Ebstein s anomaly is defined by a downward displacement
|
|
|
- Leslie Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Repair of Ebstein s Anomaly Sylvain Chauvaud, MD Ebstein s anomaly is a tricuspid valve anomaly associated with poor right ventricular contractility in severe cases. Surgery is indicated in all symptomatic patients. Tricuspid valve repair is possible in most of the cases with mobilization of the anterior leaflet and longitudinal plication of the atrialized chamber. Tricuspid valve replacement is avoided. Associated cavo-pulmonary bidirectional shunt is performed when the right ventricle is unable to sustain normal cardiac output. Oper Tech Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 9: Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. KEYWORDS Ebstein s anomaly, tricuspid valve insufficiency, right ventricular failure, partial Glenn Ebstein s anomaly is defined by a downward displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve in the right ventricle. The consequence is tricuspid valve insufficiency of varying degrees, sometimes associated with stenosis. The postero-inferior leaflet may be absent or rudimentary and displaced. Between the attachment of the septal leaflet and Department of Cardio-Vascular Surgery, Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, 20 rue Leblanc, Paris 75015, France. Address reprint requests to Dr. S. Chauvaud, Department of Cardio- Vascular Surgery, Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, 20 rue Leblanc, Paris angeline.ferry@hop.egp.ap-hop-paris.fr the tricuspid annulus (atrio-ventricular junction) is the atrialized right ventricle. The atrialized right ventricle can be extremely wide with paradoxical motion. The anterior leaflet may have various degrees of restricted motion due to abnormal attachments on the right ventricular wall. The inlet portion of the right ventricle contracts poorly in severe cases and presents thin muscular wall. Ebstein s anomaly is the association of tricuspid valve insufficiency with a right ventricle anomaly. The goals of surgery are to treat the valvular disease and, if necessary, the dysfunction of the right ventricle /04/$-see front matter 2004 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.optechstcvs
2 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 195 Surgical Technique Figure 1 The patient is monitored with a radial artery catheter, a central venous pressure in the right jugular vein, and in the femoral vein. A median sternotomy is performed with vertical incision of the pericardium. The diaphragmatic wall of the right ventricle is checked to detect an aneurysmatic or dilated atrialized right ventricle. Yellowish patches on the anterior face of a dilated right ventricle are of poor prognosis. The right appendage is bulging in the operating field. A stay suture is placed on the appendage to retract it inferiorly permitting access to the aorta and to the superior vena cava for cannulation.
3 196 S. Chauvaud Figure 2 Cannulation. A cannula is placed in the ascending aorta. The upper part of the superior vena cava (or the innominate vein) and the inferior vena cava are cannulated with right angle cannulas. The purse string of the inferior vena may induce atrial fibrillation with hypotension, in such cases bypass is initiated and the inferior vena cava cannulation is performed on an empty heart. At the onset of bypass, the right ventricle is decompressed and the thickness of the wall is evaluated. A paper like ventricular wall is an important element to consider for bidirectionnal cavopulmonary shunt after the repair. Extracorporeal circulation. Body temperature is lowered to 30 C. Superior and inferior vena cavas are snared with tapes. A double lumen catheter is placed in the ascending aorta for cardioplegia/vent. At 30 C, aorta is clamped and antegrade cold blood cardioplegia is started. Cardioplegia is repeated every 20 minutes. The right atrium must be free of cannule. A long incision is performed in the external face of the right atrium. In very severe cases, it is necessary to reduce as much as possible the ischemic time and to avoid aortic clamping. When an atrial septal defect (ASD) is present, one single shot of cardioplegia is injected for closure of the ASD, and the aorta is unclamped. In absence of atrial shunt, the operation is performed at normothermia, with a beating heart and the aorta is unclamped.
4 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 197 Figure 3 Exposure. Stay sutures are placed on the atrial walls and if necessary on the tricuspid annulus. Retractors are placed in the superior and postero-inferior borders of the tricuspid annulus for exposure of the entire atrioventricular orifice. A vent line is placed in the patent foramen ovale. If the atrial septum is intact and bulging, a stab is performed in the fossa oval is for venting the left cavities. Evaluation of the anomaly includes the examination of: the dilated tricuspid annulus, the displaced and rudimentary septal leaflet, the posterior leaflet which is absent in severe cases, the anterior leaflet for evaluation of restricted movement; chordae can be present, close to the posterior commissure, but can also be totally absent, the atrialized right ventricle with various extension, the wider it is, the more severe is the anomaly. The effective orifice of the tricuspid valve appears narrow and is situated in a high position in the infundibulum.
