C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Howard Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly spell and pronounce medical terms and major anatomical structures relating to the cardiovascular system. Describe the major organs of the cardiovascular system and their functions. Describe the anatomy of the heart. Describe the flow of blood through the heart. Explain how the electrical conduction system controls the heartbeat. List and describe the characteristics of the three types of blood vessels. Define pulse and blood pressure. Identify and define cardiovascular system anatomical terms. Identify and define selected cardiovascular system pathology terms. Identify and define selected cardiovascular system diagnostic procedures. Identify and define selected cardiovascular system therapeutic procedures. Identify and define selected medications relating to the cardiovascular system. Define selected abbreviations associated with the cardiovascular system Pearson Education, Inc. 107
2 Worksheet 5A New Combining Form and Suffix Handout Directions: For each combining form and suffix below, write out its meaning. Then locate a new term from the chapter that uses the combining form or suffix. Combining Forms Meaning Chapter Term Meaning 1. angi/o 2. aort/o 3. arteri/o 4. ather/o 5. atri/o 6. cardi/o 7. coron/o 8. corpor/o 9. embol/o 10. ischi/o 11. myocardi/o 12. pect/o 13. phleb/o 14. sphygm/o 15. steth/o 16. thromb/o 17. valv/o 18. valvul/o 19. varic/o 20. vascul/o 21. vas/o 22. ven/o 23. ventricul/o Pearson Education, Inc.
3 Suffixes Meaning Chapter Term Meaning 24. -manometer 25. -ole 26. -tension 27. -tonic 28. -ule 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 109
4 Worksheet 5B Medical Term Analysis Directions: Below are terms built from word parts used in this chapter that are not analyzed in the Word Building Table. Many are built from word parts you have learned in previous chapters. Analyze each term presented below and list and define the word parts used to build each term. Medical Term Word Part Analysis 1. pulmonary 2. atrioventricular 3. cardiology 4. arteriosclerosis 5. atherosclerosis 6. hypotension 7. thrombophlebitis 8. angiography 9. valvulitis 10. electrocardiography 11. cardiopulmonary Pearson Education, Inc.
5 Medical Term Word Part Analysis 12. thrombolytic 13. sphygmomanometer 14. cardiomyopathy 15. myocarditis 16. hypertension 17. intracoronary 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 111
6 Worksheet 5C Unscramble Directions: Unscramble each medical term below. A definition for the term is given below each scrambled term. 1. a a i h h m r r t y Irregular heartbeat 2. r c a r i s o h d e x i r A ruptured heart wall 3. a e i i m h s c Loss of blood supply from occlusion 4. o l b n i l i a t i f r Abnormal quivering of heart 5. y r e s o n e i n t p h High blood pressure 6. r r a a c y a b d i d Abnormally slow heart rate 7. m n u e r s a y A weakened and widened artery 8. r r o o c a y n Pertaining to the heart 9. l r e a r i t r o c e o s i s s Hardening of an artery 10. m k a c e a e r p Electrical device to stimulate the heart to beat Pearson Education, Inc.
7 Worksheet 5D Sound It Out Directions: The following are some of the key terms from this chapter written as their phonetic spellings. Sound out each term and write it in the blank. Pronunciations for all terms are included in the glossary at the end of the book and in the audio glossary located on Medical Terminology Interactive. 1. AN-jee-oh-plas-tee 2. in-trah-vee-nus 3. ath-er-oh-skleh-roh-sis 4. brad-ee-car-dee-ah 5. CAR-dee-ak 6. CAR-dee-oh-VAS-kyoo-lar 7. ay-or-tik 8. KOR-ah-nair-ee 9. ee-lek-troh-car-dee-og-rah-fee 10. ul-trah-son-og-rah-fee 11. is-keyh-mee-ah 12. em-boh-liz-em 13. end-ar-teh-rek-toh-mee 14. fih-brill-ay-shun 15. high-per-ten-shun 16. IN-farkt 17. VEE-nus 18. my-oh-car-dee-all 19. fleh-bye-tis 20. in-ter-ven-trik-yoo-lar 21. VAL-view-lar 22. car-dee-oh-meg-ah-lee 23. pol-ee-ar-ter-eye-tis 24. throm-boh-sis 25. STETH-oh-scope 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 113
8 Worksheet 5E Word Search Puzzle Directions: Find and circle the answer for each definition in the word search puzzle. R L H D R K M R G C K T N E R V Q H M N G D K R Z M H S T N E F B Z L N M L N Z J Y M I J D T Q M R K G M K F M P R L G C A E N L B A X T Y Z O K M M O I R M O F N Z D J N T L M N M L T T O I C M T D Y E G S R R C O Y E N T N G F F N C Y X N N N I L R A A B L B S F R A F F G P D O E M L T N I Q U C V R W T M R B C O L L O V E H B B Q D R T A M T M I N L N K G M G H L I C C O O G R Q A L L L Q K K N R A C R M Y B T B M J H C J Z M P V K H Y H I L Y R T T C R A F N I L T R P F T V A R R H Y T H M I A N L S L 1. A specialist in studying the heart. 2. A localized widening of an artery. 3. An irregular heartbeat. 4. Abnormally slow heartbeat. 5. Surgical removal of the inner lining of an artery. 6. Abnormal quivering of heart. 7. A decrease in blood pressure. 8. An area of tissue necrosis. 9. Drug that dissolves existing blood clot. 10. A blood pressure cuff Pearson Education, Inc.
