CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
|
|
|
- Isabel Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid (Fluid of of each cell) Extracellular Fluid (Blood, Lymph, Cerebrospinal fluid etc.) Blood is the most commonly used body fluid in most of the higher organisms. Lymph also transports certain substances like protein and fats. Blood Blood is a mobile connective tissue composed of a fluid, plasma and the cells, the blood corpuscles. It forms about 30-35% of the extracellular fluid. It is slightly alkaline fluid having ph7.4. Plasma is straw coloured viscous fluid that constitutes 55% of blood volume. It consists of 90-92% water, 6-8% protein (fibrinogens, albumins and globulins), glucose, amino acids and small amount of minerals like Na+, Ca++, Cl- etc. Erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets are collectively called formed elements. Erythrocytes are most abundant cells in human body. Total blood count of RBCs is million, which is slightly less in females due to menstruation. It is formed in bone marrow. Nucleus is absent in mammalian RBCs having biconcave in shape. Every 100 ml of blood contain gm. of haemoglobin. They have life span of 120 days. They are destroyed in spleen( graveyard of RBCs) Leucocytes or WBCs are colourless due to absence of haemoglobin of WBCs are present in each ml. of blood.
2 WBC Granulocycts Agranulocyctes Eosinophils Lymphocytes Basophils Monocyctes Neutrophils Neutrophils are most abundant and basophils are least abundant WBCs. Monocytes and neutrophils are phagocytic cells which destroy foreign organisms. Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin and heparin that involve in inflammatory reactions. Eosinophils resist infection and allergic reactions. B and T lymphocytes are responsible for immune response of the body. Thrombocytes or platelets are cell fragments produced from megakaryocytes in bone marrow platelets are present in each ml of blood. Platelets are involved in clotting or coagulation of blood in case of injuries. Blood Groups blood of human beings differ in certain aspects although it appear same in all individuals. Two main types of grouping are ABO and Rh. ABO grouping is based on presence or absence of two surface antigens RBC, antigen A and antigen B. The plasma of an individual also contains two antibodies produced in response of antigens. During blood transfusion, blood of donor has to be matched with blood of recipients to avoid clumping of RBCs. Group O blood can be donated to any individual with any blood group, so it is called universal donor.
3 Person with AB blood group can receive blood from any person of any group, so it is called universal recipient. Rh grouping Rh antigen (similar to Rhesus monkey) are observed on surface of RBCs of majority of individuals (about 80%). Such people are called Rh positive (Rh + ) and whom in which this antigen is absent are called Rh negative (Rh - ). Erythroblastosis foetalis- if father blood is Rh+ and mother blood is Rh-, the foetus blood is Rh+. During the delivery of first child there is a possibility of exposure of mother blood with foetus blood to develop antibodies in mother blood. In subsequent pregnancy the mother blood can leak into foetus blood that destroys the foetus RBC. This case is called erythroblastosis foetalis. Coagulation of blood (Blood Clotting) When an injury is caused to a blood vessel bleeding starts which is stopped by a process called blood clotting. An injury or trauma stimulates the platelets in the blood to release certain factors that activate the mechanism of coagulation. Calcium play important role in blood clotting. During flow of blood through capillaries, some water soluble move out in the space between cells of tissues. This fluid released out is called interstitial fluid or tissue fluid. It is similar to the blood but has fewer blood proteins, less calcium and phosphorus and high glucose concentration. It is a colourless fluid containing specialized lymphocytes that provide immune response to body. Main function of lymph is to provide immunity, carry proteins and fats molecules and transport oxygen, food materials, hormones etc. Circulatory System Open Circulatory System (Arthropods, Mulluscs) Closed Circulatory System (Annelids, Chordates) Circulatory Pathways All vertebrates have a muscular chamber heart. Fish 2 chambered heart Amphibian and Reptiles (except crocodile) - 3 chambered heart. Crocodile, Birds and Mammals 4 chambered heart. Human Circulatory System consists of 4 chambered muscular heart, closed branching blood vessels and circulatory fluid blood. Heart is the mesodermally derived muscular organ, present in thoracic cavity between the two lungs protected by double membrane of pericardium.
4 The upper two chamber is called atria and lower two chambers are called ventricles. Interatrial septum separate the right and left atrium and thick walled inter ventricle septum separate the ventricles. The opening between right atrium and right ventricle is guarded by a three muscular flaps or cusps called tricuspid valve. Bicuspid or mitral valve guards the left atrium and ventricle. The opening of right and left ventricle to pulmonary artery and aorta respectively is controlled by semilunar valve. The nodal tissue present on upper right corner of right atrium is called SAN (sino-atrial node) and those on lower left corner of right atrium is called AVN ( atrio-ventricular node). The purkinje fibres along with right and left bundles form the bundle of HIS. The nodal musculature has ability to generate action potential. SAN generate maximum number of action potential and is responsible for rhythmic contraction of heart. Therefore it is called pace maker. Cardiac Cycle To begin with, all four chambers are in relaxed state called joint disystole. The blood from pulmonary vein and vena cava flows to left and right ventricle through tricuspid and bicuspid valve. Semilunar valves are closed at this stage. SA node generates action potential that contracts the both atria (atrial systole). The action potential is passes to AV node and bundle of HIS transmit it to ventricular musculature to cause ventricular systole. At the same time atria undergoes relaxation disystole to close the bicuspid and tricuspid valve. Semilunar valves open into circulatory system that relax the ventricle and close the valves to prevent back flow of blood. As the pressure inside ventricle decreases the bicuspid and tricuspid valve open to repeat the process or cardiac cycle. During each cardiac cycle two sounds are produced. The first sound (lub) is due to closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valve and 2 nd heart sound (dub) is due to closure of semilunar valve. ECG (Electrocardiograph) is a graphical representation of electrical activity of heart during cardiac cycle. The electrocardiograph machine is used to obtain electrocardiogram. The patient is connected to three electrical leads to wrists and left ankle.