5 198 S. Chauvaud Figure 4 Mobilization of the anterior leaflet. Abnormal muscular bands and chordae are placed between the ventricular face of the anterior leaflet and the infundibulum. They are accessible in good conditions with complete exposure of the infundibulum. Detachment of the anterior leaflet. The anterior leaflet tissue is grasped with forceps and retracted to a central position in the middle of the orifice. The leaflet tissue is then totally unfolded. A stab is performed parallel to the annulus at the junction of the leaflet tissue and the annulus. Detachment is conducted from the antero-septal to the antero-posterior commissure with scalpel or scissors. The scalpel must be strictly perpendicular to the plane of the annulus in order not to enter the atrioventricular junction and thus avoid right coronary artery injury.
6 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 199 Figure 5 Section of muscular bands. The entire infundibulum is exposed. Exposure of the abnormal bands is completed with a retractor placed in the ventricle and a forceps which pulls the leaflet centrally. Division of abnormal muscular bands is performed with scissors parallel to the ventricular wall. Each band is exposed with gentle traction on the leaflet. Progressively the anterior leaflet is freed. When a lateral papillary muscle is present, the body is freed from the lateral wall and the base is individualized. When the papillary muscle is absent, chordae are also absent. Mobilization is conducted inside the ventricle until the last junction of the leaflet tissue and the muscular wall. In severe cases, the last adhesion is the moderator band on which is attached the anterior leaflet. This band is detached from the ventricular wall. Pitfalls of mobilization are perforations of: (1) The ventricular wall when the thickness is less than 2 mm and the leaflet is totally adherent. However, if perforation occurs in the anterior wall of the right ventricle, in a portion without coronary arteries, closure is easily obtained with stitches outside of the ventricle. (2) The anterior leaflet. A perforation in the upper part of the leaflet tissue requires closure with 5/0 stitches. Perforations in the lower portion are left open due to the fact that they will not be incorporated in the occluding portion of the tricuspid valve. Mobilization must be extensive, far inside the ventricle, otherwise the risk of residual insufficiency is high. When mobilization is totally performed, the PFO or the atrial septal defect is closed, the aortic vent is open and the aorta is unclamped. Rewarming is started and ventricular defibrillation usually occurs spontaneously.
7 200 S. Chauvaud Figure 6 Longitudinal plication of the atrialized right ventricle and reduction of the tricuspid annulus. In Types B and C of Carpentier, the atrialized right ventricle is well individualized. (A) The shape of this cavity is triangular with the summit in the apex of the right ventricle, the base being the tricupid annulus. The upper edge is the line of the attachment of the anterior leaflet on the ventricle. The inferior edge is the junction of the atrialized right ventricle with the ventricular septum. The muscular wall is depressive. Longitudinal plication induces a plication of the tricuspid annulus. A stitch is passed twice in the annulus 1) in the antero-posterior commissure (or when absent, where the anterior leaflet is adherent to the ventricular wall) and 2) below to the coronary sinus. (B) In children a Hegar dilator of the normal size of the tricuspid annulus for the age is placed in the orifice. Then the tricuspid is plicated posteriorly according to this diameter. (C) In adults, a 32 sizer of Carpentier tricuspid prosthetic ring is used for measurement and stitches of plication are placed on the annulus. When pulling this stitch, the triangle becomes a slit with two edges. A 4/0 suture is started from the apex toward the annulus. The running suture is purely endocardial in the white thick structures and never perforating the wall. Additional stitches are placed for reinforcement. (D) A complementary suture is placed on the atrial wall for total exclusion of this blind cavity.
8 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 201 Figure 6 (Continued)
9 202 S. Chauvaud Figure 6 (Continued)
10 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 203 Figure 7 Suture of the anterior leaflet. The anterior leaflet is rotated in a clockwise position to cover the entire surface area of the right atrioventricular orifice. A 5/0 monofilament running suture is started at the antero-septal commissure. Re-attachment should avoid reduction of the leaflet. The end of the suture is below the coronary sinus. Additional single stitches are placed.
