BLOOD & CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CHAPTERS 10 & 11
|
|
|
- Jerome Day
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BLOOD & CIRCULATORY SYSTEM CHAPTERS 10 & 11
2 BLOOD Sticky, opaque with metallic taste Alkaline ph of Temperature 38 O C 8% of body weight 5-6 L in average male
3 A. COMPONENTS Fluid tissue Living cells called formed elements suspended in nonliving fluid matrix called plasma
4
5
6 1. Plasma 90% water; straw colored fluid Plasma proteins most abundant produced by the liver Albumin aids in osmotic pressure of blood keeping water in bloodstream Fibrogen clotting protein Globulins antibodies for defense
7 May also contain: Nutrients (glucose, a.a., fatty acids, vitamins) Salts Gases (O 2 & CO 2 ) Hormones Metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid)
8 Composition varies daily Body works to maintain homeostasis Ex. Liver increase production of plasma proteins when low Respiratory systems & kidneys maintain ph acidosis or alkalosis
9 2. Formed Elements A. Erythrocytes red blood cells Anucleated & lack organelles Hemoglobin iron containing protein that transports oxygen Number of rbc determines viscosity of blood Confined to bloodstream
10 B. Leukocytes white blood cells Located in the buffy coat between plasma & formed elements Nucleated & contain organelles Fight pathogens & can slip out of bv through process called diapedesis circulatory system is just their means of transportation
11 Wbc number can indicate infection or tissue damage Leukocytosis increased wbc; indicates infection Leukopenia decreased wbc; can be caused by certain drugs, anticancer agents or corticosteroids Leukemia abnormally high wbc; defective & immature; unable to carry out functions
12 Types of Leukocytes 1. Granulocytes contain granules & lobed nuclei A. Neutrophils most abundant; phagocytes fight infection
13 B. Eosinophils response to allergies & parasitic infections
14 C. Basophils rarest; response to inflammation
15 2. Agranulocytes absence of granules & spherical nuclei A. Lymphocytes produce antibodies; fight tumors & viruses
16 B. Monocytes largest; initiate clotting ; Chronic infections
17 NEUTROPHILS LYMPHOCYTES MONOCYTES EOSINOPHILS BASOPHILS Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
18 HIGH WBC COUNT Neutrophils bacterial infection, burns, stress, inflammation Lymphocytes viral infections, some leukemias Monocytes viral or fungal infections, tuberculosis, some leukokemia, chronic diseases Eosinophils allergic reactions, parasitic infections, autoimmune diseases Basophils allergic reactions, leukemias, cancers, hypothyroidism
19 LOW WBC COUNT Neutrophils radiation, drug toxicity, vitamin B12 deficiency, lupus Lymphocytes prolonged illness, immunosuppression, cortisol treatments Monocytes bone marrow depression, cortisol Eosinophils drug toxicity, stress Basophils pregnancy, ovulation, stress, hyperthyroidism
20 C. Thrombocytes Platelets Fragments of multinucleated cells Clot damaged bv by clinging to the broken area
21 HEMATOPOIESIS (Blood Cell Formation) Occurs in the red bone marrow of skull, pelvis, ribs, sternum & epiphyes of humerus & femur Hemocytoblast stem cell in bone marrow that gives rise to a blood cell Hemocytoblast develops into either a lymphoid stem cell or myeloid stem cell Lymphoid stem cells produce lymphocytes (developing white blood cells) Myeloid stem cells produce all other types of blood cells
22
23 Red Blood Cell Formation Takes 3 5 days to produce new rbc s Rbc s circulate for days then fall apart; remains are eliminated by the liver, spleen & other tissues Controlled by erythropoitin hormone produced by the kidney Amount of oxygen in blood controls release of erythropoitin
