Volume Responsiveness in Critically Ill Patients
|
|
|
- Gabriella Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOUND JUDGMENT SERIES Volume Responsiveness in Critically Ill Patients Use of Sonography to Guide Management David Evans, MD, Giovanna Ferraioli, MD, John Snellings, MD, Alexander Levitov, MD Invited paper The Sound Judgment Series consists of invited articles highlighting the clinical value of using ultrasound first in specific clinical diagnoses where ultrasound has shown comparative or superior value. The series is meant to serve as an educational tool for medical and sonography students and clinical practitioners and may help integrate ultrasound into clinical practice. Received August 28, 2013, from the Department of Emergency Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, Richmond, Virginia USA (D.E.); Ultrasound Unit, Department of Infectious Diseases, Fondazione Istituto Di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico Policlinico San Matteo, Medical School, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy (G.F.); and Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia USA (J.S., A.L.). Revision requested September 23, Revised manuscript accepted for publication October 28, Address correspondence to Alexander Levitov, MD, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Eastern Virginia Medical School, 825 Fairfax Ave, Suite 410, Norfolk, VA USA. levitoab@evms.edu Abbreviations CCA, common carotid artery; IVC, inferior vena cava; LVOT, left ventricular outflow tract doi: /ultra Modern resuscitation has changed since the advent of goaldirected therapy. Today, practitioners providing fluid resuscitation are cognizant of the danger associated with volume depletion while being aware of the morbidity of volume overload. 1 Thus, fluid resuscitation must be rapid, precise, and individually tailored to each patient based on reliable data. 2 Critically ill patients have a mixture of intravascular volume depletion, low systemic vascular resistance, and decreased cardiac output, which makes responses to attempts at volume resuscitation difficult to predict. As a result, despite initial attempts at fluid resuscitation, persistent hypotension is common and poses the dilemma of whether the patient should receive additional fluid boluses, a vasopressor, or a positive inotropic agent. Traditionally, resuscitation was guided by static measurements, such as central venous pressure, which was thought to determine the patient s intravascular volume. 1 These static measurements have been shown to be unreliable predictors of a patient s ability to positively respond to volume expansion. 3 Clinicians have increasingly relied on fluid responsiveness, defined as an increase in cardiac output by 15% following a 500-mL fluid bolus given over 10 minutes, to guide the resuscitation process. Several minimally invasive methods have been used to determine whether a patient is fluid responsive, including pulse counter analysis, 4 transpulmonary thermodilution, 5 and reactance. 6 All of these methods have shown promise in evaluation of the volume status of septic patients; however, bedside sonography has also emerged as a useful tool for evaluating cardiac function in critically ill patients. 7 The echocardiographic methods described below are entirely noninvasive, provide real-time data, can be taught reasonably quickly, and can be repeated frequently until desirable clinical outcomes are achieved. This article will review 3 methods aimed at predicting volume responsiveness in critical ill patients: (1) measurement of the caval index; (2) measurement of cardiac output with passive leg raising; and (3) measurement of common carotid artery (CCA) blood flow with passive leg raising These latter techniques enable bedside clinicians to determine changes in blood flow in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and aorta in response to manipulations of right ventricular preload by passive leg raising, thus predicting the response to a fluid bolus without exposing the patient to potentially harmful hypervolemia by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine JUltrasoundMed2014; 33:
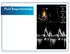
2 Technique Inferior Vena Cava Collapsibility The inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter should be measured in a supine patient in the sagittal (long-axis) subxyphoid window, making sure to angle the transducer to the patient s right. The technique is performed using a 2 5-MHz phased array transducer. The IVC should be visualized in a longitudinal view at the level of the caval right atrial junction. The IVC diameter is measured on inspiration and expiration at approximately 1 cm distal to the IVC hepatic vein junction (Figure 1) Muller et al 12 showed that caval collapse of greater than 40% indicated fluid responsiveness with 70% sensitivity and 80% specificity. However, they also showed that collapse of less than 40% had no bearing on the patient s ability to respond to fluid. Cardiac Output To date, it appears that the response to passive leg raising seems to hold the most promise for assessing volume responsiveness in a variety of critically ill patients. This maneuver rapidly mobilizes about 300 to 500 ml of blood from the lower limbs to the intrathoracic compartment, thereby increasing right ventricular preload. This increase in right ventricular preload essentially mimics the effects of intravenous fluid boluses but with the patient s own whole blood, without the untoward effects of crystalloid overload. The test consists of first putting the patient s head and upper torso at 45 upright, followed by a flat supine position, and then raising both legs of the supine patient to an angle of 45 in relation to the bed, while measuring the stroke volume and cardiac output before and directly after the maneuver (Figure 2). It should be noted that it sometimes takes up to 3 minutes to observe an increased stroke volume in patients with decreased cardiac output and high venous pressures. Beyond that exception, the increase