11 204 S. Chauvaud Figure 8 Prosthetic ring. In adult patients, a Carpentier prosthetic ring reshapes the annulus and prevents secondary dilation. U shape stitches of 3/0 braided material are placed in the annulus, except where the His bundle penetrates the ventricular septum. The size of the prosthetic ring is chosen according to the surface area of the anterior leaflet. The sizer must be equal to the surface area of the anterior leaflet The green landmarks of the commissures which are used in correction of isolated dilation of the tricuspid annulus are not useful in this situation. In Ebstein s anomaly, the posteroseptal commissure is absent and cannot be used.
12 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 205 Figure 9 Control of the valvular repair. Saline is injected in the right ventricle with a syringe while closing the pulmonary artery with forceps. The repair is satisfactory when the anterior leaflet is bulging. A small regurgitant jet is frequent along the septum because of the absence of leaflet tissue in this location. A central regurgitant flow requires to reconsider the repair. The causes of significant regurgitant flow are: residual anterior leaflet restriction due to insufficient mobilization, dilation of the annulus. Specific treatment is necessary. When the result is satisfactory, the right atrium is closed. The heart is beating and prepared to wean from bypass. Several conditions are necessary before stopping bypass: sinus rhythm or sequential pace maker, central venous pressure; left atrial pressure (needle), inhalation of nitric oxide. Bypass is stopped progressively with left atrial pressure at 5 mm Hg and central venous pressure at 10 mm Hg. The systemic pressure is usually low; mean 50 mm Hg. Filling is very progressive, control LA pressure (no more than 10 mm Hg) and CVP at 15 mm Hg. When systemic pressure is not improved, less than 70 to 80 mm Hg systolic, with LA pressure at 10 mm Hg or less, the situation is characteristic of right ventricular failure. Inotropes are usually not useful in this situation. The right ventricle dilates slowly, bypass is restarted and a bidirectionnal shunt is performed.
13 206 S. Chauvaud Figure 10 The azygos vein is divided. The superior vena cava is dissected on its entire length. The junction of the superior vena cava in the right atrium is transected between two clamps. The distal stump (atrium) is sutured. A tape is placed around the aorta for exposition of the right pulmonary artery, which is dissected from the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery (behind the aorta) and the division. A U shape clamp is placed on the superior edge of the pulmonary artery. A stab wound opens the right pulmonary artery with extension with Potts scissors. The superior vena cava is anastomosed with a 6/0 prolene running suture. The anastomosis must be as large as possible; clamps are removed, ventilation is restarted. The CVP is monitored with a catheter placed in the right atrium. Bypass is stopped. If systemic arterial pressure is still low, adrenaline is started.
14 Repair of Ebstein s anomaly 207 Associated Bidirectional Cavo-Pulmonary Shunt (BCPS) The indication is massive tricuspid valve insufficiency with depressed right ventricular contractility, such as in children with early and severe symptoms. Furthermore, the failing right ventricle detected by elevated right atrial pressure, dilation of right cavities, and low systemic pressure with low filling pressure on the left side are indications. The situation is confirmed with intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography; the left ventricle is small and empty, the right ventricle is dilated. BCPS can be life saving. The use of bypass rends the anastomosis easier because ventilation could be stopped. Summary Between 1980 and April 2003, 210 patients with Ebstein s anomaly were operated with valvular and ventricular repair. Mean age was year (1 to 70). Reconstruction was possible in 206/210 (98%) and replacement was performed in 4 cases (2%). Overall hospital mortality was 9% (18/210) due to right ventricular failure in 9 patients. Permanent pace maker implantation was performed in 5 cases (2.3%). BCPS was introduced in 1990 and used in 71 patients. In severe cases, hospital mortality without BCPS ( ) was 16% (7/43) and with BCPS ( ) was 10% (7/ 71). The difference is significant. Actuarial survival was % at 10 years and % at 20 years follow-up. Functional improvement is constant. 85% of the patients were in functional class (NYHA) 1 or 2. Reoperation was necessary in 17 patients (9%, CL 95%: 4 to 15%) with a mean delay of year (1 day to 9.4 years), for TV insufficiency in 16 patients. A total of 82% of patients were in permanent sinus rhythm after repair, compared with 61% before operation. Reconstructive surgery appears to be indicated for all symptomatic patients due to: increased life expectancy, functional improvement, and decrease of rhythm disturbances. The adjunction of BCPS decreases the operative risk.