24 Developing rbc divide & produce large amounts of hemoglobin When enough hemoglobin is present the nucleus & organelles are ejected & cell collapses inward Young rbc reticulocyte (still has an ER) enter bloodstream & transport oxygen Within 2 days ER is ejected & cell becomes a mature erythrocyte
25 HEMOCYTOBLAST MYELOID STEM CELL RETICULOCYTE ERYTHROCYTE
26 HEMOSTASIS (3 Phases Vascular Spasms, Platelet Plug Formation, Coagulation) 1. Collagen fibers of the inner lining of broken bv are exposed 2. platelets release serotonin which causes bv to spasm narrows bv & lessens blood to area 3. Platelets stick to collagen fibers forming a plug white thrombus 4. injured cells produce thromboplastin to aid in clotting
27 5. PF3, a phospholipid that coats platelets interacts with thromboplastin, blood proteins & Ca+ to form an activator that begins the clotting process 6. prothrombin in the plasma converts to active enzyme called thrombin 7. thrombin joins soluble fibrinogen proteins into hair like strands called insoluble fibrin
28 8. fibrin forms a mesh that traps rbc s & forms a clot 9. within an hour the clot begins to retract squeezing serum (plasma minus proteins) from the mass pulling ruptured edges of bv together neral/esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7 _3.htm
29 HUMAN BLOOD GROUPS Antigens (also called agglutinogens) recognize foreign substances in body & stimulate immune system to release antibodies Each person s rbc contain their own genetically determined antigens on the plasma membrane
30
31 TYPE A TYPE B TYPE AB TYPE O A ANTIGENS B ANTIGENS A & B ANTIGENS ABSENCE OF ANTIGENS GENES: AA or AO GENES: BB or BO GENES: AB GENES: OO
32
33 Universal recipient type AB ; can receive all 4 blood types Universal donor type O Type A receive type A or O Type B receive type B or O
34 Rh factor indicates the presence of a certain blood protein; same protein is found in the Rhesus Monkey Rh- means protein is absent Rh+ means protein is present
35 Situation: Rh- woman conceives an Rh+ child Result: fetal Rh+ blood can mix with mother s Rh- blood during delivery The mother s Rh- blood will build antibodies against & attack the Rh+ red blood cells Future pregnancies will be affected because the mom now has antibodies to fight Rh+ blood cells Rhogam
36 tional/landsteiner/readmore.html tional/landsteiner/index.html r/119/images/blood_typing_photos.ht m
37 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE HEART Relatively the size of a fist; 1 lb ; hollow Positioned to the left of thoracic cavity Cone shaped Apex pointed end; directed toward the left hip Base posterosuperior; leads to major bv
38 HEART COVERINGS & WALLS Pericardium sac containing heart Epicardium / visceral peritoneum hugs external surface; outermost layer of heart wall Parietal peritoneum dense c.t.; anchors heart to sternum & diaphragm
39
40
41 LAYERS OF HEART WALL Epicardium outermost Myocardium bundles of cardiac muscle; contraction Endocardium innermost; line the heart chambers
42 HEART CHAMBERS Right Atria receives deoxygenated blood from the body Left Atria receives oxygenated blood from the lungs Right Ventricle releases deoxygenated blood to the lungs Left Ventricle releases oxygenated blood to the body
43 FETAL HEART Foramen Ovale & ductus arteriosus are fetal structures that close at birth Function is to bypass blood from the fetal lungs
44
45
46 MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS Oxygen poor blood from the veins of the body is received into the right atria of the heart through the superior & inferior vena cava. The oxygen poor blood enters the right ventricle and is pumped through the pulmonary trunk, which divides into two pulmonary arteries that carry blood to the lungs. Gas exchange occurs at the lungs and the oxygen rich blood returns to the left atria of the heart through four pulmonary veins. Oxygen rich blood travels through the left ventricle and is distributed throughout the body by the aorta.