in cardiac output is nearly instantaneous. Cardiac output during passive leg raising is measured using pulsed Doppler imaging. The sample volume, with a gate of 3 to 5 mm, is positioned just proximal to the aortic valve (Figures 3 and 4). An optimal signal shows a smooth velocity curve with a narrow velocity range at each time point. The velocity time integral is measured by tracing the modal velocity as shown in Figure 5. Stroke volume is calculated as the velocity time integral multiplied by (LVOT diameter/2) 2. Cardiac output is stroke volume heart rate. Percent change is [(cardiac output after passive leg raising cardiac output before passive leg raising)/cardiac output after passive leg raising] 100%. A greater than 10% increase in cardiac output would predict volume responsiveness and constitute an indication for a 500-mL fluid bolus. Measurements can be repeated as needed, and fluid resuscitation continues until no further response to passive leg raising is noted. If a patient is still in shock at this point, vasoactive agents or inotropes are usually initiated. Carotid Artery Flow Carotid flow is measured during the passive leg raising maneuver by using a linear array transducer positioned in the long axis over the CCA. The CCA diameter is measured from opposing points of the vessel s intimal wall, with the velocity time integral determined automatically using spectral Doppler envelopes and the sample obtained from the center of the artery (Figure 6). Common carotid artery blood flow per minute is calculated by the equation (CCA diameter) 2 /4 CCA velocity time integral heart rate. This parameter is measured both before and after the passive leg raising to determine the percent change in CCA blood flow. An increase in CCA flow with passive leg raising only occurs in patients with shock, and an increase of greater than 65% is highly predictive of volume responsiveness; a disproportionate increase in carotid flow after passive leg raising, when compared to cardiac output, as well as no response to passive leg raising in healthy volunteers can be explained by further redistribution of cardiac output into low-resistance vascular beds in shock states. Figure 1. Two-dimensional and M-mode images of the IVC. Note the position of the M-mode curser. The image on the left depicts substantial respiratory variations in IVC diameter suggestive of volume responsiveness. The patient on the right is unlikely to positively respond to volume resuscitation. 4 J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:3 7
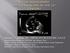
3 Figure 2. Realization of a passive leg raising maneuver in 3 steps: A, at baseline, the patient is lying in a semirecumbent position with the trunk at 45 up from the horizontal position; B, the entire bed is pivoted to obtain a head-down tilt at 45 ; C, the head of the bed is adjusted to obtain a strictly horizontal position. Reproduced with permission from Levitov A, Mayo P, Slonim A. Critical Care Ultrasonography. New York, NY: McGraw- Hill Professional; Discussion Inferior vena cava collapsibility can be a useful tool when assessing for fluid responsiveness; however, it is subject to error from extrinsic pathologic conditions such as tamponade, pulmonary hypertension, and tricuspid insufficiency. Using the aortic stroke volume change method, Monnet et al 13 demonstrated that when passive leg raising induced an increase in aortic flow of greater than 10%, it was predictive of an increase in aortic flow of greater than 15% in response to volume expansion (sensitivity, 97%; specificity, 94%). Volume expansion was performed with 500 ml of isotonic saline over 10 minutes; 37 of the 71 patients (52%) included in this study responded to volume expansion. Maizel et al 14 studied 34 spontaneously breathing patients; an increase in cardiac output or stroke volume by greater than 12% during passive leg raising was highly predictive of volume responsiveness. Sensitivity and specificity values were 63% and 89%, respectively. In addition, the study demonstrated that passive leg raising may be used to predict volume responsiveness in patients with atrial fibrillation. Increased intra-abdominal pressure, however, strongly interferes with the ability of passive leg raising to predict fluid responsiveness. 8 Similarly, Guinot et al 15 showed that in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, those whose stroke volume increased by 15% were shown to be volume responsive with 62% sensitivity and 92% specificity. The main limitation to the cardiac output method is that it requires advanced skills in echocardiography and can be directly affected by the patient s body habitus. Although it remains the gold standard, CCA flow measurement is a much simpler technique, which can be pre- Figure 3. The LVOT diameter (D) is measured in the parasternal longaxis view with the calipers at the aortic valve annulus during systole. Figure 4. Apical 5-chamber view with spectral Doppler gates set at 5 mm within the LVOT in measure the LVOT velocity time integral. J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:3 7 5
4 Failing this, the provider should attempt to evaluate the IVC for collapsibility. A rigorous, data-driven approach to fluid therapy will undoubtedly continue to be important in the treatment of critically ill patients. Through the use of bedside echocardiography, clinicians can scientifically approach the care of the critically ill patient in shock, bringing confidence to the provider and a better outcome to the patient. References Figure 5. Spectral Doppler tracing of the LVOT velocity time integral (VTI). PGmax indicates maximum pressure gradient; PGmean, mean pressure gradient; Vmax, maximum velocity; and Vmean, mean velocity. formed with less difficulty than the previously described method. Marik et al 16 recently described this technique, showing a 60% increase in carotid blood flow following passive leg raising, predicting volume responsiveness with 94% sensitivity and 86% specificity. In conclusion, we believe that according to present evidence, an