Prospect Cardiac Packages. S-Sharp
|
|
|
- Rafe Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prospect Cardiac Packages S-Sharp
2 B mode: Teichholz: Teichholz formula LV Volume 2D: modified Simpson's rule method ALM: area length method LV Volume (Intg.): integral method M mode: Long axis: Teichholz formula Short axis: Teichholz formula PW mode: VTI E/A Ratio SD RI PI Blood flow Prospect Cardiac Packages
3 B mode: Teichholz
4 Work Flow A. Click Teichholz in the cardiac package B. Enter the weight of the animal C. This package can be used in long axis view or short axis view. Find the frame where the heart is in full diastole. D. Click IVS;d or LVAW;d box to start the measurements in the following order: IVS;d/LVAW;d LVID;d LVPW;d. Ensure all the line segments are perpendicular to the walls. E. Find the systolic frame and complete the same procedure. F. The calculated parameters can be viewed in the report.
5 Measurements and Calculations LV long axis Measurements Diastolic: IVS, LVID, LVPW Systolic: IVS, LVID, LVPW Weight Calculations LV mass(u) LV mass(c) LVMI FS LA EDV LA ESV SV LVEF PWTH RWT;d RWT;s IVS;d/LVPW;d IVS;s/LVPW;s LV short axis Diastolic: LVAW, LVID, LVPW Systolic: LVAW, LVID, LVPW Weight LV mass(u) LV mass(c) LVMI FS SA EDV SA ESV SV LVEF PWTH RWT;d RWT;s
6 Parameters Definition (I) Long axis view: IVS;d/s : Inter ventricular septum (diastole/systole) LVID;d/s : Left ventricular internal diameter (diastole/systole) LVPW;d/s : Left ventricular posterior wall (diastole/systole) Short axis view: LVAW;d/s : Left ventricular anterior wall (diastole/systole) LVID;d/s : Left ventricular internal diameter (diastole/systole) LVPW;d/s : Left ventricular posterior wall (diastole/systole)
7 Parameters Definition (II) LV mass(u): uncorrected LV mass (mg) LV mass (U) = 1.05 IVS; d + LVID; d + LVPW; d 3 LVID; d 3 ; LV mass(c): corrected LV mass (mg) LV mass (C) = 0.8 LV mass (U) LVMI: LV mass index (g/m 2 ) LV mass LVMI = ; BSA: body surface area BSA **BSA is calculated according to Meeh s Formula (1879) BSA m 2 = K BW 2 3 ; BW(body weight): kg Rubner: Constant K is accepted as for rats and mice FS: fractional shortening (%) LVID;d LVID;s FS = LVID;d 100%
8 Parameters Definition (III) EDV: end diastolic volume (μl) EDV = (7.0/(2.4+LVID;d)) LVID;d 3 ESV: end systolic volume (μl) ESV = (7.0/(2.4+LVID;s)) LVID;s 3 SV: stroke volume (μl) SV = EDV ESV EF: ejection fraction (%) EF = EDV ESV 100% EDV PWTH: percentage of posterior wall thickening (%) LVPW;s LVPW;d PWTH = 100% LVPW;d RWT: Relative wall thickness RWT;d = (2 LVPW; d)/lvid; d RWT;s = (2 LVPW; s)/lvid; s
9 Diastole Systole
10 B mode: LV Volume 2D
11 Work Flow Modified Simpson's rule method is designed to be used on one long axis view along with 3 short axis views taken from mitral valve (MV), papillary muscle(pap), apical (apex) levels. This method allows more precision when the cardiac geometry isn t typical. A. Click LV Volume 2D in the cardiac package B. Find the diastolic frame in long axis view. Click LV Length;d box under Diastolic tag and complete the measurement of left ventricular length in diastole. Perform the same procedure in systole. C. Same procedures are performed to complete the measurement of area on 3 short axis view in both diastole and systole. D. End diastolic volume (EDV) and end systolic volume (ESV) will show up in the box automatically after the measurements are completed. Other calculated parameters can be viewed in the report.
