Scientific adviser: ass.prof Makharynska O.S Head of department: prof. Yabluchansky M.I.
|
|
|
- Monica Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scientific adviser: ass.prof Makharynska O.S Head of department: prof. Yabluchansky M.I.
2 Structure: Acute Renal failure (ARF) definition Anatomy and physiology of kidneys ARF diagnostic criterias ARF - classification Etiology and pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Prerenal ARF Intrinsic ARF Postrenal ARF Differential diagnosis Complications Management: prevention and treatment
3 Acute kidney injury, previously known as acute renal failure, encompasses a wide spectrum of injury to the kidneys, not just kidney failure, and characterized by the sudden impairment of kidney function resulting in retention of nitrogenous and other waste products normally cleared by the kidneys. AKI complicates 5-7% of acute care hospital admissions and up to 30% of admissions to the intensive care unit AKI is associated with a marked-increased risk of death in hospitalized individuals Risk factors for developing ARF: age, IDDM, CKD, LV dysfunction AKI may be community-acquired (volume depletion, adverse effects of medications, obstruction of the urinary tract) or hospital-acquired (sepsis, major surgical procedures, liver failure, intravenous iodinated contrast administration, and nephrotoxic medication). Acute kidney injury: NICE guideline DRAFT (March 2013) Harrison s principles of internal medicine, 19 Ed, 2015
4 Structural organization renal parenchyma: - cortex - medulla nephrons: - cortical - juxtamedullary
5 Renal blood supply: the kidneys receive 20% of the cardiac output vascular supply: - renal arteries - interlobar arteries - arcuate arteries - interlobular arteries - afferent arterioles - glomerular capillaries - efferent arterioles - peritubular capillaries quizlet.com
6 Basic Renal Physiology Nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, capable of forming urine has two major components: glomerulus tubule: proximal loop of Henle distal collecting
7 Determinants of renal blood flow (RBF) RBF= renal artery pressure - renal vein pressure total renal vasculature resistance Adjusting the resistances of the afferent and efferent arterioles, the kidneys can regulate both the hydrostatic pressures in the glomerular and peritubular capillaries, changing the rate of glomerular filtration and/or tubular reabsorption in response to homeostatic demands.
8 Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) - is widely accepted as the best overall index of kidney function in health and disease. Depends on the interplay between hydrostatic and oncotic pressures within the nephron hydrostatic pressure is usually higher in the glomerulus than within the tubule, forcing filtrate out of the capillary bed into the tubule oncotic pressure is generated by non-filtered proteins: it helps to retain fluid in the intravascular space GFR: Kf * (hydrostatic pressure - oncotic pressure) Normal GFR: 100 ml/min/1.72m 2 *Kf - filtration coefficient in the glomerulus
9 Evidence of decreasing renal function (reduced GFR): Rising BUN (blood urea nitrogen) nl about 10 mg/dl (nr = 7-25 mg/dl) Rising creatinine nl about 1 mg/dl (nr = mg/dl) Note! normal BUN: creatinine ratio = 10-20:1
10
11 The RIFLE criteria for AKI The acronym RIFLE stands for the increasing severity classes Risk, Injury, and Failure; and the two outcome classes, Loss and End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). ARF, acute renal failure; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; Screat, serum creatinine concentration; UO, urine output. Acute kidney injury: NICE guideline DRAFT (March 2013)
12 AKIN criteria for AKI Abrupt (within 48 h) reduction in kidney function currently defined as an absolute increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dl or more ( 26.4 μmol/l) or A percentage increase in serum creatinine of 50% or more (1.5-fold from baseline) or A reduction in urine output (documented oliguria of < 0.5 ml/kg/h for >6 h) The RIFLE criteria are defined as changes within 7 days, while the AKIN criteria suggest using 48 hours.
13 Acute kidney injury: NICE guideline DRAFT (March 2013),
14 KDIGO criteria for AKI AKI is defined as any of the following (Not Graded): K Increase in SCr by 0.3 mg/dl ( 26.5 lmol/l) within 48 hours; or K Increase in SCr to 1.5 times baseline, which is known or presumed to have occurred within the prior 7 days; or K Urine volume 0.5 ml/kg/h for 6 hours.
15 Types of Acute Kidney Injury 1. PRERENAL Impaired renal perfusion (shock, hypovolemia, volume shifts, CO, PVR(pulmonary vascular resistance), renal artery obstruction) 2. INTRARENAL Involves parenchymal changes (renal trauma, acute tubular necrosis, infectious diseases, glomerulonephritis) 3. POSTRENAL Obstruction to urinary tract prostate disease, obstruction, spinal cord injury, pelvic trauma)
16 Classification of the major causes of acute kidney injury Harrison s principles of internal medicine, 19 Ed, 2015
17 Acute kidney injury: pathophysiology Increase in NaCl delivered to macula densa. Damage to proximal tubule cells increases NaCl delivery to distal nephron. This causes disruption of feedback mechanism. Obstruction of tubular lumen. Casts (necrosis of tubular cells and sloughed basement membrane) clog the lumen. This will increase the tubular pressure and then GFR will fall. Backleak of fluid through the tubular basement membrane.