5 The P-wave represents the electrical excitation of atria (depolarization) which leads to contraction of atria. The PRS-wave represents the depolarization of ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The T-wave represents the return of ventricle from exited to normal state (repolarization). At the end of T-wave marks the end of systole. Counting the number of QRS complex in given period of time determine the heartbeat rate. Double Circulation Flow of same blood twice through the heart once in oxygenated form and other in deoxygenated form is called double circulation. It includes systematic and pulmonary circulation. Systematic circulation includes flow of oxygenated blood for the left ventricle to all parts of body and deoxygenated blood from various body parts to the right atrium. All systematic circulation starts form aorta and ends at superior vena cava, inferior vena cava or coronary sinus to right atrium. The systematic system provides oxygen, nutrients and other substance to the tissues of different body parts and take CO2 and other harmful substance from the body parts. Pulmonary Circulation The flow of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and the return of oxygenated blood form the lung to the left atrium is called pulmonary circulation. Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. Double circulation checks the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Regulation of Cardiac Activity Normal activities of heart are regulated by nodal tissue (SA and AV node), so the heart is myogenic. A special neural centre in medulla oblongata moderates the cardiac function by ANS. Sympathetic nerve controls the can increase the rate of heart beat and parasympathetic nerve of ANS decrease the rate of heart beat. Adrenal medullar hormone also increases the cardiac output. Disorder of Circulatory System a) Hypertension (high blood pressure) Blood pressure higher than (120/80). 120 mm Hg is the systolic that is pumping pressure and 80 mm Hg is the disystole, resting pressure. It leads to heart disease and affect vital organs like brain and kidney.
6 b) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)- commonly called atherosclerosis that affects the blood vessels that supply blood to heart muscles due to deposition of fat, calcium, cholesterol that makes the arteries lumen narrower. c) Angina- also called angina pectoris, acute chest pain due to less supply of oxygen to heart muscles. It may occur in elderly male and female. It occurs due to restricted blood flow. d) Heart failure- heart not pumps enough blood to meet the requirement of body. It is also known as congestive heart failure because congestion of lung is one of its causes. Heart failure is different from heart attack ( heart muscle is damaged by inadequate blood supply) and cardiac arrest ( when heart stops beating). e) Coronary Thrombosis- formation of clot in the coronary artery is coronary thrombosis. It occurs most frequently in the left anterior descending coronary artery.
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 278 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION 18.1 Blood 18.2 Lymph (Tissue Fluid) 18.3 Circulatory Pathways 18.4 Double Circulation 18.5 Regulation of Cardiac Activity 18.6 Disorders of Circulatory
278 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION 18.1 Blood 18.2 Lymph (Tissue Fluid) 18.3 Circulatory Pathways 18.4 Double Circulation 18.5 Regulation of Cardiac Activity 18.6 Disorders of Circulatory
1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Body Fluids And Circulation 1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. Formed Elements in Blood And Their Functions: Erythrocytes
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Body Fluids And Circulation 1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. Formed Elements in Blood And Their Functions: Erythrocytes
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD.
 SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET TEST No 220317 Time : 1 Hr BIOLOGY CIRCULATION 1) c 2) a 3) d 4) c 5) c 6) c 7) c 8) a 9) d 10) d 11) d 12) c 13) d 14) b 15) b 16) c 17) a 18) b 19) c 20) a 21) b 22)
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET TEST No 220317 Time : 1 Hr BIOLOGY CIRCULATION 1) c 2) a 3) d 4) c 5) c 6) c 7) c 8) a 9) d 10) d 11) d 12) c 13) d 14) b 15) b 16) c 17) a 18) b 19) c 20) a 21) b 22)
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Points To Remember. Biology Class - 11
 Points To Remember Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma and formed elements. Plasma : The liquid
Points To Remember Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma and formed elements. Plasma : The liquid
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter -18
 Chapter -18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma
Chapter -18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
aliasyraf.wordpress.com
 aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
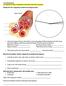 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD
 PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Class X Chapter 7 The Circulatory System Biology REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Types of Circulatory Systems Vertebrate Cardiovascular System Vertebrate Vascular Systems
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Types of Circulatory Systems Vertebrate Cardiovascular System Vertebrate Vascular Systems The Heart The Vascular System Blood The Lymphatic System Learning Objectives Types of Circulatory
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Types of Circulatory Systems Vertebrate Cardiovascular System Vertebrate Vascular Systems The Heart The Vascular System Blood The Lymphatic System Learning Objectives Types of Circulatory
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
CHAPTER 26. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
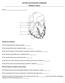 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Circulatory System. - Consists of a pumping heart and blood vessels. Two types of circulatory fluids: Blood OR Hemolymph
 Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
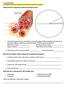 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Circulatory System. Functions and Components of the Circulatory System. Chapter 13 Outline. Chapter 13
 Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms?
 Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Circulatory System. 3. Blood. 1. Heart. 1. Veins A blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
 Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
Circulatory system of mammals
 Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS
 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 1. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 2. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 3. Which
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 1. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 2. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 3. Which
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange. d = t 2
 Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