47 Pulmonary circulation circulation of blood between the heart and lungs Systemic circulation circulation of blood throughout the body Coronary arteries vessels on the outer surface of heart that provide oxygen & nutrients to the heart muscle
48
49 ng.htm dam htm /heart_bloodflow.shtml
50 HEART VALVES Atrioventricular (AV) between atria & ventricles Bicuspid/ mitral valve located between left atria & ventricle ; 2 cusps or flaps Tricuspid located between right atria & ventricle; 3 cusps or flaps
51 Semilunar valves guard large arteries leaving the ventricle Pulmonary semilunar located between right ventricle & pulmonary trunk Aortic semilunar located between left ventricle & aorta /heart_valves.shtml
52 Chordae tendinae heart strings Anchor flaps to walls of heart
53 marieb_ehap_8/activities/chapter11/ Act11A.html
54 Hemorrhagic anemia Hemolytic anemia Decrease in rbc due to prolonged or excessive bleeding Lysis of rbc due to bacterial infection Pernicious anemia Lack of Vitamin B12 which is needed for red blood cell formation Aplastic anemia Destruction of red bone marrow by cancer, radiation or medications Iron deficiency anemia Sickle cell anemia Lack of Fe in diet; small rbc & pale color due to lack of hemoglobin Genetic disorder in which rbc shape is distorted (sickle shaped) ; easily rupture & clog blood vessels Polycythemia Increase rbc; can result from bone marrow cancer or change in altitude
55 DISORDER / DISEASE DESCRIPTION Leukemia Excessive increase in wbc; bone marrow caner; immature & defective wbc Thrombus Persistent clot in an unbroken bv; blocks blood flow Embolus Thrombus which is floating in the blood stream Thrombocytopenia Insufficient platelet number; spontaneous bleeding from vessels Hemophilia Genetic sex linked disorder; lack of clotting factors leads to bruising, joint bleeding & inability to repair damaged bv Hemolytic disease of newborns Incompatible Rh between mom & newborn; mom s antibodies destroy newborn s rbc causing anemia & hypoxia Physiological jaundice Fetal blood cells rapidly broken down; liver cannot dispose of hemoglobin in bile fast enough; leads to yellowing of skin & eyes
Blood. The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue. Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma
 Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Unit 10: Blood. 2. Buffy coat contains leukocytes and platelets (less than 1% of blood)
 Unit 10: Blood I. Blood A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells a. Formed elements 2. Non-living matrix a. Plasma D. If blood
Unit 10: Blood I. Blood A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells a. Formed elements 2. Non-living matrix a. Plasma D. If blood
Composition of Blood
 Blood Blood Blood serves as a vehicle for distributing body heat and for transporting nutrients, respiratory gases, and other substances throughout the body. Composition of Blood Blood is the only fluid
Blood Blood Blood serves as a vehicle for distributing body heat and for transporting nutrients, respiratory gases, and other substances throughout the body. Composition of Blood Blood is the only fluid
Unit 10 - Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body. c) Plasma rises to the top (55% of blood)
 Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Composition and Functions of Blood. Text p WB 193
 Chapter 10 Blood Composition and Functions of Blood Text p. 337-339 WB 193 Blood Transports everything that must be carried from one place to another. Nutrients, ions, gases, hormones, proteins Urea, waste
Chapter 10 Blood Composition and Functions of Blood Text p. 337-339 WB 193 Blood Transports everything that must be carried from one place to another. Nutrients, ions, gases, hormones, proteins Urea, waste
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood. Multiple Choice
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice 1) The matrix of blood is called: A) buffy coat B) plasma C) erythrocytes D) lymphocytes E) formed elements Diff: 1 Page
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice 1) The matrix of blood is called: A) buffy coat B) plasma C) erythrocytes D) lymphocytes E) formed elements Diff: 1 Page
Hematocrit. Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood. Plasma Formed elements:
 Blood Notes Hematocrit Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood Plasma Formed elements: Buffy Coat = Leukocytes and Platelets Erythrocytes General Facts Blood ph = 7.4 Volume
Blood Notes Hematocrit Hematocrit = using a centrifuge to separate out the parts of blood Plasma Formed elements: Buffy Coat = Leukocytes and Platelets Erythrocytes General Facts Blood ph = 7.4 Volume
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma
 The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Color range Oxygen-rich blood is scarlet red Oxygen-poor blood is dull
The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Color range Oxygen-rich blood is scarlet red Oxygen-poor blood is dull
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Blood Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Blood Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi 1. Transport of substances Functions of Blood O2: blood transports oxygen from the lungs to tissue cells, so that cellular respiration is possible. Co2: blood transports carbon
Blood Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi 1. Transport of substances Functions of Blood O2: blood transports oxygen from the lungs to tissue cells, so that cellular respiration is possible. Co2: blood transports carbon
formed elements plasma Erythrocytes Hematocrit buffy coat Plasma Albumin Clotting protein Antibodies Acidosis Alkalosis
 BLOOD I. Components A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells called the formed elements 2. Non-living matrix called plasma
BLOOD I. Components A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells called the formed elements 2. Non-living matrix called plasma
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC. A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters
 A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
Blood. Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11
 Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions. Plasma
 Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
Branch of medicine that deals with blood, its formation and disorders is called. Three main functions of cardiovascular system are,, and.
 Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Blood Clotting Functions of Blood Transportation
 1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
Blood. Plasma. The liquid part of blood is called plasma. 1. Pale yellow fluid; forms more than half the blood volume.
 11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
4/5/17. Blood. Blood. Outline. Blood: An Overview. Functions of Blood
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Chapter 11. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture.
 Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood. Functions:
 Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and
 Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and nutrients, transport of metabolic wastes for elimination,
Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and nutrients, transport of metabolic wastes for elimination,
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
Functions of Blood. Transport. Transport. Defense. Regulation. Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Blood. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Hematology. The Study of blood
 Hematology The Study of blood Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Composition: PLASMA liquid portion of blood without cellular components Serum plasma after a blood clot is formed Cellular elements are
Hematology The Study of blood Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Composition: PLASMA liquid portion of blood without cellular components Serum plasma after a blood clot is formed Cellular elements are
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 !!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
The Blood Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 The Blood Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Blood Circulation Blood leaves the heart via arteries that branch repeatedly until they become capillaries Oxygen (O 2 ) and nutrients diffuse across capillary walls
The Blood Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Blood Circulation Blood leaves the heart via arteries that branch repeatedly until they become capillaries Oxygen (O 2 ) and nutrients diffuse across capillary walls
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD
 PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood
 BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
The Circulatory System. Blood and Blood Pressure
 The Circulatory System Blood and Blood Pressure Blood Total volume = 8-9% of body mass Average person = 5 L of blood DYK? Blood is actually a tissue! Plasma: - water, proteins, salts, gases, nutrients,
The Circulatory System Blood and Blood Pressure Blood Total volume = 8-9% of body mass Average person = 5 L of blood DYK? Blood is actually a tissue! Plasma: - water, proteins, salts, gases, nutrients,
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224. Lama Alzamil 3 rd floor/ office # 119
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 119 Blood (chapter 10) 1. Composition and function of blood Components of blood Physical characteristics
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office # 119 Blood (chapter 10) 1. Composition and function of blood Components of blood Physical characteristics
Agenda. Components of blood. Blood is Fluid Connective Tissue. Blood: General functions
 Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
G. Types of White Blood Cells
 1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
Chapter 11. Oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide, hormones and more. Body temperature, water-salt balance and body ph
 Chapter 11 FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD 1. Transportation Oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide, hormones and more 2. Defense Against invasion by pathogens 3. Regulatory functions Body temperature, watersalt
Chapter 11 FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD 1. Transportation Oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide, hormones and more 2. Defense Against invasion by pathogens 3. Regulatory functions Body temperature, watersalt
Functions of Blood. 1. Transportation 2. Protection against invasion 3. Blood clotting 4. Regulation. Blood: Functions Blood clotting
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Lecture Packet 13 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII.
Outline Blood Biol 105 Lecture Packet 13 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII.
The Blood. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 The Blood Dr. Gary Mumaugh Blood is the river of life Overview of Blood Circulation Blood leaves the heart via arteries that branch repeatedly until they become capillaries Oxygen (O 2 ) and nutrients
The Blood Dr. Gary Mumaugh Blood is the river of life Overview of Blood Circulation Blood leaves the heart via arteries that branch repeatedly until they become capillaries Oxygen (O 2 ) and nutrients
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity
 Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Blood Lecture Outline : Fluid Connective Tissue Part I of the Cardiovascular Unit
 Blood Lecture Outline : Fluid Connective Tissue Part I of the Cardiovascular Unit General Characteristics: Extracellular matrix ph Volume Functions of the blood: 1. Transport 2. Regulation 3. Protection
Blood Lecture Outline : Fluid Connective Tissue Part I of the Cardiovascular Unit General Characteristics: Extracellular matrix ph Volume Functions of the blood: 1. Transport 2. Regulation 3. Protection
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
Overview: Blood Composition and Function
 Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood I. Functions of Blood A. List and describe the seven major homeostatic functions of blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. II. Plasma A. Composition 1. It is a fluid consisting
Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood I. Functions of Blood A. List and describe the seven major homeostatic functions of blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. II. Plasma A. Composition 1. It is a fluid consisting
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS. Pages Pages Pages
 Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS Pages 635-657 Pages 661-688 Pages 696-701 Homeostatic Imbalances of Erythrocytes H. I. Description Anemia blood with low O2 carrying capacity; symptomatic
Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS Pages 635-657 Pages 661-688 Pages 696-701 Homeostatic Imbalances of Erythrocytes H. I. Description Anemia blood with low O2 carrying capacity; symptomatic
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.1 Blood
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
BLOOD. Dr. Vedat Evren
 BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
temperature 38 o C (100.4 o F) The temperature of blood is slightly higher than the normal body temperature of 37 o C (98.6 o F).
