PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Griselda Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Lecture 3: Pericardium and Endocardium Shannon Martinson, 2018 VPM 2220 Systemic Pathology II
2 PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Normal structure Epicardium Double layered serosal membrane Covers the heart and the most proximal segment of the great vessels. Myocardium
3 Serous Atrophy of Fat PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Also occurs in bone marrow Normal fat Serous atrophy of fat Epicardial fat appears gelatinous Lymphatics may be prominent Seen with emaciation
4 PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericardial Hemorrhages Pericardial hemorrhages are common post-mortem findings in animals as a result of hypoxia, sepsis, toxemia, DIC, bleeding diatheses and electrocution Common agonal change in cattle According to size, hemorrhages are classified as: Petechiae Ecchymoses Paintbrush
5 PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericardial Effusions Distension of the Pericardial Sac The pericardial sac can notably enlarge to accommodate: Excess fluid Non-fatal progressive pericardial hemorrhage (hemopericardium) Exudate in pericarditis An enlarged heart
6 PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericardial Effusions Transudate Hydropericardium Clear fluid, low cellularity and low protein Blood Hemopericardium RBCs and protein Pericardiocentesis Diagnostic testing Therapeutic 52b6a1ed60b38f96f2e88d4a8cc.jpg Exudate Pericarditis Turbid fluid, high cellularity and high protein
7 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Hydropericardium Transudate in the pericardial sac Pericardial surfaces remain smooth and glistening Pathogenesis: 1. Hydrostatic pressure: Right heart failure 2. Hypoproteinemia: Emaciation, protein losing enteropathy / nephropathy, etc. 3. Vascular permeability: Sepsis, DIC, mulberry heart quizlet.com With vascular permeability may see fibrin / protein in the fluid
8 Pericardial Effusions Snake PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Duck Hydropericardium Courtesy: Dr. Carlos Lopez Mendez
9 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Hemopericardium Accumulation of blood in the pericardial sac Caused by atrial or aortic rupture Rupture of atrial hemangiosarcoma, chronic valvular regurgitation and atrial dilation, iatrogenic (cardiac puncture) Acute hemorrhage can cause cardiac tamponade if severe can cause sudden death If intrapericardial pressure > intracardial pressure compression of heart may prevent diastolic filling = cardiac tamponade
10 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Hemopericardium Idiopathic hemorrhagic pericardial effusion of dogs (cattle also)
11 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Hemopericardium
12 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericarditis Inflammation of the pericardium Usually diffuse Suppurative Fibrinous Bread and butter heart
13 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericarditis Jugular vein distension Murmur GI motility and scant feces Distended pericardium on US Pericardiocentesis fetid yellow fluid Adult Ayrshire cow Brisket edema and bottle jaw
14 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Traumatic reticuloperitonitis Pericarditis Metal object from reticulum penetrates the reticular wall, diaphragm and pericardium Pericardial sac filled with fibrinosuppurative exudate
15 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Black Leg Clostridial myositis Clostridium chauvoei Fibrinous pericarditis is common Pericarditis
16 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericarditis Glasser s Disease Haemophilus parasuis Causes fibrinous polyserositis Peritonitis, pleuritis, pericarditis, arthritis, meningitis Differentials Streptococcus suis*, Mycoplasma hyorhinis, Actinobacillus
17 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericarditis With chronicity organization of exudate leads to fibrosis and adhesions (organizing fibrinous pericarditis)
18 Pericardial Effusions Chronic constrictive pericarditis Heart is encased in fibrous tissue Obliterates the pericardial space Limits diastolic expansion PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Pericarditis
19 Pericardial Effusions PERICARDIUM AND EPICARDIUM Fibrin Pericarditis Chronic constrictive pericarditis Fibrosis Myocardium H&E stain Masson-Trichrome stain
20 ENDOCARDIUM The endocardium, the most internal layer of the heart is in intimal contact with the blood It lines the atria, ventricles, and valves Endocardium Myocardium
21 ENDOCARDIUM Normal Valves Aortic Valve Tricuspid valve Note how thin and translucent the valves are
22 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Endocardial hemorrhage Endocardial Fibrosis Endocardial hemorrhage Endocardial Mineralization Valvular Cysts Myxomatous Degeneration Rupture of Chordae Tendinae Endocarditis
23 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Endocardial Fibrosis and Fibroelastosis Jet lesions Right atrium Acquired localized endocardial fibrosis: "jet lesions" Abnormal blood turbulence in the atria or ventricles Turbulence can result in mechanical injury damaging the endocardium Most commonly seen in the atria in association with valvular insufficiencies Gross: The endocardium appears focally thickened with a rough or corrugated surface Clinical Relevance: None Image: Dr N Kaiser, AVC
24 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Endocardial Fibrosis and Fibroelastosis Acquired diffuse endocardial fibrosis Occurs secondary to prolonged cardiac dilation. Gross: The endocardium appears diffusely thickened with a rough or corrugated surface Clinical Relevance: can impair and reduce stroke volume congestive heart failure Zachary, PBVD, 2017