optimal strategy for assessing volume responsiveness involves first attempting to measure cardiac output via the apical approach; however, if this method proves unsuccessful, the CCA flow method should be attempted. Figure 6. Carotid artery Doppler flow imaging at baseline (background) and after a passive leg raising maneuver (foreground) in a fluid responder. Carotid blood flow increased by 80%, and the vascular diameter increased by 20%. Note the increase in both systolic and diastolic flow. ED indicates end-diastolic velocity; PS, peak systolic velocity; TAMAX, time-averaged maximum velocity; TAMEAN, time-averaged mean velocity; and VF, volume flow. 1. Sadaka F, Juarez M, Naydenov S, O Brien J. Fluid resuscitation in septic shock: the effect of increasing fluid balance on mortality [published online ahead of print February 27, 2013]. J Intensive Care Med. doi: / Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: Marik PE, Baram M, Vahid B. Does central venous pressure predict fluid responsiveness? A systematic review of the literature and the tale of seven mares. Chest 2008; 134: Marik PE, Cavallazzi R, Vasu T, Hirani A. Dynamic changes in arterial waveform derived variables and fluid responsiveness in mechanically ventilated patients: a systematic review of the literature. Crit Care Med 2009; 37: Boussat S, Jacques T, Levy B, et al. Intravascular volume monitoring and extravascular lung water in septic patients with pulmonary edema. Intensive Care Med 2002; 28: Benomar B, Ouattara A, Estagnasie P, Brusset A, Squara P. Fluid responsiveness predicted by noninvasive bioreactance-based passive leg raise test. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36: Manasia AR, Nagaraj HM, Kodali RB, et al. Feasibility and potential clinical utility of goal-directed transthoracic echocardiography performed by noncardiologist intensivists using a small hand-carried device (SonoHeart) in critically ill patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2005; 19: Kircher BJ, Himelman RB, Schiller NB. Noninvasive estimation of right atrial pressure from the inspiratory collapse of the inferior vena cava. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: Feissel M, Michard F, Faller JP, Teboul JL. The respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter as a guide to fluid therapy. Intensive Care Med 2004; 30: Mandeville JC, Colebourn CL. Can transthoracic echocardiography be used to predict fluid responsiveness in the critically ill patient? A systematic review. Crit Care Res Pract 2012; 2012: Cavallaro F, Sandroni C, Marano C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of passive leg raising for prediction of fluid responsiveness in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36: Muller L, Bobbia X, Toumi M, et al. Respiratory variations of inferior vena cava diameter to predict fluid responsiveness in spontaneously breathing patients with acute circulatory failure: need for a cautious use. Crit Care 2012; 16:R J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:3 7
5 13. Monnet X, Rienzo M, Osman D, et al. Passive leg raising predicts fluid responsiveness in the critically ill. Crit Care Med 2006; 34: Maizel J, Airapetian N, Lorne E, Tribouilloy C, Massy Z, Slama M. Diagnosis of central hypovolemia by using passive leg raising. Intensive Care Med 2007; 33: Guinot PG, Zogheib E, Detave M, et al. Passive leg raising can predict fluid responsiveness in patients placed on venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit Care 2011; 15:R Marik PE, Levitov A, Young A, Andrews L. The use of bioreactance and carotid Doppler to determine volume responsiveness and blood flow redistribution following passive leg raising in hemodynamically unstable patients. Chest 2013; 143: J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:3 7 7
Review Article Echocardiographic Assessment of Preload Responsiveness in Critically Ill Patients
 Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 819696, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/819696 Review Article Echocardiographic Assessment of Preload Responsiveness in Critically Ill Patients Alexander
Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 819696, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/819696 Review Article Echocardiographic Assessment of Preload Responsiveness in Critically Ill Patients Alexander
CHAPTER 13. Fluid Responsiveness
 CHAPTER 13 Fluid Responsiveness SECTION 1 Introduction Administration of an intravenous fluid challenge is a common medical intervention in the hypotensive or hypovolemic patient. Ideally, a fluid challenge
CHAPTER 13 Fluid Responsiveness SECTION 1 Introduction Administration of an intravenous fluid challenge is a common medical intervention in the hypotensive or hypovolemic patient. Ideally, a fluid challenge
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae &
 Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Prof. Dr. Iman Riad Mohamed Abdel Aal
 The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
Tailored Volume Resuscitation in the Critically Ill is Achievable. Objectives. Clinical Case 2/16/2018
 Tailored Volume Resuscitation in the Critically Ill is Achievable Heath E Latham, MD Associate Professor Fellowship Program Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Objectives Describe the goal of resuscitation
Tailored Volume Resuscitation in the Critically Ill is Achievable Heath E Latham, MD Associate Professor Fellowship Program Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Objectives Describe the goal of resuscitation
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Utility of transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) in assessing fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients a challenge for the bedside sonographer
 Continuing education Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 4, -514 DOI: 10.11152/mu-880 Utility of transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) in assessing fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients a challenge