18 Acute Kidney Injury Stages (1) 1. INITIATING PHASE Begins at time of insult until S&S seen (hours to days) 2. OLIGURIC or ANURIC PHASE Oliguria caused by GFR decrease Begins 1-7 days after insult depending on cause Usually lasts usually days (may last up to 8 weeks) Longer the phase, poorer prognosis of renal recovery Manifestations are changes in UOP, fluid & electrolyte balances, & uremiain serum levels of urea, creatinine, uric acid, K+ & Mg
19 Acute Kidney Injury Stages (2) 3. DIURETIC PHASE -Gradual increase of UOP can reach 1-2 (or more) L per day. Nephrons are still not fully functional -Caused by osmotic diuresis and inability of tubules to concentrate. -Recovered ability to excrete wastes, but not concentrate. -Monitor for hypokalemia, hyponatremia & dehydration -Hypovolemia and hypotension can occur Lasts 1-3 weeks -Acid-base, electrolyte and waste product levels begin to normalize. 4. RECOVERY PHASE Begins when GFR increases allowing BUN and creatinine to reach a plateau and decrease May still have glycosuria and decreased ability to concentrate urine Major improvements first 1-2 weeks but may take 12 months to stabilize.
20 Investigate for acute kidney injury, by measuring serum creatinine and comparing with baseline, in adults with acute illness if any of the following are likely or present: heart failure liver disease diabetes history of acute kidney injury oliguria (urine output less than 0.5 ml/kg/hour) neurological or cognitive impairment or disability, which may mean limited access to fluids because of reliance on a carer hypovolaemia use of drugs with nephrotoxic potential (such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs], aminoglycosides, angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists [ARBs] and diuretics) within the past week, especially if hypovolaemic use of iodinated contrast agents within the past week symptoms or history of urological obstruction, or conditions that may lead to obstruction sepsis deteriorating early warning scores age 65 years or over. NICE 2013
21 Monitoring and preventing deterioration in patients with or at high risk of acute kidney injury Detecting acute kidney injury with the RIFLE, AKIN or KDIGO definitions Identifying the cause(s) of acute kidney injury: - Urinalysis - Ultrasound (useful for obstructive forms) - Doppler (to assess renal blood flow) - Nuclear Medicine Scans Managing acute kidney injury: - Relieving urological obstruction - Pharmacological management - Referring for renal replacement therapy - Referring to nephrology
22 Acute kidney injury: common clinical features azotemia hypervolemia electrolytes abnormalities: K+ phosphate Na+ calcium metabolic acidosis hypertension oliguria anuria (a biomarker of tubular injury) atheroembolies in small vessels
23 Urine Findings Complete anuria early in the course of AKI is uncommon except in the following situations: complete urinary tract obstruction, renal artery occlusion, overwhelming septic shock, severe ischemia (often with cortical necrosis), or severe proliferative glomerulonephritis or vasculitis. Oliguria, defined as <500 ml/24 h) usually denotes more severe AKI (i.e., lower GFR) than when urine output is preserved. Proteinuria > 1 g/d in AKI suggests damage to the glomerular ultrafiltration barrier or excretion of myeloma light chains Extremely heavy proteinuria ("nephrotic range >3.5 g/d) can occasionally be seen in glomerulonephritis, vasculitis, or interstitial nephritis
24 Acute Kidney Injury: Urine Volume Anuria (< 100 ml/24h) Acute bilateral arterial or venous occlusion Bilateral cortical necrosis Acute necrotizing glomerulonephritis Obstruction (complete) ATN (very rare) Oliguria ( ml/24h) Pre-renal azotemia ATN Non-Oliguria (> 500 ml/24h) ATN Obstruction (partial)
25 Interpretation of urinary sediment findings in acute kidney injury
26 Red Blood Cells Monomorphic (nondysmorphic) RBC suggest non-glomerular source of bleeding i.e., bleeding from the calyces, pelvis, ureter(s), bladder, prostate or urethra. Dysmorphic red blood cells suggest glomerular injury. Red or brown urine may be seen with or without gross hematuria dysmorphic monomorphic
27 Red Blood Cell Cast White Blood Cell Cast Two examples of red blood cell casts, typical of glomerular bleeding. Glomerulonephritis may lead to dysmorphic red blood cells or red blood cell casts. Interstitial nephritis may lead to white blood cell casts. Urine eosinophils have a limited role in differential diagnosis; they can be seen in interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, atheroembolic disease, or glomerulonephritis.