12 Measurements: Area MV;d/s : short axis area at mitral valve level (diastole/systole) Area Pap;d/s : short axis area at papillary muscle level (diastole/systole) Area Apex;d/s : short axis area at apex level (diastole/systole) LV Length;d/s : left ventricular length (diastole/systole) Calculations: Measurements and Calculations LV EDV(Simp) : end diastolic volume LV ESV(Simp) : end systolic volume SV(Simp) : stroke volume EF(Simp) : ejection fraction FAC(Simp) : fractional area change FS(Simp) : fractional shortening
13 Parameters Definition (I) Volume(μl) = A mv + A Pap L + A apex L + π **Amv: area of short axis at mitral valve level Apap: area of short axis at papillary muscle level Aapex: area of short axis at apical level L 3 3
14 SV(Simp) (μl) SV(Simp)= LV EDV Simp LV ESV(Simp) EF(Simp) (%) SV(Simp) EF(Simp) = 100% LV EDV(Simp) FS(Simp) (%) FS(Simp) = R;d R;s R;d ** R;d = 2 FAC(Simp) (%) FAC(Simp) = Parameters Definition (II) 100% Area Pap;d π ; R;s = 2 Area Pap;d Area Pap;s Area Pap;d Area Pap;s π 100%
15 Diastole
16 B mode: ALM
17 Work Flow Area length method (ALM) is designed to be used on long axis view and short axis view. A. Click ALM in the cardiac package B. Enter the weight of the animal C. Click Epi. Area, Endo. Area, LV Length box to start the measurement of short axis epicardial, endocardial area and left ventricular length in long axis respectively. D. LV mass and LV mass index will show up automatically after all the diastolic measurements are completed. E. Other calculated parameters can be viewed in the report.
18 Measurements: Epi. Area;d/s : epicardial short axis area(diastole/systole) Endo. Area;d/s : endocardial short axis area (diastole/systole) LV length;d/s : left ventricular length (diastole/systole) Weight Calculations: Measurements and Calculations LV EDV(ALM) : end diastolic volume LV ESV(ALM) : end systolic volume SV(ALM) : stroke volume EF(ALM) : ejection fraction Endo FAC(ALM) : fractional area change of endocardial short axis area FS(ALM) : fractional shortening LVM(ALM) : left ventricular mass LVMI(ALM) : left ventricular mass index
19 Parameters Definition (I) LVM(ALM): LV Mass (mg) LV mass = A 1; d L + T 5 6 A 2; d L **T = A ;d 1 A ;d 2 π π **A 1 : epicardial short axis area A 2 : endocardial short axis area L : left ventricular length ; T: mean wall thickness LVMI(ALM): LV Mass Index (g/m 2 ) LVMI = LVM BSA **BSA is calculated according to Meeh s Formula (1879) BSA(m^2 )=K BW ^(2/3) ; BW(body weight): kg Rubner: Constant K is accepted as for rats and mice
20 Parameters Definition (II) Endo FAC: endocardial fractional area change (%) Endo FAC = A 2 ;d A 2 ;s A 2 ;d 100% LV Volume: using the five-sixth area length (bullet) method (μl) EDV = 5 6 A 2; d LV length; d ESV = 5 6 A 2; s LV length; s FS: fractional shortening (%) FS = R;d R;s R;d 100% **R; d = 2 A 2 ;d ; R; s = 2 A 2 ;s π π
21 Diastole
22 B mode: LV Volume Intg.
23 The total LV volume is calculated from the summation of a stack of disks in the cardiac long-axis view only. Work flow: LV Volume (Integral) A. Drawing a boundary along the endocardial border of the LV in both diastole and systole respectively. B. The LV cavity will be divided 20 sections and the volume data also will be shown up automatically. C. Other calculated parameters can be viewed in the report. Volume of each disk (μl) = π a i 2 2 L Total ventricular volume(μl) = π σ20 a i i=1 2 ** a i : the diameter of each disc L: the left ventricular length n: the number of sections n 2 L n
24 Measurements: LV EDV: end diastolic volume LV ESV: end systolic volume Calculations: Measurements and Calculations SV(Disk Intg.) : stroke volume EF(Disk Intg.) : ejection fraction
25 Diastole
26 Cardiac Package in M mode
27 Work Flow A. Cardiac package can be found in tool box measurement tools B. Enter the weight of animal and click the desired measurements on the list. C. Click on the M mode image to place the start and end points. Because IVS;d/LVAW;d LVID;d LVPW;d and IVS;s/LVAW;s LVID;s LVPW;s are continuously measurements, it can automatically start the next measurement until finishing LVPW;d/LVPW;s. D. Click heart rate for heart rate measurement. E. The cardiac index will be calculated if it has enough parameters and be shown in the box. Five sets of data measurement are allowed and the average will be calculated automatically.