 1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 C h a p t e r 11 The Cardiovascular System: Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Cardiovascular System A circulating transport system
C h a p t e r 11 The Cardiovascular System: Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Cardiovascular System A circulating transport system
Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012
 Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012 1. Leukocytes are attracted to a site of injury or disease by: a. diapedesis b. chemotaxis c. leukocytosis d. heparin e. leukomotosis 2. Leukocytes leave
Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012 1. Leukocytes are attracted to a site of injury or disease by: a. diapedesis b. chemotaxis c. leukocytosis d. heparin e. leukomotosis 2. Leukocytes leave
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
HEMOTOLOGY. B. Helps stabilize body temperature -heats up and cools down slowly which moderates body temp
 I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
Chapter 19. Openstax: Chapter 18. Blood
 Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
Good Morning! How many miles do your blood cells travel in their lifetime of 3 months? Take out your notes and blood worksheet!
 Good Morning! How many miles do your blood cells travel in their lifetime of 3 months? Take out your notes and blood worksheet! Functions of Blood Blood performs a number of functions dealing with: Substance
Good Morning! How many miles do your blood cells travel in their lifetime of 3 months? Take out your notes and blood worksheet! Functions of Blood Blood performs a number of functions dealing with: Substance
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Circulatory System Notes
 Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports nutrients B. Transports gases C. Transports wastes D. Transports hormones E. Maintain balance of fluids F. Protection from disease G. Regulate body temperature
Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports nutrients B. Transports gases C. Transports wastes D. Transports hormones E. Maintain balance of fluids F. Protection from disease G. Regulate body temperature
Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System
 Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
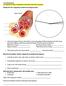 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Circulation and Blood
 Circulation and Blood Circulation A circulatory system usually consists of: 1) A in which materials are ( ) 2) A network of or body spaces in which the fluid flows ( ) 3) A means of driving or moving the
Circulation and Blood Circulation A circulatory system usually consists of: 1) A in which materials are ( ) 2) A network of or body spaces in which the fluid flows ( ) 3) A means of driving or moving the
The Cardiovascular System: The Blood, Heart, & Blood Vessels
 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood, Heart, & Blood Vessels Fluids of the Body Cells of the body are serviced by 2 fluids 1. Blood a liquid connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a liquid
The Cardiovascular System: The Blood, Heart, & Blood Vessels Fluids of the Body Cells of the body are serviced by 2 fluids 1. Blood a liquid connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a liquid
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Blood Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation Gases, nutrients, hormones, waste products 2. Regulation ph, body temperature, osmotic
Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Blood Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation Gases, nutrients, hormones, waste products 2. Regulation ph, body temperature, osmotic
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Blood Liquid connective tissue 1. Transportation - Gases, nutrients, hormones, and waste. 2. Regulation - ph, body temperature, and blood pressure. 3. Protection
Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Blood Liquid connective tissue 1. Transportation - Gases, nutrients, hormones, and waste. 2. Regulation - ph, body temperature, and blood pressure. 3. Protection
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
TOO MUCH TIME. Cardiovascular System: Blood. Cell. Cell. Transport System of the Body: O 2 / Energy. Nutrients Waste O 2 CO 2.
 Transport System of the Body: 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s distance = time 2 O 2 / Energy O 2 CO 2 Nutrients Waste Source Cell TOO MUCH TIME External environment: CO 2 / Waste Sink O 2 / Nutrients
Transport System of the Body: 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s distance = time 2 O 2 / Energy O 2 CO 2 Nutrients Waste Source Cell TOO MUCH TIME External environment: CO 2 / Waste Sink O 2 / Nutrients
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Study of Blood. 7/3/02 Mr. Davenport 1
 Study of Blood Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/3/02 Mr.
Study of Blood Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/3/02 Mr.
Cardiovascular System Blood
 Cardiovascular System Blood William T. Budd Virginia Commonwealth University Center for the Study of Biological Complexity Medical Careers College Objectives What is blood? Review metabolism Functions
Cardiovascular System Blood William T. Budd Virginia Commonwealth University Center for the Study of Biological Complexity Medical Careers College Objectives What is blood? Review metabolism Functions
Chapter 19: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood
 Blood Chapter 9: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Liquid connective tissue general functions. Transportation Gases, nutrients, hormones, waste products. Regulation ph, body temperature, osmotic pressure.
Blood Chapter 9: The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Liquid connective tissue general functions. Transportation Gases, nutrients, hormones, waste products. Regulation ph, body temperature, osmotic pressure.