The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth
 The Radial Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation Takashi Nitta, MD The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth of an alternative to the maze procedure. The atrial incisions are designed to radiate from
The Radial Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation Takashi Nitta, MD The radial procedure was developed as an outgrowth of an alternative to the maze procedure. The atrial incisions are designed to radiate from
Ebstein s anomaly is a congenital malformation of the right
 Cone Reconstruction of the Tricuspid Valve for Ebstein s Anomaly: Anatomic Repair Joseph A. Dearani, MD, Emile Bacha, MD, and José Pedro da Silva, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Cone Reconstruction of the Tricuspid Valve for Ebstein s Anomaly: Anatomic Repair Joseph A. Dearani, MD, Emile Bacha, MD, and José Pedro da Silva, MD Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection to superior
 Cavo-Atrial Anastomosis Technique for Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection to the Superior Vena Cava The Warden Procedure Robert A. Gustafson, MD Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Cavo-Atrial Anastomosis Technique for Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection to the Superior Vena Cava The Warden Procedure Robert A. Gustafson, MD Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Although most patients with Ebstein s anomaly live
 Management of Neonatal Ebstein s Anomaly Christopher J. Knott-Craig, MD, FACS Although most patients with Ebstein s anomaly live through infancy, those who present clinically as neonates are a distinct
Management of Neonatal Ebstein s Anomaly Christopher J. Knott-Craig, MD, FACS Although most patients with Ebstein s anomaly live through infancy, those who present clinically as neonates are a distinct
Ebstein s anomaly is characterized by malformation of
 Fenestrated Right Ventricular Exclusion (Starnes Procedure) for Severe Neonatal Ebstein s Anomaly Brian L. Reemtsen, MD,* and Vaughn A. Starnes, MD*, Ebstein s anomaly is characterized by malformation
Fenestrated Right Ventricular Exclusion (Starnes Procedure) for Severe Neonatal Ebstein s Anomaly Brian L. Reemtsen, MD,* and Vaughn A. Starnes, MD*, Ebstein s anomaly is characterized by malformation
An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-
 The Konno-Rastan Procedure for Anterior Aortic Annular Enlargement Mark E. Roeser, MD An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-Rastan procedure, is a useful tool for the cardiac surgeon. Originally,
The Konno-Rastan Procedure for Anterior Aortic Annular Enlargement Mark E. Roeser, MD An anterior aortoventriculoplasty, known as the Konno-Rastan procedure, is a useful tool for the cardiac surgeon. Originally,
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
The Rastelli procedure has been traditionally used for repair
 En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
En-bloc Rotation of the Truncus Arteriosus A Technique for Complete Anatomic Repair of Transposition of the Great Arteries/Ventricular Septal Defect/Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction or Double
Tricuspid Valve Repair for Ebstein's Anomaly
 Tricuspid Valve Repair for Ebstein's Anomaly Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Gordon K. Danielson, MD E bstein's anomaly is a malformation of the tricuspid valve and right ventricle that is characterized by
Tricuspid Valve Repair for Ebstein's Anomaly Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Gordon K. Danielson, MD E bstein's anomaly is a malformation of the tricuspid valve and right ventricle that is characterized by
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve
 Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot with Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Karl F. Welke, MD, and Ross M. Ungerleider, MD, MBA Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) occurs in 5%
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with increased morbidity
 Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation with Concomitant Surgery Edward G. Soltesz, MD, MPH, and A. Marc Gillinov, MD Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in coronary artery
Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation with Concomitant Surgery Edward G. Soltesz, MD, MPH, and A. Marc Gillinov, MD Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in coronary artery
14 Valvular Stenosis
 14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
14 Valvular Stenosis 14-1. Valvular Stenosis unicuspid valve FIGUE 14-1. This photograph shows severe valvular stenosis as it occurs in a newborn. There is a unicuspid, horseshoe-shaped leaflet with a
Replacement of the mitral valve in the presence of
 Mitral Valve Replacement in Patients with Mitral Annulus Abscess Christopher M. Feindel Replacement of the mitral valve in the presence of an abscess of the mitral annulus presents a major challenge to
Mitral Valve Replacement in Patients with Mitral Annulus Abscess Christopher M. Feindel Replacement of the mitral valve in the presence of an abscess of the mitral annulus presents a major challenge to
Anatomy determines the close vicinity of the sinuses of
 Aortic Valve Reimplantation According to the David Type I Technique Matthias Karck, MD, and Axel Haverich, MD Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Aortic Valve Reimplantation According to the David Type I Technique Matthias Karck, MD, and Axel Haverich, MD Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany.