28 Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Cast Pigmented Granular Casts Pigmented granular ( muddy brown ) casts are characteristic of acute tubular necrosis
29 Renal Failure Indices Several indices have been used to help differentiate prerenal azotemia from intrinsic AKI when the tubules are malfunctioning. The fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa) is the fraction of the filtered sodium load that is reabsorbed by the tubules, and is a measure of both the kidney's ability to reabsorb sodium as well as endogenously and exogenously administered factors that affect tubular reabsorption. Urine osmolality - in the patient not taking diuretics and with good baseline kidney function, urine osmolality may be above 500 mosm/kg in prerenal azotemia. Loss of concentrating ability is common in septic or ischemic AKI, resulting in urine osmolality below 350 mosm/kg Renal Failure Index (RFI) = urine [Na] urine creatinine / serum creatinine
30 Urine Chemistries Fractional Excretion of Na and Urea Since urinary indices depend on urine sodium concentration, they should be interpreted cautiously if the patient has received diuretic Spot urine Na may be affected (raised) by diuretic use and baseline impaired kidney function (chronic renal disease where maximum urine Na reabsorption is impaired) Fractional excretion of Na accounts for this by including creatinine: FE Na = urine [Na] plasma [Na] X 100 urine creatinine plasma creatinine FxExurea substitute urine urea nitrogen for Na useful if patient receiving diuretics
31 AKI: Ultrasound Findings Normal kidney on ultrasound Hydronephrosis on ultrasound Kidney Cancer Ultrasound Diabetic Kidney Ultrasound
32 AKI: Novel Biomarkers BUN and creatinine are functional biomarkers of glomerular filtration rather than tissue injury biomarkers Kidney injury molecule-l (KIM-1) is a type 1 transmembrane protein that is abundantly expressed in proximal tubular cells injured by ischemia or nephrotoxins such as cisplatin, can be detected shortly after ischemic or nephrotoxic injury in the urine Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL, also known as lipocalin-2 or siderocalin) - a protein in granules of human neutrophils, can be detected in the plasma and urine within 2 h of cardiopulmonarγ bypass-associated AKI. Interleukin (IL) 18 - a pro-inflammatory cytokine of the IL- l superfamily that may mediate ischemic proximal tubular injury L-type fatty acid binding protein - from ischemic proximal tubule cells
33 Acute Kidney Injury: Pre-renal Causes Prerenal azotemia (from "azo" meaning nitrogen, and "- emia") is the most common form of AKI. Decreased effective perfusion without cellular injury Hemorrhage Sodium depletion Pump failure Increased vascular capacity e.g., sepsis Increased renal vascular resistance (hepatorenal, NSAIDs) Vasoconstriction drugs (radio contrast, cyclosporine, amphotericin B) Decreased intraglomerular pressure (ACEI, ARB) Redistribution of ECF Third space accumulation Edematous disorders Drugs Renal tubular and glomerular functions are intact Reversible if underlying cause is corrected
34 Pre-Renal Azotemia Pathophysiology Renal hypoperfusion Decreased RBF (renal blood flow) and GFR Increased filtration fraction (GFR/RBF) Increased Na and H 2 O reabsorption Oliguria, high U osm, low U Na Elevated BUN/Cr ratio In the absence of renal artery stenosis, renal arterial pressure (RAP) is the same as systemic mean arterial pressure (commonly referred to by nephrologists as renal perfusion pressure ). Renal venous pressure (RVP) is usually, but not always, low and relatively constant. The glomerular afferent and efferent arterioles are the major sites of renal vascular resistance (Raff and Reff, respectively); changes in either will affect renal blood flow (RBF).
35 Pre-renal AKI Physical examination focus on volume status Vital signs current and preceding the development of AKI Neck veins, lungs, heart, mucous membranes Edema presacral and extremity Laboratory studies BUN : creatinine ratio elevated in pre-renal; >10-20:1 Unremarkable urinary sediment, high specific gravity May see hyaline casts Urine dipstick negative (no blood or protein) There is no intrinsic kidney damage in pre-renal ARF; rising BUN and creatinine occur because the kidneys are inadequately perfused.
36 Pre-renal AKI Urine Electrolytes Intact renal tubular function in the setting of impaired renal perfusion (due either to volume loss, pump failure, renal vasoconstriction, etc) results in avid tubular reabsorption of sodium. Therefore, low urine Na (<20 meq/l) and low fractional excretion of Na (<1%) and of urea (<35%) in pre-renal ARF. Therefore, normal renal physiologic responses occur, manifested in urine electrolytes that reflect intact kidney tubular function. Prerenal azotemia and ischemic tubular necrosis represent a continuum. Azotemia progresses to necrosis when blood flow is sufficiently compromised to result in the death of tubular cells.