Continuing education Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 4, -514 DOI: 10.11152/mu-880 Utility of transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) in assessing fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients a challenge
Echocardiography Volume assessment. Justin Mandeville 2014
 Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
Bioreactance-based passive leg raising test can predict fluid responsiveness in elderly patients with septic shock
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Bioreactance-based passive leg raising test can predict fluid responsiveness in elderly patients with septic shock Caibao Hu 1 *, Guolong Cai 1 *, Jing Yan 1, Hongjie Tong
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Bioreactance-based passive leg raising test can predict fluid responsiveness in elderly patients with septic shock Caibao Hu 1 *, Guolong Cai 1 *, Jing Yan 1, Hongjie Tong
Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series. Sepsis Reassessment
 Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series Sepsis Reassessment Presenters Nova Panebianco, MD Todd Slesinger, MD Fluid Reassessment in Sepsis Todd L. Slesinger, MD, FACEP, FCCM, FCCP, FAAEM Residency Program Director
Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series Sepsis Reassessment Presenters Nova Panebianco, MD Todd Slesinger, MD Fluid Reassessment in Sepsis Todd L. Slesinger, MD, FACEP, FCCM, FCCP, FAAEM Residency Program Director
FLUID RESUSCITATION AND MONITORING IN SEPSIS PROTOCOLIZED VS USUAL CARE DEEPA BANGALORE GOTUR MD, FCCP ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, WEILL CORNELL MEDICAL
 FLUID RESUSCITATION AND MONITORING IN SEPSIS PROTOCOLIZED VS USUAL CARE DEEPA BANGALORE GOTUR MD, FCCP ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, WEILL CORNELL MEDICAL COLLEGE NOVEMBER 10 TH 2017 TEXAS SCCM SYMPOSIUM Disclosures
FLUID RESUSCITATION AND MONITORING IN SEPSIS PROTOCOLIZED VS USUAL CARE DEEPA BANGALORE GOTUR MD, FCCP ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, WEILL CORNELL MEDICAL COLLEGE NOVEMBER 10 TH 2017 TEXAS SCCM SYMPOSIUM Disclosures
Online Supplement. Hemodynamic Assessment of Patients With Septic Shock Using Transpulmonary Thermodilution and Critical Care Echocardiography
 Online Supplement Hemodynamic Assessment of Patients With Septic Shock Using Transpulmonary Thermodilution and Critical Care Echocardiography A Comparative Study Philippe Vignon, MD, PhD; Emmanuelle Begot,
Online Supplement Hemodynamic Assessment of Patients With Septic Shock Using Transpulmonary Thermodilution and Critical Care Echocardiography A Comparative Study Philippe Vignon, MD, PhD; Emmanuelle Begot,
Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of
 Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Sepsis Update: Focus on Early Recognition and Intervention. Disclosures
 Sepsis Update: Focus on Early Recognition and Intervention Jessie Roske, MD October 2017 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation. I will
Sepsis Update: Focus on Early Recognition and Intervention Jessie Roske, MD October 2017 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation. I will
Jan M. Headley, R.N. BS
 Fluid First: Using PLR & SVV to Optimize Volume Jan M. Headley, R.N. BS Disclosure Director, Clinical Marketing & Professional Education Edwards Lifesciences Does this Patient NEED Fluid?? WE Have a Problem
Fluid First: Using PLR & SVV to Optimize Volume Jan M. Headley, R.N. BS Disclosure Director, Clinical Marketing & Professional Education Edwards Lifesciences Does this Patient NEED Fluid?? WE Have a Problem
CHEST. The cornerstone of treating patients with shock. Original Research
 CHEST The Use of Bioreactance and Carotid Doppler to Determine Volume Responsiveness and Blood Flow Redistribution Following Passive Leg Raising in Hemodynamically Unstable Patients Paul E. Marik, MD ;
CHEST The Use of Bioreactance and Carotid Doppler to Determine Volume Responsiveness and Blood Flow Redistribution Following Passive Leg Raising in Hemodynamically Unstable Patients Paul E. Marik, MD ;
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Echocardiography to guide fluid therapy in critically ill patients: check the heart and take a quick look at the lungs
 Editorial Echocardiography to guide fluid therapy in critically ill patients: check the heart and take a quick look at the lungs Federico Franchi 1 *, Luigi Vetrugno 2 *, Sabino Scolletta 1 1 Department
Editorial Echocardiography to guide fluid therapy in critically ill patients: check the heart and take a quick look at the lungs Federico Franchi 1 *, Luigi Vetrugno 2 *, Sabino Scolletta 1 1 Department
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Using Functional Hemodynamic Indicators to Guide Fluid Therapy
 CE 2.6 HOURS Continuing Education Using Functional Hemodynamic Indicators to Guide Fluid Therapy A more accurate and less invasive way to gauge responsiveness to iv volume replacement. OVERVIEW: Hemodynamic
CE 2.6 HOURS Continuing Education Using Functional Hemodynamic Indicators to Guide Fluid Therapy A more accurate and less invasive way to gauge responsiveness to iv volume replacement. OVERVIEW: Hemodynamic
Department of General Medicine, Kilpauk Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India * Corresponding author
 Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL. Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium
 FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium Why do we want to administer fluids? To correct hypovolemia? To increase
FLUIDS AND SOLUTIONS IN THE CRITICALLY ILL Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium Why do we want to administer fluids? To correct hypovolemia? To increase
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
ICU Volume 12 - Issue 4 - Winter 2012/ Matrix Features
 ICU Volume 12 - Issue 4 - Winter 2012/2013 - Matrix Features Fluid Management in Critically Ill Patients: A Guided Approach Prof. Antonio Artigas, MD, PhD ICU Management & Practice Editorial Board Member