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease
 Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
Repair of Complete Atrioventricular Septal Defects Single Patch Technique
 Repair of Complete Atrioventricular Septal Defects Single Patch Technique Fred A. Crawford, Jr., MD The first repair of a complete atrioventricular septal defect was performed in 1954 by Lillehei using
Repair of Complete Atrioventricular Septal Defects Single Patch Technique Fred A. Crawford, Jr., MD The first repair of a complete atrioventricular septal defect was performed in 1954 by Lillehei using
Obstructed total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
 Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection Richard A. Jonas, MD Children s National Medical Center, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Washington, DC. Address reprint requests to Richard A. Jonas,
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection Richard A. Jonas, MD Children s National Medical Center, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Washington, DC. Address reprint requests to Richard A. Jonas,
Repair of Congenital Mitral Valve Insufficiency
 Repair of Congenital Mitral Valve Insufficiency Roland Hetzer, MD, PhD, and Eva Maria Delmo Walter, MS, MD, PhD Principles of Mitral Valve Repair We believe that mitral valve repair for congenital mitral
Repair of Congenital Mitral Valve Insufficiency Roland Hetzer, MD, PhD, and Eva Maria Delmo Walter, MS, MD, PhD Principles of Mitral Valve Repair We believe that mitral valve repair for congenital mitral
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Techniques for repair of complete atrioventricular septal
 No Ventricular Septal Defect Patch Atrioventricular Septal Defect Repair Carl L. Backer, MD *, Osama Eltayeb, MD *, Michael C. Mongé, MD *, and John M. Costello, MD For the past 10 years, our center has
No Ventricular Septal Defect Patch Atrioventricular Septal Defect Repair Carl L. Backer, MD *, Osama Eltayeb, MD *, Michael C. Mongé, MD *, and John M. Costello, MD For the past 10 years, our center has
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions
 Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty,
 Modified Konno Procedure for Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction David P. Bichell, MD The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty, first described by Cooley and Garrett in1986, 1
Modified Konno Procedure for Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction David P. Bichell, MD The modified Konno procedure, or subaortic ventriculoplasty, first described by Cooley and Garrett in1986, 1
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction
 Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
Polytetrafluoroethylene Bicuspid Pulmonary Valve Implantation James A. Quintessenza, MD The need for right ventricular outflow tract reconstruction and pulmonary valve replacement is increasing for many
In 1980, Bex and associates 1 first introduced the initial
 Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
Technique of Aortic Translocation for the Management of Transposition of the Great Arteries with a Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis Victor O. Morell, MD, and Peter D. Wearden, MD, PhD In
Minimal access aortic valve surgery has become one of
 Minimal Access Aortic Valve Surgery Through an Upper Hemisternotomy Approach Prem S. Shekar, MD Minimal access aortic valve surgery has become one of the accepted forms of surgical therapy for patients
Minimal Access Aortic Valve Surgery Through an Upper Hemisternotomy Approach Prem S. Shekar, MD Minimal access aortic valve surgery has become one of the accepted forms of surgical therapy for patients
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
I have nothing to disclose.