37 AKI: Renal or Intrinsic The most common causes of intrinsic AKI are sepsis, ischemia and nephrotoxins, both endogenous and exogenous
38
39 Renal or Intrinsic AKI In all types of intrinsic ARF, BUN : creatinine ratio preserved (10-20:1) The history, PE, and especially, urine analysis will help to differentiate Classified according to primary site of injury: Vascular Glomerular (acute glomerulonephritis) Tubular (acute tubular necrosis or ATN) Interstitial (acute interstitial nephritis)
40 Renal or Intrinsic AKI Vascular Type Large vessels must be bilateral Renal vein thrombosis Renal artery stenosis Urine eosinophils Low C3 Small vessels Vasculitis Atheroembolic Malignant hypertension Thrombotic microangiopathies.
41 Small vessels atheroembolic Relatively common Risk factors = catheter manipulation and anticoagulation in the setting of atherosclerosis PE may reveal livedo reticularis Progressive rise then stabilization of BUN, creatinine usually without significant recovery of kidney function Cholesterol clefts occ seen on kidney biopsy but transient so bx not suggested; Dx clinically
42 Renal or Intrinsic AKI Glomerular Type History systemic or primary kidney edema PE BP (usually hypertensive) edema BUN : creatinine ratio preserved RBC Casts Urine analysis: + protein, blood (RBCs, RBC casts) Often will require kidney biopsy
43 Renal or Intrinsic AKI Interstitial Type History exposure to medications usually 7-14 days earlier penicillin, cephalosporin, dilantin PE maculopapular erythematous skin rash 1/3 have fever, arthralgias BUN : creatinine ratio 10-20:1 Urine analysis -- + protein, blood (WBCs, WBC casts, eosinophils) The most common type of Hospital - acquired ARF May Be: 1) Ischemic (ATN) or 2) Nephrotoxic (in etiology) Most common Acute Tubular Necrosis is Ischemic, most often due to a prolonged pre-renal state (prolonged reduced renal perfusion)
44 Renal or Intrinsic AKI Acute Tubular Necrosis History prolonged pre-renal state exposure to nephrotoxin aminoglycoside antibiotics ethylene glycol pigments (myoglobin, hemoglobin) PE volume status (to exclude pre-renal ARF) BUN:creat ratio preserved (10-20:1) Urine analysis usually negative protein, blood - granular casts (dirty brown casts) - renal tubular epithelial cells Urine chemistries urine Na>40 meq/l
45 The increased incidence of non-oliguric ATN during the past 25 years is most likely due to the increased usage of nephrotoxins, more frequent chemical testing, and more aggressive use of fluids, potent diuretics, and vasodilators in the management of ATN. The reduced mortality of non-oliguric compared to oliguric ATN is probably not because of the increased urine volume but rather due to a lower associated mortality of the conditions causing non-oliguric compared to oliguric ATN. (Data from Anderson et al: Non-oliguric Acute Renal Failure. New Engl J Med 296:134, 1977.) Prior to the article by Anderson, it was believed that most cases of ATN were oliguric. Today, we know that ATN can present with oliguria or non-oliguria and that both presentations are common. Any cause of ATN can present with nonoliguria ; nonoliguria is more likely with nephrotoxic causes of ATN such as aminoglycosides, contrast media, cis-platinum, and amphotericin.
46 Acute Tubular Necrosis
47 Acute Tubular Necrosis Acute tubular necrosis showing focal loss of tubular epithelial cells (arrows) and partial occlusion of tubular lumens by cellular debris (D) (H&E stain). The kidney biopsy can provide definitive diagnostic and prognostic information about acute kidney diseases and CKD. Tubular epithelial degeneration and hyaline amphophilic casts (positive with immunologic stains for myoglobin) in a patient with rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuric acute tubular necrosis.
48 Acute Interstitial Nephritis Causes: Allergic interstitial nephritis Drugs (aminoglycosides, cisplatin and carboplatin) Infections Bacterial (sepsis) Viral Sarcoidosis Radiation nephritis Iodinated contrast agents Risk factors for nephrotoxicity include older age, chronic kidney disease, and prerenal azotemia
49 Acute Interstitial Nephritis Clinical Characteristics Fever Rash Arthralgias Eosinophilia Urinalysis Microscopic hematuria Sterile pyuria Eosinophiluria
50 Acute Interstitial Nephritis Drug-induced allergic interstitial nephritis (H&E stain). Note the diffuse interstitial infiltrate, many red-staining eosinophils, and sparing of the glomerulus (on the left).