ICU Volume 12 - Issue 4 - Winter 2012/2013 - Matrix Features Fluid Management in Critically Ill Patients: A Guided Approach Prof. Antonio Artigas, MD, PhD ICU Management & Practice Editorial Board Member
Comparison of continous-wave Doppler ultrasound monitor and echocardiography to assess cardiac output in intensive care patients
 Comparison of continous-wave Doppler ultrasound monitor and echocardiography to assess cardiac output in intensive care patients Ahmad Elgendy, Ian M Seppelt and Andrew S Lane Echocardiography is commonly
Comparison of continous-wave Doppler ultrasound monitor and echocardiography to assess cardiac output in intensive care patients Ahmad Elgendy, Ian M Seppelt and Andrew S Lane Echocardiography is commonly
Hemodynamic monitoring beyond cardiac output
 Hemodynamic monitoring beyond cardiac output Prof Xavier MONNET Medical Intensive Care Unit Bicêtre Hospital Assistance publique Hôpitaux de Paris FRANCE Conflicts of interest Lilly GlaxoSmithKline Pulsion
Hemodynamic monitoring beyond cardiac output Prof Xavier MONNET Medical Intensive Care Unit Bicêtre Hospital Assistance publique Hôpitaux de Paris FRANCE Conflicts of interest Lilly GlaxoSmithKline Pulsion
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
The Doppler Examination. Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington
 The Doppler Examination Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington OUTLINE Principles/Physics Use in valvular assessment Aortic stenosis (continuity equation) Aortic regurgitation (pressure
The Doppler Examination Katie Twomley, MD Wake Forest Baptist Health - Lexington OUTLINE Principles/Physics Use in valvular assessment Aortic stenosis (continuity equation) Aortic regurgitation (pressure
Disclaimer. Improving MET-based patient care using treatment algorithms. Michael R. Pinsky, MD, Dr hc. Different Environments Demand Different Rules
 Michael R. Pinsky, MD - June 29, 26 Improving MET-based patient care using Michael R. Pinsky, MD, Dr hc Department of Critical Care Medicine University of Pittsburgh Disclaimer Michael R. Pinsky, MD is
Michael R. Pinsky, MD - June 29, 26 Improving MET-based patient care using Michael R. Pinsky, MD, Dr hc Department of Critical Care Medicine University of Pittsburgh Disclaimer Michael R. Pinsky, MD is
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Shock, Monitoring Invasive Vs. Non Invasive
 Shock, Monitoring Invasive Vs. Non Invasive Paula Ferrada MD Assistant Professor Trauma, Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Virginia Commonwealth University Shock Fluid Pressors Ionotrope Intervention
Shock, Monitoring Invasive Vs. Non Invasive Paula Ferrada MD Assistant Professor Trauma, Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Virginia Commonwealth University Shock Fluid Pressors Ionotrope Intervention
3/14/2017. Disclosures. None. Outline. Fluid Management and Hemodynamic Assessment Paul Marik, MD, FCCP, FCCM
 Fluid Management and Hemodynamic Assessment Paul Marik, MD, FCCP, FCCM Disclosures Stocks Advisory boards Grants Speakers Bureau None Outline Hemodynamic Goals Fluid Resuscitation Historical Perspective
Fluid Management and Hemodynamic Assessment Paul Marik, MD, FCCP, FCCM Disclosures Stocks Advisory boards Grants Speakers Bureau None Outline Hemodynamic Goals Fluid Resuscitation Historical Perspective
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Assessing volume status and fluid responsiveness in the emergency department
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):67-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.040 Assessing volume status and fluid responsiveness in the emergency department David C. Mackenzie 1, Vicki E. Noble 2 1 Department
Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):67-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.040 Assessing volume status and fluid responsiveness in the emergency department David C. Mackenzie 1, Vicki E. Noble 2 1 Department
Ultrasound in Emergency Medicine
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.11.040 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 270 275, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/$ - see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.11.040 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 270 275, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/$ - see front matter
Fluid Resuscitation and Monitoring in Sepsis. Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP Anne Rain T. Brown, PharmD, BCPS
 Fluid Resuscitation and Monitoring in Sepsis Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP Anne Rain T. Brown, PharmD, BCPS Learning Objectives Compare and contrast fluid resuscitation strategies in septic shock Discuss available
Fluid Resuscitation and Monitoring in Sepsis Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP Anne Rain T. Brown, PharmD, BCPS Learning Objectives Compare and contrast fluid resuscitation strategies in septic shock Discuss available
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade
 Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Hemodynamic Monitoring To Guide Volume Resuscitation
 Hemodynamic Monitoring To Guide Volume Resuscitation Nick Johnson, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Emergency Medicine Attending Physician, Medical & Neuro-Intensive Care Units Harborview Medical
Hemodynamic Monitoring To Guide Volume Resuscitation Nick Johnson, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Emergency Medicine Attending Physician, Medical & Neuro-Intensive Care Units Harborview Medical
The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter
 1 2 The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter for continuous central venous oximetry (ScvO2) 3
1 2 The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter for continuous central venous oximetry (ScvO2) 3
Patrick C. Cullinan, DO, NBPNS, FCCM, FACOEP, FACOI Associate Clinical Professor, UIWSOM, San Antonio, Texas Adjunct Assistant Professor, University