 I have nothing to disclose. New approaches in tricuspid valve repair Christian Schreiber ..more than a simple displacement.., the valvar orifice is formed within the ventricular cavity.. Ebstein Historical
I have nothing to disclose. New approaches in tricuspid valve repair Christian Schreiber ..more than a simple displacement.., the valvar orifice is formed within the ventricular cavity.. Ebstein Historical
Despite advances in our understanding of the pathophysiology
 Suture Relocation of the Posterior Papillary Muscle in Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Benjamin B. Peeler MD,* and Irving L. Kron MD,*, *Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University of Virginia, Charlottesville,
Suture Relocation of the Posterior Papillary Muscle in Ischemic Mitral Regurgitation Benjamin B. Peeler MD,* and Irving L. Kron MD,*, *Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University of Virginia, Charlottesville,
The Edge-to-Edge Technique f For Barlow's Disease
 The Edge-to-Edge Technique f For Barlow's Disease Ottavio Alfieri, Michele De Bonis, Elisabetta Lapenna, Francesco Maisano, Lucia Torracca, Giovanni La Canna. Department of Cardiac Surgery, San Raffaele
The Edge-to-Edge Technique f For Barlow's Disease Ottavio Alfieri, Michele De Bonis, Elisabetta Lapenna, Francesco Maisano, Lucia Torracca, Giovanni La Canna. Department of Cardiac Surgery, San Raffaele
Disease of the aortic valve is frequently associated with
 Stentless Aortic Bioprosthesis for Disease of the Aortic Valve, Root and Ascending Aorta John R. Doty, MD, and Donald B. Doty, MD Disease of the aortic valve is frequently associated with morphologic abnormalities
Stentless Aortic Bioprosthesis for Disease of the Aortic Valve, Root and Ascending Aorta John R. Doty, MD, and Donald B. Doty, MD Disease of the aortic valve is frequently associated with morphologic abnormalities
Cardiac tumors are unusual and cardiac malignancy, usually
 Cardiac Autotransplantation Shanda H. Blackmon, MD,* and Michael J. Reardon, MD Cardiac tumors are unusual and cardiac malignancy, usually sarcoma, is a very small subset of these. The literature on cardiac
Cardiac Autotransplantation Shanda H. Blackmon, MD,* and Michael J. Reardon, MD Cardiac tumors are unusual and cardiac malignancy, usually sarcoma, is a very small subset of these. The literature on cardiac
The pericardial sac is composed of the outer fibrous pericardium
 Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
Pericardiectomy for Constrictive or Recurrent Inflammatory Pericarditis Mauricio A. Villavicencio, MD, Joseph A. Dearani, MD, and Thoralf M. Sundt, III, MD Anatomy and Preoperative Considerations The pericardial
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with atrioventricular (AV)
 Tetralogy of Fallot with Atrioventricular Canal Defect: Two Patch Repair Sitaram M. Emani, MD, and Pedro J. del Nido, MD Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with atrioventricular (AV) canal defect is classified
Tetralogy of Fallot with Atrioventricular Canal Defect: Two Patch Repair Sitaram M. Emani, MD, and Pedro J. del Nido, MD Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with atrioventricular (AV) canal defect is classified
Concomitant procedures using minimally access
 Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
The goal of the hybrid approach for hypoplastic left heart
 The Hybrid Approach to Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Mark Galantowicz, MD The goal of the hybrid approach for hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is to lessen the cumulative impact of staged interventions,
The Hybrid Approach to Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Mark Galantowicz, MD The goal of the hybrid approach for hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is to lessen the cumulative impact of staged interventions,
Acute type A aortic dissection (Type I, proximal, ascending)
 Acute Type A Aortic Dissection R. Morton Bolman, III, MD Acute type A aortic dissection (Type I, proximal, ascending) is a true surgical emergency. It is estimated that patients suffering this calamity
Acute Type A Aortic Dissection R. Morton Bolman, III, MD Acute type A aortic dissection (Type I, proximal, ascending) is a true surgical emergency. It is estimated that patients suffering this calamity
Surgery For Ebstein Anomaly
 Surgery For Ebstein Anomaly Christian Pizarro, MD Chief, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery Director, Nemours Cardiac Center Alfred I. dupont Hospital for Children Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Sidney
Surgery For Ebstein Anomaly Christian Pizarro, MD Chief, Pediatric Cardiothoracic Surgery Director, Nemours Cardiac Center Alfred I. dupont Hospital for Children Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Sidney
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
Two semilunar valves. Two atrioventricular valves. Valves of the heart. Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve
 The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
The Heart 3 Valves of the heart Two atrioventricular valves Two semilunar valves Right atrioventricular or tricuspid valve Left atrioventricular or bicuspid valve Mitral valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve
The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure
 The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
The evolution of the Fontan procedure for single ventricle
 Hemi-Fontan Procedure Thomas L. Spray, MD The evolution of the Fontan procedure for single ventricle cardiac malformations has included the development of several surgical modifications that appear to
Hemi-Fontan Procedure Thomas L. Spray, MD The evolution of the Fontan procedure for single ventricle cardiac malformations has included the development of several surgical modifications that appear to
MODIFICATION OF THE MAZE PROCEDURE FOR ATRIAL FLUTTER AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 MODIFICATION OF THE MAZE PROCEDURE FOR ATRIAL FLUTTER AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION II. Surgical technique of the maze III procedure The operative technique of the maze III procedure for the treatment of patients
MODIFICATION OF THE MAZE PROCEDURE FOR ATRIAL FLUTTER AND ATRIAL FIBRILLATION II. Surgical technique of the maze III procedure The operative technique of the maze III procedure for the treatment of patients
Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized
 Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Danil Hammoudi.MD 1/12/2009
 Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
The Technique of the Fontan Procedure with Posterior Right Atrium-Pulmonary Artery Connection
 The Technique of the Fontan Procedure with Posterior Right Atrium-Pulmonary Artery Connection J. Ernest0 Molina, M.D., Yang Wang, M.D., Russell Lucas, M.D., - - and James Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT A detailed
The Technique of the Fontan Procedure with Posterior Right Atrium-Pulmonary Artery Connection J. Ernest0 Molina, M.D., Yang Wang, M.D., Russell Lucas, M.D., - - and James Moller, M.D. ABSTRACT A detailed
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy
 Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy Tom R. Karl, MS, MD he most commonly reported coronary artery malformation leading to sudden death in children and young
Coronary Artery from the Wrong Sinus of Valsalva: A Physiologic Repair Strategy Tom R. Karl, MS, MD he most commonly reported coronary artery malformation leading to sudden death in children and young
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Mitral valve infective endocarditis (IE) is the most
 Mitral Valve Replacement for Infective Endocarditis With Annular Abscess: Annular Reconstruction Gregory J. Bittle, MD, Murtaza Y. Dawood, MD, and James S. Gammie, MD Mitral valve infective endocarditis
Mitral Valve Replacement for Infective Endocarditis With Annular Abscess: Annular Reconstruction Gregory J. Bittle, MD, Murtaza Y. Dawood, MD, and James S. Gammie, MD Mitral valve infective endocarditis
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery
 Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery Arthur C. Beall, Jr., M.D., Kenneth L. Mattox, M.D., Mary Martin, R.N., C.C.P., Bonnie Cromack, C.C.P., and Gary Cornelius, C.C.P. * Potential for
Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery Arthur C. Beall, Jr., M.D., Kenneth L. Mattox, M.D., Mary Martin, R.N., C.C.P., Bonnie Cromack, C.C.P., and Gary Cornelius, C.C.P. * Potential for
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Eva Maria Delmo Walter Takeshi Komoda Roland Hetzer
 Surgical repair of the congenitally malformed mitral valve leaflets in infants and children Eva Maria Delmo Walter Takeshi Komoda Roland Hetzer Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin Germany Background and Objective
Surgical repair of the congenitally malformed mitral valve leaflets in infants and children Eva Maria Delmo Walter Takeshi Komoda Roland Hetzer Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin Germany Background and Objective
Ostium primum defects with cleft mitral valve
 Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Thorax (1965), 20, 405. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Ostium primum defects are common; by 1955, 37 operated cases had been reported by
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
The management of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary
 Technique of Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Isabelle Opitz, MD, and Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Pulmonary Endarterectomy Program, Toronto General Hospital, Ontario, Canada. Address reprint
Technique of Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Isabelle Opitz, MD, and Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC Toronto Pulmonary Endarterectomy Program, Toronto General Hospital, Ontario, Canada. Address reprint
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart. The Heart
 Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen
 Techniques for Repairing Posterior Leaflet Prolapse of the Mitral Valve Robin Varghese, MD, MS, and David H. Adams, MD Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen in degenerative mitral valve
Techniques for Repairing Posterior Leaflet Prolapse of the Mitral Valve Robin Varghese, MD, MS, and David H. Adams, MD Posterior leaflet prolapse is the most common lesion seen in degenerative mitral valve
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Surgical treatment of ventricular septal defect
 Thorax (1965), 20, 278. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Since the first report of direct vision closure of ventricular septal defects in
