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures Dr. Biller has no disclosures
10/19/12 Uncommon Causes of Stroke José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Chicago, IL José Biller, MD, FACP, FAAN, FAHA Disclosures Dr. Biller has no disclosures
History of revascularization
 History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
Transorbital blood flow sound recordings have the
 397 Noninvasive Detection of Intracranial Vascular Lesions by Recording Blood Flow Sounds Yasushi Kurokawa, MD; Seisho Abiko, MD; Kohsaku Watanabe, MD Background and Purpose Transorbital blood flow sound
397 Noninvasive Detection of Intracranial Vascular Lesions by Recording Blood Flow Sounds Yasushi Kurokawa, MD; Seisho Abiko, MD; Kohsaku Watanabe, MD Background and Purpose Transorbital blood flow sound
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach
 lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach tytuł pracy: Kliniczne i radiologiczne aspekty tętniaków wewnątrzczaszkowych a wybór metody leczenia Summary An aneurysm is a localized, abnormal distended lumen of the
lek Magdalena Puławska-Stalmach tytuł pracy: Kliniczne i radiologiczne aspekty tętniaków wewnątrzczaszkowych a wybór metody leczenia Summary An aneurysm is a localized, abnormal distended lumen of the
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA
 Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN
 CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
CT Imaging of Blunt and Penetrating Vascular Trauma DENNIS FOLEY MEDICAL COLLEGE WISCONSIN THORACO ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 5 cc/sec 30 secs 1.25 mm/ 55 mm Z1.375 2.5 mm/ 55 mm Z 1.375 Grade
Letter to the Editor: test occlusion under monitoring of motor-evoked potentials for giant distal
 Letter to the Editor: test occlusion under monitoring of motor-evoked potentials for giant distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm Acta Neurochirurgica Kampei Shimizu, Shoichi Tani, Hirotoshi Imamura,
Letter to the Editor: test occlusion under monitoring of motor-evoked potentials for giant distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm Acta Neurochirurgica Kampei Shimizu, Shoichi Tani, Hirotoshi Imamura,
The current optimized approach for patients with a ruptured
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I. Oran C. Cinar Continuous Intra-Arterial Infusion of Nimodipine During Embolization of Cerebral Aneurysms Associated With Vasospasm BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite rigorous efforts,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I. Oran C. Cinar Continuous Intra-Arterial Infusion of Nimodipine During Embolization of Cerebral Aneurysms Associated With Vasospasm BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Despite rigorous efforts,
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
SCAI Fall Fellows Course Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation
 SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2012 Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation Daniel J. McCormick DO, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiovascular Interventional Therapy Pennsylvania Hospital University of Pennsylvania
SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2012 Subclavian/Innominate Case Presentation Daniel J. McCormick DO, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiovascular Interventional Therapy Pennsylvania Hospital University of Pennsylvania
Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion
 Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion Paul Hsien-Li Kao, MD Assistant Professor National Taiwan University Medical School and Hospital ICA stenting
Recanalization of Chronic Carotid Artery Occlusion Objective Improvement Of Cerebral Perfusion Paul Hsien-Li Kao, MD Assistant Professor National Taiwan University Medical School and Hospital ICA stenting
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically necessary for the following strongly suspected vascular diseases:
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: September 5, 2014 I. POLICY Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: September 5, 2014 I. POLICY Head MRA/MRV studies of the head may be considered medically
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Anomalous External Carotid Artery-Internal Carotid Artery Anastomosis in Two Patients with Proximal Internal Carotid Arterial Remnants
 Case Report Neurointervention http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.914 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):914-918 Anomalous External Carotid Artery-Internal Carotid Artery Anastomosis
Case Report Neurointervention http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.914 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):914-918 Anomalous External Carotid Artery-Internal Carotid Artery Anastomosis
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Hrushchak N.M. The Pharma Innovation Journal 2014; 3(9): 38-42
 2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
2014; 3(9): 38-42 ISSN: 2277-7695 TPI 2014; 3(9): 38-42 2013 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 10-10-2014 Accepted: 23-11-2014 Ivano-Frankivsk national medical university Kalush regional hospital.
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 461 466 461 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0074 Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion*,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 461 466 461 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0074 Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion*,
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open techniques.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Retrospective analytical six months study of vascular abnormalities of brain
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20160185 Retrospective analytical
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20160185 Retrospective analytical