 Patrick C. Cullinan, DO, NBPNS, FCCM, FACOEP, FACOI Associate Clinical Professor, UIWSOM, San Antonio, Texas Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Texas Health Science Center, Department of Emergency
Patrick C. Cullinan, DO, NBPNS, FCCM, FACOEP, FACOI Associate Clinical Professor, UIWSOM, San Antonio, Texas Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Texas Health Science Center, Department of Emergency
Cardiac Output Monitoring - 6
 Cardiac Output Monitoring - 6 How to use Wrexham s Cardiac Output Monitors. Wrexham Maelor Critical Care Version 02.05.16 Introduction Types of Devices: NICOM - Cheetah Oesophageal Doppler +/- Pulse Contour
Cardiac Output Monitoring - 6 How to use Wrexham s Cardiac Output Monitors. Wrexham Maelor Critical Care Version 02.05.16 Introduction Types of Devices: NICOM - Cheetah Oesophageal Doppler +/- Pulse Contour
Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies
 Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
Assessing Preload Responsiveness Using Arterial Pressure Based Technologies. Patricia A. Meehan, RN, MS Education Consultant Edwards Lifesciences, LLC
 Assessing Preload Responsiveness Using Arterial Pressure Based Technologies Patricia A. Meehan, RN, MS Education Consultant Edwards Lifesciences, LLC Content Description : Fluid administration is a first
Assessing Preload Responsiveness Using Arterial Pressure Based Technologies Patricia A. Meehan, RN, MS Education Consultant Edwards Lifesciences, LLC Content Description : Fluid administration is a first
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT AND COMPARISON OF CARDIAC FUNCTION AND VOLUME STATUS USING BEDSIDE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH OTHER CONVENTIONAL METHODS Priyanka Dwivedi, Shahbaz Ahmad, Vivek Pushp 3,
ASSESSMENT AND COMPARISON OF CARDIAC FUNCTION AND VOLUME STATUS USING BEDSIDE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH OTHER CONVENTIONAL METHODS Priyanka Dwivedi, Shahbaz Ahmad, Vivek Pushp 3,
Transthoracic Echocardiography:
 Transthoracic Echocardiography: An essential tool for the obstetric anaesthetist? Brendan Carvalho MBBCh, FRCA Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University, California Focused TTE Stethoscope of the
Transthoracic Echocardiography: An essential tool for the obstetric anaesthetist? Brendan Carvalho MBBCh, FRCA Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University, California Focused TTE Stethoscope of the
Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter,
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2009) 27, 71 75 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter, David
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2009) 27, 71 75 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter, David
Bedside Ultrasound. US Guided Fluid Resuscitation. Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H
 Bedside Ultrasound US Guided Fluid Resuscitation Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H Outline Shock and Fluid Resuscitation in ICU Ultrasound in Shock Ultrasound Guided Fluid Resuscitation
Bedside Ultrasound US Guided Fluid Resuscitation Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H Outline Shock and Fluid Resuscitation in ICU Ultrasound in Shock Ultrasound Guided Fluid Resuscitation
Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive
 Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive therapy S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Flow-directed vs goal directed strategy for management of hemodynamics S Magder Curr
Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive therapy S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Flow-directed vs goal directed strategy for management of hemodynamics S Magder Curr
Point of Care Ultrasound in the ICU
 Point of Care Ultrasound in the ICU JENNIFER P. KANAAN, M.D. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT I have no disclosures 1 Ultrasound Ultrasound imaging is among the fastest, safest
Point of Care Ultrasound in the ICU JENNIFER P. KANAAN, M.D. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT I have no disclosures 1 Ultrasound Ultrasound imaging is among the fastest, safest
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments
 Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES
 THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Method, Technology and Validity
 Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices
 Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
What is the mechanism of the audible carotid bruit? How does one calculate the velocity of blood flow?
 CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
Fluid optimization strategies in critical care patients
 Perioperative & Critical Care Medicine Page 1 of 5 Fluid optimization strategies in critical care patients X García*, G Gruartmoner, J Mesquida Abstract Introduction Fluid optimization is an important
Perioperative & Critical Care Medicine Page 1 of 5 Fluid optimization strategies in critical care patients X García*, G Gruartmoner, J Mesquida Abstract Introduction Fluid optimization is an important
Questions on Chamber Quantitation
 Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Preload optimisation in severe sepsis and septic shock
 Preload optimisation in severe sepsis and septic shock Prof. Jean-Louis TEBOUL Medical ICU Bicetre hospital University Paris South France Conflicts of interest Member of themedical Advisory Board ofpulsion
Preload optimisation in severe sepsis and septic shock Prof. Jean-Louis TEBOUL Medical ICU Bicetre hospital University Paris South France Conflicts of interest Member of themedical Advisory Board ofpulsion
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE. There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood
 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy A 44 year old female undergoing 10 hour Cytoreductive (CRS) procedure followed by Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC).
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy A 44 year old female undergoing 10 hour Cytoreductive (CRS) procedure followed by Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC).