25 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Endocardial Mineralization Endocardial Mineralization = abnormal deposition of calcium or mineral in the endocardium and arteries Metastatic: High levels of circulating calcium in hypercalcemic states Dystrophic: Secondary calcification in injured endocardium The endocardium is hardened and the surface is roughened with pale yellow white gritty plaques Differentials for endocardial mineralization Hypervitaminosis D Iatrogenic Calciferol rodenticides Toxic plants (Solanum, Cestrum) Cachectic disease Johne s disease Tuberculosis Renal failure (uremia) Paraneoplastic syndrome
26 Valvular Cysts PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Particularly common in calves There is no clinical significance Incidental finding Cysts may rupture and disappear
27 Valvular Cysts PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Valvular Hematocyst According to content, cyst are classified as: Lymphocyst when the content is clear fluid Hemocyst when the content is blood Valvular Lymphocyst Zachary, PBVD, 2017 Zachary, PBVD, 2017
28 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Myxomatous Valvular Degeneration Common in dogs Incidence increases with age: 1-yr-old = 5% 16-yr-old = 75% Toy and small- med. breed dogs Cavalier King Charles spaniel Mitral valve (80% of cases) Mitral and tricuspid (15% of cases Tricuspid only (5%) May or may not cause valvular dysfunction and clinical signs =Degenerative Heart Valve Disease =Endocardiosis
29 ENDOCARDIUM Myxomatous Valvular Degeneration Characterized by nodular thickening of the valve with a smooth shiny surface Zachary, PBVD, 2017
30 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Myxomatous Valvular Degeneration The thickened nodular valve is composed of loose (myxomatous) connective tissue If mild typically no clinical signs When more severe can cause valvular regurgitation and volume overload eccentric hypertrophy
31 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Myxomatous Valvular Degeneration Rupture of the Chordae Tendineae Sudden collapse and death If you suspect rupture of the chordae tendinae at the time of necropsy, it is recommended to open the left atrium, remove the blood, fill the ventricle and atria with water, and rhythmically compress the heart. Zachary, PBVD, 2017
32 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Endocarditis It is most frequently caused by bacteria, and to a much lesser extent, by fungi or parasites Clinical signs: Pyrexia Lameness Murmurs According to location, endocarditis can be classified as: Valvular endocarditis (valves)*** Mural endocarditis (myocardial wall) According to gross appearance: Vegetative: cauliflower-like mass of exudate and fibrin attached to a heart valve or endocardium Ulcerative when the endocardium is denuded Mural endocarditis, RV
33 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Common isolates in cattle: Trueperella pyogenes Most often affects the right AV valve As a result of venal caval thrombosis
34 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Common isolates in pigs: Streptococcus suis Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
35 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Common isolates in horses: Streptococcus equi Actinobacillus equuli
36 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Endocarditis is not common in dogs and cats Common isolates in dogs: Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus spp Bartonella Common isolates in cats: Bartonella Streptococcus
37 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Fibrin Histopathology Bacterial colonies Neutrophils and cell debris Connective tissue, neutrophils and macrophages VALVE
38 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Pulmonary trunk Common sequelae: Thromboembolism: Mitral or aortic endocarditis renal infarcts Tricuspid and pulmonic endocarditis embolic pneumonia or, less commonly, pulmonary infarcts Congestive heart failure because of valvular dysfunction *
39 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Vegetative Valvular Endocarditis Passive hepatic congestion Yearling heifer with a history of poor doing and inappetence Pyrexia and anorexia some response to antibiotics recurrent Tachycardia, muffled heart sounds, and jugular pulses developed Died on the way to the barn for milking Right AV valve, vegetative endocarditis, fibrinous, chronic-active, severe Hydrothorax
40 PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCARDIUM Ulcerative Endocarditis Occurs with chronic kidney disease Uremia damages the endocardium (= uremic endocarditis) Thickened, wrinkled, ulcerated endocardium +/-mineralization
41 Sincere thanks to Drs A Lopez and E Aburto, AVC, for their contribution to this material.
Cardiovascular Pathology Lab. Shannon Martinson,
 Cardiovascular Pathology Lab Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH Cat History Heart murmur detected on PE recommended cardiac US Blood work was
Cardiovascular Pathology Lab Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH Cat History Heart murmur detected on PE recommended cardiac US Blood work was
Saluki heart pathology study
 Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES. VPM Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB
 CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES VPM 222 2009 Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB Case 1 Heart - Echoplane section from a 7-month-old Labrador retriever Give two morphologic diagnoses 1.
CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES VPM 222 2009 Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB Case 1 Heart - Echoplane section from a 7-month-old Labrador retriever Give two morphologic diagnoses 1.
Alfonso López. Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation
 Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Veterinary Internal Medicine. Cardiology. Dr. Khaled M. Al-Qudah
 Veterinary Internal Medicine Cardiology Dr. Khaled M. Al-Qudah 1 Pericarditis; Endocarditis; Myocarditis 2 Pericarditis Dr. Khaled M. Al-Qudah 3 Inflammation of the pericardial sac, characterized by: Audible
Veterinary Internal Medicine Cardiology Dr. Khaled M. Al-Qudah 1 Pericarditis; Endocarditis; Myocarditis 2 Pericarditis Dr. Khaled M. Al-Qudah 3 Inflammation of the pericardial sac, characterized by: Audible
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Lecture 5: Vascular System Shannon Martinson, 2018 VPM 2220 Systemic Pathology II http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VASCULAR SYSTEM The vascular system is formed
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Lecture 5: Vascular System Shannon Martinson, 2018 VPM 2220 Systemic Pathology II http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VASCULAR SYSTEM The vascular system is formed
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New?
 Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV
 Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Inflammation Laboratory 2. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: March 2012
 Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia. Shannon Martinson, Feb
 Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
VPM Pigment and other tissue deposits. Shannon Martinson
 VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days Tachycardia,
VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days Tachycardia,
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION. Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions
 5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
Cardiovascular System
 System examination The initial examination of the cardiovascular system should be done in-situ on opening the thoracic cavity, to evaluate abnormalities of size and position. The four major areas for gross
System examination The initial examination of the cardiovascular system should be done in-situ on opening the thoracic cavity, to evaluate abnormalities of size and position. The four major areas for gross
VPM Pigment and other tissue deposits. Shannon Martinson
 VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1: Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days. Tachycardia,
VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1: Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days. Tachycardia,
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Alfonso Lopez Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College Version March 21, 2013 REFERENCE TEXTS:
 PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Alfonso Lopez Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College Version March 21, 2013 REFERENCE TEXTS: Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Diseases. Zachary JF and
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Alfonso Lopez Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College Version March 21, 2013 REFERENCE TEXTS: Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Diseases. Zachary JF and
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ohmmtqkgs50 Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 Introduction The functions of the cardiovascular system are: to bring oxygen & nutrients to
The Cardiovascular System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ohmmtqkgs50 Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 Introduction The functions of the cardiovascular system are: to bring oxygen & nutrients to
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
Pathology of the Respiratory System 5: Lung and Thoracic Cavity
 Pathology of the Respiratory System 5: Lung and Thoracic Cavity Shannon Martinson, Jan 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology DISORDERS OF THE LUNG Congenital Pigmentary deposition
Pathology of the Respiratory System 5: Lung and Thoracic Cavity Shannon Martinson, Jan 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology DISORDERS OF THE LUNG Congenital Pigmentary deposition
Circulatory Disturbances 5: Thrombosis, Embolism, Infarction, Shock
 Circulatory Disturbances 5: Thrombosis, Embolism, Infarction, Shock Shannon Martinson, Feb 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 152 General Pathology Thrombosis, Embolism, Infarction, Shock Learning
Circulatory Disturbances 5: Thrombosis, Embolism, Infarction, Shock Shannon Martinson, Feb 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 152 General Pathology Thrombosis, Embolism, Infarction, Shock Learning
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Figure Myocardial necrosis, intracardiac injection, euthanasia solution, left
 Slide 1 Figure 10-03. Myocardial necrosis, intracardiac injection, euthanasia solution, left ventricle, dog. Injections of barbiturates and other euthanasia solutions into the myocardium itself will cause
Slide 1 Figure 10-03. Myocardial necrosis, intracardiac injection, euthanasia solution, left ventricle, dog. Injections of barbiturates and other euthanasia solutions into the myocardium itself will cause
Infective Endocarditis عبد المهيمن أحمد
 Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Infective Endocarditis إعداد : عبد المهيمن أحمد أحمد علي Infective endocarditis Inflammation of the heart valve or endocardium of the heart. The agents are usually bacterial, but other organisms can also
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University
 Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