51 AKI - Cholesterol Embolization Cholesterol embolization may occur after a sentinel procedure (e.g., cardiac catherization) or be associated with slowly progressive renal failure over a period of months or years. Whatever the time course, it is generally irreversible. Cholesterol emboli usually lodge in vessels 100 to 200 microns in diameter, and are visualized as clear spaces where the cholesterol crystals have been dissolved by routine processing. The early response of platelets and occasional mononuclear cells is seen in the medium size artery occluded by acute cholesterol emboli in the left panel (Jones Silver stain). In later stages of organization the lumen may have more fibrous reorganization surrounding the cholesterol clefts, as shown in the right lower diagram (PAS stain).
52 Acute Kidney Injury: Post-renal Intra-renal Obstruction Acute uric acid nephropathy Drugs (e.g., acyclovir) Extra-renal Obstruction Causes Renal pelvis or ureter ;must be bilateral unless solitary kidney (e.g., stones, clots, tumors, papillary necrosis, retroperitoneal fibrosis) Bladder (e.g., BPH, neuropathic bladder) Urethra (e.g., stricture)
53 Acute Kidney Injury: Post-renal Postrenal AKI occurs when the normally directional flow of urine is acutely blocked either partially or totally, leading to increased retrograde hydrostatic pressure and interference with glomerular filtration. Obstruction to urinary flow - from the renal pelvis to the tip of the urethra. For AKI to occur in healthy individuals, obstruction must affect both kidneys unless only one kidney is functional, in which case unilateral obstruction can cause AKI. Elevated pressure in urinary conduits results in renal parenchymal destruction if unrelieved - an initial period of hyperemia from afferent arteriolar dilation is followed by intrarenal vasoconstriction from the generation of angiotensin II, thromboxane A2, and vasopressin, and a reduction in NO production Important to rule out quickly: potential for recovery of renal function is often inversely related to the duration of the obstruction
54 History symptoms (frequency, hesitancy, etc) - carcinoma, DM, stones, medications in anamnesis PE distended bladder, prostatic enlargement, pelvic masses, lymph nodes Laboratory studies -- elevated BUN:creat ratio -- unremarkable urine sediment -- variable urine chemistries Bladder catheterization Renal ultrasound hydronephrosis Treatment is to relieve the obstruction: - Bladder catheterization - Nephrostomy tubes
55 AKI: Differential Diagnosis AKD, acute kidney diseases and disorders; AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; NKD, no known kidney disease; SCr, serum creatinine. Acute kidney injury: NICE guideline DRAFT (March 2013),
56 Prerenal azotemia vs Renal azotemia Urine sediment: hyaline and fine granular casts Urinary to plasma creatinine ratio: high Urinary Na: low FENa: low Increased urine output in response to hydration Urine sediment: brown granular casts and tubular epithelial cells Urinary to plasma creatinine ratio: low Urinary Na: high FENa: high
57 Prenal Renal BUN/Cr >20 <20 FeNa <1% >1% RFI <1% >1% UNa (meq/l) <20 > 40 Specific gravity high low
58 AKI vs progression of Chronic Kidney Disease Distinction important (etiology, prognosis, therapy differ) Past BUN, creatinine values; course of BUN, creatinine rise Half and half nails Kidney size and echogenicity by ultrasound (10 cm lower limit of normal; normal size usually cm depending on height)
59 AKI: Complications Uremia Hypo- or hypervolemia Hyponatremia Hyperkalemia Acidosis Hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia Bleeding Infections Cardiac complications Malnutrition
60 Acute Kidney Injury: Prevention Recognize Patients At Risk (Postoperative States, Cardiac Surgery, Septic Shock) The management of individuals with and at risk for AKI varies according to the underlying cause Prevent Progression From Prerenal To Renal Preserve Renal Perfusion: Isovolemia, Cardiac Output, Normal Blood Pressure Avoid Nephrotoxins (Aminoglycosides, NSAIDS, Amphotericin)
61 Treatment of AKI Based on type/etiology of AKI (acute kidney injury) i.e., pre-renal, post-renal, or intrinsic renal initially Pre-renal volume, improve renal perfusion Post-renal relieve obstruction Intrinsic glomerular, tubular, interstitial, vascular depends on type
62 (Na< 125 meq/l)
63
64
65 AKI: Hemoglobinuria + Myoglobinuria Hemoglobinuria: Transfusion Reactions, HUS (Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome), ECMO (Extra-corporeal Membrane Oxygenation) Myoglobinuria: Crush Injuries, Rhabdomyolysis Urine (+) Blood, But (-) Red Blood Cells CFK, K+ Treatment Aggressive Hydration + Urine Alkalinization, Mannitol / Furosemide
66 Acute Kidney Injury: fluid therapy If patient is fluid overloaded fluid restriction (insensible losses) attempt furosemide 1-2 mg/kg Renal replacement therapy (see later) If patient is dehydrated: restore intravascular volume first then treat as euvolemic (below) If patient is euvolemic: restrict to insensible losses (30-35 ml/100kcal/24 hours) + other losses (urine, chest tubes, etc)
67 AKI Indications for Dialysis Dialysis is indicated when medical management fails to control volume overload, hyperkalemia, or acidosis. The timing of dialysis is still a matter of debate. Late initiation of dialysis carries the risk of avoidable volume, electrolyte and metabolic complications of AKI. On the other hand, initiating dialysis too early may unnecessarily expose individuals to intravenous lines and invasive procedures, with the attendant risks of infection, bleeding, procedural complications, a n d hypotension. The initiation of dialysis should not await the development of a lifethreatening complication of renal failure. A acidosis E electrolyte disturb., usually hyperkalemia I intoxications (lithium, ethylene glycol, etc) O overload (volume overload) U uremia (symptoms, signs)
68
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Dr.Nahid Osman Ahmed 1
 1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
1 ILOS By the end of the lecture you should be able to Identify : Functions of the kidney and nephrons Signs and symptoms of AKI Risk factors to AKI Treatment alternatives 2 Acute kidney injury (AKI),
A Practical Approach to Acute Kidney Injury
 A Practical Approach to Acute Kidney Injury Elise Barney, DO Nephrologist Phoenix VA Medical Center Clinical Assistant Professor, Medicine University of Arizona College of Medicine A Tribute to the Kidney!