28 Measurements and Calculations LV long axis Measurements Diastolic: IVS, LVID, LVPW Systolic: IVS, LVID, LVPW Weight Calculations LV mass(u) LV mass(c) LVMI FS LA EDV LA ESV SV CO EF PWTH RWT;d RWT;s IVS;d/LVPW;d IVS;s/LVPW;s LV short axis Diastolic: LVAW, LVID, LVPW Systolic: LVAW, LVID, LVPW Weight LV mass(u) LV mass(c) LVMI FS SA EDV SA ESV SV CO EF PWTH RWT;d RWT;s
29 Parameters Definition (I) Long axis view: IVS;d/s : Inter ventricular septum (diastole/systole) LVID;d/s : Left ventricular internal diameter (diastole/systole) LVPW;d/s : Left ventricular posterior wall (diastole/systole) Short axis view: LVAW;d/s : Left ventricular anterior wall (diastole/systole) LVID;d/s : Left ventricular internal diameter (diastole/systole) LVPW;d/s : Left ventricular posterior wall (diastole/systole) HR : Heart rate Beats per minutes (BPM)
30 EDV/ESV : Left ventricle volume (diastole/systole) μl EDV = (7.0/(2.4+LVID;d))*LVID;d 3 ESV = (7.0/(2.4+LVID;s))*LVID;s 3 FS : Fractional shortening % FS = LVID;d LVID;s LVID;d 100% EF : Ejection fraction % EF = EDV ESV EDV Parameters Definition (II) 100% SV : Stroke volume μl SV = EDV ESV CO : Cardiac output ml/min CO = SV HR LV mass mg LV mass (U) = 1.05 IVS; d + LVID; d + LVPW; d 3 LVID; d 3 ; U: uncorrected LV mass (C) = LV mass(u) 0.8; C: corrected RWT : Relative wall thickness RWT;d = (2 LVPW; d)/lvid; d RWT;s = (2 LVPW; s)/lvid; s
31 Uncorrected/Corrected LV Mass Uncorrected LV mass in M-mode Left ventricular mass was calculated according to a cubic formula, suggested by Litwin et al. (1993): LV mass (U) = 1.05 IVS; d + LVID; d + LVPW; d 3 LVID; d 3 ; (mg) U: uncorrected Corrected LV mass in M-mode Since the cubic model calculation doesn t correlate with postmortem findings optimally, the LV mass formula was modified as below (T. Reffelmann and R. A. Kloner, 2003): LV mass (C) = LV mass(u) 0.8; (mg) C: corrected
32
33 Short Axis Long Axis
34 PW mode: VTI
35 Work Flow Manual VTI A. Drawing a trace along the envelope of the blood flow waveforms for one cycle. B. After clicking the last point of the drawing trace, the value of the cardiac parameters in PW mode will be shown up automatically. Auto VTI A. Choose the Auto trace function +, - or +/- in the Image adjustment, and then adjust the bar of auto trace to find the most clearly envelope trace of blood flow waveforms. B. Choose a cycle of the blood flow waveforms which you interested in. Click the start point and the end point of the single cycle duration. C. After clicking the end point of the single cycle duration, the value of the cardiac parameters in PW mode will be shown up automatically.