9 Worksheet 5F Crossword Puzzle Directions: Use the definitions given to complete the crossword puzzle ACROSS 4 Low blood pressure 6 Heart chamber that receives blood 7 Abnormal heart sound 9 Removal of inner lining of artery 10 Also called cardioversion DOWN 1 Electrical device to stimulate heart 2 Pumping heart chamber 3 Area of tissue necrosis from ischemia 5 Abnormally fast heart rate 8 Stainless steel tube placed in a vessel 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 115
10 Crossword Puzzle Directions: Use the definitions given to complete the crossword puzzle ACROSS 1 Largest artery in the body 4 veins are swollen and distended veins 5 Heart divided into halves by the 7 High blood pressure 9 Term meaning small vein 10 Slow heart beat DOWN 1 Listening to body sounds such as heart sounds 2 Term meaning pertaining to between ventricles 3 Term meaning hardening of an artery 5 Instrument used to listen to body sounds 6 Widening of artery due to weak arterial wall 8 Blood vessel carries blood toward heart Pearson Education, Inc.
11 Worksheet 5G Chapter Review Anatomy and Physiology 1. The circulation transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs to get oxygen. 2. The is the muscular middle layer of the heart. 3. The are the upper chambers of the heart, and the are the lower pumping chambers. 4. The and valves are atrioventricular valves. 5. Another name for the mitral valve is the valve. 6. Blood ejected from the right ventricle enters the, and blood ejected from the left ventricle enters the. 7. The sinoatrial node is known as the of the heart. 8. are the blood vessels carrying blood away from the heart, and are the blood vessels carrying blood toward the heart. 9. The narrowest blood vessels are the. 10. The arteries carry blood to the heart muscle. Word Building Directions: Build a term that means: 1. narrowing of a vessel 2. enlarged heart 3. study of the heart 4. surgical repair of a valve 5. small vein 6. pertaining to between ventricles 7. heart muscle disease 8. insufficient tension 9. process of recording a vessel 10. removal of fatty substance 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 117
12 Matching 1. systolic 2. auscultation 3. infarct 4. murmur 5. palpitations 6. angina pectoris 7. cardiac arrest 8. prolapse 9. MI 10. aneurysm 11. embolus 12. hypotension 13. catheter 14. plaque 15. stent 16. regurgitation 17. endocarditis 18. CoA 19. flutter 20. hemorrhoid 21. HTN 22. cardiac scan 23. CHF 24. Holter monitor 25. cardiotonic a. Racing, pounding heartbeat b. Thin flexible tube inserted into body c. Chest pain d. Bacterial infection of inner layer of heart e. Congenital narrowing of aorta f. High blood pressure g. Highest blood pressure reading h. Portable EKG i. Floating blood clot j. Stainless steel tube placed within vessel k. Varicose vein in anal region l. Area of necrosis in an organ m. Left ventricle is too weak to pump efficiently n. Increases force of cardiac muscle contraction o. Listening to body sounds p. Heart attack q. Uses radioactive thallium r. Loose heart valve s. To flow backwards t. Also called a bruit u. Atria beats too fast but in regular pattern v. Deposit of fatty lipids in an artery w. Localized widening of an arterial wall x. Low blood pressure y. Complete stopping of heart activity Pearson Education, Inc.