A Practical Approach to Acute Kidney Injury Elise Barney, DO Nephrologist Phoenix VA Medical Center Clinical Assistant Professor, Medicine University of Arizona College of Medicine A Tribute to the Kidney!
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management
 AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
HTN, retenopathy, edema, encephalopathy
 ARF Uremic syndrom Uremic syndrome (uremia) is a serious complication of CRF & ARF. It occurs when urea and other waste products build up in the body because the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. These
ARF Uremic syndrom Uremic syndrome (uremia) is a serious complication of CRF & ARF. It occurs when urea and other waste products build up in the body because the kidneys are unable to eliminate them. These
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE COLLEGE OF NURSING KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT-VI Advance Nursing Management of Genitourinary (GU) Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Thambi, M. (2017). Acute Kidney Injury. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. AKI This
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Thambi, M. (2017). Acute Kidney Injury. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. AKI This
1. Disorders of glomerular filtration
 RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Acute Kidney Injury. Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1
 Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Acute Kidney Injury Eleanor Haskey BSc(hons) RVN VTS(ECC) VPAC A1 Anatomy and Physiology The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood through the glomerulus to form filtrate. The filtrate is then reabsorbed
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD, Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte, H
Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology. Financial Disclosure. Some History Trivia. Key Points. What is AKI
 Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology Financial Disclosure Current support: Center for Sepsis and Critical Illness Award P50 GM-111152 from the National Institute of General Medical
Acute kidney injury definition, causes and pathophysiology Financial Disclosure Current support: Center for Sepsis and Critical Illness Award P50 GM-111152 from the National Institute of General Medical
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Zekeriyya ALANOGLU, MD, DESA. Ahmet Onat Bermede, MD. Ankara University School of Medicine Dept. Anesthesiology and ICM Kidneys Stabilize the composition of the ECF (electrolyte,
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders. Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November
 Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers HOW
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers HOW
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Acute Renal Failure & Malaria Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Definitions Inability of
Acute Renal Failure & Malaria Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Definitions Inability of
AN UPDATE ON THE RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY DISEASE IN DOGS AND CATS
 AN UPDATE ON THE RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY DISEASE IN DOGS AND CATS Richard E. Goldstein DVM, Dip. ACVIM, Dip. ECVIM-CA The Animal Medical Center New York, NY Azotemia refers
AN UPDATE ON THE RECOGNITION, PREVENTION, AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY DISEASE IN DOGS AND CATS Richard E. Goldstein DVM, Dip. ACVIM, Dip. ECVIM-CA The Animal Medical Center New York, NY Azotemia refers
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS. Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY A PRIMER FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Myriam Farah, MD, FRCPC Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Nephrology, University of British Columbia November 2016 1. How to recognize acute
Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome
 And Renocardiac Syndrome A Vicious Cycle Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome Type 1 (acute) Acute HF results in acute kidney injury Type 2 Chronic cardiac dysfunction (eg, chronic HF) causes progressive
And Renocardiac Syndrome A Vicious Cycle Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome Type 1 (acute) Acute HF results in acute kidney injury Type 2 Chronic cardiac dysfunction (eg, chronic HF) causes progressive
Learning Objectives. How big is the problem? ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Karen Innocent, DNP, RN, CRNP, ANP-BC, CMSRN Executive Director, Continuing Education Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc May 2016 Orlando FL Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors and