36 VTI: Velocity time integral Flow velocity varies during ejection in a pulsatile system, so the VTI measurement represents the average velocity-time integral during an area enclosed by baseline and Doppler spectrum. Peak velocity The maximum velocity of the chose cycle. Peak pressure: Peak pressure gradient Gradients are calculated from velocity information, and peak gradient obtained from the peak velocity using the Bernoulli equation as: Peak pressure gradient (ΔP max ) = 4 V max / (mmhg) **V(mm/s) Mean velocity The average value of the velocities during the chose cycle. V mean = σn i=1 VΤn ; n: the number of velocity values in chose cycle Mean pressure: Mean pressure gradient The mean gradient is calculated by averaging the instantaneous gradients over the ejection period. Mean pressure gradient = [σ n i=1 Acceleration Deceleration Parameters Definition ΔP i ]/n = [4 σn i=1 V i / ]/n (mmhg) **V(mm/s)
37 Manual VTI Auto VTI
38 PW mode: E/A Ratio
39 E/A ratio (I) Work flow A. Click 8~9 points on the mitral valve or tricuspid valve flow waveform according to the inflection points and the time duration definition in one cycle. B. Start the first point is from the start of E wave. C. After clicking the end point of the single cycle duration, the parameters of the mitral valve flow or tricuspid valve flow in PW mode will show up automatically. Acc: Acceleration rate of E wave of mitral inflow The acceleration rate is presented as the slope of early E wave. E: E wave The filling velocity during the weight of the collected blood in each atrium causes it to fall into the ventricles below when the atrioventricular valves open. DT: Deceleration time The time taken from the maximum E point to baseline.
40 A: A wave The speed of the blood filling the ventricle in the second step occurs in which the atria contract to squeeze out that last bit. E/A: EA ratio The E/A ratio is the ratio of the early (E) to late (A) ventricular filling velocities. IVCT: Isovolumic contraction time During the time period between the closure of the atrioventricular valves and the opening of the aortic and pulmonic valves ET: Ejection time The time of ejection of blood from the left ventricle beginning with aortic valve opening and ending with aortic valve closure. IVRT: Isovolumic relaxation time IVRT is an interval in the cardiac cycle from the closure of the aortic valve to onset of filling by opening of the atrioventricular valve. MPI: Myocardial Performance Index (Tei index) MPI = IVCT+IVRT ET E/A ratio (II)
41
42 PW mode: SD RI PI
43 Work Flow (I) Step 1 : Click tool box button, then click measurement tools Step 2 : Click in S/D ratio button In the cardiac package panel Step 3 : Choose the Auto Trace function Max +/- for the image adjustment, and then adjust the bar of auto trace to find the most clearly envelope trace of blood flow waveforms
44 Work Flow (II) Step 4 : Choose a cycle of the blood flow waveforms which you re interested in. Click the start point and the end point of the single cycle duration Step 5 : After clicking the end point of the single cycle duration, the value of the cardiac parameters in PW mode will be shown up automatically.
45 Parameters Definitions (I)
46 Parameters Definitions (II)
47 Parameters Definitions (III) Resistive Index (RI): The arterial resistivity index, developed by Leandre Pourcelot, is a measure of pulsatile blood flow that reflects the resistance to blood flow caused by microvascular bed distal to the site of measurement. Pulsability index (PI): Blood velocities in arteries are higher during systole than during diastole. This value decreases with distance from the heart. It is also to observe the resistance of blood vessels. A reversal of diastolic flow would be indicate severe abnormal pattern. S/D ratio: The umbilical artery blood flow systolic to end-diastolic ratio is used as a measure of fetal compromise. The ratio decreases towards term, from about 3.5 at 24 weeks to about 2.2 at term. As the diastolic flow becomes diminished in fetal compromise, the systolic/diastolic ratio will rise. All indices theoretically independent of the angle of insonation
48 Blood Flow
49 Volume of Blood Flow Work flow A. Click vessel diameter box to start measurement of internal vessel diameter in B mode. B. Measure VTI of the same vessel in PW spectrum. VTI can be completed by using either manual/auto-trace VTI in cardiac package or directly clicking VTI box to start manual VTI. C. After completing measurement of vessel diameter and VTI, the volume of blood flow will be calculated and show up in the box automatically. Volume(μl) = VTI π D 2 2 ; D: vessel diameter
50
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements. Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc.
 Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
Vevo 2100 System Cardio Measurements Dieter Fuchs, PhD FUJIFILM VisualSonics, Inc. dfuchs@visualsonics.com Instructions This document is a guideline on how to assess cardiac function in rodents imaged
B-Mode measurements protocols:
 Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Imaging Guide Echocardiography
 Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
5 Working With Measurements
 5 Working With Measurements Measurement Overview Measurements accompanying ultrasound images supplement other clinical procedures available to the attending physician. Accuracy of the measurements is determined
5 Working With Measurements Measurement Overview Measurements accompanying ultrasound images supplement other clinical procedures available to the attending physician. Accuracy of the measurements is determined
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD
 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD Board Review Course 2017 43 year old health assistant Severe resistant HTN LT BSA 2 Height 64 1 Here is the M mode echocardiogram
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD Board Review Course 2017 43 year old health assistant Severe resistant HTN LT BSA 2 Height 64 1 Here is the M mode echocardiogram
Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine
 Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine Measurement of end-diastolic LV internal diameter (LVIDd) made by properly-oriented M-Mode techniques in the Parasternal Long Axis View (PLAX):
Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Temple University School of Medicine Measurement of end-diastolic LV internal diameter (LVIDd) made by properly-oriented M-Mode techniques in the Parasternal Long Axis View (PLAX):
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY
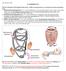 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY The left ventricular wall comprises three layers- middle circumferential layer and superficial and deep longitudinal layers: 1. Subepicardial longitudinal layer (25%
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY The left ventricular wall comprises three layers- middle circumferential layer and superficial and deep longitudinal layers: 1. Subepicardial longitudinal layer (25%
Gilles HANTON, BVSc, DVM, DABT, ERT GH Toxconsulting Brussels, Belgium
 Gilles HANTON, BVSc, DVM, DABT, ERT GH Toxconsulting Brussels, Belgium What is echocardiography (EC) Ultrasounds (US) are emitted by a transducer Reflection of US on tissues depends on their physical properties
Gilles HANTON, BVSc, DVM, DABT, ERT GH Toxconsulting Brussels, Belgium What is echocardiography (EC) Ultrasounds (US) are emitted by a transducer Reflection of US on tissues depends on their physical properties
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size
 2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle
 Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle Roxy Senior MD DM FRCP FESC FACC and Vinay Kumar Bhatia PhD MRCP Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Northwick Park Hospital and Institute for Medical
Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle Roxy Senior MD DM FRCP FESC FACC and Vinay Kumar Bhatia PhD MRCP Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Northwick Park Hospital and Institute for Medical
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze
 LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction page 3 2. Segmentation page 4 3. Measurement Instructions page 11 4. Calculation Instructions page 14 5. References
LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction page 3 2. Segmentation page 4 3. Measurement Instructions page 11 4. Calculation Instructions page 14 5. References
MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS
 MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS Type of Volcano: Stratovolcano Elevation: 2.46 km Base Diameter: 20 km Base Circumference: 62.8 km Area: 314.1 km 2 Reference: http://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/html/update_vmepd/volcano/volcanolist/mayon.htm
MAYON VOLCANO: FAST FACTS Type of Volcano: Stratovolcano Elevation: 2.46 km Base Diameter: 20 km Base Circumference: 62.8 km Area: 314.1 km 2 Reference: http://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/html/update_vmepd/volcano/volcanolist/mayon.htm
Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference?
 17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS
 Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY
 OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT
 HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT INTRODUCTION Conventionally hemodynamics were obtained by cardiac catheterization. It is possible to determine the same by echocardiography. Methods M-mode & 2D echo alone can provide
HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT INTRODUCTION Conventionally hemodynamics were obtained by cardiac catheterization. It is possible to determine the same by echocardiography. Methods M-mode & 2D echo alone can provide
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm
 Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Diastology Disclosures: None. Dias2011:1
 Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle
 Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS
 LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS Mike Mallin, MD Why is LV function important? Systolic Dysfunction is bad... Is it worse? Is it the cause of my patients dyspnea? Does my patient need a inotrope? Why is
LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS Mike Mallin, MD Why is LV function important? Systolic Dysfunction is bad... Is it worse? Is it the cause of my patients dyspnea? Does my patient need a inotrope? Why is
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES
 THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
10/7/2013. Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast. Thanks to our Course Director: Neil J.
 Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume
 How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography Control (n=4)
 Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review. Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC
 Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Left Ventricle Remodeling for Patients with Heart Failure and its Influence on Cardiac Performance
 Original Article Left Ventricle Remodeling for Patients with Heart Failure and its Influence on Cardiac * Mutaz F. Hussain** Anmar Z. Saleh* BSc FICMS BSc,PhD J Fac Med Baghdad 2013; Vol.55, No. 2 Received:
Original Article Left Ventricle Remodeling for Patients with Heart Failure and its Influence on Cardiac * Mutaz F. Hussain** Anmar Z. Saleh* BSc FICMS BSc,PhD J Fac Med Baghdad 2013; Vol.55, No. 2 Received:
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
M.2.2_003. TREAT-NMD Activity A07: Accelerate preclinical phase of new therapeutic treatment developement
 TREAT-NMD Activity A07: Accelerate preclinical phase of new therapeutic treatment developement Work package 7.4: Develop standardised protocols and procedures for harmonising and accelerating pre-clinical
TREAT-NMD Activity A07: Accelerate preclinical phase of new therapeutic treatment developement Work package 7.4: Develop standardised protocols and procedures for harmonising and accelerating pre-clinical
The cardiovascular system is composed of a pump the heart and blood
 5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) of cats is the
 J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants
 Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Normal values for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in adults and children
 Kawel-Boehm et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (2015) 17:29 DOI 10.1186/s12968-015-0111-7 REVIEW Normal values for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in adults and children Nadine Kawel-Boehm
Kawel-Boehm et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (2015) 17:29 DOI 10.1186/s12968-015-0111-7 REVIEW Normal values for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in adults and children Nadine Kawel-Boehm
SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006
 SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006 The goal of this exercise to explore the behavior of the heart as a mechanical pump. For
SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006 The goal of this exercise to explore the behavior of the heart as a mechanical pump. For
The athlete s heart: Different training responses in African and Caucasian male elite football players
 The athlete s heart: Different training responses in African and Caucasian male elite football players Gard Filip Gjerdalen Oslo University Hospital, Aker. Bjørknes College Co-writers: Hisdal J, Solberg
The athlete s heart: Different training responses in African and Caucasian male elite football players Gard Filip Gjerdalen Oslo University Hospital, Aker. Bjørknes College Co-writers: Hisdal J, Solberg
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension:
 Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension: a 3-D echocardiographic study B.W. De Boeck,* S. Kiencke, C. Dehnert, K. Auinger, # M. Maggiorini,
Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension: a 3-D echocardiographic study B.W. De Boeck,* S. Kiencke, C. Dehnert, K. Auinger, # M. Maggiorini,
SIKLUS JANTUNG. Rahmatina B. Herman
 SIKLUS JANTUNG Rahmatina B. Herman The Cardiac Cycle Definition: The cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next The cardiac cycle consists of: - Diastole
SIKLUS JANTUNG Rahmatina B. Herman The Cardiac Cycle Definition: The cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next The cardiac cycle consists of: - Diastole
The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation
 Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING M-MODE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics.
 Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence
 New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence Rashmi Ram, Deanne M. Mickelsen, Catherine Theodoropoulos and Burns C. Blaxall Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1765-H1780,
New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence Rashmi Ram, Deanne M. Mickelsen, Catherine Theodoropoulos and Burns C. Blaxall Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1765-H1780,
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Cardiac Output. Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com ( Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (
 Interactive Physiology Cardiac Output Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Cardiac output is
Interactive Physiology Cardiac Output Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Cardiac output is
IP: Regulation of Cardiac Output
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know. Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts 2/8/2012
 Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus
 ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C.
 AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Transthoracic echocardiography in the evaluation of pediatric pulmonary hypertension and ventricular dysfunction
 REVIEW ARTICLE Transthoracic echocardiography in the evaluation of pediatric pulmonary hypertension and ventricular dysfunction Martin Koestenberger, 1 Mark K. Friedberg, 2 Eirik Nestaas, 3 Ina Michel-Behnke,
REVIEW ARTICLE Transthoracic echocardiography in the evaluation of pediatric pulmonary hypertension and ventricular dysfunction Martin Koestenberger, 1 Mark K. Friedberg, 2 Eirik Nestaas, 3 Ina Michel-Behnke,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Left Venticular Diastolic Dysfunction in Essential Hypertension
 & Left Venticular Diastolic Dysfunction in Essential Hypertension Sevleta Avdić¹, Zulfo Mujčinović¹, Mensura Ašćerić²*, Sabrija Nukić¹, Zumreta Kušljugić³, Elnur Smajić³, Sedija Arapčić¹ 1. House of Health,
& Left Venticular Diastolic Dysfunction in Essential Hypertension Sevleta Avdić¹, Zulfo Mujčinović¹, Mensura Ašćerić²*, Sabrija Nukić¹, Zumreta Kušljugić³, Elnur Smajić³, Sedija Arapčić¹ 1. House of Health,
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Valve Quantification
 Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
From PV loop to Starling curve. S Magder Division of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre
 From PV loop to Starling curve S Magder Division of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Otto Frank 1890 s Frank-Starling Relationship ( The Law of the Heart ) The greater the initial stretch
From PV loop to Starling curve S Magder Division of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Otto Frank 1890 s Frank-Starling Relationship ( The Law of the Heart ) The greater the initial stretch
Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration SINE Wave Curve On Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. Michel Slama Amiens France
 Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function Michel Slama Amiens France Left ventricular pressure Pressure A wave [ LVEDP LVEDP préa Congestive cardiac failure with preserved systolic
Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function Michel Slama Amiens France Left ventricular pressure Pressure A wave [ LVEDP LVEDP préa Congestive cardiac failure with preserved systolic
P = 4V 2. IVC Dimensions 10/20/2014. Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography. The Simplified Bernoulli Equation
 Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W. Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W
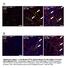 A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS.
 EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS. Cardiovascular Medicine Department, Cairo University ABSTRACT Background: Systemic hypertension is a common cause of left
EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS. Cardiovascular Medicine Department, Cairo University ABSTRACT Background: Systemic hypertension is a common cause of left
Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona
 Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona 1. In which scenario will applying the simplified Bernoulli equation to the peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity and adding
Right Ventricle Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona 1. In which scenario will applying the simplified Bernoulli equation to the peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity and adding
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System
 Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New?
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines: What is New? Roberto M Lang, MD J AM Soc Echocardiogr 2005; 18:1440-1463 1 Approximately 10,000 citations iase in itune Cardiac Chamber Quantification: What is New? Database
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental methods Pericardium In several studies, it has been shown that the pericardium significantly modulates ventricular interaction. 1-4 Since ventricular interaction has
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental methods Pericardium In several studies, it has been shown that the pericardium significantly modulates ventricular interaction. 1-4 Since ventricular interaction has
Ref 1. Ref 2. Ref 3. Ref 4. See graph
 Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
Ref 1 Ref 2 Ref 3 1. Ages 6-23 y/o 2. Significant LVM differences by gender 3. For males 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 103 b. LVM/height = 100 4. For females 95 th percentiles: a. LVM/BSA = 84 b. LVM/height
What is the Definition of Small Systemic Ventricle. Hong Ryang Kil, MD Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University
 What is the Definition of Small Systemic Ventricle Hong Ryang Kil, MD Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University Contents Introduction Aortic valve stenosis Aortic coarctation
What is the Definition of Small Systemic Ventricle Hong Ryang Kil, MD Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University Contents Introduction Aortic valve stenosis Aortic coarctation
Some Questions Concerning Non Invasive Diagnosis In Arterial Hypertension
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Some Questions Concerning Non Invasive Diagnosis In Arterial Hypertension M Adamek Citation M Adamek. Some Questions Concerning Non
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Some Questions Concerning Non Invasive Diagnosis In Arterial Hypertension M Adamek Citation M Adamek. Some Questions Concerning Non
Congenital. Unicuspid Bicuspid Quadricuspid
 David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism
 Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
Clinical Proceedings. 2016;12(1):13-19 Original Article Left Ventricular Function In Subclinical Hypothyroidism NK Thulaseedharan, P Geetha, TM Padmaraj Department of Internal Medicine, Govt. Medical College
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