Swan Ganz catheter: Does it still have a role? Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium
 Swan Ganz catheter: Does it still have a role? Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium How can cardiac output be measured? Thermodilution Arterial waveform
Swan Ganz catheter: Does it still have a role? Daniel De Backer Department of Intensive Care Erasme University Hospital Brussels, Belgium How can cardiac output be measured? Thermodilution Arterial waveform
How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care?
 How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care? Azriel Perel Professor and Chairman Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel ESICM, Vienna 2009 Disclosure
How can the PiCCO improve protocolized care? Azriel Perel Professor and Chairman Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel ESICM, Vienna 2009 Disclosure
Troubleshooting Audio
 Welcome! Audio for this event is available via ReadyTalk Internet Streaming. No telephone line is required. Computer speakers or headphones are necessary to listen to streaming audio. Limited dial-in lines
Welcome! Audio for this event is available via ReadyTalk Internet Streaming. No telephone line is required. Computer speakers or headphones are necessary to listen to streaming audio. Limited dial-in lines
The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial Anthony J. Weekes, MD, Margaret R.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial Anthony J. Weekes, MD, Margaret R.
Invasive Cardiac Output Monitoring and Pulse Contour Analysis. Harshad B. Ranchod Paediatric Intensivist Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital COPICON 2011
 Invasive Cardiac Output Monitoring and Pulse Contour Analysis Harshad B. Ranchod Paediatric Intensivist Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital COPICON 2011 Introduction The primary goal of haemodynamic monitoring
Invasive Cardiac Output Monitoring and Pulse Contour Analysis Harshad B. Ranchod Paediatric Intensivist Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital COPICON 2011 Introduction The primary goal of haemodynamic monitoring
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Jarisch A. Kreislauffragen, Dünser et al. Critical Care 2013, 17:326 Sunday, March 30, 14
 It was fatal for the development of our understanding of circulation that blood flow is relatively difficult while blood pressure so easy to measure: This is the reason why the sphygmomanometer has gained
It was fatal for the development of our understanding of circulation that blood flow is relatively difficult while blood pressure so easy to measure: This is the reason why the sphygmomanometer has gained
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Review Article. Interactive Physiology in Critical Illness : Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Systems. Introduction
 310 Indian Deepak J Physiol Shrivastava Pharmacol 2016; 60(4) : 310 314 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2016; 60(4) Review Article Interactive Physiology in Critical Illness : Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Systems
310 Indian Deepak J Physiol Shrivastava Pharmacol 2016; 60(4) : 310 314 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2016; 60(4) Review Article Interactive Physiology in Critical Illness : Pulmonary and Cardiovascular Systems
Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography
 Chapter 32 Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography Dev Maulik Introduction Evaluation of the fetal heart constitutes one of the critical areas of prenatal diagnosis. Advances in diagnostic medical
Chapter 32 Introduction to Fetal Doppler Echocardiography Dev Maulik Introduction Evaluation of the fetal heart constitutes one of the critical areas of prenatal diagnosis. Advances in diagnostic medical
Purist? or Pragmatist? Assessment & Management of ICU Volume Status
 Assessment & Management of ICU Volume Status 9 th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium Denver, Colorado Paula Dennen, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Nephrology and Critical Care Medicine
Assessment & Management of ICU Volume Status 9 th Annual Rocky Mountain Hospital Medicine Symposium Denver, Colorado Paula Dennen, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Nephrology and Critical Care Medicine
Editor s key points. Y. Song 1,2, Y. L. Kwak 1,2,3, J. W. Song 1,2, Y. J. Kim 1 and J. K. Shim 1,2 *
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 113 (1): 61 6 (2014) Advance Access publication 9 April 2014. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu057 Respirophasic carotid artery peak velocity variation as a predictor of fluid responsiveness
British Journal of Anaesthesia 113 (1): 61 6 (2014) Advance Access publication 9 April 2014. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu057 Respirophasic carotid artery peak velocity variation as a predictor of fluid responsiveness
DESIGNER RESUSCITATION: TITRATING TO TISSUE NEEDS
 DESIGNER RESUSCITATION: TITRATING TO TISSUE NEEDS R. Phillip Dellinger MD, MSc, MCCM Professor and Chair of Medicine Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Chief of Medicine Cooper University Hospital
DESIGNER RESUSCITATION: TITRATING TO TISSUE NEEDS R. Phillip Dellinger MD, MSc, MCCM Professor and Chair of Medicine Cooper Medical School of Rowan University Chief of Medicine Cooper University Hospital
Fluid responsiveness Monitoring in Surgical and Critically Ill Patients
 Fluid responsiveness Monitoring in Surgical and Critically Ill Patients Impact clinique de la Goal-directed-therapy Patrice FORGET, M.D Cliniques universitaires Saint Luc Université catholique de Louvain,
Fluid responsiveness Monitoring in Surgical and Critically Ill Patients Impact clinique de la Goal-directed-therapy Patrice FORGET, M.D Cliniques universitaires Saint Luc Université catholique de Louvain,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Sepsis Management: Past, Present, and Future
 Sepsis Management: Past, Present, and Future Benjamin Ferrell, MD Tennessee ACP Meeting October 28, 2017 Learning Objectives Identify the most updated definition and clinical criteria for sepsis Describe
Sepsis Management: Past, Present, and Future Benjamin Ferrell, MD Tennessee ACP Meeting October 28, 2017 Learning Objectives Identify the most updated definition and clinical criteria for sepsis Describe
Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial curve development
 Haines et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 22, 4:2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial
Haines et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 22, 4:2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Imaging Guide Echocardiography
 Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Imaging Guide Guide to Small Animal Echocardiography using the Vevo Imaging Systems System Compatibility: This guide contains instructions and suggestions for work on the Vevo2100, VevoLAZR, Vevo 3100
Definition- study of blood flow Haemodynamic monitoring refers to monitoring of blood in the cardiovascular system Uses Is NB in the critically ill
 By Craig Definition- study of blood flow Haemodynamic monitoring refers to monitoring of blood in the cardiovascular system Uses Is NB in the critically ill pt Can assist diagnosis and decision making
By Craig Definition- study of blood flow Haemodynamic monitoring refers to monitoring of blood in the cardiovascular system Uses Is NB in the critically ill pt Can assist diagnosis and decision making
Sepsis and septic shock: can we win the battle against this hidden crisis?