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY Karen Innocent, DNP, RN, CRNP, ANP-BC, CMSRN Executive Director, Continuing Education Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc May 2016 Orlando FL Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors and
Acute Renal Failure aka Acute Kidney Injury. Dr H Bierman
 Acute Renal Failure aka Acute Kidney Injury Dr H Bierman RIFLE criteria for diagnosis of AKI based on The Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Increase in S Cr Urine output Risk of renal injury Injury to
Acute Renal Failure aka Acute Kidney Injury Dr H Bierman RIFLE criteria for diagnosis of AKI based on The Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Increase in S Cr Urine output Risk of renal injury Injury to
L17: Acute. Kidney Injury
 L17: Acute Medicine433@yahoo.com Kidney Injury objectives 1. Define Acute Kidney Injury 2. Know the epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury 3. Know the etiology of Acute Kidney Injury 4. Manage Acute Kidney
L17: Acute Medicine433@yahoo.com Kidney Injury objectives 1. Define Acute Kidney Injury 2. Know the epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury 3. Know the etiology of Acute Kidney Injury 4. Manage Acute Kidney
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Acute Kidney Injury IM Resident Lecture. Yongen Chang, MD, PhD Nephrology July 2018
 Acute Kidney Injury IM Resident Lecture Yongen Chang, MD, PhD Nephrology July 2018 Objectives Epidemiology Definition and Staging Etiology and Diagnostic Approach Specific syndromes of AKI Treatment Biomarkers
Acute Kidney Injury IM Resident Lecture Yongen Chang, MD, PhD Nephrology July 2018 Objectives Epidemiology Definition and Staging Etiology and Diagnostic Approach Specific syndromes of AKI Treatment Biomarkers
Clinical Significance of ARF. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency. Case - Acute Renal Failure. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency
 Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Kidney Fun and Failure
 Kidney Fun and Failure Tom Ozbirn, M.D. General Session 2, Saturday, 9/8/12 9:30 a.m. to 11:30 a.m. Thomas W. Ozbirn, Jr DO, FACP Nephrology Associates, PC Birmingham, Alabama 1 Objectives Understand Categories
Kidney Fun and Failure Tom Ozbirn, M.D. General Session 2, Saturday, 9/8/12 9:30 a.m. to 11:30 a.m. Thomas W. Ozbirn, Jr DO, FACP Nephrology Associates, PC Birmingham, Alabama 1 Objectives Understand Categories
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
The Renal System. Dr Noel Sharkey
 The Renal System Dr Noel Sharkey Learning Objectives Function Anatomy Physiology Pharmacology Pathophysiology The Function of the Kidney Excretion - Urea - Metabolites - Drugs Regulation - BP control (RAAS)
The Renal System Dr Noel Sharkey Learning Objectives Function Anatomy Physiology Pharmacology Pathophysiology The Function of the Kidney Excretion - Urea - Metabolites - Drugs Regulation - BP control (RAAS)
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Acute Kidney Injury in the ED
 + Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
+ Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
DIABETES MELLITUS. Kidney in systemic diseases. Slower the progression: Pathology: Patients with diabetes mellitus are prone to other renal diseases:
 Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Acute Kidney Injury. APSN JSN CME for Nephrology Trainees May Professor Robert Walker
 Acute Kidney Injury APSN JSN CME for Nephrology Trainees May 2017 Professor Robert Walker Kidney International (2017) 91, 1033 1046; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ j.kint.2016.09.051 Case for discussion 55year
Acute Kidney Injury APSN JSN CME for Nephrology Trainees May 2017 Professor Robert Walker Kidney International (2017) 91, 1033 1046; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ j.kint.2016.09.051 Case for discussion 55year
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney:
 Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
DIAGNOSIS AND INVESTIGATIONS (Table 13.3) 362 INTENSIVE CARE
 362 INTENSIVE CARE the administration of NSAIDs, an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker during an episode of renal underperfusion. Dangerous hyperkalaemia, out of proportion to the degree
362 INTENSIVE CARE the administration of NSAIDs, an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker during an episode of renal underperfusion. Dangerous hyperkalaemia, out of proportion to the degree
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Physiology Lecture 2. What controls GFR?
 Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
II.Tubulointerstitial diseases
 II.Tubulointerstitial diseases two major groups of processes (1) ischemic or toxic tubular injury, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) and acute renal failure, and (2) inflammatory reactions of the tubules
II.Tubulointerstitial diseases two major groups of processes (1) ischemic or toxic tubular injury, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) and acute renal failure, and (2) inflammatory reactions of the tubules
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Classifications and Interventions for Children and Adults
 Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Classifications and Interventions for Children and Adults Teresa V. Lewis, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice University of Oklahoma College
Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Classifications and Interventions for Children and Adults Teresa V. Lewis, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice University of Oklahoma College
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Acute Kidney Injury. Alan M. Green MPHM13: Acute Kidney Injury. Slide 1 of 47
 MPharm Programme Acute Kidney Injury Alan M. Green 2017 Slide 1 of 47 Overview Renal Function What is it? Why does it matter? What causes it? Who is at risk? What can we (Pharmacists) do? How do you recognise
MPharm Programme Acute Kidney Injury Alan M. Green 2017 Slide 1 of 47 Overview Renal Function What is it? Why does it matter? What causes it? Who is at risk? What can we (Pharmacists) do? How do you recognise
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year Three Developed Summer 2017 Objectives Understand Acute Kidney Injury and its relevance to patient care. Brief revision of the Anatomy and physiology
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM
 DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. Dr Boldizsár CZÉH
 THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Dr Boldizsár CZÉH The kidneys are vital organs Functional unit: Nephron RENAL FUNCTIONS Electrolyte & Fluid Balances Acid-Base Balances Elimination of Metabolic
Acute kidney injury. Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology
 Acute kidney injury Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology Introduction Is common in critically ill patients e.g. post cardiac surgery Occurs when renal function is diminished to a point where body fluid and
Acute kidney injury Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric nephrology Introduction Is common in critically ill patients e.g. post cardiac surgery Occurs when renal function is diminished to a point where body fluid and
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones
 4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
USMLE and COMLEX Review Nephrology Supplement
 USMLE and COMLEX Review Nephrology Supplement Glomerulonephritis, Acute Tubular Necrosis and Acute Interstitial Nephritis Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan
USMLE and COMLEX Review Nephrology Supplement Glomerulonephritis, Acute Tubular Necrosis and Acute Interstitial Nephritis Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING
 OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
Renal diseases. Acute renal failure Chronic renal failure Nephrotic syndrome
 Renal diseases Acute renal failure Chronic renal failure Nephrotic syndrome Acute renal failure Acute renal failure (ARF) is characterized by sudden loss of the ability of the kidneys: to excrete wastes
Renal diseases Acute renal failure Chronic renal failure Nephrotic syndrome Acute renal failure Acute renal failure (ARF) is characterized by sudden loss of the ability of the kidneys: to excrete wastes
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered
 URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC
 RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012
 Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012 Kidney disease is currently one of the most pressing health issues for the Bracco Italiano breed, as the etiology is
Renal Disease Survey Bracco Italiano Club of America Heath Committee, November 2012 Kidney disease is currently one of the most pressing health issues for the Bracco Italiano breed, as the etiology is
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
Pathology. Acute Renal Failure (ARF, Acute Kidney Failure) Symptoms and Treatment. Definition of Acute Renal Failure
 Pathology Acute Renal Failure (ARF, Acute Kidney Failure) Symptoms and Treatment See online here No matter in which clinical field you will be working in the future, you will be confronted with cases of
Pathology Acute Renal Failure (ARF, Acute Kidney Failure) Symptoms and Treatment See online here No matter in which clinical field you will be working in the future, you will be confronted with cases of
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture
 #Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
#Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function
 Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function Carol J. Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Assistant Director, Clinical Pharmacy Services University Medical Center, Tucson, Arizona Top
Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function Carol J. Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Assistant Director, Clinical Pharmacy Services University Medical Center, Tucson, Arizona Top
Conflict of Interest. Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function. Top 5 Things to Know for CE: 3/31/10
 Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function Carol J. Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Assistant Director, Clinical Pharmacy Services University Medical Center, Tucson, Arizona Top
Providing Home Infusion for the Patient with Compromised Renal Function Carol J. Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Assistant Director, Clinical Pharmacy Services University Medical Center, Tucson, Arizona Top
Acute kidney injury it personal! Spring 2018
 Objectives Acute kidney injury it personal! Spring 2018 Mitzi Glover, PhD, MT(ASCP) mglov1@lsuhsc.edu Differentiate between acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease Describe RIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO
Objectives Acute kidney injury it personal! Spring 2018 Mitzi Glover, PhD, MT(ASCP) mglov1@lsuhsc.edu Differentiate between acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease Describe RIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
PRE-RENAL AKI: DOES IT LEAD TO ATN. Sushma Bhusal
 PRE-RENAL AKI: DOES IT LEAD TO ATN Sushma Bhusal 9.9.14 CASE PRESENTATION CC : 31 AAM presented with Fatigue, malaise and body aches x 10 days HPI: STD testing done 2 weeks prior, all results negative
PRE-RENAL AKI: DOES IT LEAD TO ATN Sushma Bhusal 9.9.14 CASE PRESENTATION CC : 31 AAM presented with Fatigue, malaise and body aches x 10 days HPI: STD testing done 2 weeks prior, all results negative
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System. Short Answer. Figure 15.1
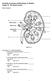 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 15 The Urinary System Short Answer Figure 15.1 Using Figure 15.1, identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter. Answer: B Diff:
Renal Disease. Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs
 Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Doppler ultrasound, see Ultrasonography. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), kidney oxygenation assessment 75
 Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