Thorax (1965), 20, 278. VIKING OLOV BJORK From the Department of Thoracic Surgery, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Since the first report of direct vision closure of ventricular septal defects in
Minimally invasive mitral valve surgery: tips, tricks and technique
 Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Page 1 of 6 Minimally invasive mitral valve surgery: tips, tricks and technique Allen Cheng, Amy M. Ramsey Division of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Oklahoma
Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Page 1 of 6 Minimally invasive mitral valve surgery: tips, tricks and technique Allen Cheng, Amy M. Ramsey Division of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Oklahoma
Heart transplantation is the gold standard treatment for
 Organ Care System for Heart Procurement and Strategies to Reduce Primary Graft Failure After Heart Transplant Masaki Tsukashita, MD, PhD, and Yoshifumi Naka, MD, PhD Primary graft failure is a rare, but
Organ Care System for Heart Procurement and Strategies to Reduce Primary Graft Failure After Heart Transplant Masaki Tsukashita, MD, PhD, and Yoshifumi Naka, MD, PhD Primary graft failure is a rare, but
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Atrioventricular valve repair: The limits of operability
 Atrioventricular valve repair: The limits of operability Francis Fynn-Thompson, MD Co-Director, Center for Airway Disorders Surgical Director, Pediatric Mechanical Support Program Surgical Director, Heart
Atrioventricular valve repair: The limits of operability Francis Fynn-Thompson, MD Co-Director, Center for Airway Disorders Surgical Director, Pediatric Mechanical Support Program Surgical Director, Heart
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection
 AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART
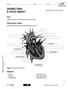 DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Aortic valve repair is an accepted option for aortic valve
 Complex Aortic Valve Disease in Children Christopher W. Baird, MD,* and Pedro J. del Nido, MD Aortic valve repair is an accepted option for aortic valve pathologic conditions in children and young adults.
Complex Aortic Valve Disease in Children Christopher W. Baird, MD,* and Pedro J. del Nido, MD Aortic valve repair is an accepted option for aortic valve pathologic conditions in children and young adults.
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle
 Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Aortic Valve Replacement By Mini-Sternotomy
 Aortic Valve Replacement By Mini-Sternotomy Steven R. Gundry The introduction of the laparoscopic procedure, as well as later scope-based interventions by other surgical disciplines have resulted in the
Aortic Valve Replacement By Mini-Sternotomy Steven R. Gundry The introduction of the laparoscopic procedure, as well as later scope-based interventions by other surgical disciplines have resulted in the
Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
 Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
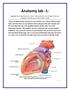 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1
 Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard. Frank Hanley
 The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard Frank Hanley No relationships to disclose CCTGA Interesting Points for Discussion What to do when. associated defects must be addressed surgically:
The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard Frank Hanley No relationships to disclose CCTGA Interesting Points for Discussion What to do when. associated defects must be addressed surgically:
Introduction. Aortic Valve. Outflow Tract and Aortic Valve Annulus
 Chapter 1: Surgical anatomy of the aortic and mitral valves Jordan RH Hoffman MD, David A. Fullerton MD, FACC University of Colorado School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic
Chapter 1: Surgical anatomy of the aortic and mitral valves Jordan RH Hoffman MD, David A. Fullerton MD, FACC University of Colorado School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
Thorax, 1978, 33, 418-424 Anatomy of the coronary arteries in transposition of the great arteries and methods for their transfer in anatomical correction MAGDI H YACOUB AND ROSEMARY RADLEY-SMITH From Harefield
Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE) is indicated for
 Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Steven R. Meyer, MD, PhD, and Christopher G.A. McGregor, MB, FRCS, MD (Hons) Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota.
Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy Steven R. Meyer, MD, PhD, and Christopher G.A. McGregor, MB, FRCS, MD (Hons) Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota.
Kent Bundles in the Anterior Septal Space Will C. Sealy, M.D.
 Kent Bundles in the Anterior Septal Space Will C. Sealy, M.D. ABSTRACT Kent bundles in the anterior septal area of the heart occupy a region of complex morphology. In this study, the anatomical characteristics
Kent Bundles in the Anterior Septal Space Will C. Sealy, M.D. ABSTRACT Kent bundles in the anterior septal area of the heart occupy a region of complex morphology. In this study, the anatomical characteristics
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis
 JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