 REVIEW ARTICLE Sepsis and septic shock: can we win the battle against this hidden crisis? V.G. Dassanayake Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Key words : Sepsis;
REVIEW ARTICLE Sepsis and septic shock: can we win the battle against this hidden crisis? V.G. Dassanayake Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Key words : Sepsis;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Patient Safety Safe Table Webcast: Sepsis (Part III and IV) December 17, 2014
 Patient Safety Safe Table Webcast: Sepsis (Part III and IV) December 17, 2014 Presenters Mark Blaney, RN Regional Nurse Educator CHI Franciscan Health Karen Lautermilch Director, Quality & Performance
Patient Safety Safe Table Webcast: Sepsis (Part III and IV) December 17, 2014 Presenters Mark Blaney, RN Regional Nurse Educator CHI Franciscan Health Karen Lautermilch Director, Quality & Performance
Focused Comprehensive, Quantitative, Functionally Based Echocardiographic Evaluation in the Critical Care Unit is Feasible and Impacts Care
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 180, 3:74, 2015 Focused Comprehensive, Quantitative, Functionally Based Echocardiographic Evaluation in the Critical Care Unit is Feasible and Impacts Care Sarah B. Murthi, MD, FACS*;
MILITARY MEDICINE, 180, 3:74, 2015 Focused Comprehensive, Quantitative, Functionally Based Echocardiographic Evaluation in the Critical Care Unit is Feasible and Impacts Care Sarah B. Murthi, MD, FACS*;
Trends In Hemodynamic Monitoring: A Review For Tertiary Care Providers
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 12 Number 1 Trends In Hemodynamic Monitoring: A Review For Tertiary Care Providers M E Zerlan Citation M E Zerlan.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 12 Number 1 Trends In Hemodynamic Monitoring: A Review For Tertiary Care Providers M E Zerlan Citation M E Zerlan.. The Internet Journal
Hemodynamic Monitoring in Critically ill Patients in Arthur Simonnet, interne Tuteur : Pr. Raphaël Favory
 Hemodynamic Monitoring in Critically ill Patients in 2017 Arthur Simonnet, interne Tuteur : Pr. Raphaël Favory Rationale for Hemodynamic Monitoring Identify the presence of hemodynamic instability Identify
Hemodynamic Monitoring in Critically ill Patients in 2017 Arthur Simonnet, interne Tuteur : Pr. Raphaël Favory Rationale for Hemodynamic Monitoring Identify the presence of hemodynamic instability Identify
6/5/2014. Sepsis Management and Hemodynamics. 2004: International group of experts,
 Sepsis Management and Hemodynamics Javier Perez-Fernandez, M.D., F.C.C.P. Medical Director Critical Care Services, Baptist t Hospital of Miamii Medical Director Pulmonary Services, West Kendall Baptist
Sepsis Management and Hemodynamics Javier Perez-Fernandez, M.D., F.C.C.P. Medical Director Critical Care Services, Baptist t Hospital of Miamii Medical Director Pulmonary Services, West Kendall Baptist
Fluid responsiveness and extravascular lung water
 Fluid responsiveness and extravascular lung water Prof. Jean-Louis TEBOUL Medical ICU Bicetre hospital University Paris-South France Conflicts of interest Member of the Medical Advisory Board of Maquet/Pulsion
Fluid responsiveness and extravascular lung water Prof. Jean-Louis TEBOUL Medical ICU Bicetre hospital University Paris-South France Conflicts of interest Member of the Medical Advisory Board of Maquet/Pulsion
The Hemodynamic Puzzle
 The Hemodynamic Puzzle SVV NIRS O 2 ER Lactate Energy Metabolism (Oxygen Consumption) (Ml/min/m 2 ) Oxygen Debt: To Pay or Not to Pay? Full Recovery Possible Delayed Repayment of O 2 Debt Oxygen Deficit
The Hemodynamic Puzzle SVV NIRS O 2 ER Lactate Energy Metabolism (Oxygen Consumption) (Ml/min/m 2 ) Oxygen Debt: To Pay or Not to Pay? Full Recovery Possible Delayed Repayment of O 2 Debt Oxygen Deficit
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