13 Name Date Score Quiz 5A New Word Parts Directions: Define the combining form or suffix in the spaces provided. 1. angi/o 2. ather/o 3. cardi/o 4. atri/o 5. isch/o 6. phleb/o 7. sphygm/o 8. steth/o 9. thromb/o 10. valvul/o 11. vascul/o 12. vas/o 13. ven/o 14. ventricul/o 15. aort/o 16. arteri/o 17. coron/o 18. valv/o 19. -ule 20. -ole 21. -manometer 22. -tension 23. pect/o 24. varic/o 25. myocardi/o 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. 119
Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
Biomedical Terminology. Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System
 Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System at a Glance
 Cardiovascular System at a Glance Functions of Cardiovascular (CV) System Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed substances to cells Removal of wastes Cardiovascular System at a Glance
Cardiovascular System at a Glance Functions of Cardiovascular (CV) System Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed substances to cells Removal of wastes Cardiovascular System at a Glance
This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system
 SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Heart: hollow muscular organ, pumps blood full of nutrients throughout the body Arteries: carry blood away from the heart Capillaries: smaller vessels, microscopic, exchange of nutrients
Cardiovascular System Heart: hollow muscular organ, pumps blood full of nutrients throughout the body Arteries: carry blood away from the heart Capillaries: smaller vessels, microscopic, exchange of nutrients
9 Review. Labeling Exercise. Blood high in oxygen. Blood low in oxygen. Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195
 Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Chapter 10. Cardiovascular, Immune, Lymphatic Systems and Blood. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 10 Cardiovascular, Immune, Lymphatic Systems and Blood Chapter 10 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures. Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and
Chapter 10 Cardiovascular, Immune, Lymphatic Systems and Blood Chapter 10 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures. Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Cardiovascular System
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System. Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh
 Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh sarmednabhan@ibnsina.edu.iq Outlines Terms Cardiovascular System (CVS) Respiratory System
Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh sarmednabhan@ibnsina.edu.iq Outlines Terms Cardiovascular System (CVS) Respiratory System
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System
 C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly spell
C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly spell
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Anatomy of the Heart and the. ICD-10 Codes
 Anatomy of the Heart and the Diseases ICD-10 Codes Sharon J. Oliver CPC, CPMA, CPC-I All Rights Reserved 1 Anatomy of the Heart Pulmonary Tricuspid (AV) Valve Mitral Aortic Semilunar Valve Chordae Tendineae
Anatomy of the Heart and the Diseases ICD-10 Codes Sharon J. Oliver CPC, CPMA, CPC-I All Rights Reserved 1 Anatomy of the Heart Pulmonary Tricuspid (AV) Valve Mitral Aortic Semilunar Valve Chordae Tendineae
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System
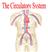 Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings. Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular System 8/3/2010. Version 1/Fall 2010
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
Cardiovascular & Lymphatic. Anatomy
 Cardiovascular & Lymphatic Chapter Ten Medical Terminology HIT # 141 Anatomy Heart = muscular organ, circulates blood, two upper chambers = right & left atrium and two lower chambers, right & left ventricle,
Cardiovascular & Lymphatic Chapter Ten Medical Terminology HIT # 141 Anatomy Heart = muscular organ, circulates blood, two upper chambers = right & left atrium and two lower chambers, right & left ventricle,
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Blood must move! 4/15/2014. Heart Basics
 What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 8 The Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: 8.1 Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the cardiovascular system. 8.2 Break
Chapter 8 The Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: 8.1 Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the cardiovascular system. 8.2 Break
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Spelling & Pronunciation
 Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Diseases. Cardiovascular System
 Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
: thick middle layer; cardiac muscles : thin inner layer; endothelial lining
 1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Control of Heart Rate
 Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Your Heart Anatomy and Procedures
 Your heart is a muscular organ about the size of your fist. It is located behind the lower part of your sternum (breast bone). With each beat of the heart, the heart muscle pumps and circulates blood through
Your heart is a muscular organ about the size of your fist. It is located behind the lower part of your sternum (breast bone). With each beat of the heart, the heart muscle pumps and circulates blood through
Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction. Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction
 Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Aneurysm > an-yur-izm > localized weakening of an arterial wall that enlarges over time. Angina
Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Aneurysm > an-yur-izm > localized weakening of an arterial wall that enlarges over time. Angina
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation. Biology 2201
 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Medical Terminology. Chapter 5: The Cardiovascular System
 Medical Terminology Chapter 5: The Cardiovascular System CHAPTER OBJECTIVES This chapter covers the cardiovascular system, which is the body s delivery service, and the combining terms and abbreviations
Medical Terminology Chapter 5: The Cardiovascular System CHAPTER OBJECTIVES This chapter covers the cardiovascular system, which is the body s delivery service, and the combining terms and abbreviations
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
UNIT 11: THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions of the Heart PUMPS Blood Transports Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Carbon Dioxide and Metabolic Wastes Thermoregulation Immunological Function Clotting Mechanisms
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: HOMEWORK: Due Tues, Online Quiz: OBJECTIVES:
 AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