Constrictive Pericarditis Pitfalls in MR Diagnosis Cylen Javidan-Nejad Associate Professor Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University in St. Louis Goal o To review the imaging criteria of
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
General Pathology. Hemorrhage (Web)
 General Pathology Hemorrhage (Web) Paul Hanna Feb 2015 Hemorrhage escape of blood from the cardiovascular system may be external or internal Hemorrhage Causes Trauma Sepsis, viruses or toxins Coagulation
General Pathology Hemorrhage (Web) Paul Hanna Feb 2015 Hemorrhage escape of blood from the cardiovascular system may be external or internal Hemorrhage Causes Trauma Sepsis, viruses or toxins Coagulation
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
efferent fibers from t.. Heart Surface anatomy and heart sounds -Dry lecture -Gray s 169,
 A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis
 Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Shock, Hemorrhage and Thrombosis 1 Shock Systemic hypoperfusion due to: Reduction in cardiac output Reduction in effective circulating blood volume Hypotension Impaired tissue perfusion Cellular hypoxia
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Abstract Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog
 Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
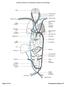 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS
 HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
According to the etiology, edema may be:
 What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
What is edema? Edema : It refers to the accumulation of excess liquid in the interstitial (extracellular) spaces of a tissue or in pre-existing cavities. It may affect any organ, but most often it appears
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy
 2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Lecture 4 - Myocardium Shannon Martinson, 2018 VPM 2220 Systemic Pathology II http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Normal structure MYOCARDIUM The myocardium has striations
PATHOLOGY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Lecture 4 - Myocardium Shannon Martinson, 2018 VPM 2220 Systemic Pathology II http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Normal structure MYOCARDIUM The myocardium has striations
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
Traumatic Reticulitis and Heart Conditions in Cattle
 Traumatic Reticulitis and Heart Conditions in Cattle Phil Scott DVM&S, DipECBHM, CertCHP, DSHP, FRCVS Traumatic Reticulitis(wire, hardware disease) Traumatic reticulitis occurs sporadically in adult cattle
Traumatic Reticulitis and Heart Conditions in Cattle Phil Scott DVM&S, DipECBHM, CertCHP, DSHP, FRCVS Traumatic Reticulitis(wire, hardware disease) Traumatic reticulitis occurs sporadically in adult cattle
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Pericardial Effusion
 Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
VPM 152 GENERAL PATHOLOGY Gross Pathology Lab 1
 VPM 152 GENERAL PATHOLOGY Gross Pathology Lab 1 CELLULAR ADAPTATIONS AND POST MORTEM CHANGES Dr Enrique Aburto 421N Path / Micro 15 Jan 2016 Bone Marrow Atrophy Atrophy Serous atrophy of fat Gelatinous
VPM 152 GENERAL PATHOLOGY Gross Pathology Lab 1 CELLULAR ADAPTATIONS AND POST MORTEM CHANGES Dr Enrique Aburto 421N Path / Micro 15 Jan 2016 Bone Marrow Atrophy Atrophy Serous atrophy of fat Gelatinous
Liver Pathology Lab 1. Shannon Martinson, 2017
 Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Liver Pathology Lab 1 Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH cat History: Inappetence and weight loss Fluid in the abdomen noted on US Esophageal
Rheumatic heart disease
 Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection
 AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
EDEMA. Learning Objectives
 EDEMA Learning Objectives Define edema Recognize and be able to describe the gross and microscopic appearance of edema Know the four pathophysiological mechanisms by which edema develops Understand the
EDEMA Learning Objectives Define edema Recognize and be able to describe the gross and microscopic appearance of edema Know the four pathophysiological mechanisms by which edema develops Understand the
Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura
 Tutorial Module 6 Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Sept 28, 2014 Thoracic Cavity There are anatomical differences
Tutorial Module 6 Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Sept 28, 2014 Thoracic Cavity There are anatomical differences
An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Case Report An Uncommon Cardiac Etiology of Liver Cirrhosis, Recurrent Ascites, Atrial Fibrillation and Congestive Heart Failure Montaser Y Ismail 1 *, Mohammed I Nassar
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOCARDITIS
 015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
015 // Endocarditis CONTENTS 140 Principles of Endocarditis 141 Native Valve Endocarditis 143 Complications of Native Valve Endocarditis 145 Right Heart Endocarditis 145 Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis 146
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System. Clicker Questions Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Circulatory Disturbances 1: Introduction and Edema
 Circulatory Disturbances 1: Introduction and Edema Shannon Martinson, January 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 152 General Pathology INTRODUCTION NORMAL CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Important concepts
Circulatory Disturbances 1: Introduction and Edema Shannon Martinson, January 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 152 General Pathology INTRODUCTION NORMAL CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Important concepts
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
